HPDA/Zn as a CREB Inhibitor for Ultrasound Imaging and Stabilization of Atherosclerosis Plaque†
Correction(s) for this article
-
Corrigendum
- Volume 41Issue 6Chinese Journal of Chemistry
- pages: 741-741
- First Published online: February 15, 2023
Linzi Chen
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Search for more papers by this authorZhenqi Jiang
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
School of Medical Technology, Institute of Engineering Medicine, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Search for more papers by this authorLifei Yang
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Search for more papers by this authorYe Fang
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuwei Lu
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
Search for more papers by this authorOzioma U. Akakuru
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuaishuai Huang
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Juan Li
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Suya Ma
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Aiguo Wu
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorLinzi Chen
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Search for more papers by this authorZhenqi Jiang
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
School of Medical Technology, Institute of Engineering Medicine, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Search for more papers by this authorLifei Yang
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
† Dedicated to Professor Erkang Wang on the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.
Search for more papers by this authorYe Fang
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuwei Lu
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
Search for more papers by this authorOzioma U. Akakuru
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuaishuai Huang
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Juan Li
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Suya Ma
Ningbo Yinzhou No.2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315192 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Aiguo Wu
Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, International Cooperation Base of Biomedical Materials Technology and Application, CAS Key Laboratory of Magnetic Materials and Devices, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Biomedical Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
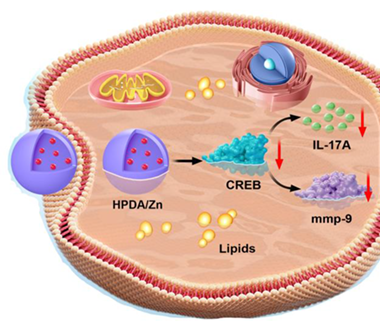
Thrombosis, secondary to rupture of unstable plaque, is a fatal risk factor for myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. At present, more novel methods are needed for the diagnosis and treatment of vulnerable plaque. Here, we report a hollow polydopamine/Zn (HPDA/Zn) ultrasound contrast agent. Through western-blot, Elisa, and other experiments, we found that in addition to having a good contrast-enhancement capability in ultrasound imaging in vitro and in vivo, HPDA/Zn also has the effect of reducing the expression of CREB. CREB protein and its downstream-regulated proteins and factors are closely related to the stability of plaque. HPDA/Zn has the effect of reducing the expression of CREB protein, which leads to the decrease of expression of MMP-9, the regulatory protein downstream of the CREB protein. In addition, it also reduces the secretion of inflammatory factors hs-CRP and IL-17A. Thus, HPDA/Zn can stabilize plaque by inhibiting CREB and reducing plaque vulnerable markers and inflammatory factors. In a word, HPDA/Zn is a kind of ultrasound contrast agent, which can stabilize plaques by inhibiting CREB protein.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202200406-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 10.7 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Benjamin. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, E33–E33.
- 2 Libby, P. Molecular bases of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 1995, 91, 2844–2850.
- 3 Peng, L. P.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, S. L.; Huang, Y. X.; Yang, K.; Huang, W. Memory T cells delay the progression of atherosclerosis via AMPK signaling pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 782.
- 4 Kolodgie, F. D.; Gold, H. K.; Burke, A. P.; Fowler, D. R.; Kruth, H. S.; Weber, D. K.; Farb, A.; Guerrero, L. J.; Hayase, M.; Kutys, R.; Narula, J.; Finn, A. V.; Virmani, R. Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2316–2325.
- 5 Winkels, H.; Ehinger, E.; Vassallo, M.; Buscher, K.; Dinh, H. Q.; Kobiyama, K.; Hamers, A. a. J.; Cochain, C.; Vafadarnejad, E.; Saliba, A. E.; Zernecke, A.; Pramod, A. B.; Ghosh, A. K.; Michel, N. A.; Hoppe, N.; Hilgendorf, I.; Zirlik, A.; Hedrick, C. C.; Ley, K.; Wolf, D. Atlas of the Immune Cell Repertoire in Mouse Atherosclerosis Defined by Single- Cell RNA-Sequencing and Mass Cytometry. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1675–1688.
- 6 Kullo, I. J.; Edwards, W. D.; Schwartz, R. S. Vulnerable plaque: pathobiology and clinical implications. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 1050–1060.
- 7 Tian, L.; Lu, L.; Feng, J.; Melancon, M. P. Radiopaque nano and polymeric materials for atherosclerosis imaging, embolization and other catheterization procedures. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 360–370.
- 8 Gertz, S. D.; Roberts, W. C. Hemodynamic shear force in rupture of coronary arterial atherosclerotic plaques. Am. J. Cardiol. 1990, 66, 1368–1372.
- 9 Rothwell, P. M. Incidence, risk factors and prognosis of stroke and TIA: the need for high-quality, large-scale epidemiological studies and meta-analyses. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2003, 16(Suppl. 3), 2–10.
- 10 Mccarthy, C. P.; Vaduganathan, M.; Mccarthy, K. J.; Januzzi, J. L., Jr.; Bhatt, D. L.; Mcevoy, J. W. Left Ventricular Thrombus After Acute Myocardial Infarction: Screening, Prevention, and Treatment. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 642–649.
- 11 Shaywitz, A. J.; Greenberg, M. E. CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 821–861.
- 12 Carlezon, W. A., Jr.; Duman, R. S.; Nestler, E. J. The many faces of CREB. Trends. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 436–445.
- 13 Ichiki, T. Role of cAMP response element binding protein in cardiovascular remodeling: good, bad, or both? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 449–455.
- 14 Jeon, S. H.; Chae, B. C.; Kim, H. A.; Seo, G. Y.; Seo, D. W.; Chun, G. T.; Yie, S. W.; Eom, S. H.; Kim, P. H. The PKA/CREB pathway is closely involved in VEGF expression in mouse macrophages. Mol. Cells 2007, 23, 23–29.
- 15 Kotla, S.; Singh, N. K.; Heckle, M. R.; Tigyi, G. J.; Rao, G. N. The Transcription Factor CREB Enhances Interleukin-17A Production and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, 13.
- 16 Wang, X.; Cui, H.; Lou, Z.; Huang, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, P.; Weng, G. Cyclic AMP responsive element-binding protein induces metastatic renal cell carcinoma by mediating the expression of matrix metallopeptidase-2/9 and proteins associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4191–4198.
- 17 Cheng, H. L.; Hsieh, M. J.; Yang, J. S.; Lin, C. W.; Lue, K. H.; Lu, K. H.; Yang, S. F. Nobiletin inhibits human osteosarcoma cells metastasis by blocking ERK and JNK-mediated MMPs expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35208–35223.
- 18 Gough, P. J.; Gomez, I. G.; Wille, P. T.; Raines, E. W. Macrophage expression of active MMP-9 induces acute plaque disruption in apoE-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 59–69.
- 19 Eldrup, N.; Gronholdt, M. L.; Sillesen, H.; Nordestgaard, B. G. Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 associated with stroke or cardiovascular death in patients with carotid stenosis. Circulation 2006, 114, 1847–1854.
- 20 Melzer, S.; Ankri, R.; Fixler, D.; Tarnok, A. Nanoparticle uptake by macrophages in vulnerable plaques for atherosclerosis diagnosis. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 871–883.
- 21 Xiao, X.; Li, B. X.; Mitton, B.; Ikeda, A.; Sakamoto, K. M. Targeting CREB for cancer therapy: friend or foe. Curr. Cancer. Drug. Targets. 2010, 10, 384–391.
- 22 Tatiparti, K.; Sau, S.; Kashaw, S. K.; Iyer, A. K. siRNA Delivery Strategies: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Developments. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 17.
- 23 Zhu, M. L.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y. M.; Song, P.; Xu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, S. X.; Yang, L. Amorphous nano-selenium quantum dots improve endothelial dysfunction I it in rats and prevent atherosclerosis in mice through Na+/H+ exchanger 1 inhibition. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 115, 26–32.
- 24 Guo, Y. S.; Li, W. X.; Liu, S. W.; Jing, D.; Wang, Y. F.; Feng, Q. F.; Zhang, K. X.; Xu, J. J. Construction of Nanocarriers Based on Endogenous Cell Membrane and Their Application in Nanomedicine. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1623–1640.
- 25 Hu, J.; Ortgies, D. H.; Rodriguez, E. M.; Rivero, F.; Torres, R. A.; Alfonso, F.; Fernandez, N.; Carreno-Tarragona, G.; Monge, L.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Iglesias, M. D.; Granado, M.; Garcia-Villalon, A. L.; Sole, J. G.; Jaque, D. Optical Nanoparticles for Cardiovascular Imaging. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 23.
- 26 Gautam, M.; Thapa, R. K.; Poudel, B. K.; Gupta, B.; Ruttala, H. B.; Nguyen, H. T.; Soe, Z. C.; Ou, W. Q.; Poudel, K.; Choi, H. G.; Ku, S. K.; Yong, C. S.; Kim, J. O. Aerosol technique-based carbon-encapsulated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 448–461.
- 27 Liu, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Nakamura, M. Nanomedicine for drug delivery and imaging: a promising avenue for cancer therapy and diagnosis using targeted functional nanoparticles. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 2527–2537.
- 28 Lv, J. L.; Xu, Y. J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H. Y.; Tang, Z. H. A Novel Vascular Disrupting Agents Noncovalent Polymeric Nanomedicine: Significantly Increased Antitumor Therapeutic Efficiency. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1447–1456.
- 29 Song, X. Y.; Zhang, H. R.; Yan, T.; Hong, T. T.; Zhang, S. S. Controllable Growth and Assembling Strategies Based on Nanomaterials for Targeted and Precise Therapy of Malignant Cancers. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1489–1496.
- 30 Kheirolomoom, A.; Kim, C. W.; Seo, J. W.; Kumar, S.; Son, D. J.; Gagnon, M. K. J.; Ingham, E. S.; Ferrara, K. W.; Jo, H. Multifunctional Nanoparticles Facilitate Molecular Targeting and miRNA Delivery to Inhibit Atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) Mice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8885–8897.
- 31 Nguyen, M. A.; Wyatt, H.; Susser, L.; Geoffrion, M.; Rasheed, A.; Duchez, A. C.; Cottee, M. L.; Afolayan, E.; Farah, E.; Kahiel, Z.; Cote, M.; Gadde, S.; Rayner, K. J. Delivery of MicroRNAs by Chitosan Nanoparticles to Functionally Alter Macrophage Cholesterol Efflux in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6491–6505.
- 32 Gao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Cai, M.; Cao, W.; Liu, Z.; Tong, L.; Cui, G.; Tang, B. H2O2-responsive and plaque-penetrating nanoplatform for mTOR gene silencing with robust anti-atherosclerosis efficacy. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 439–445.
- 33 Shang, B.; Zhang, X.; Ji, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Peng, B.; Deng, Z. Preparation of colloidal polydopamine/Au hollow spheres for enhanced ultrasound contrast imaging and photothermal therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 106, 110174.
- 34 Xie, Y. J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Krug, K. A.; Rinehart, J. D. Perfluorocarbon-loaded polydopamine nanoparticles as ultrasound contrast agents. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12813–12819.
- 35 Johansen, M. L.; Perera, R.; Abenojar, E.; Wang, X.; Vincent, J.; Exner, A. A.; Brady-Kalnay, S. M. Ultrasound-Based Molecular Imaging of Tumors with PTPmu Biomarker-Targeted Nanobubble Contrast Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22.
- 36 Ran, J. Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. J.; Wang, W.; Xiao, L. H.; Jia, S. Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W. D.; Xiao, J.; Wu, X. Y. New Insight into Polydopamine@ ZIF-8 Nanohybrids: A Zinc-Releasing Container for Potential Anticancer Activity. Polymers 2018, 10, 11.
- 37 Choi, S. Y.; Liu, X.; Pan, Z. Zinc deficiency and cellular oxidative stress: prognostic implications in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1120–1132.
- 38 Zago, M. P.; Oteiza, P. I. The antioxidant properties of zinc: Interactions with iron and antioxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 266–274.
- 39 Dou, J.; Chen, Q. Zinc Stannate Nanostructures for Energy Conversion(dagger). Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 367–380.
- 40 Bao, S. Y.; Liu, M. J.; Lee, B.; Besecker, B.; Lai, J. P.; Guttridge, D. C.; Knoell, D. L. Zinc modulates the innate immune response in vivo to polymicrobial sepsis through regulation of NF-kappa B. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, L744–L754.
- 41 Baltaci, A. K.; Yuce, K. Zinc Transporter Proteins. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 517–530.
- 42 Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115.
- 43 Lee, H.; Dellatore, S. M.; Miller, W. M.; Messersmith, P. B. Mussel- inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430.
- 44 Ran, J. Y.; Xiao, L. H.; Wu, W. D.; Liu, Y. K.; Qiu, W.; Wu, J. M. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) as a sacrificial template: one-pot synthesis of hollow poly(dopamine) nanocapsules and yolk-structured poly(dopamine) nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 8.
- 45 Zhang, T.; Jiang, Z.; Xve, T.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Ren, W.; Wu, A.; Huang, P. One-pot synthesis of hollow PDA@DOX nanoparticles for ultrasound imaging and chemo-thermal therapy in breast cancer. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 21759–21766.
- 46 Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yuan, B.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, A. Dual ATP and pH responsive ZIF-90 nanosystem with favorable biocompatibility and facile post-modification improves therapeutic outcomes of triple negative breast cancer in vivo. Biomaterials 2019, 197, 41–50.
- 47 Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Fang, Y.; Ma, S. Downregulation of GSK-3beta Expression via Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction Enhances Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability in New Zealand Rabbits. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 710–722.
Citing Literature
15 January 2023
Pages 199-206




