Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture: A Conjugated Polycarbazole Ring around a Porphyrin (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 28/2006)
- Page: 4527
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Like the rings of Saturn a fully conjugated cyclododeca-2,7-carbazole surrounds a porphyrin template. The macrocycle can be released from the template. The cover shows a single-molecule STM measurement with the structure of cyclododeca-2,7-carbazole in the foreground. The tunneling current is dominated by the conjugated cyclic structure and shows an “electronic hole” in the center. For further details on these molecules and their self-assembly into columnar stacks see the Communication by K. Müllen et al. on page 4685 ff.
Supramolecular Chirality in Layered Crystals of Achiral Ammonium Salts and Fatty Acids: A Hierarchical Interpretation
- Page: 4539
- First Published: 03 July 2006
A Stable Silylenoid and a Donor-Stabilized Chlorosilylene: Low-Coordinate Silicon Compounds—A Never-Ending Story?
- Page: 4539
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Nanoscale Assembly. Chemical techniques. Edited by Wilhelm T. S. Huck.
- Pages: 4544-4545
- First Published: 03 July 2006
The First Crystal Structure of Tyrosinase: All Questions Answered?
- Pages: 4546-4550
- First Published: 03 July 2006
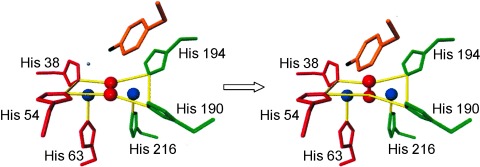
Tyrosinases are essential enzymes that occur in all organisms and belong to the class of type3 copper proteins. The first crystal structure of a tyrosinase (from Streptomyces castaneoglobisporus) has been achieved and offers important insights into the mechanism of phenol hydroxylation (see scheme; Cu blue, O red, substrate orange; trans-axial position on CuA: gray dot), the process of activation, and the incorporation of copper.
Small Molecule Modulators of Transcription
- Pages: 4552-4560
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Small can do too: Recent research on transcriptional factors has uncovered small-molecule ligands that are able to modulate gene transcription by interacting with multiprotein complexes. Some of these compounds bind to different sites on the target proteins and therefore exert different functions. The picture shows the association of the HDM2 protein (bronze) with the tumor suppressor p53 (green), and two small molecules that influence p53 function positively.
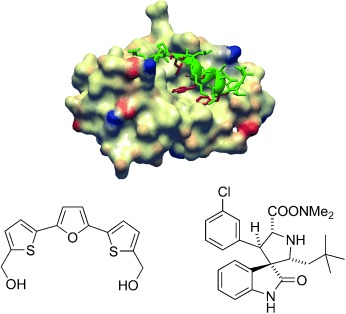
Materials for Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Analysis: Beyond Traditional Donor–Acceptor Combinations†
- Pages: 4562-4589
- First Published: 03 July 2006
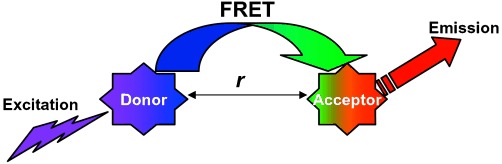
Dye another day: Modern donor and acceptor materials for fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) analyses (see picture) comprise photochromic dyes, semiconductor nanocrystals, nanoparticles, fluorescent amino acids, polymers, and genetically encoded protein, in additional to “traditional” organic dyes. The scope and boundaries of such systems, as well as avaible methods for bioconjugation are discussed, with an emphasis on the combination of different materials.
Very High Rate Enhancement of Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation by an Artificial Enzyme†
- Pages: 4590-4593
- First Published: 03 July 2006
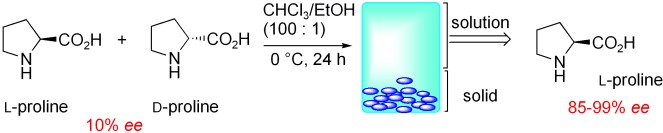
Large Nonlinear Effect Observed in the Enantiomeric Excess of Proline in Solution and That in the Solid State†
- Pages: 4593-4597
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Polyhedral Silver Nanocrystals with Distinct Scattering Signatures†
- Pages: 4597-4601
- First Published: 03 July 2006
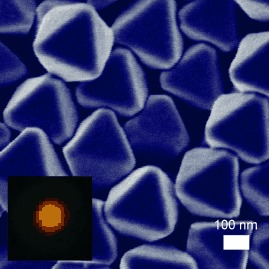
A scattering of silver: Polyhedral silver nanocrystals display complex and distinct scattering signatures dictated by their shape and size (see picture). The ability to engineer specific plasmon modes should have profound consequences for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, subwavelength optics, and plasmonic transport.
Reversible Photochemical Conversion of Helicity in Self-Assembled Nanofibers from a 1,ω-Thymidylic Acid Appended Bolaamphiphile
- Pages: 4601-4604
- First Published: 03 July 2006
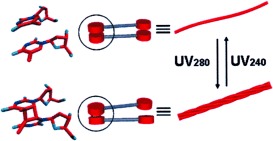
Light twisting and untwisting: UV light was found to drive reversible helical-nanofiber formation based on the photodimerization and photodissociation of the thymine residue in the 1,ω-thymidylic acid appended bolaamphiphile. 1H NMR spectroscopy revealed that UV irradiation of the self-assembled nanofibers induces a helical structure through the formation of a cis–syn isomer of the thymine moiety.
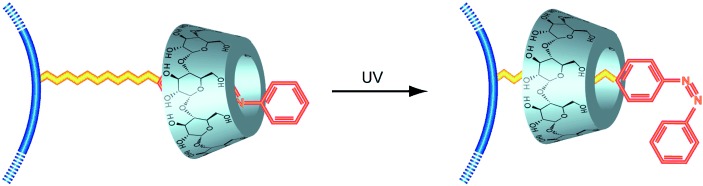
Cyclodextrin-Based Side-Chain Polyrotaxane with Unidirectional Inclusion in Aqueous Media†
- Pages: 4605-4608
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Self-Assembly of Ultrathin Hexagonal In2S3 Nanoplates†
- Pages: 4608-4612
- First Published: 03 July 2006
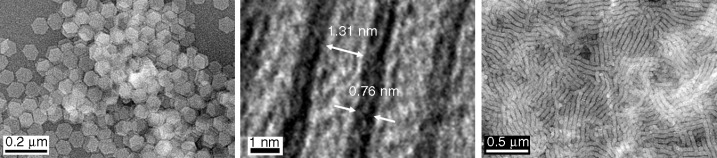
Arrested precipitation of In2S3 affords ultrathin hexagonal nanoplates with 0.76-nm thickness and controllable sizes of 22–63 nm. The pictures show (from left to right) TEM images of 63-nm nanoplates aligned parallel to a support, a side view of nanoplates, and 45-nm nanoplates self-assembled into microwires.
Laser-Induced Release of Encapsulated Materials inside Living Cells†
- Pages: 4612-4617
- First Published: 03 July 2006
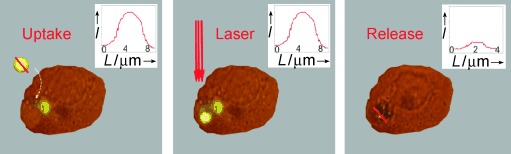
Escape route: The laser-initiated release of fluorescently labeled polymers from polyelectrolyte-multilayer microcapsules is demonstrated inside living cancer cells. A polymer is incorporated in capsules with metal nanoparticles in their walls, which serve as light-absorbing centers. The capsules are internalized by cells and near-infrared light ruptures the walls of the capsules, thus releasing the content into the cells.
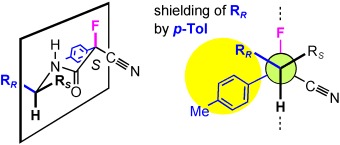
The CFTA Method: A Reliable Procedure for the Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Chiral Primary Amines by 1H NMR Spectroscopic Analysis†
- Pages: 4617-4619
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Electric-Field Modulation of Component Exchange in Constitutional Dynamic Liquid Crystals†
- Pages: 4619-4624
- First Published: 03 July 2006

Playing the field: Application of an electric field to the thermodynamic equilibria of constitutionally dynamic sets of imines and amines that contain an imine with liquid-crystalline properties and a negative dielectric anisotropy leads to the amplification of the constituent that couples most strongly to the electric field, namely the liquid crystal (LC, see example). The field can thus induce a liquid to nematic phase transition.
Cross-Hybridization of Pyridinedicarboxamide Helical Strands and Their N-Oxides†
- Pages: 4625-4628
- First Published: 03 July 2006
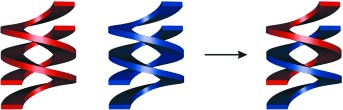
Swapping partners: The presence of N-oxide functions in double-helical dimers formed from oligo(pyridinecarboxamide)s promotes heterodimerization (see picture). This process mimicks the essence of base pairing and information storage in DNA through heterologous A/T and G/C Watson–Crick base pairing.
Porous Coordination Polymer with π Lewis Acidic Pore Surfaces, {[Cu3(CN)3{hat(CN)3(OEt)3}]⋅3 THF}n†
- Pages: 4628-4631
- First Published: 03 July 2006
![Porous Coordination Polymer with π Lewis Acidic Pore Surfaces, {[Cu3(CN)3{hat(CN)3(OEt)3}]⋅3 THF}n](/cms/asset/a3010251-3350-439a-b801-51f0c3b8fda7/mcontent.jpg)
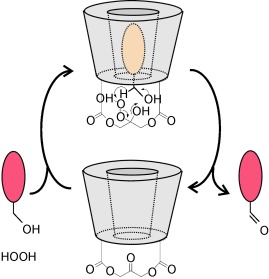
Neutral organic guest molecules are confined within the cavities of a porous coordination polymer. The key interaction is that of electron-deficient π planes of the polymer surface with electronegative atoms of the guest molecules (see picture). Evidence from thermogravimetric analysis suggests that guests with two electronegative atoms form more-stable complexes with the polymer than those with one electronegative atom.
Tris(organozinc) Phosphazenates as Templates for Trimeric and Hexameric Zinc Oxide Clusters†
- Pages: 4632-4634
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Casting clusters from the mold: Tris(ethylzinc) phosphazenates exhibit a bowl-shaped coordination surface of three Lewis acidic EtZn moieties and three Lewis basic N sites. This surface provides a perfect mold for planar {(ZnO)3} rings and hexagonal {(ZnO)6} prisms. The zinc oxide clusters were generated in situ by reaction of phosphazene hydrates with diethylzinc.
Short Synthesis of (+)-Cylindricine C by Using a Catalytic Asymmetric Michael Reaction with a Two-Center Organocatalyst†
- Pages: 4635-4637
- First Published: 03 July 2006

Two for the price of one: The total synthesis of (+)-cylindricine C has been achieved in six steps using a catalytic asymmetric Michael reaction and tandem cyclization. A newly designed two-center organocatalyst gives good selectivity in this Michael reaction. TaDiAS=tartrate-derived diammonium salt.
Exceptionally Strong Electronic Communication through Hydrogen Bonds in Porphyrin–C60 Pairs†
- Pages: 4637-4641
- First Published: 03 July 2006

Hooking up: Self-assembly of a porphyrin amidine and fulleropyrrolidine carboxylic acid based on a two-point amidinium–carboxylate motif leads to supramolecular dyads of high stability (Ka≈107 M−1 in toluene/acetonitrile (9:1)). The synergy of the hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions has been shown to be particularly beneficial in terms of electronic coupling between both electroactive components of the dyads.
Efficient Diastereoselective Intermolecular Rhodium-Catalyzed CH Amination†
- Pages: 4641-4644
- First Published: 03 July 2006
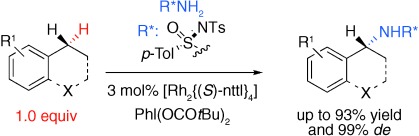
Successful matchmaking: The combination of a chiral nitrene precursor with a chiral rhodium(II) catalyst is the key factor that allows efficient intermolecular regioselective CH amination. Good-to-excellent yields and excellent diastereoselectivities can be obtained with a stoichiometric amount of the CH bond containing substrate. nttl=N-1,8-naphthoyl-tert-leucine.
Water-Soluble Dendrimeric Two-Photon Tracers for In Vivo Imaging†
- Pages: 4645-4648
- First Published: 03 July 2006
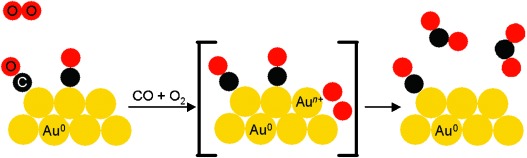
Formation of Acetic Acid by Aqueous-Phase Oxidation of Ethanol with Air in the Presence of a Heterogeneous Gold Catalyst†
- Pages: 4648-4651
- First Published: 03 July 2006
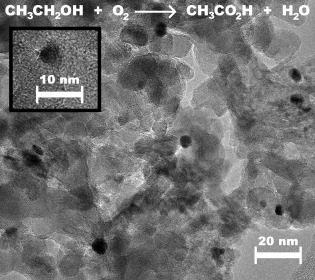
Wine into vinegar: It is possible to selectively oxidize ethanol into acetic acid in aqueous solution with air as the oxidant and a heterogeneous gold catalyst (see TEM image of supported gold particles) at temperatures of about 423 K and O2 pressures of 0.6 MPa. This reaction proceeds readily in aqueous acidic media with yields of up to 90 % and CO2 as the only major by-product.
Activation of Oxygen on Gold/Alumina Catalysts: In Situ High-Energy-Resolution Fluorescence and Time-Resolved X-ray Spectroscopy†
- Pages: 4651-4654
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Hollow and Tin-Filled Nanotubes of Single-Crystalline In(OH)3 Grown by a Solution–Liquid–Solid–Solid Route†
- Pages: 4655-4658
- First Published: 03 July 2006
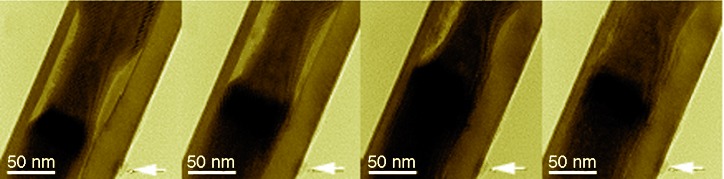
Tin inside In: Hollow and tin-filled nanotubes of single-crystalline In(OH)3 are grown in a one-step solution–liquid–solid–solid (SLSS) process, and the structural properties of nanotubes synthesized under different growth conditions characterized and studied. The nanofluidic properties of the interior Sn (see picture) are demonstrated by its response to a rising environmental temperature brought about by electron-beam irradiation.
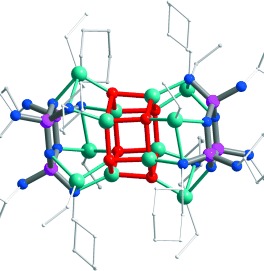
A Nonanuclear Dysprosium(III)–Copper(II) Complex Exhibiting Single-Molecule Magnet Behavior with Very Slow Zero-Field Relaxation†
- Pages: 4659-4662
- First Published: 03 July 2006
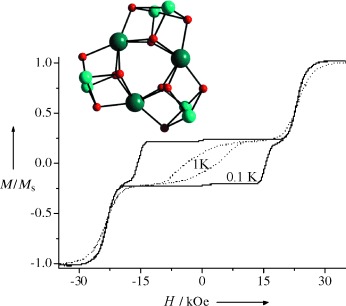
Highly attractive: Features typical of a single-molecule magnet (that is, a high anisotropy barrier of 25 K, very slow zero-field relaxation, and a large coercive field of 15 kOe) are exhibited by a DyIIICuII nonanuclear complex, which was synthesized by using a Schiff base ligand. The picture shows the {DyCuO} core of the cluster (dark green Dy, light green Cu, red O) and low-temperature magnetization curves.
Self-Assembly of a Highly Stable, Topologically Interesting Metallamacrocycle by Bridging Gold(I) Ions with Pyridyl-2,6-diphenyl2− and Diphosphanes†
- Pages: 4663-4666
- First Published: 03 July 2006
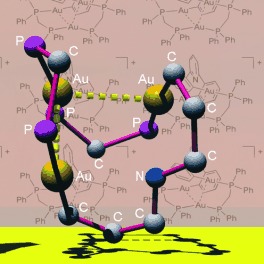
A Möbius arrangement of the bonds directly attached to a metallamacrocycle was observed for the AuI complex [Au3(CNC)(μ-Ph2PCH2PPh2)2]+, which was self-assembled by treating the lithium salt of pyridyl-2,6-diphenyl2− (CNC) with [Au2Cl2(μ-Ph2PCH2PPh2)]. The trinuclear AuI complex has intramolecular Au⋅⋅⋅Au and CH⋅⋅⋅π interactions, exhibits a remarkable stability in solution, and is cytotoxic toward cancer cell lines.
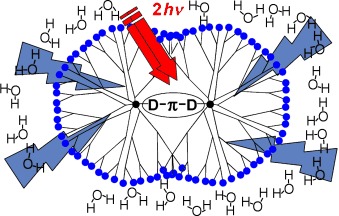
First Evidence for a Uniquely Spin-Polarized Quartet Photoexcited State of a π-Conjugated Spin System Generated via the Ion-Pair State†
- Pages: 4666-4670
- First Published: 03 July 2006
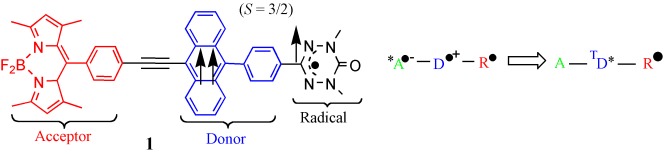
A novel spin-polarization mechanism involving the intramolecular ion pair *A.−-D.+-R, which competes with a spin–orbit intersystem crossing, is proposed for the formation of the uniquely spin-polarized quartet photoexcited state observed for 1, which consists of a bodipy acceptor (A), a phenylanthracene donor (D), and a stable verdazyl radical (R).
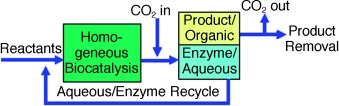
Biocatalytic Reaction And Recycling by Using CO2-Induced Organic–Aqueous Tunable Solvents†
- Pages: 4670-4673
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Rhenium Trichloride Dioxide, ReO2Cl3†
- Pages: 4675-4677
- First Published: 03 July 2006
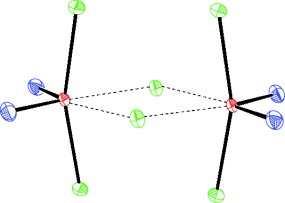
Re-discovery: The only rhenium(VII)–chlorine compound known previously was ReO3Cl, and chloride oxides of composition AO2Cl3 (A=nonmetal or metal) were completely unknown. The synthesis of ReO2Cl3 has now been achieved. The compound exists as a chlorine-bridged dimer (see Figure; Re red, O blue, Cl green) in the solid state, and as a monomer in solution.
Gas-Phase Oxidation of Propane and 1-Butene with [V3O7]+: Experiment and Theory in Concert†
- Pages: 4677-4681
- First Published: 03 July 2006
Thermal Activation of Methane by Tetranuclear [V4O10]+†
- Pages: 4681-4685
- First Published: 03 July 2006
![Thermal Activation of Methane by Tetranuclear [V4O10]+](/cms/asset/61845991-f167-47cb-a110-945fd10befbc/mcontent.jpg)
Hand in hand: In a combination of experimental (mass spectrometry) and theoretical (density functional theory) studies [V4O10]+ is described as the first polynuclear transition-metal oxide capable of activating methane at room temperature (see picture). The [V4O10]+ cation can be considered a prototype of oxide clusters of early 3d transition metals.
A Conjugated Polycarbazole Ring around a Porphyrin†
- Pages: 4685-4690
- First Published: 03 July 2006
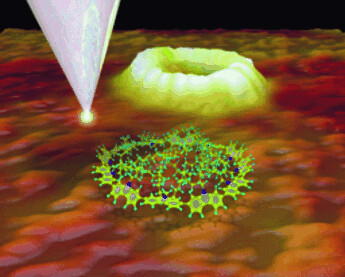
Round up: A fully conjugated cyclododeca-2,7-carbazole is prepared around a porphyrin template and the corresponding empty macrocycle then released. Single molecules could be visualized by STM (see image) and their arrangement by atomic force microscopy. The macrocycles self-assemble into a hexagonal array of columns. Efficient energy transfer occurs from the peripheral carbazole π system to the central porphyrin core.





![Gas-Phase Oxidation of Propane and 1-Butene with [V3O7]+: Experiment and Theory in Concert](/cms/asset/2629bb14-101f-4624-adad-3791064aea79/mcontent.jpg)


































