Fluorescent Silk Obtained by Feeding Silkworms with Fluorescent Materials†
Zhao-Fan Wu
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhao-Nan Sun
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Huan-Ming Xiong
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorZhao-Fan Wu
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhao-Nan Sun
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Huan-Ming Xiong
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Carbon Dots Based Functional Materials.
Comprehensive Summary
Fluorescent silk has potential application in many fields such as bioimaging, tissue engineering scaffolds, luminescent marks, and dazzling fabrics. Among the methods to endow natural silk with fluorescent properties, feeding silkworms with fluorescent additives is facile, low-cost and environment friendly, which has the prospect of large-scale production. In this paper, we reviewed the research progress for this aim in the past ten years, and summarized the unified characteristics for the substances that can enter the silk gland by digestive tract of silkworms. The advantages and disadvantages of various fluorescent materials for this application are compared in detail. And the future research directions are suggested to overcome the shortcomings of the present research.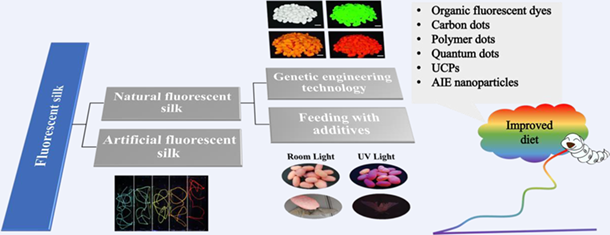
References
- 1 Huang, W.; Ling, S.; Li, C.; Omenetto, F. G.; Kaplan, D. L. Silkworm Silk-Based Materials and Devices Generated Using Bio-Nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6486–6504.
- 2 Glausiusz, J. The Internet of the Ancient World. Nature 2009, 462, 574–574.
- 3 Ma, L.; Akurugu, M. A.; Andoh, V.; Liu, H.; Song, J.; Wu, G.; Li, L. Intrinsically Reinforced Silks Obtained by Incorporation of Graphene Quantum Dots into Silkworms. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 245–255.
- 4 Badawy, I. M.; Ali, B. A.; Abbas, W. A.; Allam, N. K. Natural Silk for Energy and Sensing Applications: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2141–2155.
- 5 Holland, C.; Numata, K.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Seib, F. P. The Biomedical Use of Silk: Past, Present, Future. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1800465.
- 6 Reizabal, A.; Costa, C. M.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Vilas-Vilela, J. L.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Silk Fibroin as Sustainable Advanced Material: Material Properties and Characteristics, Processing, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2210764.
- 7 Chand, S.; Chand, S.; Raula, B. Usage of Silkworm Materials in Various Ground of Science and Research. J. Nat. Fibers. 2022, 20, 1–14.
- 8 Gore, P. M.; Naebe, M.; Wang, X.; Kandasubramanian, B. Progress in Silk Materials for Integrated Water Treatments: Fabrication, Modification and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 437–470.
- 9 Tansil, N. C.; Koh, L. D.; Han, M.-Y. Functional Silk: Colored and Luminescent. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1388–1397.
- 10 Liu, C.; Bai, H.; He, B.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, R.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Functionalization of Silk by AIEgens through Facile Bioconjugation: Full-Color Fluorescence and Long-Term Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12424–12430.
- 11 Arai, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Freddi, G.; Winkler, S.; Tsukada, M. Chemical Modification of Bombyx Mori Silk Using Isocyanates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 79, 1756–1763.
- 12 Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, C. Chemical Modification of Silk Proteins: Current Status and Future Prospects. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 705–719.
- 13 Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W. Nucleophilic Modification of Flavonoids for Enhanced Solubility and Photostability towards Uniform Colouration, Bio-Activation and Ultraviolet-Proof Finishing of Silk Fabric. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104343.
- 14 Cao, J.; Wang, C. Multifunctional Surface Modification of Silk Fabric via Graphene Oxide Repeatedly Coating and Chemical Reduction Method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 380–388.
- 15 Ali, B. A.; Allam, N. K. Silkworms as a Factory of Functional Wearable Energy Storage Fabrics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12649.
- 16 Fometu, S. S.; Wu, G.; Ma, L.; Davids, J. S. A Review on the Biological Effects of Nanomaterials on Silkworm (Bombyx Mori). Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 190–202.
- 17 Leem, J. W.; Fraser, M. J.; Kim, Y. L. Transgenic and Diet-Enhanced Silk Production for Reinforced Biomaterials: A Metamaterial Perspective. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 22, 79–102.
- 18 Shimizu, K. Genetic Engineered Color Silk: Fabrication of a Photonics Material through a Bioassisted Technology. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2018, 13, 041003.
- 19 Xu, H.; O'Brochta, D. A. Advanced Technologies for Genetically Manipulating the Silkworm Bombyx Mori, a Model Lepidopteran Insect. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20150487.
- 20 Iizuka, T.; Sezutsu, H.; Tatematsu, K.; Kobayashi, I.; Yonemura, N.; Uchino, K.; Nakajima, K.; Kojima, K.; Takabayashi, C.; Machii, H.; et al. Colored Fluorescent Silk Made by Transgenic Silkworms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5232–5239.
- 21 Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J. Progress in Modification of Silk Fibroin Fiber. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 919–930.
- 22 Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Y.; Marelli, B.; Xia, X.; Tao, T. H. Engineering the Future of Silk Materials through Advanced Manufacturing. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706983.
- 23 Ramos, N.; Miranda, M. S.; Franco, A. R.; Silva, S. S.; Azevedo, J.; Dias, I. R.; Reis, R. L.; Viegas, C.; Gomes, M. E. Toward Spinning Greener Advanced Silk Fibers by Feeding Silkworms with Nanomaterials. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11872–11887.
- 24 Hu, L.; Han, Y.; Ling, S.; Huang, Y.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Direct Observation of Native Silk Fibroin Conformation in Silk Gland of Bombyx Mori Silkworm. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1874–1879.
- 25 Das, S.; Soundar, S.; Gunaseelan, N. P. Colored Cocoon Silk. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 14067–14076.
- 26 Campbell, F. L. Preliminary Experiments on the Toxicity of Certain Coal-Tar Dyes for the Silkworm. J. Econ. Entomol. 1932, 25, 905–917.
- 27 Wang, J.-T.; Li, L.-L.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Liu, S.-L.; Jiang, L.-H.; Shen, Q. Directly Obtaining High Strength Silk Fiber from Silkworm by Feeding Carbon Nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 417–421.
- 28 Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Jian, M.; Zhang, Y. Feeding Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene to Silkworms for Reinforced Silk Fibers. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6695–6700.
- 29 Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Dai, F.; Zhao, H. Characterization of Silkworm Larvae Growth and Properties of Silk Fibres after Direct Feeding of Copper or Silver Nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2017, 129, 125–134.
- 30 Nambajjwe, C.; Musinguzi, W. B.; Rwahwire, S.; Kasedde, A.; Namuga, C.; Nibikora, I. Improving Electricity from Silk Cocoons through Feeding Silkworms with Silver Nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1221–1226.
- 31 Lu, H.; Jian, M.; Yin, Z.; Xia, K.; Shi, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Silkworm Silk Fibers with Multiple Reinforced Properties Obtained through Feeding Ag Nanowires. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 547–555.
- 32 Cai, L.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Reinforced and Ultraviolet Resistant Silks from Silkworms Fed with Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2551–2557.
- 33 Guo, Z.; Xie, W.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.; Gao, F.; Li, S.; Zhao, L. In Situ Biomineralization by Silkworm Feeding with Ion Precursors for the Improved Mechanical Properties of Silk Fiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 21–26.
- 34 Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Z.; Tong, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Dai, F. Effect of Different Additives in Diets on Secondary Structure, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Silkworm Silk. Materials 2019, 12, 14.
- 35 Wu, G.; Song, P.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Y. Robust Composite Silk Fibers Pulled Out of Silkworms Directly Fed with Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 533–538.
- 36 Tansil, N. C.; Li, Y.; Teng, C. P.; Zhang, S.; Win, K. Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Y.; Han, M.-Y. Intrinsically Colored and Luminescent Silk. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1463–1466.
- 37 Tansil, N. C.; Li, Y.; Koh, L. D.; Peng, T. C.; Win, K. Y.; Liu, X. Y.; Han, M.-Y. The Use of Molecular Fluorescent Markers to Monitor Absorption and Distribution of Xenobiotics in a Silkworm Model. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9576–9583.
- 38 Cheng, L.; Zhao, H.; Huang, H.; Li, B.; Li, R. K. Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Dai, F. Quantum Dots-Reinforced Luminescent Silkworm Silk with Superior Mechanical Properties and Highly Stable Fluorescence. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 9945–9957.
- 39 Fan, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shao, H.; Wang, J.; Cao, C.; Zhu, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y. Super-Strong and Intrinsically Fluorescent Silkworm Silk from Carbon Nanodots Feeding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 75.
- 40 Liu, J.; Kong, T.; Xiong, H.-M. Mulberry-Leaves-Derived Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Feeding Silkworms to Produce Brightly Fluorescent Silk. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200152.
- 41 Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, L. Dual-Performance Optimized Silks from Ultra-Low Dose Polymer Dots Feeding and Its Absorption, Distribution and Excretion in the Silkworms. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 845–858.
- 42 Zhan, Q.; Fan, S.; Wang, D.; Yao, X.; Shao, H.; Zhang, Y. Super-Strong and Uniform Fluorescent Composite Silk from Trace AIE Nanoparticle Feeding. Compos. Commun. 2020, 21, 100414.
- 43 Zheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Fan, S.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Intrinsically Fluorescent Silks from Silkworms Fed with Rare-Earth Upconverting Phosphors. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 4021–4027.
- 44 Yan, M.; Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheong, W.-C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lian, C.; et al. Biofabrication Strategy for Functional Fabrics. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6017–6021.
- 45 Lin, N.; Cao, L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.-Y. Functionalization of Silk Fibroin Materials at Mesoscale. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8885–8902.
- 46 Xiao, L.; Liu, K.; Duan, L.; Cheng, X. Reaction-Based Fluorescent Silk Probes with High Sensitivity and Selectivity to Hg2+ and Ag+ Ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4877–4887.
- 47 Yin, J.; Huang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; James, T. D.; Lin, W. Small Molecule Based Fluorescent Chemosensors for Imaging the Microenvironment within Specific Cellular Regions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12098–12150.
- 48 Pashaei, B.; Karimi, S.; Shahroosvand, H.; Abbasi, P.; Pilkington, M.; Bartolotta, A.; Fresta, E.; Fernandez-Cestau, J.; Costa, R. D.; Bonaccorso, F. Polypyridyl Ligands as a Versatile Platform for Solid-State Light-Emitting Devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5033–5139.
- 49 Karaman, O.; Alkan, G. A.; Kizilenis, C.; Akgul, C. C.; Gunbas, G. Xanthene Dyes for Cancer Imaging and Treatment: A Material Odyssey. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214841.
- 50 Sun, Y.; Lei, Z.; Ma, H. Twisted Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens (AIEgens) Contribute to Mechanochromism Materials: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 14834–14867.
- 51 Wang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Xu, P.; Xiao, R.; Huang, D.; Chen, S.; He, Y.; Zhou, C.; et al. Bismuth-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks and Their Derivatives: Opportunities and Challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 439, 213902.
- 52 Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Ao, H.; Fan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W. Rational Molecular Engineering of Organic Semiconducting Nanoplatforms for Advancing NIR-II Fluorescence Theranostics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2201067.
- 53 Rasheed, T. Carbon Dots as Potential Greener and Sustainable Fluorescent Nanomaterials in Service of Pollutants Sensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116841.
- 54 Amouri, H. Luminescent Complexes of Platinum, Iridium, and Coinage Metals Containing N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands: Design, Structural Diversity, and Photophysical Properties. Chem. Rev. 2022, 123, 230–270.
- 55 Yuan, L.; Lin, W.; Zheng, K.; He, L.; Huang, W. Far-Red to near Infrared Analyte-Responsive Fluorescent Probes Based on Organic Fluorophore Platforms for Fluorescence Imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 622–661.
- 56 Beija, M.; Afonso, C. A. M.; Martinho, J. M. G. Synthesis and Applications of Rhodamine Derivatives as Fluorescent Probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2410–2433.
- 57 Tian, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Qin, C. Design, Synthesis and Application in Analytical Chemistry of Photo-Sensitive Probes Based on Coumarin. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 565–581.
- 58 Yan, F.; Fan, K.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zu, F.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Fluorescein Applications as Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Analytes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 15–35.
- 59 Li, H.; Kim, H.; Xu, F.; Han, J.; Yao, Q.; Wang, J.; Pu, K.; Peng, X.; Yoon, J. Activity-Based NIR Fluorescent Probes Based on the Versatile Hemicyanine Scaffold: Design Strategy, Biomedical Applications, and Outlook. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1795–1835.
- 60 Yan, M.; He, D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, P.; Sun, Y.; Qu, L.; Li, Z. Explorations into the Meso-Substituted BODIPY-Based Fluorescent Probes for Biomedical Sensing and Imaging. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116771.
- 61 Poronik, Y. M.; Vygranenko, K. V.; Gryko, D.; Gryko, D. T. Rhodols – Synthesis, Photophysical Properties and Applications as Fluorescent Probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5242–5265.
- 62 Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H. J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W. A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737.
- 63 Shi, L.; Lu, S. Precise Carbon Dots Synthesis: Building Bridges between Organic Chemistry and Inorganic Chemistry. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2369–2371.
- 64 Li, S.; Li, L.; Tu, H.; Zhang, H.; Silvester, D. S.; Banks, C. E.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. The Development of Carbon Dots: From the Perspective of Materials Chemistry. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 188–207.
- 65 Li, J.; Gong, X. The Emerging Development of Multicolor Carbon Dots. Small 2022, 18, 2205099.
- 66 Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, T.; Meng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, L. Recent Advance in Carbon Dots: From Properties to Applications. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1364–1388.
- 67 Ðorđević, L.; Arcudi, F.; Cacioppo, M.; Prato, M. A Multifunctional Chemical Toolbox to Engineer Carbon Dots for Biomedical and Energy Applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 112–130.
- 68 Zhai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shi, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Zhang, T.; Lu, S. Carbon Dots as New Building Blocks for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Electrocatalysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103426.
- 69 Wang, B.; Yu, J.; Sui, L.; Zhu, S.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Rational Design of Multi-Color-Emissive Carbon Dots in a Single Reaction System by Hydrothermal. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001453.
- 70 Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and Synthesis of Carbon Dots: From Carbon Dots to Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316.
- 71 Ai, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chang, J.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Insights into Photoluminescence Mechanisms of Carbon Dots: Advances and Perspectives. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 839–856.
- 72 Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Ushakova, E. V.; He, B.; Xing, G.; Tang, Z.; Rogach, A. L.; Qu, S. Assignment of Core and Surface States in Multicolor-Emissive Carbon Dots. Small 2022, online, 2204158.
- 73 Cao, L.; Zan, M.; Chen, F.; Kou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Mei, Q.; Hou, Z.; Dong, W.-F.; Li, L. Formation Mechanism of Carbon Dots: From Chemical Structures to Fluorescent Behaviors. Carbon 2022, 194, 42–51.
- 74
Wang, B.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Lu, S. Carbon Dots: Mysterious Past, Vibrant Present, and Expansive Future. Trends Chem. 2022, 5, 76–87.
10.1016/j.trechm.2022.10.005 Google Scholar
- 75 Fu, R.; Song, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Zou, B.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Lu, S. Disulfide Crosslinking-Induced Aggregation: Towards Solid-State Fluorescent Carbon Dots with Vastly Different Emission Colors. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1007–1014.
- 76 Pirsaheb, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Salimi, A. Current Advances of Carbon Dots Based Biosensors for Tumor Marker Detection, Cancer Cells Analysis and Bioimaging. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 83–99.
- 77 Wareing, T. C.; Gentile, P.; Phan, A. N. Biomass-Based Carbon Dots: Current Development and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15471–15501.
- 78 Jia, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, G.; Shuang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, C.; Du, F. Nitrogen Doped Biomass Derived Carbon Dots as a Fluorescence Dual-Mode Sensing Platform for Detection of Tetracyclines in Biological and Food Samples. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134245.
- 79 Hoang, V. C.; Dinh, K. N.; Gomes, V. G. Iodine Doped Composite with Biomass Carbon Dots and Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Versatile Bifunctional Electrode for Energy Storage and Oxygen Reduction Reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 22650–22662.
- 80 Liu, H.; Ding, J.; Zhang, K.; Ding, L. Construction of Biomass Carbon Dots Based Fluorescence Sensors and Their Applications in Chemical and Biological Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 315–337.
- 81 Xiang, S.; Tan, M. Carbon Dots Derived from Natural Sources and Their Biological and Environmental Impacts. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 3206–3225.
- 82 Ma, H.; Guan, L.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, F.; Li, X. Synthesis and Enhancement of Carbon Quantum Dots from Mopan Persimmons for Fe3+ Sensing and Anti-Counterfeiting Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139906.
- 83 Zhang, Y.; Zhuo, P.; Yin, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z. Solid-State Fluorescent Carbon Dots with Aggregation-Induced Yellow Emission for White Light-Emitting Diodes with High Luminous Efficiencies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2019, 11, 24395−24403.
- 84 He, C.; Li, X.-Q.; Feng, G.-L.; Long, W.-J. A Universal Strategy for Green and in situ Synthesis of Carbon Dot-Based Pickling Solution. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 5842–5855.
- 85 Liu, C.; Li, H.; Cheng, R.; Guo, J.; Li, G.-X.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.-F.; Yang, X.; Chen, S. Facile Synthesis, High Fluorescence and Flame Retardancy of Carbon Dots. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 163–171.
- 86 Li, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Xia, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Sustainable Silk-Derived Multimode Carbon Dots. Small 2021, 17, 2103623.
- 87 Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Liang, G.; Gu, A. Preparation of Multicolor-Emissive Carbon Dots with High Quantum Yields and Their Epoxy Composites for Fluorescence Anti-Counterfeiting and Light-Emitting Devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 8441–8458.
- 88 Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Z. Solvent-Dependent Red Emissive Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Sensing and Solid-State Luminescence. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 360, 131645.
- 89 Ren, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, X.; Song, R.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, S. Precisely Controlled Up/Down-Conversion Liquid and Solid State Photoluminescence of Carbon Dots. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800115.
- 90 Ding, H.; Wei, J.-S.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Xiong, H.-M. Solvent-Controlled Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Carbon Dots with a Wide Color Gamut and Narrowed Emission Peak Widths. Small 2018, 14, 1800612.
- 91 Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ding, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Xiong, H. Rational Synthesis of Silane-Functionalized Carbon Dots with High- Efficiency Full-Color Solid-State Fluorescence for Light Emitting Diodes. Carbon 2023, 203, 1–10.
- 92 Zheng, Y.; Arkin, K.; Hao, J.; Zhang, S.; Guan, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Shang, Q. Multicolor Carbon Dots Prepared by Single-Factor Control of Graphitization and Surface Oxidation for High-Quality White Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100688.
- 93 Russo, C.; Apicella, B.; La Rocca, A.; Sirignano, M. Fluorescent Carbon Dots Synthesis in Premixed Flames: Influence of the Equivalence Ratio. Carbon 2023, 201, 659–666.
- 94 Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Huang, H.; Lu, F.; Kang, Z. Chiral Control of Carbon Dots via Surface Modification for Tuning the Enzymatic Activity of Glucose Oxidase. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5877–5886.
- 95 Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Multiple Color Emission by Controlled Graphitization and Surface Functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740.
- 96 Das, A.; Kundelev, E. V.; Vedernikova, A. A.; Cherevkov, S. A.; Danilov, D. V.; Koroleva, A. V.; Zhizhin, E. V.; Tsypkin, A. N.; Litvin, A. P.; Baranov, A. V.; et al. Revealing the Nature of Optical Activity in Carbon Dots Produced from Different Chiral Precursor Molecules. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 92.
- 97 Geng, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; et al. Retrosynthesis of Tunable Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Precise Long-Term Mitochondrial Tracking. Small 2019, 15, 1901517.
- 98 Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Quan, T.; Tao, Y.; Tian, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Gao, D. Sulfuric-Acid-Mediated Synthesis Strategy for Multi-Colour Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Application in Anti-Counterfeiting, Information Encryption, and Rapid Cytoplasmic Imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 650–663.
- 99 Senanayake, R. D.; Yao, X.; Froehlich, C. E.; Cahill, M. S.; Sheldon, T. R.; McIntire, M.; Haynes, C. L.; Hernandez, R. Machine Learning-Assisted Carbon Dot Synthesis: Prediction of Emission Color and Wavelength. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 5918−5928.
- 100 Wang, Q.; Pang, E.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, S.; Yi, J.; Zeng, J.; Lan, M. Regulating Photochemical Properties of Carbon Dots for Theranostic Applications. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, e1862.
- 101 Jin, Z.; Hildebrandt, N. Semiconductor Quantum Dots for in Vitro Diagnostics and Cellular Imaging. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 394–403.
- 102 Pitkänen, L.; Striegel, A. M. Size-Exclusion Chromatography of Metal Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 311–320.
- 103 Zhou, W.; Coleman, J. J. Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 20, 352–360.
- 104 Zhou, R.; Xu, J.; Luo, P.; Hu, L.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L. Near-Infrared Photoactive Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101923.
- 105 Solhi, E.; Hasanzadeh, M. Recent Advances on the Biosensing and Bioimaging Based on Polymer Dots as Advanced Nanomaterial: Analytical Approaches. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 840–852.
- 106 Li, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L. Toxicity, Uptake and Transport Mechanisms of Dual-Modal Polymer Dots in Penny Grass (Hydrocotyle Vulgaris L.). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114877.
- 107 Algar, W. R.; Massey, M.; Rees, K.; Higgins, R.; Krause, K. D.; Darwish, G. H.; Peveler, W. J.; Xiao, Z.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Gupta, R.; et al. Photoluminescent Nanoparticles for Chemical and Biological Analysis and Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 9243–9358.
- 108 Massey, M.; Wu, M.; Conroy, E. M.; Algar, W. R. Mind Your P's and Q's: The Coming of Age of Semiconducting Polymer Dots and Semiconductor Quantum Dots in Biological Applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 30–40.
- 109 Wu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, G.; Sun, H.; Yin, S. Recent Advances in the Development and Applications of Conjugated Polymer Dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2995–3015.
- 110 Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Hong, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Fabrication of Fluorescent Nanoparticles Based on AIE Luminogens (AIE Dots) and Their Applications in Bioimaging. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 283–293.
- 111 Würthner, F. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE): A Historical Perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14192–14196.
- 112 Lee, M. M. S.; Yu, E. Y.; Chau, J. H. C.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Inspiration from Nature: BioAIEgens for Biomedical and Sensing Applications. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121712.
- 113 Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Gong, G.; Chen, H.; He, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tang, B. Z. Tetraphenylnaphthosiline (TPNS): A Potential Building Block for Deep-Blue Emitter Featured Aggregation-Induced Blue-Shifted Emission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 14517–14524.
- 114 Chen, B.; Wang, F. Emerging Frontiers of Upconversion Nanoparticles. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 427–439.
- 115 Cheng, X.; Zhou, J.; Yue, J.; Wei, Y.; Gao, C.; Xie, X.; Huang, L. Recent Development in Sensitizers for Lanthanide-Doped Upconversion Luminescence. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15998–16050.
- 116 Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Yuan, W.; Su, Q.; Li, F. Upconversion Nanoprobes for Biodetections. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 354, 155–168.
- 117 Ansari, A. A.; Parchur, A. K.; Thorat, N. D.; Chen, G. New Advances in Pre-Clinical Diagnostic Imaging Perspectives of Functionalized Upconversion Nanoparticle-Based Nanomedicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 440, 213971.
- 118 Ansari, A. A.; Parchur, A. K.; Chen, G. Surface Modified Lanthanide Upconversion Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery, Cellular Uptake Mechanism, and Current Challenges in NIR-Driven Therapies. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 457, 214423.
- 119 Wu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, K. Crystalline Phase and Morphology Controlling to Enhance the Up-Conversion Emission from NaYF4:Yb,Er Nanocrystals. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 373–379.
Citing Literature
15 August, 2023
Pages 2035-2046




