Yellow-Fluorescence Carbon Dots Employed for pH Sensing and Detection of Tigecycline†
Jingwen Zhao
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715 China
Chongqing Academy of Metrology and Quality Inspection, Chongqing, 401121 China
Search for more papers by this authorJunchen Wang
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715 China
Search for more papers by this authorLinggao Zeng
NMPA Key Laboratory for Quality Monitoring of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, Chongqing Institute for Food and Drug Control, Chongqing, 401121 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sen Zhou
Chongqing Academy of Metrology and Quality Inspection, Chongqing, 401121 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoming Yang
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715 China
NMPA Key Laboratory for Quality Monitoring of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, Chongqing Institute for Food and Drug Control, Chongqing, 401121 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJingwen Zhao
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715 China
Chongqing Academy of Metrology and Quality Inspection, Chongqing, 401121 China
Search for more papers by this authorJunchen Wang
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715 China
Search for more papers by this authorLinggao Zeng
NMPA Key Laboratory for Quality Monitoring of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, Chongqing Institute for Food and Drug Control, Chongqing, 401121 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sen Zhou
Chongqing Academy of Metrology and Quality Inspection, Chongqing, 401121 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoming Yang
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing, 400715 China
NMPA Key Laboratory for Quality Monitoring of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, Chongqing Institute for Food and Drug Control, Chongqing, 401121 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Carbon Dots Based Functional Materials.
Comprehensive Summary
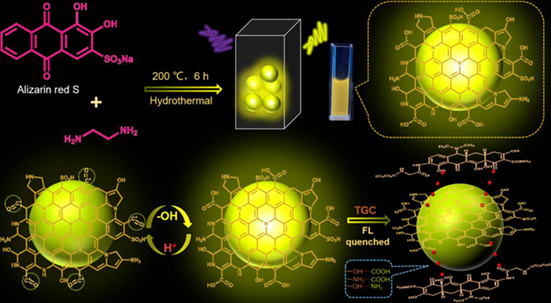
Long-wavelength fluorescence carbon dots (CDs) show great importance in multiple fields, especially for the biochemical sensing. Here, we proposed one type of CDs doped with nitrogen and sulfur through the hydrothermal method, which exhibited obvious yellow-fluorescence in aqueous solution. Importantly, the fluorescence intensity of CDs decreased with pH decreasing in the acidic range, thus a linear relationship between pH and fluorescence intensity was established, exhibiting the potential of pH sensing. Additionally, introducing tigecycline into CDs resulted in their decreased fluorescence, thus, we further established a strategy of detecting tigecycline with the concentration range of 200 μM to 7 nM. Meanwhile, we elucidated the static quenching as the major mechanism for CDs responding tigecycline, which was induced by the formed new complex between CDs and tigecycline. Furthermore, the practicality of the method was verified by examining the recovery of tigecycline in the actual lake-water samples.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300421-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 527.9 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Shi, X.; Hu, Y.; Meng, H.-M.; Yang, J.; Qu, L.; Zhang, X.-B.; Li, Z. Red Emissive Carbon Dots with Dual Targetability for Imaging Polarity in Living Cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 306, 127582.
- 2 Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, T.; Ran, G.; Song, Q. Cadmium Induced Aggregation of Orange–Red Emissive Carbon Dots with Enhanced Fluorescence for Intracellular Imaging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 128092.
- 3 Meng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Facile Synthesis of Orange Fluorescence Multifunctional Carbon Dots for Label-Free Detection of Vitamin B12 and Endogenous/Exogenous Peroxynitrite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124422.
- 4 Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Jiao, Y.; Li, J.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Facile Synthesis of Multifunctional Carbon Dots with 54.4% Orange Emission for Label-Free Detection of Morin and Endogenous/Exogenous Hypochlorite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127289.
- 5 Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Peng, H.; Zhu, J. Synthesis, Characterization and Cells and Tissues Imaging of Carbon Quantum Dots. Opt. Mater. 2017, 72, 15–19.
- 6 Jana, P.; Dev, A. Carbon Quantum Dots: A Promising Nanocarrier for Bioimaging and Drug Delivery in Cancer. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104068.
- 7 Liu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.; Song, H.; Yang, B. One-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Conjugated Carbonized Polymer Dots with 31% Efficient Red Emission for in vivo Imaging. Small 2018, 14, 1703919.
- 8 Yang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, W.; Cao, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, X. Orange-Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots: Toward Application in Wound pH Monitoring based on Colorimetric and Fluorescent Changing. Small 2019, 15, 1902823.
- 9 Chen, J.; Wei, J.-S.; Zhang, P.; Niu, X.-Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Ding, H.; Xiong, H.-M. Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Fingerprints Detection by Spray Method: Coffee Ring Effect and Unquenched Fluorescence in Drying Process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18429–18433.
- 10 Chen, J.; Yuan, N.; Jiang, D.; Lei, Q.; Liu, B.; Tang, W.; Row, K. H.; Qiu, H. Octadecylamine and Glucose-Coderived Hydrophobic Carbon Dots-Modified Porous Silica for Chromatographic Separation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3398–3401.
- 11 Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, R.; Qu, L.; Li, Z. Simultaneous Monitoring of Mitochondrial Viscosity and Membrane Potential based on Fluorescence Changing and Location Switching of Carbon Dots in Living Cells. Carbon 2022, 195, 112–122.
- 12 Lv, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, C.; Li, S.; Sun, S.; Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Long-WaveLength (Red to Near-infrared) Emissive Carbon Dots: Key Factors for Synthesis, Fluorescence Mechanism, and Applications in Biosensing and Cancer Theranostics. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3653–3664.
- 13 Lan, M.; Guo, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Q.; Yan, L.; Xia, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Carbon Dots as Multifunctional Phototheranostic Agents for Photoacoustic/Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1800077.
- 14 Lan, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Guo, L.; Niu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhu, G.; Lee, C.-S.; Zhang, W. Two-Photon-Excited near-Infrared Emissive Carbon Dots as Multifunctional Agents for Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3113–3123.
- 15 Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Rao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, C.; Shan, Z.; Ren, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, X. Green and High-Yield Synthesis of Carbon Dots for Ratiometric Fluorescent Determination of pH and Enzyme Reactions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111264.
- 16 Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, X. Carbon-Dot-Based Probe Designed to Detect Intracellular pH in Fungal Cells for Building its Relationship with Intracellular Polysaccharide. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3718–3726.
- 17 Tan, Z.; Gao, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Ge, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, H.; You, Y. A Multifunctional Fluorescence MOF Material: Triple- Channel pH Detection for Strong Acid and Strong Base, Recognition of Moxifloxacin and Tannic acid. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2023, 441, 114708.
- 18 Kong, L.; Du, X.; Ren, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Chi, M.; Wang, Y.; Fang, H. Lab-in-Fibers: Single Optical Fiber with Three Channels for Simultaneous Detection of pH Value, Refractive Index and Temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 385, 133727.
- 19 Daghrir, R.; Drogui, P. Tetracycline Antibiotics in the Environment: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett 2013, 11, 209–227.
- 20 Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Qin, P.; Guo, X.; Bi, B.; Wang, L.; Xi, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T. Occurrence and Fate of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Typical Urban Water of Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 163–173.
- 21 He, T.; Wang, R.; Liu, D.; Walsh Timothy, R.; Zhang, R.; Lv, Y.; Ke, Y.; Ji, Q.; Wei, R.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, L.; Lei, L.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Pang, M.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Fu, Y.; Song, H.; Hao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Wu, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y. Emergence of Plasmid-Mediated High-Level Tigecycline Resistance Genes in Animals and Humans. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1450–1456.
- 22 Guo, P.; Zeng, W.; Tian, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Chen, C. Quantitative Detection of Nanomolar Drug Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Combined with Internal Standard Method and Two-Step Centrifugation Method. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105202.
- 23 Wu, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, T.; Wan, X.; Zheng, L.; Huang, C. A General Quantitative pH Sensor Developed with Dicyandiamide N-doped High Quantum Yield Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3868–3874.
- 24 Pasandideh-Nadamani, M.; Omrani, A.; Sadeghi-Maleki, M. R.; Samadi-Maybodi, A. Application of CdS Quantum Dots Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Monitoring the Process of Acetaminophen Preparation. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 502, 36–42.
- 25 Zhu, M.; Kim, S.; Mao, L.; Fujitsuka, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Majima, T. Metal-Free Photocatalyst for H2 Evolution in Visible to Near-Infrared Region: Black Phosphorus/Graphitic Carbon Nitride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13234–13242.
- 26 Gong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Shuang, S.; Choi Martin, M. F.; Dong, C. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Dual-doped Hollow Carbon Dot as a Nanocarrier for Doxorubicin Delivery and Biological Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11288–11297.
- 27 Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Multiple Color Emission by Controlled Graphitization and Surface Functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740.
- 28 Long, P.; Feng, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Li, S.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Feng, W. Self-protective Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Fluorine and Nitrogen Codoped Carbon Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800791.
- 29 Qu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, R.; Qi, W.; Su, R.; He, Z. Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotics in Water over Functionalized N,S-doped Carbon Quantum Dots Embedded ZnO Nanoflowers under Sunlight Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123016.
- 30 Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Wang, H.; Meng, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhou, D.; Sun, H. Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Strong Luminescence in both Dispersed and Aggregated States by Tailoring Sulfur Doping. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 609, 54–64.
- 31 Kang, J.-W.; Kang, D.-H. Effect of Amino Acid-Derived Nitrogen and/or Sulfur Doping on the Visible-Light-Driven Antimicrobial Activity of Carbon Quantum Dots: A Comparative Study. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129990.
- 32 Zhao, J.-L.; Luo, Q.-Y.; Ruan, Q.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Redshaw, C.; Jin, Z. Red/Green Tunable-Emission Carbon Nanodots for Smart Visual Precision pH Sensing. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 6091–6098.
- 33 Sun, Z.; Zhou, W.; Luo, J.; Fan, J.; Wu, Z.-C.; Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X. High-Efficient and pH-Sensitive Orange Luminescence from Silicon- Doped Carbon Dots for Information Encryption and Bio-Imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 16–23.
- 34 Liu, X.; Shang, Y. Chen, Z.-R. Vinyl Groups Containing Tetraphenylethylene Derivatives as Fluorescent Probes Specific for Palladium and the Quenching Mechanism. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1599–1605.
- 35 Wang, L.; Jana, J.; Chung, J. S.; Hur, S. H. Glutathione Modified N-Doped Carbon Dots for Sensitive and Selective Dopamine Detection. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 186, 109028.
- 36 Chu, X.; Ning, G.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, S. Bright Mn-Doped Carbon Dots for the Determination of Permanganate and L-ascorbic Acid by a Fluorescence on-off-on Strategy. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–11.
15 December 2023
Pages 3677-3683




