Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Programmable Analytical Feature of Ratiometric Electrochemical Biosensor by Alternating the Binding Site of Ferrocene to DNA Duplex for the Detection of Aflatoxin B1†
- First Published: 13 June 2022
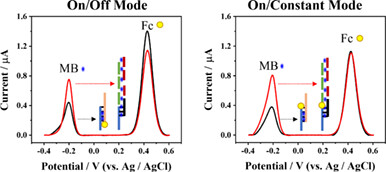
Ratiometric sensing with different detection modes (i.e., On/Off mode, On/Constant mode) could provide varied analytical performances. Here, we demonstrated that the analytical feature of ratiometric electrochemical biosensor can be programmed by alternating the binding site of ferrocene to DNA duplex to achieve detections with different modes.
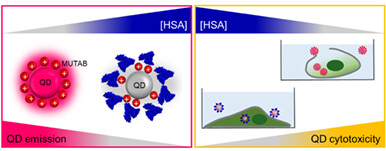
Highly Luminescent Positively Charged Quantum Dots Interacting with Proteins and Cells†
- First Published: 04 August 2022
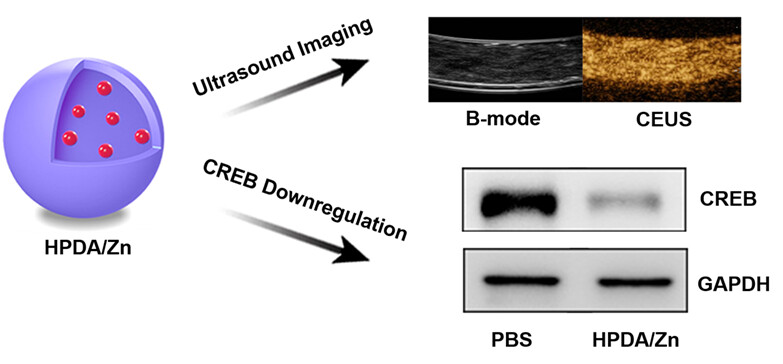
HPDA/Zn as a CREB Inhibitor for Ultrasound Imaging and Stabilization of Atherosclerosis Plaque†
- First Published: 09 October 2022
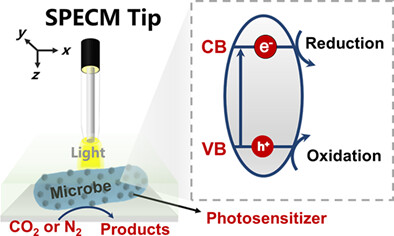
Prospective Roles of Scanning Photoelectrochemical Microscopy in Microbial Hybrid Photosynthesis†
- First Published: 30 September 2022
Light-Harvesting Artificial Cells for the Generation of ATP and NADPH†
- First Published: 30 September 2022
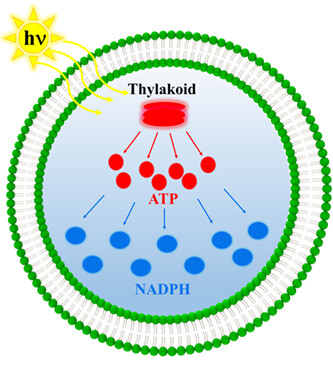
Self-powered artificial cells were developed by encapsulating thylakoids, which continuously convert light energy into chemical energy to produce ATP molecules under illumination. The production of ATP supplies energy for the biological enzyme cascade reactions to promote the generation of NADPH. The self-powered artificial cells were demonstrated to generate ATP and NADPH inside GUVs.
Unlocking G-Quadruplexes as Targets and Tools against COVID-19
- First Published: 13 October 2022
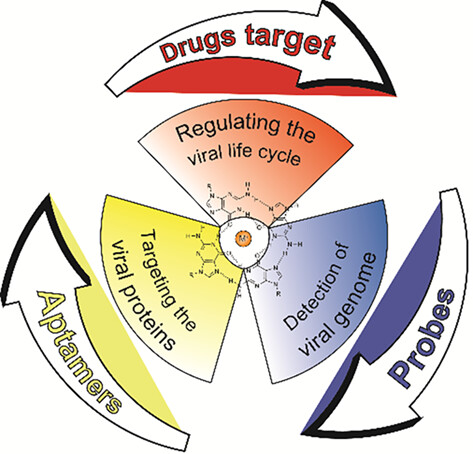
This review summarized the recent advance in the applicability of G-quadruplexes (G4s) as antiviral targets, therapeutic agents and diagnostic tools for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Meanwhile, some challenges and perspectives were also presented, looking forward to advancing the G4s for COVID-19 therapy and diagnosis.
Recent Developments of Atomically Dispersed Metal Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction†
- First Published: 12 October 2022
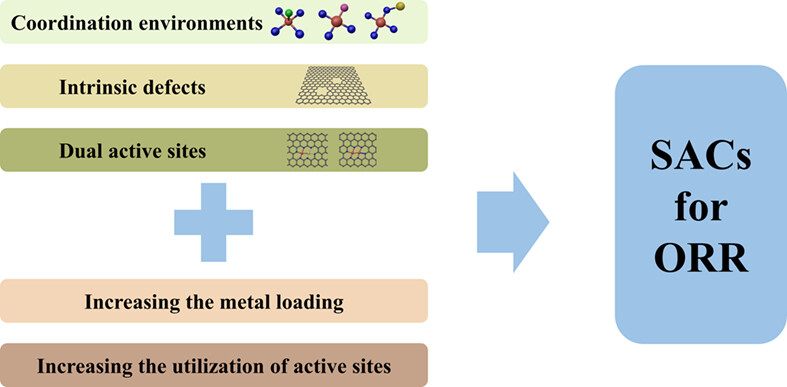
In this review, three main strategies for achieving single-atom catalysts (SACs) with excellent intrinsic activity in the context of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) mechanism are involved including the modulation of coordination environments, the construction of intrinsic defects, and the introduction of dual active sites. And discussions to improve the loading and utilization of active sites are given. This timely review may provide inspiration and reference for the future research of developing advanced SACs for ORR.
Coulometric Response of H+-Selective Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrodes and Its Application in Flexible Sensors†
- First Published: 30 September 2022
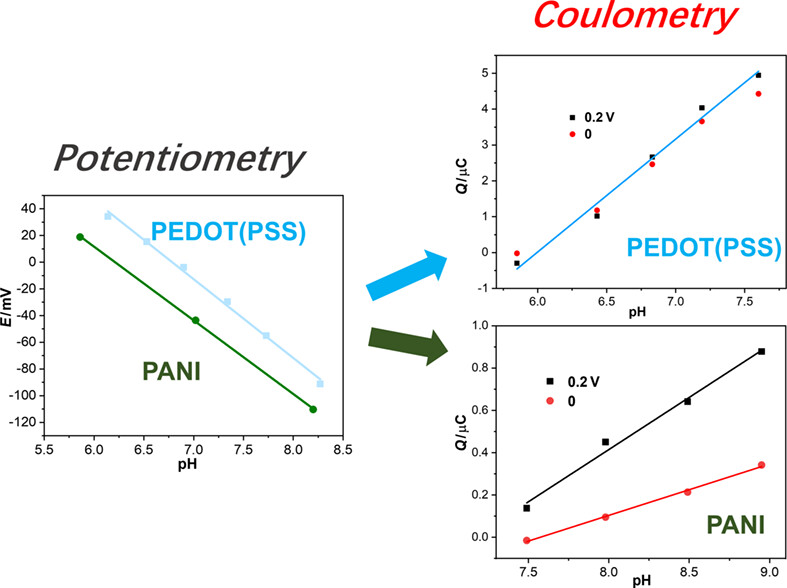
The analytical performance of H+-selective solid-contact ion-selective electrodes (SCISEs) based on solid contact polyaniline doped with chloride (PANI(Cl)) and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with poly(styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT(PSS)) was characterized by a developed coulometric signal transduction method. The exceptional behavior of PANI(Cl) H+-SCISEs from coulometric response and impedance spectrum shows that the capacitance estimated from impedance spectrum at low frequency 10 mHz and coulometric signal of PANI(Cl) based SCISEs is influenced by the applied potentials, whereas PEDOT(PSS) solid contact is independent from the chosen applied potentials.
Stretchable Electrochemical Sensors: From Electrode Fabrication to Cell Mechanotransduction Monitoring†
- First Published: 17 October 2022
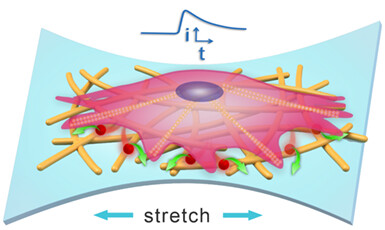
The rising stretchable electrochemical sensors integrated with cell culture, mechanical loading and electrochemical sensing provide a new approach to monitor mechanically evoked biochemical signals from deformed cells. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the fabrication and functionalization of stretchable sensors, and highlight their application in real-time monitoring of cell mechanotransduction.
Recent Advances in Real-Time Analysis of Electrochemical Reactions by Electrochemical Mass Spectrometry†
- First Published: 23 September 2022
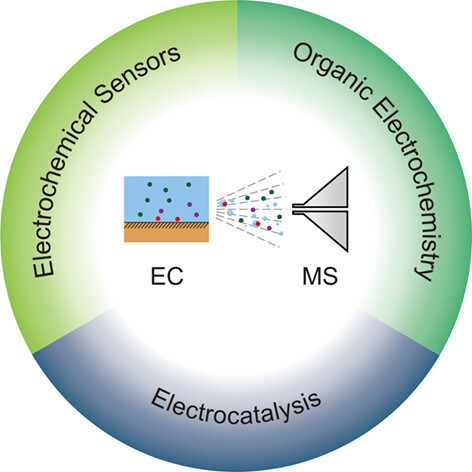
In this review, we introduce the recent advances in electrochemical mass spectrometry (EC-MS) techniques and their applications in real-time analysis and mechanism studies of reactions in electrochemical sensors, organic electrochemistry, and electrocatalysis. We hope this summary will attract the interest of scientists in related areas, who can cooperate and jointly promote the development of this interdisciplinary area.
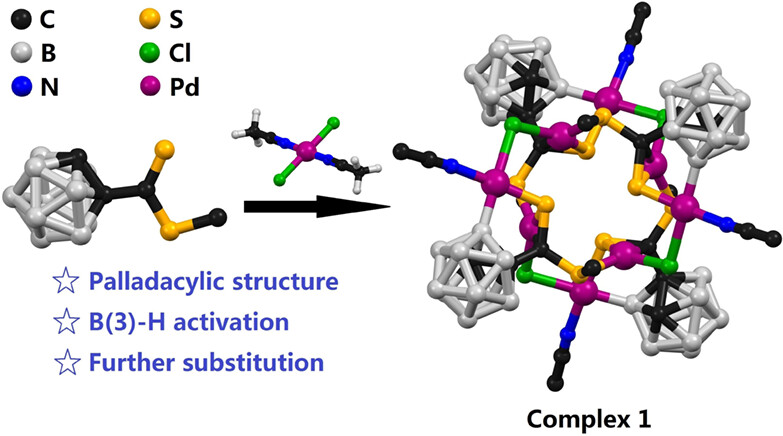
Octanuclear Palladacycles with B(3)–H Bond Activation of o-Carborane†
- First Published: 22 October 2022