Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Single-Molecule Observation of Intermediates in Bioorthogonal 2-Cyanobenzothiazole Chemistry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2020)
- Page: 15269
- First Published: 13 August 2020

A single-molecule look at cyanobenzothiazole-based click chemistry is reported by Y. Qing, H. Bayley et al. in their Research Article on page 15711. Individual bond-breaking and bond-making events are recorded as alterations in the ionic current passing through a protein nanoreactor. Snapshots of the intermediates are taken for the reactions of cyanobenzothiazole with thiols and aminothiols, which reveal mechanistic and kinetic information that impacts applications in chemistry.
Inside Cover: Controlling the Product Platform of Carbon Dioxide Reduction: Adaptive Catalytic Hydrosilylation of CO2 Using a Molecular Cobalt(II) Triazine Complex (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2020)
- Page: 15270
- First Published: 13 August 2020

Organometallic treasure hunt A molecular cobalt catalyst “navigates” the CO2 reduction with phenylsilanes to arrive at each product level individually with high selectivity and activity. This demonstrates the possibility of developing adaptive catalytic systems for the use of carbon dioxide as raw material for chemicals or energy carriers, as detailed by C. Werlé, W. Leitner et al. in their Research Article on page 15674.
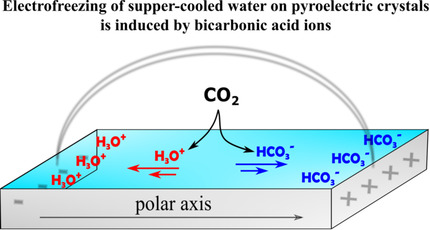
Inside Back Cover: Heterogeneous Electrofreezing of Super-Cooled Water on Surfaces of Pyroelectric Crystals is Triggered by Trigonal Planar Ions (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2020)
- Page: 15763
- First Published: 13 August 2020
Electrofreezing experiments of super-cooled water with different ions were performed on the charged hemihedral faces of pyroelectric LiTaO3 and AgI crystals. In their Communication on page 15575,D. Harries, M. Lahav, I. Lubomirsky et al. demonstrate that HCO3− ions elevate the icing temperature near the positively charged faces, whereas H3O+ slightly reduces the icing temperature.
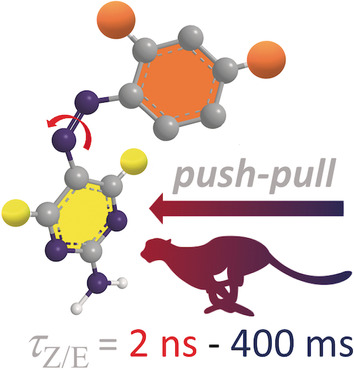
Back Cover: Polysubstituted 5-Phenylazopyrimidines: Extremely Fast Non-ionic Photochromic Oscillators (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2020)
- Page: 15764
- First Published: 20 July 2020

Non-ionic polysubstituted azopyrimidines with strong push–pull character are promising candidates for extremely fast photochromic oscillators. The fast oscillation is based on photoinduced (E)-to-(Z) isomerization of the azo group and the accordingly very fast (Z)-to-(E) thermal relaxation. In their Communication on page 15590, E. Procházková, M. Cigáň et al. demonstrate how the relaxation lifetime can be tuned by proper substitution over eight orders of magnitude from hundreds of milliseconds to several nanoseconds.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Transition-Metal-Free Oxidative Cross-Coupling of Tetraarylborates to Biaryls Using Organic Oxidants
- First Published: 25 August 2020

Oxidative Coupling In their Communication on page 15468, C. Gerleve and A. Studer report the transition-metal-free oxidative cross-coupling of tetraarylborates to generate biaryls by using organic oxidants.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2020
- Pages: 15273-15288
- First Published: 25 August 2020
Author Profile
Viewpoints
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Chain Mail for Catalysts
- Pages: 15294-15297
- First Published: 30 May 2020
Carbon encapsulation constitutes a novel concept for improving the stability and tuning the activity of metal catalysts. The key aspects concerning the working principle of this “chain-mail” approach, as well as the physicochemical properties of the chain mail and metal core that affect the catalytic properties, are considered to highlight directions for applying this strategy in catalyst design.
Minireviews
Electrocatalysis
Electrocatalysis as the Nexus for Sustainable Renewable Energy: The Gordian Knot of Activity, Stability, and Selectivity
- Pages: 15298-15312
- First Published: 30 June 2020
Water, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide are “magic” molecules whose efficient electrocatalytic conversion into suitable energy can deliver limitless renewable energy. Discussed in this Minireview are the key fundamental and experimental factors that aid in the understanding of the dynamic nature of active sites, reaction kinetics, and mechanisms, as well as selectivities and catalyst stabilities on a molecular level.
Advances in Understanding Mechanisms of Perovskites and Pyrochlores as Electrocatalysts using In-Situ X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
- Pages: 15314-15324
- First Published: 27 February 2020
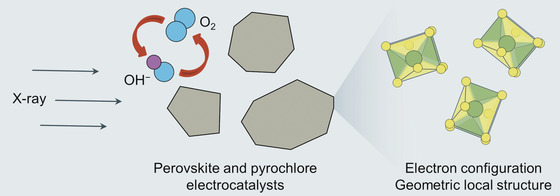
Ray of light: In-situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy methods for electrochemical tests have been developed to follow the changes of electron configurations and geometric local structures of metal oxides during electrocatalysis. This Minireview gives a brief introduction to recent progress in understanding catalytic mechanisms of perovskite and pyrochlore oxides by using this method.
Soft Porous Crystals
Chemistry of Soft Porous Crystals: Structural Dynamics and Gas Adsorption Properties
- Pages: 15325-15341
- First Published: 27 May 2020
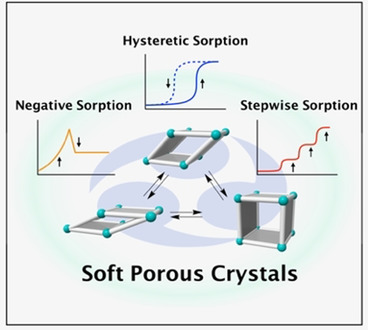
Soft porous crystals (SPCs) can undergo cooperative stimuli-responsive structural transitions that strongly impact the physical properties and pore structure of the crystal. Hysteretic behavior and counterintuitive adsorption phenomena are a consequence of the complex energy landscapes and cooperativity of SPCs with regard to adsorption/desorption-induced deformation.
Reviews
Hydrogels
Stimuli-Responsive Biomolecule-Based Hydrogels and Their Applications
- Pages: 15342-15377
- First Published: 15 November 2019
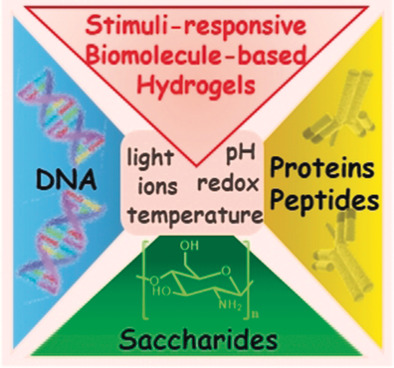
Having control: Stimuli-responsive hydrogels with triggered stiffness properties are attracting growing interest as smart materials for different applications. The Review discusses the design of biomolecule-based stimuli-responsive hydrogels and their applications as self-healing, shape-memory, and controlled drug-release matrices, as well as mechanical actuators. Surface-confined switchable hydrogels and their uses are also introduced.
Capping Agents
Surface Capping Agents and Their Roles in Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Colloidal Metal Nanocrystals
- Pages: 15378-15401
- First Published: 09 October 2019
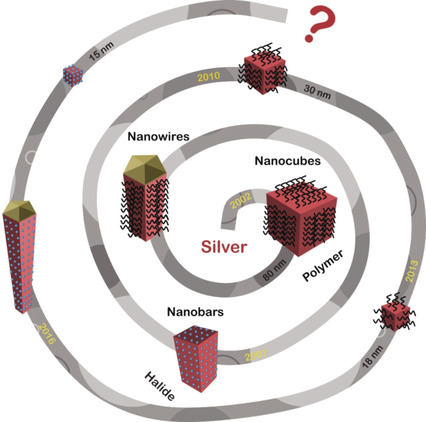
A pivotal role in directing the growth of colloidal metal nanocrystals into diverse but well-controlled shapes is played by surface capping agents. This article offers a comprehensive review of capping agents as well as their use in engineering the surface structures and catalytic properties of metal nanocrystals.
Plastic Recycling
Beyond Mechanical Recycling: Giving New Life to Plastic Waste
- Pages: 15402-15423
- First Published: 11 March 2020
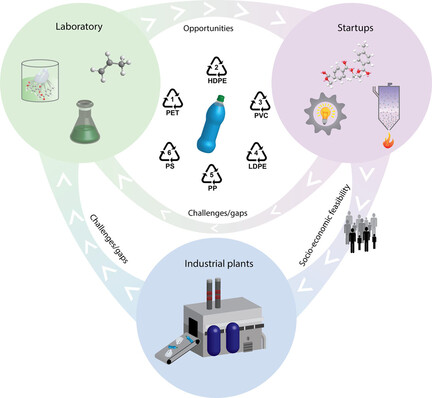
Plastic fantastic: Plastic can rise again and again as a new product. Researchers now know methods with which new plastics can be produced from 100 % recycled material, products that can even be used for food applications. This development is possible thanks to chemical recycling, through which polymer chains are first broken to then be reformed into new molecules, such as plastics but also other chemicals.
Nanoarchitectonics
Nanoarchitectonics beyond Self-Assembly: Challenges to Create Bio-Like Hierarchic Organization
- Pages: 15424-15446
- First Published: 14 March 2020
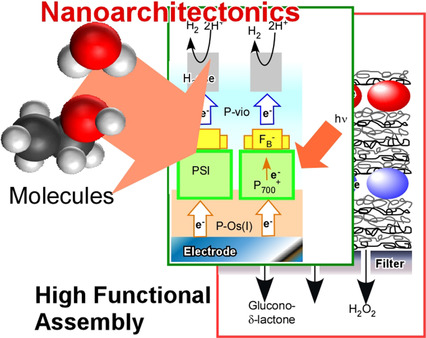
Simple self-assembly methods cannot be used to attain high-level organizations such as those found in biological systems. The introduction of non-equilibrium processes and harmonization of multiple actions is required. As a novel methodology beyond self-assembly, nanoarchitectonics, whose main conceptual aim is the formation of functional materials from nanoscopic units through the fusion of different scientific disciplines, has been proposed for the creation of bio-like high functionality hierarchically organized structures.
Targeted Protein Degradation
Prey for the Proteasome: Targeted Protein Degradation—A Medicinal Chemist's Perspective
- Pages: 15448-15466
- First Published: 19 May 2020

Targeted protein degradation has created tremendous excitement in chemical biology and drug discovery. This Review gives a comprehensive overview of chemical biology tools as well as therapeutic approaches inducing targeted protein degradation and discusses them from a medicinal chemist's perspective.
Communications
Oxidative Coupling | Hot Paper
Transition-Metal-Free Oxidative Cross-Coupling of Tetraarylborates to Biaryls Using Organic Oxidants
- Pages: 15468-15473
- First Published: 11 March 2020
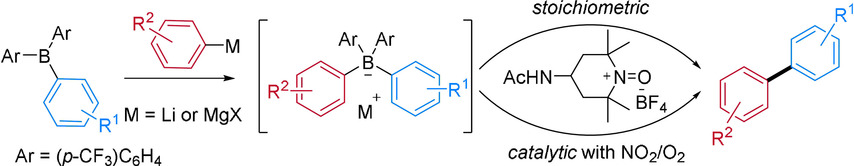
From B-aryl to biaryl: Various biaryl and heterobiaryl systems are accessible via selective (cross)-coupling of readily prepared tetraarylborates through oxidation with Bobbitt's salt. The oxoammonium salt can either be used as a stoichiometric oxidant or as a catalyst in combination with in situ generated NO2 as a cocatalyst and O2 as the terminal oxidant. For reactive borate salts, coupling can also be achieved without the Bobbitt salt by using NO2 as the sole catalyst.
Hybrid Materials
DNA–Polymer Nanostructures by RAFT Polymerization and Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly
- Pages: 15474-15479
- First Published: 17 April 2020
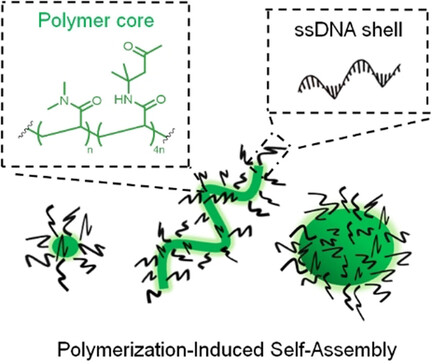
Pisa requirements: Polymerization-induced self-assembly (PISA) is a novel platform technology for preparing intricate DNA–polymer nanostructures of various shapes by using RAFT polymerization directly from single-stranded DNA. Due to the single-stranded DNA shell, these nanostructures can be rationally functionalized by leveraging the complementarity of DNA. Thus, PISA offers a powerful pathway towards intrinsically functional DNA–polymer nanostructures.
Boron Chemistry
Diborane(4) Azides: Surprisingly Stable Sources of Transient Iminoboranes
- Pages: 15480-15486
- First Published: 08 April 2020
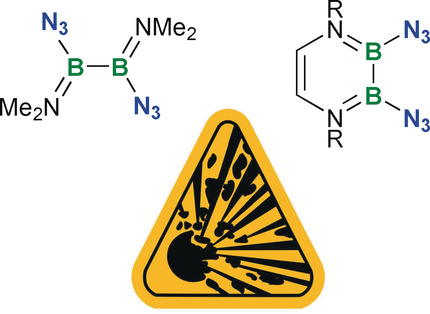
Potentially explosive yet mild-mannered! The synthesis and reactivity of diamino-substituted diborane(4) diazides, the first diborane(4) azides, is reported. Despite the presence of energetic and oxidizing azide groups and of reactive B−B bonds, they are astonishingly robust. The species do not decompose below 100 °C. Two diazides could be pyrolyzed in a controlled manner to diazadiboretidines, the dimerization product of transient iminoboranes.
Electrocatalysis
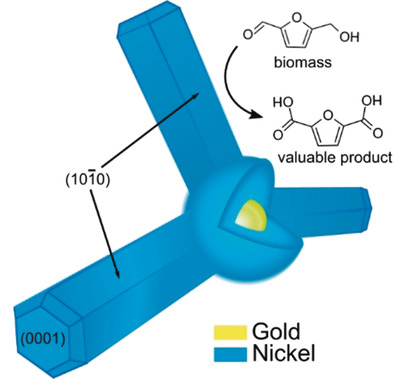
Faceted Branched Nickel Nanoparticles with Tunable Branch Length for High-Activity Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Biomass
- Pages: 15487-15491
- First Published: 25 May 2020
Metal-Free Catalysis
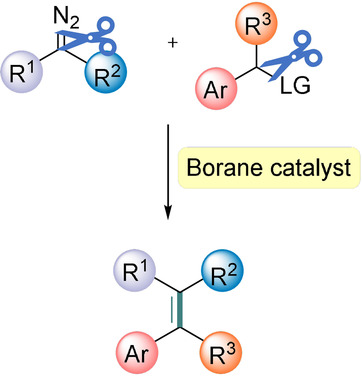
Triarylborane-Catalyzed Alkenylation Reactions of Aryl Esters with Diazo Compounds
- Pages: 15492-15496
- First Published: 02 June 2020
Photocatalysis
Photocatalytic Conversion of Waste Plastics into C2 Fuels under Simulated Natural Environment Conditions
- Pages: 15497-15501
- First Published: 31 January 2020
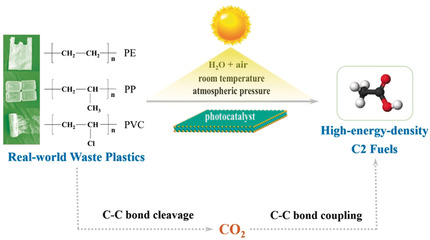
Waste conversion: Reported is the first highly selective conversion of various waste plastics into C2 fuels by a sequential photoinduced C−C bond cleavage and coupling pathway under simulated natural environment conditions. The first step is degradation of plastics into CO2, which is reduced in a second step to C2 fuels over the same photocatalyst.
Zeolites
Disentangling Reaction Processes of Zeolites within Single-Oriented Channels
- Pages: 15502-15506
- First Published: 05 February 2020
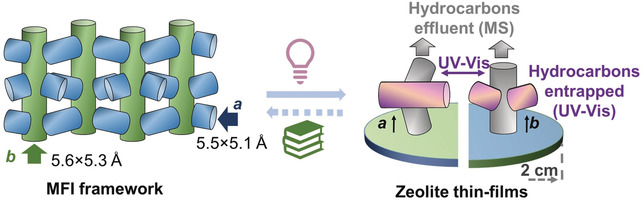
A well-defined model system was developed to establish structure–reactivity relationships for specific zeolite-channel orientations during catalytic reactions, such as the methanol-to-hydrocarbons process. Straight zeolite-channels favor the formation of internal coke, promoting the aromatic cycle, and sinusoidal zeolite-channels produce aromatics that eventually grow into condensed polyaromatics at the surface leading to deactivation of the zeolites.
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Selective Enzymatic Oxidation of Silanes to Silanols
- Pages: 15507-15511
- First Published: 24 March 2020
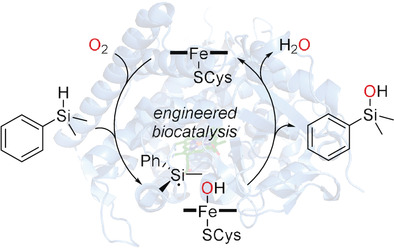
In rerum natura: Wild-type cytochrome P450BM3 catalyzes the oxidation of hydrosilanes to silanols both in vivo and in vitro. Directed evolution was used to generate an efficient and selective biocatalyst that delivers a broad range of aryl- and alkyl-substituted silanols. Computational studies revealed a sequence of H atom abstraction and OH rebound as the mechanism, in analogy to the native C−H hydroxylation activity.
Synthetic Methods
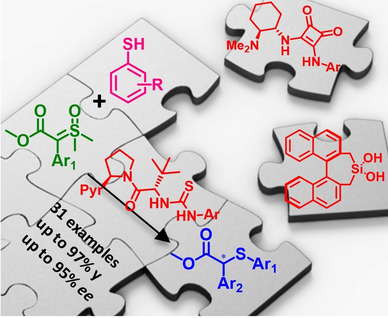
Electrophilic Vinylation of Thiols under Mild and Transition Metal-Free Conditions
- Pages: 15512-15516
- First Published: 12 May 2020
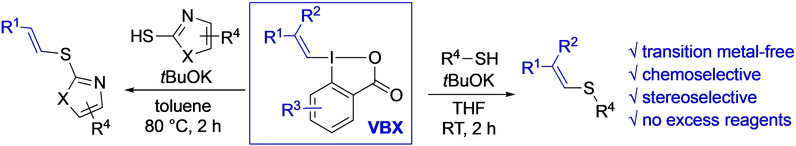
Novel vinylation reagent: The iodine(III) reagents vinylbenziodoxolones (VBX) have been employed to vinylate aliphatic and aromatic thiols, as well as mercaptothiazoles. The methodology proceeds under mild and transition metal-free conditions to provide alkenyl sulfides with excellent stereoselectivity. A novel VBX reagent with a substituted benziodoxolone core had superior efficiency.
Host–Guest Chemistry
Structural-Deformation-Energy-Modulation Strategy in a Soft Porous Coordination Polymer with an Interpenetrated Framework
- Pages: 15517-15521
- First Published: 01 April 2020
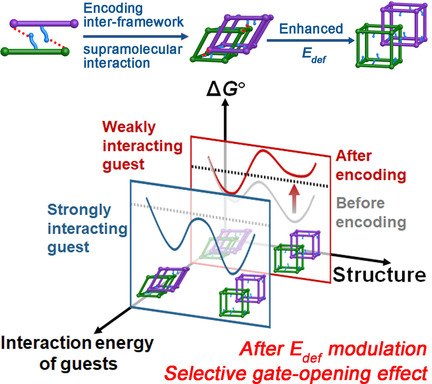
Easy PCPs: The competitive relationship between the structural deformation energy (Edef) of soft PCPs and guest interactions is key for their selective guest-triggered structural-transformation behavior. The flexibility of PCPs can be well controlled by modulating Edef to change the adsorption-energy landscape of guests for precise molecular recognition.
Photoswitches | Hot Paper
Photochromic Free MOF-Based Near-Infrared Optical Switch
- Pages: 15522-15526
- First Published: 27 April 2020
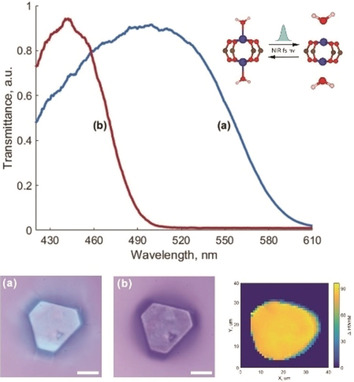
Ultrafast near-infrared laser pulses stimulate reversible blue shift of the absorption band of photochromic-free MOFs with rates up to hundreds of s−1. This optical switching can be applied for MOF-based communication devices allowing the remote modulation of the intensities of initial photoluminescence and the visible light passing through the MOFs.
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
POM-Incorporated CoO Nanowires for Enhanced Photocatalytic Syngas Production from CO2
- Pages: 15527-15531
- First Published: 06 May 2020
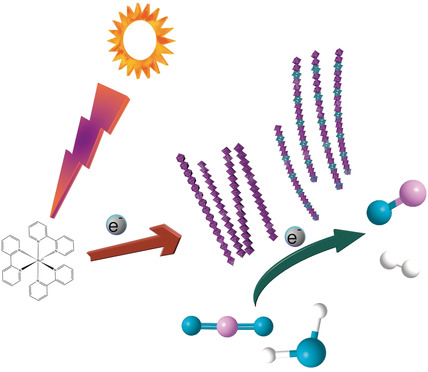
POM-incorporated CoO ultrathin nanowires (CoO UNWs) were fabricated by a facile solvothermal method. The UNWs with and without POM incorporation both present superior photocatalysis activities towards syngas production compared with nanowire bundle. Mechanistic studies indicate that size, structure, and composition all contribute to the high performance.
Inhibitors | Hot Paper
Topology-Matching Design of an Influenza-Neutralizing Spiky Nanoparticle-Based Inhibitor with a Dual Mode of Action
- Pages: 15532-15536
- First Published: 18 May 2020
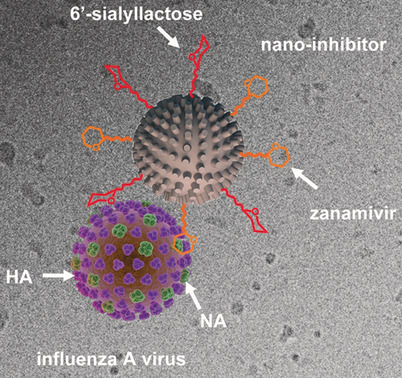
Influenza meets its match: Based on the principle of topology matching, a potent nanoparticle-based inhibitor for influenza A was designed that shows heteromultivalent inhibition of the receptor-binding viral proteins. This inhibitor is capable of neutralizing influenza A virus extracellularly and blocking its interaction with the host cell receptors. This principle could potentially also be applied to the inhibition of other viruses with spiky surfaces.
Magnetic Catalysts
Magnetically Induced CO2 Methanation Using Exchange-Coupled Spinel Ferrites in Cuboctahedron-Shaped Nanocrystals
- Pages: 15537-15542
- First Published: 23 June 2020
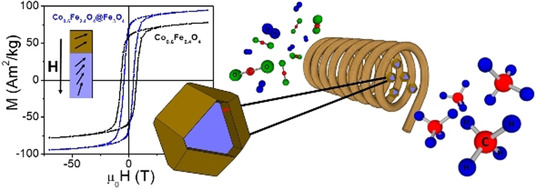
Core–shell ferrite nanoparticles for CO2 methanation: The magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 and CoFe2O4–Fe3O4 nanoparticles were controlled by the exchange-spring magnetic approach. These nanoparticles showed excellent performance as air-stable heating agents in CO2 methanation, resulting in CH4 yields above 95 %.
Synthetic Methods | Hot Paper
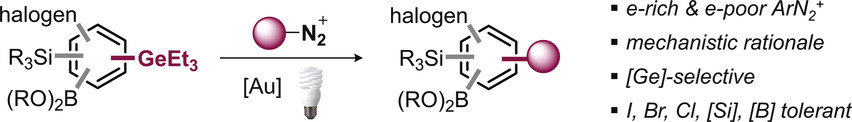
Modular and Selective Arylation of Aryl Germanes (C−GeEt3) over C−Bpin, C−SiR3 and Halogens Enabled by Light-Activated Gold Catalysis
- Pages: 15543-15548
- First Published: 11 May 2020
Alkene Isomerization | Hot Paper
Stereoselective Access to Fully Substituted Aldehyde-Derived Silyl Enol Ethers by Iridium-Catalyzed Alkene Isomerization
- Pages: 15549-15553
- First Published: 11 May 2020
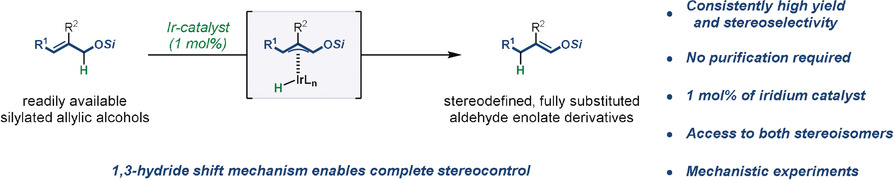
Zig-zag forever: An Ir-based alkene isomerization catalyst generates fully substituted aldehyde enolate derivatives with complete stereocontrol, starting from simple silylated allylic alcohols. The stereo- and regioselectivity of isomerization are dictated by the preference towards zig-zig-shaped allyliridium hydride intermediates, enabling selective access to either stereoisomer of a given enolate.
Organocatalysis
Enantioselective S−H Insertion Reactions of α-Carbonyl Sulfoxonium Ylides
- Pages: 15554-15559
- First Published: 30 April 2020
Mass Spectrometry | Hot Paper
Correlating Glycoforms of DC-SIGN with Stability Using a Combination of Enzymatic Digestion and Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry
- Pages: 15560-15564
- First Published: 07 July 2020
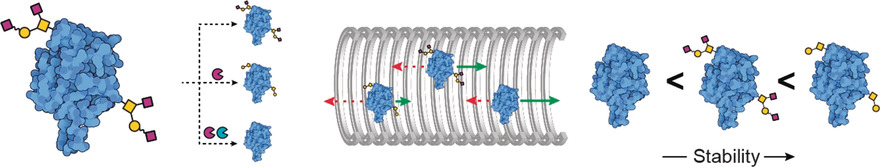
Uncovering stability of DC-SIGN glycoforms with native mass spectrometry: A combined strategy of exoglycosidase sequencing, native mass spectrometry, ion mobility, and gas-phase unfolding uncovered the occupancy and structural detail of O-glycans present on the carbohydrate binding domain of DC-SIGN. Collision-induced unfolding by ion mobility revealed differences in stability among glycoforms, independent of glycoprotein mass.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Manganese-Catalyzed anti-Selective Asymmetric Hydrogenation of α-Substituted β-Ketoamides
- Pages: 15565-15569
- First Published: 25 May 2020
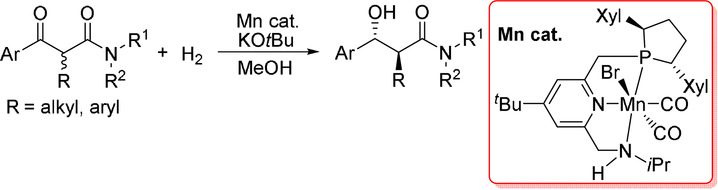
A Mn-catalyzed diastereo- and enantioselective asymmetric hydrogenation of α-substituted β-ketoamides was realized by using lutidine-based chiral PNN ligands via a dynamic kinetic resolution to afford optically active anti-α-substituted β-hydroxy amides in high yields with excellent stereoselectivity (up to >99 % dr and >99 % ee). The anti stereoselectivity is ascribed to an attractive π⋅⋅⋅π stacking between the substrate phenyl and ligand pyridyl rings.
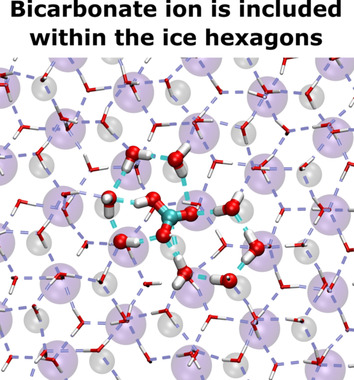
Electrofreezing
Heterogeneous Electrofreezing Triggered by CO2 on Pyroelectric Crystals: Qualitatively Different Icing on Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces
- Pages: 15570-15574
- First Published: 04 July 2020
Electrofreezing | Very Important Paper
Heterogeneous Electrofreezing of Super-Cooled Water on Surfaces of Pyroelectric Crystals is Triggered by Trigonal Planar Ions
- Pages: 15575-15579
- First Published: 05 July 2020
Crystal Engineering
Designed Synthesis of a 1D Polymer in Twist-Stacked Topology via Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Polymerization
- Pages: 15580-15585
- First Published: 23 June 2020
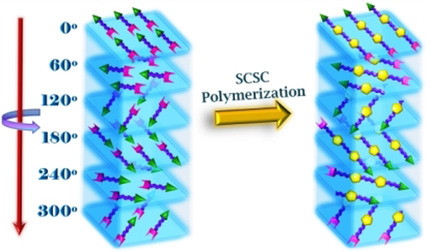
Strong and stable: A designed dipeptide with azide and alkyne groups at its termini crystallizes in an anticipated topology with the molecules pre-organized in a topochemically reactive arrangement. Upon heating, it undergoes a single-crystal-to-single-crystal topochemical azide–alkyne cycloaddition polymerization to yield a 1D polymer with a twist-stacked layered topology.
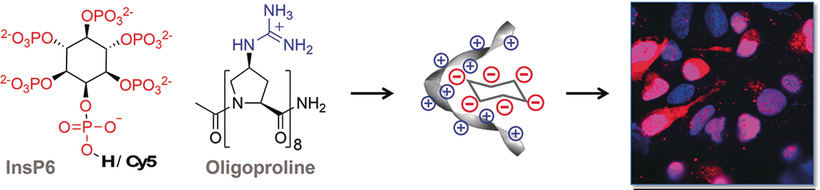
Cell-Penetrating Peptides | Hot Paper
Delivery of myo-Inositol Hexakisphosphate to the Cell Nucleus with a Proline-Based Cell-Penetrating Peptide
- Pages: 15586-15589
- First Published: 18 June 2020
Photochromic Oscillators | Hot Paper
Polysubstituted 5-Phenylazopyrimidines: Extremely Fast Non-ionic Photochromic Oscillators
- Pages: 15590-15594
- First Published: 20 May 2020
Platinum Complexes
Can an Elusive Platinum(III) Oxidation State be Exposed in an Isolated Complex?
- Pages: 15595-15598
- First Published: 30 June 2020
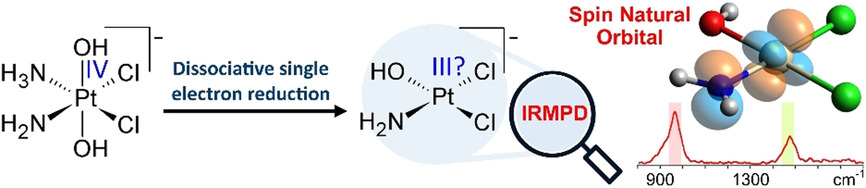
Formal platinum(III) complexes obtained after collisional activation of PtIV prodrugs are assayed using IR ion spectroscopy to identify vibrational features characteristic of their electronic structure. The role of the non-innocent NH2 ligand in the formation of these elusive PtIII complexes is discussed on the basis of spin natural orbital analyses.
Metal–Organic Frameworks
Anisotropic Electron Conductance Driven by Reaction Byproducts on a Porous Network of Dibromobenzothiadiazole on Cu(110)
- Pages: 15599-15602
- First Published: 06 July 2020
Research Articles
Homogeneous Catalysis
Hydrogenolysis of Polysilanes Catalyzed by Low-Valent Nickel Complexes
- Pages: 15603-15609
- First Published: 12 February 2020
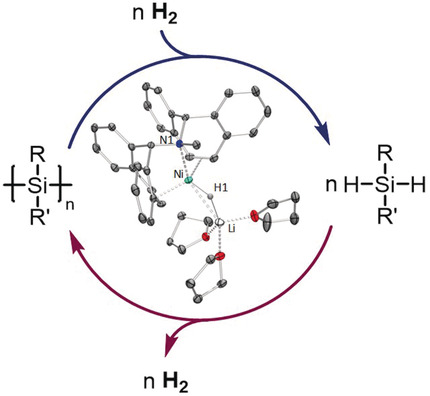
Si−Si bonds in polysilanes can be converted to Si−H bonds under mild conditions by using low-valent anionic Ni0 hydride catalysts. The reaction is reversible and dehydrogenative coupling of hydrosilanes is also possible. Experiments and DFT calculations indicate that low-coordinated 14- and 16-electron d10-Ni hydrides, silyl, and silane intermediates are involved in the catalytic cycle.
Catalyst Deactivation
Deactivation of Cu-Exchanged Automotive-Emission NH3-SCR Catalysts Elucidated with Nanoscale Resolution Using Scanning Transmission X-ray Microscopy
- Pages: 15610-15617
- First Published: 03 February 2020
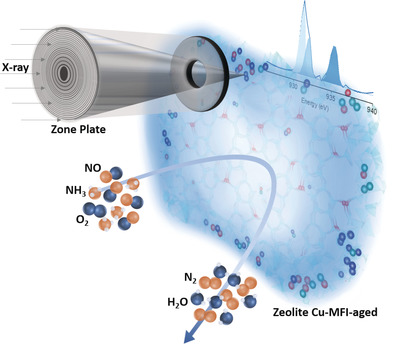
A look at the exhaust: The deactivation of NOx-reduction catalysts based on Cu-exchanged SSZ-13 and ZSM-5 zeolites was studied by scanning transmissionX-ray microscopy, which enables a spatial analysis of the local environment of both Al and Cu species at nanoscale resolution. The importance of isolated Cu species was shown and a correlation between zeolite lattice destruction and an inactive Cu phase was established.
Biomaterials | Hot Paper
Polyphenol-Mediated Assembly of Proteins for Engineering Functional Materials
- Pages: 15618-15625
- First Published: 01 March 2020
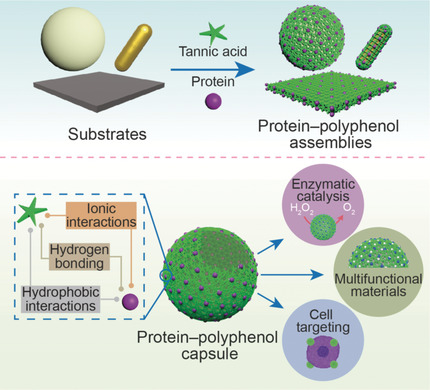
In a material world: A simple and versatile strategy for assembling functional materials was established through the interfacial assembly of proteins and polyphenols on various substrates. Protein–polyphenol capsules were used to elucidate the dominant interaction(s) between different proteins and polyphenols. The assembled proteins retain their structure and function, thereby enabling their use in various applications, for example, biocatalysis or cell targeting.
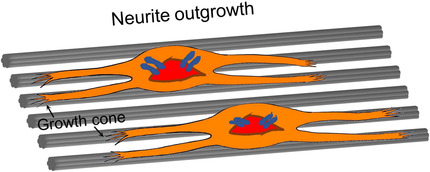
Nanotechnology
Engraving the Surface of Electrospun Microfibers with Nanoscale Grooves Promotes the Outgrowth of Neurites and the Migration of Schwann Cells
- Pages: 15626-15632
- First Published: 13 March 2020
Electrocatalysis
A Precious-Metal-Free Hybrid Electrolyzer for Alcohol Oxidation Coupled to CO2-to-Syngas Conversion
- Pages: 15633-15641
- First Published: 06 April 2020
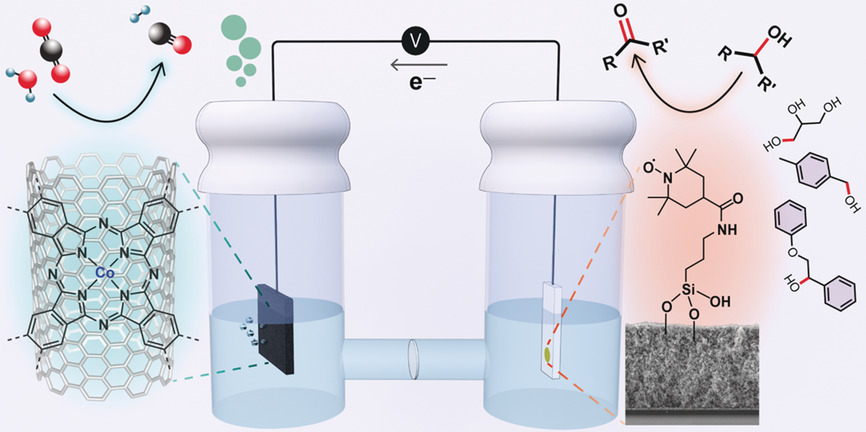
Inspirational device: A molecularly engineered electrolyzer was constructed for the selective oxidation of glycerol to glyceraldehyde, with a turnover number (TON) of ≈1000 and a Faradaic efficiency (FE) of 83 %, coupled with aqueous CO2 reduction to generate a stoichiometric amount of syngas, with a CO:H2 ratio of 1.25±0.25, an overall TON of 894 and FE of 82 %.
Single-Molecule Studies
Cryogenic Correlative Single-Particle Photoluminescence Spectroscopy and Electron Tomography for Investigation of Nanomaterials
- Pages: 15642-15648
- First Published: 24 April 2020
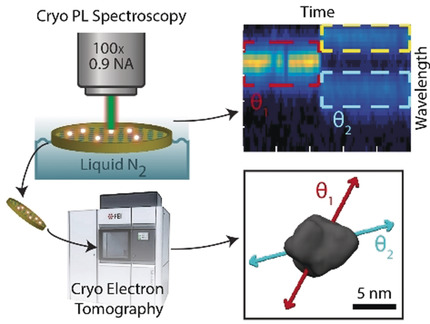
A closer look: Correlative single-particle cryogenic photoluminescence spectroscopy and cryogenic electron tomography analysis of CdSSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots reveals spontaneous splitting of the photoluminescence spectrum of single quantum dots into two distinct emission bands ≈80 meV apart. These surprising photoluminescence dynamics are directly correlated with tomographic structures.
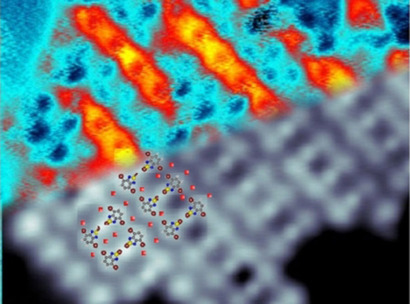
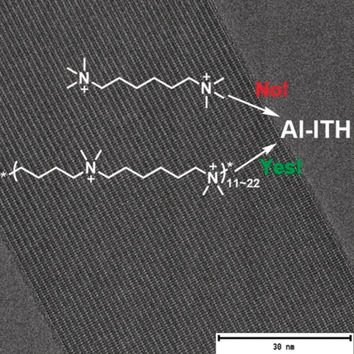
Zeolites
A Cationic Oligomer as an Organic Template for Direct Synthesis of Aluminosilicate ITH Zeolite
- Pages: 15649-15655
- First Published: 26 May 2020
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors | Hot Paper
Light Dynamics of the Retinal-Disease-Relevant G90D Bovine Rhodopsin Mutant
- Pages: 15656-15664
- First Published: 30 June 2020
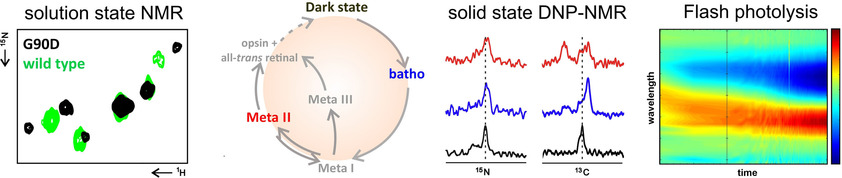
Rhodopsin is the major dim light receptor in vertebrate eyes. Numerous mutations associated with impaired visual cycles are known. The G90D mutation leads to a constitutively active mutant form of rhodopsin that causes congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB). We investigated the consequences of this mutation on the visual cycle, both in terms of structural aspects and dynamic changes.
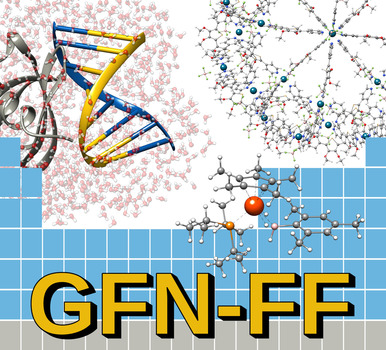
Computational Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Robust Atomistic Modeling of Materials, Organometallic, and Biochemical Systems
- Pages: 15665-15673
- First Published: 28 April 2020
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Controlling the Product Platform of Carbon Dioxide Reduction: Adaptive Catalytic Hydrosilylation of CO2 Using a Molecular Cobalt(II) Triazine Complex
- Pages: 15674-15681
- First Published: 28 April 2020
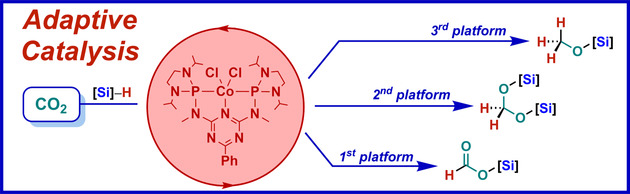
Let it be adaptive: A cobalt-based molecular system capable of selectively reducing carbon dioxide either to the formic acid, formaldehyde, or methanol level has been developed. This approach shows that molecular control over product formation is possible with suitable catalysts that allow the reaction conditions to be adapted appropriately.
Prebiotic Chemistry
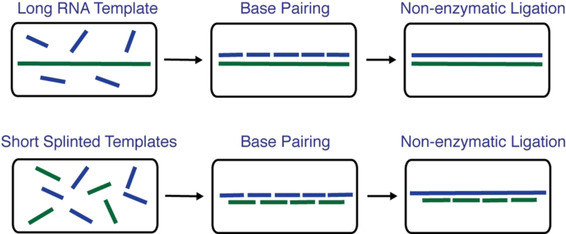
Template-Directed Copying of RNA by Non-enzymatic Ligation
- Pages: 15682-15687
- First Published: 18 June 2020
Perovskite Solar Cells
Stabilization of Highly Efficient and Stable Phase-Pure FAPbI3 Perovskite Solar Cells by Molecularly Tailored 2D-Overlayers
- Pages: 15688-15694
- First Published: 12 May 2020
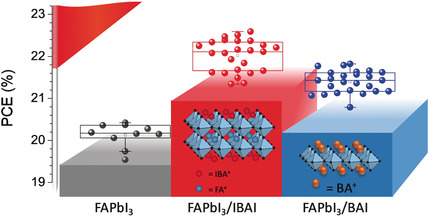
The desired α-FAPbI3 perovskite phase is stabilized by protecting it with a two-dimensional (2D) IBA2FAPb2I7 (IBA=iso-butylammonium) overlayer, formed via stepwise annealing. The α-FAPbI3/IBA2FAPb2I7-based perovskite solar cell (PSC) reached a high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of close to 23 %. It showed excellent operational stability, retaining around 85 % of its initial efficiency under severe combined heat and light stress.
Zeolites
Regioselective Generation of Single-Site Iridium Atoms and Their Evolution into Stabilized Subnanometric Iridium Clusters in MWW Zeolite
- Pages: 15695-15702
- First Published: 25 June 2020
Rotational Spectroscopy | Hot Paper
Conformational Panorama and Chirality Controlled Structure–Energy Relationship in a Chiral Carboxylic Acid Dimer
- Pages: 15703-15710
- First Published: 04 June 2020
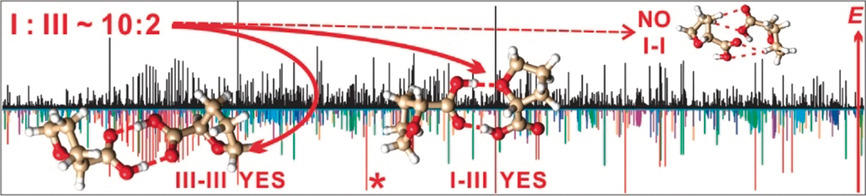
Rotational spectra of tetrahydro-2-furoic acid dimers reveal that simple considerations of thermodynamic or kinetic control are insufficient to rationalize the abundances of the observed dimers. Instead, understanding the energetic interconnectivity of the dimeric network driven in part by chirality is required to unravel the mysteries. A novel chiral self-tag approach for ee determination is tested.
Single-Molecule Studies | Very Important Paper
Single-Molecule Observation of Intermediates in Bioorthogonal 2-Cyanobenzothiazole Chemistry
- Pages: 15711-15716
- First Published: 26 June 2020
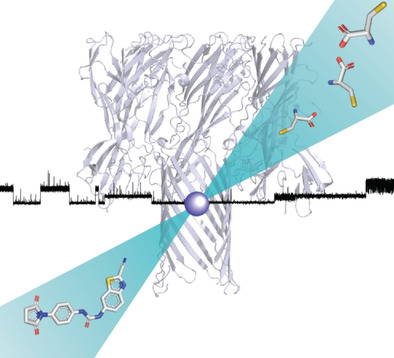
Better off alone: A nanoreactor approach was used to investigate the chemistry of2-cyanobenzothiazole (CBT), an important bioorthogonal reagent, at the single-molecule level. Reactions with thiols and aminothiols revealed mechanistic and kinetic information with important implications for several essential applications of CBT reagents.
Structure Elucidation
Oxidation, Coordination, and Nickel-Mediated Deconstruction of a Highly Electron-Rich Diboron Analogue of 1,3,5-Hexatriene
- Pages: 15717-15725
- First Published: 25 May 2020
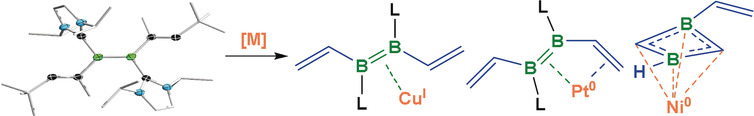
A complex twist: A highly electron-richN-heterocyclic carbene stabilized 1,2-divinyldiborene, which displays no delocalized π conjugation because of twisting of the C2B2C2 chain, coordinates to CuI and Pt0 in an η2-B2 and η4-C2B2 mode, respectively, while undergoing a complex rearrangement to an η4-1,3-diborete upon complexation with Ni0.
CO2 Reduction
Electroreduction of CO2 to Formate with Low Overpotential using Cobalt Pyridine Thiolate Complexes
- Pages: 15726-15733
- First Published: 16 July 2020
Molecular cobalt-based CO2 electroreduction catalysts achieved the conversion of CO2 into HCOOH as the major product with very low overpotential by tuning the electronic properties of the metal centers using pyridine-thiolate ligands. Formation of a stable carbonyl complex caused deactivation. The active catalyst is regenerate by re-oxidation, promoting CO ligand release.
Graphene Liquid Cells
Synthesis of Honeycomb-Structured Beryllium Oxide via Graphene Liquid Cells
- Pages: 15734-15740
- First Published: 28 May 2020
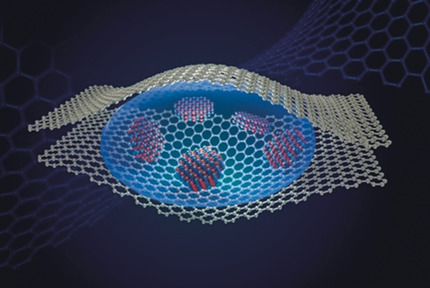
Hexagonal, exceptional: In a graphene liquid cell, beryllium oxide can crystallize in a rare sp2-coordinated, hexagonal BeO polymorph. The thickness of the crystals produced this way is beyond the thermodynamic ultra-thin limit above which the wurtzite phase is energetically more favorable. Calculations show that the energy barrier of the phase transition is responsible for the observed occurrence of hexagonal layers.
Switchable Materials
Octacyanidorhenate(V) Ion as an Efficient Linker for Hysteretic Two-Step Iron(II) Spin Crossover Switchable by Temperature, Light, and Pressure
- Pages: 15741-15749
- First Published: 02 June 2020
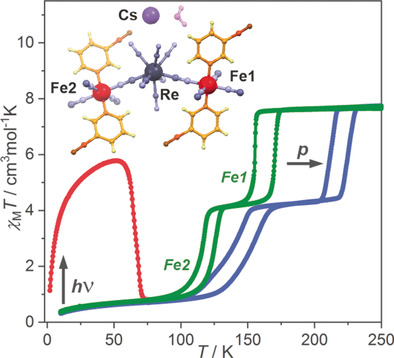
Perfect rhenium mediator: Octacyanidorhenate(V) ion is presented as a promising molecular precursor for the construction of an advanced spin-crossover material linking a multistep spin transition with strong cooperativity. An anionic layered FeII-ReV cyanido-bridged framework non-covalently bonded to Cs+ counterions is reported. It exhibits a two-step hysteretic FeII spin-crossover effect controlled by temperature, light irradiation, and pressure.
Covalent Organic Frameworks
Ionothermal Synthesis of Imide-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 15750-15758
- First Published: 23 June 2020
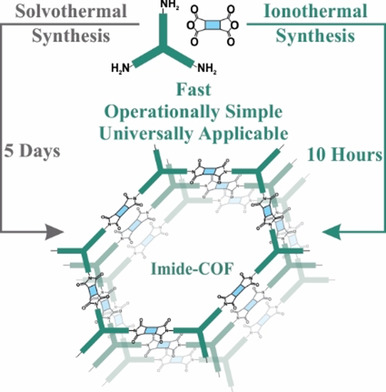
Aiming for synthetic diversity and simplification of the synthesis, a generic ionothermal approach for imide-linked covalent organic frameworks has been developed. By using ZnCl2 and eutectic salt mixtures, highly crystalline COFs were synthesized with a significantly reduced reaction time of 10 hours. Unlike common solvothermal methods this approach does not require soluble precursor molecules.