Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
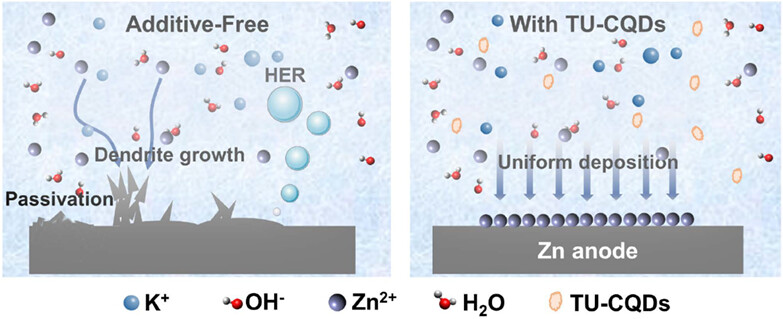
N, S-Doped Carbon Dots as Additive for Suppression of Zinc Dendrites in Alkaline Electrolyte
- First Published: 15 February 2023
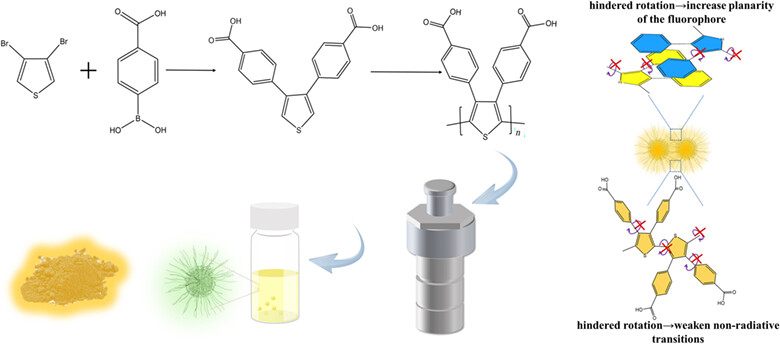
Polythiophene Derivatives Carbonized Polymer Dots: Aggregation Induced Solid-State Fluorescence Emission
- First Published: 10 April 2023
Fluorescent Silk Obtained by Feeding Silkworms with Fluorescent Materials
- First Published: 23 March 2023
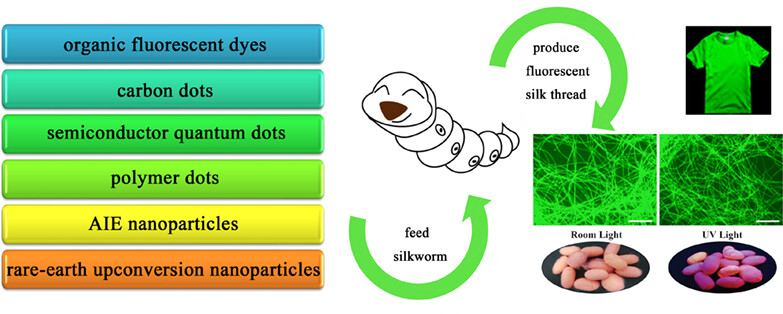
In this paper, we reviewed the research progress for feeding silkworm with fluorescent additives to obtain naturally fluorescent silk in the past ten years, and summarized the unified characteristics and rules for the substances that can enter the silk gland by digestive tract of silkworms. The advantages and disadvantages of various fluorescent materials for this application are compared in detail, and the future research directions are suggested to overcome the shortcomings of the present research.
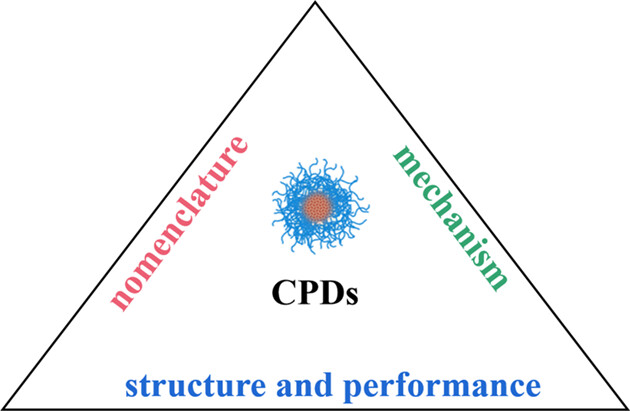
The Classification of Carbon Dots and the Relationship between Synthesis Methods and Properties
- First Published: 10 April 2023
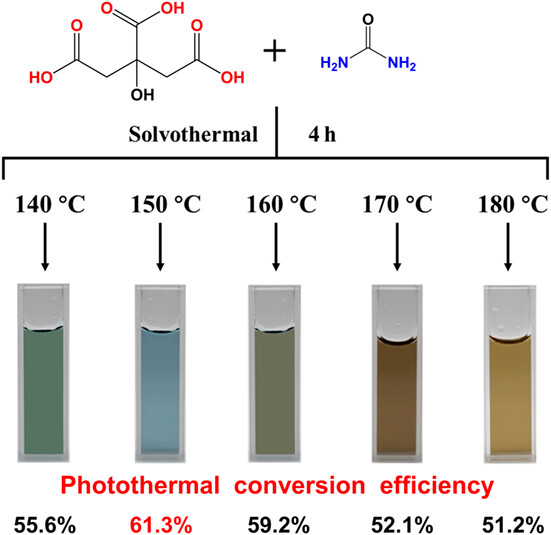
Toward Rational Design of Carbon Nanodots with High Photothermal Efficiency for Tumor Photothermal Therapy
- First Published: 05 April 2023
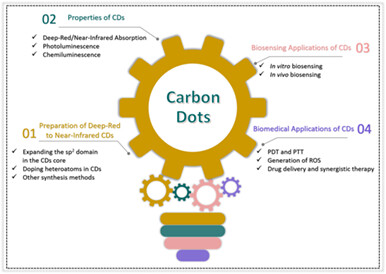
Deep-Red to Near-Infrared Carbon Dots in Biosensing and Bio-medical Applications
- First Published: 08 May 2023
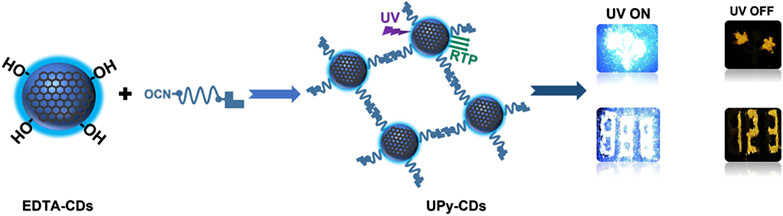
Supramolecular Surface Engineering of Carbon Dots Enables Matrix-Free Room Temperature Phosphorescence
- First Published: 10 May 2023
Yellow-Fluorescence Carbon Dots Employed for pH Sensing and Detection of Tigecycline†
- First Published: 11 September 2023
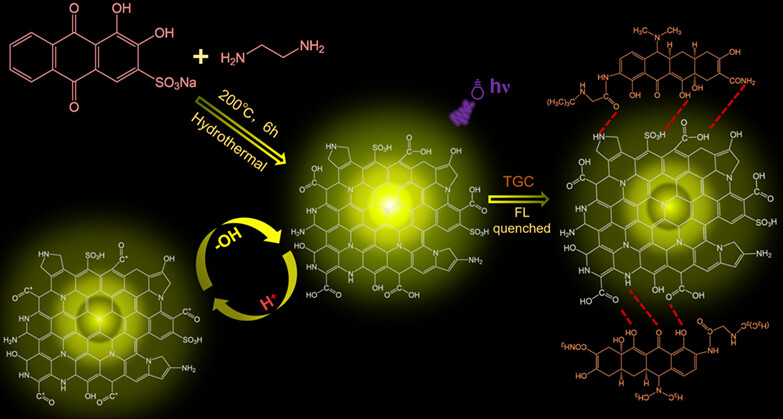
Here, we proposed one type of CDs doped with nitrogen and sulfur through the hydrothermal method, which exhibited the obvious yellow-fluorescence in aqueous solution. Importantly, the fluorescence intensity of CDs decreased with pH decreasing in the acidic range, thus exhibiting the potential of pH sensing. Importantly, introducing tigecycline into these CDs resulted in their decreased fluorescence, thus we further established a strategy of detecting tigecycline.