Photoredox-Catalyzed Metal-Free Regio- & Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Amination of Enamides with N-Aminopyridium Salts
Zheng-Bao Qin
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorKun Ni
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorLi Wang
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Di Wu
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Zhang
College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210037 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kai Zhao
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorZheng-Bao Qin
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorKun Ni
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorLi Wang
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Di Wu
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Zhang
College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210037 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kai Zhao
Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 211816 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
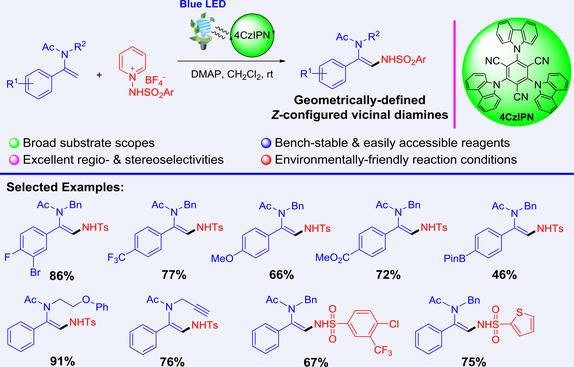
A visible-light-induced photoredox-catalyzed regioselective and stereoselective C(sp2)–H amination of enamides with bench-stable and easily accessible N-aminopyridium salts is developed, affording synthetically and biologically prominent vicinal 1,2-diamine scaffolds with broad substrate scope and excellent functional group compatibility. The transformation proceeded through a radical pathway involving the Giese addition of the relatively electrophilic N-centered sulfonamidyl radical species to nucleophilic β-olefinic position of enamides followed by the ensuing single electron oxidation and β-H elimination, delivering geometrically-defined Z-configured β-sulfonamidylated enamides. The operational simplicity, environmental friendliness and cost efficiency of this methodology allowed it to pave a new avenue to enrich the arsenal of synthetically crucial functionalized enamides and their related derivatives.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| CJOC202400350-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 8.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Lucet, D.; Le Galle, T.; Mioskowski, C. The Chemistry of Vicinal Diamines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2580−2627;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19981016)37:19<2580::AID-ANIE2580>3.0.CO;2-L CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar(b) Viso, A.; Fernández De La Pradilla, R.; García, A.; Flores, A. α,β-Diamino Acids: Biological Significance and Synthetic Approaches. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3167–3196; (c) Viso, A.; Fernández de la Pradilla, R.; Tortosa, M.; García, A.; Flores, A. Update 1 of: α,β-Diamino Acids: Biological Significance and Synthetic Approaches. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, PR1−PR42; (d) Saibabu Kotti, S. R. S.; Timmons, C.; Li, G. Vicinal Diamino Functionalities as Privileged Structural Elements in Biologically Active Compounds and Exploitation of Their Synthetic Chemistry. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 101–114.
- 2(a) Park, Y.; Chang, S. Asymmetric Formation of γ-Lactams via C–H Amidation Enabled by Chiral Hydrogen-Bond-Donor Catalysts. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 219–227; (b) Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation: Chiral Ligands and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236; (c) Beeson, T. D.; Mastracchio, A.; Hong, J.-B.; Ashton, K.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective Organocatalysis Using SOMO Activation. Science 2007, 316, 582–585; (d) Kizirian, J.-C. Chiral Tertiary Diamines in Asymmetric Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 140–205; (e) Zhang, L.; Fu, N.; Luo, S. Pushing the Limits of Aminocatalysis: Enantioselective Transformations of α-branched β-ketocarbonyls and Vinyl Ketones by Chiral Primary Amines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 986–997.
- 3(a) Bandar, J. S.; Lambert, T. H. Cyclopropenimine-Catalyzed Enantioselective Mannich Reactions of tert-Butyl Glycinates with N-Boc-Imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11799–11802; (b) Yan, X.-X.; Peng, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, K.; Yao, J.; Hou, X.-L.; Wu, Y.-D. Highly Diastereoselective Switchable Enantioselective Mannich Reaction of Glycine Derivatives with Imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14362–14363; (c) Chen, J.; Gong, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Hou, C.; Zhao, G.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, B. Carbonyl Catalysis Enables a Biomimetic Asymmetric Mannich Reaction. Science 2018, 360, 1438–1442; (d) Gan, X.-C.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhong, F.; Tian, P.; Yin, L. Synthesis of Chiral Anti-1,2-Diamine Derivatives through Copper(I)-Catalyzed Asymmetric α-Addition of Ketimines to Aldimines. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4473–4480; (e) Kano, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Maruoka, K. Versatile in situ Generated N-Boc-Imines: Application to Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Asymmetric Mannich-Type Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8471–8474.
- 4(a) Zhu, Y.; Cornwall, R. G.; Du, H.; Zhao, B.; Shi, Y. Catalytic Diamination of Olefins via N–N Bond Activation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3665–3678; (b) Makai, S.; Falk, E.; Morandi, B. Direct Synthesis of Unprotected 2-Azidoamines from Alkenes via an Iron-Catalyzed Difunctionalization Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21548–21555; (c) Tan, G.; Das, M.; Kleinmans, R.; Katzenburg, F.; Daniliuc, C.; Glorius, F. Energy Transfer-Enabled Unsymmetrical Diamination Using Bifunctional Nitrogen-Radical Precursors. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 1120–1130; (d) Muñiz, K.; Barreiro, L.; Romero, R. M.; Martínez, C. Catalytic Asymmetric Diamination of Styrenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4354–4357; (e) Olson, D. E.; Su, J. Y.; Roberts, D. A.; Du Bois, J. Vicinal Diamination of Alkenes under Rh-Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13506–13509.
- 5(a) Mohiti, M.; Lu, Y.; He, H.; Ni, S.; Somfai, P. Regio- and Enantioselective Synthesis of 1,2-Diamines by Formal Hydroamination of Enamines: Scope, Mechanism, and Asymmetric Synthesis of Orthogonally Protected Bis-Piperazines as a Privileged Scaffold. Chem. – Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202303078; (b) Yu, L.; Somfai, P. Regio- and Enantioselective Formal Hydroamination of Enamines for the Synthesis of 1,2-Diamines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8551–8555; (c) MacDonald, M. J.; Hesp, C. R.; Schipper, D. J.; Pesant, M.; Beauchemin, A. M. Highly Enantioselective Intermolecular Hydroamination of Allylic Amines with Chiral Aldehydes as Tethering Catalysts. Chem. – Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2597–2601.
- 6(a) Trost, B. M.; Fandrick, D. R.; Brodmann, T.; Stiles, D. T. Dynamic Kinetic Asymmetric Allylic Amination and Acyl Migration of Vinyl Aziridines with Imido Carboxylates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6123–6125; (b) Chai, Z.; Yang, P. J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, G. Synthesis of Chiral Vicinal Diamines by Silver(I)-Catalyzed Enantioselective Aminolysis of N-Tosylaziridines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 56, 650–654; (c) Lee, S.; Jang, Y. J.; Phipps, E. J. T.; Lei, H.; Rovis, T. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Three-Component 1,2-Diamination of Unactivated Terminal Alkenes. Synthesis 2020, 52, 1247–1252.
- 7 Reetz, M. T.; Jaeger, R.; Drewlies, R.; Hübel, M. Stereoselective Synthesis of Vicinal Diamines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1991, 30, 103–106.
- 8(a) Galkin, K. I.; Krivodaeva, E. A.; Romashov, L. V.; Zalesskiy, S. S.; Kachala, V. V.; Burykina, J. V.; Ananikov, V. P. Critical Influence of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Aging and Decomposition on the Utility of Biomass Conversion in Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8338–8342;
(b) Dong, K. K.; Damaghi, N.; Kibitel, J.; Canning, M. T.; Smiles, K. A.; Yarosh, D. B. A Comparison of the Relative Antioxidant Potency of L-ergothioneine and Idebenone. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2007, 6, 183–188;
(c) Jin, A.; Feng, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Changes of the Toxic Potential of Drinking Water Containing Aminopyrine before and after Chlorine Disinfection as Determined by the Algal Toxicity Assay and the SOS/Umu Assay. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 269–275;
(d) Bartzatt, R. Potential Antineoplastic Structural Variations of Uracil Mustard (Uramustine) Retaining Cytotoxic Activity and Drug-Likeness Suitable for Oral Administration. JCTI 2015, 2, 50–58.
10.9734/JCTI/2015/17780 Google Scholar
- 9(a) Gopalaiah, K.; Kagan, H. B. Use of Nonfunctionalized Enamides and Enecarbamates in Asymmetric Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 4599–4657; (b) Tong, S.; Wang, D.-X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.-X. Enantioselective Synthesis of 4-Hydroxytetrahydropyridine Derivatives by Intramolecular Addition of Tertiary Enamides to Aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4417–4420; (c) Lei, C.-H.; Wang, D.-X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.-X. Synthesis of Substituted Pyridines from Cascade [1+5] Cycloaddition of Isonitriles to N-Formylmethyl- Substituted Enamides, Aerobic Oxidative Aromatization, and Acyl Transfer Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4708–4711; (d) Hu, N.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Tang, W. Synthesis of Chiral α-Amino Tertiary Boronic Esters by Enantioselective Hydroboration of α-Arylenamides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6746–6749; (e) Yang, H.; Carter, R. G.; Zakharov, L. N. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Lycopodine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9238–9239; (f) Beltran, F.; Miesch, L. Tertiary Enamides as Versatile and Valuable Substrates to Reach Chemical Diversity. Synthesis 2020, 52, 2497–2511; (g) Bernadat, G.; Masson, G. Enamide Derivatives: Versatile Building Blocks for Highly Functionalized α,β-Substituted Amines. Synlett 2014, 25, 2842–2867.
- 10(a) Xie, J.-H.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Enamines and Imines. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1713–1760; (b) Friedfeld, M. R.; Zhong, H.; Ruck, R. T.; Shevlin, M.; Chirik, P. J. Cobalt-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Enamides Enabled by Single-Electron Reduction. Science 2018, 360, 888–893; (c) Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Cobalt-Catalyzed Chemo- and Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Conjugated Enynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16989–16993; (d) Salomó, E.; Orgué, S.; Riera, A.; Verdaguer, X. Highly Enantioselective Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Cyclic Enamides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7988–7992; (e) Biosca, M.; Magre, M.; Pàmies, O.; Diéguez, M. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Disubstituted, Trisubstituted, and Tetrasubstituted Minimally Functionalized Olefins and Cyclic β-Enamides with Easily Accessible Ir−P,Oxazoline Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10316–10320; (f) Gao, M.; Meng, J.-J.; Lv, H.; Zhang, X. Highly Regio- and Enantioselective Synthesis of γ,δ-Unsaturated Amido Esters by Catalytic Hydrogenation of Conjugated Enamides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1885–1887; (g) Li, C.; Wan, F.; Chen, Y.; Peng, H.; Tang, W.; Yu, S.; McWilliams, J. C.; Mustakis, J.; Samp, L.; Maguire, R. J. Stereoelectronic Effects in Ligand Design: Enantioselective Rhodium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Aliphatic Cyclic Tetrasubstituted Enamides and Concise Synthesis of (R)-Tofacitinib. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13573–13583; (h) Zhang, J.; Jia, J.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gridnev, I. D.; Zhang, W. Chemo- and Enantioselective Hydrogenation of α-Formyl Enamides: An Efficient Access to Chiral α-Amido Aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11505–11512.
- 11(a) Jiang, H.; Huang, C.; Guo, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S. Direct C-H Functionalization of Enamides and Enecarbamates by Using Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis. Chem. – Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15158–15166; (b) Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Xia, C.; Li, F. Direct Oxidative Coupling of Enamides and 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds: A Facile and Versatile Approach to Dihydrofurans, Furans, Pyrroles, and Dicarbonyl Enamides. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5992–5995; (c) Guo, J.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Guan, T.; Mao, L.-W.; Ban, Q.; Zhao, K.; Loh, T.-P. Photoredox-Catalyzed Stereoselective Alkylation of Enamides with N-Hydroxyphthalimide Esters via Decarboxylative Cross-Coupling Reactions. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 8792–8798; (d) Guo, J.-Y.; Guan, T.; Tao, J.-Y.; Zhao, K.; Loh, T.-P. Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Alkylation of Enamides with Unactivated Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids via Decarboxylative Cross-Coupling Reactions. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8395–8399; (e) Tao, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Ni, K.; Zhu, T.-H.; Zhao, K. Transition-Metal-Free Regioselective and Stereoselective C(sp2)–C(sp3) Coupling of Enamides with Ethers or Alkanes via Photoredox-Catalyzed Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reactions. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4004–4011; (f) Guan, T.; Guo, J.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Xu, X.-W.; Yu, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K. Photoredox-Catalyzed Regio- & Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Cyanoalkylation of Enamides with Cycloketone Oximes via Selective C–C Bond Cleavage/Radical Addition Cascade. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 6524–6530; (g) Su, X.-D.; Zhang, B.-B.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.-T.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y. Additive-Free, Visible-Light-Enabled Decarboxylative Alkylation of Enamides. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 8262–8266.
- 12(a) Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, S. Visible-Light-Promoted and Photocatalyst-Free Trifluoromethylation of Enamides. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 195–198; (b) Rey-Rodriguez, R.; Retailleau, P.; Bonnet, P.; Gillaizeau, I. Iron-Catalyzed Trifluoromethylation of Enamide. Chem. – Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3572–3575; (c) Zhu, T.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Tao, J.-Y.; Zhao, K.; Loh, T.-P. Regioselective and Stereoselective Difluoromethylation of Enamides with Difluoromethyltriphenylphosphonium Bromide via Photoredox Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6155–6159; (d) Zhao, K.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Cui, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-X.; Wu, X.-D.; Li, W.-M.; Wu, J.-X.; Zhao, L.-L.; Guo, J.-Y.; Loh, T.-P. Visible-Light-Induced Regio- and Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Trifluoroethylation of Enamides with 2,2,2-Trifluoroethyl Iodide. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 9029–9035; (e) Zhao, K.; Guo, J.-Y.; Guan, T.; Wang, Y.-X.; Tao, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Ni, K.; Loh, T.-P. Photoinitiated stereoselective direct C(sp2)–H perfluoroalkylation and difluoroacetylation of enamides. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4086–4094.
- 13(a) Gigant, N.; Gillaizeau, I. Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Direct Alkenylation of Nonaromatic Enamides. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3304–3307; (b) Besset, T.; Kuhl, N.; Patureau, F. W.; Glorius, F. RhIII-Catalyzed Oxidative Olefination of Vinylic C-H Bonds: Efficient and Selective Access to Di-unsaturated α-Amino Acid Derivatives and Other Linear 1,3-Butadienes, Chem. – Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7167–7171; (c) Xu, Y.-H.; Chok, Y. K.; Loh, T.-P. Synthesis and Characterization of a Cyclic Vinylpalladium(II) Complex: Vinylpalladium Species as the Possible Intermediate in the Catalytic Direct Olefination Reaction of Enamide. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1822–1825; (d) Zhu, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.-X. Synthesis of 2,3-Dihydro-1H-azepine and 1H-Azepin-2(3H)-one Derivatives from Intramolecular Condensation between Stable Tertiary Enamides and Aldehydes. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12047–12057.
- 14(a) Stuart, D. R.; Alsabeh, P.; Kuhn, M.; Fagnou, K. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Arene and Alkene C−H Bond Functionalization Leading to Indoles and Pyrroles, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18326–18339; (b) Zhao, M.-N.; Ren, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Guan, Z.-H. Pd-Catalyzed Oxidative Coupling of Enamides and Alkynes for Synthesis of Substituted Pyrroles. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 608–611; (c) Feng, C.; Feng, D.-M.; Loh, T.-P. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Olefinic C–H Alkynylation of Enamides at Room Temperature. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9865–9868; (d) Li, B.; Wang, N.; Liang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, B. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Pyrrole Synthesis via Oxidative Annulation of Enamides and Alkynes. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 136–139.
- 15(a) Pankajakshan, S.; Xu, Y.-H.; Cheng, J. K.; Low, M. T.; Loh, T.-P. Palladium-Catalyzed Direct C-H Arylation of Enamides with Simple Arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5701–5705; (b) Gigant, N.; Chausset-Boissarie, L.; Belhomme, M.; Poisson, T.; Pannecoucke, X. Gillaizeau, I. Copper-Catalyzed Direct Arylation of Cyclic Enamides Using Diaryliodonium Salts. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 278–281; (c) Bartoccini, F.; Cannas, D. M.; Fini, F.; Piersanti, G. Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling (CDC) of N-Phthaloyl Dehydroalanine Esters with Simple Arenes: Stereoselective Synthesis of Z-Dehydrophenylalanine Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2762–2765.
- 16(a) Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.-C.; Tao, J.-Y.; Wu, X.-D.; Wu, J.-X.; Li, W.-M.; Zhu, T.-H.; Loh, T.-P. Regio- and Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Acylation of Enamides with Aldehydes via Transition-Metal-Free Photoredox Catalysis. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5497–5503; (b) Wang, H.; Guo, L.-N.; Duan, X.-H. Decarboxylative Acylation of Cyclic Enamides with α-Oxocarboxylic Acids by Palladium-Catalyzed C–H Activation at Room Temperature. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4358–4361.
- 17(a) Jiang, H.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.-Y. C-H Functionalization of Enamides: Synthesis of β-Amidovinyl Sulfones via Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2013, 355, 809–813; (b) Zhu, T.-H.; Zhang, X.-C.; Cui, X.-L.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Jiang, H.; Sun, S.-S.; Zhao, L.-L.; Zhao, K.; Loh, T.-P. Direct C(sp2)–H Arylsulfonylation of Enamides via Iridium(III)-Catalyzed Insertion of Sulfur Dioxide with Aryldiazonium Tetrafluoroborates, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 3593–3598; (c) Zhu, T.-H.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zhao, K.; Loh, T.-P. Cu(OTf)2-M Mediated C(sp2)–H Arylsulfonylation of Enamides via the Insertion of Sulfur Dioxide. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 94–98; (d) Sun, D.-L.; Zhang, R.-H. Transition-Metal-Free, Visible-Light-Induced Oxidative Cross-Coupling for Constructing β-Acetylamino Acrylosulfones from Sodium Sulfinates and Enamides. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 92–97; (e) Li, Y.; Cheng, K.; Lu, X.; Sun, J. A Facile and Efficient Approach to N-Protected-β-Sulfinylenamines via C-Sulfinylation of Enamides and Enecarbamates. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 1876–1880.
- 18(a) Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, C. Manganese(III) Acetylacetonate-Mediated Phosphorylation of Enamides at Room Temperature. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 3492–3496; (b) Pal, S.; Gaumont, A.-C.; Lakhdar, S.; Gillaizeau, I. Diphenyliodonium Ion/Et3N Promoted Csp2-H Radical Phosphorylation of Enamides. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5621–5625; (c) Tao, J.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Zhu, T.-H.; Xu, X.-W.; Ni, K.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, Z.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, K. Visible-Light-Initiated Regio- and Stereoselective C(sp2)–H Phosphorylation of Enamides under Transition-Metal-Free Conditions. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 6540–6546; (d) Fu, Q.; Bo, Z.-Y.; Ye, J.-H.; Ju, T.; Huang, H.; Liao, L.-L.; Yu, D.-G. Transition Metal-Free Phosphonocarboxylation of Alkenes with Carbon Dioxide via Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3592–3600; (e) Zhang, D.-L.; Li, C.-K.; Zeng, R.-S.; Shoberu, A.; Zou, J.-P. Manganese(iii)-Mediated Selective Phosphorylation of Enamides: Direct Synthesis of β-Phosphoryl Enamides. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 236–240.
- 19(a) Chen, M.; Ren, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Guan, Z.-H. Palladium-Catalyzed Oxidative Carbonylation of the Alkenyl C-H Bonds of Enamides: Synthesis of 1,3-Oxazin-6-ones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 14196–14199; (b) Zhang, Z.; Zhu, C.-J.; Miao, M.; Han, J.-L.; Lu, T.; Song, L.; Ye, J.-H.; Li, J.; Yu, D.-G. Lactonization of C(sp2)-H Bonds in Enamides with CO2. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 430–436; (c) Hesp, K. D.; Bergman, R. G.; Ellman, J. A. Expedient Synthesis of N-Acyl Anthranilamides and β-Enamine Amides by the Rh(III)-Catalyzed Amidation of Aryl and Vinyl C–H Bonds with Isocyanates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11430–11433; (d) Ju, T.; Fu, Q.; Ye, J.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, L.-L.; Yan, S.-S.; Tian, X.-Y.; Luo, S.-P.; Li, J.; Yu, D.-G. Selective and Catalytic Hydrocarboxylation of Enamides and Imines with CO2 to Generate α,α-Disubstituted α-Amino Acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13897–13901; (e) Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-N.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Ren, Z.-H.; Guan, Z.-H. Palladium-Catalyzed Oxidative Cyclopropanation of Enamides and Norbornenes Initiated by C–H Activation. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 695–701.
- 20(a) Jiang, H.; Studer, A. Chemistry with N-Centered Radicals Generated by Single-Electron Transfer-Oxidation Using Photoredox Catalysis. CCS Chem. 2019, 1, 38–49; (b) Pratley, C.; Fenner, S.; Murphy, J. A. Nitrogen-Centered Radicals in Functionalization of sp2 Systems: Generation, Reactivity, and Applications in Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 8181–8260; (c) Jiang, H.; Studer, A. Amidyl Radicals by Oxidation of α-Amido-Oxy Acids: Transition-Metal-Free Amidofluorination of Unactivated Alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10707−10711; (d) Miller, D. C.; Ganley, J. M.; Musacchio, A. J.; Sherwood, T. C.; Ewing, W. R.; Knowles, R. R. Anti-Markovnikov Hydroamination of Unactivated Alkenes with Primary Alkyl Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16590−16594; (e) Geunes, E. P.; Meinhardt, J. M.; Wu, E. J.; Knowles, R. R. Photocatalytic Anti-Markovnikov Hydroamination of Alkenes with Primary Heteroaryl Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 21738–21744; (f) Chinn, A. J.; Sedillo, K.; Doyle, A. G. Phosphine/Photoredox Catalyzed Anti-Markovnikov Hydroamination of Olefins with Primary Sulfonamides via α-Scission from Phosphoranyl Radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18331−18338; (g) Jiang, H.; Studer, A. Transition-Metal-Free Three-Component Radical 1,2-Amidoalkynylation of Unactivated Alkenes. Chem. – Eur. J. 2019, 25, 516–520; (h) Chen, J.; Guo, H.-M.; Zhao, Q.-Q.; Chen, J.-R.; Xiao, W.-J. Visible Light-Driven Photocatalytic Generation of Sulfonamidyl Radicals for Alkene Hydroamination of Unsaturated Sulfonamides. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6780−6783; (i) Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Gu, G.; Zhang, J. Visible Light Driven Copper(I) Catalyzed Oxyamination of Electron Deficient Alkenes. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1116–1122.
- 21(a) Rössler, S. L.; Jelier, B. J.; Magnier, E.; Dagousset, G.; Carreira, E. M.; Togni, A. Pyridinium Salts as Redox-Active Functional Group Transfer Reagents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9264–9280; (b) Yu, X.-Y.; Zhao, Q.-Q.; Chen, J.; Xiao, W.-J.; Chen, J.-R. When light meets nitrogen-centered radicals: from reagents to catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1066–1083; (c) Xiong, T.; Zhang, Q. New amination strategies based on nitrogen-centered radical chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3069–3087; (d) Chen, J.-R.; Hu, X.-Q.; Lu, L.-Q.; Xiao, W.-J. Visible light photoredox-controlled reactions of N-radicals and radical ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2044–2056; (e) Kärkäs, M. D. Photochemical generation of nitrogen-centered amidyl, hydrazonyl, and imidyl radicals: Methodology developments and catalytic applications. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4999–5022; (f) He, F.-S.; Ye, S.; Wu, J. Recent Advances in Pyridinium Salts as Radical Reservoirs in Organic Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 8943–8960; (g) Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Tang, M.; Ye, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, G. Recent Advances in Difunctionalization of Alkenes Using Pyridinium Salts as Radical Precursors. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 3847–3864; (h) Yang, Z.; Cao, K.; Peng, X.; Lin, L.; Fan, D.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, J. Micellar Catalysis: Visible-Light Mediated Imidazo[1,2-a] Pyridine C–H Amination with N–Aminopyridinium Salt Accelerated by Surfactant in Water. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3347–3352.
- 22(a) Mo, J.-N.; Yu, W.-L.; Chen, J.-Q.; Hu, X.-Q.; Xu, P.-F. Regiospecific Three-Component Aminofluorination of Olefins via Photoredox Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4471–4474; (b) Yu, W.-L.; Chen, J.-Q.; Wei, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xu, P.-F. Alkene Functionalization for the Stereospecific Synthesis of Substituted Aziridines by Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1948–1951; (c) Liu, W.-D.; Xu, G.-Q.; Hu, X.-Q.; Xu, P.-F. Visible-Light-Induced Aza-Pinacol Rearrangement: Ring Expansion of Alkylidenecyclopropanes. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6288–6291; (d) Yu, W.-L.; Jiang, H.-W.; Yan, L.; Feng, Z.-T.; Luo, Y.-C.; Xu, P.-F. Visible-Light Induced Generation of Bifunctional Nitrogen-Centered Radicals: A Concise Synthetic Strategy to Construct Bicyclo[3.2.1] Octane and Azepane Cores. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 274–280; (e) Chen, J.-Q.; Yu, W.-L.; Wei, Y.-L.; Li, T.-H.; Xu, P.-F. Photoredox-Induced Functionalization of Alkenes for the Synthesis of Substituted Imidazolines and Oxazolidines. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 243–249.
- 23 Miyazawa, K.; Koike, T.; Akita, M. Regiospecific Intermolecular Aminohydroxylation of Olefins by Photoredox Catalysis. Chem. – Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11677–11680.
- 24(a) Pan, C.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.-T.; Zhu, C. Organic Photoredox Catalytic Radical Sulfonamidation/Cyclization of Unactivated Alkenes towards Polycyclic Quinazolinones. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 6290–6294; (b) Pan, C.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.-T.; Zhu, C. Photo-Induced Cyclization of Olefinic Amides towards Sulfonamidylated Iminoisobenzofurans and Benzoxazines. Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 3479–3484; (c) Pan, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.-T.; Zhu, C. Substituent-Controlled Regioselective Photoinduced Cyclization of N-Allylbenzamides with N-Sulfonylaminopyridinium Salts. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 494–499.
- 25 Ma, T.-C.; Yao, S.; Qiao, M.-M.; Yuan, F.; Shi, D.-Q.; Xiao, W.-J. Photoredox-Mediated N-Centered Radical Addition/Semipinacol Rearrangement for the Convenient Synthesis of β-Amino (Spiro)Cyclic Ketones. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4224–4229.
- 26 Moon, Y.; Park, B.; Kim, I.; Kang, G.; Shin, S.; Kang, D.; Baik, M.-H.; Hong, S. Visible Light Induced Alkene Aminopyridylation Using N-Aminopyridinium Salts as Bifunctional Reagents. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4117–4125.
- 27 Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J. Selective 1,2-Aminoisothiocyanation of 1,3-Dienes Under Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4085–4089.
- 28Product 3va (CCDC 2277106) contains the crystallographic data for this paper. Other Z-configured enamides in Scheme 2 and Scheme 3 exhibit signals similar to 3va for its olefinic and benzylic hydrogens in 1H NMR.
- 29In consideration of the 81% deuterated ratio of 1a-d2, 0.185 mmol of 1a-d2 (a H-D mixture containing 81% deuterated enamide and 19% undeuterated one) was added along with 0.115 mmol of undeuterated enamide 1a in the same reaction vessel, so that the real amount of pure deuterated enamide (and its undeuterated competitor) was calculated to be 0.15 mmol approximately. The ratio of deuterated enamide 3aa-d1 vs 3aa in the isolated mixture was 34:66 as determined by 1H NMR, thus giving a calculated KH/KD = 0.66/0.34 = 1.94.




