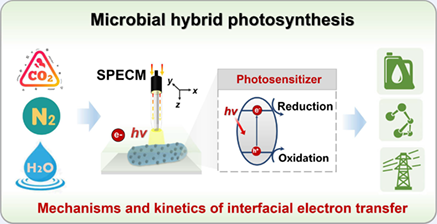
Prospective Roles of Scanning Photoelectrochemical Microscopy in Microbial Hybrid Photosynthesis†
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Abstract
Microbial hybrid photosynthesis has attracted great interests in recent years since it integrates the advantages of natural and artificial photosynthesis for solar-to-chemical conversion. Coupling a light source with scanning electrochemical microscopy, scanning photoelectrochemical microscopy (SPECM) shows great potential in investigating the interfacial reactions of microbial hybrid photosynthesis. In this Emerging Topic, the potential roles of SPECM in revealing biotic–abiotic interfacial electron transfer mechanisms and calculating electrode process kinetics are proposed for hybrid photosynthesis, and this will also inspire the applications of SPECM in the fields including biomineralization, photocatalytic-biodegradation and microbial photoelectrochemical systems.