Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 2273
- First Published: 01 September 2024

Chemical synthesis of mirror-image D-version of the immunoglobulin-like domain of TrkA (DlgCTrkA), a protein molecule needed for mirror-image screening of D-peptide ligands targeting TrkA, was found to be difficult due to the poor efficiency of intermediate synthesis and final protein folding. To solve this problem, the strategy of removable glycosylation modification was used and found to effectively improve the yield of peptide segment synthesis and ligation. Interestingly, it is important to note that temporary glycosylation at distinct sites of DlgCTrkA led to significant differences in the process of protein folding. More details are discussed in the article by Li et al. on pages 2316—2322.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 2274
- First Published: 01 September 2024
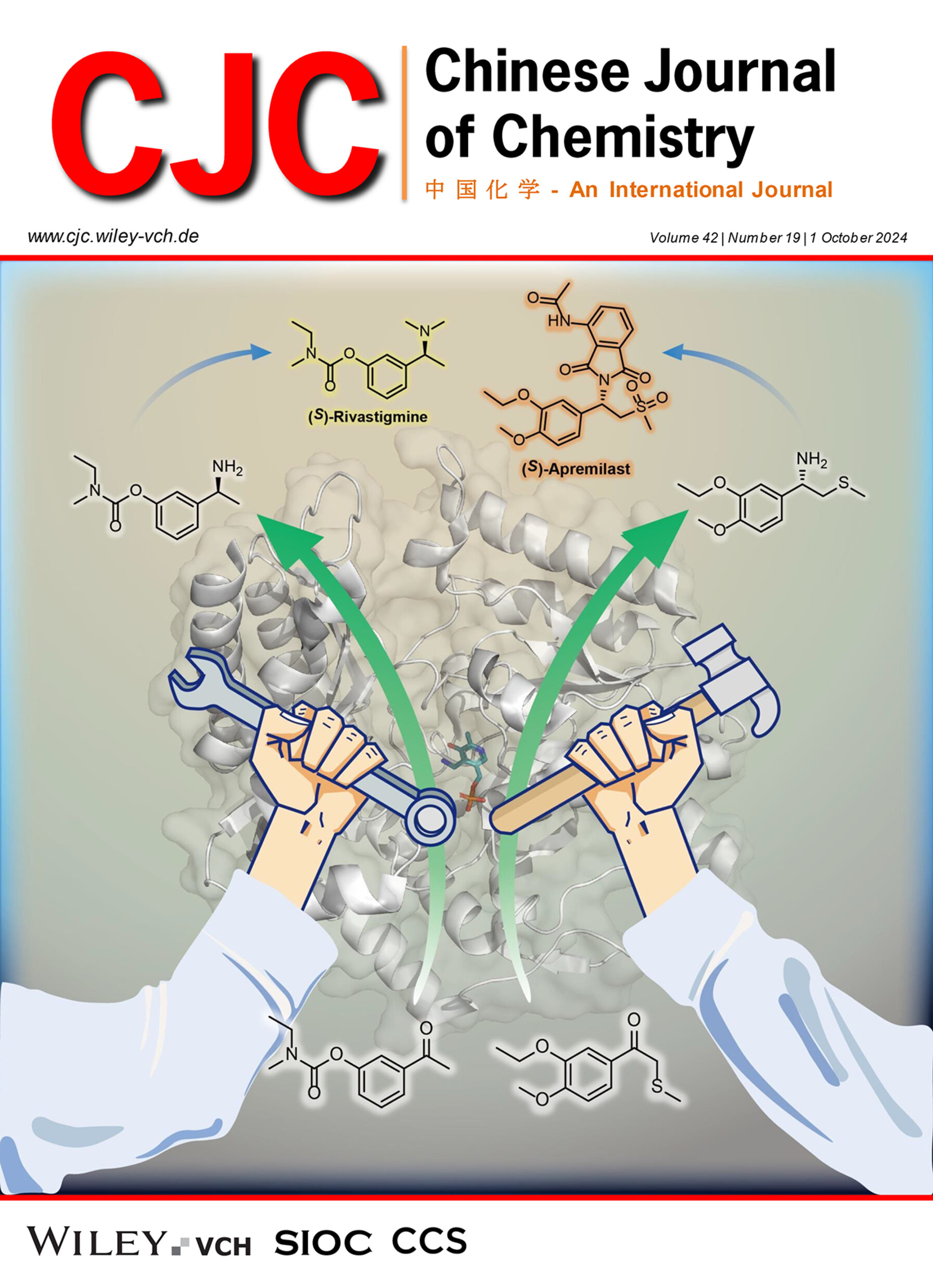
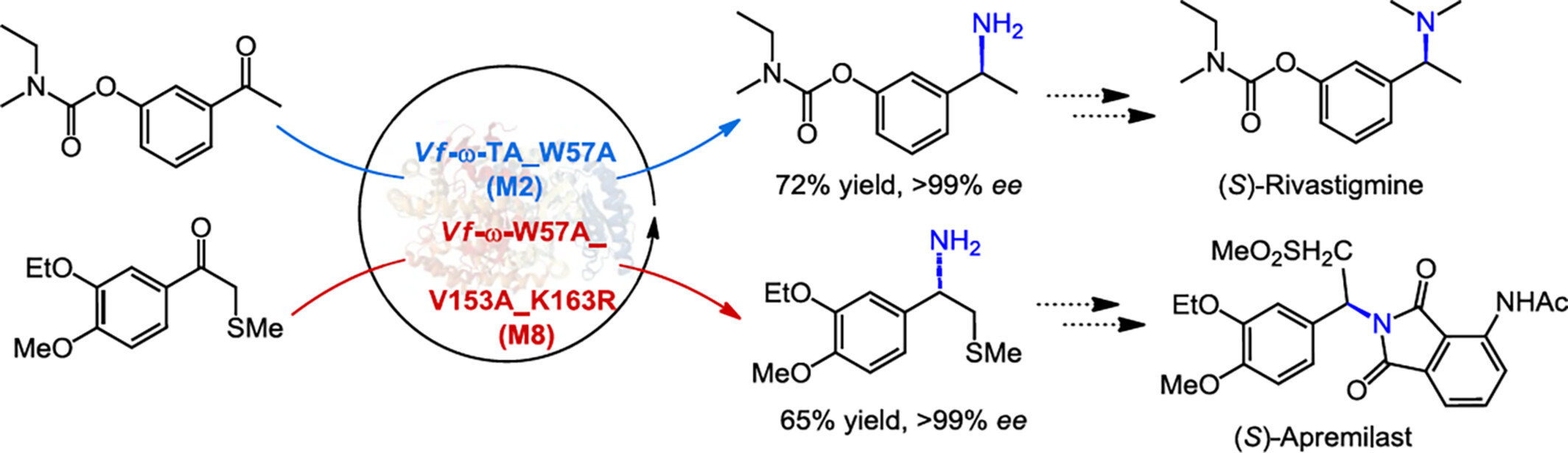
Divergent protein engineering of the natural transaminase Vf-ω-TA produced two effective mutants for synthesizing chiral amine precursors of Rivastigmine and Apremilast. Guided by crystal structures and focused mutagenesis, these mutants efficiently addressed challenging ketone substrates with high steric hindrance. Optimized reaction parameters achieved smooth transamination with excellent conversions and perfect stereochemical control (> 99% ee). More details are discussed in the article by Zhong et al. on pages 2335—2340.
Contents
Concise Report
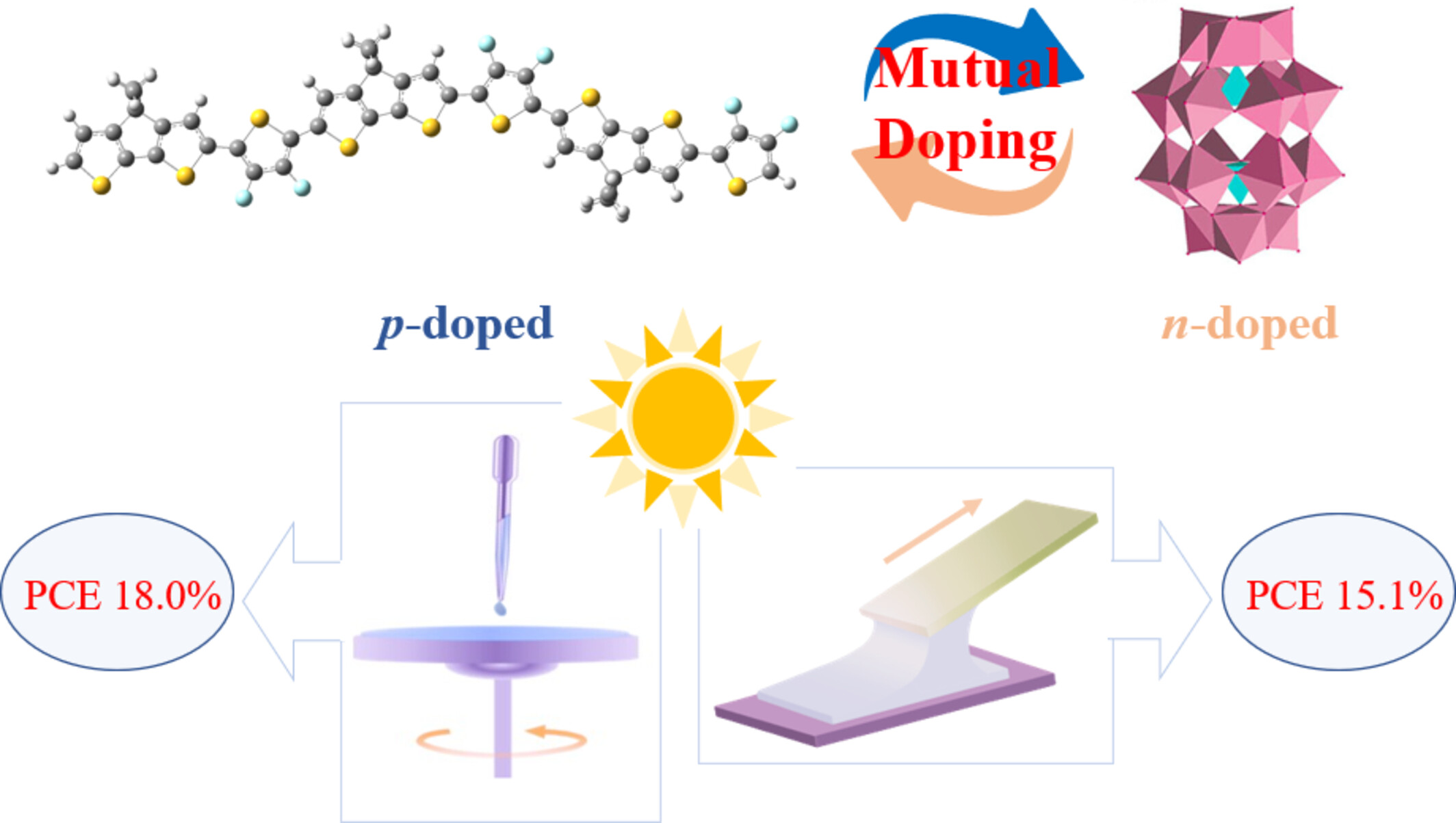
“Mutually Doped” Conjugated Polyelectrolyte-Polyoxometalate Complex as Hole Transporting Material for Efficient Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 2285-2292
- First Published: 22 May 2024
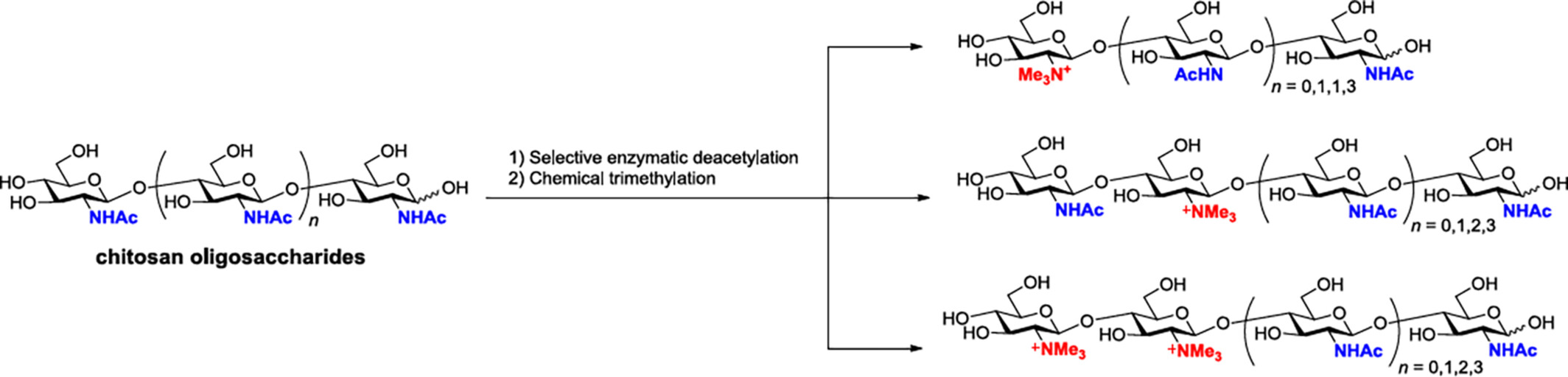
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of N,N,N-Trimethyl-D-Glucosamine Chitotriomycin and Its Analogues
- Pages: 2293-2298
- First Published: 22 May 2024
Copper-Mediated Selective Multiple Inert Chemical Bonds Cleavage for Cyanation of Indoles via Tandem Carbon and Nitrogen Atom Transfer
- Pages: 2299-2304
- First Published: 22 May 2024
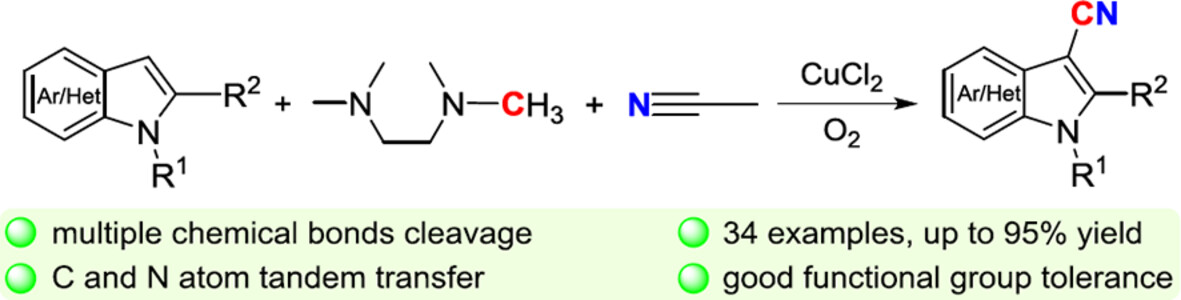
Selective activation and transformation of multiple inert chemical bonds is a challenging yet intriguing direction in synthetic chemistry. We report a copper-mediated complete cleavage and selective transformation of sp2C—H bond in indoles, three sp3C—H bonds and one C—N bond in a methyl carbon atom in TMEDA, and the C≡N triple bond in CH3CN for cyanation of indoles via tandem carbon and nitrogen atom transfer.
Unlocking Biomolecular Activity through Pd-Catalyzed Azides Reduction
- Pages: 2305-2315
- First Published: 22 May 2024
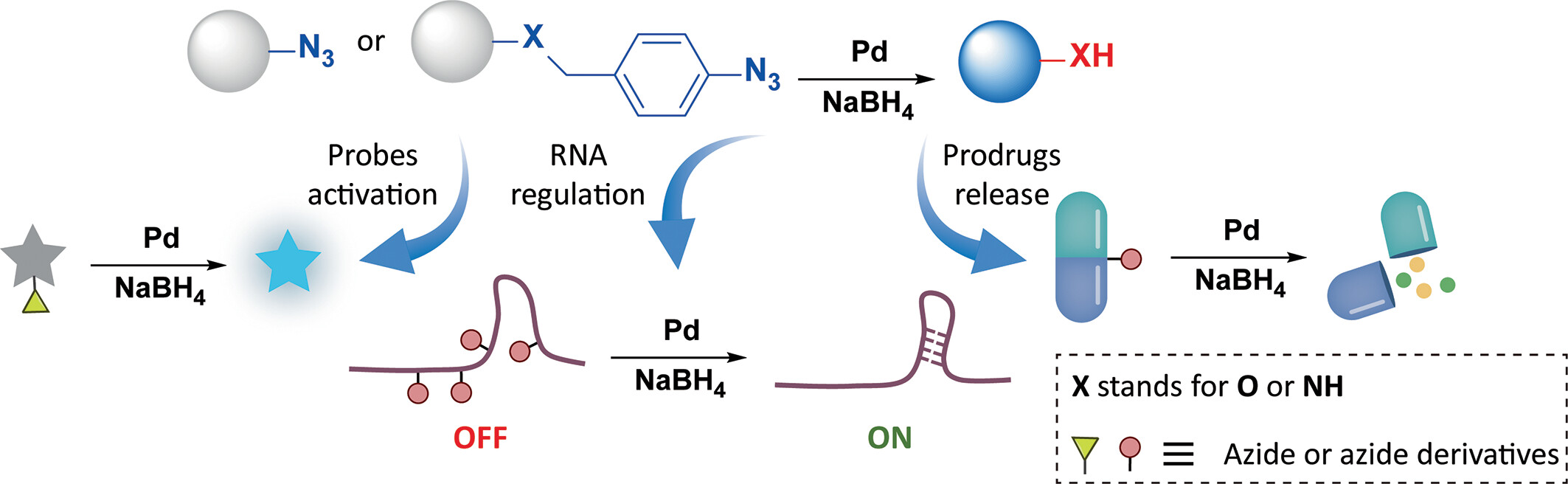
In this study, we introduce a decaging strategy utilizing Pd-catalyzed reductive amination of azides to activate biomolecules, encompassing fluorescent probes, prodrugs, and RNA functionalities. This approach offers an efficient and controllable "OFF to ON" biological switch, enabling substantial regulatory effects even at substoichiometric levels.
Efficient Chemical Synthesis and Folding of Mirror-Image Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A Using the Strategy of Removable Glycosylation Modification
- Pages: 2316-2322
- First Published: 22 May 2024
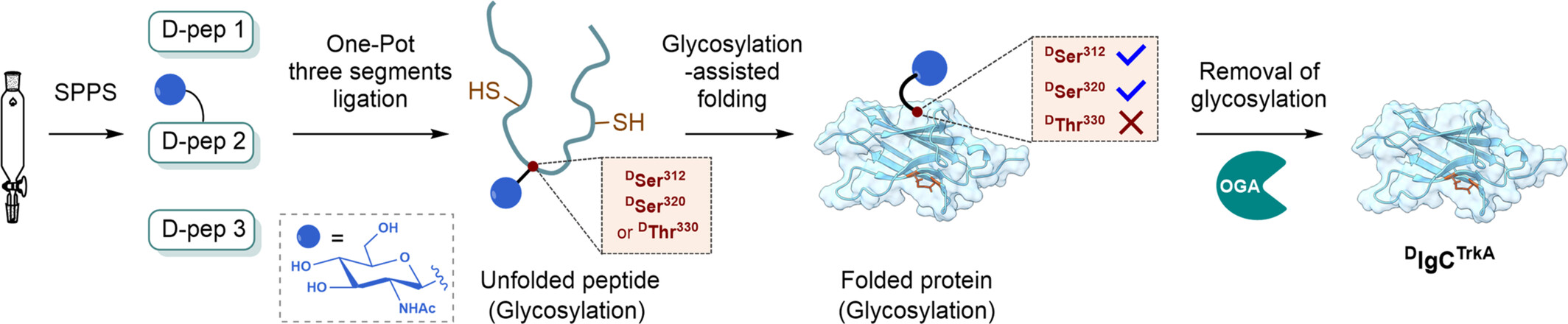
We report the study on the use of removable glycosylation modification strategy to overcome the low-efficiency problem encountered in the chemical synthesis of the mirror-image D-version of the immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain of tropomyosin receptor kinase A (DlgCTrkA). It is interesting to note that temporary glycosylation at distinct sites of DlgCTrkA led to significant differences in the process of protein folding.
Photochemical Radical Cascade 6-endo Cyclization of Dienes with α-Carbonyl Bromides for the Synthesis of Six-Membered Benzo-Fused Lactams
- Pages: 2323-2328
- First Published: 22 May 2024
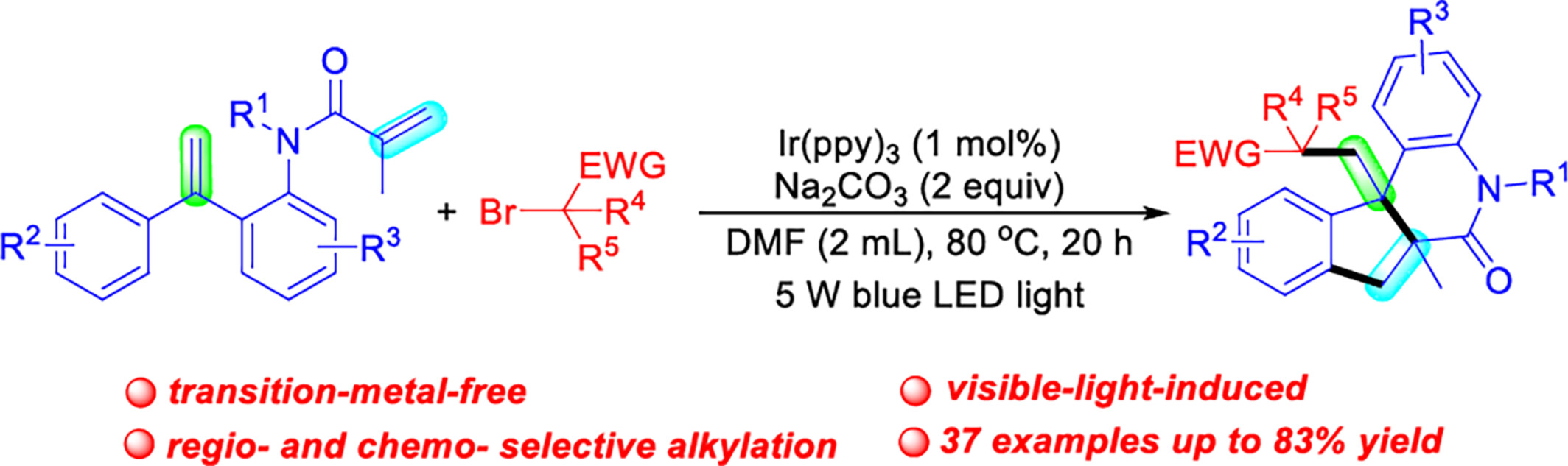
A novel visible-light-induced radical cascade 6-endo cyclization of dienes (N-(2-vinylphenyl)acryl amides) is developed utilizing α-carbonyl bromides as alkyl reagents. This approach affords an efficient way for synthesizing six-membered benzo-fused lactam derivatives with chemo- and regio-selectivity and good functional group tolerance. Primary, secondary, and tertiary bromides are well-compatible with this cascade cyclization reaction.
Photocatalytic [3+2] Cycloaddition of Alkyl/aryl Iodides and Internal Alkynes by Merging Halogen and Hydrogen Atom Transfer
- Pages: 2329-2334
- First Published: 22 May 2024
![Photocatalytic [3+2] Cycloaddition of Alkyl/aryl Iodides and Internal Alkynes by Merging Halogen and Hydrogen Atom Transfer](/cms/asset/6e62cf27-cccf-4bc8-8efc-34cb953a2189/cjoc202400366-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Enabled by merging halogen atom transfer and hydrogen atom transfer, a novel photocatalytic [3+2] cycloaddition of alkynes and alkyl/aryl iodides is accomplished, providing a highly regio- and diastereoselective approach for the direct assembly of ubiquitous and important cyclopentane derivatives from readily available chemicals.
Divergent Protein Engineering of Transaminase for the Synthesis of Chiral Rivastigmine and Apremilast Precursors
- Pages: 2335-2340
- First Published: 23 May 2024
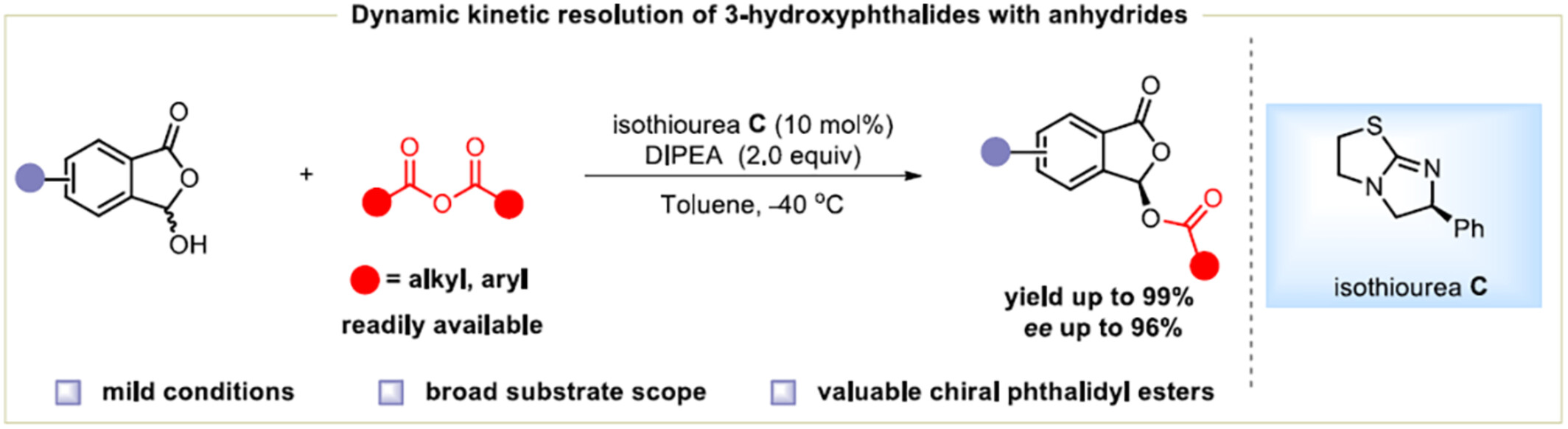
Chiral Isothiourea-Catalyzed Acylative Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of 3-Hydroxyphthalides for Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthalidyl Esters
- Pages: 2341-2345
- First Published: 27 May 2024
Visible-Light-Induced Domino Cyclization to Access Pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-diones via a Radical-Polar Crossover Reaction
- Pages: 2346-2350
- First Published: 27 May 2024
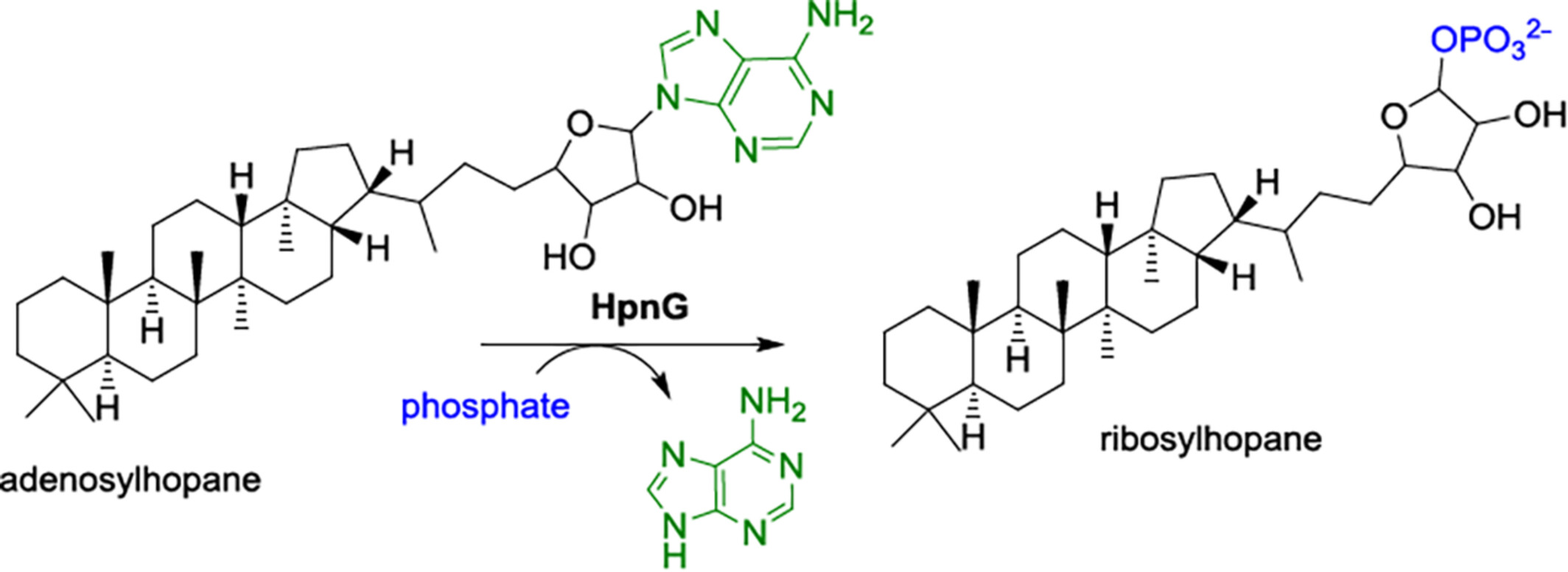
Characterization of HpnG as a Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase in Bacteriohopanepolyol Biosynthesis
- Pages: 2351-2356
- First Published: 27 May 2024
Palladium-Catalyzed Selective Syntheses of 2,3-Allenyl Amines via Double Functionalization Coupling of 2-Alkynyl-1,4-diol Dicarbonates
- Pages: 2357-2362
- First Published: 31 May 2024
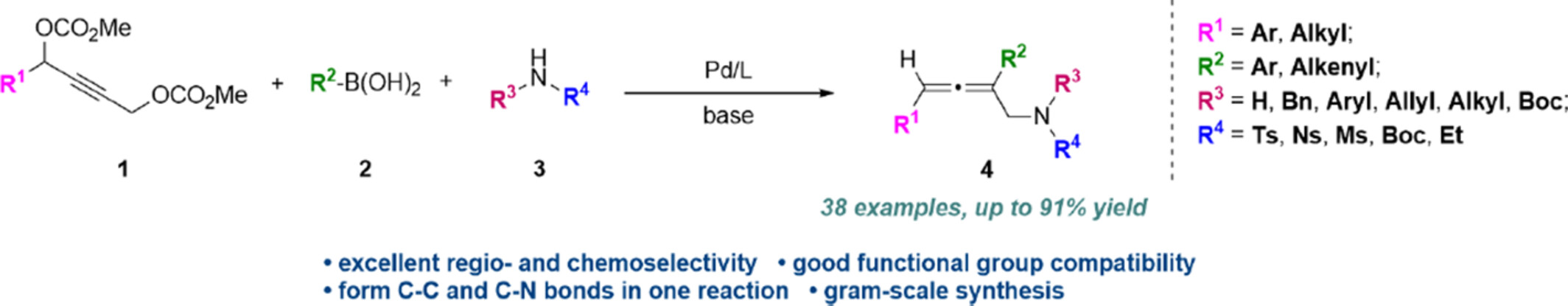
Herein, we report a palladium-catalyzed three-component reaction of 2-alkynyl-1,4-diol dicarbonates, organoboronic acids, and nitrogen nucleophiles forming 2,3-allenyl amines. The reaction shows an excellent regio- and chemoselectivity and a broad substrate scope. The mechanistic experiments demonstrate an unique β-O elimilation pathway generating 1,2,3-triene intermediate.
Multicolor Anti-counterfeiting Strategy and Synchronous High Capacity Storage Based on Acidochromic Organic Fluorescent Materials
- Pages: 2363-2369
- First Published: 27 May 2024
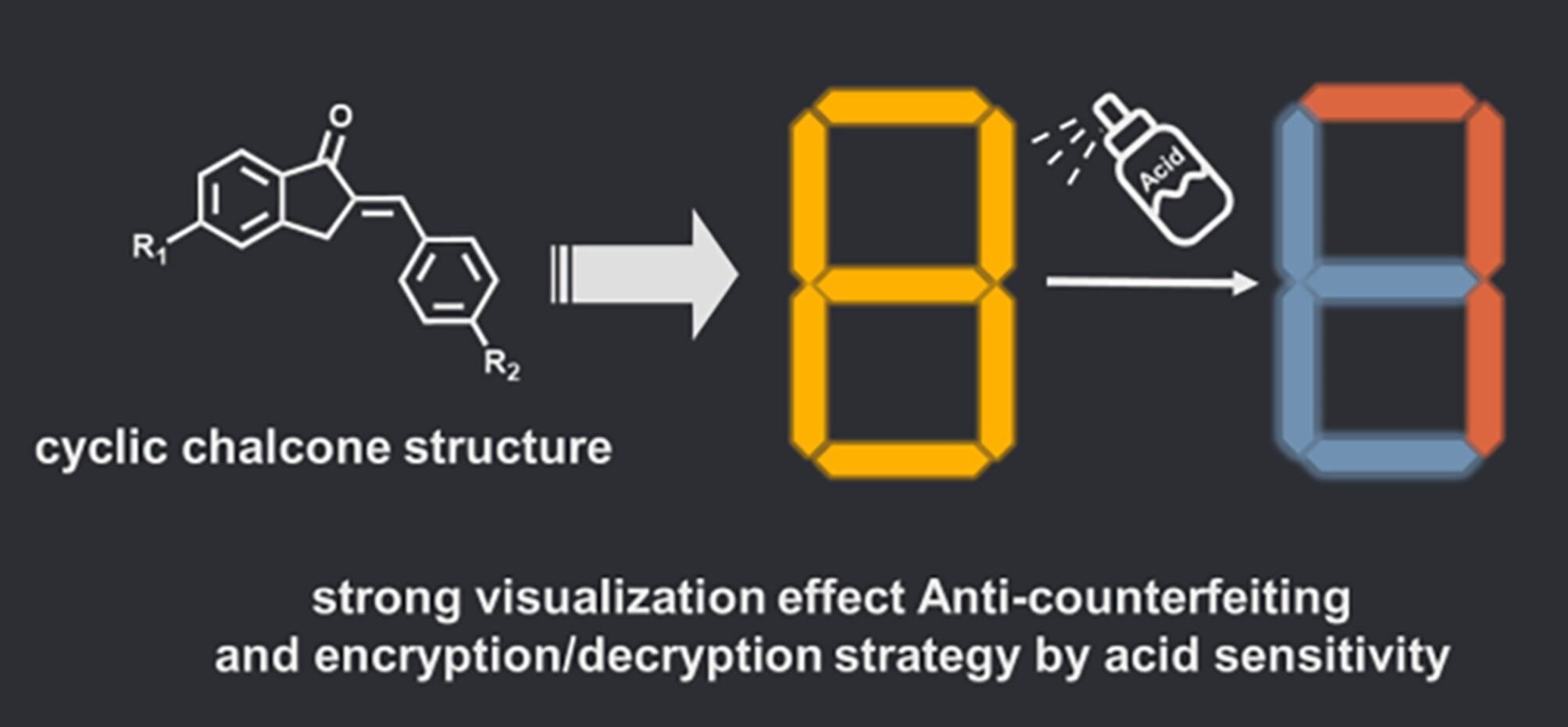
Six kinds of fluorescent dyes A—F are constructed based on the structure of cyclic chalcone. Fluorescent anti-counterfeiting Powder X and Y are constructed by mixing dye with montmorillonite. They have the same orange appearance and fluorescence, but upon contact with the acid developer, the fluorescence of Powder X redshifts and the fluorescence of Powder Y blueshifts. Anti-counterfeiting and information storage can be synchronously achieved by using Powder X and Y.
Comprehensive Report
Rational Designing MxSy@C (M=Ni, Co, Zn, Cu, Mn) Composites with Controlled Polysuifides Shuttling Behaviors towards Advanced Stable Room Temperature Na-S Batteries†
- Pages: 2370-2380
- First Published: 27 May 2024
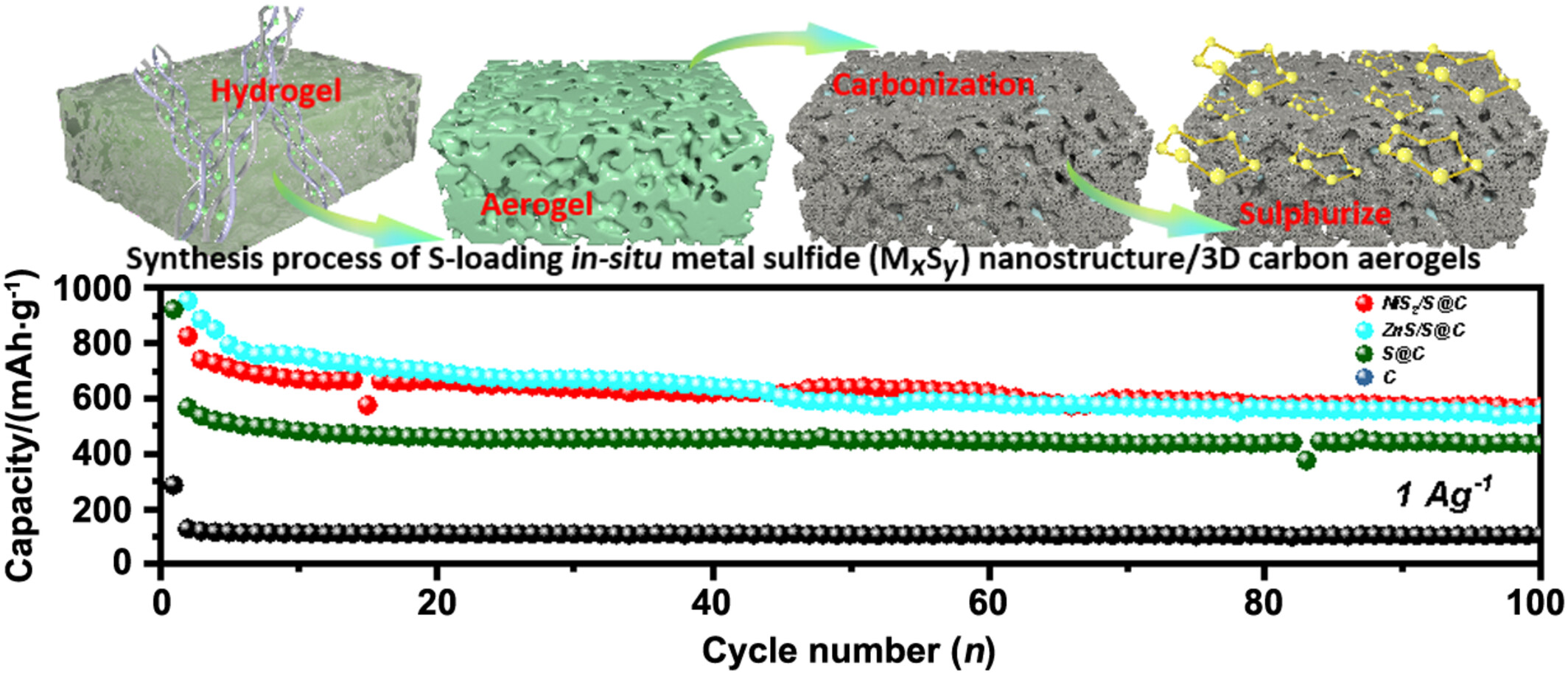
A series of MxSy/S@C composites were designed for R-T sodium ion batteries, which have rich porous structure, in situ sulfide catalysts and high sulfur elemental loading capacity, achieving a high storage capacity, splendid rate performance and long cycling performance (over 10000 cycles). The work is expected to provide promising insights for designing advanced cathode materials for RT-Na/S batteries.
Gradual or Hysteretic Transition: Anion Effects on Cobalt(II) Spin Crossover Complexes
- Pages: 2381-2390
- First Published: 27 May 2024
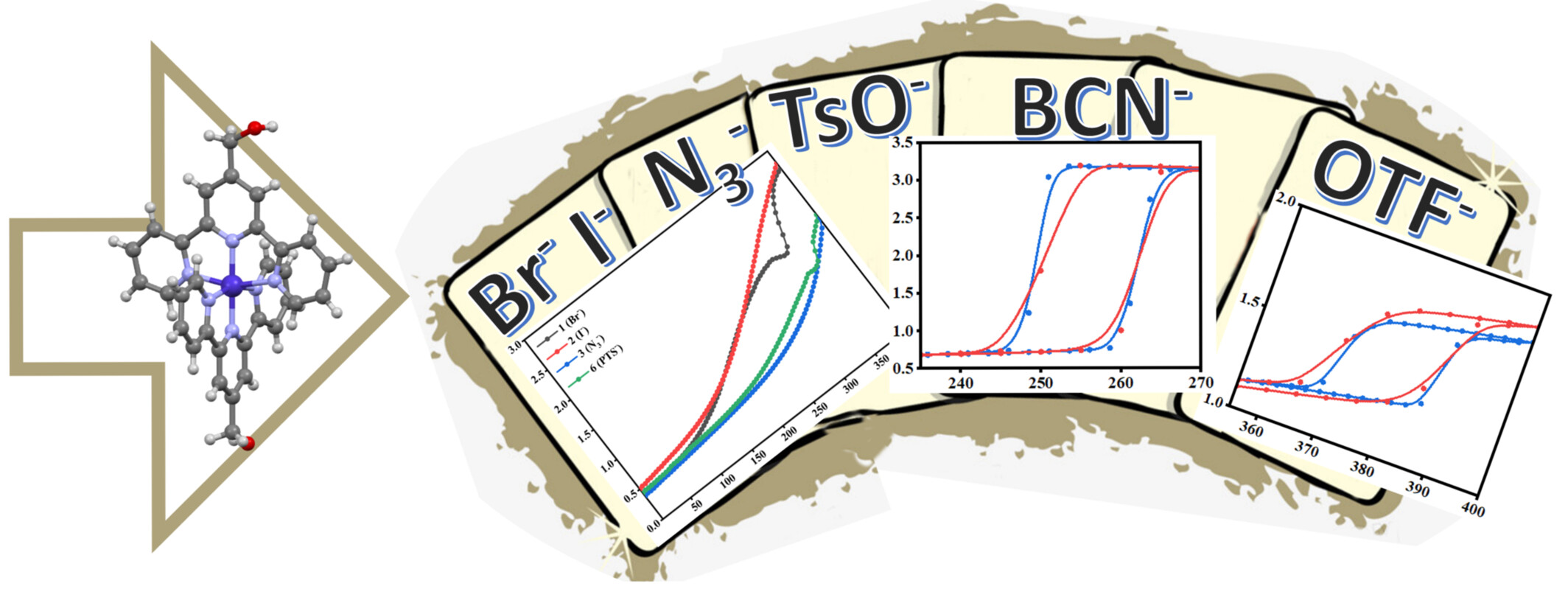
A series of CoII complexes ([Co(terpy-CH2OH)2]A2∙sol (A = Br–, I–, N3–, H3BCN–, OTf–, and TsO–, sol = solvents) with different structures and SCO properties have been prepared. Detailed studies revealed different SCO properties, including gradual transitions and hysteretic SCO transitions with loops. Their structures and SCO properties can be effectively tuned by the size, shape, and hydrogen bonding ability of the anions.
Chemistry Authors Up Close
Interfacing DNA and Aptamers with Gold Nanoparticles: From Fundamental Colloid and Interface Sciences to Biosensors
- Pages: 2391-2400
- First Published: 28 May 2024
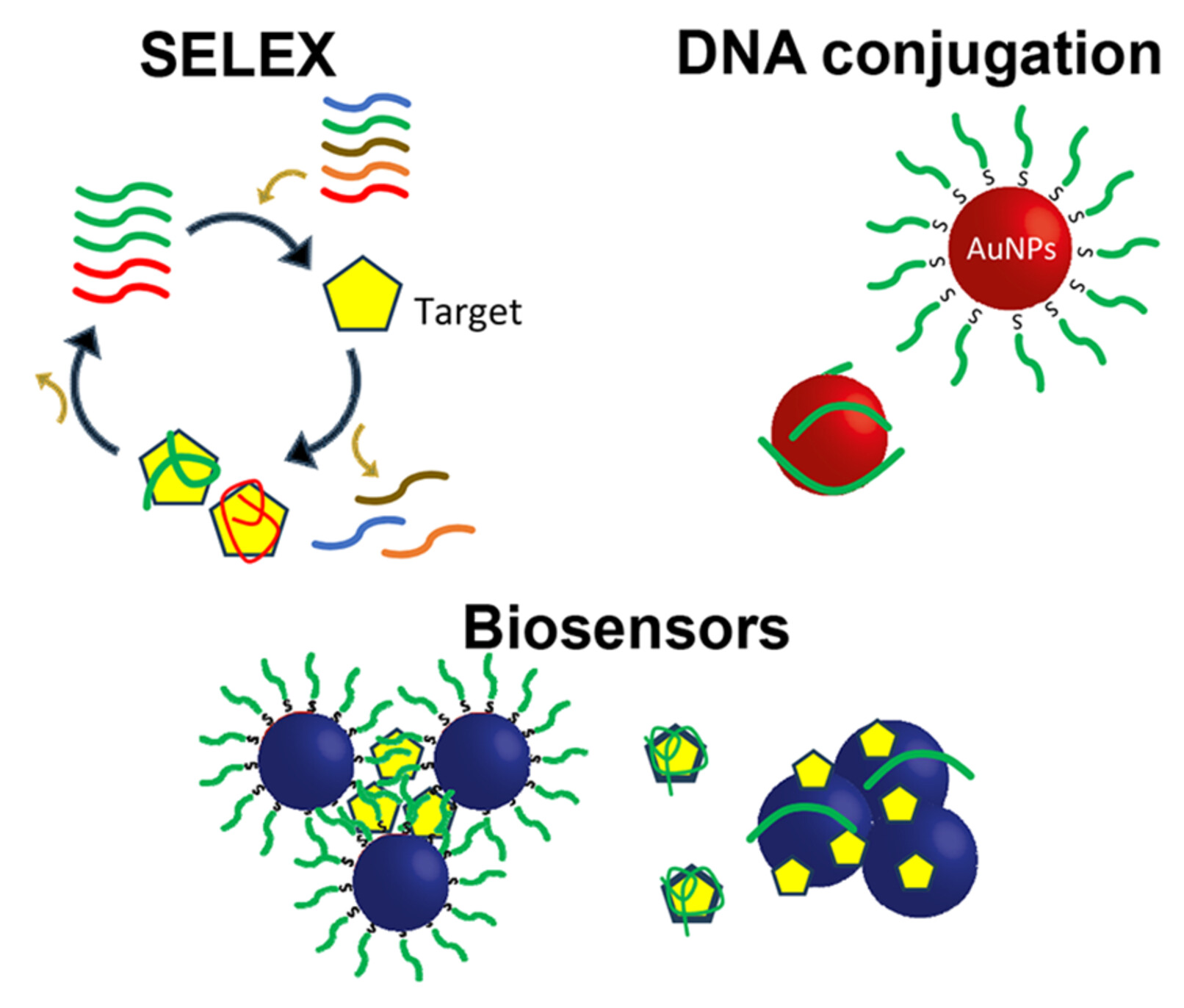
In this article, the current understanding of the adsorption of DNA to gold nanoparticles is summarized, and related application of attaching DNA is described. In addition, problems of using gold nanoparticles to signaling aptamer binding is discussed. Finally, re-selection of aptamers for previously reported targets using the new library-immobilization method is reviewed.
Recent Advances
Boron-Stereogenic Compounds: Synthetic Developments and Opportunities
- Pages: 2401-2411
- First Published: 27 May 2024
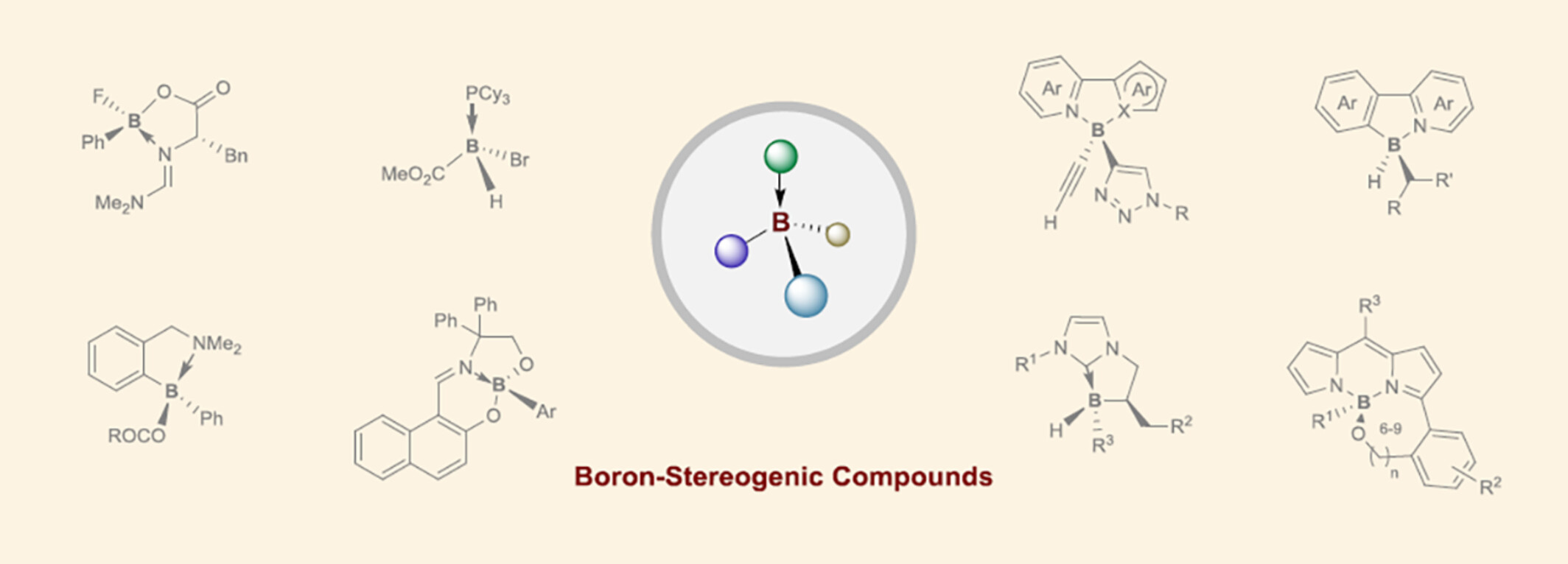
Tetracoordinate organoborons are a highly important class of molecules, that have found wide applications in areas ranging from synthetic chemistry, medicinal chemistry, to materials science. In this review, we summarized and discussed the significant progress and recent advances in the synthesis and application of enantioenriched tetracoordinate boron-stereogenic compounds, according to the synthetic method: (1) resolution of racemates, (2) chiral substrate induced asymmetric synthesis, and (3) asymmetric catalysis.
Emerging Topic
Radicals as Chiral Catalysts for Asymmetric Radical Cyclization Reactions
- Pages: 2412-2416
- First Published: 31 May 2024
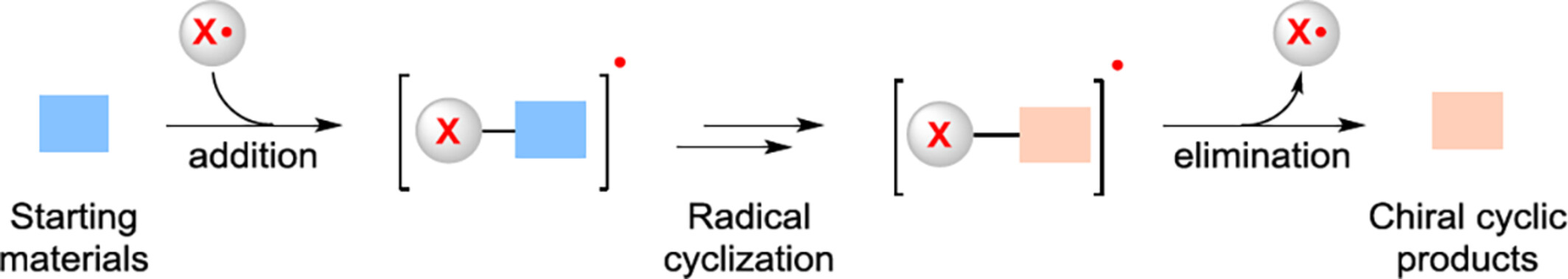
Chiral radical covalent catalysis represents an emerging strategy for the stereocontrol of radical cyclization reactions. This distinct catalytic strategy mainly involves three key steps: (1) reversible intermolecular addition of chiral radical catalyst toward substrates to form new radical intermediates poised for subsequent new-bond-forming cyclization, (2) intramolecularly stereo-determining radical cyclization process, (3) final elimination process with regeneration of chiral radical catalyst.
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 2419
- First Published: 01 September 2024

The serious dissolution of polysulfides restricted the practical application of Room-temperature sodium-sulfur (RT-Na/S) batteries which displayed attractive potential in large-scale energy-storage. Utilizing the double-helix structure of carrageenan-metal hydrogels as precursors, in-situ metal sulfide (MxSy) nanostructure/3D carbon aerogels (3D CAs) can be successfully constructed. Importantly, with the assistance of the vulcanization process, 3D carbon architecture was maintained in the composites and acted as a skeleton to optimize Storage environment of sulfur element. More details are discussed in the article by Yang et al. on page 2370—2380.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 2420
- First Published: 01 September 2024

Bacteriohopanepolyols are a group of triterpenoids that play important roles in cell membrane function. As an essential step in bacteriohopanepolyol biosynthesis, HpnG phosphorolyzes adenosylhopane to form phosphoribosylhopane, and demonstrates remarkable tolerance to various nucleoside substrates. More details are discussed in the article by Zhang et al. on page 2351—2356.





![Visible-Light-Induced Domino Cyclization to Access Pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-diones via a Radical-Polar Crossover Reaction](/cms/asset/83155335-a3ed-4f5a-9fe3-747197ab5c1e/cjoc202400315-toc-0001-m.jpg)