Streptavidin-Biotin Complexes as Tools for Modulating an Important DNA Epigenetic Modification†
Yongjie Liu
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorXinyan Xu
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorXingyu Liu
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWei Xiong
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorQianqian Qi
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuanyuan Zhang
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jinxuan Hou
Department of Thyroid & Breast Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tian Tian
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Zhou
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongjie Liu
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorXinyan Xu
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorXingyu Liu
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWei Xiong
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorQianqian Qi
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuanyuan Zhang
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jinxuan Hou
Department of Thyroid & Breast Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tian Tian
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Zhou
Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Allergy and Immunology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2024.
Comprehensive Summary
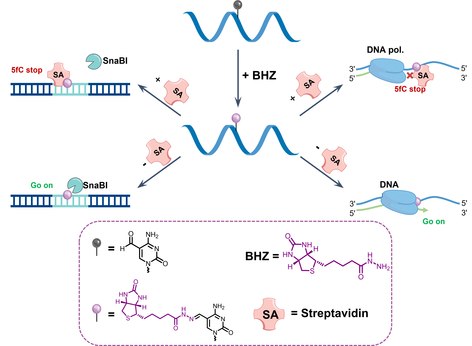
DNA 5-formylcytosine (5fC) is a prominent epigenetic modification within biological systems. Recent investigations have shed light on its pivotal role in governing cell fate, gene expression, and disease pathways. However, our comprehension of the precise control of the 5fC site structure to influence its functionality remains limited. In this study, we have successfully achieved precise control over 5fC activity by harnessing the interaction between streptavidin and biotin. This research underscores the potential application of interactions between biomacromolecules and small molecules in advancing the field of DNA epigenetic functional regulation.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400236-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Suzuki, M. M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 465–476.
- 2 Spruijt, C. G.; Vermeulen, M. DNA methylation: old dog, new tricks? Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 949–954.
- 3 Liu, R.; Zhao, E.; Yu, H.; Yuan, C.; Abbas, M. N.; Cui, H. Methylation across the central dogma in health and diseases: new therapeutic strategies. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 310.
- 4 Jones, P. A. Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492.
- 5 Baylin, S. B. DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, S4–S11.
- 6 Ballestar, E.; Sawalha, A. H.; Lu, Q. Clinical value of DNA methylation markers in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 514–524.
- 7 Niederberger, E.; Resch, E.; Parnham, M. J.; Geisslinger, G. Drugging the pain epigenome. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 434–447.
- 8 Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Epigenetic regulation in the tumor microenvironment: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Sig. Transd. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 210.
- 9 Brunner, J. S.; Finley, L. W. S. Metabolic determinants of tumour initiation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 134–150.
- 10 Jasielec, J.; Saloura, V.; Godley, L. A. The mechanistic role of DNA methylation in myeloid leukemogenesis. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1765–1773.
- 11 Stener-Victorin, E.; Deng, Q. Epigenetic inheritance of polycystic ovary syndrome — challenges and opportunities for treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 521–533.
- 12 Plongthongkum, N.; Diep, D. H.; Zhang, K. Advances in the profiling of DNA modifications: cytosine methylation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 647–661.
- 13 Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. TET-mediated active DNA demethylation: mechanism, function and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 517–534.
- 14 Branco, M. R.; Ficz, G.; Reik, W. Uncovering the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the epigenome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 7–13.
- 15 Kohli, R. M.; Zhang, Y. TET enzymes, TDG and the dynamics of DNA demethylation. Nature 2013, 502, 472–479.
- 16 Berney, M.; McGouran, J. F. Methods for detection of cytosine and thymine modifications in DNA. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 332–348.
- 17 Guo, C.; Dong, G.; Liang, X.; Dong, Z. Epigenetic regulation in AKI and kidney repair: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 220–239.
- 18 Raiber, E.-A.; Hardisty, R.; van Delft, P.; Balasubramanian, S. Mapping and elucidating the function of modified bases in DNA. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0069.
- 19 Pastor, W. A.; Aravind, L.; Rao, A. TETonic shift: biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 341–356.
- 20 Deniz, Ö.; Frost, J. M.; Branco, M. R. Regulation of transposable elements by DNA modifications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 417–431.
- 21 Zhang, Q.; Cao, X. Epigenetic regulation of the innate immune response to infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 417–432.
- 22 Wang, S.-R.; Song, Y.-Y.; Wei, L.; Liu, C.-X.; Fu, B.-S.; Wang, J.-Q.; Yang, X.-R.; Liu, Y.-N.; Liu, S.-M.; Tian, T.; Zhou, X. Cucurbit[7]uril-Driven Host–Guest Chemistry for Reversible Intervention of 5-Formylcytosine-Targeted Biochemical Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16903–16912.
- 23 Wang, S.-R.; Wang, J.-Q.; Fu, B.-S.; Chen, K.; Xiong, W.; Wei, L.; Qing, G.; Tian, T.; Zhou, X. Supramolecular Coordination-Directed Reversible Regulation of Protein Activities at Epigenetic DNA Marks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15842–15849.
- 24 Green, N. M. Avidin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1975, 29, 85–133.
- 25 Dundas, C. M.; Demonte, D.; Park, S. Streptavidin–biotin technology: improvements and innovations in chemical and biological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9343–9353.
- 26 Fairhead, M.; Veggiani, G.; Lever, M.; Yan, J.; Mesner, D.; Robinson, C. V.; Dushek, O.; van der Merwe, P. A.; Howarth, M. SpyAvidin Hubs Enable Precise and Ultrastable Orthogonal Nanoassembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12355–12363.
- 27 Murar, C. E.; Thuaud, F.; Bode, J. W. KAHA Ligations That Form Aspartyl Aldehyde Residues as Synthetic Handles for Protein Modification and Purification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 18140–18148.
- 28 Loeb, L. A.; Monnat, R. J. DNA polymerases and human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 594–604.
- 29 Wu, W.-J.; Yang, W.; Tsai, M.-D. How DNA polymerases catalyse replication and repair with contrasting fidelity. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0068.
- 30 Rodriguez, R.; Krishnan, Y. The chemistry of next-generation sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1709–1715.
- 31 Tan, B. G.; Gustafsson, C. M.; Falkenberg, M. Mechanisms and regulation of human mitochondrial transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 119–132.
- 32 Schierling, B.; Noël, A.-J.; Wende, W.; Hien, L. T.; Volkov, E.; Kubareva, E.; Oretskaya, T.; Kokkinidis, M.; Römpp, A.; Spengler, B.; Pingoud, A. Controlling the enzymatic activity of a restriction enzyme by light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 1361–1366.
- 33 Chandler, M.; de la Cruz, F.; Dyda, F.; Hickman, A. B.; Moncalian, G.; Ton-Hoang, B. Breaking and joining single-stranded DNA: the HUH endonuclease superfamily. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 525–538.
- 34 Dehé, P.-M.; Gaillard, P.-H. L. Control of structure-specific endonucleases to maintain genome stability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 315–330.
- 35 Wozniak, K. J.; Simmons, L. A. Bacterial DNA excision repair pathways. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 465–477.
- 36 Kong, Y.; Mead, E. A.; Fang, G. Navigating the pitfalls of mapping DNA and RNA modifications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 363–381.




