Efficient Chemical Synthesis and Folding of Mirror-Image Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A Using the Strategy of Removable Glycosylation Modification†
Tongyue Wang
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWeiwei Shi
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guo-Chao Chu
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
School of Food and Biological Engineering, Engineering Research Center of Bio-process, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Animal Source of Anhui Province, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui, 230009 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yi-Ming Li
School of Food and Biological Engineering, Engineering Research Center of Bio-process, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Animal Source of Anhui Province, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui, 230009 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorTongyue Wang
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWeiwei Shi
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guo-Chao Chu
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
School of Food and Biological Engineering, Engineering Research Center of Bio-process, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Animal Source of Anhui Province, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui, 230009 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yi-Ming Li
School of Food and Biological Engineering, Engineering Research Center of Bio-process, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Animal Source of Anhui Province, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui, 230009 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2024.
Comprehensive Summary
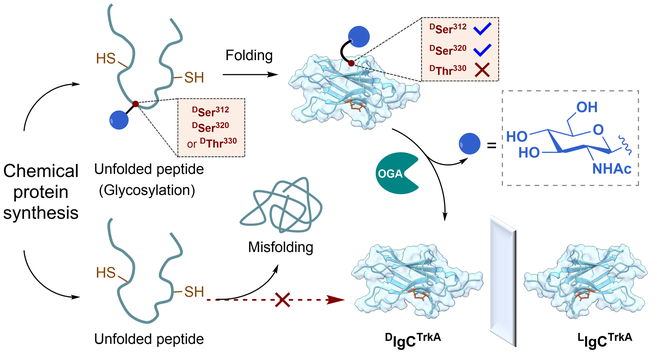
The strategy of removable glycosylation modification was used to overcome the low-efficiency problem encountered in the chemical synthesis of the mirror-image D-version of the immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain of tropomyosin receptor kinase A (DlgCTrkA), a protein molecule needed for mirror-image screening of D-peptide ligands targeting this cell membrane receptor. It was found that O-linked-β-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (O-GlcNAc) modification at DSer312, or DSer320 can significantly improve the efficiency of DlgCTrkA synthesis and folding, while O-GlcNAc modification at DSer330 showed barely any improvement. This study provides a new example demonstrating the power of the removable glycosylation modification strategy in the chemical synthesis and folding of difficult-to-obtain proteins. It also presents evidence that removable glycosylation modification at different sites would significantly affect the efficiency of protein folding promoted by this strategy.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400381-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.4 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Dong, S.; Zheng, J.-S.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Fang, G.; Guo, J.; He, C.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Pan, M.; Tang, S.; Tian, C.; Wang, P.; Wu, B.; Wu, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L. Recent advances in chemical protein synthesis: method developments and biological applications. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 1060–1096.
- 2 Tan, Y.; Wu, H.; Wei, T.; Li, X. Chemical Protein Synthesis: Advances, Challenges, and Outlooks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20288–20298.
- 3 Conibear, A. C. Deciphering protein post-translational modifications using chemical biology tools. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 674–695.
- 4 Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Precision in protein chemical modification and total synthesis. Chem 2024, 10, 767–799.
- 5 Kent, S. B. H. Total chemical synthesis of proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 338–351.
- 6 Agouridas, V.; Ollivier, N.; Vicogne, J.; Diemer, V.; Melnyk, O. Redox-controlled chemical protein synthesis: sundry shades of latency. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2685–2697.
- 7 Dawson, P. E.; Kent, S. B. H. Synthesis of native proteins by chemical ligation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 923–960.
- 8 Sun, H.; Brik, A. The journey for the total chemical synthesis of a 53 kDa protein. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3361–3371.
- 9 Murakami, M.; Kiuchi, T.; Nishihara, M.; Tezuka, K.; Okamoto, R.; Izumi, M.; Kajihara, Y. Chemical synthesis of erythropoietin glycoforms for insights into the relationship between glycosylation pattern and bioactivity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500678.
- 10 Wang, P.; Dong, S.; Shieh, J.-H.; Peguero, E.; Hendrickson, R.; Moore, M. A. S.; Danishefsky, S. J. Erythropoietin Derived by Chemical Synthesis. Science 2013, 342, 1357–1360.
- 11 Maki, Y.; Okamoto, R.; Izumi, M.; Kajihara, Y. Chemical Synthesis of an Erythropoietin Glycoform Having a Triantennary N-Glycan: Significant Change of Biological Activity of Glycoprotein by Addition of a Small Molecular Weight Trisaccharide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20671–20679.
- 12 Lv, P.; Du, Y.; He, C.; Peng, L.; Zhou, X.; Wan, Y.; Zeng, M.; Zhou, W.; Zou, P.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Dong, S.; Chen, X. O-GlcNAcylation modulates liquid–liquid phase separation of SynGAP/PSD-95. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 831–840.
- 13 Li, Y.; Heng, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, W.-W.; Wang, T.-Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.-S.; Kobilka, B. K.; Liu, L. Chemical Synthesis of a Full-Length G-Protein-Coupled Receptor β2-Adrenergic Receptor with Defined Modification Patterns at the C-Terminus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17566–17576.
- 14 Ai, H.; Chu, G.-C.; Gong, Q.; Tong, Z.-B.; Deng, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.-B.; Tian, C.; Liu, L. Chemical Synthesis of Post-Translationally Modified H2AX Reveals Redundancy in Interplay between Histone Phosphorylation, Ubiquitination, and Methylation on the Binding of 53BP1 with Nucleosomes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18329–18337.
- 15 Ai, H.; Tong, Z.; Deng, Z.; Tian, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Du, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Q.; Liang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Li, J.-B.; Pan, M.; Liu, L. Synthetic E2-Ub-nucleosome conjugates for studying nucleosome ubiquitination. Chem 2023, 9, 1221–1240.
- 16 Ai, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, A.; Sun, Z.; Liu, T.; Cao, L.; Liang, L.; Qu, Q.; Li, Z.; Deng, Z.; Tong, Z.; Chu, G.; Tian, X.; Deng, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.-B.; Lou, Z.; Liu, L. H2B Lys34 Ubiquitination Induces Nucleosome Distortion to Stimulate Dot1L Activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 972–980.
- 17 Hu, J.; Xia, W.; Zeng, S.; Lim, Y.-J.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Le, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.-M. Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation at the same α-synuclein site generate distinct fibril structures. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2677.
- 18 Ye, F.; Zhao, J.; Xu, P.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Shangguan, W.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Li, C.; Ying, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, P. Synthetic Homogeneous Glycoforms of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Reveals Different Binding Profiles of Monoclonal Antibodies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12904–12910.
- 19 Pan, M.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, T.; Liang, L.; Mao, J.; Zuo, C.; Ding, R.; Ai, H.; Xie, Y.; Si, D.; Yu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M. Structural insights into Ubr1-mediated N-degron polyubiquitination. Nature 2021, 600, 334–338.
- 20 Chu, G.-C.; Pan, M.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Zuo, C.; Tong, Z.-B.; Bai, J.-S.; Gong, Q.; Ai, H. S.; Fan, J.; Meng, X.; Huang, Y.-C.; Shi, J.; Deng, H.; Tian, C.; Li, Y.-M.; Liu, L. Cysteine-aminoethylation-assisted chemical ubiquitination of recombinant histones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3654–3663.
- 21 Jbara, M.; Sun, H.; Kamnesky, G.; Brik, A. Chemical chromatin ubiquitylation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 45, 18–26.
- 22 Müller, M. M.; Muir, T. W. Histones: at the crossroads of peptide and protein chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2296–2349.
- 23 Fierz, B.; Chatterjee, C.; McGinty, R. K.; Bar-Dagan, M.; Raleigh, D. P.; Muir, T. W. Histone H2B ubiquitylation disrupts local and higher-order chromatin compaction. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 113–119.
- 24 Wang, P.; Dong, S.; Brailsford, J. A.; Iyer, K.; Townsend, S. D.; Zhang, Q.; Hendrickson, R. C.; Shieh, J.; Moore, M. A. S.; Danishefsky, S. J. At last: erythropoietin as a single glycoform. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11576–11584.
- 25 Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Liu, L.; Ye, F.; Wang, C.; Shao, H.; Xue, D.; Tao H.; Li, B.; Yu, B.; Wang, P. Revealing Functional Significance of Interleukin-2 Glycoproteoforms Enabled by Expressed Serine Ligation. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 787–793.
- 26 Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, F.; Wei, B.; Deng, M.; Li, T.; Huang, P.; Wang, P. Chemical Synthesis Creates Single Glycoforms of the Ectodomain of Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Glycoprotein D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2615–2623.
- 27 Ye, F.; Li, C.; Liu, F.-L.; Liu, X.; Xu, P.; Luo, R.-H.; Song, W.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Ying, T.; Yu, B.; Wang, P. Semisynthesis of homogeneous spike RBD glycoforms from SARS-CoV-2 for profiling the correlations between glycan composition and function. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwae030.
- 28 Mandal, K.; Uppalapati, M.; Ault-Riché, D.; Kenney. J.; Lowitz, J.; Sidhu, S. S.; Kent, S. B. H. Chemical synthesis and X-ray structure of a heterochiral {D-protein antagonist plus vascular endothelial growth factor} protein complex by racemic crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012, 109, 14779–14784.
- 29 Kent, S. B. H. Racemic & quasi-racemic protein crystallography enabled by chemical protein synthesis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 46, 1–9.
- 30 Pan, M.; Gao, S.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, X.; Lan, H.; Tan, X.; Sun, D.; Lu, L.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. Quasi-Racemic X-ray Structures of K27-Linked Ubiquitin Chains Prepared by Total Chemical Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7429–7435.
- 31 Harrison, K.; Mackay, A. S.; Kambanis, L.; Maxwell, J. W. C.; Payne, R. J. Synthesis and applications of mirror-image proteins. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 383–404.
- 32 Zuo, C.; Shi, W.-W.; Chen, X.-X.; Glatz, M.; Riedl, B.; Flamme, I.; Pook, E.; Wang, J.; Fang, G.-M.; Bierer, D.; Liu, L. Chimeric protein probes for C5a receptors through fusion of the anaphylatoxin C5a core region with a small-molecule antagonist. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1371–1378.
- 33 Zhang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, G.; Deng, X.; Wang, T.; Shi, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, S.; Zheng, J.-S.; Liu, L. Backbone-Installed Split Intein-Assisted Ligation for the Chemical Synthesis of Mirror-Image Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306270.
- 34 Gao, S.; Pan, M.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, D.; Lu, L.; Tan, X.; Tan, X-L.; Lan, H.; Wang, J; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. Monomer/oligomer quasi-racemic protein crystallography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14497–14502.
- 35 Pentelute, B. L.; Gates, Z. P.; Dashnau, J. L.; Vanderkooi, J. M.; Kent, S. B. H. Mirror image forms of snow flea antifreeze protein prepared by total chemical synthesis have identical antifreeze activities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9702–9707.
- 36 Zheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shi, W.-W.; Deng, X.; Wang, T.-Y.; Han, D.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.-K.; Kuang, J.; Wang, Z.-W.; Tang, S.; Zheng, J.-S. An Enzyme-Cleavable Solubilizing-Tag Facilitates the Chemical Synthesis of Mirror-Image Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202318897.
- 37 Dawson, P. E.; Muir, T. W.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Kent, S. B. H. Synthesis of Proteins by Native Chemical Ligation. Science 1994, 266, 776–779.
- 38 Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Wei, T.; Li, X. D.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Chemical Synthesis of Proteins with Base-Labile Posttranslational Modifications Enabled by a Boc-SPPS Based General Strategy Towards Peptide C-Terminal Salicylaldehyde Esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214053.
- 39 Agouridas, V.; Mahdi, O. E.; Diemer, V.; Cargoët, M.; Monbaliu, J.-C. M.; Melnyk, O. Native chemical ligation and extended methods: mechanisms, catalysis, scope, and limitations. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7328–7443.
- 40 Fang, G.-M.; Li, Y.-M.; Shen, F.; Huang, Y.-C.; Li, J.-B.; Lin, Y.; Cui, H.-K.; Liu, L. Protein Chemical Synthesis by Ligation of Peptide Hydrazides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7645–7649.
- 41 Fang, G.-M.; Wang, J.-X.; Liu, L. Convergent Chemical Synthesis of Proteins by Ligation of Peptide Hydrazides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10347–10350.
- 42 Zheng, J.-S.; Tang, S.; Qi, Y.-K.; Wang, Z.-P.; Liu, L. Chemical synthesis of proteins using peptide hydrazides as thioester surrogates. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2483–2495.
- 43 Zhang, Y. F.; Xu, C.; Lam, H. Y.; Lee, C. L.; Li, X. Protein chemical synthesis by serine and threonine ligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 6657–6662.
- 44 Pusterla, I.; Bode, J. W. An oxazetidine amino acid for chemical protein synthesis by rapid, serine-forming ligations. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 668–672.
- 45 Chisholm, T. S.; Kulkarni, S. S.; Hossain, K. R.; Cornelius, F.; Clarke, R. J.; Payne, R. J. Peptide ligation at high dilution via reductive diselenide-selenoester ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 1090–1100.
- 46
Chu, G.-C.; Liang, L.-J.; Zhao, R.; Guo, Y.-Y.; Li, C.-T.; Zuo, C.; Ai, H.; Hua, X.; Li, Z.-C.; Li, Y.-M.; Liu, L. Ferricyanide-Promoted Oxidative Activation and Ligation of Protein Thioacids in Neutral Aqueous Media. CCS Chem. 2024, DOI: https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.023.202303397.
10.31635/ccschem.023.202303397 Google Scholar
- 47 Sun, Z.; Li, X. Studies on 2-Formylphenylboronic Acid-Based Ser/Thr Ligation and Cys/Pen Ligation. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2795–2800.
- 48 Wang, J.-X.; Fang, G.-M.; He, Y.; Qu, D.-L.; Yu, M.; Hong, Z.-Y.; Liu, L. Peptide o-Aminoanilides as Crypto-Thioesters for Protein Chemical Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2194–2198.
- 49 Zuo, C.; Ding, R.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chu, G.-C.; Liang, L.-J.; Ai, H.; Tong, Z.-B.; Mao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Sun, D. Thioester-Assisted Sortase-A-Mediated Ligation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201887.
- 50 Zheng, J.-S.; Yu, M.; Qi, Y.-K.; Tang, S.; Shen, F.; Wang, Z.-P.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, L.; Tian, C.-L.; Liu, L. Expedient Total Synthesis of Small to Medium-Sized Membrane Proteins via Fmoc Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3695–3704.
- 51 Li, Y.-M.; Li, Y.-T.; Pan, M.; Kong, X.-Q.; Huang, Y.-C.; Hong, Z.-Y.; Liu, L. Irreversible Site-Specific Hydrazinolysis of Proteins by Use of Sortase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2198–2202.
- 52 Wu, H.; Wei, T.; Ngai, W. L.; Zhou, H.; Li, X. Ligation Embedding Aggregation Disruptor Strategy Enables the Chemical Synthesis of PD-1 Immunoglobulin and Extracellular Domains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14748–14757.
- 53 Liu, J.; Dong, S. Synthetic studies toward human interleukin-5. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1131–1134.
- 54 Li, H.; Zhang, J.; An, C.; Dong, S. Probing N-Glycan Functions in Human Interleukin-17A Based on Chemically Synthesized Homogeneous Glycoforms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2846–2856.
- 55 Petersen, M. E.; Jacobsen, M. T.; Kay, M. S. Synthesis of tumor necrosis factor α for use as a mirror-image phage display target. Org. Biol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5298–5303.
- 56 Weinstock, M. T.; Jacobsen, M. T.; Kay, M. S. Synthesis and folding of a mirror-image enzyme reveals ambidextrous chaperone activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111, 11679–11684.
- 57 Shi, W.-W.; Shi, C.; Wang, T.-Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhou, Y.-K.; Zhang, X.-H.; Bierer, D.; Zheng, J.-S.; Liu, L. Total Chemical Synthesis of Correctly Folded Disulfide-Rich Proteins Using a Removable O-Linked β-N-Acetylglucosamine Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 349–357.
- 58 Shi, W.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Han, D.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, X.; Tang, S.; Zheng, J.-S. L-Glycosidase-Cleavable Natural Glycans Facilitate the Chemical Synthesis of Correctly Folded Disulfide-Bonded D-Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202313640.
- 59 Wiesmann, C.; Ultsch, M. H.; Bass, S. H.; de Vos, A. M. Crystal structure of nerve growth factor in complex with the ligand-binding domain of the TrkA receptor. Nature 1999, 401, 184–188.
- 60 Schumacher, T. N.; Mayr, L. M.; Minor, D. L.; Milhollen, M. A.; Burgess, M. W.; Kim, P. S. Identification of d-peptide ligands through mirror-image phage display. Science 1996, 271, 1854–1857.
- 61 Minnone, G.; Benedetti, F. D.; Bracci-Laudiero, L. NGF and its receptors in the regulation of inflammatory response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1028.
- 62 Donato, M. D.; Cernera, G.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Nerve growth factor induces proliferation and aggressiveness in prostate cancer cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 784.
- 63 Chang, H. N.; Liu, B. Y.; Qi, Y. K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. P.; Pan, K. M.; Li, W. W.; Zhou, X. M.; Ma, W. W.; Fu, C. Y.; Qi, Y. M.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y. F. Blocking of the PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction by a D-Peptide Antagonist for Cancer Immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11760–11764.
- 64 Zhou, X.; Zuo, C.; Li, W.; Shi, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Du, J.; Chen, G.; Zhai, W.; Zhao, W.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y. A Novel D-Peptide Identified by Mirror-Image Phage Display Blocks TIGIT/PVR for Cancer Immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15114–15118.
- 65 Flood, D. T.; Hintzen, J. C. J.; Bird, M. J.; Cistrone, P. A.; Chen, J. S.; Dawson, P. E. Leveraging the Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis for the Facile Generation of Thioester Surrogates for use in Native Chemical Ligation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11634–11639.




