Small Molecule Modulators of Transcription
Hans-Dieter Arndt Dr.
Universität Dortmund, Fachbereich Chemie, Otto-Hahn-Str. 6, 44221 Dortmund, Germany
Max-Planck-Institut für molekulare Physiologie, Otto-Hahn-Str. 11, 44227 Dortmund, Germany, Fax: (+49) 231-133-2498
Search for more papers by this authorHans-Dieter Arndt Dr.
Universität Dortmund, Fachbereich Chemie, Otto-Hahn-Str. 6, 44221 Dortmund, Germany
Max-Planck-Institut für molekulare Physiologie, Otto-Hahn-Str. 11, 44227 Dortmund, Germany, Fax: (+49) 231-133-2498
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
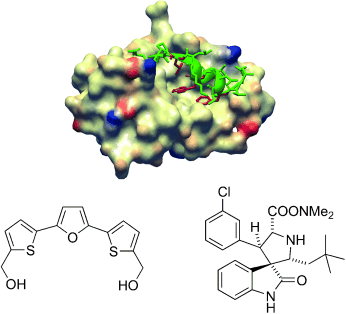
Small can do too: Recent research on transcriptional factors has uncovered small-molecule ligands that are able to modulate gene transcription by interacting with multiprotein complexes. Some of these compounds bind to different sites on the target proteins and therefore exert different functions. The picture shows the association of the HDM2 protein (bronze) with the tumor suppressor p53 (green), and two small molecules that influence p53 function positively.
Abstract
Signal transduction cascades ultimately trigger transcriptional programs that are executed by transcription factors interacting with coactivator or corepressor proteins in large multi-protein complexes. Despite the difficulties associated with discovering and verifying potent antagonists (or agonists) of protein–protein interaction events, several small molecules have been identified within the last few years that modulate transcription by directly interacting with transcriptional proteins. Some of these small molecules display surprising selectivity and some even show efficacy in vivo. This review summarizes the current status in this developing field to illustrate the emerging opportunities in the chemical biology of transcription.
References
- 1M. Levine, R. Tjian, Nature 2003, 424, 147–151.
- 2For recent reviews, see:
- 2aA. Ananda, A. Pascual, Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1269–1304;
- 2bN. J. McKenna, B. W. O'Malley, Cell 2002, 108, 465–474;
- 2cV. Perissi, M. G. Rosenfeld, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 542–554.
- 3
- 3aH. Gronemeyer, J.-A. Gustafsson, V. Laudet, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2004, 3, 950–964;
- 3bK. W. Nettles, G. L. Greene, Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 309–333.
- 4J. E. Darnell Jr., Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 740–749.
- 5This account focuses on non-oligomeric compounds. Targeting protein–protein interactions in general has been recently reviewed, see:
- 5aT. Berg, Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 2566–2586; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2462–2481;
- 5bM. R. Arkin, J. A. Wells, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2004, 3, 301–317;
- 5cH. Yin, A. D. Hamilton, Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 4200–4235; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4130–4163.
- 6T. I. Lee, R. A. Young, Annu. Rev. Genet. 2000, 34, 77–137.
- 7A. M. Näär, B. D. Lemon, R. Tjian, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 475–501.
- 8
- 8aM. Boube, L. Joulia, D. L. Cribbs, H. M. Bourbon, Cell 2002, 110, 143–150;
- 8bR. D. Kornberg, Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 235–239;
- 8c H.-M. Bourbon, A. Aguilera, A. Z. Ansari, F. J. Asturias, A. J. Berk, S. Bjorklund, T. K. Blackwell, T. Borggrefe, M. Carey, M. Carlson, J. W. Conaway, R. C. Conaway, S. W. Emmons, J. D. Fondell, L. P. Freedman, T. Fukasawa, C. M. Gustafsson, M. Han, X. He, P. K. Herman, A. G. Hinnebusch, S. Holmberg, F. C. Holstege, J. A. Jaehning, Y.-J. Kim, L. Kuras, A. Leutz, J. T. Lis, M. Meisterernest, A. M. Naar, K. Nasmyth, J. D. Parvin, M. Ptashne, D. Reinberg, H. Ronne, I. Sadowski, H. Sakurai, M. Sipiczki, P. W. Sternberg, D. J. Stillman, R. Strich, K. Struhl, J. Q. Svejstrup, S. Tuck, F. Winston, R. G. Roeder, R. D. Kornberg, Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 553–557;
- 8dCertain conditions allow transcription without a mediator: X. Fan, D. M. Chou, K. Struhl, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 117–120.
- 9
- 9aH. Kimura, K. Sugaya, P. R. Cook, J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 777–782;
- 9bR. T. Phair, P. Scaffidi, C. Elbi, J. Vecerová, A. Dey, K. Ozato, D. T. Brown, G. Hager, M. Bustin, T. Misteli, Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 6393–6402.
- 10
- 10aR. Métivier, G. Penot, M. R. Hübner, G. Reid, H. Brand, M. Koš, F. Gannon, Cell 2003, 115, 751–763;
- 10bReview: X. Darzacq, R. H. Singer, Y. Shav-Tal, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 332–339.
- 11T. Berg, S. B. Cohen, J. Desharnais, C. Sonderegger, D. J. Maslyar, J. Goldberg, D. L. Boger, P. K. Vogt, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3830–3835.
- 12
- 12aC. E. Nesbitt, J. M. Tersak, E. V. Prochovnik, Oncogene 1999, 18, 3004–3016;
- 12bS. K. Oster, C. S. Ho, E. L. Soucie, L. Z. Penn, Adv. Cancer Res. 2002, 84, 81–154.
- 13X. Yin, C. Giap, J. S. Lazo, E. V. Prochownik, Oncogene 2003, 22, 6151–6159.
- 14Y. Xu, J. Shi, N. Yamamoto, J. A. Moss, P. K. Vogt, K. D. Janda, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 2660–2673.
- 15Reviews:
- 15aG. R. Stark, I. M. Kerr, B. R. Williams, R. H. Silverman, R. D. Schreiber, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 227–264;
- 15bH. Yu, R. Jove, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 97–105.
- 16J. Turkson, J. S. Kim, S. Zhang, J. Yuan, M. Huang, M. Glenn, E. Haura, S. Sebti, A. D. Hamilton, R. Jove, Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 261–269.
- 17Peptidomimetics with submicromolar affinities for STAT3 in vitro have recently been reported, see: D. R. Coleman, Z. Y. Ren, P. K. Mandal, A. G. Cameron, G. A. Dyer, S. Muranjan, M. Campbell, X. M. Chen, J. S. McMurray, J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 6661–6670.
- 18A. N. Koehler, A. F. Shamji, S. L. Schreiber, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8420–8421.
- 19R. Mantovani, Gene 1999, 239, 15–27.
- 20For reviews, see:
- 20aC. Wolberger, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1999, 28, 29–56;
- 20bK. Ogata, K. Sato, T. Tahirov, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 40–48;
- 20cR. Marmorstein, M. X. Fitzgerald, Gene 2003, 304, 1–12.
- 21
- 21aV. Korinek, N. Barker, P. J. Morin, D. van Wichen, R. de Weger, K. W. Kinzler, B. Vogelstein, H. Clevers, Science 1997, 275, 1784–1787;
- 21bP. Polakis, Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1999, 9, 15–21;
- 21cM. Bienz, H. Clevers, Cell 2000, 103, 311–320.
- 22T. A. Graham, C. Weaver, F. Mao, D. Kimelman, W. Xu, Cell 2000, 103, 885–896.
- 23M. Lepourcelet, Y.-N. P. Chen, D. S. France, H. Wang, P. Crews, F. Petersen, C. Bruseo, A. W. Wood, R. A. Shivdasani, Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 91–102.
- 24In an earlier screening effort, piperazinones were reported to depress LEF-1/β-catenin mediated transcription: D. L. Boger, J. Goldberg, S. Satoh, Y. Ambroise, S. B. Cohen, P. K. Voigt, Helv. Chim. Acta 2000, 83, 1825–1845. The exact target of these compounds remains unresolved at present; a different piperazinone (6) was reported to bind to CBP (see reference [26]).
- 25N. Vo, R. H. Goodman, J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13505–13508.
- 26K. H. Emami, C. Nguyen, H. Ma, D. H. Kim, K. W. Jeong, M. Eguchi, R. T. Moon, J. L. Teo, S. W. Oh, H. Y. Kim, S. H. Moon, J. R. Ha, M. Kahn, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12682–12687.
- 27J. L. Best, C. A. Amezcua, B. Mayr, L. Flechner, C. M. Murawsky, B. Emerson, T. Zor, K. H. Gardner, M. Montminy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17622–17627.
- 28A. L. Kung, S. D. Zabludoff, D. S. France, S. J. Freedman, E. A. Tanner, A. Vieira, S. Cornell-Kennon, J. Lee, B. Wang, J. Wang, K. Memmert, H.-U. Naegeli, F. Petersen, M. J. Eck, K. W. Bair, A. W. Wood, D. M. Livingston, Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 33–43.
- 29L. Nagy, J. W. R. Schwabe, Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 317–324.
- 30
- 30aT. R. Geistlinger, R. K. Guy, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1525–1526;
- 30bT. R. Geistlinger, R. K. Guy, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6852–6853;
- 30cA. M. Leduc, J. O. Trent, J. L. Wittliff, K. S. Bramlett, S. L. Briggs, N. Y. Chirgadze, Y. Wang, T. P. Burris, A. F. Spatola, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11273–11278.
- 31A. L. Rodriguez, A. Tamrazi, M. L. Collins, J. A. Katzenellenbogen, J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 600–611.
- 32L. A. Arnold, E. Estébanez-Perpiña, M. Togashi, N. Jouvarel, A. Shelat, A. C. McReynolds, E. Mar, P. Nguyen, J. D. Baxter, R. J. Fletterick, P. Webb, R. K. Guy, J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43048–43055.
- 33K. H. Vousden, X. Lu, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 594–604.
- 34P. Chène, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 102–109.
- 35P. H. Kussie, S. Gorina, V. Marechal, B. Elenbaas, J. Moreau, A. J. Levine, N. P. Pavletich, Science 1996, 274, 948–953.
- 36L. T. Vassilev, B. T. Vu, B. Graves, D. Carvajal, F. Podlaski, Z Filipovic, N. Kong, U. Kammlott, C. Lukacs, C. Klein, N. Fotouhi, E. A. Liu, Science 2004, 303, 844–848.
- 37B. L. Grasberger et al., J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 909–912.
- 38K. Ding, Y. Lu, Z. Nikolovska-Coleska, S. Qiu, Y. Ding, W. Gao, J. Stuckey, K. Krajewski, P. P. Roller, Y. Tomita, D. A. Parrish, J. R. Deschamps, S. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10130–10131.
- 39N. Issaeva, P. Bozko, M. Enge, M. Protopopova, L. G. G. C. Verhoef, M. Masucci, A. Pramanik, G. Selivanova, Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1321–1328.
- 40L. D′Silva, P. Ozdowy, M. Krajewski, U. Rothweiler, M. Singh, T. A. Holak, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13220–13226.
- 41
- 41aJ. Ma, M. Ptashne, Cell 1987, 51, 113–119;
- 41bO. Nyanguile, M. Uesugi, D. J. Austin, G. L. Verdine, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13402–13406;
- 41cFor a review, see: A. Z. Ansari, A. K. Mapp, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 765–772.
- 42H. Shimogawa, Y. Kwon, Q. Mao, Y. Kawazoe, Y. Choi, S. Asada, H. Kigoshi, M. Uesugi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3461–3471.
- 43Z. Wu, G. Belanger, B. B. Brennan, J. K. Lum, A. R. Minter, S. P. Rowe, A. Plachetka, C. Y. Majmudar, A. K. Mapp, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 12390–12391.
- 44
- 44aA. R. Minter, B. B. Brennan, A. K. Mapp, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10504–10505;
- 44bS. J. Buhrlage, B. B. Brennan, A. R. Minter, A. K. Mapp, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12456–12457.
- 45Y. Kwon, H.-D. Arndt, Q. Mao, Y. Choi, Y. Kawazoe, P. B. Dervan, M. Uesugi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15940–15941.
- 46Review on DNA-binding hairpin polyamides: P. B. Dervan, B. S. Edelson, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 284–299.
- 47B. Liu, P. G. Alluri, P. Yu, T. Kodadek, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8254–8255.
- 48S. J. Teague, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2003, 2, 527–541.