Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover Image, Volume 121, Number 1, January 2020
- Page: i
- First Published: 25 November 2019
Front Cover: The cover image is based on the Research Article Oleanolic acid exerts inhibitory effects on the late stage of osteoclastogenesis and prevents bone loss in osteoprotegerin knockout mice by Dongfeng Zhao et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28994.
Cover Credit: Cover image © Dongfeng Zhao Images
BACK COVER
Back Cover Image, Volume 121, Number 1, January 2020
- Page: i
- First Published: 25 November 2019

Back Cover: The cover image is based on the Research Article Hypoxia alters the release and size distribution of extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer cells to support their adaptive survival by Mary C. Patton et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29328.
Cover Credit: Cover image © Haseeb Zubair Images
ISSUE INFORMATION
VIEW POINTS
Exosomes: New insights into cancer mechanisms
- Pages: 7-16
- First Published: 08 November 2019
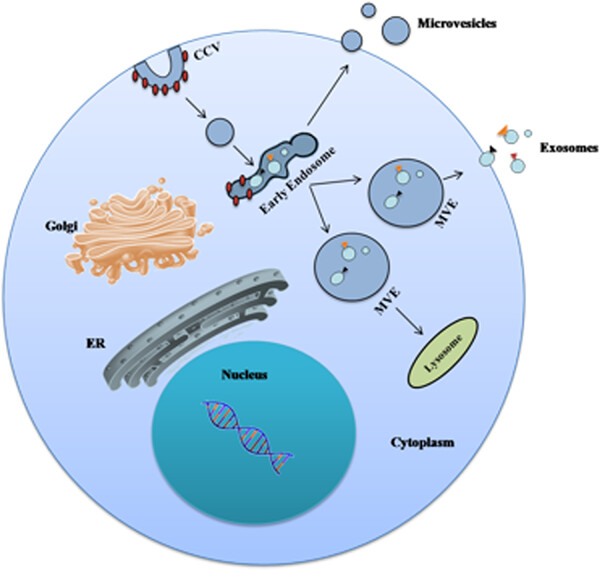
Exosomes play a critical role in several processes such as the development of cancers, intercellular signaling, drug resistance mechanisms, and cell-to-cell communication by fusion onto the cell membrane of recipient cells. These vesicles contain endogenous proteins and both noncoding and coding RNAs (microRNAs and messenger RNAs) that can be delivered to various types of cells. Furthermore, exosomes exist in body fluids such as plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine. Therefore, they could be used as a novel carrier to deliver therapeutic nucleic-acid drugs for cancer therapy.
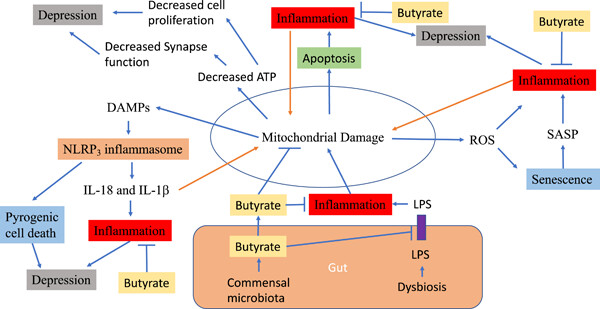
Mitochondria could be a potential key mediator linking the intestinal microbiota to depression
- Pages: 17-24
- First Published: 05 August 2019
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: AT1R knockdown confers cardioprotection against sepsis-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway in rats
- Pages: 25-42
- First Published: 22 November 2018
RESEARCH ARTICLES
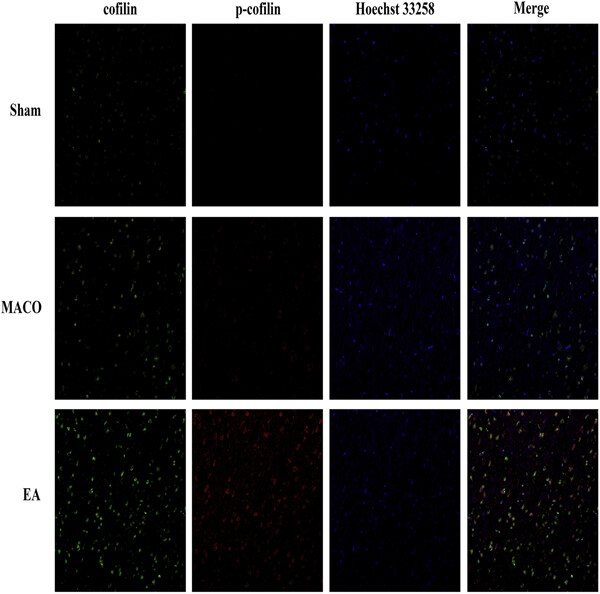
Electroacupuncture protects rats from ischemic brain injury via coffilin in mice
- Pages: 43-48
- First Published: 09 October 2019
MicroRNA-9 overexpression suppresses vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque and enhances vascular remodeling through negative regulation of the p38MAPK pathway via OLR1 in acute coronary syndrome
- Pages: 49-62
- First Published: 30 September 2019
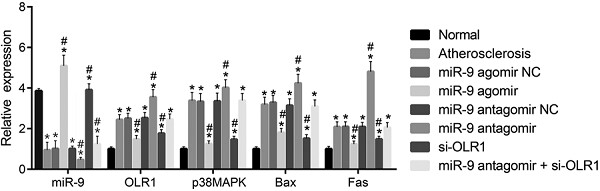
Our current study included the following highlights: (1) microRNA-9 (miR-9) specifically inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1 (OLR1). (2) Upregulated miR-9 reduces atherosclerosis. (3) Upregulated miR-9 promotes vascular remodeling. (4) miR-9 inhibits p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) pathway to alleviate atherosclerosis via knockdown of OLR1. (5) miR-9 targeting OLR1 might be a novel target for the treatment of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
HSPB1 rs2070804 polymorphism is associated with the depth of primary tumor
- Pages: 63-69
- First Published: 30 July 2019
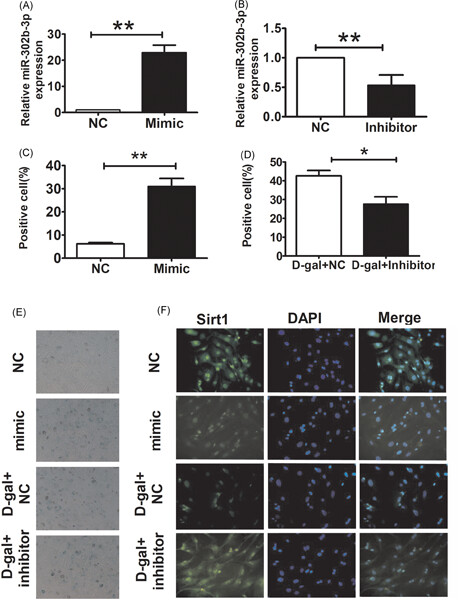
miRNA expression profiling uncovers a role of miR-302b-3p in regulating skin fibroblasts senescence
- Pages: 70-80
- First Published: 09 May 2019
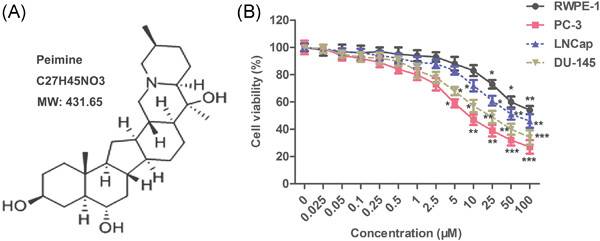
Peimine inhibits the growth and motility of prostate cancer cells and induces apoptosis by disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis through Ca2+/CaMKII/JNK pathway
- Pages: 81-92
- First Published: 12 May 2019
Research on the roles of genes coding ATP-binding cassette transporters in Porphyromonas gingivalis pathogenicity
- Pages: 93-102
- First Published: 12 May 2019
The effects of nanocurcumin on Treg cell responses and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- Pages: 103-110
- First Published: 09 May 2019
MicroRNA-194 reduces inflammatory response and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells permeability through suppression of TGF-β/SMAD pathway by inhibiting THBS1 in chronic idiopathic urticaria
- Pages: 111-124
- First Published: 12 June 2019
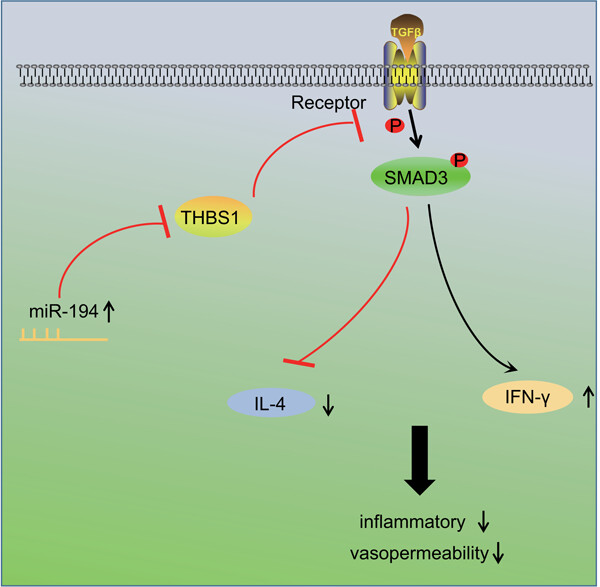
Our study provides evidence that miR-194 negatively modulates thrombospondin 1 (THBS1) and inhibits the activation of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/SMAD pathway, thereby alleviating the inflammatory response and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMECs) permeability of mast cells in chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU).
LC-MS/MS-based metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli under heterologous gene expression stress
- Pages: 125-134
- First Published: 24 June 2019
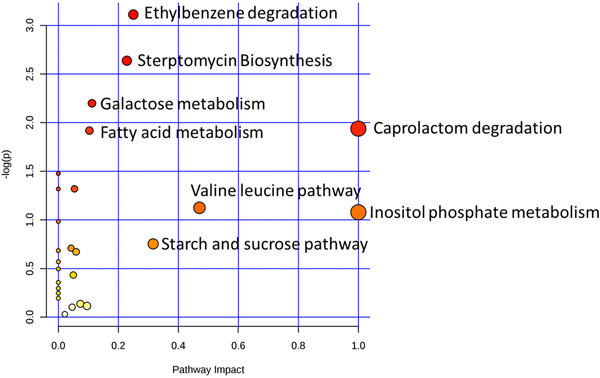
Our study provides a broader insight into the metabolic adaptations of bacterial cells during gene manipulation experiments that can be prolonged to improve the yield of heterologous gene products and concomitant production of valuable biomolecules. In the bacterial metabolite pathway figure. X-axis represents the impact of the identified metabolites on the indicated pathway. Y-axis indicates the extent to which the designated pathway is enriched in the identified metabolites. All the values were ascertained from MetaboAnalyst. Circle colors (see color scale for reference) indicate pathway enrichment significance. Circle size indicates pathway impact.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Upregulation of acetylcholinesterase caused by downregulation of microRNA-132 is responsible for the development of dementia after ischemic stroke
- Pages: 135-141
- First Published: 02 October 2019

MicroRNA-132 (miR-132) has been shown to participate in many diseases. The aim of this study was to understand the relationship between the level of miR-132 and the severity of dementia post-ischemic stroke. Accordingly, we found that acetylcholinesterase (ACHE) was a virtual target of miR-132 and a negative regulatory relationship is present between miR-132 and ACHE. Additionally, miR-132 and ACHE have been shown to affect the cell viability and apoptosis in the central nervous system.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
DNA hypomethylation promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by regulating the binding of SP1 to the CDCA3 promoter
- Pages: 142-151
- First Published: 18 June 2019
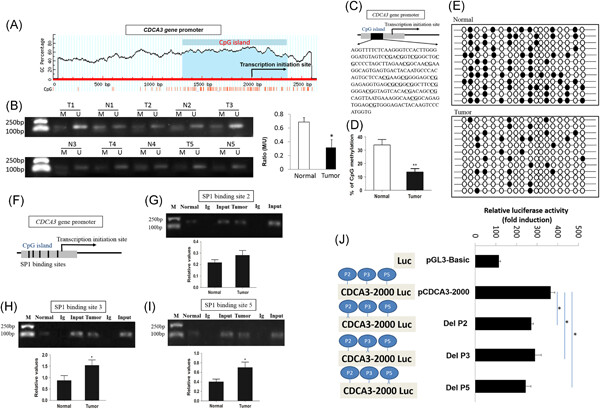
The process by which specificity protein 1 (SP1) bound to the nearest promoter region was expedited in GC cells, by which DNA was hypomethylated and CDCA3 expression was promoted. The effect on cell proliferation and progression by CDCA3 was under the regulation of SP1 and also affected by hypomethylation of DNA.
Oleanolic acid exerts inhibitory effects on the late stage of osteoclastogenesis and prevents bone loss in osteoprotegerin knockout mice
- Pages: 152-164
- First Published: 18 July 2019
Salidroside ameliorated hypoxia-induced tumorigenesis of BxPC-3 cells via downregulating hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and LOXL2
- Pages: 165-173
- First Published: 04 June 2019
miR-4319 inhibited the development of thyroid cancer by modulating FUS-stabilized SMURF1
- Pages: 174-182
- First Published: 30 May 2019
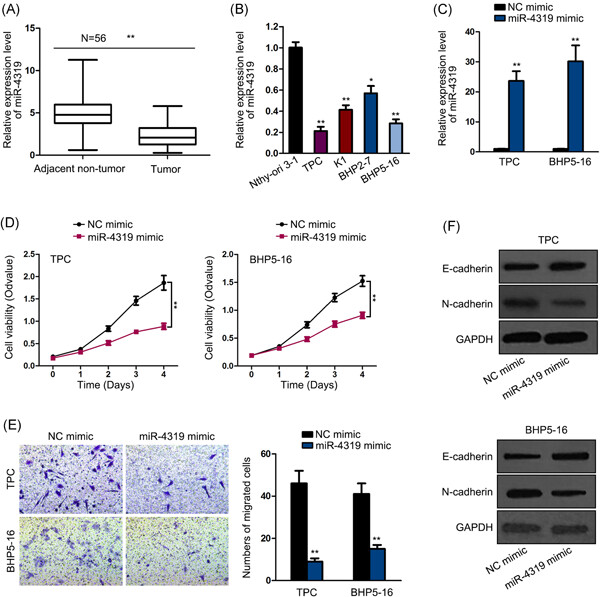
miR-4319 was found to be downregulated in thyroid cancer cells and its overexpression inhibited proliferation, migration, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in thyroid cancer. miR-4319 was found to target SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (SMURF1) in thyroid cancer cells. miR-4319 inhibited the stabilization of SMURF1 messenger RNA by competing with fused in sarcoma to target SMURF1. miR-4319 inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and EMT through SMURF1 in thyroid cancer.
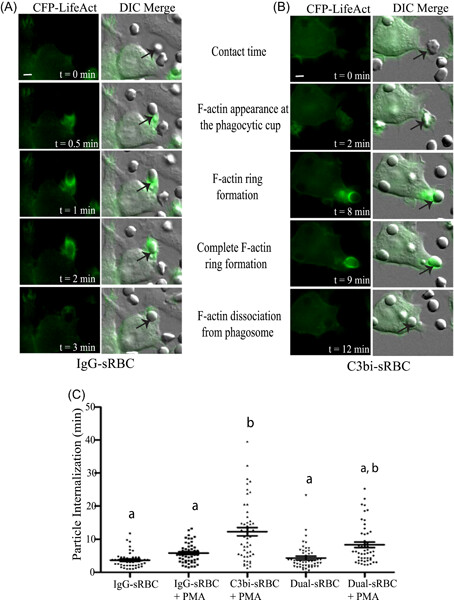
Binding and uptake of single and dual-opsonized targets by macrophages
- Pages: 183-199
- First Published: 06 June 2019
Complementation of dopaminergic signaling by Pitx3–GDNF synergy induces dopamine secretion by multipotent Ntera2 cells
- Pages: 200-212
- First Published: 16 July 2019
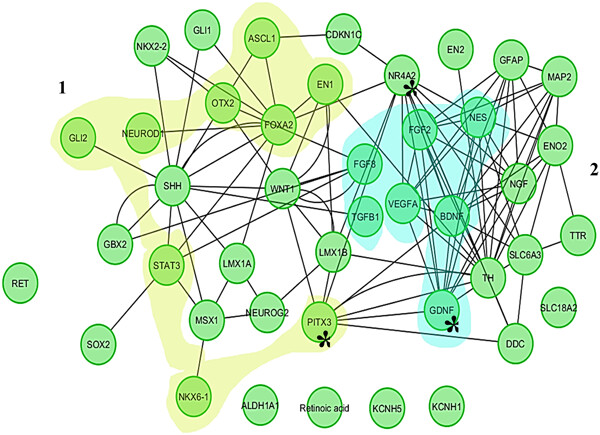
Our findings highlight the importance of Pitx3–glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) interplay in dopamine signaling and indicate that our strategy might be useful for restoration of dopaminergic (DAergic) fate of Ntera2 (NT2) cells to make them clinically applicable toward cell replacement therapy of Parkinson's disease (PD).
Overexpression of miR-623 suppresses progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting XRCC5
- Pages: 213-223
- First Published: 12 June 2019
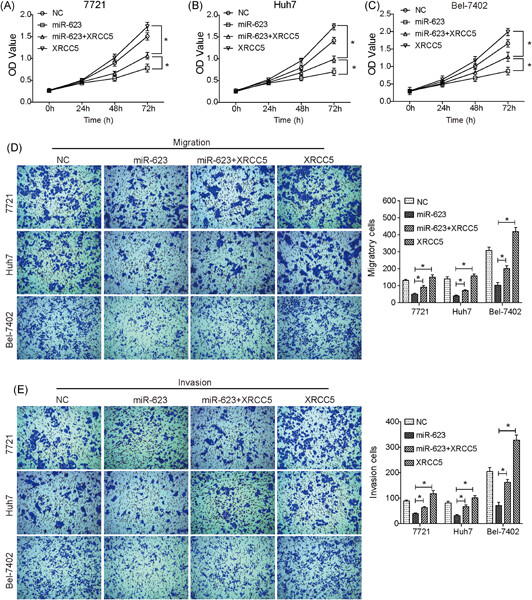
miR-623 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its expression is associated with poor clinical outcomes of patients with HCC. miR-623 suppresses the progression of HCC by regulating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B, Wnt/β-catenin, and ERK/JNK pathways by targeting X-ray repair cross complementing 5 in HCC in vitro
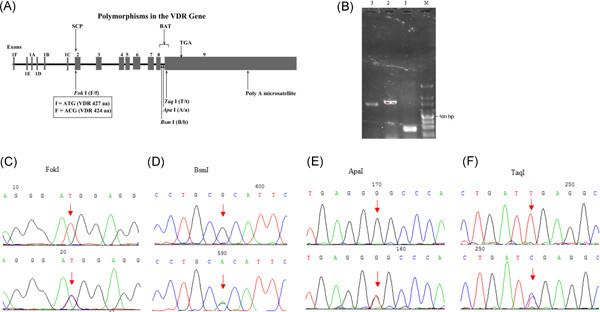
Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism is associated with multiple myeloma
- Pages: 224-230
- First Published: 06 June 2019
ARPC4 promotes bladder cancer cell invasion and is associated with lymph node metastasis
- Pages: 231-243
- First Published: 12 June 2019
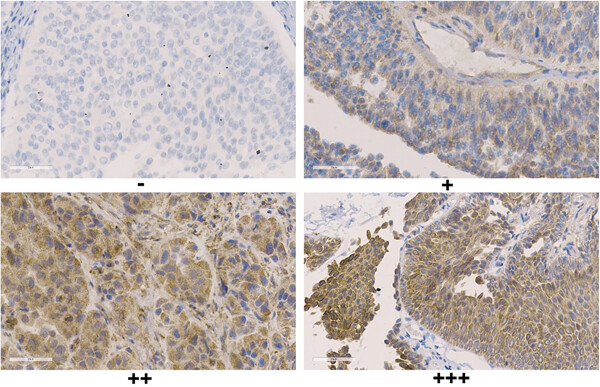
The objective of this study was to identify the correlation between actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 (ARPC4) and lymph node metastasis, and to examine the role of ARPC4 in the invasive migration of T24 bladder cancer cells. Finally, we found that the expression of ARPC4, as a risk factor, was associated with lymphatic metastasis and was elevated in bladder cancer tissues when compared with normal bladder tissues. Besides, inhibition of ARPC4 expression significantly attenuated bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, possibly as a consequence of defects in pseudopodia formation.
Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 inhibition suppresses cytokine production and osteoclast bone resorption in vitro
- Pages: 244-258
- First Published: 21 June 2019
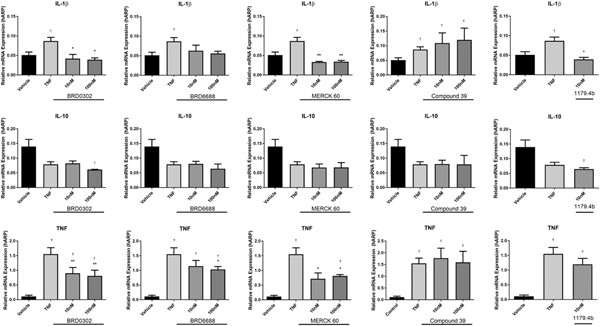
Epigenetic modulation through targeted histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition has recently been identified as an effective method for regulating inflammatory and bone destructive profiles in osteolytic diseases. This study identified the importance of the individual HDAC 1 and HDAC 2 isoform during proinflammatory signaling in monocytes/macrophages and osteoclastic bone resorption, whereby inhibition of these individual HDACs significantly suppresses the inflammatory processes and bone destruction in vitro.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
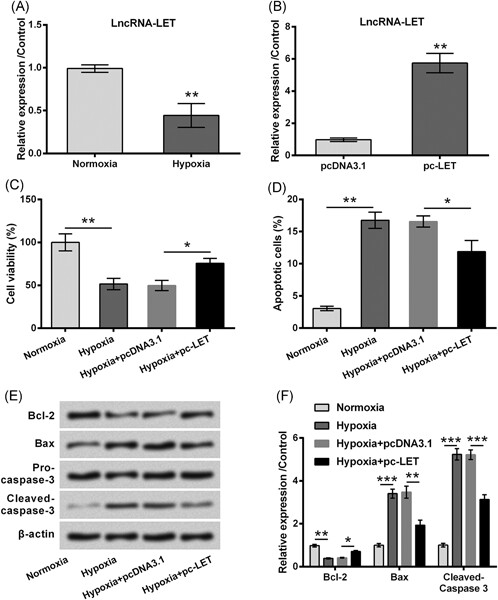
Retracted: LncRNA-LET relieves hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2 cells through regulation of miR-138
- Pages: 259-268
- First Published: 21 June 2019
RESEARCH ARTICLES
The effect of extracellular matrix on the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
- Pages: 269-283
- First Published: 06 June 2019
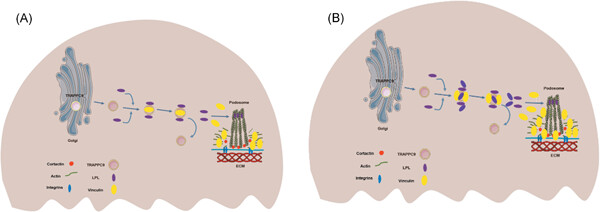
A novel regulatory role of TRAPPC9 in L-plastin-mediated osteoclast actin ring formation
- Pages: 284-298
- First Published: 27 August 2019
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
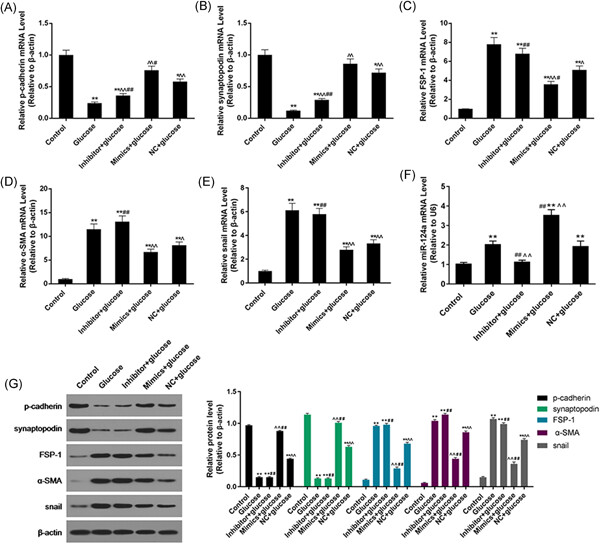
Retracted: miR-124a enhances therapeutic effects of bone marrow stromal cells transplant on diabetic nephropathy-related epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis
- Pages: 299-312
- First Published: 12 June 2019
RESEARCH ARTICLES
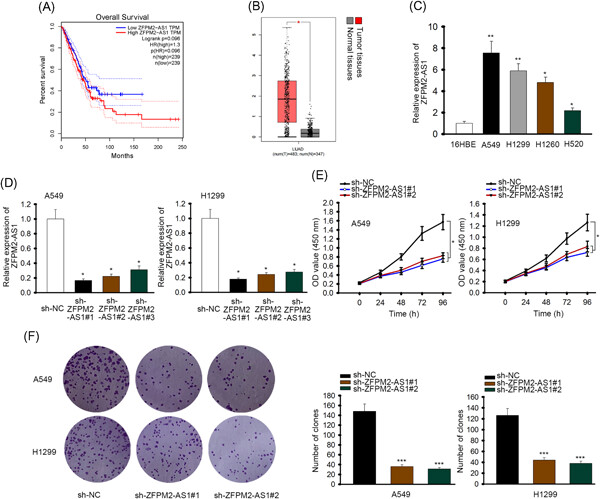
lncRNA ZFPM2-AS1 promotes proliferation via miR-18b-5p/VMA21 axis in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 313-321
- First Published: 11 July 2019
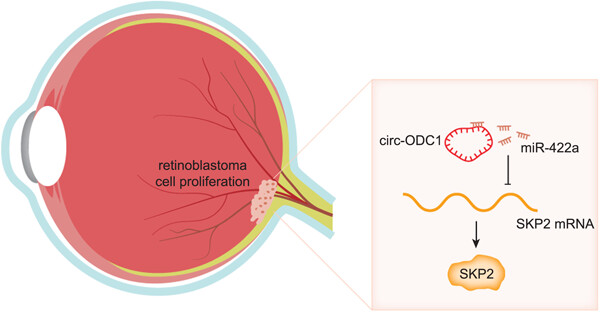
SKP2, positively regulated by circ_ODC1/miR-422a axis, promotes the proliferation of retinoblastoma
- Pages: 322-331
- First Published: 11 July 2019
Regulatory effects of lncRNA ATB targeting miR-200c on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells
- Pages: 332-343
- First Published: 21 June 2019
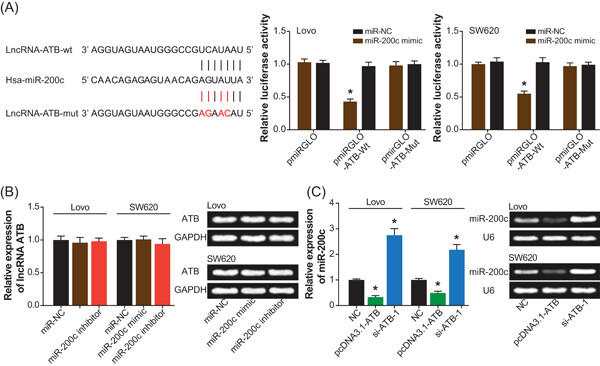
(a) Overexpressed activated by transforming growth factor-β (ATB), underexpressed miR-200c were proposed as independent predictors for shortened survival of the patients with CRC. (b) Transfection of pcDNA3.1-ATB and miR-200c inhibitor could boost viability and proliferation and suppress apoptosis. (c) ATB was discovered to downregulate miR-200c expression by targeting it, and CDK2 was subjected to dual regulation of both ATB and miR-200c.
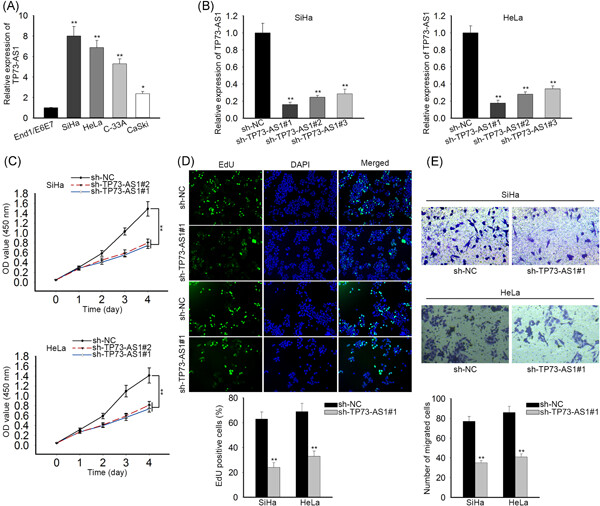
LncRNA TP73-AS1 is a novel regulator in cervical cancer via miR-329-3p/ARF1 axis
- Pages: 344-352
- First Published: 24 June 2019
Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 aggravates cell proliferation, migration in gastric cancer by epigenetically silencing NLRP6 expression via binding EZH2
- Pages: 353-362
- First Published: 20 June 2019
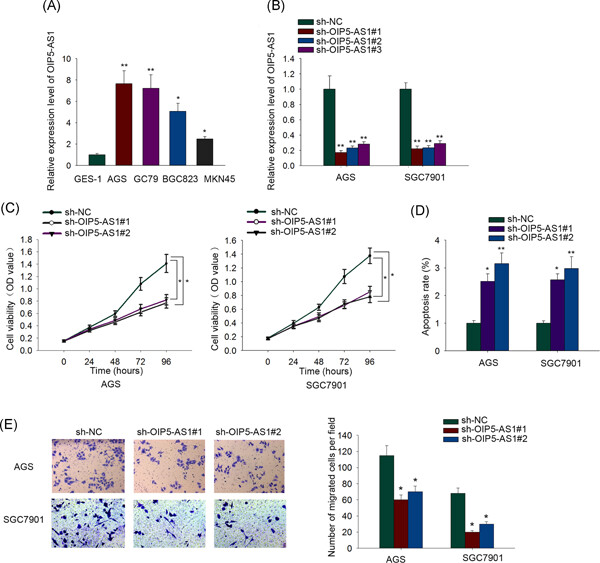
OIP5 antisense RNA 1 (OIP5-AS1) silencing impairs cell growth and induces promotion of cell apoptosis in gastric cancer (GC). Nuclear OIP5-AS1 interacts with enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and negatively mediates Nod-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 6 (NLRP6) expression in GC cells. OIP5-AS1 represses NLRP6 expression by recruiting EZH2, increasing the H3K27me3 enrichment of NLRP6 promoter.
C allele of -786 T>C polymorphism in the promoter region of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is responsible for endothelial dysfunction in the patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Pages: 363-370
- First Published: 18 June 2019
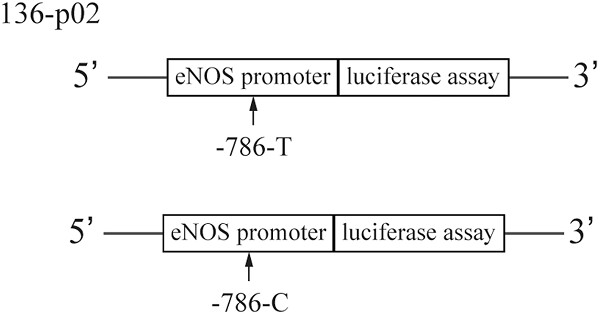
This study aimed to explore the roles of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in the control of metastasis of infection with endothelial dysfunction, and how -786T>C polymorphism in gene promoter in the control of metastasis of endothelial function. Accordingly, these findings provide support that down-expression of -786T>C located on the promoter of eNOS is associated with an increased risk of endothelial dysfunction.
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate TGF-β to adjust neuroinflammation in postoperative central inflammatory mice
- Pages: 371-384
- First Published: 19 June 2019
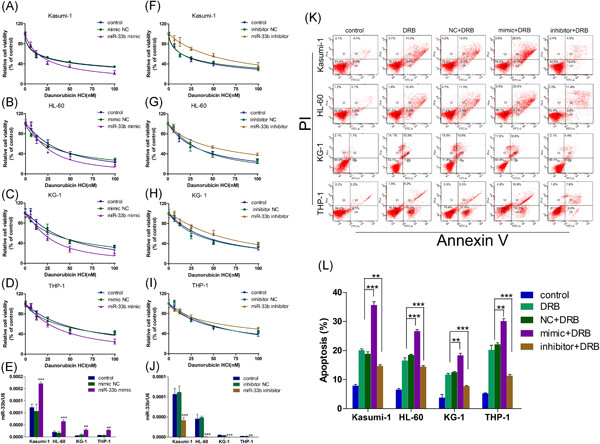
MicroRNA-33b regulates sensitivity to daunorubicin in acute myelocytic leukemia by regulating eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-2
- Pages: 385-393
- First Published: 21 June 2019
Construction of a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network to explore the pathogenesis and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 394-406
- First Published: 24 June 2019
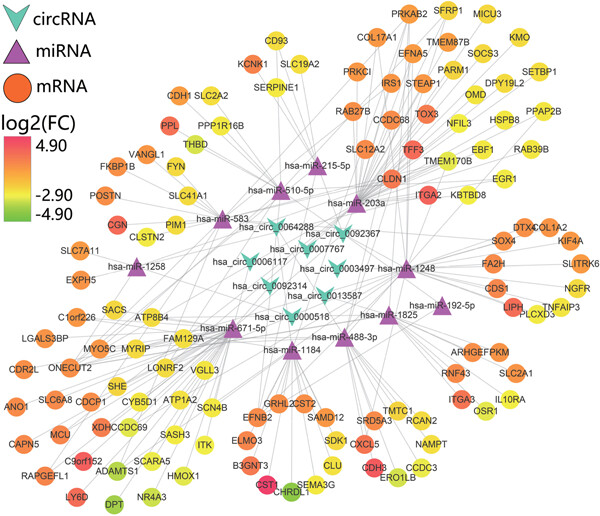
The potential roles of circular RNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma were explored from the perspectives of competitive endogenous RNA-related networks. Two circular RNAs (hsa_circ_0007767 and hsa_circ_0092367) were proven to be key regulators in the pathogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by functioning as competitive endogenous RNAs, and four genes (CDH1, SERPINE1, IRS1 and FYN) were identified as their critical downstream targets. Additionally, three compounds (celastrol, 5109870 and MG-132) were determined to be therapeutic options for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
The heat shock protein 70 inhibitor VER155008 suppresses the expression of HSP27, HOP and HSP90β and the androgen receptor, induces apoptosis, and attenuates prostate cancer cell growth
- Pages: 407-417
- First Published: 21 June 2019
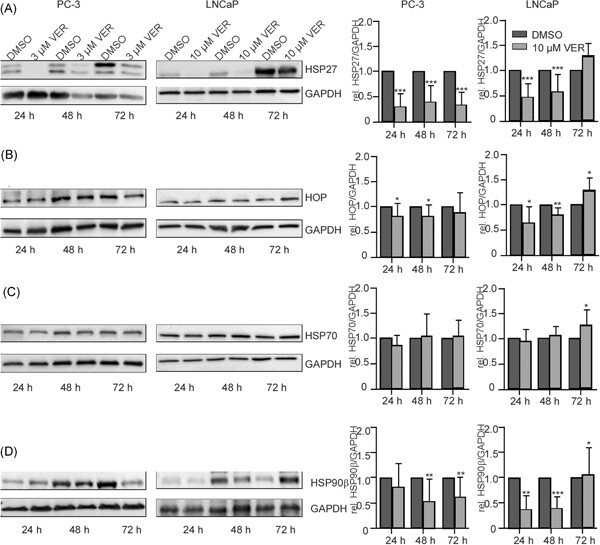
We could demonstrate antitumor activity of the HSP70 inhibitor VER155008 in both AR-positive and -negative prostate cancer cell lines by inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis in a low micromolar range. In addition, VER155008 induced a distinct diminishing of HSP27, HOP and HSP90α expression, whereas the expression of HSP40, HSP60, HSP90βta, and HSP70 itself was not altered. VER155008 treatment also led to suppression of the AR and might represent a promising therapeutic agent for prostate cancer.
circRNA_0058097 promotes tension-induced degeneration of endplate chondrocytes by regulating HDAC4 expression through sponge adsorption of miR-365a-5p
- Pages: 418-429
- First Published: 21 June 2019
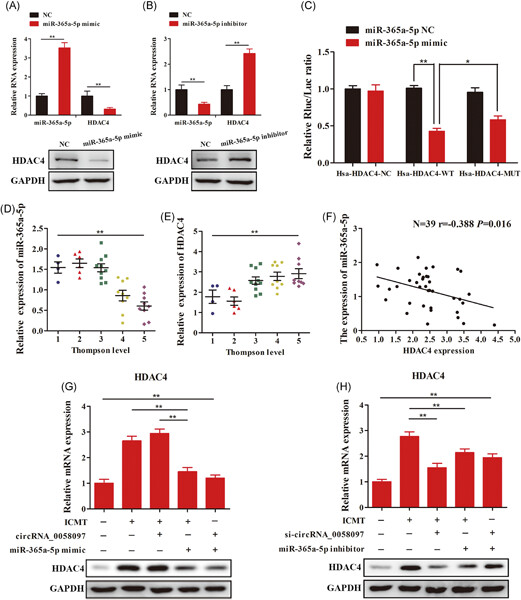
Excessive intermittent cyclic mechanical tension can induce the degeneration of endplate chondrocytes. Tension-sensitive circRNA_0058097 can upregulate the expression of downstream target gene histone deacetylase 4 by sponge adsorption of miR-365a-5p, which promoted morphological changes of endplate chondrocytes, and increased extracellular matrix degradation and degeneration of endplate cartilage.
Sulforaphane administration alleviates diffuse axonal injury (DAI) via regulation signaling pathway of NRF2 and HO-1
- Pages: 430-442
- First Published: 24 June 2019
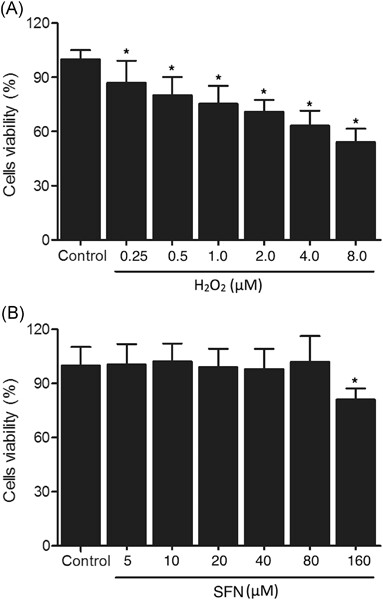
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) can alleviate diffuse axonal injury (DAI)-induced apoptosis by regulating the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), while sulforaphane (SFN) was shown to reduce oxidative stress by increasing the expression of Nrf2. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the therapeutic effect of SFN in the treatment of DAI and the ability of SFN to reduce oxidative stress. Accordingly, we came to the conclusion that by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and reducing the activity of caspase-3, SFN reduces the apoptosis of neurons in brain trauma-induced DAI.
Silencing of long noncoding RNA HOXD-AS1 inhibits proliferation, cell cycle progression, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through MEK/ERK pathway
- Pages: 443-457
- First Published: 23 June 2019
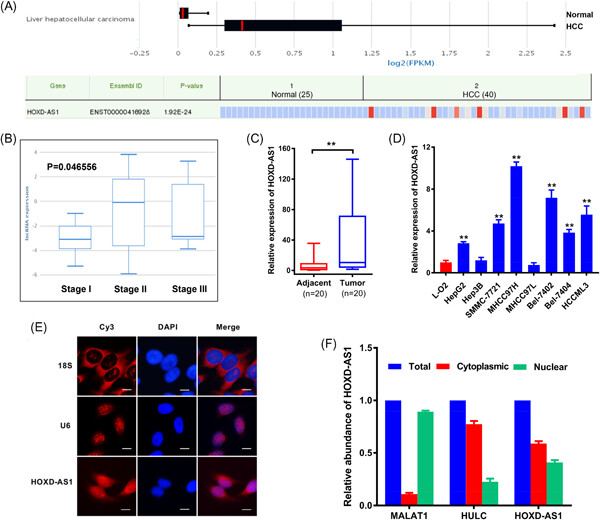
This manuscript aims to investigate the biological function and underlying mechanisms of long noncoding RNA HOXD cluster antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA HOXD-AS1) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. We demonstrated that knockdown of lncRNA HOXD-AS1 could inhibit the proliferation, cell cycle progression, migration, and invasion of HCC cells through the MEK/ERK pathway, suggesting that HOXD-AS1, as an oncogene, might play a critical role in HCC progression and serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker as well as a therapeutic target for HCC.
MicroRNA-330 inhibits growth and migration of melanoma A375 cells: In vitro study
- Pages: 458-467
- First Published: 25 June 2019
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis identifies lncRNA HCG22 as a migration inhibitor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 468-481
- First Published: 25 June 2019
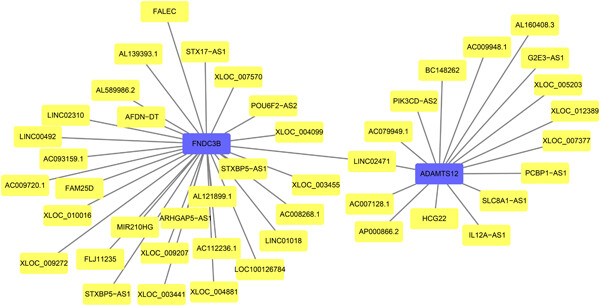
Esophageal cancer is one of the most lethal malignancies in the world. But the altered long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues require a deeper excavation, and the regulatory mechanisms are barely discussed. In this study, we combined lncRNA microarray datasets from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and performed bioinformatic analysis to identify differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs in ESCC tissues to determine novel lncRNA-protein regulatory mechanisms. We would like to claim that these findings are novel and significant considering about the following issues: (a) first study confirmed the downregulation of lncRNA HCG22 in ESCC tumors, and identified lncRNA HCG22 as a novel prognostic predictor for patients with ESCC and (b) first study inferred SPINK7 and ADAMTS12 as the potential regulatory targets of lncRNA HCG22.
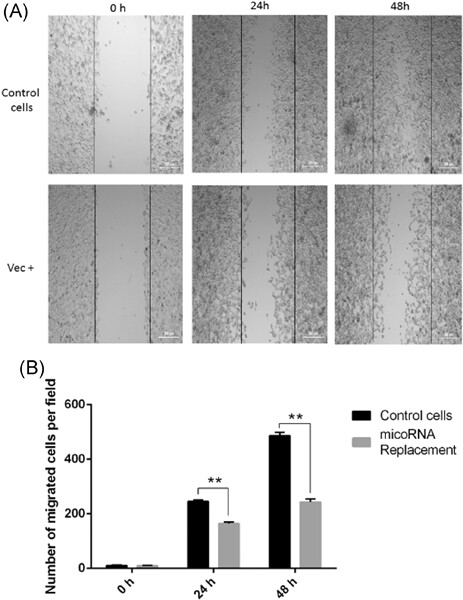
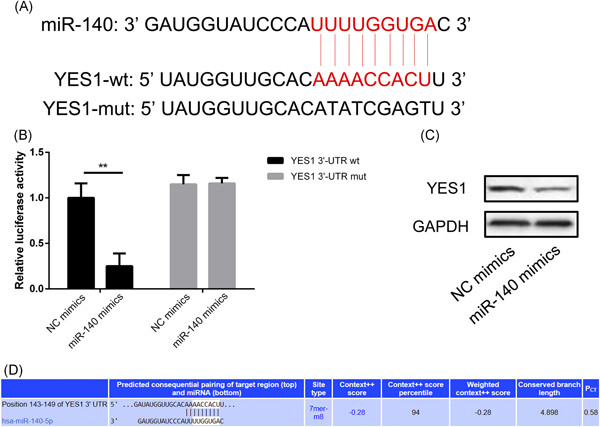
MicroRNA-140 inhibit prostate cancer cell invasion and migration by targeting YES proto-oncogene 1
- Pages: 482-488
- First Published: 16 July 2019
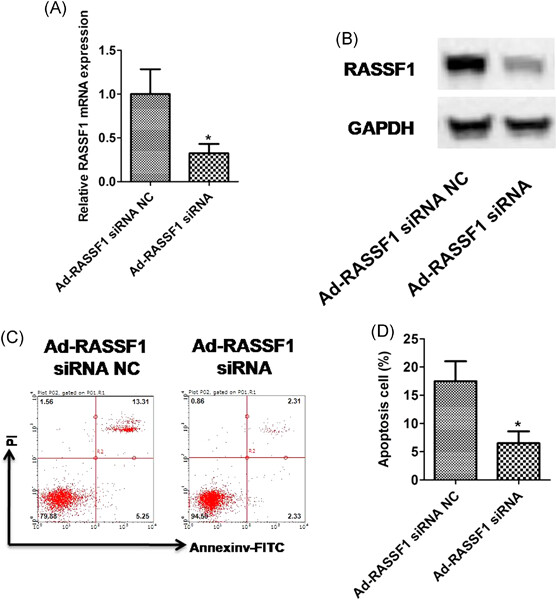
RASSF1 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction and is regulated by miR-125b
- Pages: 489-496
- First Published: 08 October 2019
Amifostine inhibited the differentiation of RAW264.7 cells into osteoclasts by reducing the production of ROS under 2 Gy radiation
- Pages: 497-507
- First Published: 03 July 2019
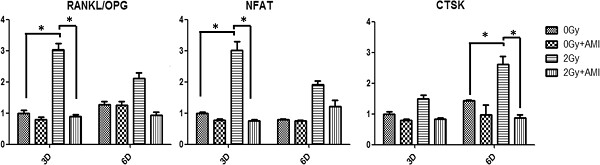
In this research, we studied the effect of amifostine (AMI) on osteoclasts under irradiation condition. The result showed that AMI inhibits the maturation and differentiation of osteoclasts under radiation condition by reducing DNA damage and reactive oxygen species induced by radiation, thereby reducing the effect of radiation on the skeletal system, indicating that AMI could be a potential therapeutic target for radiation-induced osteoporosis.
Palbociclib, a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, restricts cell survival and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells
- Pages: 508-523
- First Published: 01 July 2019
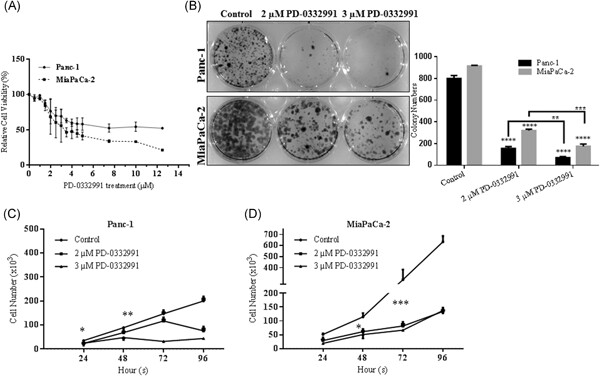
Palbociclib (PD-0332991) treatment was effective to reduce cell viability and proliferation in a dose-dependent manner in Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. Panc-1 cells were more sensitive to PD-0332991 compared with MiaPaCa-2 cells. MiaPaCa-2 cells were resistant to PD-0332991 treatment due to its expression profile of Rb and cyclin E.
The N6-methyladenosine mRNA methylase METTL14 promotes renal ischemic reperfusion injury via suppressing YAP1
- Pages: 524-533
- First Published: 18 July 2019
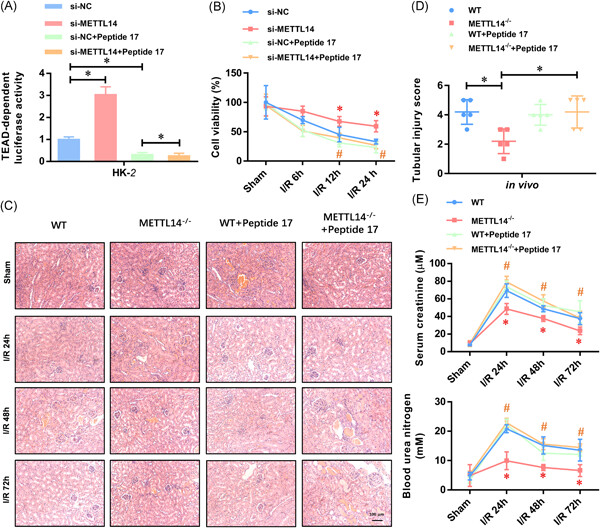
This study reveals, for the first time, that N6-methyladenosine mRNA methylase METTL14 promotes renal ischemic reperfusion injury via suppressing YAP1. Thus, the discovery of the pathway of METTL14-YAP1 provides significant new insights into the understanding of AKI and unveils new therapeutic strategies and targets.
Codon usage of human hepatitis C virus clearance genes in relation to its expression
- Pages: 534-544
- First Published: 16 July 2019
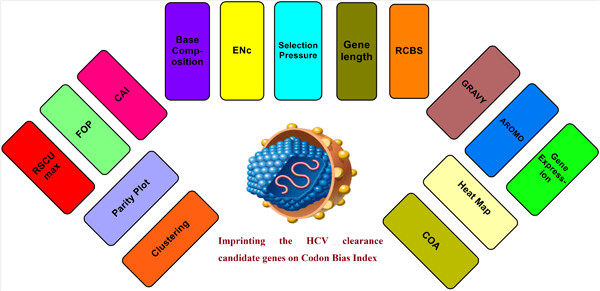
This paper highlights the interplay of codon usage and the key hepatitis C virus clearance candidate genes in relation to its expression. A total of 112 genes are collected from GenBank and subjected to major codon indices, such as relative synonymous codon usage, an effective number of codon, frequency of optimal codon, codon adaptation index, codon bias index, and base compositions.
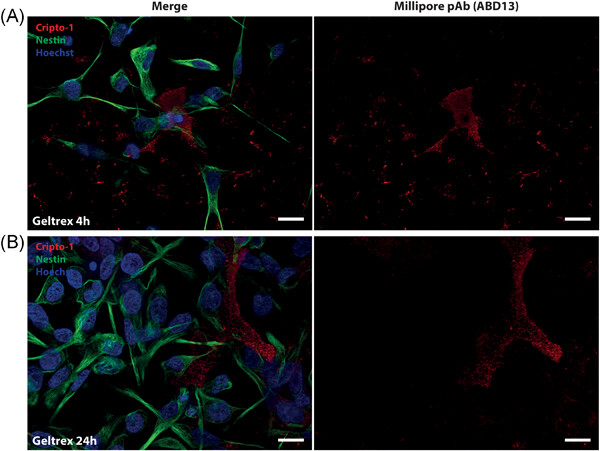
An evaluation of different Cripto-1 antibodies and their variable results
- Pages: 545-556
- First Published: 16 July 2019
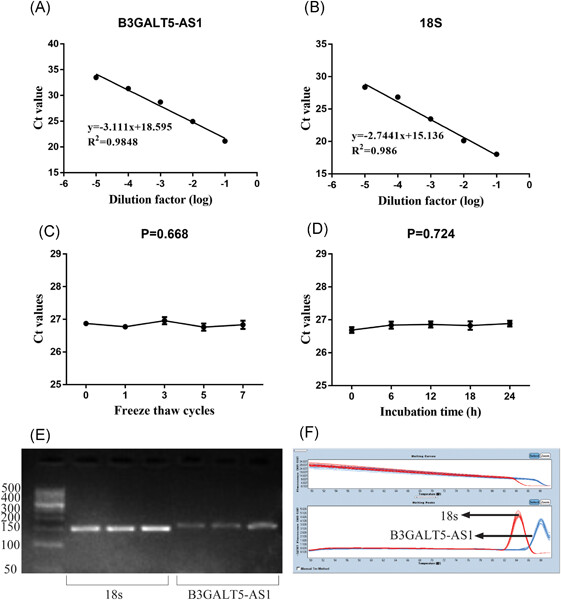
Abnormally expressed long noncoding RNA B3GALT5-AS1 may serve as a biomarker for the diagnostic and prognostic of gastric cancer
- Pages: 557-565
- First Published: 24 July 2019
Inducing differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells by coculturing with human hepatocyte L02 cells
- Pages: 566-573
- First Published: 12 August 2019
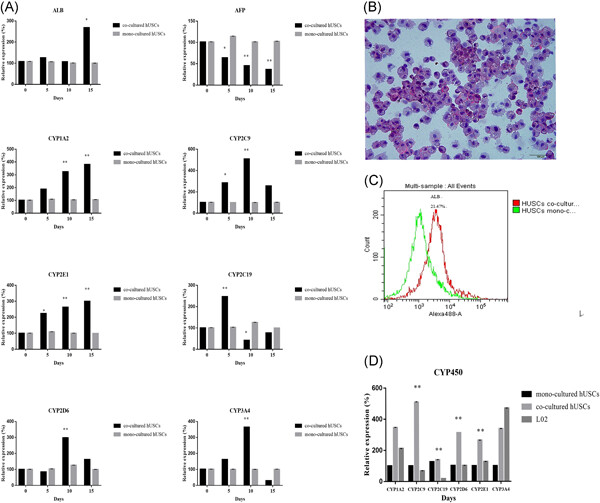
In this study, we have successfully collected and subcultured human-derived stem cells (hUSCs) from fresh human urine. HUSCs had various biological characteristics of adult mesenchymal stem cells and could be induced to differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells by coculturing with human hepatocyte L02 cells.
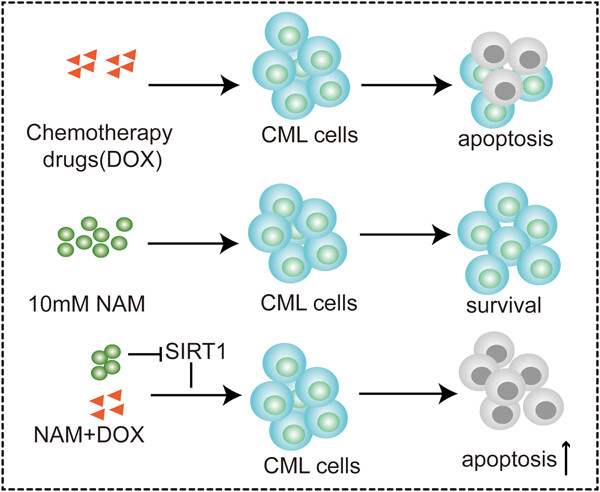
Nicotinamide increases the sensitivity of chronic myeloid leukemia cells to doxorubicin via the inhibition of SIRT1
- Pages: 574-586
- First Published: 12 August 2019
Ribosomal protein small subunit 15A (RPS15A) inhibits the apoptosis of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via upregulating phosphorylated ERK1/2, Bad, and Chk1
- Pages: 587-595
- First Published: 18 September 2019
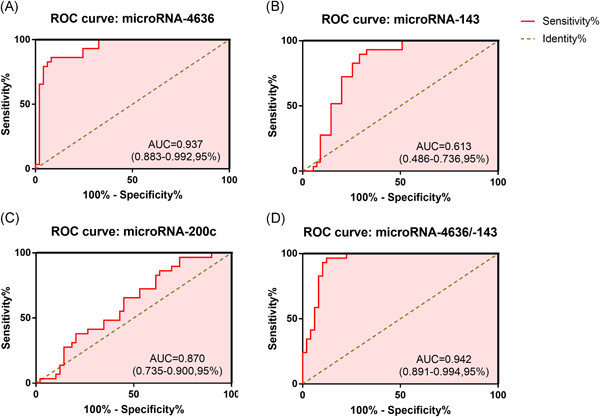
Peripheral blood circulating microRNA-4636/−143 for the prognosis of cervical cancer
- Pages: 596-608
- First Published: 12 August 2019
ssc-miR-204 regulates porcine preadipocyte differentiation and apoptosis by targeting TGFBR1 and TGFBR2
- Pages: 609-620
- First Published: 28 July 2019
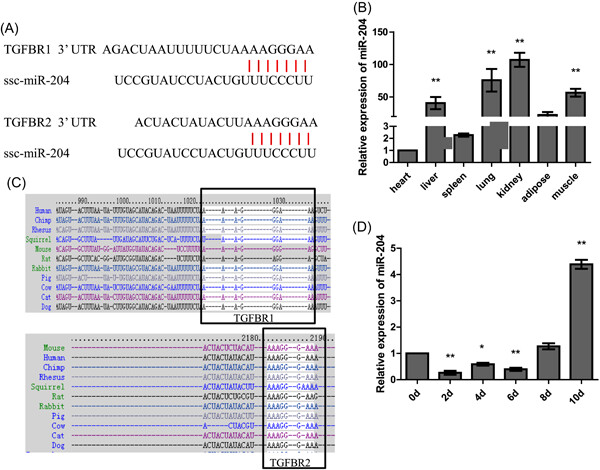
Collectively, our results indicate that ssc-miR-204 is a negative regulator that targets transforming growth factor β receptor 1 (TGFBR1) and TGFBR2 in the TGF-β signaling pathway to promote preadipocyte differentiation and apoptosis. A better understanding of ssc-miR-204 in the context of preadipocytes will be beneficial for human medical research.
LncRNA CCAT1 functions as apoptosis inhibitor in podocytes via autophagy inhibition
- Pages: 621-631
- First Published: 29 August 2019
Linc-RoR promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion via the Hippo/YAP pathway in pancreatic cancer cells
- Pages: 632-641
- First Published: 26 August 2019
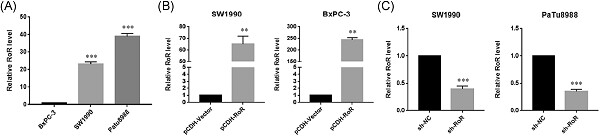
Large intergenic noncoding RNA regulator of reprogramming (Linc-RoR) promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by activating the Hippo/YAP pathway. YAP might be an underlying target of Linc-RoR and mediate EMT in pancreatic cancer (PC); thus, Linc-RoR might be a very meaningful biomarker for PC
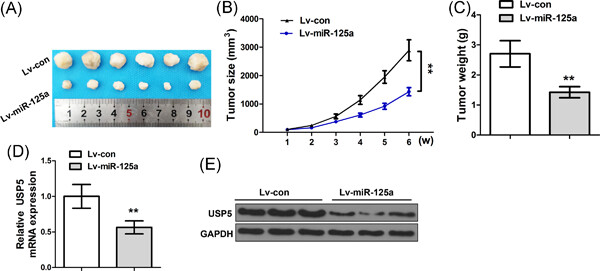
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: miR-125a suppresses malignancy of multiple myeloma by reducing the deubiquitinase USP5
- Pages: 642-650
- First Published: 26 August 2019
RESEARCH ARTICLES
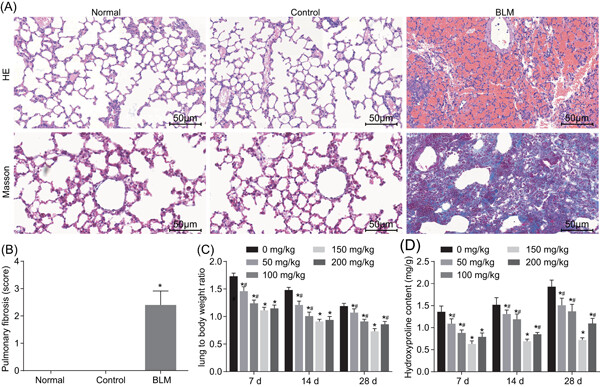
Protective effect of bicyclol against pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of microRNA-455-3p in rats
- Pages: 651-660
- First Published: 12 August 2019
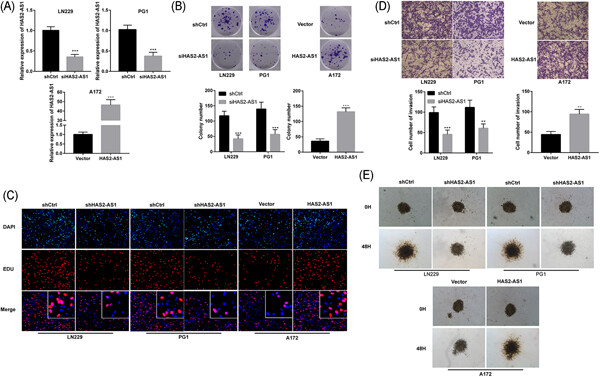
Long noncoding RNA HAS2-AS1 promotes tumor progression in glioblastoma via functioning as a competing endogenous RNA
- Pages: 661-671
- First Published: 05 August 2019
Identification of novel prognostic alternative splicing signature in papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 672-689
- First Published: 12 August 2019
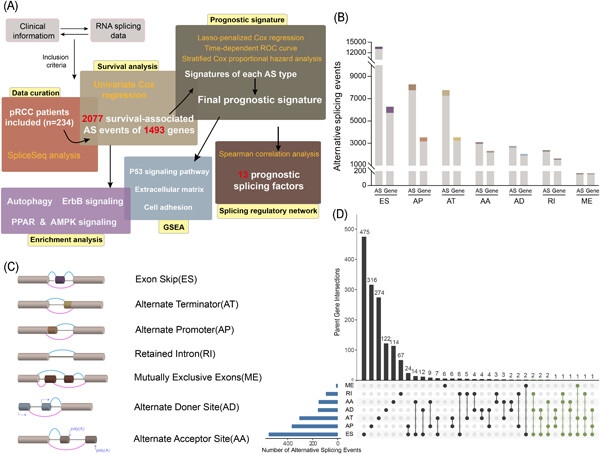
In the current study, we provided a comprehensive portrait of global changes in alternative splicing (AS) signature in papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) for the first time. Furthermore, we constructed an independent prognostic signature comprised of 21 AS events, which showed robust prognostic capacity in both short- and long-term prognosis prediction for clinical patients with pRCC. Moreover, functional enrichment analysis, gene set enrichment analysis and splicing correlation network with prognostic splicing factors were performed to decipher the underlying mechanisms of AS in pRCC.
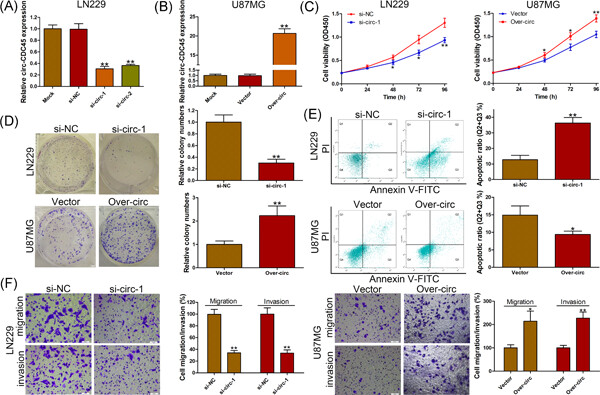
Overexpression of circular RNA circ-CDC45 facilitates glioma cell progression by sponging miR-516b and miR-527 and predicts an adverse prognosis
- Pages: 690-697
- First Published: 12 August 2019
miR-496 remedies hypoxia reoxygenation–induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte apoptosis via Hook3-targeted PI3k/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway activation
- Pages: 698-712
- First Published: 22 August 2019
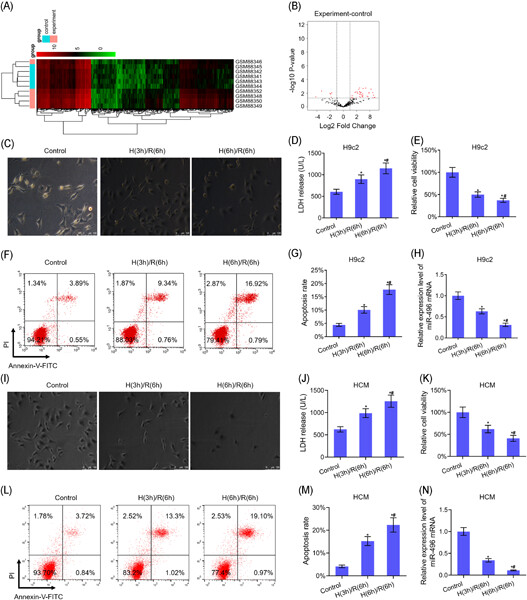
microRNA-496 (miR-496) exercises a defensive function in H9c2 ischemia-reperfusion–injury via direct hook microtubule tethering protein 3 (Hook3) downregulation that suppresses cell apoptosis. And miR-496 targets Hook3 to activate the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) signaling pathway as well for antiapoptotic and proliferative effects.
Differentially expressed circular RNAs in maternal and neonatal umbilical cord plasma from SGA compared with AGA
- Pages: 713-722
- First Published: 05 August 2019
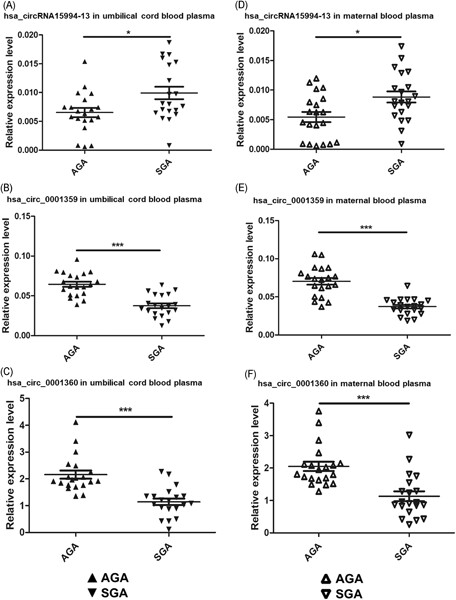
- 1.
The first study to detect the expression of circRNAs in the umbilical cord blood of small for gestational age (SGA).
- 2.
Expression of different circular RNA (circRNA) in maternal and umbilical cord blood were consistent.
- 3.
A new circRNA15994-13 → miR-3619-5p → β-catenin network in SGA was predicted by biochemical function analysis and literature search.
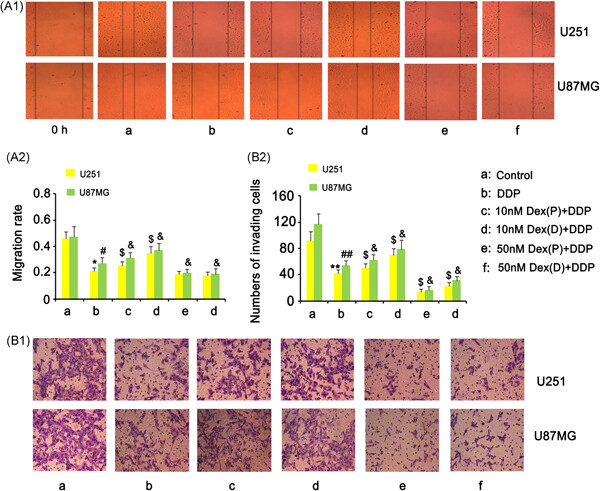
Effects of dexmedetomidine on glioma cells in the presence or absence of cisplatin
- Pages: 723-734
- First Published: 26 August 2019
LINC00346 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via activating the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway
- Pages: 735-742
- First Published: 03 September 2019
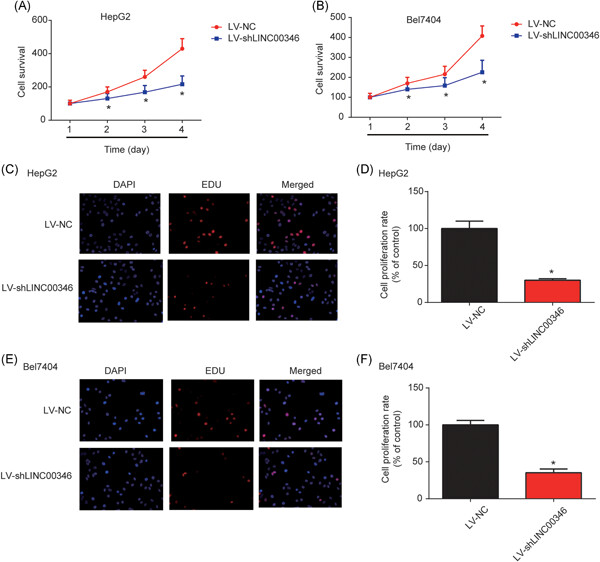
We newly described the role of LINC00346 and elucidated a potential mechanism in which Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK-STAT3) signaling was regulated by LINC00346. Knockdown of LINC00346 contributed to the inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression. We revealed that LINC00346 participated in HCC and that it might be a novel HCC biomarker via modulating JAK-STAT3.
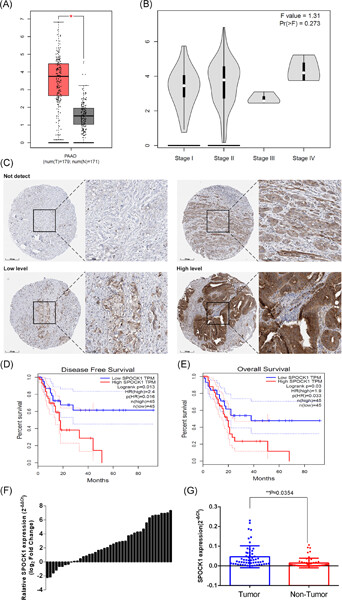
A potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target: SPOCK1 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells
- Pages: 743-754
- First Published: 03 September 2019
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-TF crosstalks and identification of prognostic regulatory feedback loops of glioblastoma using lncRNA/TF-mediated ceRNA network
- Pages: 755-767
- First Published: 03 September 2019
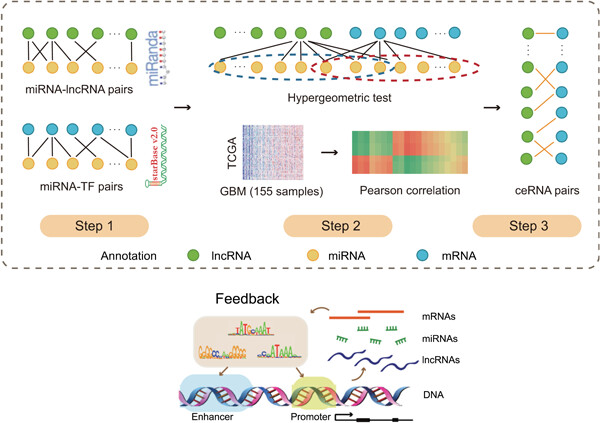
- 1.
A global view of long noncoding RNA transcription factor (lncRNA-TF) crosstalks was constructed for glioblastoma (GBM) investigation.
- 2.
Integration of competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) crosstalks and TF-DNA binding, some core lncRNA-TF feedback loops with strong prognostic effect were identified.
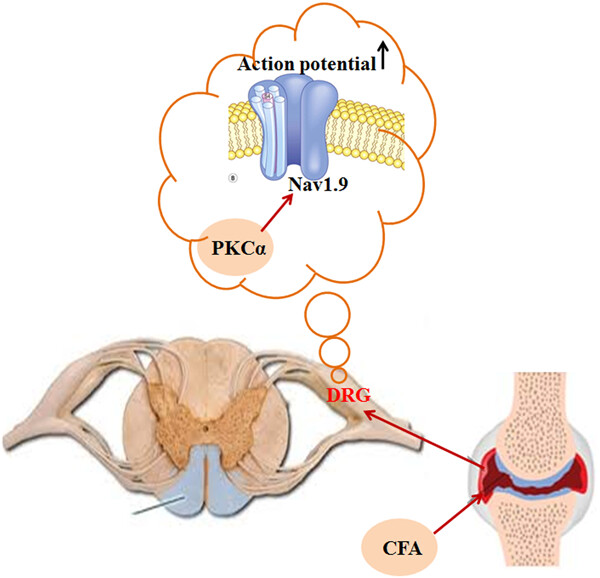
Protein kinase C-α upregulates sodium channel Nav1.9 in nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons in an inflammatory arthritis pain model of rat
- Pages: 768-778
- First Published: 05 August 2019
miR-605-5p promotes invasion and proliferation by targeting TNFAIP3 in non–small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 779-787
- First Published: 26 August 2019
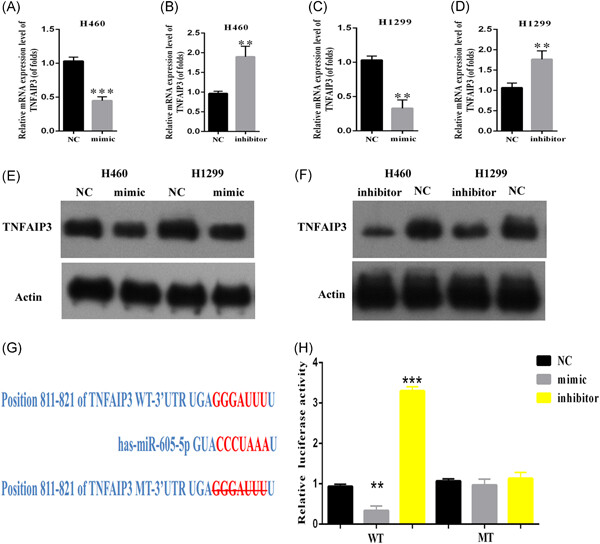
We showed that miR-605-5p plays a tumor-suppressor role in non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It functions mainly by targeting tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) expression. These findings suggest a specific mechanism of NSCLC progression and suggest miR-605-5p as a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC.
Resistance of human primary mesenchymal stem cells to cytotoxic effects of nutlin-3 in vitro
- Pages: 788-796
- First Published: 26 August 2019
SETD2 reduction adversely affects the development of mouse early embryos
- Pages: 797-803
- First Published: 12 August 2019
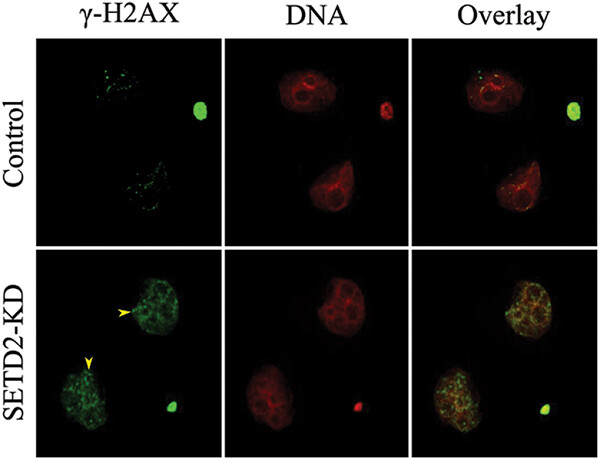
Our data indicate that SET domain-containing protein 2 (SETD2) maintains genome stability perhaps via regulating trimethylation status of histone H3 at lysine 36, consequently controlling the embryo quality. These findings pave the avenue for understanding the cross-talk between epigenome and SETD2 during early embryo development.
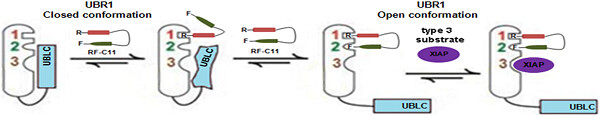
N-end rule pathway inhibitor sensitizes cancer cells to antineoplastic agents by regulating XIAP and RAD21 protein expression
- Pages: 804-815
- First Published: 12 August 2019
Effect of metformin on myotube BCAA catabolism
- Pages: 816-827
- First Published: 05 August 2019
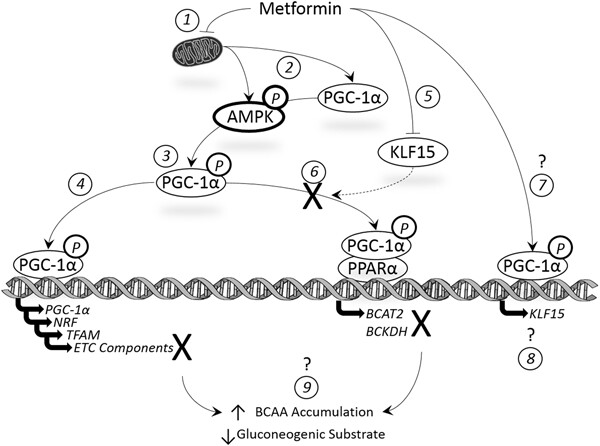
Metformin is an anti-hyperglycemic drug commonly prescribed for type II diabetes mellitus that functions by activating numerous molecular targets including 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α (PGC-1α). Population data shows circulating branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) positively correlate with the severity of insulin resistance/type II diabetes. Because metformin activates PGC-1α (which governs BCAA catabolic enzyme expression), we measured the effects of metformin on indicators of BCAA metabolism in cultured myotubes. We found that metformin suppresses BCAA catabolic enzyme expression and activity in cultured myotubes.
Hypoxia alters the release and size distribution of extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer cells to support their adaptive survival
- Pages: 828-839
- First Published: 12 August 2019
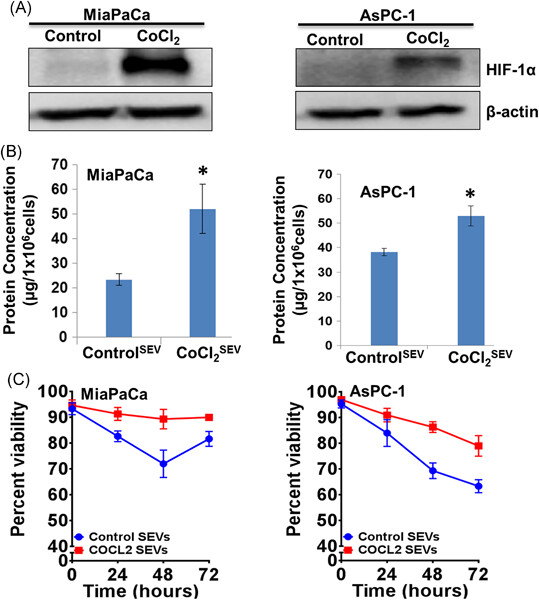
Hypoxia-induced changes in the release of extracellular vesicles (EV) by pancreatic tumor cells is an adaptive response mechanism. One of the functional significance is to promote their adaptive survival under hypoxia. Mechanistically, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) plays an important role in altered release of EVs and their potency to promote cell survival.
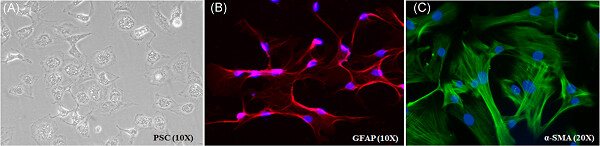
Pancreatic stellate cell-potentiated insulin secretion from Min6 cells is independent of interleukin 6-mediated pathway
- Pages: 840-855
- First Published: 26 August 2019
Identification of five long noncoding RNAs signature and risk score for prognosis of bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pages: 856-866
- First Published: 02 August 2019
A set of lncRNAs played a vital role in the progression of bladder carcinoma through certain signaling pathways. The current analysis indicated that the newly-constructed risk prediction model might benefit the early diagnosis and the underlying pathways might be a potential therapeutic target in the future. The pathways, containing PI3K-Akt, HIF-1, and Jak-STAT signaling pathways, ought to be applied to clinical usage and warranted by advanced cytobiology technologies.
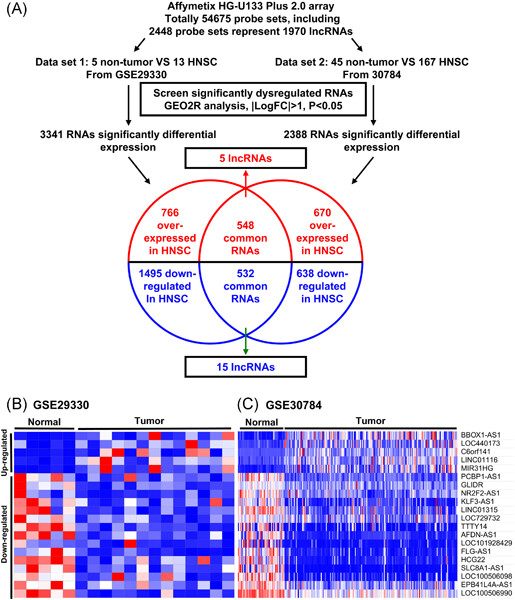
Knockdown of LINC01116 inhibits cell migration and invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway
- Pages: 867-875
- First Published: 26 August 2019
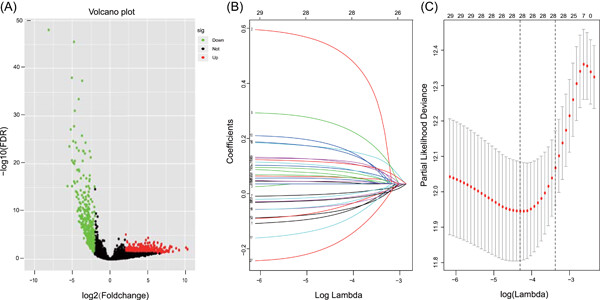
Identification of the complex regulatory relationships related to gastric cancer from lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network
- Pages: 876-887
- First Published: 26 August 2019
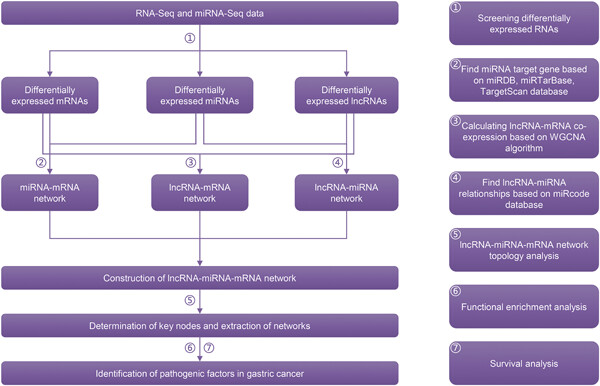
We constructed lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in gastric cancer and identified the key nodes based on complex network theory. Functional enrichment analysis and survival analysis of key genes in network related to key nodes were performed. The key factors in gastric cancer regulatory network can provide new insights into understanding the pathogenesis of gastric cancer and the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer.