Self-assembling Monolayer-Assisted Perovskite Growth Enables High-Performance Solar Cells
Jun Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310018 China
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lisha Xie
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorShuncheng Yang
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXinyu Tong
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenwei Pu
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorMengjin Yang
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorYujie Wu
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310018 China
Search for more papers by this authorDaobin Yang
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tao Wang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310018 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ziyi Ge
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJun Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310018 China
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lisha Xie
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorShuncheng Yang
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXinyu Tong
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenwei Pu
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorMengjin Yang
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorYujie Wu
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310018 China
Search for more papers by this authorDaobin Yang
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tao Wang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310018 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ziyi Ge
Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Energy Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315201 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
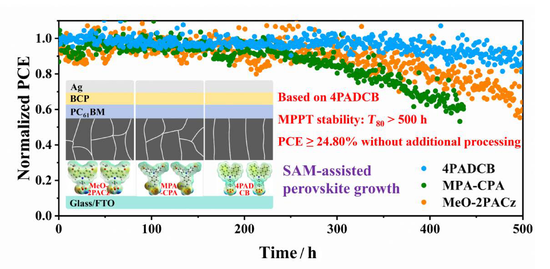
Inverted (p-i-n) perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are favored by researchers owing to their superior compatibility with flexible substrates and tandem device fabrication. Additionally, the hole transport layer (HTL) serves as a template for perovskite growth, which is critical for enhancing the device performance. However, the current research on how the HTL promotes perovskite crystallization is insufficient. Here, 4PADCB, a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) hole transport material, was optimized as a superior template for perovskite growth through comparative analysis; accordingly, compact perovskite film with vertical growth was prepared. The better matched energy level alignment between 4PADCB and perovskite suppressed nonradiative recombination at the interface and enabled rapid hole extraction. Moreover, high-quality perovskite film growth on 4PADCB exhibited lower Young's modulus and less residual stress. By integrating 4PADCB into p-i-n PSCs, the optimal device achieved a power conversion efficiency of 24.80%, with an open-circuit voltage of 1.156 V, thus achieving the best rank among devices without perovskite post-treatment, additives, dopants, or intermediate layers. Furthermore, the unencapsulated device demonstrated exceptional thermostability and photostability under maximum power point tracking. Thus, this work provides a new understanding for the development of novel SAMs and perovskite growth, and it is expected to further improve device performance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400384-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.6 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Huang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Niu, X.; Li, N.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zai, H.; Chen, Q.; Lei, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H. Anion-π Interactions Suppress Phase Impurities in FAPbI3 Solar Cells. Nature 2023, 623, 531–537.
- 2 Yu, S.; Xiong, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ma, F.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, X.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Homogenized NiOx Nanoparticles for Improved Hole Transport in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Science 2023, 382, 1399–1404.
- 3 Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, B.; Gao, D.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Gong, J.; Luther, J. M.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z. Stabilized Hole-Selective Layer for High-Performance Inverted p-i-n Perovskite Solar Cells. Science 2023, 382, 284–289.
- 4 Ullah, A.; Park, K. H.; Nguyen, H. D.; Siddique, Y.; Shah, S. F. A.; Tran, H.; Park, S.; Lee, S. I.; Lee, K.; Han, C.; Kim, K.; Ahn, S.; Jeong, I.; Park, Y. S.; Hong, S. Novel Phenothiazine-Based Self-Assembled Monolayer as a Hole Selective Contact for Highly Efficient and Stable P-i-n Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103175.
- 5 Xie, L.; Du, S.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Pu, Z.; Tong, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, W.; Ge, Z. Molecular Dipole Engineering-Assisted Strain Release for Mechanically Robust Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 5423–5433.
- 6 He, R.; Wang, W.; Yi, Z.; Lang, F.; Chen, C.; Luo, J.; Zhu, J.; Thiesbrummel, J.; Shah, S.; Wei, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Lai, H.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zou, B.; Yin, X.; Ren, S.; Hao, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Stolterfoht, M.; Fu, F.; Tang, W.; Zhao, D. Improving Interface Quality for 1-cm2 All-Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells. Nature 2023, 618, 80–86.
- 7 Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Duan, W.; Yang, J.; Mahmud, M. A.; Lian, Q.; Tang, S.; Liao, C.; Bing, J.; Yi, J.; Leung, T. L.; Cui, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, F.; Huang, Y.; Lambertz, A.; Jankovec, M.; Topič, M.; Bremner, S.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Cheng, C.; Ding, K.; Ho-Baillie, A. Molecular Engineering of Hole-Selective Layer for High Band Gap Perovskites for Highly Efficient and Stable Perovskite-Silicon Tandem Solar Cells. Joule 2023, 7, 2583–2594.
- 8 Sun, X.; Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Xiong, B.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z.; Jen, A. K.-Y. Dopant-Free Crossconjugated Hole-Transporting Polymers for Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903331.
- 9 Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Qi, F.; Lin, F. R.; Jen, A. K. -Y. π-Expanded Carbazoles as Hole-Selective Self-Assembled Monolayers for High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202213560.
- 10 Liu, M.; Bi, L.; Jiang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Tsang, S.; Lin, F. R.; Jen, A. K.-Y. Compact Hole-Selective Self-Assembled Monolayers Enabled by Disassembling Micelles in Solution for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304415.
- 11 Kim, M.; Hohman, J. N.; Cao, Y.; Houk, K. N.; Ma, H.; Jen, A. K.-Y.; Weiss, P. S. Creating Favorable Geometries for Directing Organic Photoreactions in Alkanethiolate Monolayers. Science 2011, 331, 1312–1315.
- 12 Hossain, K.; Kulkarni, A.; Bothra, U.; Klingebiel, B.; Kirchartz, T.; Saliba, M.; Kabra, D. Resolving the Hydrophobicity of the Me-4PACz Hole Transport Layer for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Efficiency >20%. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3860–3867.
- 13 Bi, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Beresneviciute, R.; Tavgeniene, D.; Kapil, G.; Ding, C.; Baranwal, A. K.; Sahamir, S. R.; Sanehira, Y.; Segawa, H.; Grigalevicius, S.; Shen, Q.; Hayase, S. All-Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells Approach 26.5% Efficiency by Employing Wide Bandgap Lead Perovskite Solar Cells with New Monomolecular Hole Transport Layer. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3852–3859.
- 14 Zhang, S.; Ye, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, M.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Liu, Z.; Ning, Z.; Neher, D.; Han, L.; Lin, Y.; Tian, H.; Chen, W.; Stolterfoht, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.-H.; Wu, Y. Minimizing Buried Interfacial Defects for Efficient Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Science 2023, 380, 404–409.
- 15 Al-Ashouri, A.; Köhnen, E.; Li, B.; Magomedov, A.; Hempel, H.; Caprioglio, P.; Márquez, J. A.; Morales Vilches, A. B.; Kasparavicius, E.; Smith, J. A.; Phung, N.; Menzel, D.; Grischek, M.; Kegelmann, L.; Skroblin, D.; Gollwitzer, C.; Malinauskas, T.; Jošt, M.; Matič, G.; Rech, B.; Schlatmann, R.; Topič, M.; Korte, L.; Abate, A.; Stannowski, B.; Neher, D.; Stolterfoht, M.; Unold, T.; Getautis, V.; Albrecht, S. Monolithic Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cell with >29% Efficiency by Enhanced Hole Extraction. Science 2020, 370, 1300–1309.
- 16 Paniagua, S. A.; Li, E. L.; Marder, S. R. Adsorption Studies of a Phosphonic Acid on ITO: Film Coverage, Purity, and Induced Electronic Structure Changes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 2874.
- 17 Magomedov, A.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Kasparavičius, E.; Strazdaite, S.; Niaura, G.; Jošt, M.; Malinauskas, T.; Albrecht, S.; Getautis, V. Self-Assembled Hole Transporting Monolayer for Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801892.
- 18 Liu, J.; Aydin, E.; Yin, J.; De Bastiani, M.; Isikgor, F. H.; Rehman, A. U.; Yengel, E.; Ugur, E.; Harrison, G. T.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Khan, J. I.; Babics, M.; Allen, T. G.; Subbiah, A. S.; Zhu, K.; Zheng, X.; Yan, W.; Xu, F.; Salvador, M. F.; Bakr, O. M.; Anthopoulos, T. D.; Lanza, M.; Mohammed, O. F.; Laquai, F.; De Wolf, S. 28.2%-Efficient, Outdoor-Stable Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cell. Joule 2021, 5, 3169–3186.
- 19 Levine, I.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Musiienko, A.; Hempel, H.; Magomedov, A.; Drevilkauskaite, A.; Getautis, V.; Menzel, D.; Hinrichs, K.; Unold, T.; Albrecht, S.; Dittrich, T. Charge Transfer Rates and Electron Trapping at Buried Interfaces of Perovskite Solar Cells. Joule 2021, 5, 2915–2933.
- 20 Zheng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, T.; Xiao, C.; Gao, D.; Patel, J. B.; Kuciauskas, D.; Magomedov, A.; Scheidt, R. A.; Wang, X.; Harvey, S. P.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Morales, D.; Pruett, H.; Wieliczka, B. M.; Kirmani, A. R.; Padture, N. P.; Graham, K. R.; Yan, Y.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; McGehee, M. D.; Zhu, Z.; Luther, J. M. Co-Deposition of Hole-Selective Contact and Absorber for Improving the Processability of Perovskite Solar Cells. Nat. Energy 2023, 8, 462–472.
- 21 Al-Ashouri, A.; Magomedov, A.; Roß, M.; Jošt, M.; Talaikis, M.; Chistiakova, G.; Bertram, T.; Márquez, J. A.; Köhnen, E.; Kasparavičius, E.; Levcenco, S.; Gil-Escrig, L.; Hages, C. J.; Schlatmann, R.; Rech, B.; Malinauskas, T.; Unold, T.; Kaufmann, C. A.; Korte, L.; Niaura, G.; Getautis, V.; Albrecht, S. Conformal Monolayer Contacts with Lossless Interfaces for Perovskite Single Junction and Monolithic Tandem Solar Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3356–3369.
- 22 Zhumekenov, A. A.; Saidaminov, M. I.; Haque, M. A.; Alarousu, E.; Sarmah, S. P.; Murali, B.; Dursun, I.; Miao, X.-H.; Abdelhady, A. L.; Wu, T.; Mohammed, O. F.; Bakr, O. M. Formamidinium Lead Halide Perovskite Crystals with Unprecedented Long Carrier Dynamics and Diffusion Length. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 32–37.
- 23 Ma, C.; Kang, M.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Kwon, S. J.; Cha, H.-W.; Yang, C.-W.; Park, N.-G. Photovoltaically Top-Performing Perovskite Crystal Facets. Joule 2022, 6, 2626–2643.
- 24 Li, J.; Xie, L.; Liu, G.; Pu, Z.; Tong, X.; Yang, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ge, Z. Multifunctional Trifluoroborate Additive for Simultaneous Carrier Dynamics Governance and Defects Passivation to Boost Efficiency and Stability of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202316898.
- 25 Zhu, C.; Niu, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Hu, C.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Na, G.; Liu, P.; Zai, H.; Ge, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ke, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Sui, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Q. Strain Engineering in Perovskite Solar Cells and Its Impacts on Carrier Dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 815.
- 26 Li, J.; Xie, L.; Pu, Z.; Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Meng, Y.; Han, B.; Bu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Ge, Z. The Synergistic Effect of Pemirolast Potassium on Carrier Management and Strain Release for High-Performance Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301956.
- 27 Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Liu, L.; Ma, S.; Liu, P.; Wu, J.; Shi, C.; Du, Q.; Hao, Y.; Xiang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, P.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q. Interfacial Residual Stress Relaxation in Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Stability. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904408.
- 28 Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, K.; Yang, M.; Xie, L.; Yang, S.; Meng, Y.; Lin, S.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Qiu, Q.; Ge, Z. Rational Design of Ferroelectric 2D Perovskite for Improving the Efficiency of Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells Over 23%. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217526.
- 29 Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Pu, Z.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Yang, M.; Ge, Z. A Deformable Additive on Defects Passivation and Phase Segregation Inhibition Enables the Efficiency of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells over 24%. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2302752.
- 30 Zhu, J.; Luo, Y.; He, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yi, Z.; Thiesbrummel, J.; Wang, C.; Lang, F.; Lai, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, W.; Cui, G.; Ren, S.; Hao, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, F.; Lin, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Stolterfoht, M.; Fu, F.; Zhao, D. A Donor-Acceptor-Type Hole-Selective Contact Reducing Non-Radiative Recombination Losses in Both Subcells towards Efficient All-Perovskite Tandems. Nat. Energy 2023, 8, 714–724.
- 31 Xie, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Bao, Q.; Yang, M.; Niu, X.; Hao, F.; Ge, Z. Multifunctional Anchoring of O-ligands for High-performance and Stable Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. InfoMat 2023, 5, e12379.
- 32 Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Gan, X.; Yu, L.; Yuan, H.; Shang, M.; Lu, C.; Hou, D.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Han, L. Pb-Reduced CsPb0.9Zn0.1I2Br Thin Films for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900896.
- 33 Lee, J.-W.; Bae, S.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; De Marco, N.; Wang, M.; Sun, P.; Yang, Y. A Bifunctional Lewis Base Additive for Microscopic Homogeneity in Perovskite Solar Cells. Chem 2017, 3, 290–302.
- 34 Long, M.; Zhang, T.; Chen, D.; Qin, M.; Chen, Z.; Gong, L.; Lu, X.; Xie, F.; Xie, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, J. Interlayer Interaction Enhancement in Ruddlesden-Popper Perovskite Solar Cells toward High Efficiency and Phase Stability. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1025–1033.
- 35 Yang, T.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhao, K.; Liu, S. (Frank). Lead(II) 2-Ethylhexanoate for Simultaneous Modulated Crystallization and Surface Shielding to Boost Perovskite Solar Cell Efficiency and Stability. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211006.
- 36 Zhang, J.; Che, B.; Zhao, W.; Fang, Y.; Han, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, T.; Chen, T.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J.; Liu, S. (Frank). Polar Species for Effective Dielectric Regulation to Achieve High-Performance CsPbI3 Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202735.
- 37 Cheng, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Ding, J.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Green Solvent Processable, Asymmetric Dopant-Free Hole Transport Layer Material for Efficient and Stable N-i-p Perovskite Solar Cells and Modules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202312231.
- 38 Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, W.; Qiu, W.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Q. Synergistic Transition Metal Ion Co-Doping and Multiple Functional Additive Passivation for Realizing 25.30% Efficiency Perovskite Solar Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 5243–5254.
- 39 Pu, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, L.; Tong, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Yang, D.; Ge, Z. Non-Fullerene Acceptors Assisted Target Therapy for Interface Treatment Enable High Performance Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Small 2024, 2310742.
- 40 Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, W.; Peng, Q. Stable Perovskite Solar Cells with 25.17% Efficiency Enabled by Improving Crystallization and Passivating Defects Synergistically. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 4700–4709.