Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover Image, Volume 233, Number 12, December 2018
- Page: i
- First Published: 12 October 2018
Cover: The cover image, by Chammaa et al., is based on Original Research Article, RUMI is a novel negative prognostic marker and therapeutic target in non-small-cell lung cancer, DOI: 10.1002/jcp.26858.
ISSUE INFORMATION
Table of Contents, Editor's Choice, Highlights
- Pages: 9031-9042
- First Published: 12 October 2018
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS
STAC3 incorporation into skeletal muscle triads occurs independent of the dihydropyridine receptor
- Pages: 9045-9051
- First Published: 02 August 2018
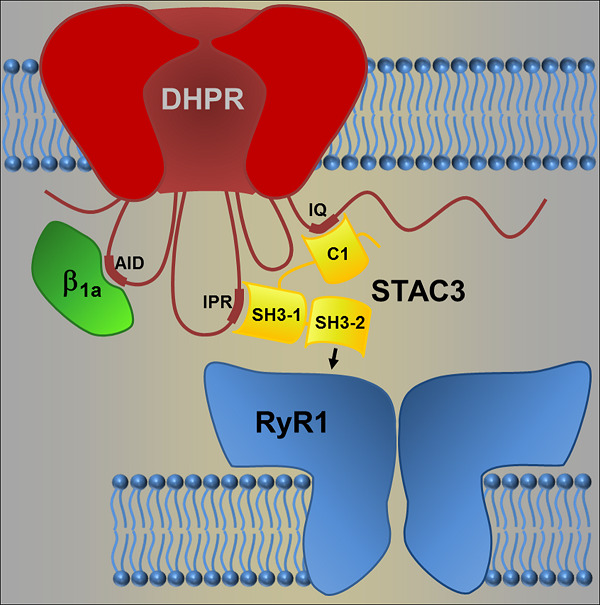
STAC3 has been demonstrated to establish two discrete interactions with the DHPR: its C1 domain interacts with the IQ domain in the C-terminus, and the SH3-1 domain interacts with the IPR motif in the II–III loop of the DHPR. Here, we provide evidence of a third, hitherto unidentified, interaction, which anchors STAC3 in the triad junctions independent of the DHPR. Because of the crucial role of STAC3 in excitation-contraction coupling and because no additional proteins are necessary to restore voltage-induced calcium release in heterologous cells, STAC3 may thus directly couple the DHPR with the RyR1.
High prevalence of serum IgG antibodies reacting to specific mimotopes of BK polyomavirus, a human oncogenic polyomavirus, in patients affected by uveal melanoma
- Pages: 9052-9059
- First Published: 03 July 2018
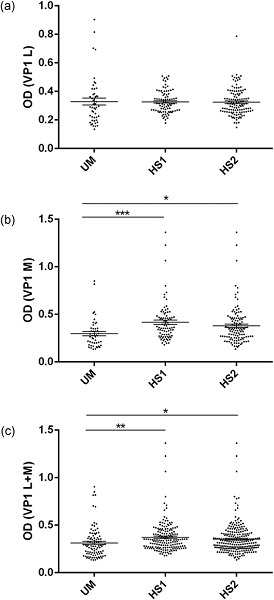
Serologic profile of serum antibody reactivity to BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) mimotopes viral capsid protein 1 (VP1) L (a) and VP1 M (b) and VP1 L+M (c). Immunologic data are from serum samples from uveal melanoma (UM) and healthy subjects (HS1). Results are presented as values of optical density (OD) readings at λ = 405 nm, of serum samples diluted at 1:20, detected in indirect ELISA. In scatter–dot plotting, each plot represents the dispersion of OD values to a mean level indicated by the line inside the scatter with the standard deviation (SD) for each group of subjects analyzed. (a) The mean OD of sera (VP1 L ± std error) in UM (0.329 ± 0.024) does not differ from that of HS1 (0.327 ± 0.008), p > 0.05, and from that of HS2 (0.324 ± 0.009), p > 0.05. (b) The mean OD of sera (VP1 M ± std error) in UM (0.298 ± 0.022) is lower than that detected in HS1 (0.417 ± 0.022), ***p < 0.001, and in HS2 (0.379 ± 0.018), *p < 0.05. (c) The mean OD of sera (VP1 L + M ± std error) in UM (0.314 ± 0.016) is lower than that detected in HS1 (0.372 ± 0.012), **p < 0.005, and in HS2 (0.352 ± 0.009), *p < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and the t test.
Peroxidase expression is decreased by palmitate in cultured podocytes but increased in podocytes of advanced diabetic nephropathy
- Pages: 9060-9069
- First Published: 21 August 2018
Our results suggest that podocytes are susceptible to palmitic acid (PA)–induced oxidative damage with impaired peroxidase activity and that peroxidases have futile antioxidant effects in the podocytes in the late stages of diabetic nephropathy (DN). Given this, PA-induced podocyte injury via inadequate peroxidase response to H2O 2 appears to play an important role in the pathogenesis of DN.
FROM THE BENCH
Enhancing developmental rate and quality of mouse single blastomeres into blastocysts using a microplatform
- Pages: 9070-9076
- First Published: 26 June 2018
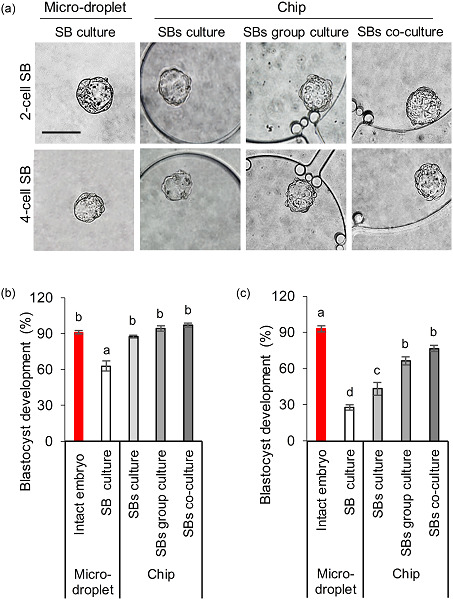
The present work, for the first time, reports the beneficial effects of using a microplatform on development of mouse single blastomeres (SBs) to the blastocyst stage. Three chips were introduced that provide the possibility of culturing SBs separately, in groups, and in the vicinity of the intact embryo. The quality of developed blastocysts was also examined.
MINI-REVIEWS
Potential role of microRNAs in the regulation of adipocytes liposecretion and adipose tissue physiology
- Pages: 9077-9086
- First Published: 22 June 2018
Role of microRNAs in adipogenic process. Role of microRNAs in liposecretion process. Role of microRNAs in obesity.
MINI REVIEWS
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in angiogenesis
- Pages: 9087-9098
- First Published: 03 July 2018
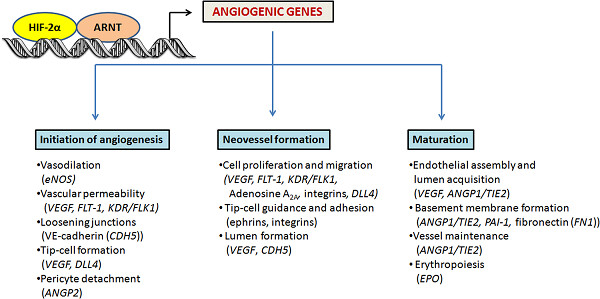
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2α has been shown to regulate multiple aspects of angiogenesis, including cell proliferation, migration, maturation of blood vessels, and metastasis. In this review, we focus on recent insights into HIF-2α expression, activation, and function under hypoxic and nonhypoxic conditions. We also summarize the current knowledge on the crosstalk between HIF-2 and angiogenesis, describing reported phenotypical changes of HIF-2α genetic models and HIF-2 target genes implicated in angiogenesis. Finally, we provide a survey of recent pharmacologic strategies to specifically target HIF-2 activity.
Fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells: Two sides of the same coin?
- Pages: 9099-9109
- First Published: 26 June 2018
The role of ErbB3 binding protein 1 in cancer: Friend or foe?
- Pages: 9110-9120
- First Published: 04 August 2018
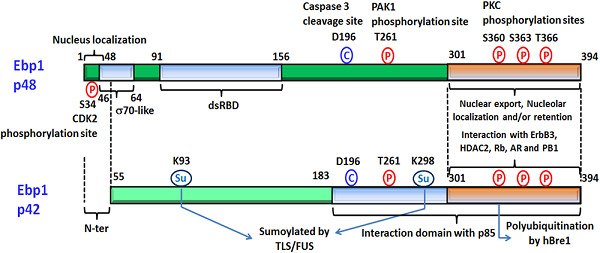
Numerous studies have indicated that ErbB3 binding protein 1 (Ebp1), a binding partner for ErbB3, plays an important regulatory role in the expression and function of ErbB3, but there is no agreement as to whether Ebp1 also has an ErbB3-independent function in cancer and how it might contribute to tumorigenesis. In this review, we will discuss the different functions of the two Ebp1 isoforms, p48 and p42, that may be responsible for the potentially dual role of Ebp1 in cancer growth.
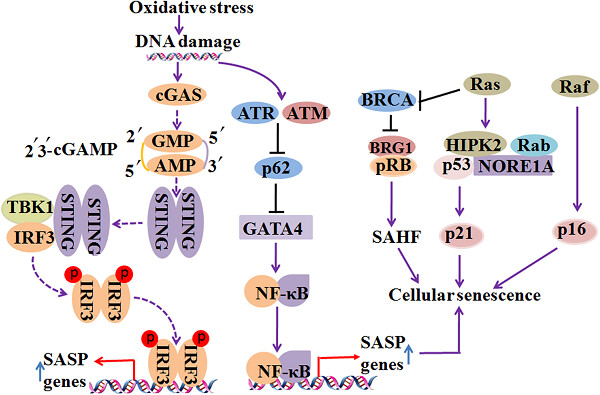
Cellular senescence: Molecular mechanisms and pathogenicity
- Pages: 9121-9135
- First Published: 05 August 2018
REVIEW ARTICLES
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells contribute to breast cancer heterogeneity
- Pages: 9136-9144
- First Published: 03 July 2018
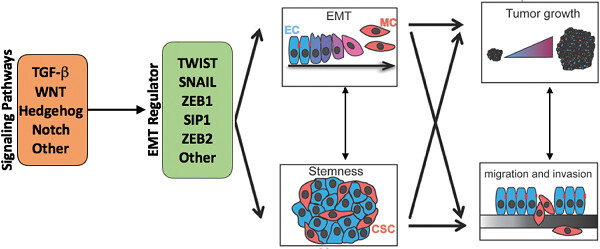
Breast tumors exhibit both inter- and intratumor heterogeneity as a result of both genetic and nongenetic alterations. Intertumor heterogeneity reflects the different cells of origin. Intratumor heterogeneity can be explained by the cancer stem cell theory, which is associated with activation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.
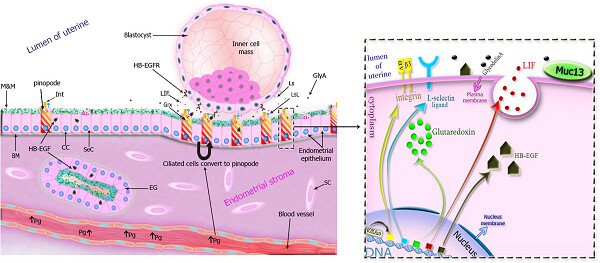
Endometrial pinopode biomarkers: Molecules and microRNAs
- Pages: 9145-9158
- First Published: 03 July 2018
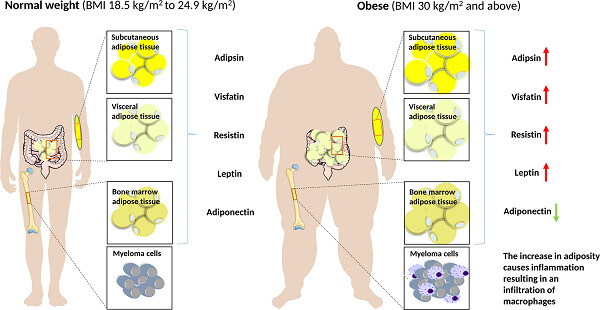
Adipokines, adiposity, and bone marrow adipocytes: Dangerous accomplices in multiple myeloma
- Pages: 9159-9166
- First Published: 26 June 2018
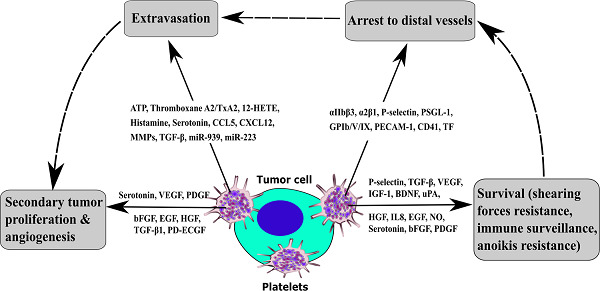
Cancer metastasis versus stem cell homing: Role of platelets
- Pages: 9167-9178
- First Published: 13 August 2018
Ferritinophagy/ferroptosis: Iron-related newcomers in human diseases
- Pages: 9179-9190
- First Published: 04 August 2018
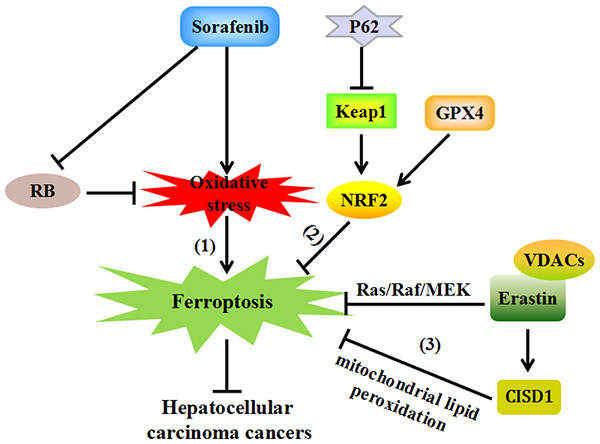
Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4)-mediated ferritinophagy is an autophagic phenomenon that specifically involves ferritin to release intracellular free iron. Ferritinophagy plays a central role in maintaining efficient erythropoiesis and driving urinary tract infections. Ferritinophagy is critical to induce ferroptosis, a newly nonapoptotic form of cell death that inhibits some types of cancers and accelerates neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Therapeutic potential of microRNAs in osteoporosis function by regulating the biology of cells related to bone homeostasis
- Pages: 9191-9208
- First Published: 05 August 2018
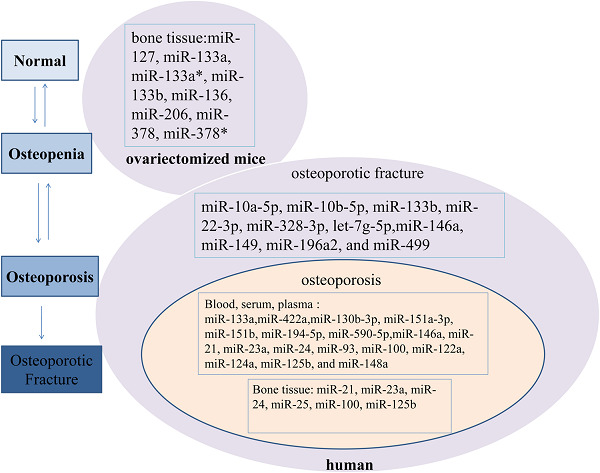
In this review, the roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the regulation of cells related to bone homeostasis as well as miRNAs that deregulate in human or animal are discussed. Moreover, the miRNAs that act as clusters in the biology of cells in the bone microenvironment and the difference of some important miRNAs for bone homeostasis between bone and other organs are mentioned. Overall, miRNAs that contribute to the pathogenesis of osteoporosis and their therapeutic potential are considered.
The MicroRNA-326: Autoimmune diseases, diagnostic biomarker, and therapeutic target
- Pages: 9209-9222
- First Published: 05 August 2018
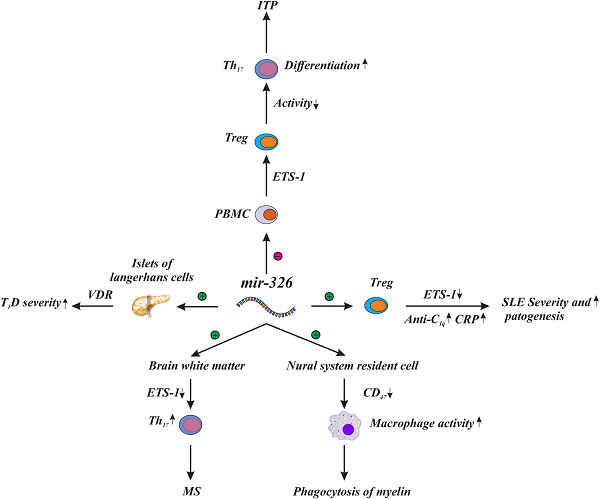
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are uniquely regulated in healthy, inflamed, activated, and cancerous cells and tissues. Most recently, miR-326 has been explored widely and has emerged as a key regulator of different biological processes such as metabolism of glucose and lipids; cell growth and proliferation; immune cell lineage obligation; maturation, differentiation, and maintenance of immune homeostasis; TH17 differentiation; as well as dendritic cells function. In this review, we will explain the history and classification of epigenetic changes, especially miRNAs and describe the role of miR-326 in different pathologic conditions, especially autoimmune diseases.
Tumor-associated macrophages and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer: Nanotechnology comes into view
- Pages: 9223-9236
- First Published: 05 August 2018
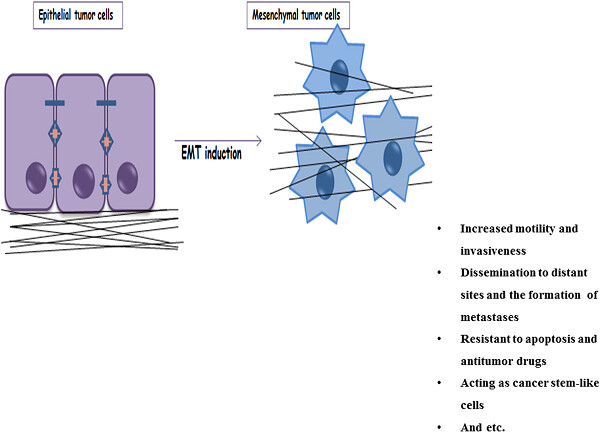
Here, we will focus on selected molecular pathways underlying epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)—in particular, the role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in the induction and maintenance of EMT—and further discuss how the targeting of TAMs through the application of nanotechnology tools allows the development of a whole new range of therapeutics.
Monocyte-to-HDL-cholesterol ratio as a prognostic marker in cardiovascular diseases
- Pages: 9237-9246
- First Published: 04 August 2018
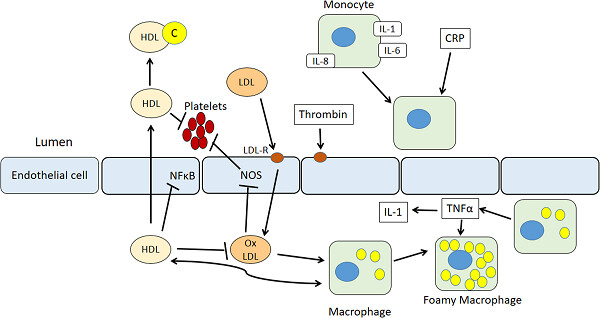
Monocytes are a major source of proinflammatory species during atherogenesis; in atherosclerosis, modified low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) are removed by macrophages and these are recruited in the vessel wall, inducing the release of inflammatory cytokines in inflamed tissue generating inflammatory cholesterol ester-loaded plaque. High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) exhibits antiatherosclerotic effects by neutralizing the proinflammatory and pro-oxidant effects of monocytes via inhibiting the migration of macrophages and LDL oxidation in addition to the efflux of cholesterol from these cells; furthermore, HDL plays a role in suppressing the activation of monocytes and proliferation–differentiation of monocyte progenitor cells. Thus, accumulation of monocytes and reduction of HDL-C may participate in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases (CVD); given that the relationship between the high number of monocytes and low HDL-C levels has been reported in inflammatory disorders, this review focused on understanding whether the monocyte-to-HDL ratio could be a convenient marker to predict atherosclerosis development and progression, hallmarks of CV events, instead of the individual monocyte count or HDL-C level.
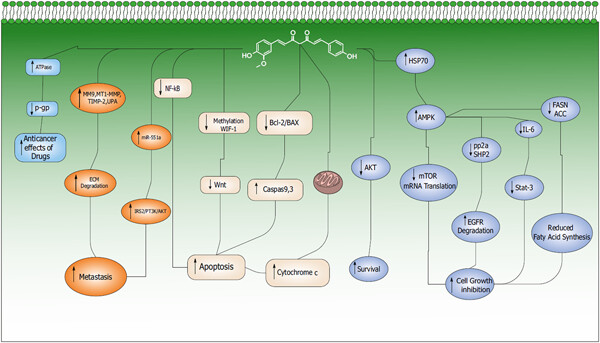
Demethoxycurcumin: A naturally occurring curcumin analogue with antitumor properties
- Pages: 9247-9260
- First Published: 04 August 2018
Infection-associated epigenetic alterations in gastric cancer: New insight in cancer therapy
- Pages: 9261-9270
- First Published: 04 August 2018
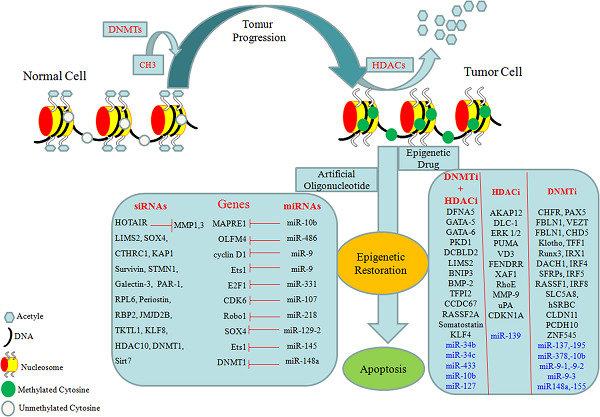
(a) Infections are strongly linked to gastric cancer; (b) infections induce epigenetic alterations in gastric cancer; (c) antiviral treatments in combination with epigenetic therapeutic approaches along with standard chemotherapy are potentially superior to monotherapies in gastric cancer prevention and treatment.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Gut microbiota-derived endotoxin enhanced the incidence of cardia bifida during cardiogenesis
- Pages: 9271-9283
- First Published: 08 September 2017
ΔFosB regulates rosiglitazone-induced milk fat synthesis and cell survival
- Pages: 9284-9298
- First Published: 20 November 2017
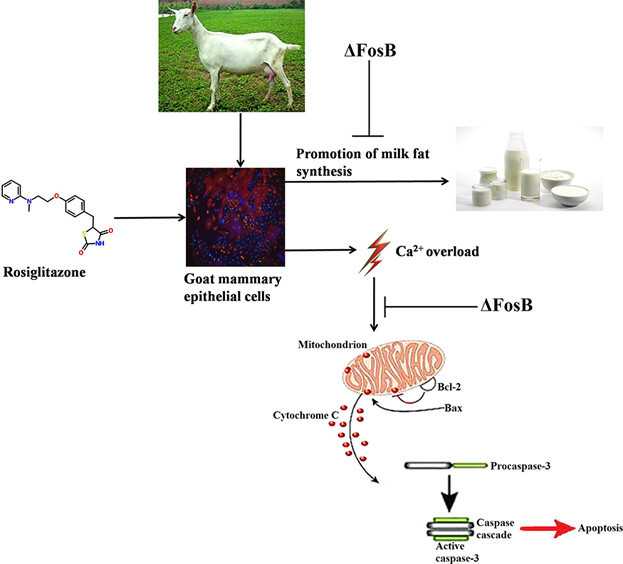
ΔFosB suppresses PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone-induced cellular lipid-droplets accumulation and protects cells from PPARγ activated-induced apoptosis. ΔFosB also increased MMP-9 gelatinolytic activity, and inhibition of MMP-9 suppressed the expression of Bcl-2 and increased intracellular calcium levels, and these effects were improved by overexpression of ΔFosB.
Network analysis of hippocampal neurons by microelectrode array in the presence of HIV-1 Tat and cocaine
- Pages: 9299-9311
- First Published: 05 December 2017
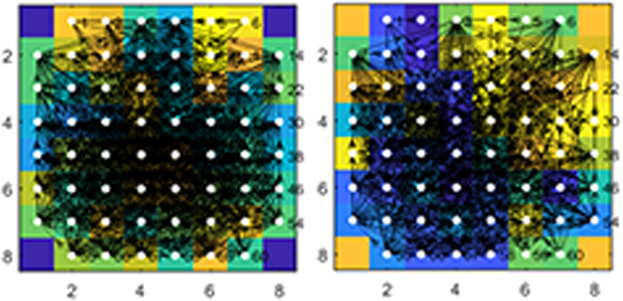
HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders are caused by HIV-1 infection of the CNS and include neurotoxic effects of the HIV-1 Tat protein. In addition to increasing the risk for becoming HIV infected, cocaine abuse enhances the neuropathogenic impacts of HIV-1. We employed microelectrode arrays to investigate the effects of Tat and cocaine on the hippocampal neuronal network. Tat and cocaine differentially disturbed neuronal activity within the hippocampal neuronal network via potentiation of inhibitory neurotransmission and the presence of astrocytes co-cultured with neuronal networks diminished the effects of Tat and cocaine. This suggests a role for astrocytes in stabilizing neuronal behavior pointing to a newly discovered pathway through which ionic homeostasis is maintained by neuron-glial crosstalk in the CNS.
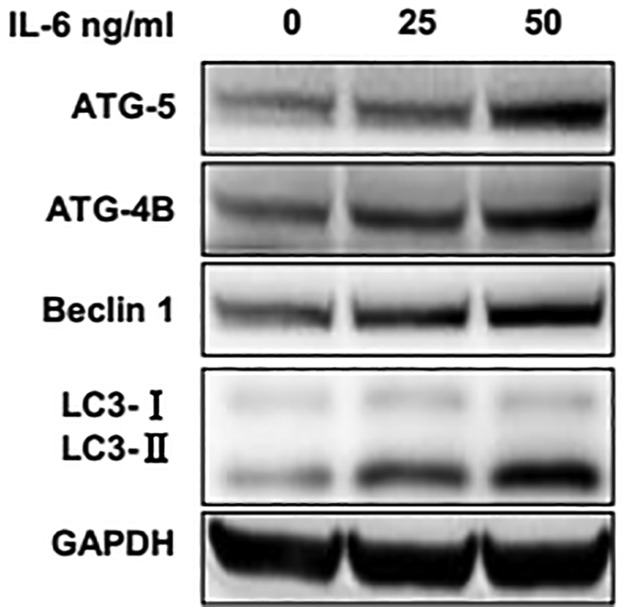
Role of IL-6-mediated expression of NS5ATP9 in autophagy of liver cancer cells
- Pages: 9312-9319
- First Published: 11 December 2017
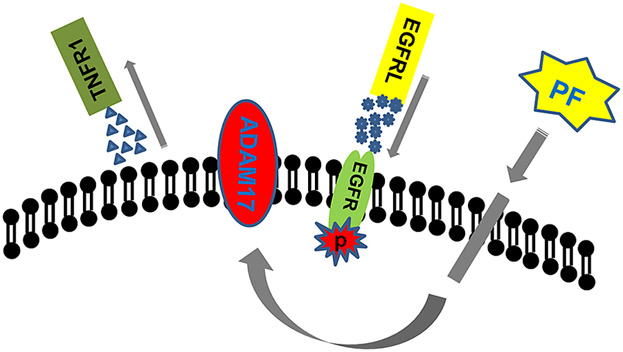
ADAM17 participates in the protective effect of paeoniflorin on mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells
- Pages: 9320-9329
- First Published: 07 December 2017
Extracellular vesicles derived from human embryonic stem cell-MSCs ameliorate cirrhosis in thioacetamide-induced chronic liver injury
- Pages: 9330-9344
- First Published: 21 December 2017
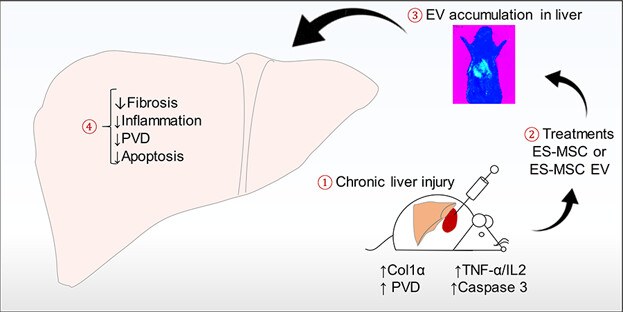
In present study, we found the superiority of ES-MSC and ES-MSC EVs regarding immunomodulatory potential in comparison to those from BM- and AD-MSCs through the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines in vitro. ES-MSCs and ES-MSC EVs also offer anti-fibrotic, anti-necrotic and immunosuppressive effects to modulate TAA-induced cirrhotic livers after successfully engraftment in recipient damaged livers. To our knowledge, this is the preliminary evidence explaining hepatoprotective effects of ES-MSCs and their EVs in chronic liver disease model.
Effect of restriction vegan diet's on muscle mass, oxidative status, and myocytes differentiation: A pilot study
- Pages: 9345-9353
- First Published: 10 January 2018
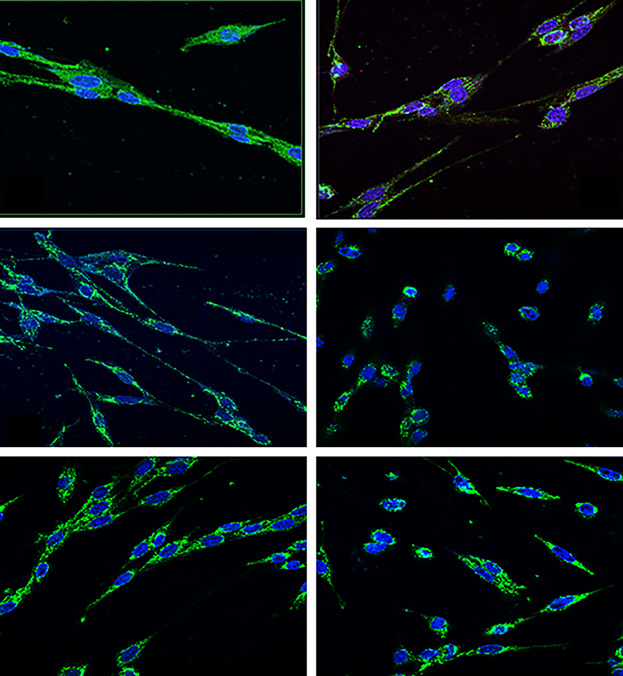
This study was conceived to evaluate the effects of three different diets on body composition, metabolic parameters, and serum oxidative status, and growth and differentiation of cardiomyoblast cell line H9c2 treated with H2O2 (H-H9c2). We demonstrated that the vegan diets induced a decrease in muscle mass index and lean body mass. Therefore our data showed that the omnivorous sera have major antioxidant and differentiation property compared to vegetarian and vegan sera. The results obtained in this study demonstrated that restrictive vegan diet could not prevent the onset of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases nor protect by oxidative damage.
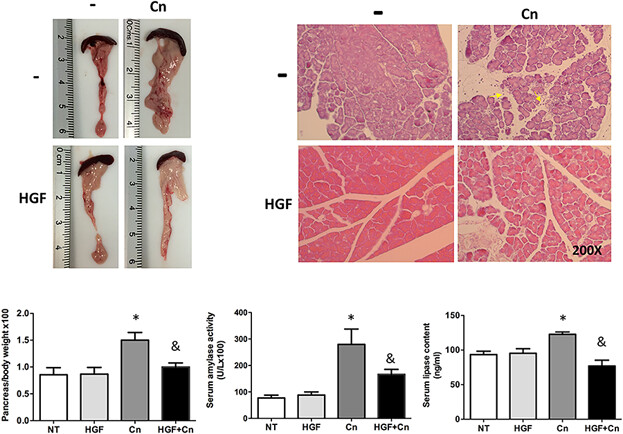
Recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor provides protective effects in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice
- Pages: 9354-9364
- First Published: 17 January 2018
Over-expression of DEC1 inhibits myogenic differentiation by modulating MyoG activity in bovine satellite cell
- Pages: 9365-9374
- First Published: 19 January 2018
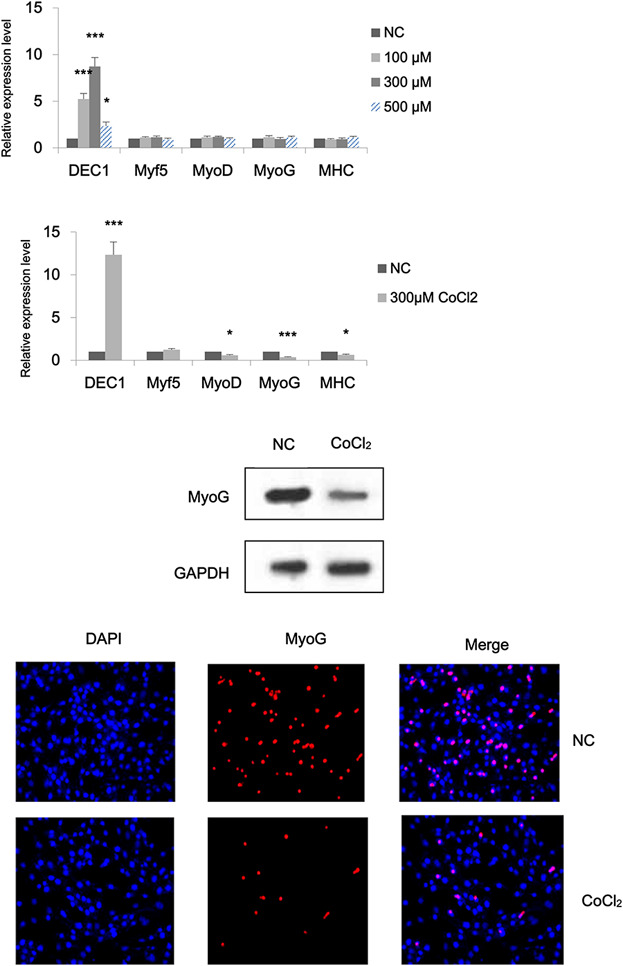
DEC1 was ubiquitously expressed in most tissues in bovine and down-regulated in differentiating bovine satellite cells. Either CoCl2-simulated hypoxia or ectopic expression of DEC1 blocked bovine myoblast differentiation. Over-expression of bovine DEC1 inhibited MyoG promoter activity. The present study gives new insight into the mechanisms involved in myogenic differentiation.
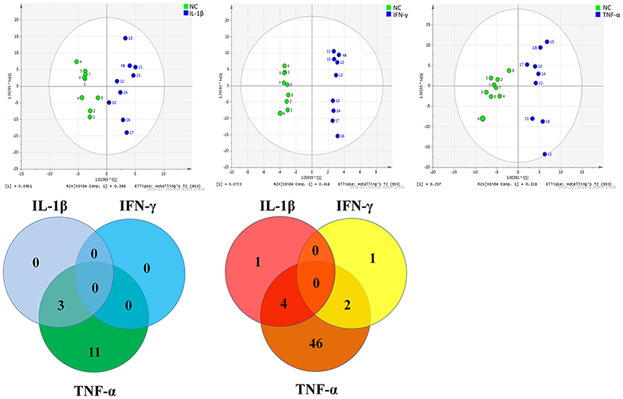
A multi-method evaluation of the effects of Inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IFN-γ, TNF-α) on pancreatic β-cells
- Pages: 9375-9382
- First Published: 19 June 2018
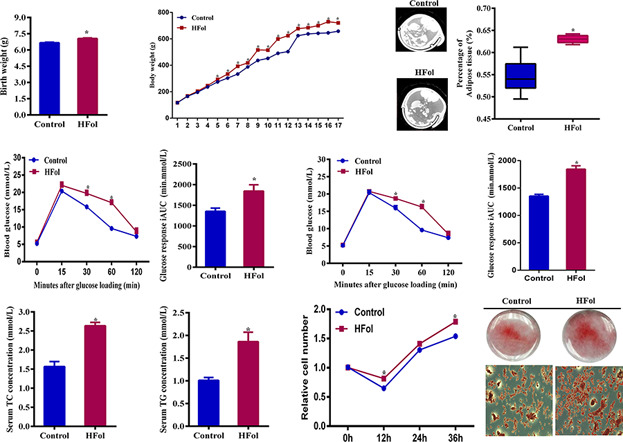
High folate intake contributes to the risk of large for gestational age birth and obesity in male offspring
- Pages: 9383-9389
- First Published: 19 June 2018
RESEARCH ARTICLES
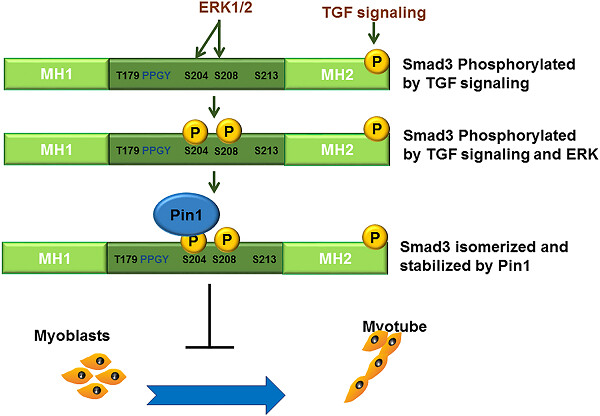
Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase NIMA interacting 1 regulates skeletal muscle fusion through structural modification of Smad3 in the linker region
- Pages: 9390-9403
- First Published: 21 August 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
NLRP3 inflammasome mediates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury implication of the microRNA-155/FOXO3a signaling pathway
- Pages: 9404-9415
- First Published: 28 June 2018
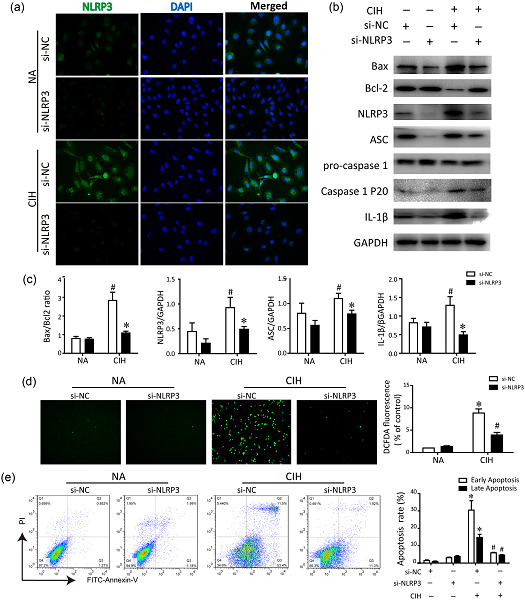
Nucleotide-binding domain like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH)-induced renal injury. NLRP3 inflammasome is required for microRNA-155 (miR-155) expression. miR-155 modulates NLRP3 and interleukin-1 cytokine signaling cascade through targeting FOXO3a to form a positive feedback loop, thus enhancing inflammatory cytokines production.
CerS6 regulates cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma by altering mitochondrial fission and autophagy
- Pages: 9416-9425
- First Published: 27 July 2018
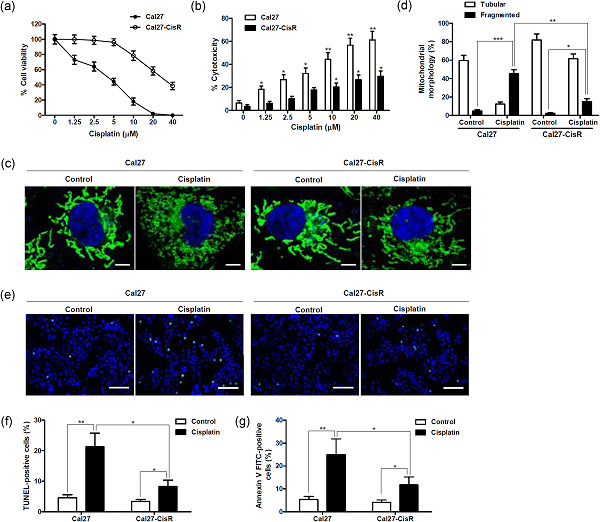
In the current study, we observed that cisplatin-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells process lower levels of fission-state mitochondria and cell apoptosis than cisplatin-sensitive cells, and autophagy was activated in cisplatin-resistant OSCC cells. Overexpression of CerS6 increases cisplatin sensitivity via enhancement of mitochondrial fission and apoptosis and attenuation of cisplatin-induced autophagy in cisplatin-resistant OSCC cells.
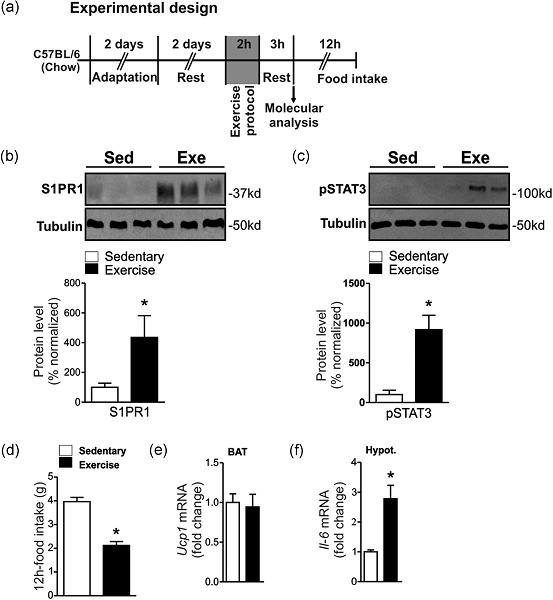
Exercise activates the hypothalamic S1PR1–STAT3 axis through the central action of interleukin 6 in mice
- Pages: 9426-9436
- First Published: 31 July 2018
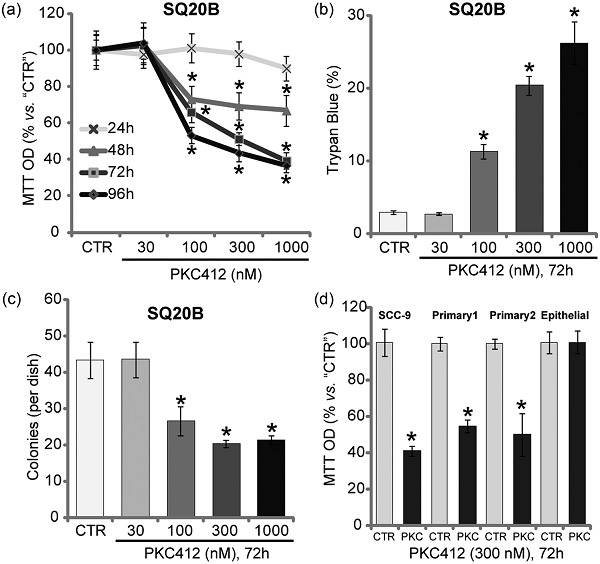
C6 ceramide motivates the anticancer sensibility induced by PKC412 in preclinical head and neck squamous cell carcinoma models
- Pages: 9437-9446
- First Published: 03 July 2018
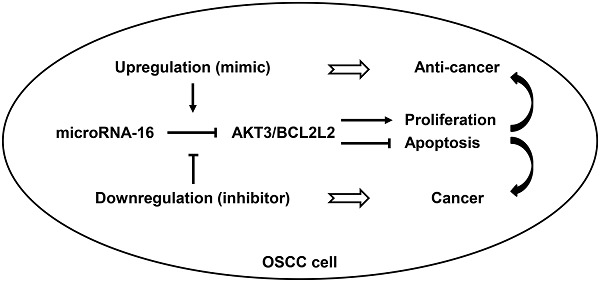
MicroRNA-16 functions as a tumor-suppressor gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting AKT3 and BCL2L2
- Pages: 9447-9457
- First Published: 22 August 2018
Differentiated adipose-derived stem cell cocultures for bone regeneration in RADA16-I in vitro
- Pages: 9458-9472
- First Published: 11 July 2018
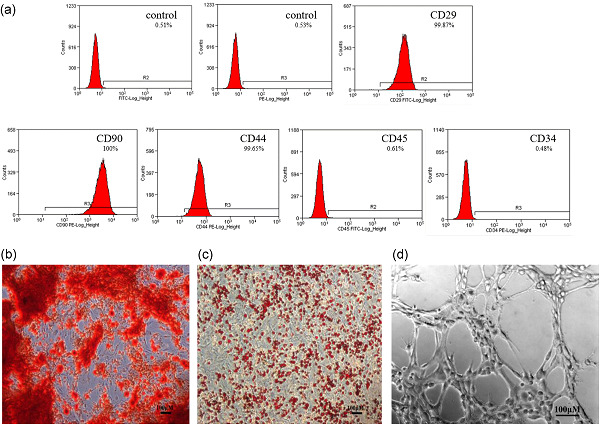
The objective of this study was to coculture osteogenic ADSCs (os-ADSCs) and endothelial ADSCs in three types of ratios and then compare the osteogenesis and angiogenesis effects, preliminarily exploring the best cocultured proportion that will be seeded in RADA16-I. We performed the study was because there is limited research illustrating the interactions between cocultured os-ADSCs and endothelial ADSCs.
Cleavage of caspase-12 at Asp94, mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), contributes to stretch-induced apoptosis of myoblasts
- Pages: 9473-9487
- First Published: 26 June 2018
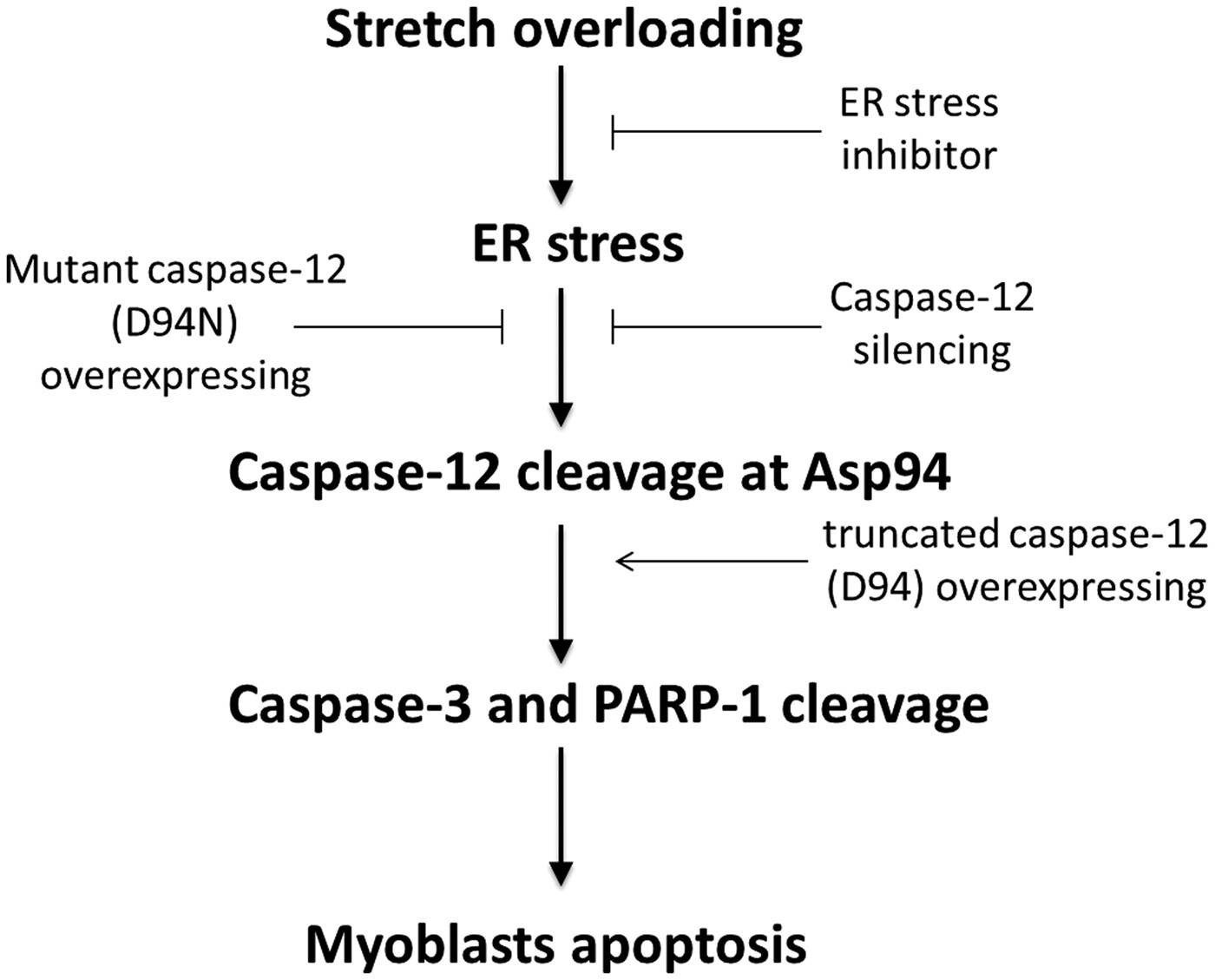
Apoptosis was elevated in a time-dependent manner when myoblasts were subjected to cyclic mechanical stretch (CMS) for 12, 24, and 36 hr. Notably, caspase-12 cleavage at Asp94, induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress under stretch stimuli, is the key molecule in initiating the CMS-triggered apoptosis of myoblasts.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
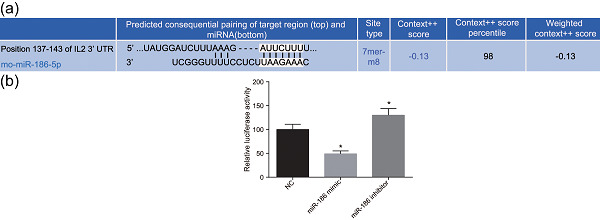
Retracted: Effect of microRNA-186 on oxidative stress injury of neuron by targeting interleukin 2 through the janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease
- Pages: 9488-9502
- First Published: 11 July 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Study on the mechanism behind lncRNA MEG3 affecting clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-7/RASL11B signaling
- Pages: 9503-9515
- First Published: 03 July 2018
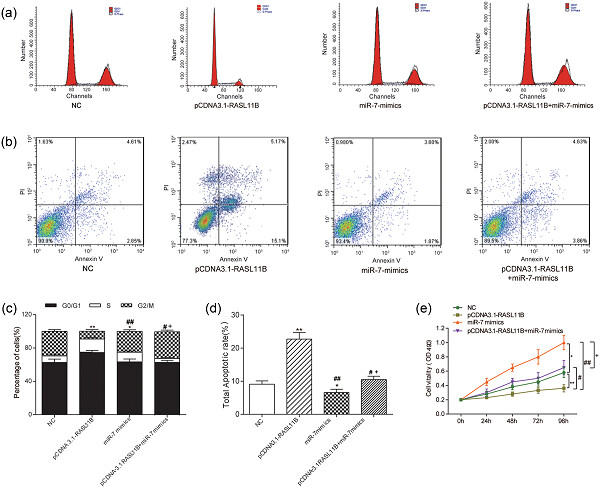
The goal of this study was to study the relationships between maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3), microRNA-7 (miR-7), and RASL11B, and explore their influence on the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC). MEG3 could up-regulate RASL11B to inhibit cell proliferation, invasion and migration; induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest; and promote cell apoptosis by suppressing miR-7 in CCRCC.
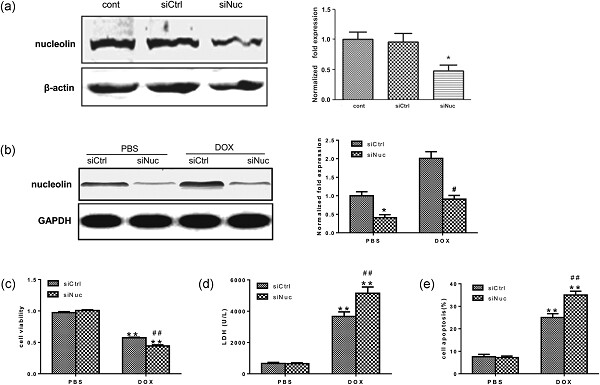
Nucleolin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via upregulating microRNA-21
- Pages: 9516-9525
- First Published: 03 July 2018
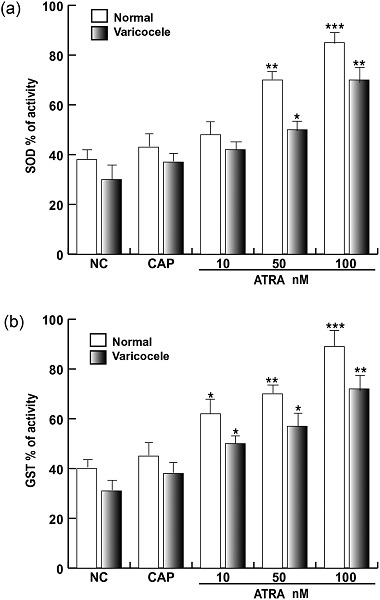
Influence of all-trans retinoic acid on sperm metabolism and oxidative stress: Its involvement in the physiopathology of varicocele-associated male infertility
- Pages: 9526-9537
- First Published: 26 June 2018
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Zerumbone inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells properties by inhibiting the β-catenin pathway through miR-200c
- Pages: 9538-9547
- First Published: 26 June 2018
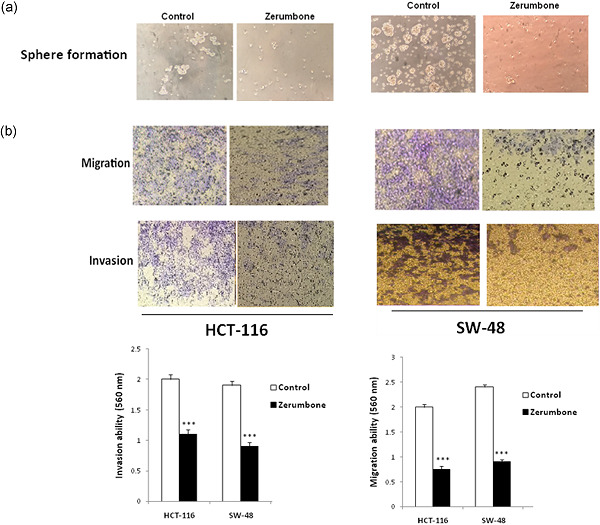
Our results showed, for the first time, that Zerumbone, as a natural substance, reduced the cell viability of colorectal cancer cell lines. Zerumbone is able to reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) through the upregulation of miR-200c. In addition, Zerumbone decreased β-catenin in the WNT signaling pathway, which led to inhibiting the transcription of genes involved in EMT and cancer stem cells.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
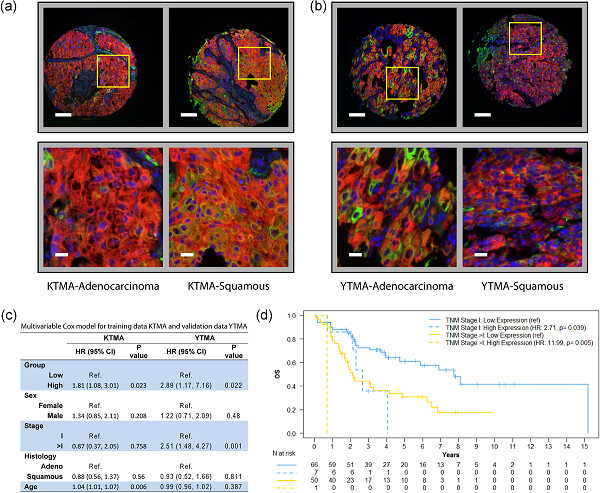
RUMI is a novel negative prognostic marker and therapeutic target in non–small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 9548-9562
- First Published: 28 June 2018
BMAL1 and CLOCK proteins in regulating UVB-induced apoptosis and DNA damage responses in human keratinocytes
- Pages: 9563-9574
- First Published: 26 June 2018
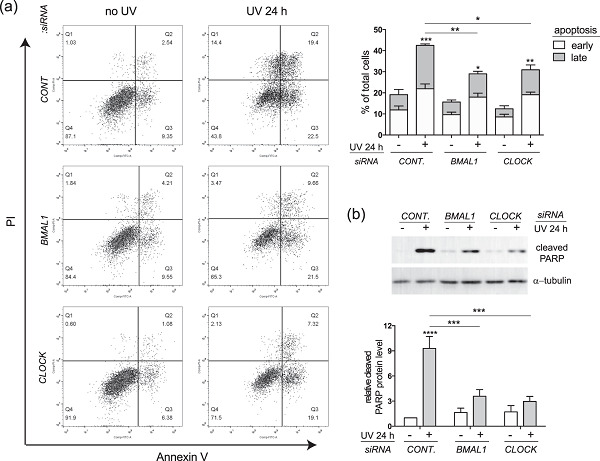
In this study, we investigate the impact of the circadian clock on UVB responses in human keratinocytes. We found that the two clock proteins brain and muscle ARNT-like 1 (BMAL1) and circadian locomotor output cycles kaput (CLOCK) regulate UVB induced apoptosis in both immortal and primary human keratinocytes, but likely through different molecular mechanisms.
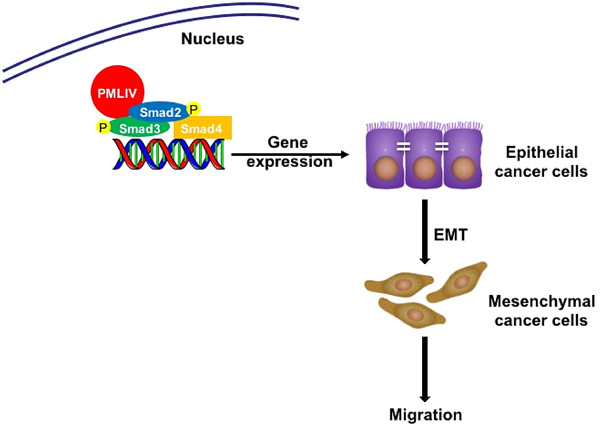
PMLIV overexpression promotes TGF-β-associated epithelial–mesenchymal transition and migration in MCF-7 cancer cells
- Pages: 9575-9583
- First Published: 26 June 2018
Methylation-independent ITGA2 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in de novo acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 9584-9593
- First Published: 21 August 2018
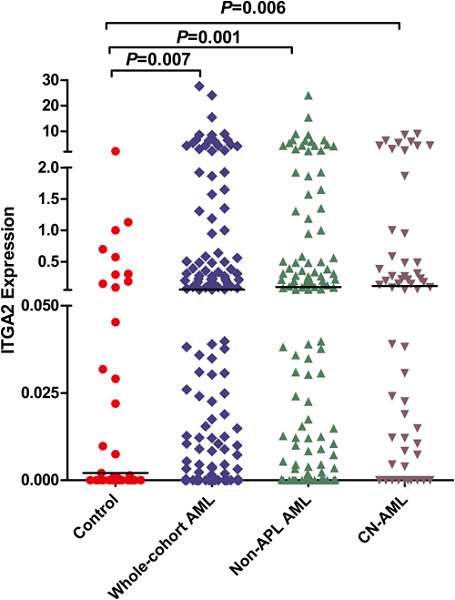
Integrin α2 (ITGA2) expression was significantly upregulated in 134 de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients compared with 33 controls (p = 0.007). Furthermore, the overall survival in high ITGA2 expression patients was significantly shorter than low ITGA2 expression patients throughout AML cohort, non–acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), and cytogenetic normal-AML (p = 0.001, 0.002, and 0.044, respectively). Multivariate analysis confirmed that ITGA2 overexpression served as an independent prognostic factor in both whole-cohort AML patients (p = 0.018) and non-APL AML patients (p = 0.021).
A new copper ionophore DPMQ protects cells against ultraviolet B irradiation by inhibiting the TRPV1 channel
- Pages: 9594-9610
- First Published: 26 June 2018
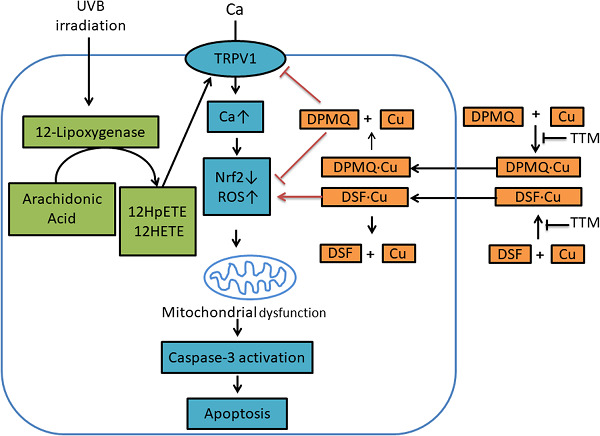
Treatment of cells with ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation results in increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and decreased Nrf2 levels by a mechanism involving lipoxygenase stimulation and TRPV1 channel activation. Increased ROS results in mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. DPMQ inhibits the TRPV1 channel and scavenges ROS, and hence protects cells against UVB irradiation–induced cytotoxicity, whereas disulfiram induces copper influx and increases ROS generation, and therefore causes apoptosis.
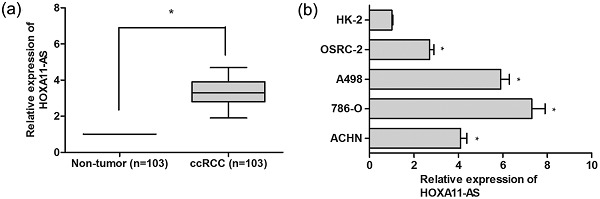
HOXA11-AS promotes the growth and invasion of renal cancer by sponging miR-146b-5p to upregulate MMP16 expression
- Pages: 9611-9619
- First Published: 28 June 2018
P2Y12 shRNA treatment decreases SGC activation to relieve diabetic neuropathic pain in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats
- Pages: 9620-9628
- First Published: 26 June 2018
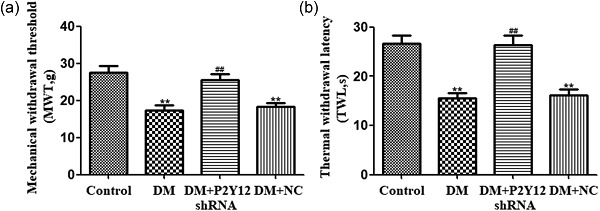
Upregulated P2Y12 in satellite glial cells (SGCs) of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) was involved in diabetic neuropathic pain. Targeting the P2Y12 receptor by short hairpin RNA decreased the upregulated expression of the P2Y12 receptor in DRG SGCs and relieved mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in type 2 DM rats.
Oxidative stress regulates autophagy in cultured muscle cells of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Pages: 9629-9639
- First Published: 26 June 2018
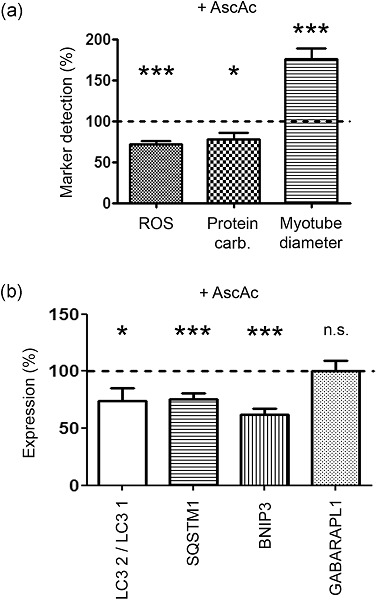
Autophagosome formation, the LC3 2/LC3 1 ratio, autophagy-related gene expression, and the autophagic flux are increased in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) muscle cells. Treatment of COPD myotubes with an antioxidant molecule decreased the reactive oxygen species (ROS) concentration, ROS-induced protein carbonylation, the LC3 2/LC3 1 ratio, the expression of SQSTM1 and BNIP3 and increased the COPD myotube diameter. The oxidative stress level contributes to the regulation of autophagy, which is involved in the atrophy of COPD myotubes in vitro.
Deficiency of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) leads to abnormal spermatogenesis and altered sperm physiology
- Pages: 9640-9651
- First Published: 27 July 2018
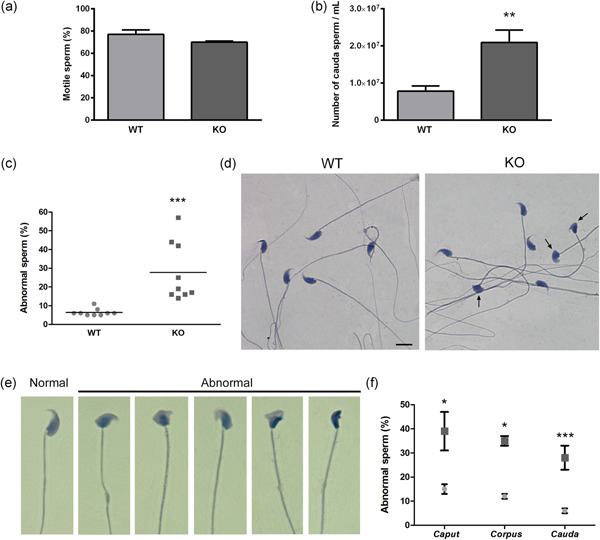
Our findings showed that in wild type (WT) animals, FGF-2 is expressed in germ cells of the seminiferous epithelium, in epithelial cells of the epididymis, and in the flagellum and acrosomal region of epididymal sperm. In the FGF-2 knockout (KO) mice, we found alterations in spermatogenesis kinetics and enhanced daily sperm production compared to the WT males. A significant increase in sperm concentration and in sperm head abnormalities, as well as alterations in other sperm parameters (reduced tyrosine phosphorylation and increased acrosomal loss) were observed in FGF-2 KO animals. Overall, the results suggest that FGF-2 exerts a role in mammalian spermatogenesis, and that the lack of FGF-2 leads to dysregulated sperm production and altered sperm morphology and function.
Aerobic exercise, but not metformin, prevents reduction of muscular performance by AMPk activation in mice on doxorubicin chemotherapy
- Pages: 9652-9662
- First Published: 28 June 2018
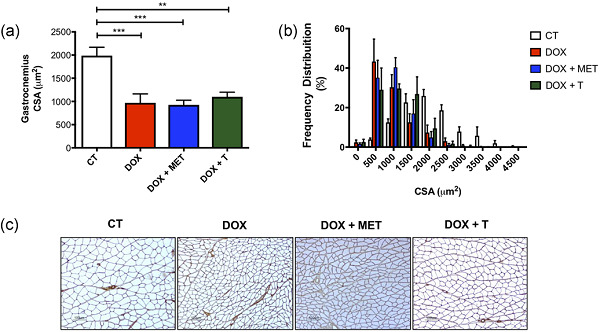
Pharmacological and nonpharmacological adjuvant strategies in chemotherapy treatment are presented. Decreased muscle performance caused by chemotherapeutic treatment can be recovered with aerobic exercise. Aerobic training is able to bring important benefits to counteract doxorubicin metabolic effects in the whole body and skeletal muscle.
The metabolic and molecular mechanisms of hyperammonaemia- and hyperethanolaemia-induced protein catabolism in skeletal muscle cells
- Pages: 9663-9673
- First Published: 24 August 2018
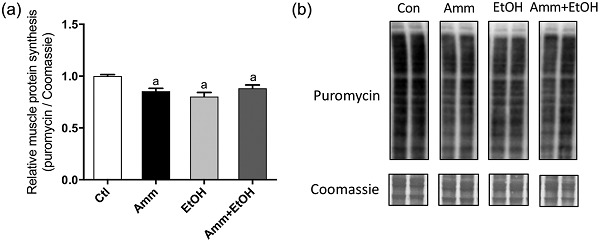
The findings from this study indicate that a combination of ammonia and ethanol incubation of C2C12 myotubes exacerbated muscle atrophy and dysregulation of anabolic and catabolic signalling pathways associated with either component individually. Our findings provide novel insight into the interactions between hyperammonaemia and hyperethanolaemia in relation to their regulation of muscle catabolism in vitro.
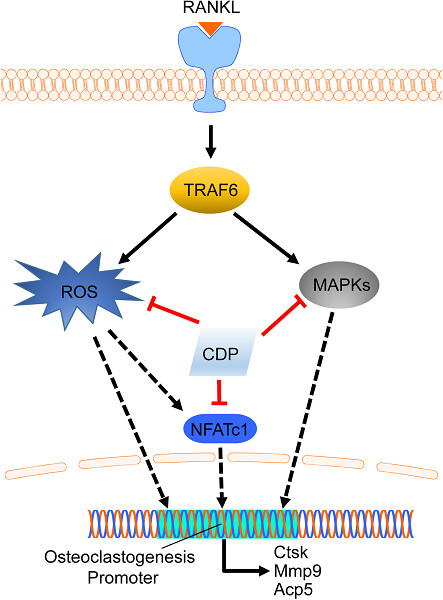
Cistanche deserticola polysaccharide attenuates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via inhibiting RANKL signaling and reactive oxygen species production
- Pages: 9674-9684
- First Published: 03 July 2018
Only a subpopulation of mouse sperm displays a rapid increase in intracellular calcium during capacitation
- Pages: 9685-9700
- First Published: 28 June 2018
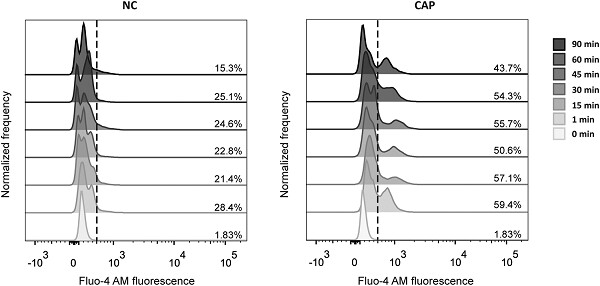
A rise in [Ca2+]i occurs after 1 min of incubation under capacitating conditions. Intracellular [Ca2+] was measured by flow cytometry in sperm collected after swim-out (0 min) and incubated under noncapacitating and capacitating conditions for different time periods (1–90 min). Histograms of normalized frequency versus Fluo-4 AM fluorescence of non-propidium-iodide stained sperm are presented.
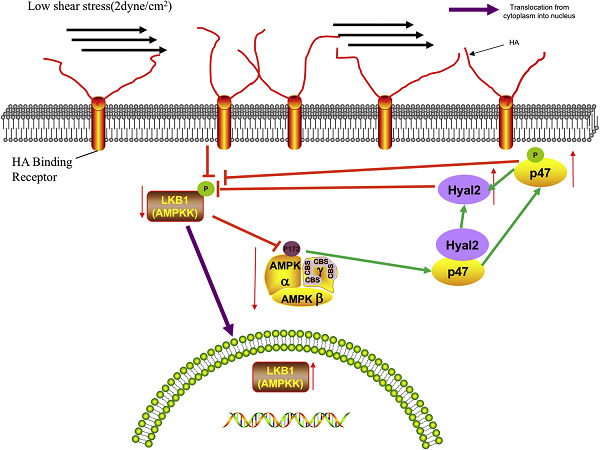
Hyaluronidase2 (Hyal2) modulates low shear stress-induced glycocalyx impairment via the LKB1/AMPK/NADPH oxidase-dependent pathway
- Pages: 9701-9715
- First Published: 05 August 2018
Analysis of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine gene variants and serum cytokine levels as prognostic markers in breast cancer
- Pages: 9716-9723
- First Published: 04 August 2018
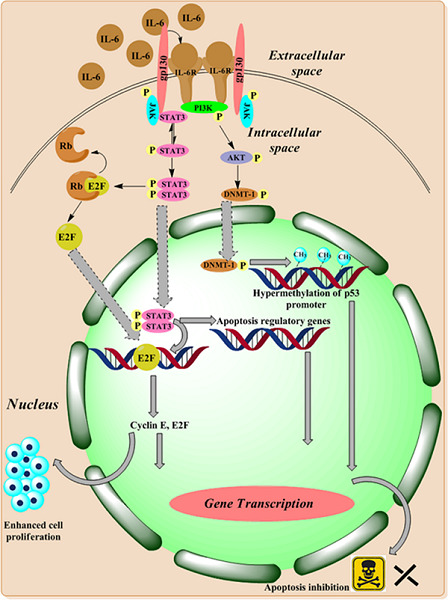
This study was carried in the Malwa region of Punjab where breast cancer was widely feared, and the levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines were analysed in female breast cancer patients. There was a significant difference in the serum levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-17a between patients and controls, and the elevated levels of these two cytokines associated significantly with poor outcome in breast cancer patients and, therefore, can be used as prognostic markers.
Small molecule inhibitor RepSox prevented ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by suppressing osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption
- Pages: 9724-9738
- First Published: 30 July 2018
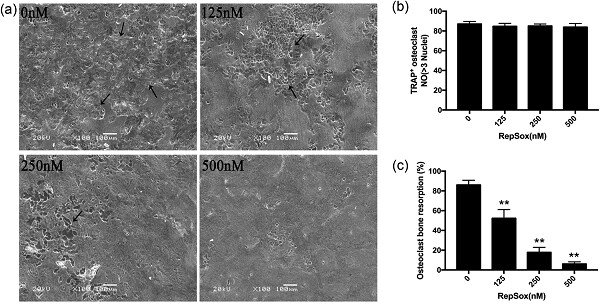
Bone destruction or osteolysis, marked by excessive osteoclastic bone resorption, is a very common medical condition. Identification of agents that can effectively suppress excessive osteoclast formation and function is crucial for prevention and treatment of osteolytic conditions, such as osteoporosis. In the present paper, we report that RepSox inhibits osteoclast formation in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that it is potentially valuable in the treatment of osteoclast-related diseases.
Stable overexpression of p130/E2F4 affects the multipotential abilities of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- Pages: 9739-9749
- First Published: 10 July 2018
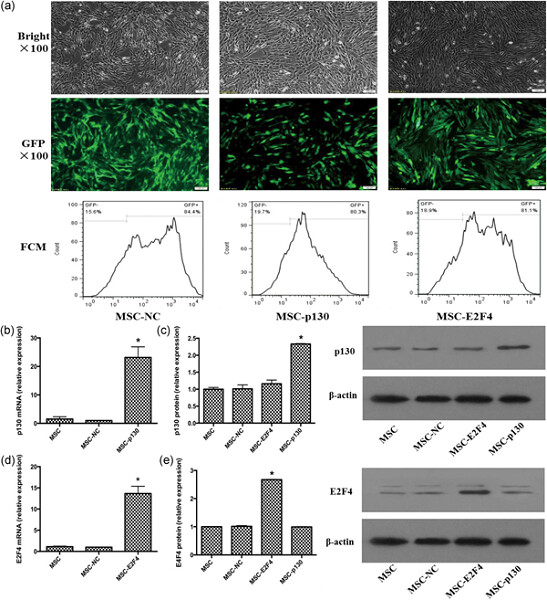
The controlled differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is one of the key aspects of effective clinical transplantation. Growing evidence suggests that the cell cycle plays an important role in regulating differentiation, while p130 and E2F4 are key to cell cycle checkpoints. Our data suggest that cell cycle regulation may be involved in p130/E2F4-mediated changes in the multipotential abilities of bone-marrow-derived mouse MSCs (mMSCs).
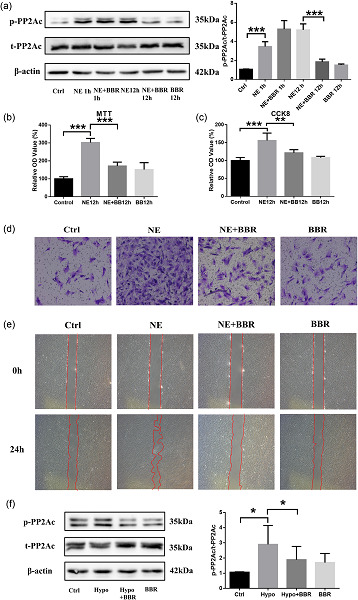
Berberine attenuates pulmonary arterial hypertension via protein phosphatase 2A signaling pathway both in vivo and in vitro
- Pages: 9750-9762
- First Published: 05 August 2018
Establishment and characterization of a telomerase-immortalized porcine bronchial epithelial cell line
- Pages: 9763-9776
- First Published: 05 August 2018
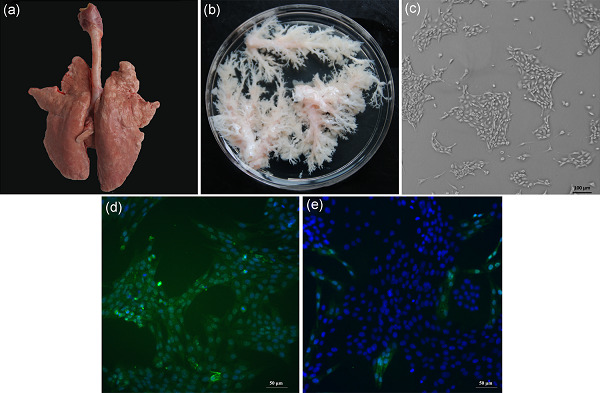
In summary, we provided detailed protocols for bronchus isolation from piglets and in vitro expansion of primary PBECs. Furthermore, we established the immortalized hTERT-PBEC line, which retains the morphological and functional features of primary PBECs. The establishment of immortal hTERT-PBECs is of great importance as an in vitro model for pathogenicity studies of porcine respiratory pathogens.
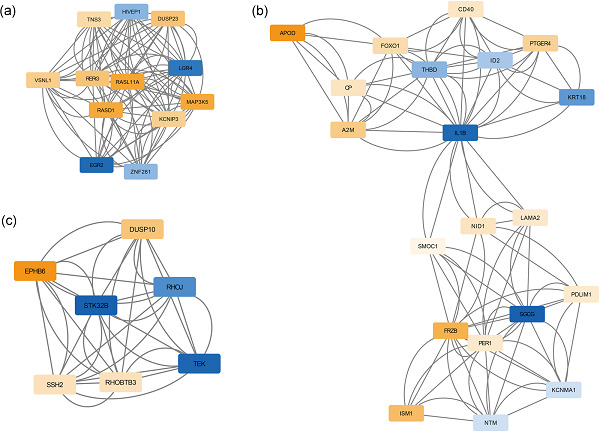
Identification of key genes and pathways associated with osteogenic differentiation of adipose stem cells
- Pages: 9777-9785
- First Published: 05 August 2018
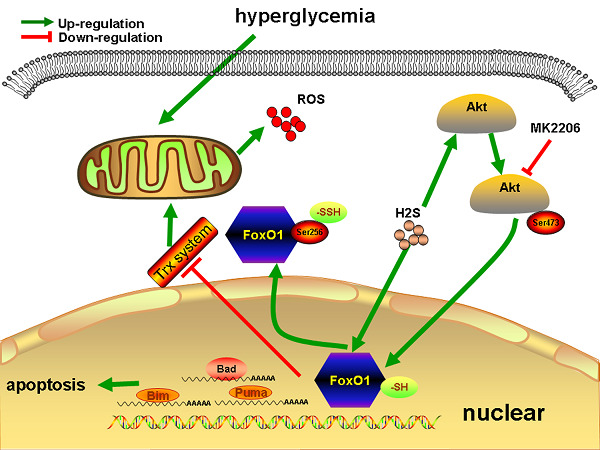
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide attenuates the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy via the FoxO1 pathway
- Pages: 9786-9798
- First Published: 05 August 2018
Inhibition of smoothened in breast cancer cells reduces CAXII expression and cell migration
- Pages: 9799-9811
- First Published: 21 August 2018
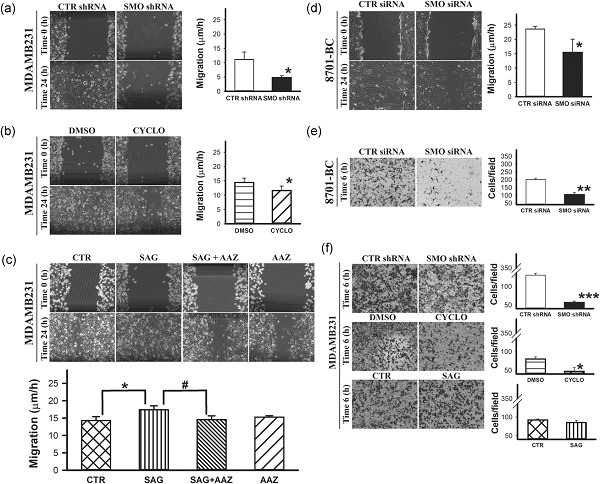
We here demonstrated that Smoothened (SMO) silencing resulted in a reduction of CAXII expression at messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein level in breast cancer (BC) cell lines. This led to a decrease in cell migration, which was restored when cells were treated with a SMO agonist. The reduction was confirmed also within hypoxic and inflammatory microenvironment, typical of BC, indicating a key role of the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway in controlling CAXII expression. Our results indicate that the Hh pathway controls BC cell migration and cell invasion through CAXII, with important implications in identifying novel therapeutic targets.