Electron Reservoir MoO3–x-Driven Cu+ Doped Nanozyme with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity via Disrupting Redox Homeostasis
Xiaoning Wang
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorMengyu Cao
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorXuehui Zhu
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorJinping Yu
College of Life Sciences, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuting Liu
College of Life Sciences, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Aihua Li
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuanhong Xu
College of Life Sciences, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiaoning Wang
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorMengyu Cao
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorXuehui Zhu
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorJinping Yu
College of Life Sciences, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuting Liu
College of Life Sciences, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Aihua Li
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuanhong Xu
College of Life Sciences, Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Qingdao University, Ningxia Road 308, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
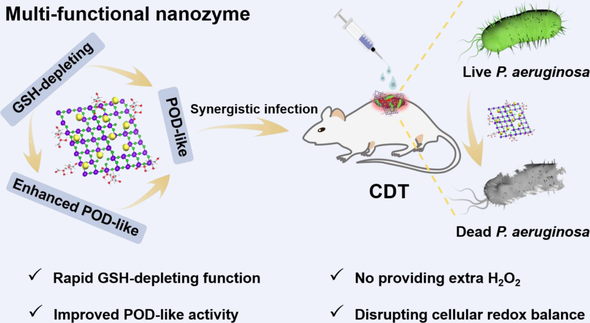
Redox nanozymes offer an appealing reactive oxygen species (ROS)-based antibacterial strategy via disrupting intracellular homeostasis, however, they still face many obstacles such as low enzymic activity and irreversible loss of catalytic active center. Meanwhile, the antioxidant glutathione (GSH) overexpressed in infected sites would limit the therapy efficiency. Herein, we develop a multifunctional nanozyme based on copper(I) (Cu+) ion doped MoO3–x (Cu+-MoO3–x) by a simple yet efficient oxygen vacancy-reduced strategy without any pretreatment or additional agents. The resultant Cu+-MoO3–x hybrid possesses enhanced peroxidase-like (POD-like) activity, rapid GSH-depleting function and biodegradable ability. It can achieve highly efficient elimination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) via disrupting cellular redox balance. More intriguingly, GSH-depleting redox reaction between Cu+-MoO3–x and GSH could translate Mo6+ into Mo5+, thereby leading to partial recovery of POD-like activity of Cu+-MoO3–x hybrid for continuous ∙OH generation. In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that Cu+-MoO3–x hybrid had stronger antibacterial property compared to MoO3–x by rapid GSH consumption and plentiful ∙OH generation without providing extra H2O2, as well as neglective toxicity to healthy organs. In view of its remarkable enzymic activity and good biosafety, the developed Cu+-MoO3–x redox nanozyme can be used as a promising antimicrobial for P. aeruginosa infection.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400066-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 2.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Li, G. Y.; Lai, Z. H.; Shan, A. S. Advances of Antimicrobial Peptide- based Biomaterials for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206602.
- 2 Tang, Q.; Precit, M.; Thomason, M. K.; Blanc, S.; Ahmed-Qadri, F.; McFarland, A.; Wolter, D.; Hoffman, L.; Woodward, J. Thymidine Starvation Promotes C-di-AMP-dependent Inflammation During Pathogenic Bacterial Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 961–974.
- 3 Tomlinson, K.; Chen, Y.; Junker, A.; Urso, A.; Wong Fok Lung, T.; Ahn, D.; Hofstaedter, C.; Baskota, S.; Ernst, R.; Prince, A.; Riquelme, S. Ketogenesis Promotes Tolerance to Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pulmonary Infection. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1767–1781.
- 4 Karami, P.; Khaledi, A.; Mashoof, R.; Yaghoobi, M.; Karami, M.; Dastan, D.; Alikhani, M. The Correlation between Biofilm Formation Capability and Antibiotic Resistance Pattern in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Gene Rep. 2020, 18, 100561.
- 5 Konstantinović, J.; Kany, A. M.; Alhayek, A.; Abdelsamie, A.; Sikandar, A.; Voos, K.; Yao, Y.; Andreas, A.; Shafiei, R.; Loretz, B.; Schönauer, E.; Bals, R.; Brandstetter, H.; Hartmann, R.; Ducho, C.; Lehr, C.; Beisswenger, C.; Müller, R.; Rox, K.; Haupenthal, J. Inhibitors of the Elastase lasB for the Treatment of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa lung Infections. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 26, 2108–2123.
- 6 Li, A. H.; Zhang, M.; Ma, W. S.; Li, D. X.; Xu, Y. H. Sugar-disguised Bullets for Combating Multidrug-resistant Bacteria Infections Based on an Oxygen Vacancy-engineered Glucose-functionalized MoO3–x Photo-coordinated Bienzyme. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133943.
- 7 Mei, J. W.; Xu, D. D; Wang, L. T.; Kong, L. T.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X. Z.; Su, Z.; Hu, X. L.; Zhu, W. B.; Ye, M.; Wang, J. X.; Zhu, C. Biofilm Microenvironment-responsive Self-assembly Nanoreactors for All-stage Biofilm Associated Infection Through Bacterial Cuproptosis-like Death and Macrophage Re-rousing. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303432.
- 8 Zhang, D. D.; Xu, R.; Chen, S. H.; Du, H. H.; Qian, S.; Peng, F.; Liu, X. Y. Surface Defect Engineered-Mg-based Implants Enable the Dual Functions of Superhy Drophobic and Synergetic Photothermal/Chemodynamic Therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 30, 15–28.
- 9 Lu, J.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Chen, Z. Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Tang, B. One-Pot Synthesis of Multifunctional Carbon- Based Nanoparticle-Supported Dispersed Cu2+ Disrupts Redox Homeostasis to Enhance CDT. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114373.
- 10 Jia, C. Y.; Guo, Y. X.; Wu, F. G. Chemodynamic Therapy via Fenton and Fenton-Like Nanomaterials: Strategies and Recent Advances. Small 2022, 18, 50.
- 11 Zhang, Y. X.; Liu, W. Z.; Huang, Y. M.; Wang, Y. H.; Chen, X. Y.; Chen, Z. Bacterial Biofilm Microenvironment Responsive Copper-doped Zinc Peroxide Nanocomposites for Enhancing Chemodynamic Therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 11.
- 12 Liu, Z. W.; Zhao, X. Y.; Yu, B. R.; Zhao, N. N.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F. J. Rough Carbon-Iron Oxide Nanohybrids for Near-Infrared-II Light-Responsive Synergistic Antibacterial Therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7482–7490.
- 13 Mei, J. W.; Xu, D. D.; Wang, L. T.; Kong, L. T.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q. M.; Zhang, X. Z.; Su, Z.; Hu, X. L.; Zhu, W. B.; Ye, M.; Wang, J. X.; Zhu, C. Biofilm Microenvironment-Responsive Self-Assembly Nanoreactors for All-Stage Biofilm Associated Infection through Bacterial Cu proptosis-like Death and Macrophage Re-Rousing. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303432.
- 14 Wang, H. M.; Li, N.; Lin, Y. Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, X. M.; Wu, P. X.; Fu, Q.; Wang, W. j.; Liu, Z.; He, S. Y.; Zhou, M. Y.; Song, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q. L.; Tan, X. F. Norepinephrine-induced Hydrophilic Pd Aerogels with Photothermal-boosted Multienzyme-like Activity for Chemodynamic Therapy of MRSA Infections. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484,149447.
- 15 Xiao, J. Y.; Hai, L.; Li, Y. Y.; Li, H.; Gong, M. H.; Wang, Z. F.; Tang, Z. F.; Deng, L.; He, D. G. An Ultrasmall Fe3O4-decorated Polydopamine Hybrid Nanozyme Enables Continuous Conversion of Oxygen into Toxic Hydroxyl Radical via GSH-depleted Cascade Redox Reactions for Intensive Wound Disinfection. Small 2022, 18, 2105465.
- 16 Knoke, L.; Zimmermann, J.; Lupilov, N.; Schneider, J.; Celebi, B.; Morgan, B.; Leichert, L. The Role of Glutathione in Periplasmic Redox Homeostasis and Oxidative Protein Folding in Escherichia Coli. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102800.
- 17 Wu, K. L.; Zhu, D. D.; Dai, X. L.; Wang, W.; Zhong, X. Y.; Fang, Z. B.; Peng, C.; Wei, X. W.; Qian, H. S.; Chen, X. L.; Wang, X. W.; Zha, Z. B.; Cheng, L. Bimetallic Oxide Cu1.5Mn1.5O4 Cage-like Frame Nanospheres with Triple Enzyme-like Activities for Bacterial-infected Wound Therapy. Nano Today 2022, 43, 101380.
- 18 Wu, W. F.; Qin, Y. N.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y. K.; Shao, S. X.; Meng, F. X.; Zhang, M. W. Based on Multi-omics Technology Study the Antibacterial Mechanisms of pH-dependent N-GQDs Beyond ROS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129954.
- 19 Ge, C. C.; Wu, R. F.; Chong, Y.; Fang, G.; Jiang, X. M.; Pan, Y.; Chen, C. Y.; Yin, J. J. Synthesis of Pt Hollow Nanodendrites with Enhanced Peroxidase-like Activity Against Bacterial Infections: Implication for Wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801484.
- 20 Li, Y.; Fu, R. Z.; Duan, Z. G., Zhi, C. H.; Fan, D. D. Construction of Multifunctional Hydrogel Based on the Tannic Acid-metal Coating Decorated MoS2 Dual Nanozyme for Bacteria-infected Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 9, 461–474.
- 21 Xu, M. R.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Sun, K. L.; Wu, T.; Lv, N.; Wang, W. S.; Ding, W. P.; Li, F. F.; Qiu, B. S.; Li, J. B. Near-infrared-controlled Nanoplatform Exploiting Photothermal Promotion of Peroxidase-like and OXD-like Activities for Potent Antibacterial and Anti-biofilm Therapies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50260–50274.
- 22 Fang, L. Y.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, S. K.; Wei, J. Y.; Feng, L. L.; He, F.; Gai, S. L.; Dong, Y. Z.; Yang, P. P. PdCux Bimetallic Nanoalloys with “Hand-in-Hand” Collaboration in POD-like Activity and “Back-to-Back” Confrontation in SPR Effect for Tumor Redox System Control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2309338.
- 23 Qian, M.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, G.; Galluzzi, M.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Yu, X.-F. Molybdenum Diphosphide Nanorods with Laser-Potentiated Peroxidase Catalytic/Mild-Photothermal Therapy of Oral Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2101527.
- 24 Lee, I.; Cheon, H. J.; Adhikari, M. D.; Tran, T. D.; Yeon, K. M.; Kim, M. I.; Kim, J. Glucose Oxidase-copper Hybrid Nanoflowers Embedded with Magnetic Nanoparticles as an Effective Antibacterial Agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1520–1531.
- 25 Tripathi, K. M.; Ahn, H. T.; Chung, M.; Le, X. A.; Saini, D.; Bhati, A.; Sonkar, S. K.; Kim, M. I.; Kim, T. N, S, and P-Co-doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Intrinsic Peroxidase Activity in a Wide pH Range and Its Antibacterial Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 5527–5537.
- 26 Yu, B.; Wang, W.; Sun, W. B.; Jiang, C. H.; Lu, L. H. Defect Engineering Enables Synergistic Action of Enzyme-mimicking Active Centers for High-efficiency Tumor Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8855–8865.
- 27 Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. L.; Peng, F.; Meng, F. Q.; Zha, J. J.; Ma, L.; Du, Y. H.; Peng, N.; Ma, L. F.; Zhang, Q. H.; Gu, L.; Yin, W. Y.; Gu, Z. J.; Tan, C. L. Intercalation-activated layered MoO3 Nanobelts as Biodegradable Nanozymes for Tumor-specific Photo-enhanced Catalytic Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115939.
- 28 Hu, X.; Li, F. Y.; Xia, F.; Guo, X.; Wang, N.; Liang, L. L.; Yang, B.; Fan, K. L.; Yan, X. Y.; Ling, D. S. Biodegradation-mediated Enzymatic Activity-tunable Molybdenum Oxide Nanourchins for Tumor-specific Cascade Catalytic Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 1636–1644.
- 29 Yu, L.; Sun, Y. P.; Niu, Y. S.; Zhang, P. F.; Hu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y. H. Microenvironment-adaptive Nanozyme for Accelerating Drug-resistant Bacteria-infected Wound Healing. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12, 2202596.
- 30 Cao, M. Y.; Chang, Z. S.; Tan, J. S.; Wang, X. N.; Zhang, P. F.; Lin, S.; Liu, J. Q.; Li, A. H. Superoxide Radical-mediated Self-synthesized Au/MoO3–x Hybrids with Enhanced Peroxidase-like Activity and Photothermal Effect for Anti-MRSA Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 13025–13037.
- 31 Zhao, Q.; Zheng, L. R.; Gao, Y. X.; Li, J. J.; Wei, J. J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J. H.; Ouyang, J.; Na, N. Dual Active Centers Linked by a Reversible Electron Station as a Multifunctional Nanozyme to Induce Synergetically Enhanced Cascade Catalysis for Tumor-specific Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 12586–12600.
- 32 Liu, T. F.; Xiao, B. W.; Xiang, F.; Tan, J. L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X. R.; Wu, C. Z.; Mao, Z. W.; Luo, G. X.; Chen, X. Y.; Deng, J. Ultrasmall Copper- based Nanoparticles for Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging and Alleviation of Inflammation Related Diseases. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2788.
- 33
Coleman, J. Structure and Mechanism of Copper Oxidases. In Food Related Enzymes, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1974.
10.1021/ba-1974-0136.ch011 Google Scholar
- 34 Shi, Y. F.; Zhang, G.; Xiang, C.; Liu, C. Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. H.; Ge, R.; Ma, H. X.; Niu, Y. S.; Xu, Y. H. Defect Engineering-mediated Long-lived Charge Transfer Excited State in Fe-gallate Complex Improves Iron Cycle and Enables Sustainable Fenton-like Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2305162.
- 35 Zhao, L.; Li, T. T.; Xu, X. L.; Xu, Y.; Li, D. X.; Song, W. L.; Zhan, T. R.; He, P.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Polyhedral Au Nanoparticle/MoOx Heterojunction-enhanced Ultrasensitive Dual-Mode Biosensor for MiRNA Detection Combined with a Nonenzymatic Cascade DNA Amplification Circuit. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9271–9279.
- 36 Wang, X. W.; Shi, Q. Q.; Zha, Z. B.; Zhu, D. D.; Zheng, L. R.; Shi, L. X.; Wei, X.; Lian, L.; Wu, K. L.; Cheng, L. Copper Single-atom Catalysts with Photothermal Performance and Enhanced Nanozyme Activity for Bacteria-infected Wound Therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4389–4401.
- 37 Liang, N.; Ge, X. Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, L.; Song, Z. L.; Kong, R. M.; Qu, F. L. Promoting Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Hydroquinone and Hg2+ via ZIF-8 Dispersion Enhanced Oxidase-mimicking Activity of MnO2 Nanozyme. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131455.
- 38 Muhammad, F.; Huang, F. T.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X. W.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, C. X.; Zhang, Y. H.; Yang, X. H. ; Wang, P.; Wei, H. Nanoceria as an Electron Reservoir: Spontaneous Deposition of Metal Nanoparticles on Oxides and Their Anti-inflammatory Activities. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 20567–20576.
- 39 Liu, H. H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H. F.; Xue, J. R.; Guo, Y. M.; Qian, Q. Z.; Zhang, G.Q. Oxygen Vacancy Engineered Unsaturated Coordination in Cobalt Carbonate Hydroxide Nanowires Enables Highly Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5339–5346.
- 40 Zhu, C. Q.; Osherov, A.; Panzer, M. J. Surface Chemistry of Electrodeposited Cu2O Films Studied by XPS. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 771–778.
- 41 Liu, P.; Li, T.; Chen, H. P.; Hensen, E. J. M. Optimization of Au0-Cu+ Synergy in Au/MgCuCr2O4 Catalysts for Aerobic Oxidation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde. J. Catal. 2017, 347, 45–56.
- 42 Khattak, G. D.; Mekki, A.; Gondal, M. A. Effect of Laser Irradiation on The Structure and Valence States of Copper in Cu-phosphate Glass by XPS Studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3630–3635.
- 43 Sivkov, D. V.; Petrova, O. V.; Nekipelov, S. V.; Vinogradov, A. S.; Skandakov, R. N.; Isaenko, S. I.; Ob'edkov, A. M.; Kaverin, B. S.; Vilkov, I. V.; Korolev, R. I.; Sivkov, V. N. The Identification of Cu-O-C Bond in Cu/MWCNTs Hybrid Nanocomposite by XPS and NEXAFS Spectroscopy. J. Nanomater. 2021, 11, 19.
- 44 Poulston, S.; Parlett, P. M.; Stone, P.; Bowker, M. Surface Oxidation and Reduction of CuO and Cu2O Studied Using XPS and XAES. Surf. Interface Anal. 1996, 24, 811–820.
- 45 Ji, F. X.; Huang, Y. Q.; Wang, F.; Kobera, L.; Xie, F. Y.; Klarbring, J.; Abbrent, S.; Brus, J.; Yin, C. Y.; Simak, S. I.; Abrikosov, I. A.; Buyanova, I. A.; Chen, W. M.; Gao, F. Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Cu-Doped Cs2AgBiBr6. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 7.
- 46 Araujo, A. T. S.; Saraiva, M.; Lúcia M.; Lima, C. Determination of Total and Oxidized Glutathione in Human Whole Blood with a Sequential Injection Analysis System. Talanta 2008, 74, 1511–1519.
- 47 Gao, X. Y.; Wei, M. T.; Ma, D. C.; Yang, X. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, L. M.; Deng, Y.; Yang, W. Z. Engineering of a Hollow-structured Cu2−XS Nano-homojunction Platform for Near Infrared-triggered Infected Wound Healing and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106700.
- 48 Xie, X. Y.; Chen, X. F.; Wang, Y. H.; Zhang, M. S.; Fan, Y. X.; Yang, X. P. High-loading Cu Single-atom Nanozymes Supported by Carbon Nitride with Peroxidase-like Activity for the Colorimetric Detection of Tannic Acid. Talanta 2023, 257, 124387.
- 49 Song, G.; Hao, J.; Liang, C.; Liu, T.; Gao, M.; Cheng, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z. Degradable Molybdenum Oxide Nanosheets with Rapid Clearance and Efficient Tumor Homing Capabilities as a Therapeutic Nanoplatform. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2122–2126.




