Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 2121
- First Published: 15 August 2024

Heterometallic complexes have played an increasingly important role in both small molecule activation and catalysis due to the potential metal-metal synergies. The trimetallic Mg-Ni-Mg complex was found to effectively catalyze the hydrosilylation of a variety of alkenes with anti-Markonikov selectivity. Capitalizing on the Mg-Ni synergistic effect, the possible intermediates were successfully isolated, thereby deepening comprehension of the intrinsic mechanism of this catalytic system. More details are discussed in the article by Xu et al. on page 2133—2139.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 2122
- First Published: 15 August 2024

3,4-Dihydroquinazoline frameworks which have frequently been encountered in natural products and bioactive molecules, prompted the development of creative pharmaceuticals owing to their prominent biological properties, such as trypanothione reductase inhibitor, Hepatitis B virus inhibitive activities, anticancer activities, etc. De novo assembling of chiral 3,4-dihydroquinazolines from simple chemical feedstocks via multicomponent reactions remains several great obstacles, and this scenario is capable of the divergent and flexible modulation of these skeletons which is urgently required for drug discovery. More details are discussed in the article by Yu et al. on page 2140—2146.
Contents
Breaking Report
Heterometallic Mg-Ni-Mg Complex Promoted Hydrosilylation of Alkenes: Catalytic Performance and Intermediates Characterization†
- Pages: 2133-2139
- First Published: 07 May 2024
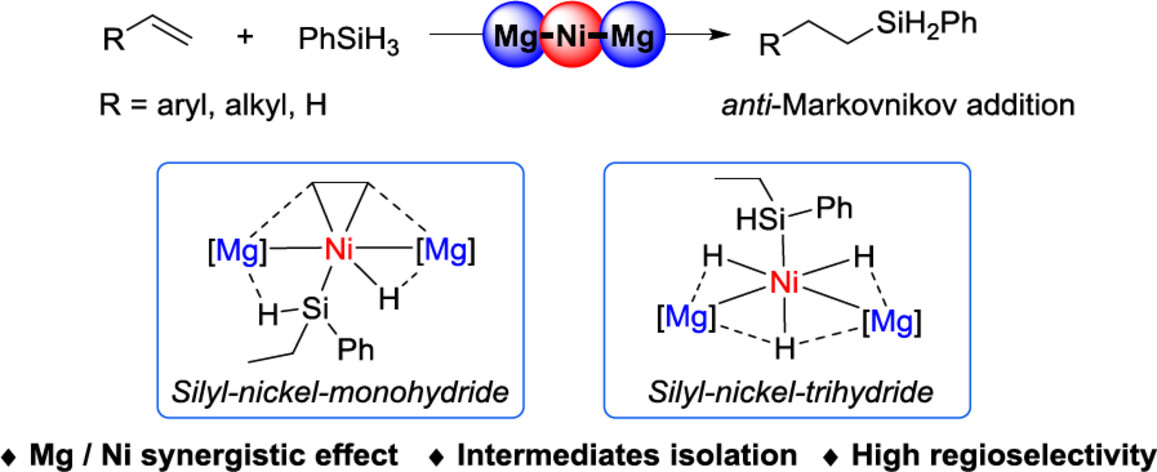
The heterometallic Mg-Ni-Mg complex [(LMg)2Ni(C2H4)2] was found to effectively catalyze the hydrosilylation of terminal alkenes with anti-Markonikov selectivity. Capitalizing on the Mg-Ni synergistic effect, the active intermediates, i.e., silyl-nickel-monohydride and silyl-nickel-trihydride species supported by Mg-metalloligands were successfully isolated, thereby deepening comprehension of the intrinsic mechanisms of this catalytic system.
Concise Report
De novo Synthesis of Chiral 3,4-Dihydroquinazolines via One-Pot Enantioselective Ugi-Azide/Cyclization Sequences†
- Pages: 2140-2146
- First Published: 07 May 2024
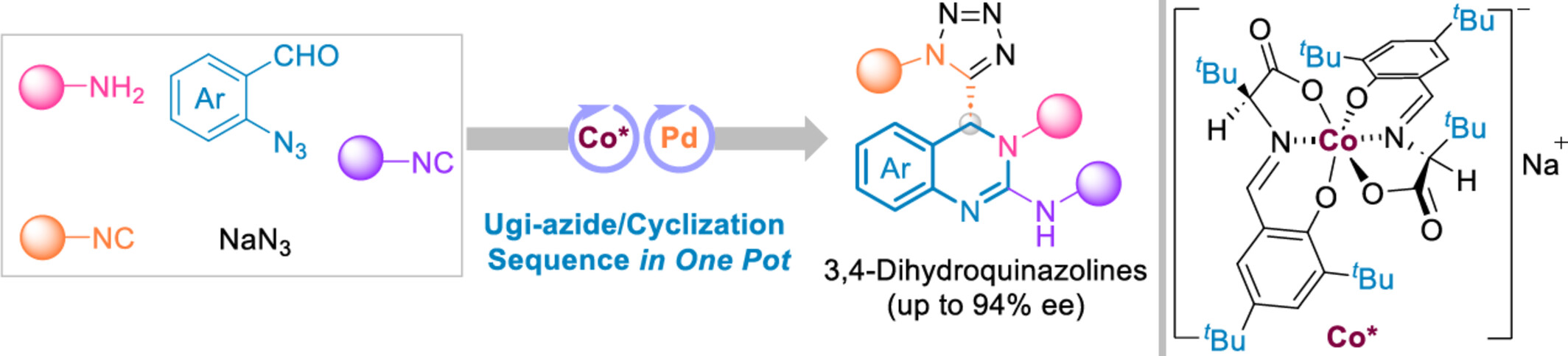
A precise de novo synthesis of chiral 3,4-dihydroquinazoline frameworks is achieved via a one-pot anionic stereogenic-at-cobalt(III) complex-catalyzed enantioselective Ugi-azide/Pd-catalyzed cyclization sequence. This powerful protocol tolerates an intricate reaction system, involving 5 components and 2 catalytic systems, delivering chiral 3,4-dihydroquinazolines with excellent enantioselectivities (up to 94% ee).
Stereoselective Synthesis of 2-Deoxy-α-N-Glycosides from Glycals with 1,4,2-Dioxazol-5-ones
- Pages: 2147-2152
- First Published: 07 May 2024

This study presents a novel approach for the stereoselective synthesis of 2-deoxy-α-N-glycosides from glycals and 1,4,2-dioxazol-5-ones via a nickel-catalyzed hydroamination reaction. This transformation facilitates the incorporation of (het)aryl, benzyl, or alkyl amide moieties into the glycals scaffold, all achieved under mild reaction conditions, showcasing outstanding α-stereoselectivity.
Side-Chain Engineering of Non-Fullerene Acceptors with Trialkylsilyloxy Groups for Enhanced Photovoltaic Performance
- Pages: 2153-2160
- First Published: 12 May 2024
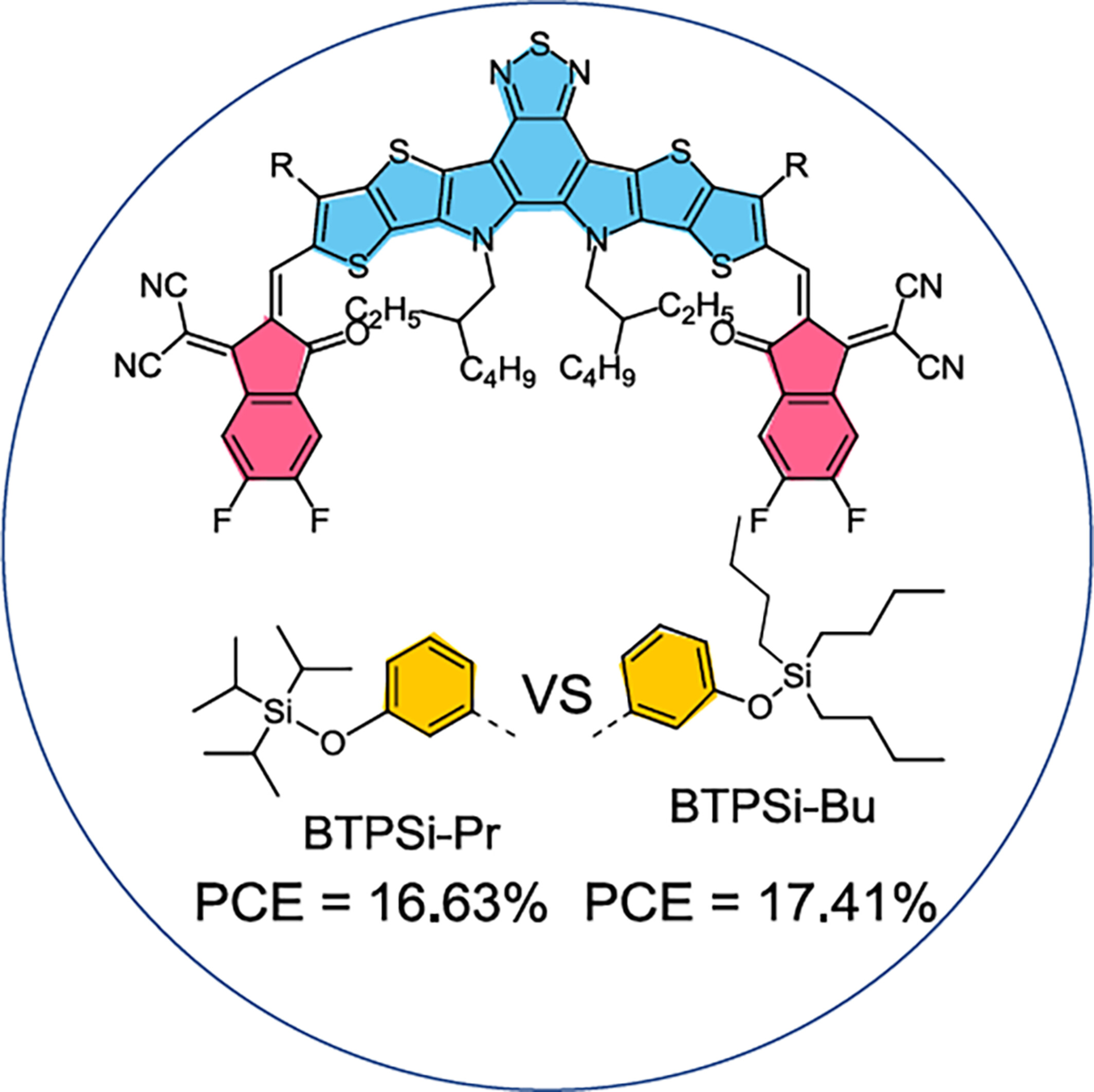
Here, we report two non-fullerene small molecule acceptors (SMAs) synthesized via side-chain engineering, namely BTPSi-Bu and BTPSi-Pr, incorporating tributylsilyloxy and triisopropylsilyloxy groups in their respective outer positions. Notably, the increased planarity of BTPSi-Bu led to a significant device efficiency of 17.41%. These results emphasize the importance of integrating trialkylsilyloxy side chains into SMAs as a strategic design approach for enhancing their device performance.
Enantioselective Alkylation of Aldehydes with Organoborons Enabled by Nickel/N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis
- Pages: 2161-2165
- First Published: 11 May 2024
Streptavidin-Biotin Complexes as Tools for Modulating an Important DNA Epigenetic Modification
- Pages: 2166-2172
- First Published: 12 May 2024
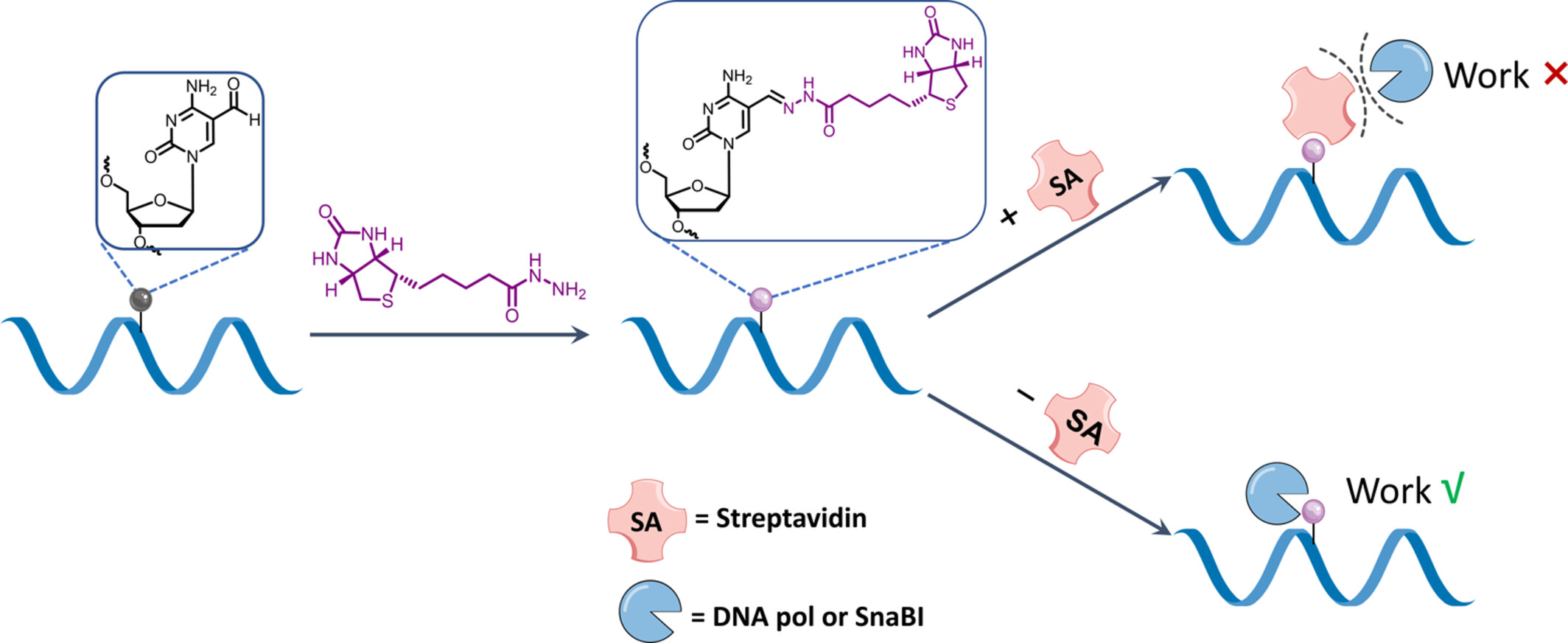
In this study, we have successfully achieved precise control over 5fC activity by harnessing the interaction between streptavidin and biotin. This research underscores the potential application of interactions between biomacromolecules and small molecules in advancing the field of DNA epigenetic functional regulation.
Stable Electron Spin Pan on Aromatic Oxalic Acid Radical
- Pages: 2173-2179
- First Published: 12 May 2024
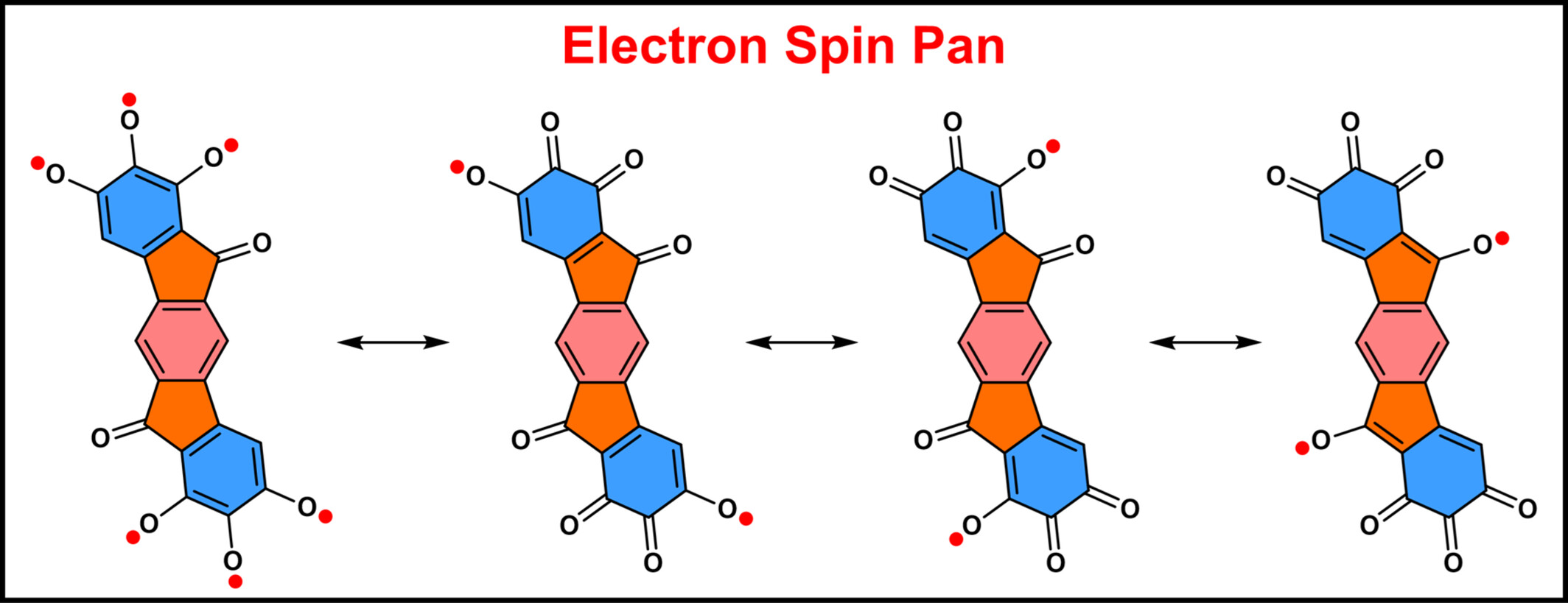
Based on concept of aromatic inorganic acid radical, a planar electron spin pan IDF-O8 is prepared, and its stability is attributed to the resonance structures between the multiple electron-withdrawing carbonyl groups and phenol radicals, pancake bond formation and aggregation-induced radical effect.
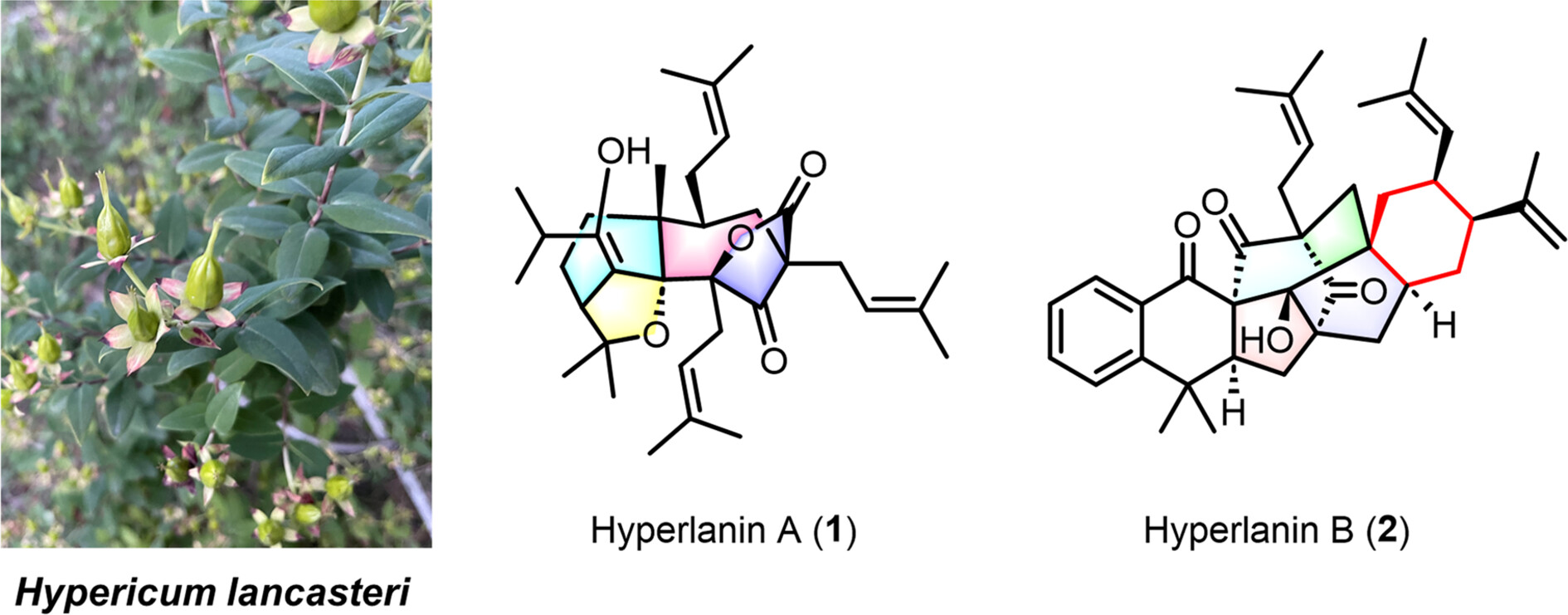
Hyperlanins A and B, Two Highly Rearranged Meroterpenoids from Hypericum lancasteri
- Pages: 2180-2186
- First Published: 14 May 2024
Electron Reservoir MoO3–x-Driven Cu+ Doped Nanozyme with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity via Disrupting Redox Homeostasis
- Pages: 2187-2196
- First Published: 14 May 2024
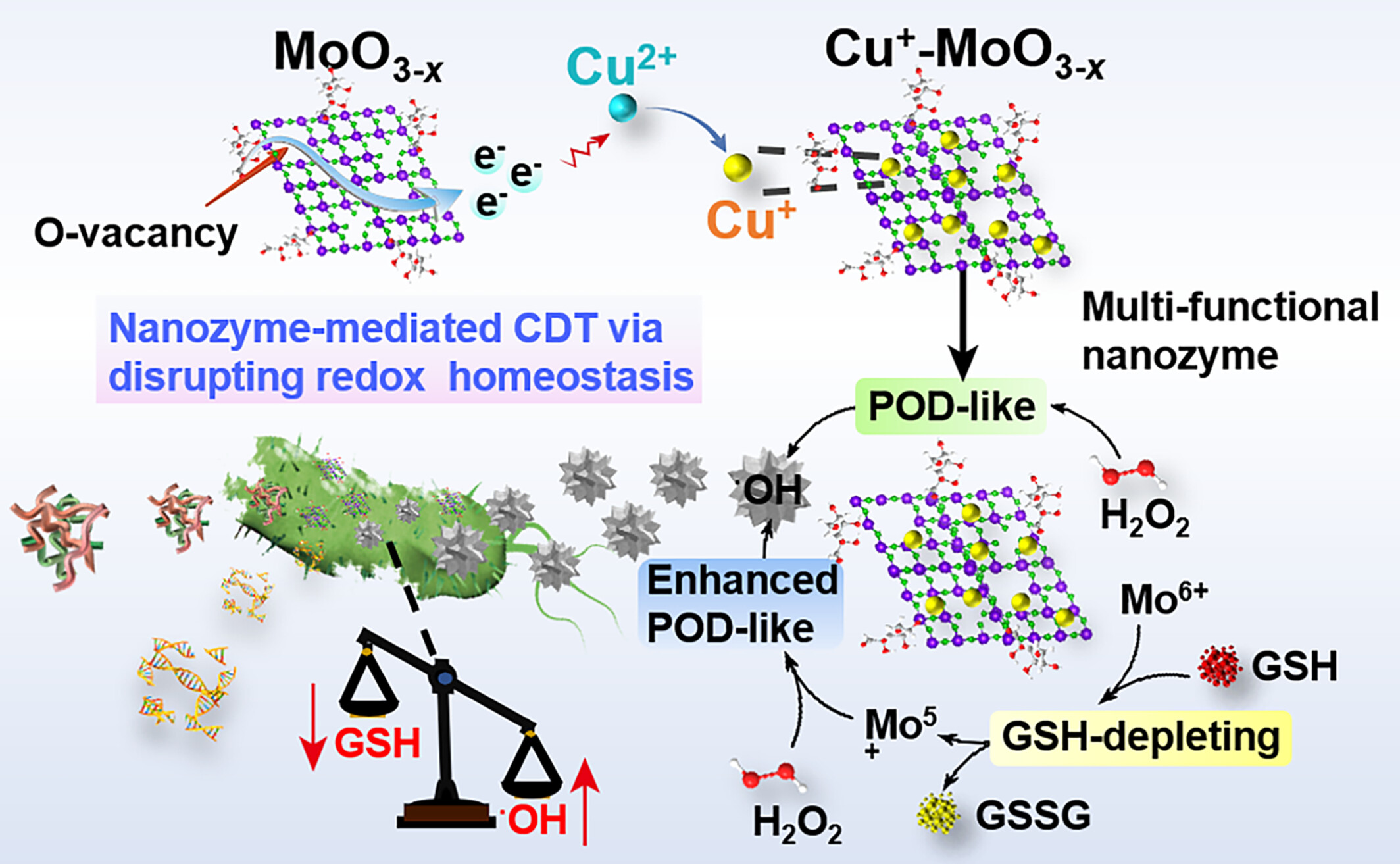
A multi-functional nanozyme consisting of Cu+ doped glycosylated MoO3–x (Cu+-MoO3–x) is developed through in-situ reduction strategy using degradable carrier MoO3–x as the electron reservoir, which exhibits improved antimicrobial efficacy by simultaneous GSH rapid depletion and oxidative ∙OH generation.
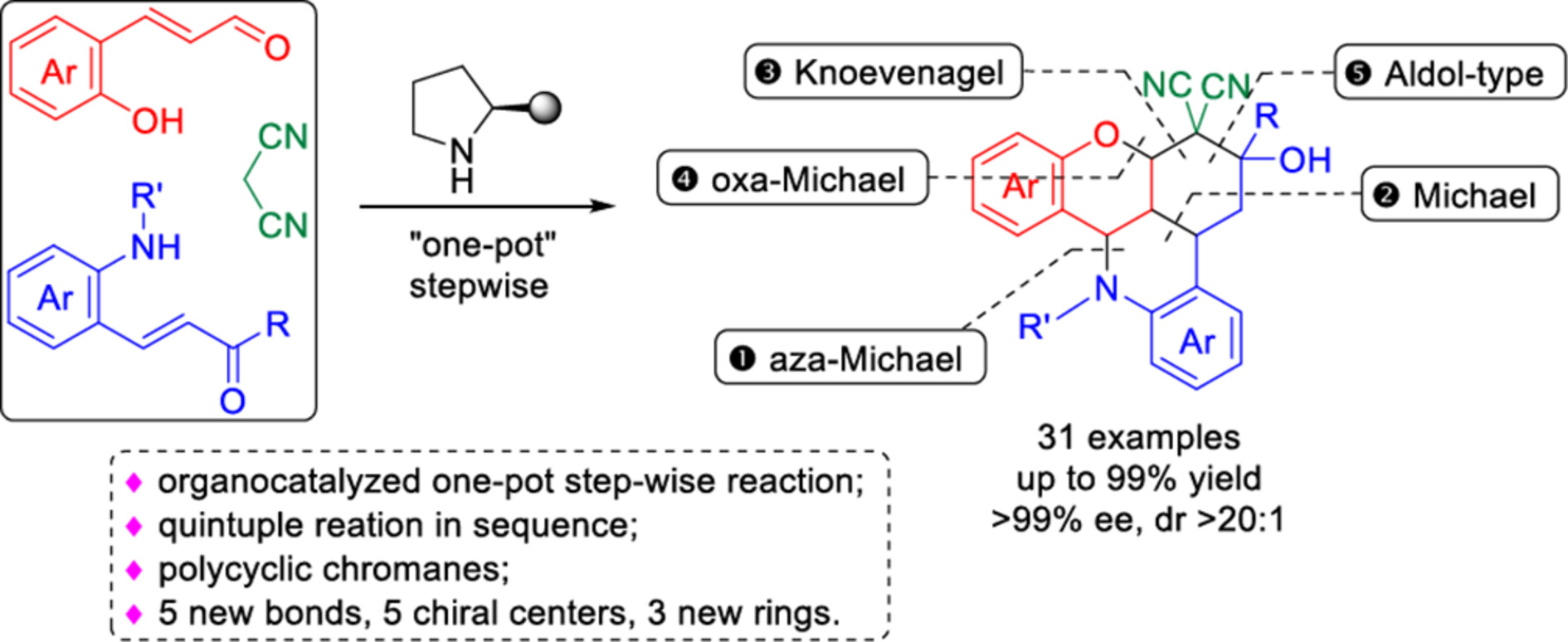
Enantioselective Construction of Polycyclic Chromanes through Organocatalytic Sequential Quintuple Reaction via One-Pot Step-Wise Procedure
- Pages: 2197-2202
- First Published: 14 May 2024
Photocatalytic C(sp3)-H gem-Difluoroallylation and Alkylation with Alkenes via a Base-Assisted Formal 1,2-Hydrogen Atom Transfer of Amidyl Radicals
- Pages: 2203-2210
- First Published: 14 May 2024
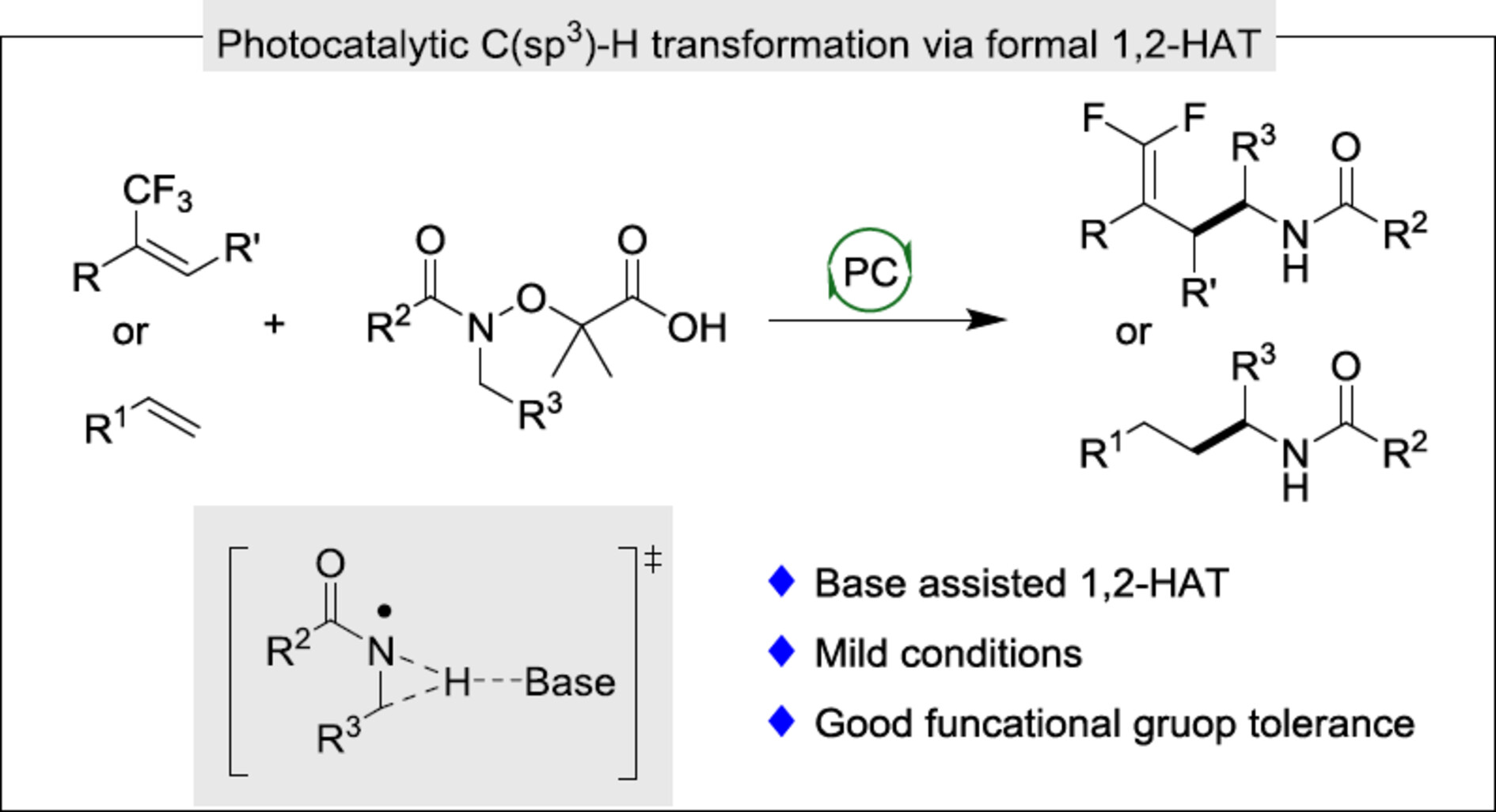
Here, we have developed a novel C—H gem-difluoroallylation via a base assisted formal 1,2-HAT of amidyl radicals with the reductive quenching cycle of photocatalyst. This transformation enables the efficient formation of α-aminoalkyl radicals via 1,2-HAT and showcases good functional group tolerance.
Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Stable NH Imines for the Synthesis of Enantiopure α-Chiral Primary Amines
- Pages: 2211-2216
- First Published: 14 May 2024
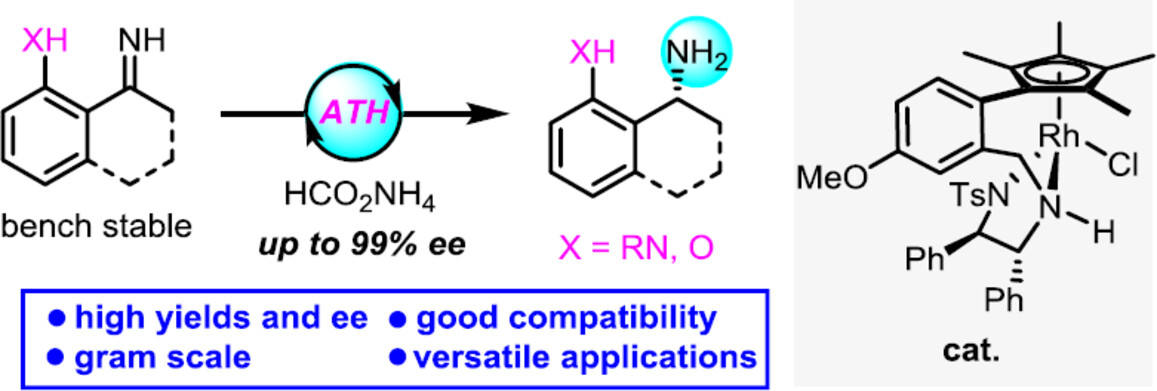
Herein, we report a Rh-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of NH imines, which produces synthetically versatile and enantioenriched 2-(1-aminoalkyl)anilines with up to 99% ee. A gram-scale reaction using 0.2 mol% of catalyst has been successfully achieved. Furthermore, the products can be derivatized into bioactive molecules as well as chiral tridentate ligands for metal catalysis.
Photoinduced Perfluoroalkyloximation of Alkenes with Simple Perfluoroalkyl Halides
- Pages: 2217-2222
- First Published: 14 May 2024
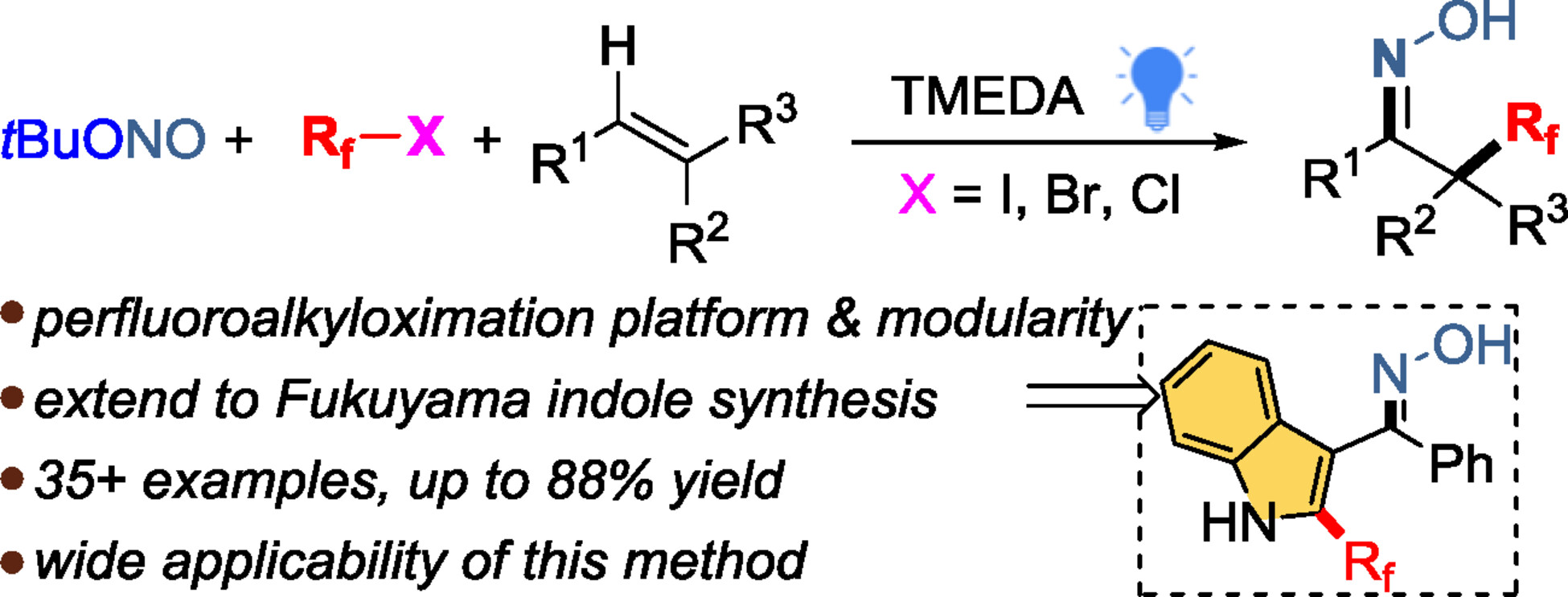
This paper introduces a new difunctionalizative perfluoroalkyloximation method for alkenes, efficiently synthesizing diverse perfluoroalkyl ethanone oximes with high regioselectivity and functional group tolerance. Notably, it shows potential in Fukuyama indole synthesis, creating novel 2-perfluoroalkylated indoles via a radical cascade. The method is efficient, scalable, and useful for modifying bioactive molecules.
Sequence [2,3]-Sigmatropic Rearrangement: One-Pot Synthesis of Propargyl Allenylamines
- Pages: 2223-2227
- First Published: 14 May 2024
![Sequence [2,3]-Sigmatropic Rearrangement: One-Pot Synthesis of Propargyl Allenylamines](/cms/asset/30239efe-6beb-4233-999f-74d327207b5b/cjoc202400307-toc-0001-m.jpg)
We reported a novel and eco-friendly strategy for propargyl allenylamines via [2,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of propargylamines without the introduction of electron-withdrawing groups under metal-free catalysis. This method provides a mild and efficient route for the construction of propargyl allenylamines from propargylamines with high chemical selectivity under mild conditions.
Nickel/Photoredox Dual Catalytic Chan-Lam Coupling of Aryl Azides and Arylboric Acids
- Pages: 2228-2234
- First Published: 14 May 2024

A redox-neutral Chan-Lam amination reaction employing aryl azides and aryboronic acids as coupling reagents was discovered, which was facilitated by nickel/photoredox dual catalysis. This protocol promotes the reaction via a proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) process, thus effectively inhibiting the natural nitrene pathway of aryl azides.
Photoredox-Catalyzed Metal-Free Regio- & Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Amination of Enamides with N-Aminopyridium Salts
- Pages: 2235-2242
- First Published: 11 May 2024
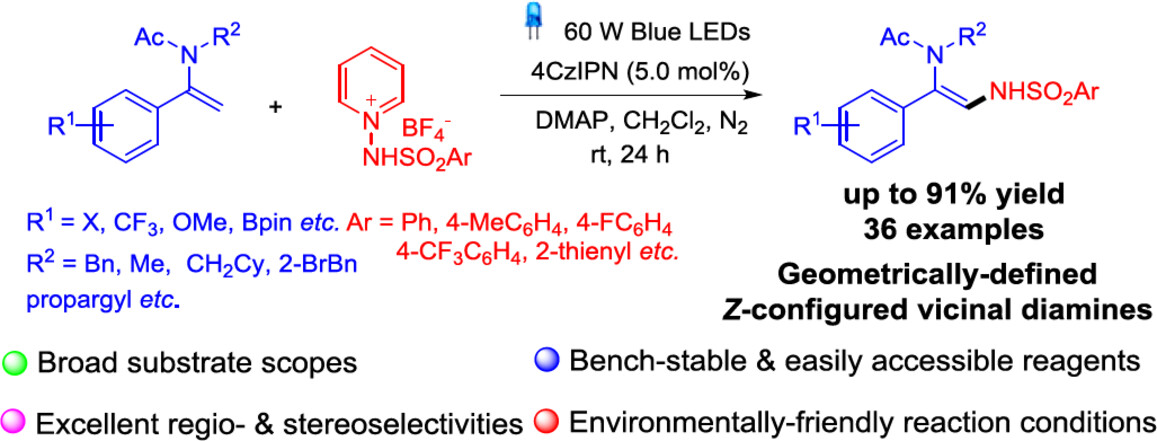
A visible-light-induced photoredox-catalyzed regioselective and stereoselective C(sp2)–H amination of enamides with bench-stable and easily accessible N-aminopyridium salts under environmentally benign metal-free conditions is developed, affording synthetically and biologically prominent vicinal 1,2-diamine scaffolds in broad substrate scope and excellent functional group compatibility.
Rhodium-Catalyzed N-Arylation Addition of Arylboronic Acids to Ketimines
- Pages: 2243-2248
- First Published: 05 June 2024
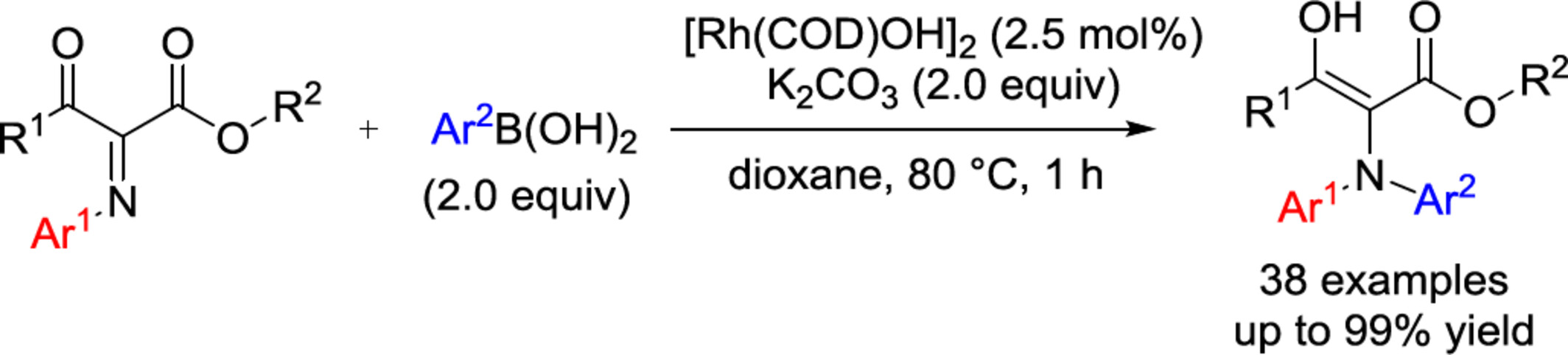
Arylboronic acids were added to electron-deficient α-iminoesters, which can be efficiently prepared using easily accessible β-carbonyl esters, to access rhodium-catalyzed N-arylation. The reaction is highly regiospecific to achieve the N-aryl addition efficiently with up to 99% yield under mild conditions. The corresponding product can be further efficiently converted into indoles and a series of other important building blocks.
Recent Advances
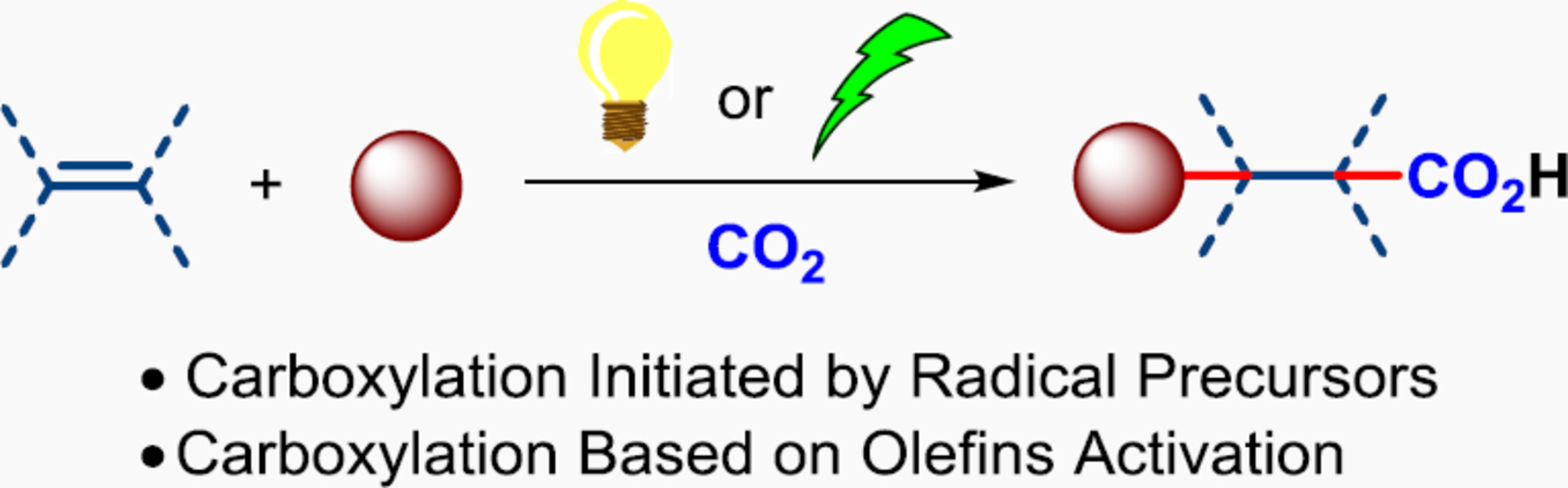
Recent Advances in Photochemical/Electrochemical Carboxylation of Olefins with CO2
- Pages: 2249-2266
- First Published: 15 May 2024
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 2271
- First Published: 15 August 2024

Efficient and high regioselective N-arylation via addition of arylboronic acids to ketimines has been realized. The possible mechanistic pathway was proposed. The corresponding product was further converted into indoles and other important building blocks. More details are discussed in the article by Sun et al. on page 2243—2248.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 2272
- First Published: 15 August 2024

Allenes remain a prevalent structural motif that is found in a large percentage of bioactive organic molecules and natural products. Molecular rearrangements provide access to extensive structural diversity in the construction of bioactive compounds with high atom- and step-economy. For example, [2,3]-sigmatropic rearrangements have been successively developed for the preparation of allenylamines. More details are discussed in the article by Feng et al. on page 2223—2227.