Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Dual Responsive Magnetic DCR3 Nanoparticles: A New Strategy for Efficiently Targeting Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

Dual-Responsive Nanoparticles
Dual-responsive nanoparticles combine magnetic motion with chemotactic behavior, enabling precise navigation along DCR3-protein gradients in blood and tissue. This synergistic functionality significantly improves targeted drug delivery to cancer cells while reducing side effects, offering great potential for advancing cancer therapy. More in article number 2402909, Junjie Xu, Guangming Li, Lin Feng, and co-workers.
Inside Front Cover
Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Analysis of Genomic DNA Visualized with Nanoparticle-Tagged Peptides under Electron Microscopy (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

DNA Visualization
In article number 2405065, Byoungsang Lee, Kyubong Jo, Jung Heon Lee, and co-workers developed a novel staining method utilizing gold nanoparticle-tagged peptides, enabling genomic-scale, sequence-specific, and multi-conformational visualization of DNA molecules under an electron microscope. The stained DNA molecules undergo detailed structural and dimensional analysis through an artificial intelligence-enabled image analysis system. This comprehensive approach offers significant potential for applications in DNA sequence mapping and structural genomics.
Inside Back Cover
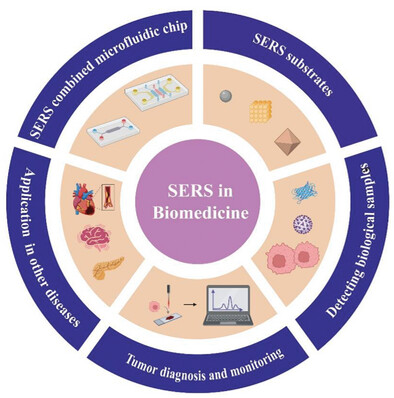
Innovative Applications and Perspectives of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Technology in Biomedicine (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

Surface-Enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) demonstrates significant potential in biomedicine. In article number 2409698, Tianan Jiang, Aiguo Wu, Jie Lin, and co-workers highlight recent advancements in using SERS for the precise diagnosis of chronic conditions such as tumors, myocardial infarction, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, the major challenges and potential solutions associated with these applications are discussed, offering insights into the future of SERS in the biomedical field.
Back Cover
Advanced Vitrimer with Spiropyran Beads: A Multi-Responsive, Shape Memory, Self-Healing, and Reprocessable Smart Material (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

Smart Materials
Epoxy vitrimers, based on dynamic covalent bonds, offer a recyclable alternative to traditional thermosets. In article number 2407022, Sung-Kon Kim, Jaewoo Kim, Yong-Seok Choi, and co-workers develop a self-healing and mechano-responsive vitrimer using epoxide spiropyran beads, enabling crack self-reporting via color or fluorescent changes. The vitrimer effectively exhibits additional properties, including shape memory, reconfiguration and reprocessability. Its smart properties suit applications like sensors, actuators, 4D printing, and safety diagnostics.
Issue Information
Correction
Comment
Enhanced Acidic CO2-to-C2+ Reduction via Ionic Liquid Layer Modification
- First Published: 24 February 2025
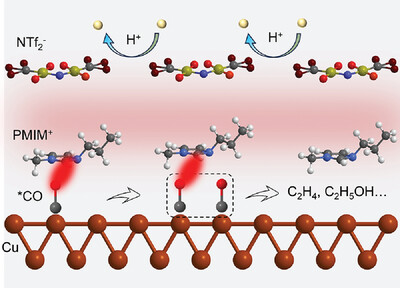
Construction of hydrophobic ionic liquid layer on the Cu surface strengthens *CO adsorption for robust acidic CO2 reduction. As such, the [PMIM][NTf2] modified Cu catalyst exhibits a partial current density of ≈640 mA cm−2 for C2+ products with faradaic efficiency of 80.1% and durability of ≈20 h at a partial current density exceeding 500 mA cm−2.
Frontispiece
Prospects of Improving Efficiency and Stability of Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells by Alumina Ultrathin Films (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

Perovskite Solar Cells
Presence of intrinsic defect states in the atomic layer deposited alumina on the hybrid perovskite films enables an easy charge transfer and neutralization at its interfaces with neighboring layers and thus the entire lifetime of the perovskite solar cells is improved and the occurrence of hysteresis in the current density–voltage characteristics of the perovskite solar cells is suppressed. More in article number 2408435, Malgorzata Kot and co-workers.
Perspective
Prospects of Improving Efficiency and Stability of Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells by Alumina Ultrathin Films
- First Published: 13 November 2024
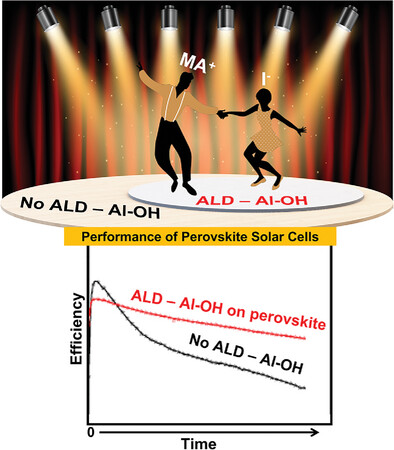
A subnanometer-thick atomic layer deposited alumina at room temperature is shown to be very effective in neutralizing mobile charges and maintaining high performance of perovskite solar cells during their long-term operation and storage. Thicker alumina films or those deposited at higher temperatures are nearly stoichiometric but are unfavorable for effective charge extraction and transfer due to stronger electrical insulation.
Review
Innovative Applications and Perspectives of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Technology in Biomedicine
- First Published: 28 November 2024
MOF-Derived Transition Metal Phosphides for Supercapacitors
- First Published: 25 February 2025
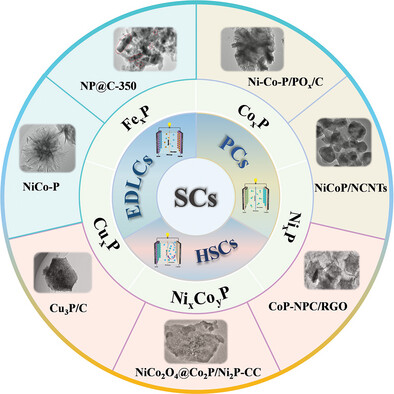
This review first introduces the energy storage mechanism of SCs and emphasizes the importance of electrode materials. Then, the latest research on MOF-derived TMPs as SCs electrode materials is summarized, including advancements in synthesis and structure modulation. Finally, the review provides a discussion of the application and challenges of MOF-derived TMPs in SCs.
Lithographic Innovations in the Development of Solid Oxide Cells: Techniques, Advancements, and Prospects
- First Published: 24 February 2025
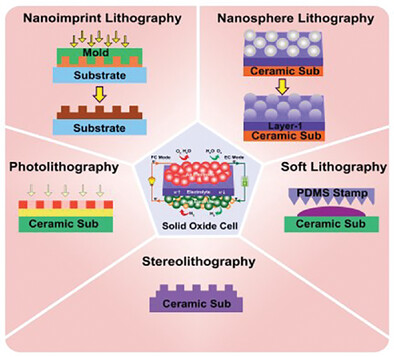
Here how lithographic techniques advance solid oxide cells (SOCs) by enabling precise micro- and nanoscale patterning and fabrication is highlighted. These improvements enhance conductivity, reducing operating temperatures, and addressing material degradation. Scalability challenges and fabrication defects are also covered, while exploring future advancements to improve SOC efficiency for commercial clean energy applications.
Enhancing Performance of NiOx-Based Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells: Advances in Buried Interface Material Modification Strategy
- First Published: 13 February 2025
Advances in the Catalytic Mechanism of Metal Oxides for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 14 February 2025
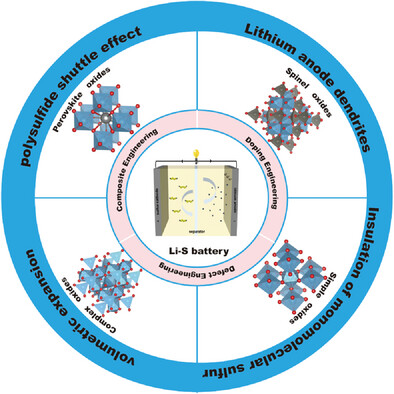
The working principle and key challenge of Li–S batteries are first introduced to highlight the crucial role of catalytic conversion of polysulfides. The catalysts design concept and recent progress in the reaction mechanism of metal oxide catalysts in Li–S batteries are further emphatically discussed for guiding the development of polysulfide catalysts.
Amorphous/Crystalline Heterostructured Nanomaterials: An Emerging Platform for Electrochemical Energy Storage
- First Published: 28 February 2025
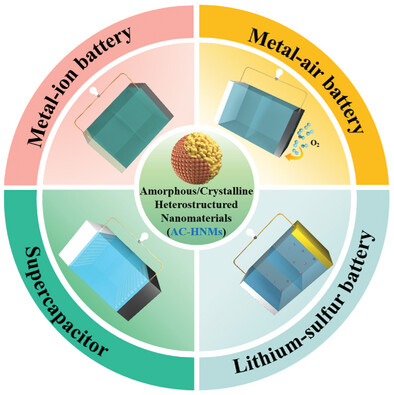
This is a comprehensive review of amorphous/crystalline heterostructured nanomaterials (AC-HNMs), highlighting their synthesis strategies and applications in electrochemical energy storage devices, including metal-ion batteries, metal–air batteries, lithium–sulfur batteries, and supercapacitors. The structure–activity relationships among amorphous/crystalline heterostructure, performance, and mechanism are thoroughly analyzed. Challenges and future perspectives for the optimization of AC-HNMs are also proposed.
Design and Modification of Layered Double Hydroxides-Based Compounds in Electrocatalytic Water Splitting: a Review
- First Published: 21 February 2025
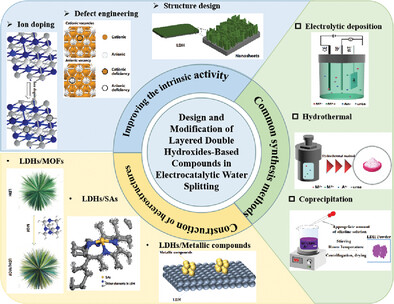
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) exhibit great potential in electrocatalytic water splitting. Herein, the design and modification of LDH-based compounds in electrocatalytic water splitting are systematically summarized. The basic properties and commonly used preparation methods of LDHs are introduced. The electrocatalytic performance of LDHs in oxygen evolution reaction, hydrogen evolution reaction, and overall water splitting is discussed in detail. The advanced strategies for improving LDH performance, as well as challenges and future prospects, are also provided.
Advancements in Chemical Vapor Deposited Carbon Films for Secondary Battery Applications
- First Published: 21 February 2025
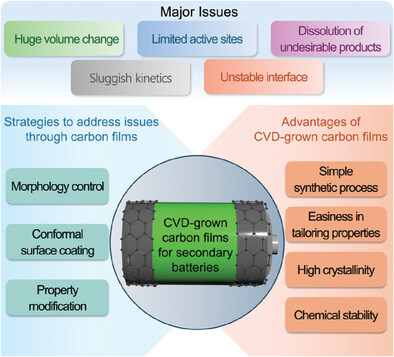
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)-grown carbon films offer significant advantages for secondary battery applications. This review discusses the tunable morphology, structural properties, and electrochemical performance of carbon films in batteries, covering their role in cathodes, anodes, and current collectors, and highlighting potential applications in advanced battery systems such as lithium-sulfur and all-solid-state batteries.
Nanomaterial-Triggered Ferroptosis and Cuproptosis in Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 28 February 2025
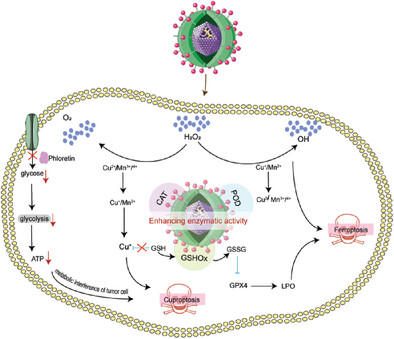
Several nanomaterials serve as inducers for ferroptosis and cuproptosis, two regulated cell death pathways with emerging applications in cancer therapy. This review article explores the mechanisms of nanomaterial-induced ferroptosis and cuproptosis, their advantages over conventional treatments, and the challenges in clinical translation, highlighting their promise for precision oncology.
Chiral Biomineral Structures: Synthesis and Inspiring Functional Materials
- First Published: 21 February 2025
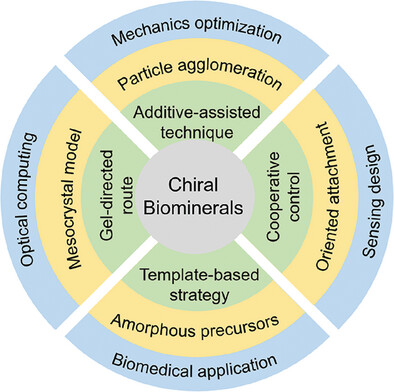
This review focuses on the synthesis and inspiring functional materials from the chiral biominerals. The additive-assisted and template-oriented strategies can regulate the chiral minerals through the intermolecular interaction, and gel-based limited space prompts the chiral morphology or structure evolution. The inspirations from the chiral functional materials on the mechanics optimization and sensing design are also presented.
Frontispiece
Facile Construction of Soft Plasmonic Sensors with Exceptional Optical Activity for Quantitative Chiral Detection (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

Soft Plasmonic Sensors
In article number 2408176, Xichong Ye, Feng Liu, and co-workers propose a facile strategy for fabricating flexible polymer-plasmon hybrid films. These films exhibit ultrastrong and broadband circular dichroism (200–2500 nm) upon twisted stacking. The optical activity is highly sensitive to intervening medium, enabling efficient chiral detection of various analytes.
Research Article
Facile Construction of Soft Plasmonic Sensors with Exceptional Optical Activity for Quantitative Chiral Detection
- First Published: 09 December 2024
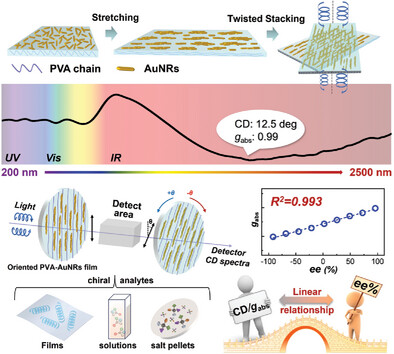
A one-step, stretch-induced orientation method efficiently arranges gold nanorods (AuNRs) on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) substrates. By twisting these oriented hybrid films, soft chiral plasmonic devices with ultrastrong optical activity (ellipticity≈104 mdeg, gabs≈1) across 200–2500 nm can be developed, enabling quantitative, non-destructive, non-contact, and reusable chiral sensing across various states of matter.
Frontispiece
Dynamically Tunable Chiroptical Activities of Flexible Chiral Plasmonic Film via Surface Buckling (Small 12/2025)
- First Published: 26 March 2025

Plasmonic Films
A flexible chiral plasmonic film composed of asymmetrical 3D “S-liked” assembly of plasmonic nanoparticles is achieved, facilitated by mechanically induced surface wrinkling of the elastic polymeric substrate. The structure exhibits a strong circular dichroism (CD) response up to 2.5 degrees and a g-factor of 0.11in NIR region, along with dynamically modulated CD properties, including switchable CD handedness and tunable intensity. More in article number 2407635, Kun Liu, Chunhong Ye, and co-workers.
Research Article
Dynamically Tunable Chiroptical Activities of Flexible Chiral Plasmonic Film via Surface Buckling
- First Published: 15 December 2024
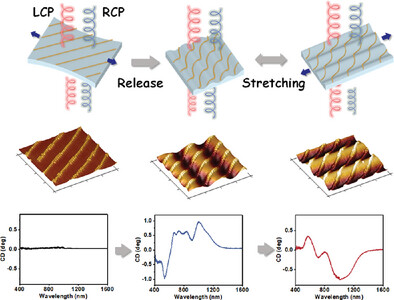
Flexible chiral plasmonic films, featuring a high-order array of “S-liked” chiral assemblies of gold nanospheres, are realized through mechanically induced surface wrinkling of elastomeric polymers. These chiral plasmonic structures exhibit not only strong CD signal and high g-factor, but also the capability for dynamic and reversible tuning of chiroptical properties over intensity and handedness switching across the vis-to-NIR range.
Dual Responsive Magnetic DCR3 Nanoparticles: A New Strategy for Efficiently Targeting Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- First Published: 27 November 2024
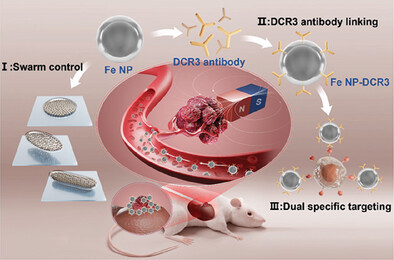
Decoy receptor 3 (DCR3) is prominently expressed in cancer cells and can specifically bind to DCR3 antibodies. Magnetically controlled drug delivery micro/nanorobots offer significant improvements in drug dosage at the targeted site. In this study, dual-responsive nanoparticles that exhibit both magnetically driven motion and chemotactic behavior are developed. These nanoparticles can navigate along the DCR3-protein gradient, highlighting their potential for targeted drug delivery.
Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Analysis of Genomic DNA Visualized with Nanoparticle-Tagged Peptides under Electron Microscopy
- First Published: 09 October 2024
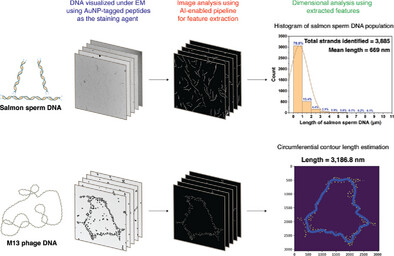
A novel staining method using gold nanoparticle-tagged peptides has been developed, enabling genomic-scale, sequence-specific, and multi-conformational visualization of DNA molecules under an electron microscope (EM). They are then extensively analyzed for their structural and dimensional features through an artificial intelligence-enabled image analysis system. This comprehensive pipeline holds promise as a valuable tool with potential applications in DNA sequence mapping.
Advanced Vitrimer with Spiropyran Beads: A Multi-Responsive, Shape Memory, Self-Healing, and Reprocessable Smart Material
- First Published: 21 October 2024
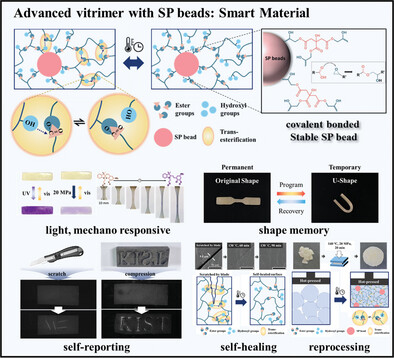
Epoxy vitrimers, based on dynamic covalent bonds, offer a recyclable alternative to traditional thermosets. This research develops a self-healing and mechano-responsive vitrimer using epoxide spiropyran beads, enabling crack self-reporting via color or fluorescent changes. The vitrimer effectively exhibits additional properties, including shape memory, reconfiguration, and reprocessability. Its smart properties suit applications like sensors, actuators, 4D printing, and safety diagnostics.
High-Performance Broad-Spectrum UV Photodetectors with Uniform Response: Engineering β-Ga2O3:Si/GaN:Si Heterojunctions via Thermal Oxidation for Optoelectronic Logic Gate and Multispectral Imaging
- First Published: 01 December 2024
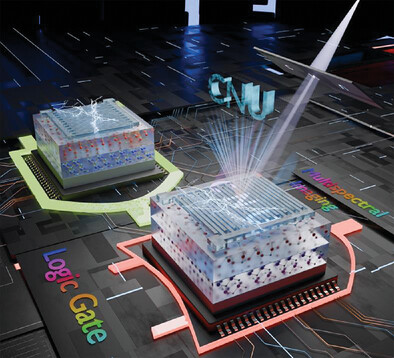
A study on n-n type β-Ga2O3/GaN:Si heterojunction photodetectors reveals an exceptional UV response from UV-A to UV-C. The thermal oxidation process, involving hole formation, vortex structure development, channel formation, and grain growth, achieves uniform Si doping and significantly enhances device performance. These photodetectors demonstrate high sensitivity, uniformity, and superior performance, with applications in optoelectronic logic gates and multispectral imaging.
Room-Temperature CsPbI3-Quantum-Dot Reinforced Solid-State Li-Polymer Battery
- First Published: 10 January 2025
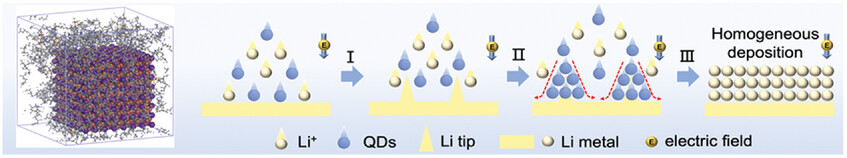
A novel CsPbI3 quantum dots reinforced polyacrylonitrile (PAN) polymer solid-state electrolyte (PIL) is developed to address the issues of low Li-ion conductivity and small transference number of PAN electrolyte through Lewis acid–base interaction, ordered polarization of PAN, and interface chemical regulation. Consequently, all-solid-state Li|PIL|LFP and Li|PIL|NCM batteries exhibit good rate-capability, long-term cyclability, and very high Coulombic efficiency at room-temperature.
Turn the Harm into A Benefit: Axial Cl Adsorption on Curved Fe-N4 Single Sites for Boosted Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Seawater
- First Published: 26 February 2025
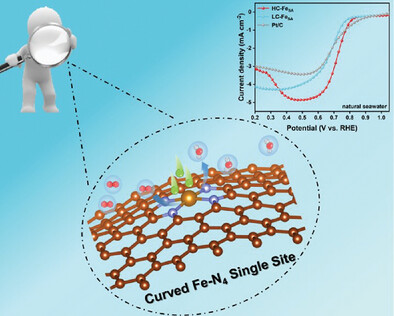
It has been confirmed both experimentally and theoretically that the curvature effect can optimize the electronic structure of FeN4 sites, turning harmful Cl adsorption into an advantage on Fe single sites in seawater. By increasing the curvature configuration, optimal ORR activity can be achieved for Fe single-atom catalysts (HC-FeSA), providing high half-wave potentials in natural seawater media.
Intranasal Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Neuronal PANoptosis via Microglial Pathway
- First Published: 26 February 2025
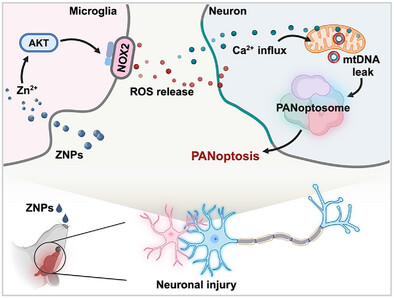
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZNPs) are widely used nanomaterials that pose a notable health risk, particularly due to potential respiratory exposure during their manufacturing and application processes. The study elucidates that ZNPs when administered intranasally, gain access to the brain and initiate neuronal PANoptosis. Importantly, the findings underscore the pivotal role of the intricate crosstalk between microglia and neurons in mediating this pathological process.
"Bifunctional Strontium-Iron Doped Neodymium Cobaltite: A Promising Electrocatalyst for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and CO2 Electrolyzer"
- First Published: 21 February 2025
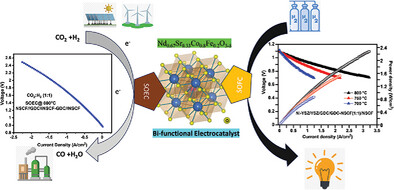
This graphical abstract presents Nd₀.₆₇Sr₀.₃₃Co₀.₈Fe₀.₂O₃-δ (NSCF) as a bi-functional electrocatalyst for solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) and solid oxide electrolysis cell (SOEC) applications. It facilitates the reverse water-gas shift reaction in SOEC mode using renewable electricity, with CO + H₂O product serving as feedstock for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. i-V and i-P curves illustrate performance in both modes.
Crystalline Structural Engineering of an Electrical Insulator Into A Highly-Active Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution
- First Published: 26 February 2025
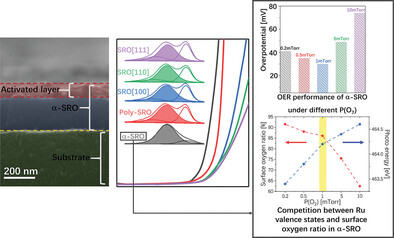
This study demonstrates the fabrication of amorphous SRO films on GC substrates via pulsed laser deposition, revealing superior OER catalytic activity compare to crystalline counterparts. The influence of oxygen partial pressure on OER performance is systematically explored, showing that oxygen vacancies and active site valence regulate activity. Amorphous SRO also exhibits a self-adaptive process, highlighting its potential for high-performance catalyst design.
Reversible Microadhesives with Good Adhesion Anisotropy via Dual-Gradient Modulus Constructing
- First Published: 25 February 2025
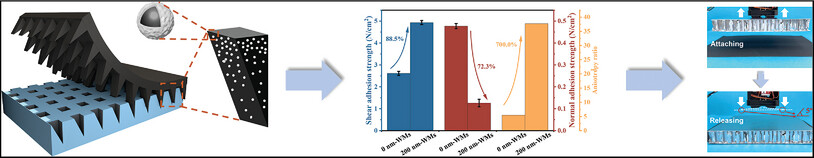
The wedged microadhesives (WMs) with dual-gradient modulus are fabricated, which not only achieved structural stability and compliance but also balanced strong adhesion with easy detachment. The designed mechanism, with its excellent anisotropic adhesion, enables stable attachment and on-demand rapid release, demonstrating significant potential for applications in on-orbit servicing technologies.
Constructing Artificial Zincophilic Interphases Based on Indium–Organic Frameworks as Zinc Dendrite Constraint for Rechargeable Zinc–Air Battery
- First Published: 26 February 2025
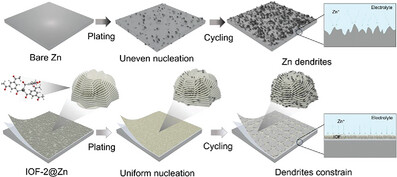
An artificial solid–electrolyte interphase (SEI) based on indium–organic frameworks (IOFs) is developed to enhance Zn–air battery performance. The IOF, featuring zincophilic In3⁺ sites and nanosheets-assembled microspheres with a porous architecture, provides chemical and physical constraints on Zn dendrites. This SEI regulates Zn plating and extends battery life to 800 h—four times longer than pristine Zn anodes.
Regulation of Electron and Mass Transport Pathways in Efficient and Stable Low-Loading PEM Water Electrolyzers
- First Published: 26 February 2025
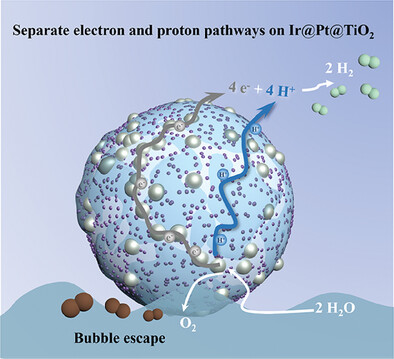
A novel strategy concerning the catalyst-ionomer interface is devised to separate the transport pathways for electrons, protons, and bubbles. The continuous ionomer and metal networks demonstrate significantly enhanced performance and stability in the oxygen evolution reaction, presenting promising prospects for practical applications in low-loading PEM water electrolyzers.
Ultrasensitive Bi-Mode Lateral-Flow Assay via UCNPs-Based Host-Guest Assembly of Fluorescent-Colorimetric Nanoparticles
- First Published: 04 March 2025
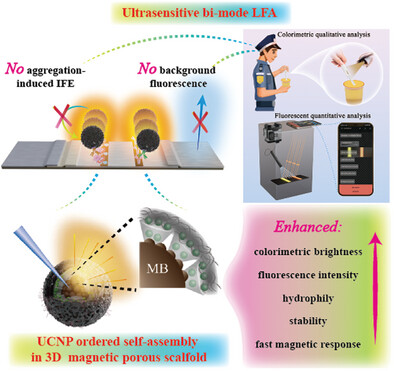
A novel “colorimetric@fluorescent@magneto” core-shell structure (MSUD) is reasonably designed with improved hydrophilicity, loading efficiency, luminescence stability, and intensity. Moreover, it eradicates the internal filtration effect and fluorescence background interference on LFA strips. Based on it, a dual-mode LFA is developed with the LOD as low as 2116 times that of gold nanoparticle LFA.
Electronic Structure Tunable Metallosupramolecular Polymers as Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Rechargeable Zn-Air Battery
- First Published: 28 February 2025
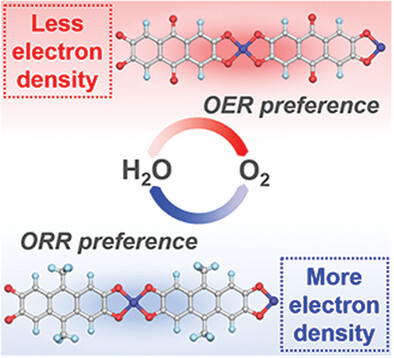
Metallosupramolecular polymers have been prepared as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts with different oxygen electrocatalytic preferences by adjusting the electronic structure of organic linkers. The electronic effects of the linkers effectively modulate the charge density of the metal site and optimize the formation of the key intermediate, controlling the preference for oxygen electrocatalysis.
Supramolecular Synthesis of Dithienylethene-Albumin Complexes for Enhanced Photoswitching In Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Near-Infrared Photothermal Therapy
- First Published: 26 February 2025
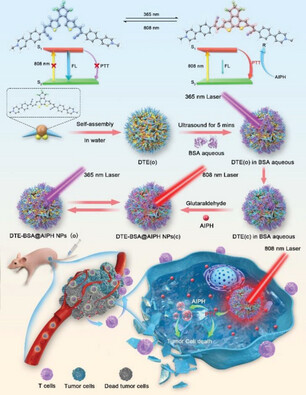
NIR-excitable photoswitchable dithienylethenes (DTEs) are synthesized for enhancing photoacoustic imaging (PAI) and photothermal therapy (PTT). When assembled with albumin and combined with a thermal initiator, these DTEs show efficient NIR absorption, reversible photoswitching, and synergistic PTT and chemodynamic therapy (CDT) for effective tumor treatment and metastasis prevention.
A Rocking-Chair Type Aqueous Nickel–Organic Battery with Azobenzene Anode
- First Published: 26 February 2025
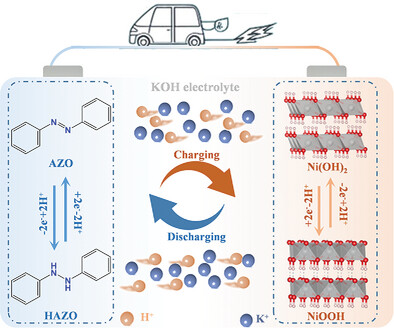
An aqueous nickel-organic battery is developed with azobenzene anode and Ni(OH)2 cathode. This battery operates based on “rocking-chair” mechanism and protons serve as charge carriers. Benefiting from the small ionic radius and fast transport of protons, the battery provides excellent rate performance (release 93.2% theoretical capacity within 33 s) and superb long-cycle stability (maintain 92.5% capacity retention after 10 000 cycles).
Carbon Molecular Sieve Membranes Derived From Dual-Cross–linked Polybenzimidazole for Enhanced H2/CO2 Separation
- First Published: 10 February 2025
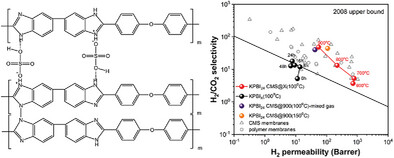
This study presents a novel dual-cross–linking approach using potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) to enhance H2/CO2 separation in polybenzimidazole (PBI)-derived carbon molecular sieve (CMS) membranes. The CMS membrane prepared from PBI cross-linked with K2S2O8 for 24 h and pyrolyzed at 900 °C (donated as KPBI24 CMS@900) demonstrates exceptional performance, achieving an H2 permeability of 55 Barrer and an H2/CO2 selectivity of 48 at 100 °C, far surpassing the 2008 Robeson upper bound. This work offers a robust and effective strategy for advancing molecular selective membranes for high-efficiency hydrogen purification.
Oxygen-Doped γ-Mo2N as High-Performance Catalyst for Ammonia Decomposition
- First Published: 16 February 2025
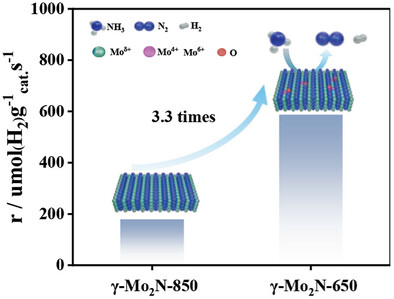
A relatively high oxygen content γ-Mo2N catalyst is synthesized for H2 production from ammonia decomposition. The H2 formation rate of γ-Mo2N-650 is 3.3 times that of γ-Mo2N-850 at 550 °C. This is mainly attributed to stronger NH3 adsorption, stronger hydrogen species migration, and desorption ability of γ-Mo2N-650 with high oxygen content.
Facile and Ultrafast Microfluidic Photothermal PCR for Autonomous and Quantitative Point-of-Care Pathogen Detection
- First Published: 13 February 2025
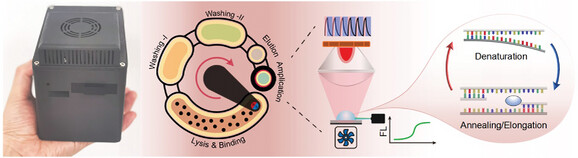
This work describes a novel platform to address the challenge in transforming fast photonic polymerase chain reaction (PCR) into low-cost and rapid point-of-care diagnostics. This platform uses a cheap black tape as a fast photothermally-responsive heater to attach to a magnetically-driven sample-to-answer microfluidic cartridge, thereby enabling to combine the advantages of microfluidic assay and photonic PCR.
Double-Phase Ga-Doped In2O3 Nanospheres and Their Self-Assembled Monolayer Film for Ultrasensitive HCHO MEMS Gas Sensors
- First Published: 17 February 2025
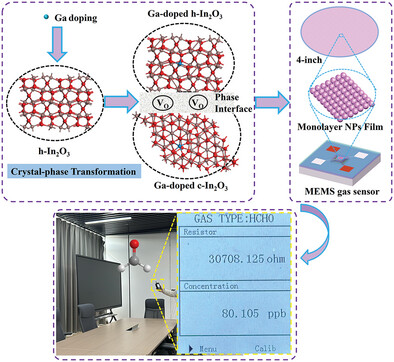
By Ga doping, rhombohedral In2O3 is transformed to form the double-phase Ga-doped In2O3 with the tunable electronic structure, and then a universal approach is developed for mass production of high-consistency and ultra-sensitive MEMS HCHO gas sensors with monolayer sensing film. A handheld detector provides real-time monitoring of ppb-level HCHO in the renovated house.
A Hyperstable Aqueous Zinc-Ion Battery Based on Mo1.74CTz MXene
- First Published: 18 February 2025
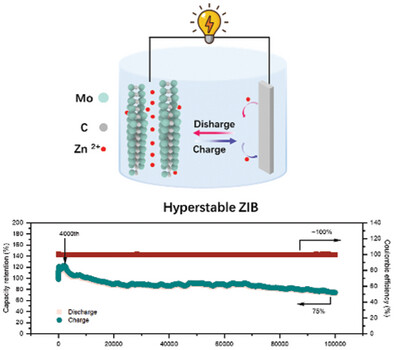
A defect-engineered Mo1.74CTz MXene-based zinc-ion battery achieves high capacity as well as 75% capacity retention and nearly 100% Coulombic efficiency even after up to 100 000 cycles. The mechanism of hyperstability is revealed to be the intrinsic structural stability and abundant vertical holes of the Mo1.74CTz MXene, which contribute to alleviating the collapse of MXene under repeated charge and discharge.
Self-Powered Linear Pressure Sensor Based on MXene/CNT Nanofluid Membrane
- First Published: 12 February 2025
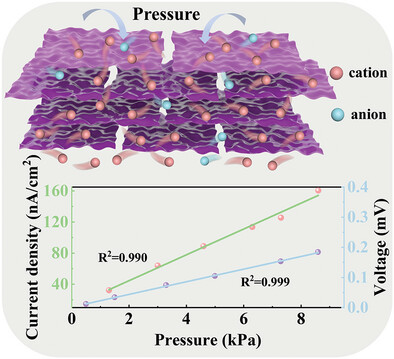
The MXene/CNT nanofluid membrane is fabricated, which can realize the conversion of pressure to electricity. The sensor based on the membrane realizes self-powered characteristics and demonstrates good linearity between the input pressure signal and output electrical signal. In addition, the self-powered linear sensor can be used to monitor body movements and detect sound.
Enhancing Kinetic Performance and Structural Stability of Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) Cathode via La Doping Defect Engineering
- First Published: 25 February 2025
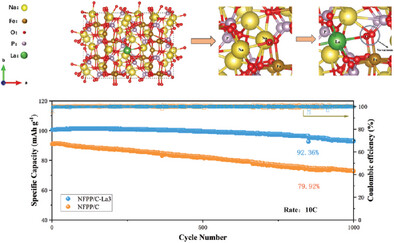
In this work, a doping modification strategy of selecting La3+ with a large ion radius at the Na site has been designed, and the nano-micro architectural Na3.91La0.03□0.06Fe3P2O7(PO4)2/C (NFPP/C-La3) cathode material with Na vacancies is successfully synthesized via the mechanical activation solid-state method. Consequently, the diffusion energy barrier of Na+ has been lowered, and La3+ also acts as a pillar to reduce lattice stress, stabilizing the crystal structure during long cycling. The excellent rate performance (99.45 mAh g−1 at 20 C) and long-term cycle stability (92.36% capacity retention over 1000 cycles at 10 C) are achieved.
Mn0.75Ru0.25O2 with Low Ru Concentration for Active and Durable Acidic Oxygen Evolution
- First Published: 16 February 2025
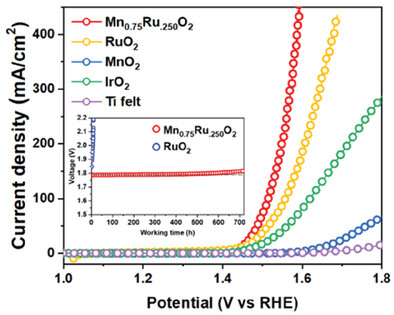
An asymmetrical Mn-O-Ru active center integrated into rutile Mn0.75Ru0.25O2 achieves active and durable acidic oxygen evolution. Benefiting from the electron redistribution between Mn and Ru and the stabilized lattice oxygen, the electrocatalyst works at 1 A cm−2 for 700 h with a low degradation rate of 53 uV h−1.
Highly Deformable Van der Waals Chalcogenides with Superior Thermoelectric Performance from Interpretable Machine Learning
- First Published: 18 February 2025
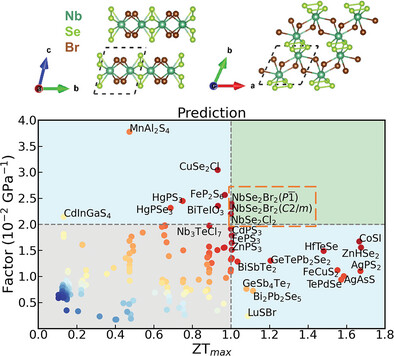
In this study, over 1000 van der Waals layered chalcogenides are high-throughput screened for flexible thermoelectric applications. Deformability factor and machine learning model are used to accurately predict the performance. NbSe2Br2 is identified as a top candidate, achieving a ZTmax of 1.35 at 1000 K and a power factor of 8.1 µW cm−1 K−2 at 300 K, surpassing most flexible thermoelectric materials.
Whole-Component Antigen Nanovaccines Combined With aTIGIT for Enhanced Innate and Adaptive Anti-tumor Immunity
- First Published: 18 February 2025
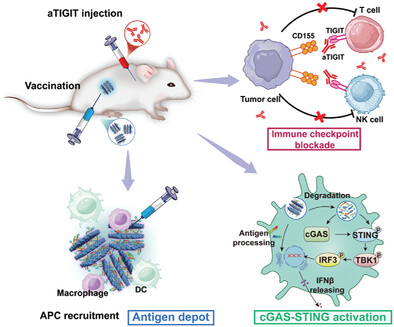
The MMAT nanovaccine is fabricated by MA, TLs, and Mn2+ through electrostatic interaction. It can effectively form antigen reservoirs in situ at the site of administration, thereby recruiting antigen-presenting cells to take up antigens and promoting APCs maturation and cGAS-STING pathway activation. In addition, aTIGIT is combined to relieve T-cell and NK-cell exhaustion, which together with the nanovaccine induces a robust and durable innate and adaptive immune response, inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis.
Oxygen Modulation by Ni Metal Sites in Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Resins for Boosted Photocatalytic H2O2 Production From Pure Water
- First Published: 18 February 2025
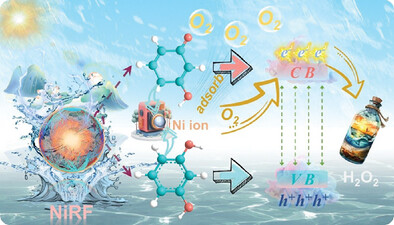
The potential of using polymeric catalysts for the photocatalytic generation of H2O2 for various industrial applications is limited by their low oxygen adsorption and activation capabilities. The incorporation of nickel doping into the resin provides active sites conducive to the transformation of oxygen. Enhancing the adsorption capacity of NiRF for O2 and ensuring a suitable adsorption configuration and energy.
Linkage Engineering of Semiconductive Covalent-Organic Frameworks toward Room-Temperature Ppb-Level Selective Ammonia Sensing
- First Published: 16 February 2025
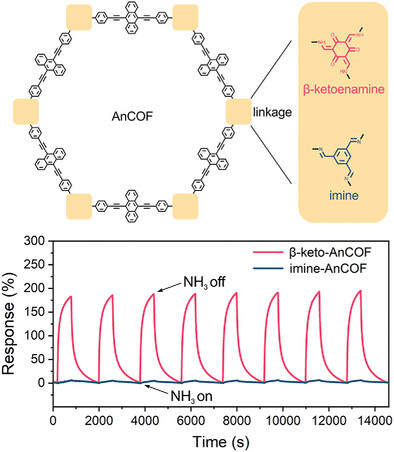
Two isostructural covalent-organic frameworks (COFs), β-keto-AnCOF with ─C═O and imine-AnCOF without ─C═O, are constructed with the same conjugated backbones but different side functional groups via linkage engineering. β-keto-AnCOF shows far superior room-temperature ppb-level ammonia (NH3) sensing performance than imine-AnCOF owing to the additional charge transfer between NH3 molecules and the ─C═O sites.
Water-Dynamics Monitoring Using a Flexible Resistive Sensor and Reservoir Computing
- First Published: 13 February 2025
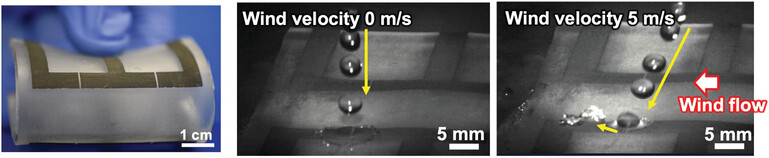
This study reveals the sensing mechanism of water dynamics using a pair of superhydrophobic electrodes analyzed by the vertical impact energy systematically and estimates water droplet volume and wind velocity at different sensor tilt angles using an echo state network by monitoring water droplets dynamics upon contact with an object.
Membrane Fusion-Based Drug Delivery Liposomes Transiently Modify the Material Properties of Synthetic and Biological Membranes
- First Published: 25 February 2025
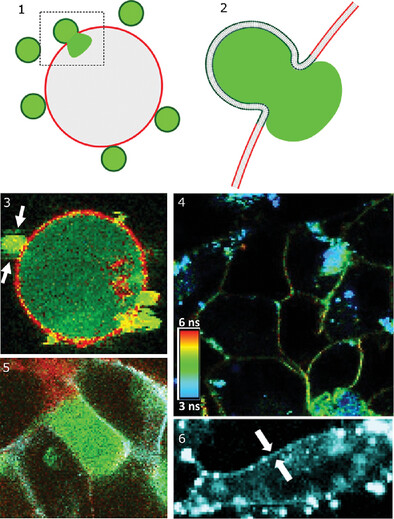
The table of content summarizes the main development and findings of this study. Fusion of small liposomes with acceptor model or biomembranes modify the material properties of these membranes. In sketch 1, several liposomes interacting with an acceptor model vesicle. A single fusion event is shown and highlighted in sketch 2, showing lipid and content mixing. Sketches 3 and 4 show content mixing results in transfer of entrapped cargo to lipid vesicles and living cells, respectively. Docked liposomes are shown (arrows). In sketch 5, FLIM images showing that fusion fluidizes cell membranes and internalizes excess of lipids. In sketch 6, the arrows point to the labeled plasma membrane after liposome fusion with cells.
Near-infrared Emission Carbon Dots Derived from Bromo-Substituted Perylene Derivatives with Simultaneously High Type I/II ROS Generation for Effective Bacterial Elimination and Tumor Ablation
- First Published: 17 February 2025
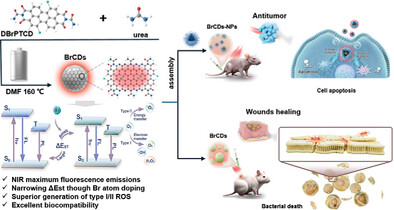
This study introduces bromine-doped CDs with NIR absorption and emission (peak >700 nm), enhancing tissue penetration and ROS generation (types I and II) for PDT. These nanomaterials demonstrate high efficacy in antibacterial and antitumor applications, showing significant therapeutic potential for treating skin infections and tumors in complex, oxygen-varied microenvironments.
High-Performing Nanofiber Memristor via Field-Induced Ion Migration Concentration at Highly-Curved Interwoven Interface
- First Published: 16 February 2025
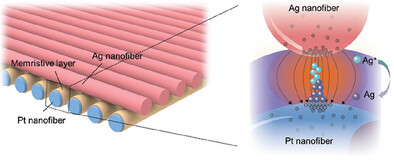
A high-performing nanofiber memristor with a highly-curved interface structure is prepared by dielectrophoretic assembling nanofiber electrodes. The nanofiber memristor exhibits high operation uniformity with an ultralow set voltage standard deviation of 0.014 V, benefiting from the local enhancement of electric field and confined growth of conductive filaments at the nanofiber junction.
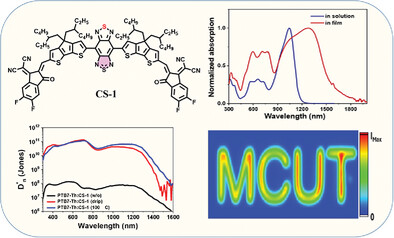
Efficient SWIR Organic Photodetectors with Spectral Detection Extending to 1.4 µm Using a Benzobisthiadiazole-Based Acceptor
- First Published: 11 February 2025
Flexible Temperature Sensor with 2D In2Se3 Ferroelectric-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor Exhibiting Record High Sensitivity
- First Published: 11 February 2025
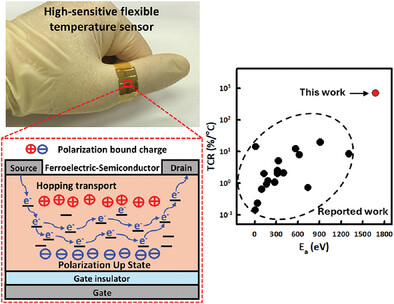
A temperature sensor with In2Se3 ferroelectric-semiconductor field-effect transistor exhibits the record high thermal sensitivity of 696%/°C. Integration of ferroelectricity and semiconducting behavior of In2Se3 can give a highly sensitive thermal response. The flexible In2Se3 temperature sensor shows a hysteresis-free and stable real-time temperature sensing ability.
Upcycling of Multi-Metal Contaminated Wastewater into High-Entropy Layered Double Hydroxide for Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 12 February 2025
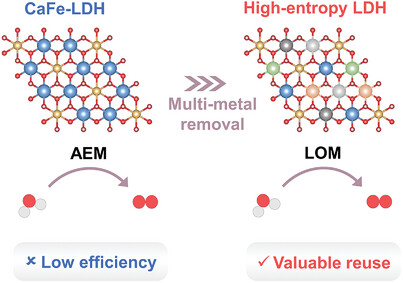
The CaFe exhibits efficient mixed metals removal of Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+, resulting in the formation of CaCoNiCuZnFe high-entropy LDH through Ca2+ substitution. This leads to lattice distortion and the generation of metal vacancies, enhancing the OER performance of CaCoNiCuZnFe. The CaCoNiCuZnFe achieves 250 h of stable performance without secondary pollution, highlighting LDH's potential in treating multi-metals solutions and resource utilization.
Tradeoff between Mechanical Strength and Electrical Conductivity of MXene Films by Nacre-Inspired Subtractive Manufacturing
- First Published: 12 February 2025
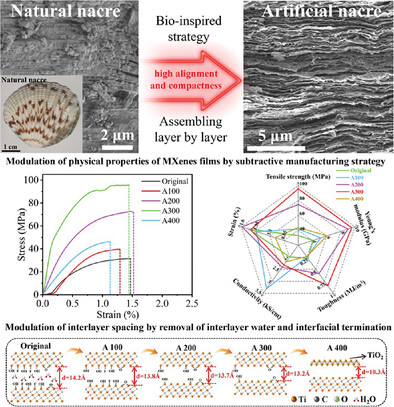
MXene films improve mechanical properties and conductivity by adding binders. However, it is difficult to investigate the dominant relationship between the mechanical properties of nanosheet bricks and interlayer van der Waals forces due to the multi-component system. Here, the study constructs pure subtractively manufactured MXene films through layer-by-layer self-assembly and negative pressure vacuum annealing. The complicated interaction mechanisms are revealed on cross-scales.
Dual-Functional Benzotrithiophene-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Photocatalytic Detoxification of Mustard Gas Simulants and Antibacterial Defense
- First Published: 17 February 2025
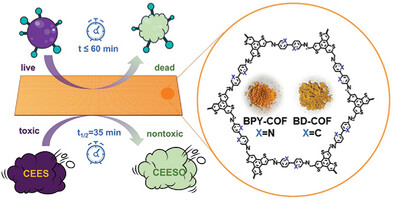
This study introduces two benzotrithiophene-based COFs, BPY-COF, and BD-COF, as dual-functional photocatalysts for mustard gas detoxification and antibacterial defense. With broad-spectrum light absorption, enhanced ROS generation, and excellent efficiency, BPY-COF achieves ultrafast chemical detoxification and robust antibacterial activity, demonstrating its potential for environmentally sustainable applications in mitigating chemical and biological threats.
A Copper-Manganese Based Nanocomposite Induces Cuproptosis and Potentiates Anti-Tumor Immune Responses
- First Published: 16 February 2025
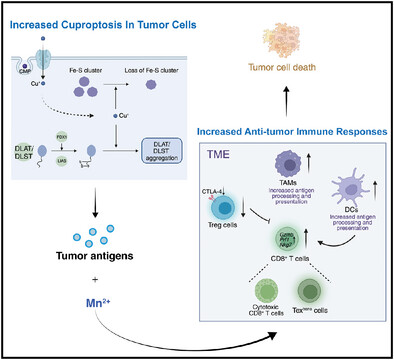
Cu2O-MnO@PEG (CMP) induces cuproptosis in tumor cells, during which tumor antigens are released and processed by dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages. Mn2+ from CMP acts as an adjuvant, potentiating tumor antigen processing and presentation of DCs and macrophages, thereby eliciting potent T cell responses, including cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and Textrans cells. CMP downregulated the suppressive function of Treg cells.
Selective A-Site Exsolution and Phase Transition in Perovskite Electrode for Efficient Flexible Znic-Air Batteries
- First Published: 14 February 2025
Graphene-Based Vitrimeric Ink with Self-Healing Properties Enables Simple E-Textile Triboelectric Coating Development
- First Published: 17 February 2025
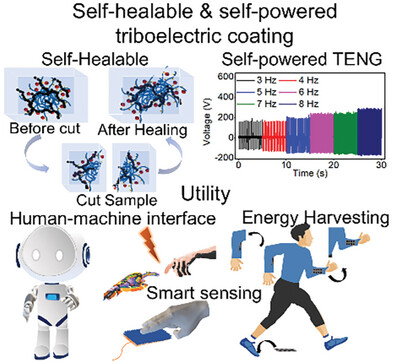
A self-powered and self-healable triboelectric coating is devised with a sustainable elastomer and graphene nanocomposite by leveraging dynamic covalent crosslinking to coat cellulose-based textiles. The developed triboelectric nanogenerator-based E-Textiles demonstrate excellent power density with a value of 4.69 W m−2 with a coating thickness of 0.56 mm. Developed E-Textiles can be utilized in applications, including smart sensing, human-machine interfaces, and energy harvesting.
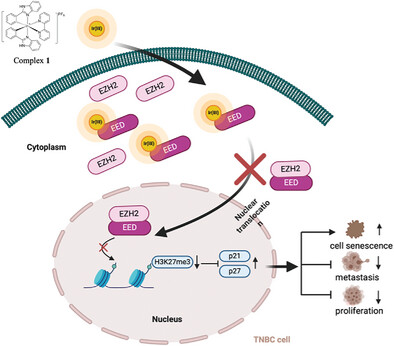
A Bioactive Benzimidazole-Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complex as an Epigenetic Regulator through Effectively Interrupting the EED–EZH2 Interaction
- First Published: 19 February 2025
Experimental Evidence of Curvature Gradient Driven Domain Wall Automotion
- First Published: 16 February 2025
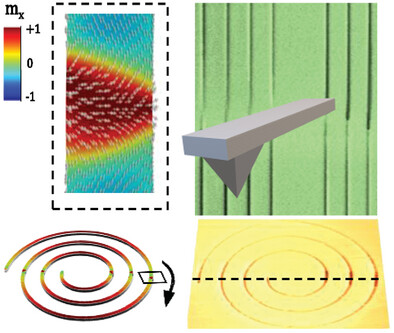
Experimental evidence of domain wall automotion driven by curvature gradient is shown a propulsion effect in absence of external stimuli. Advanced Magnetic Force Microscopy measurements are conducted to measure the depinning fields of domain walls induced in Archimedean spirals, complemented by micromagnetic simulations an analytical model. The findings emphasis the importance of harnessing geometrical design to build low power consumption domain wall-based devices.
Excited State Transient Phenomena in Two Different Phases of the Photoactive MOF MIP-177(Ti)
- First Published: 19 February 2025
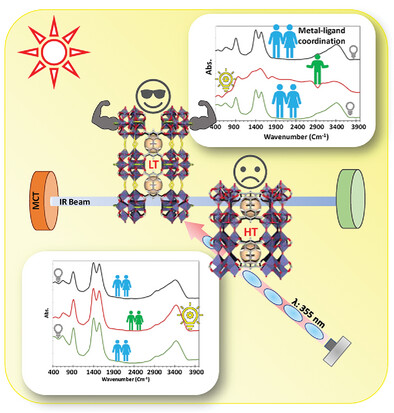
MIP-177(Ti)-high temperature (HT) and MIP-177(Ti)-low temperature (LT) are stable, photoresponsive metal organic frameworks (MOFs). Despite its structural advantages, MIP-177(Ti)-HT has lower hydrogen evolution reaction photoactivity than MIP-177(Ti)-LT. Advanced time dependent spectroscopies and theoretical models reveal that MIP-177(Ti)-LT demonstrates a long lasting, reversible coordination change of carboxylate coordination and enhanced electron delocalization, which contribute to its superior photocatalytic performance.
Tenon-and-Mortise Structure-Inspired MOF/PVDF Composites with Enhanced Piezocatalytic Performance via Dipole-Engineering Strategy
- First Published: 14 February 2025
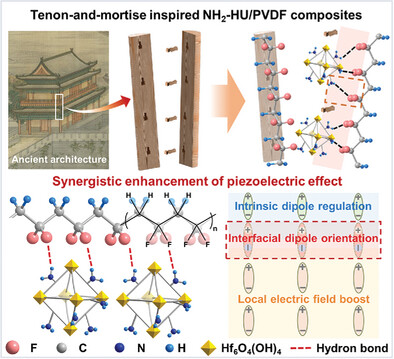
An amino-anchored MOF/PVDF piezoelectric composite is configured through a dipole-engineering strategy to achieve high-efficiency piezocatalysis by mimicking the tenon-and-mortise joint structure found in ancient Chinese architecture. The incorporation of periodic amino anchors provides a synergistic enhancement of both the local electric field and collaborative dipole alignment, resulting in efficient piezocatalytic bactericidal performance and improved CT imaging during implantation.
Harsh Environment-Immune All-Carbon Visible Light Photodetector: Sensitivity Improvement by Nitrogen-Vacancy Center Density Enhancement Through Electron Irradiation
- First Published: 16 February 2025
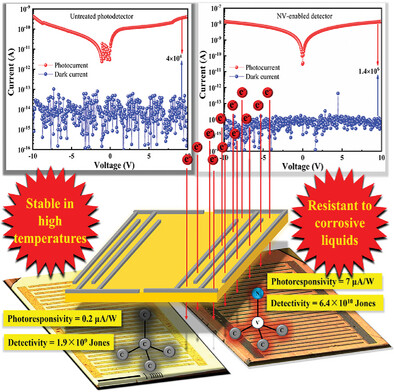
A novel strategy for enhancing the visible light detection sensitivity of diamond photodetectors is demonstrated. The NV quantum center density is augmented in the photoabsorption layer by 2 MeV electron irradiation, and a significant improvement in photosensitivity, photoresponsivity, and detectivity of the photodetector is achieved. Additionally, an all-carbon device strategy immune to harsh corrosive, and thermal environments is presented.
Transition Metal-Based Perovskite Derivatives for Selective CO2 Photoreduction: Role of Orbital Occupancy
- First Published: 25 February 2025
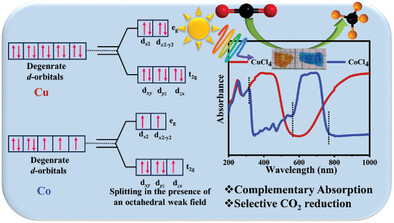
Orbital occupancy plays a crucial role in CO2 photoreduction. Cu and Co exhibit complementary absorption properties attributed to their d-orbital, facilitating electron wavefunction overlap in complementary energy regions. (DMAP)2CuCl4 (DMAP = 4-Dimethylaminopyridine)exhibits the highest performance in CO2 photoreduction, demonstrating remarkable selectivity for CH4 formation (≈97%). Its more delocalized conduction band edge enhances electron mobility, making mobile electrons readily available for CO2 reduction.
Ultrathin Azine Covalent Organic Framework Membrane for Highly-Efficient Nanofluidic Osmotic Energy Generator
- First Published: 13 February 2025
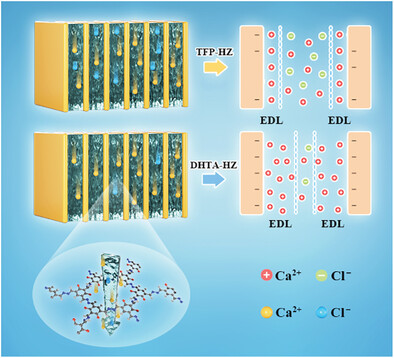
The novel azine DHTA-HZ membrane displays a high density of “ions hopping” sites around the ─OH and azine groups region, which contributes to the elevated ion selective transportation. As a result, the DHTA-HZ membrane delivers both higher output power density in NaCl and CaCl2 environment than the TFP-HZ membrane.
Integration of Electrohydrodynamic Printing and Hydroprinting for the Cost-Effective Fabrication of Microscale Conformal Transparent Electrodes on Diverse Curved Surfaces
- First Published: 16 February 2025
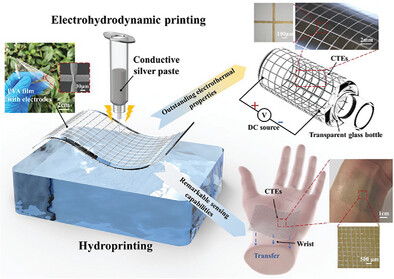
An integrated strategy of electrohydrodynamic printing and hydroprinting is proposed to simply and effectively fabricate microscale conformal transparent electrodes (CTEs) on diverse curved surfaces of different materials or even dynamic skin surfaces. The hydroprinted CTEs achieve a record-high resolution compared to most hydroprinting methods while demonstrating remarkable electrical/thermal/sensing capabilities coupled with robust mechanical stability under severe testing.
Synergistic Hydrophilic and Electrostatic Induction for Liquid Photonic Crystals of Poly (Acrylic Acid)-block-Polystyrene Colloidal Nanospheres From RAFT-Mediated Emulsion Polymerization
- First Published: 17 February 2025
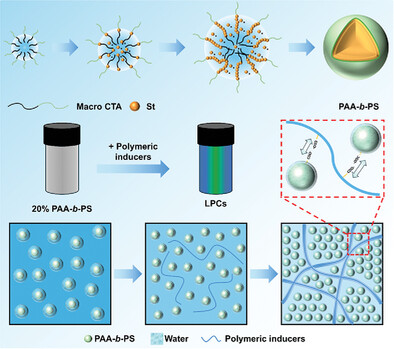
A novel strategy for the rapid formation of liquid photonic crystals (LPCs) with low solid content nanospheres dispersion is proposed. By employing RAFT polymerization, the nanospheres have achieved a uniform surface of highly charged carboxylate anions. Under the synergistic effects of the water absorption and electrostatic repulsion, dispersion forms LPCs with apparent low solid content and localized high solid content.
Double-Edged Dissolving Microneedle Patches Loaded with Zn/Ce Composites and Vancomycin for Treatment of Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infected Skin Abscess
- First Published: 16 February 2025
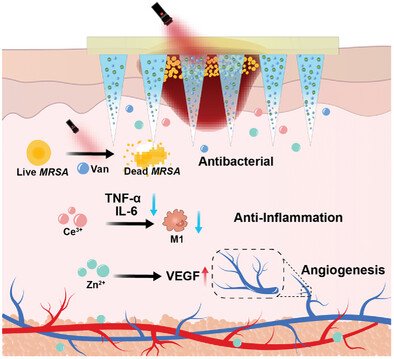
A dissolvable microneedle patch loaded with photothermal core–shell Au@ZnO/Ce nanoparticles (AZC) and vancomycin is meticulously engineered, demonstrating augmented antibacterial efficacy and superior anti-inflammatory properties for the synergistic application of antibiotics and mild photothermal therapy in abscess treatment. This double-edged microneedle patch not only enhances the precision targeting of bacterial infections but also mitigates inflammation and expedites tissue regeneration.
Silk Nanofibrillar Aerogel as Sustainable Filters for Environmental Purification
- First Published: 16 February 2025
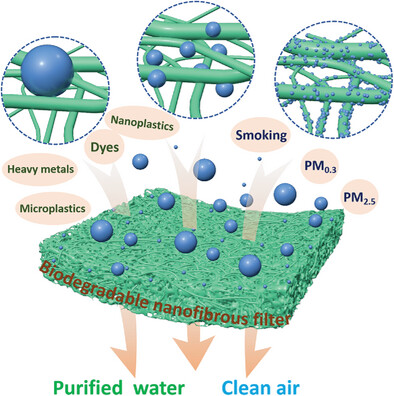
Natural silk nanofibers obtained by exfoliation are used as building blocks to fabricate aerogel filters with a 3D nanofibrous structure and biodegradability for sustainable environmental purification based on a modified freeze-drying method. These filters exhibit extraordinary water purification capability and excellent air filtration performance.
Engineering Nitrogen-Coordinated Single-Atom Catalysts for Efficient CO2 Cycloaddition
- First Published: 16 February 2025
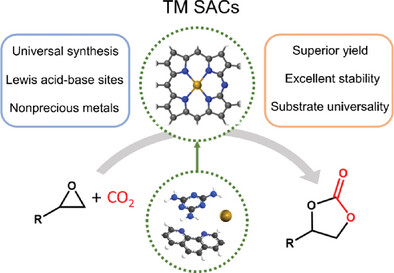
The nitrogen-coordinated transition-metal single-atom catalysts are synthesized via a facile and scalable pyrolysis approach. The optimum Zn single-atom catalyst with 13.2 wt.% Zn content achieves excellent catalytic performance for the cycloaddition of CO2 to cyclic carbonates, owing to the high density of Lewis acid–base sites that can appropriately regulate the activation of epoxide and CO2 and reaction energy.
Ti3C2Tx-Based Cross-Scale Laminated Structural Structures: Enabling Sub-Wavelength Impedance Modulation and Underwater Broadband Sound Absorption
- First Published: 21 February 2025
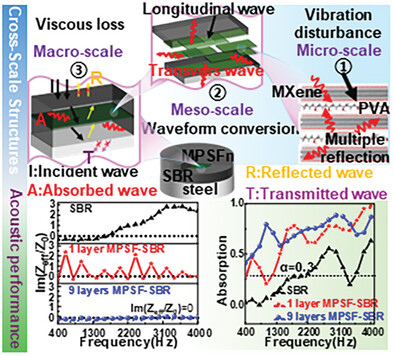
This study presents an underwater sound-absorbing material designed with a cross-scale dynamic structure. The structure's synergy across scales enables broad-frequency, deep sub-wavelength sound absorption within the challenging 0.4–4.0 kHz range. The material achieves near-zero acoustic impedance and high sound absorption across the full frequency spectrum.
Lipid/ZIF-8 Biocomposites Based on Liposomes or Vesicles: In Situ Formation, and Preliminary Evaluation as Delivery Vehicles for Hydrophobic Drugs
- First Published: 21 February 2025
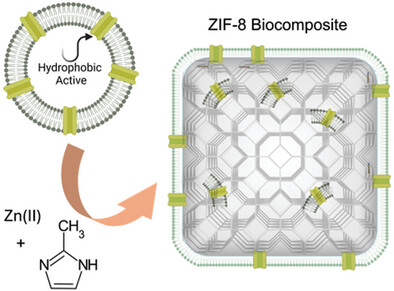
Integrating lipid self-assemblies with metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) creates biocomposites ideal for encapsulation, protection, and delivery of functional species. This study reports the in situ formation of ZIF-8 MOF particles with lipid self-assemblies, generating hybrid lipid/ZIF-8 biocomposites. These biocomposites encapsulate hydrophobic molecules like Astaxanthin drug, showing distinct release kinetics and potential crystalline phase transitions in various media, valuable for drug delivery applications.
A Dual-Responsive Fe₃O₄@ZIF-8 Nanoplatform Combining Magnetic Targeting and pH Sensitivity for Low Back Pain Therapy
- First Published: 21 February 2025
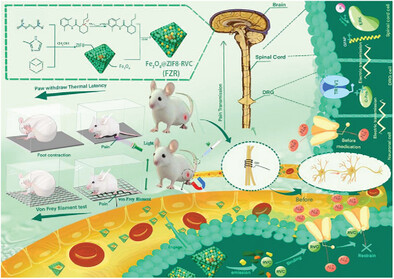
A dual-responsive Fe3O4@ZIF-8-RVC (FZR) nanoplatform is developed to address low back pain (LBP) caused by sciatic nerve compression. This platform combines magnetic targeting with pH-sensitive drug release for prolonged, localized analgesia. In vitro and in vivo results demonstrate high drug loading, sustained release, and excellent biocompatibility, offering a promising, safe, and effective solution for neuropathic pain management.
Controllable Transition Metal Cations Doping Enable Efficient and Spectral Stable Pure-Red Perovskite QLED
- First Published: 16 February 2025
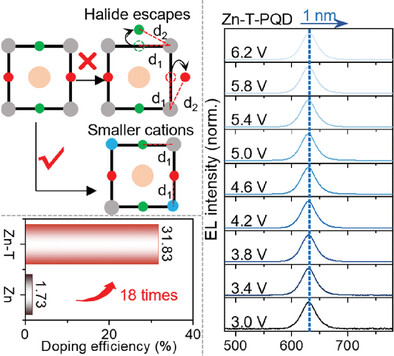
The different doping capacity of transition metal cations are revealed with different ionic sizes and the resulting various effect on the improvement of PQDs and PeLEDs. TOP is introduced to form strong coordination with metal cations and ensure their participation in the reaction. It fabricates spectrally stable PeLEDs with only 1 nm red-shift from 3 to 6 V.
Structural Changes of NiFe Layered Double Hydroxides During the Oxygen Evolution Reaction: A Diffraction and Total Scattering Operando Study
- First Published: 21 February 2025
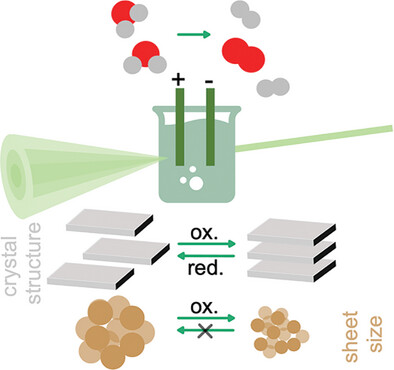
Operando X-ray diffraction and Pair Distribution Function analysis are used to follow the structural changes taking place in NiFe-layered double hydroxides when used as electrocatalysts in the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. The analysis shows that the operating conditions induce a breakdown of the particles.
Engineering Multiresponsive Alginate/PNIPAM/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Hydrogels as On-Demand Drug Delivery Platforms
- First Published: 16 February 2025
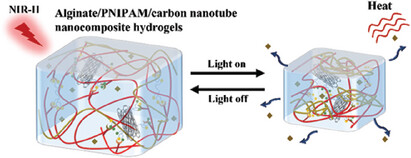
A versatile nanocomposite hydrogel is developed by engineering interfacial crosslinks (i.e., imine bonds and boronate ester bonds) and selecting materials (i.e., second near-infrared responsive carbon nanotube (CNT) and thermal-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM)). The presence of both CNT and PNIPAM in the hydrogel network provides an effective platform to control drug release in vitro and in vivo under light exposure.
Sensitive and Anisotropic Room-Temperature Terahertz Photodetection in Quasi-1D Nodal-Line Semimetal NbNiTe5
- First Published: 17 February 2025
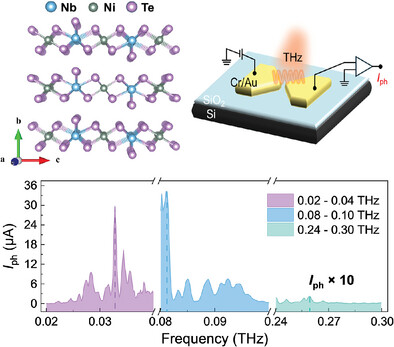
The quasi-1D nodal-line semimetal NbNiTe5, showing distinct in-plane anisotropy alongside robust Dirac nodal-line points, is utilized for sensitive and anisotropic room-temperature terahertz photodetection. Leveraging the enhanced carrier transport characteristics derived from nontrivial band topology, the NbNiTe5-based photodetector efficiently accomplishes the photoelectric conversion process. Additionally, the intrinsic anisotropy imparts exceptional polarization-sensitive detection capabilities.
Linear Dichroism of the Optical Properties of SnS and SnSe Van der Waals Crystals
- First Published: 21 February 2025
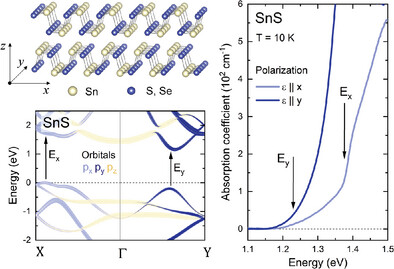
SnS and SnSe van der Waals crystals exhibit strong anisotropy of the optical properties, which makes them perfect candidates for applications in polarization-sensitive photodetection. The phenomenon is investigated by means of optical spectroscopy and explained in terms of its origins in the electronic band structure.
Hollow Mn/Co-MOF as a Powerful Oxidase-Like Nanozyme for Detection of Total Antioxidant Capacity and Black Tea Fermentation Degree
- First Published: 16 February 2025
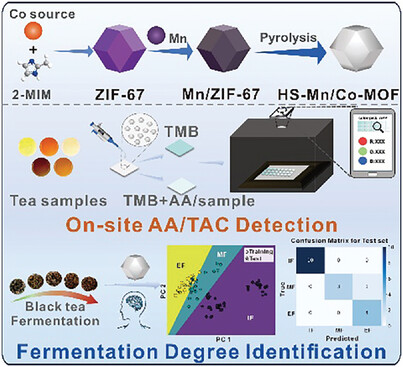
HS-Mn/Co-MOF nanozyme is synthesized via facile doping and low-temperature pyrolysis process. The HS-Mn/Co-MOF possesses abundant surface active oxygen species, negative surface charges, and rapid mass transport, thus resulting in powerful oxidase-like catalytic activity. Colorimetric detection of AA/TAC is developed based on HS-Mn/Co-MOF nanozyme. Additionally, the identification and prediction of the fermentation quality during the black tea fermentation process is realized.
Electron Density Engineering at the Bond Critical Points in Solvation Sheath of Sodium Ions for High-Rate Hard Carbon in Ether-Based Electrolyte
- First Published: 21 February 2025
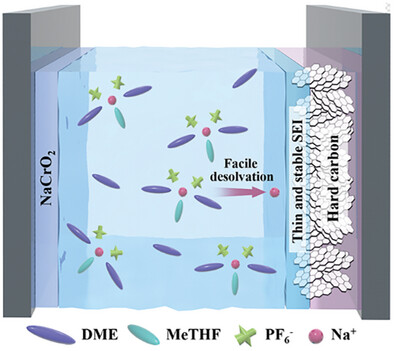
Strong-Weak Marriage: Merging strong and weak coordination solvent molecules in sodium ion solvation structures boosts the electrochemical performance of sodium ion batteries. Based on the atom-in-molecules topology analysis, this study finds the electron density engineering at the bond critical points in sodium ion solvation sheath is important for regulating the rate capability of hard carbon electrodes.
Room-Temperature Deuterium Separation in van Der Waals Gap Engineered Vermiculite Quantum Sieves
- First Published: 19 February 2025
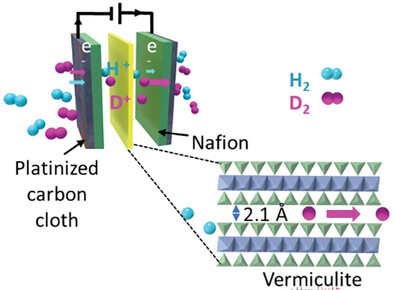
By intercalating deuterium inside the vermiculite, van der Waals gap of 2.1 Å is achieved. This gap makes it possible to observe room temperature quantum sieving effects in hydrogen isotopes, where the deuterium transports more due to its smaller wavelength, and a D2/H2 selectivity of 2.2 is achieved.
Regulating Bifacial Surface Potential of Perovskite Film Enables Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells Universal for Different Charge Transport Layers
- First Published: 25 February 2025
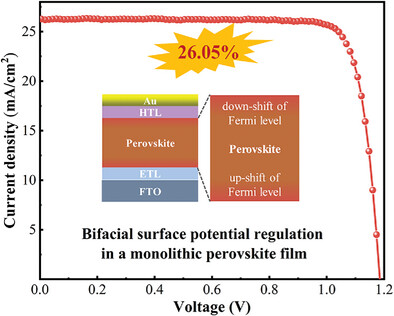
This work realizes bifacial surface potential regulation in a monolithic perovskite film through interface doping, leading to optimized dual-interfacial energy level alignment, which shows a universal effect on performance improvement of devices with different charge transport layers. Both experimental measurements and theoretical simulation demonstrates that the bifacial surface potential regulation can promote interfacial carrier transport and reduce carrier recombination, further leading to an efficiency of 26.05% (certificated 25.80%).
Synergistic Photoelectric/Photothermal Effects Guided Ion Transport for Enhancing Multiple Climatic Osmotic Energy Conversion Efficiency
- First Published: 16 February 2025
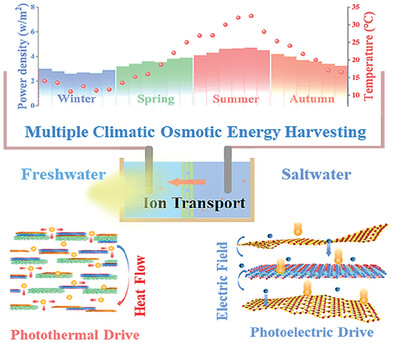
Novel nanofluidic membranes for osmotic energy harvesting applications are fabricated from a composite of g-C3N4 modified MXene and regenerated cellulose. Optimizing advanced membrane structures enables an ordered layer arrangement that reduces membrane impedance while enhancing ion selectivity. The innovative nanofluidic membrane with synergistic photoelectric/photothermal effect achieves excellent osmotic energy harvesting efficiency over multiple climatic conditions.
Cobalt-Silicon Coordination-Induced Nonradical Activation of Peroxymonosulfate for Enhancing the Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Real Wastewater
- First Published: 16 February 2025
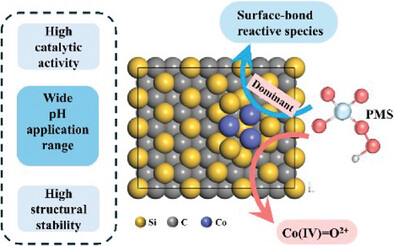
Silicon carbide-supported cobalt single-atom catalyst (Co/SiC) efficiently activates peroxymonosulfate (PMS) via nonradical pathways for sulfamethoxazole (SMX) degradation. The unique Co-Si coordination enhances electron transfer, ensuring high activity and resistance to interference. Continuous column experiments confirm its stability in real wastewater. This study offers a promising strategy for removing emerging pollutants from complex water matrices.
Substrate Stabilized Charge Transfer Scheme In Coverage Controlled 2D Metal Organic Frameworks
- First Published: 17 February 2025
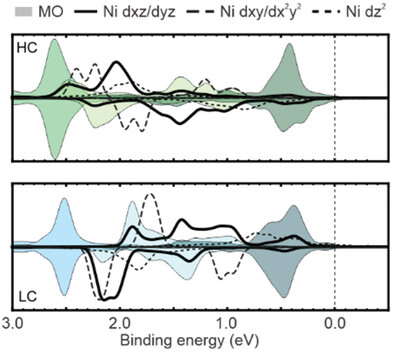
The synthetic process of 2D frameworks composed of nickel and 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane on Ag(100) involves the formation of multiple phases. Two distinct architectures with atom: ligand ratios of 1:2 and 1:1 are studied with a multi-technique approach and stable electronic properties are observed, except for slight differences in magnetic responses.
Ultra-Thick Graphene Films with High Thermal Conductivity Through a Non-Stacking Strategy
- First Published: 21 February 2025
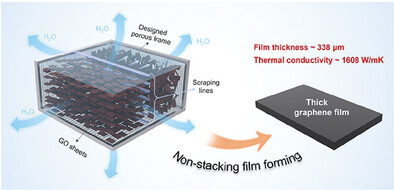
A “non-stacking” strategy significantly facilitates the fabrication of ultra-thick graphene film (≈338 µm) with exceptional thermal conductivity (≈1608 W m−1 K−1) by eliminating the film interface. This approach effectively promotes larger grain size and superior heat transfer capability (0.544 W K−1) compared to the conventional multi-layer stacking method.