Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Strategy for Enhancing Catalytic Active Site: Introduction of 1D material InSeI for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Formate (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Front Cover
In article number 2401157, Yu, Choi, Oh, and co-workers introduce a one-dimensional material indium selenide iodide (InSeI) for electrocatalytic template. Oxygen vacancies emerge through electrochemical treatment and boosting local pH and stabilizing active sites. The catalyst achieves over 97% formate selectivity and excellent stability over 50 hours, highlighting the potential of utilizing one-dimensional material as an electrochemical catalyst.
Inside Front Cover
Chemo-optogenetic Dimerization Dissects Complex Biological Processes (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Inside Front Cover
In recent years, chemo-optogenetic dimerization tools, represented by photo-responsive chemical inducers of dimerization (pCIDs), have been developed for spatiotemporal regulation of cellular functions. These dimerizers enable turning ON (paCID), turning OFF (pdCID), or switching between ON/OFF (psCID) of cellular activities. Apart from small molecule pCIDs, nanobody-conjugate photodimerizers are also emerging. These advancements create new opportunities for dissecting complex biological processes. More in article number 2401271, Chen and co-workers.
Inside Back Cover
Modular Micromotor Fabrication with Self-Focusing Lithography (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Inside Back Cover
In article number 2401388, Zeng, Tang, and co-workers introduce a mass production method for micromotors featuring a particle-tip structure, achieved through self-focusing lithography induced by an array of TiO2 microspheres. By adjusting the tip composition, various capabilities such as photo-redox reaction-induced propulsion, fluorescent imaging, and electric and magnetic navigation are successfully demonstrated. Furthermore, the fabrication of double-tipped motors showcases the method's flexibility and potential for multifunctional combinations.
Back Cover
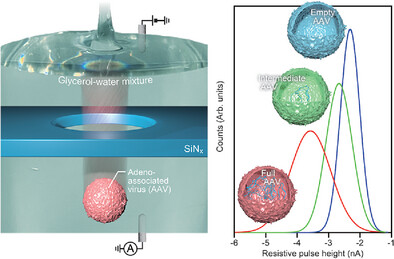
Enhanced Discriminability of Viral Vectors in Viscous Nanopores (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Back Cover
In article number 2401321, Tsutsui, Okada, and co-workers demonstrated the precise discrimination of full, intermediate, and empty adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors by solid-state nanopore sensing. This innovative method represents a significant advancement in quality control for AAV products, facilitating their broader application in gene therapy.
Issue Information
Special Section: Intelligent Biomedical Engineering
Special Section: Guest Editorial
Pioneering Biomedical Applications with Intelligent Engineering
- First Published: 17 June 2025
Special Section: Perspective
Chirality Quantification for High-Performance Nanophotonic Biosensors
- First Published: 08 April 2025
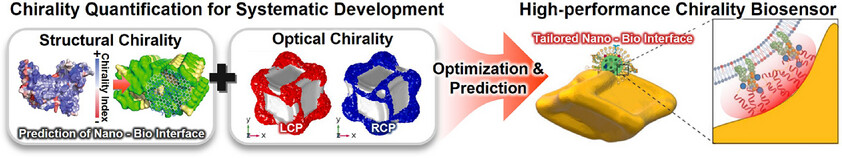
This work investigates the critical role of quantifying structural and optical chirality in advancing biosensing. By leveraging these analyses, this work predicts and optimizes nano-bio interfaces, enabling the development of high-performance chiral biosensors tailored to specific bioanalytes. This tailored approach to nano-bio interface engineering is poised to drive innovative advancements in next-generation biosensing technologies.
Special Section: Review
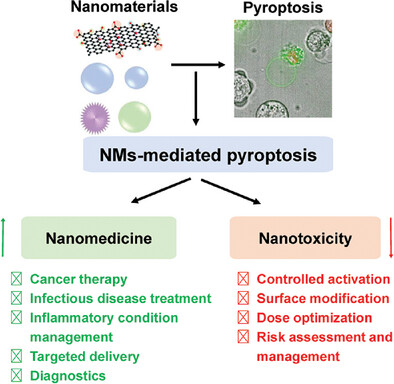
Nanomaterials-Induced Pyroptosis: Advancing Novel Therapeutic Pathways in Nanomedicine
- First Published: 24 January 2025
Oral Delivery Strategies for Biological Drugs
- First Published: 21 March 2025
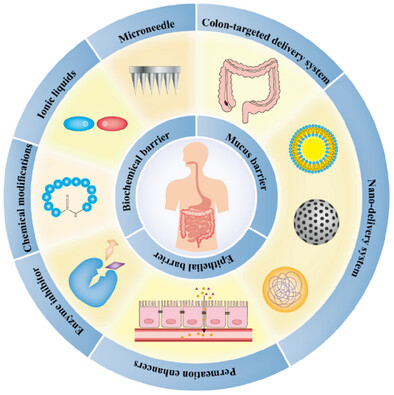
This review summarizes the oral biologics on the market and oral biologics-based technologies, discusses the advantages and disadvantages of advanced oral delivery technologies, and concludes that, with further in-depth study of biological drugs and rapid development of delivery methods, new opportunities will emerge for the oral delivery of macromolecular drugs.
Nanomedicine in Immunotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Applications and Perspectives
- First Published: 28 January 2025
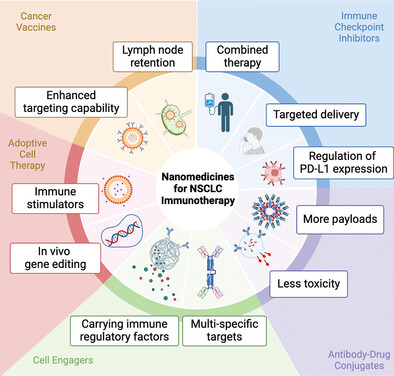
This review delineates the current clinical panorama of immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), highlighting the deployment and anticipated advancements of nanomedicine in NSCLC immunotherapy. It stands as a purposeful reference for researchers and clinicians actively involved in NSCLC immunotherapy research and practice.
Recent Advances in DNA-Templated Protein Patterning
- First Published: 02 February 2025
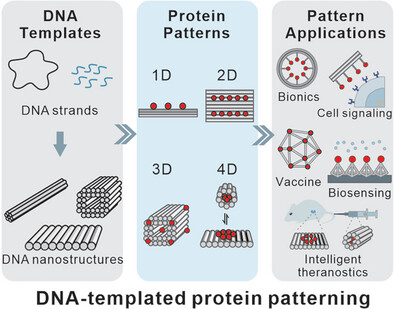
This review summarizes recent advancements in the fabrication of protein patterns across various dimensions using DNA nanostructural templates, exemplifying their applications in biological analysis and biomedicine. DNA-protein patterns are highlighted with programmable dynamics. Current challenges and proposed promising future directions in this field are discussed.
Synchrotron-Based X-Ray Molecular Probes for Imaging in Intelligent Biomedicine
- First Published: 28 February 2025
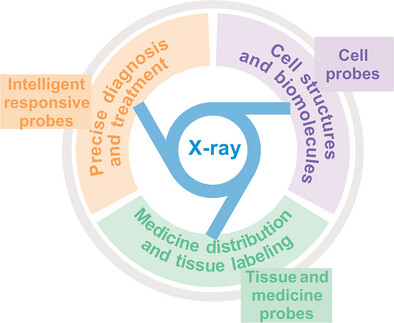
This review provides an overview of synchrotron-based X-ray imaging techniques and emphasizes the applications of X-ray molecular probes across various fields associated with intelligent biomedicine. Building on this foundation, it further discusses future advancements in X-ray molecular probes and forecasts their application trends in intelligent biomedicine.
Responsive Microneedles for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications of Ocular Diseases
- First Published: 17 March 2025
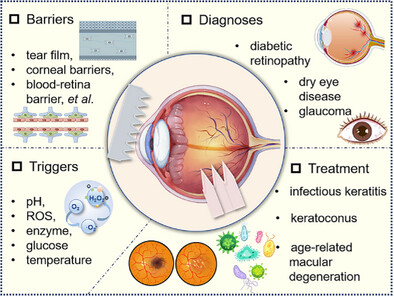
Owing to their strength in targeting, precision, and noninvasiveness, intelligent responsive microneedles showcase vast potential for broad clinical application in ocular diseases. This review focuses on the exciting achievements of intelligent responsive microneedles for the management of various ocular diseases and their capacity for real-time disease monitoring.
Exosome-Based Theranostic for Gastrointestinal Cancer: Advances in Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutic Engineering
- First Published: 25 February 2025
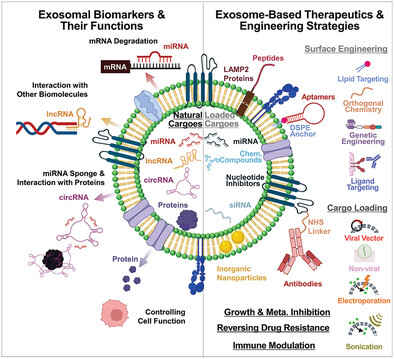
This review explores the dual roles of exosomes in gastrointestinal (GI) cancers as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic agents. It highlights advancements in exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs, circRNAs, and proteins for cancer detection and prognosis. The study also examines engineering strategies for exosome-based drug delivery systems, their potential to inhibit growth, reverse drug resistance, modulate immunity, and addresses challenges in clinical translation.
Opportunities and Challenges for Nanomaterials as Vaccine Adjuvants
- First Published: 25 April 2025
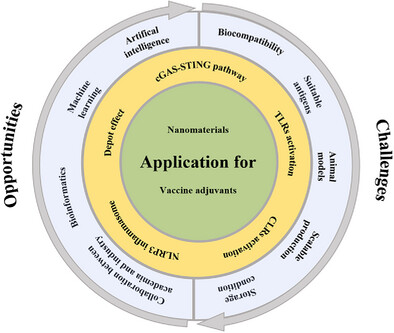
This review summarizes various nanomaterials with adjuvant potential, from inorganic to organic types, and highlights common mechanisms of action. It also discusses opportunities and challenges, such as integrating artificial intelligence and fostering industry-research collaboration, which are thoroughly discussed.
Intelligent Nanomaterials Design for Osteoarthritis Managements
- First Published: 30 March 2025
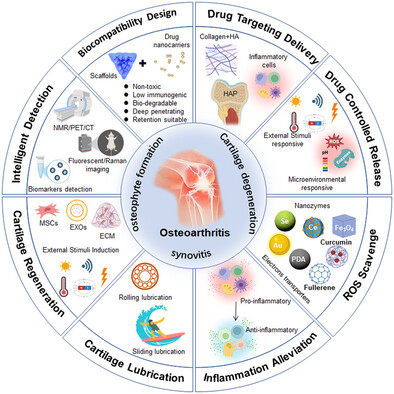
Intelligent nanomaterials are engineered to address the pathological features of osteoarthritis (OA), such as cartilage degeneration, synovitis, and osteophyte formation. The advancements focus on enhancing biocompatibility, targeted drug delivery, controlled release, ROS scavenging, inflammation reduction, cartilage lubrication, and regeneration. This review provides insights into effective OA treatment strategies and encourages further innovation in the clinical translation of smart nanomedicines. (Created with BioRender.com).
Bioinspired Soft Robots with Integrated Biological Motion Mechanisms and Rigid–Flexible Coupling Systems
- First Published: 06 May 2025
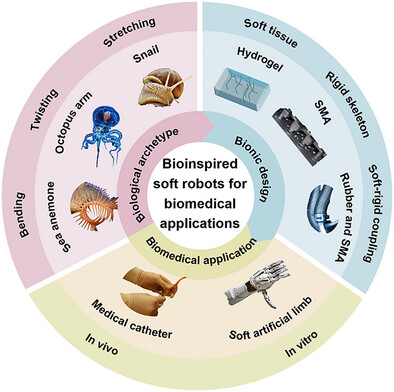
Soft robots inherently exhibit flexibility, safety, and biocompatibility, demonstrating significant potential in biomedical engineering. Their unique in vivo and in vitro operating environments necessitate exceptionally flexible movement capabilities. Inspired by nature's shape-morphing creatures, researchers have developed bioinspired soft robots (BSR). This review systematically examines the biological prototypes, motion mechanisms, and design strategies of BSR, along with their biomedical applications, while analyzing the associated challenges and future opportunities (created with https://pixabay.com/).
Recent Advances in Nanomedicine-Mediated Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Treatment
- First Published: 19 May 2025
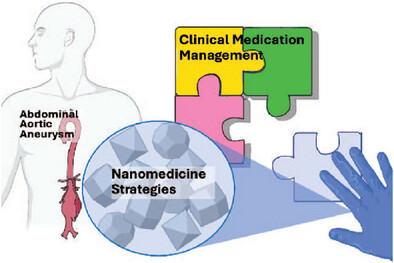
Bridge the gap. Emerging strategies such as nanoparticle platforms and cell therapies may help advance the medication management of abdominal aortic aneurysm from laboratory to clinical application. By enhancing the precision, efficacy, ad comprehensiveness of drug delivery, a wide range of studies have obtained positive outcomes and are summarized in this review.
Deep Learning Based Models for CRISPR/Cas Off-Target Prediction
- First Published: 04 June 2025
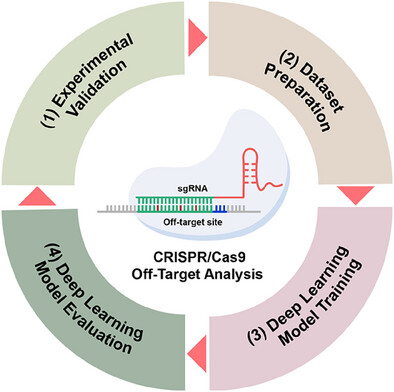
This review highlights the recent advancements in using deep learning models for CRISPR/Cas9 off-target sites (OTS) prediction. Incorporating validated OTS datasets into model training significantly enhances the overall performance and predictive robustness. Among the models evaluated, CRISPR-Net, R-CRISPR, and Crispr-SGRU demonstrate strong performance. These findings underscore the importance of integrating high-quality datasets with advanced model architectures to improve the accuracy of CRISPR/Cas off-target site predictions.
Exosome-Based Vaccines: Pioneering New Frontiers in Combating Infectious Diseases and Cancer
- First Published: 08 April 2025
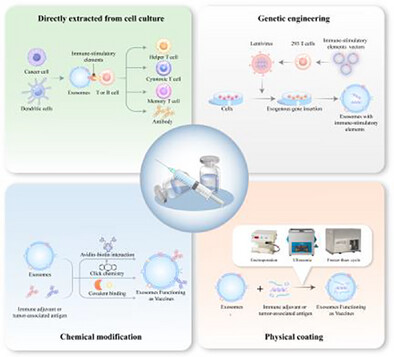
Exosome-based vaccines are emerging as a promising form of immunotherapy. This review introduces the sources, biogenesis mechanisms, and components of exosomes and describes their regulatory roles in the immune system. It explores the preparation, administration, and personalized therapy of exosome-based vaccines. The review highlights the applications and clinical trials of exosome-based vaccines in the fields of anti-infection and anti-tumor therapies.
Special Section: Research Article
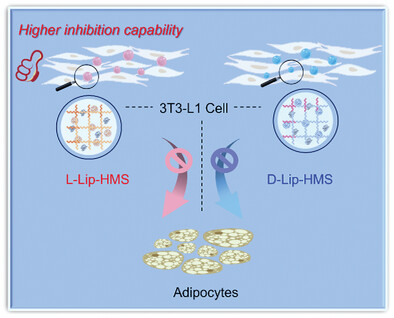
Improved Catalytic Performance of Lipase Within Hydrogel Microspheres Incorporating L/D-Co3O4 Nanoparticles
- First Published: 12 December 2024
Luteolin-Loaded Hyaluronidase Nanoparticles with Deep Tissue Penetration Capability for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment
- First Published: 06 October 2024
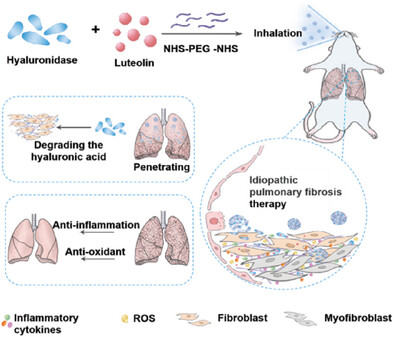
Lut@HAase, which promotes luteolin permeation through hyaluronidase-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix. These particles are suitable for noninvasive inhalation and accumulation in the lungs, and hyaluronidase at the site of lesions can degrade hyaluronic acid in the interstitial tissue, enabling efficient penetration of luteolin. The particles exert anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-fibrosis, thereby treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
An Intelligent Hydrogel Platform with Triple-Triggered On-Demand Release for Accelerating Diabetic Wound Healing
- First Published: 19 September 2024
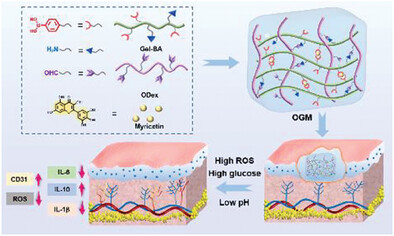
An intelligent hydrogel platform (OGM) with triple-triggered (pH, ROS, and glucose) on-demand release is constructed through Schiff base reaction and borate ester bonds. The intelligent OGM hydrogel can intelligently scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and modulate the wound microenvironment to accelerate diabetic wound healing through the rapid release of myricetin.
Platelet Activation-Induced In Situ Trapping Metastatic Tumor Cells Strategy for Post-Surgery Tumor Recurrence Immunochemotherapy
- First Published: 21 November 2024
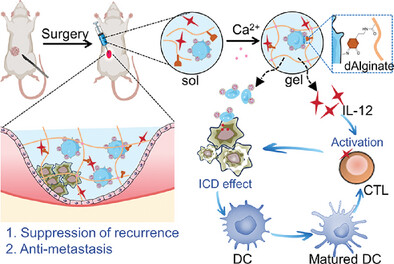
To combat breast cancer metastasis post-surgery, a platelet-based hydrogel delivery system is designed to capture metastatic tumor cells and modulate the immune microenvironment. Small-sized drug-loaded vesicles are responsively released from platelets for effectively trapping metastatic tumor cells and inducing immunogenic cell death. Furthermore, the incorporation of IL-12 can synergistically enhance the immunosuppressive microenvironment following surgery. In a mouse model of 4T1 tumor recurrence and metastasis, this system has demonstrated effective suppression of both tumor recurrence and metastasis.
Neutrophil Hitchhiking-Mediated Delivery of ROS-Scavenging Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Treatment of Atherosclerosis
- First Published: 20 March 2025
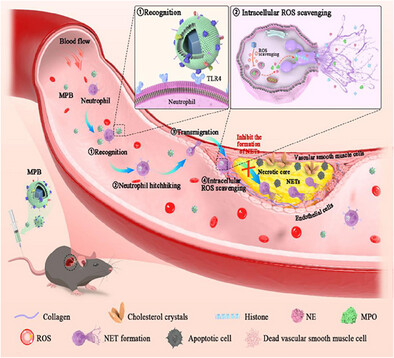
The study presents a biomimetic nanosystem for the targeted inhibition of NET formation to treat Atherosclerosis (AS). Upon modification with the bacterial biomimetic membrane, MPB specifically targets the neutrophils. By effectively scavenging ROS within neutrophils, it inhibits the formation of NETs, protects smooth muscle from damage, and significantly reduces the plaque area. This strategy remarkably reduces plaque burden and enhances stability, providing new insights for AS treatment.
DNA Nanoflower-Powered CRISPR/Cas12a Biosensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Protein Detection in Clinical Samples
- First Published: 27 March 2025
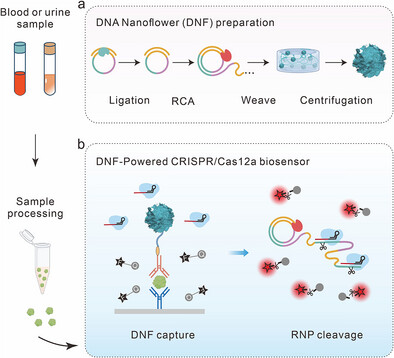
A DNA Nanoflower-Powered CRISPR/Cas12a biosensor (DNF-CRISPR) is constructed that amplifies protein marker input signals by DNF and output signals by CRISPR-Cas12a, achieving a cascade amplification of signal input and output. DNF-CRISPR enables high sensitivity (500 fg mL−1) and rapid (≤2 h) detection of protein, exhibiting a strong correlation with clinical diagnoses of kidney injury (91% accuracy).
Engineered Intelligent Microenvironment Responsive Prodrug Conjugates Navigated by Bioinspired Lipoproteins for Reversing Liver Fibrosis
- First Published: 19 March 2025
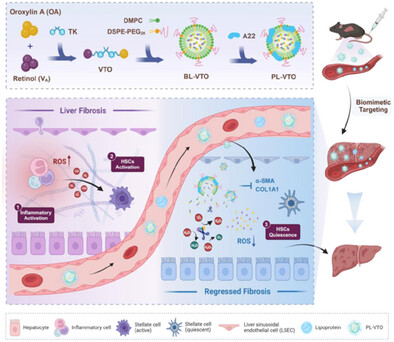
In this study, PL-VTO, an intelligent prodrug conjugate delivery system based on self-navigating biomimetic lipoprotein nanoparticles, is constructed. It can stimulate the microenvironment of the lesion, releasing two maternal drugs, effectively removing ROS, induce quiescence of activated HSCs, and eventually reversing liver fibrosis. This work provides an idea for achieving the codelivery requirements of multiple drugs in complex lesions and for the effective treatment of liver fibrosis.
Tracking In Vivo Lipolysis of Lipid Nanocarriers Using NIR-II Polarity-Sensitive Fluorescent Probes
- First Published: 11 March 2025
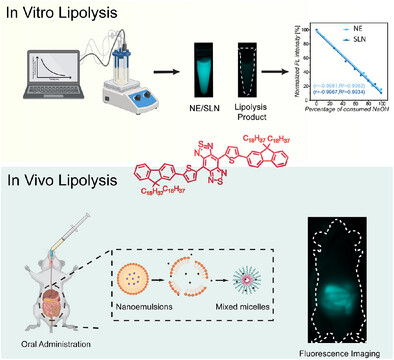
A novel polarity-sensitive probe (PN-C18) with aggregation-caused quenching property is developed to label lipid nanocarriers. PN-C18 labeling eliminates interferences from both free probes and mixed micelles during lipolysis. This provides an excellent correlation between fluorescence intensity and lipolysis progression in vitro and precise visualization of lipid nanocarriers in vivo.
A General Approach to Predict and Tailor the Nanoscale Permeability of Comb-Shaped Polymer Coatings
- First Published: 02 June 2025
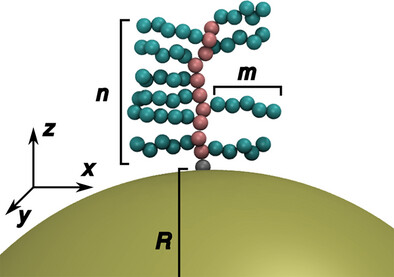
Comb-shaped polymers are used to produce ‘molecular sieving’ coatings. The steric and size-selective permeability characteristics of comb-polymer coatings are systematically explored in silico across a very broad parameter space. All features of the data can be understood when three distinct regimes are considered: i) no-interactions, ii) weak-interactions, and iii) strong-interactions between adjacent polymer chains.
Immune-Vascular Synergy: A Photodynamic Hydrogel Activating ALDH2 to Combat Inflammation and Enhance Angiogenesis in Diabetic Wound Healing
- First Published: 13 May 2025
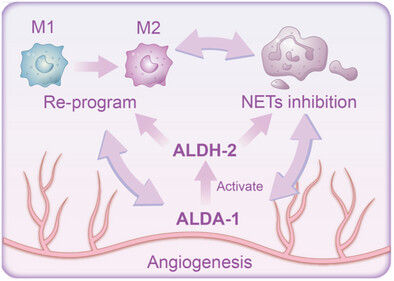
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 released from the hydrogel provides a multifaceted function of modulating immune responses, enhancing angiogenesis, and reprogramming the crosstalk between immunity and vascularization, providing a pro-healing loop in the wound site and promoting tissue regeneration and wound closure.
Review
Chemo-optogenetic Dimerization Dissects Complex Biological Processes
- First Published: 15 January 2025
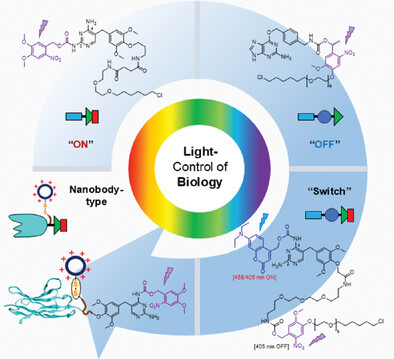
Chemo-optogenetic dimerization uses photosensitive small molecules with genetically introduced protein tags as a versatile platform for regulating diverse cellular processes and dissecting complex biological networks. Currently, chemo-optogenetic dimerization can be classified into several types: photoactivatable dimerizers (ON), photocleavable dimerizers (OFF), photoswitchable dimerizers (Switch), and nanobody conjugate versions, each associated with different features and application scenarios.
Research Article
Modular Micromotor Fabrication with Self-Focusing Lithography
- First Published: 07 November 2024
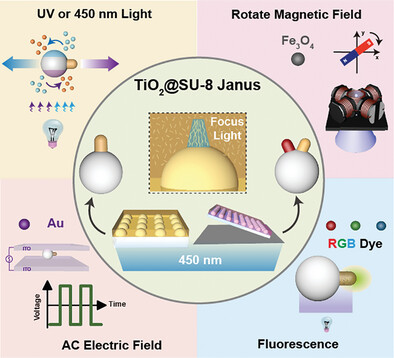
A versatile and high-yield fabrication method is developed for Janus micromotors featuring a spherical tip configuration, achieved through the localized photocuring of SU-8 on a TiO2 microsphere array. These motors exhibit various functionalities by loading dyes onto the spheres or modifying the composition of tips. Moreover, the efficacy of this method in the production of multifunctional double-tipped motors is demonstrated.
Review
Circulating Tumor Cells Culture: Methods, Challenges, and Clinical Applications
- First Published: 27 December 2024
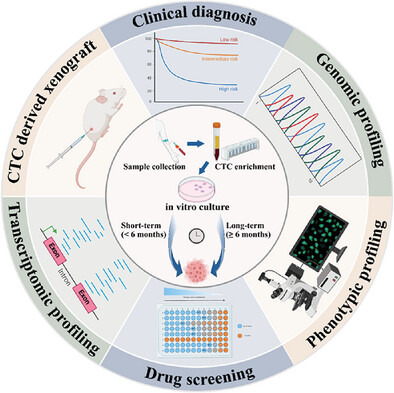
Procedural steps involved in processing and applications of in vitro culture of CTCs. Various methods are employed to expand CTCs, which are subsequently utilized in diverse analyses including phenotypic profiling, clinical diagnosis, genomic and transcriptomic profiling, drug screening, and CTC-derived xenograft models. These applications offer valuable insights into cancer metastasis mechanisms, patient prognosis assessment, and clinical drug guidance. Created with BioRender.com.
Research Article
Enhanced Non-Invasive Radio Frequency Heating Using 2D Pyrite (Pyritene)
- First Published: 05 February 2025
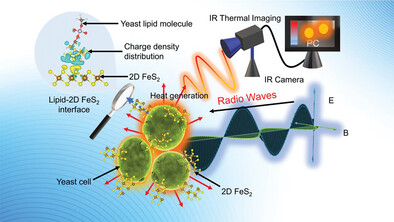
This study demonstrates effective non-invasive RF heating using a hybrid yeast-2D FeS₂ system, attaining a fast-heating rate of 1.27 °C s−1 at 3W RF power (50 MHz), which results from ionic diode-like properties and polar conductive channels identified by DFT calculations. The results provide insights into leveraging interactions between 2D materials and biomolecules for specific RF heating applications.
Catalyst-Free Polymorphic β-Ga2O3 Nanomaterials for Solar-Blind Optoelectronic Devices: Applications in Imaging and Neural Communication
- First Published: 11 December 2024
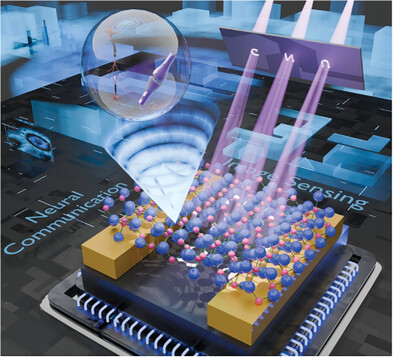
A study on polymorphic β-Ga2O3 nanomaterials synthesized via a low-cost tube sealing and muffle calcination process reveals their exceptional ultraviolet-C (UV-C) optoelectronic performance. High-sensitivity UV-C photodetectors fabricated with β-Ga2O3 nanobelts enable clear imaging, while β-Ga2O3 nanowire-based optoelectronic synapses demonstrate neural signal transmission. These devices showcase significant potential in advanced UV-C optoelectronics, particularly in image sensing and neural communication applications.
Enhanced Discriminability of Viral Vectors in Viscous Nanopores
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Strategy for Enhancing Catalytic Active Site: Introduction of 1D material InSeI for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Formate
- First Published: 12 November 2024
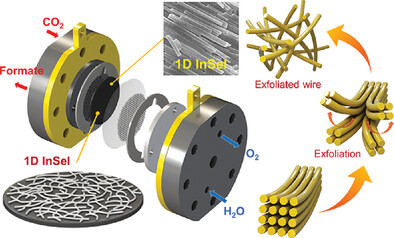
A strategy for electrochemical CO2 conversion to formate production utilizing InSeI 1D materials is described. This study suggests that the use of 1D materials improves the absolute particle size and chemically active sites. This indicates the potential for further research on 1D materials as electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR).
Frontispiece
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Approach for Measuring the Diffusion Range in Optical Fibers with Nanostructured Cores (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Optical Fibers
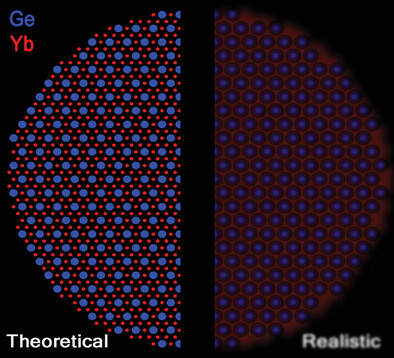
A SIMS sputtering process of an optical fiber reveals the interplay between theory and reality. While an idealized model predicts dopant placement, real-world diffusion alters the picture. The measured 1D profile requires precise angle correction, leading to the determination of diffusion lengths. The results highlight stark contrasts—germanium retains structure, while ytterbium forms a nearly homogeneous distribution. More in article number 2401601, Michalowski and co-workers.
Research Article
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Approach for Measuring the Diffusion Range in Optical Fibers with Nanostructured Cores
- First Published: 08 December 2024
Frontispiece
A Strategy for Mitigating Lattice Stress and Enhancing Cycle Stability Through Modulating Transition Metal Redox Sequence (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Transition Metal Redox Properties
Manipulating the redox properties of transition metals in layered cathode structures is crucial for developing high-performance cathode materials. Incorporating Mg2+ into LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 alters the oxidation sequence of transition metals during lithium extraction, with Co3+ replacing Ni2+ as the primary oxidized species initially. Investigating the mechanism and electrochemical impact of this effect could offer valuable insights for designing materials with superior cycle stability. More in article number 2401868, Wang, Cheng, Zhang, and co-workers.
Research Article
A Strategy for Mitigating Lattice Stress and Enhancing Cycle Stability Through Modulating Transition Metal Redox Sequence
- First Published: 23 December 2024
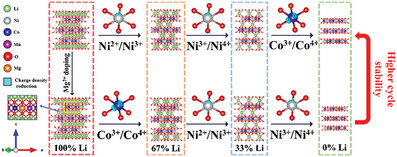
Tailoring the redox characteristics of transition metals within layered cathode structures is a pivotal strategy for the advancement of high-performance cathode materials. Recent findings have uncovered a novel phenomenon: the incorporation of Mg2+ into LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 results in a shift in the oxidation sequence of transition metals during lithium extraction, with Co3+ replacing Ni2+ as the primary oxidized species during the initial stages of lithium extraction. The investigation into the underlying mechanism of this induced effect and its impact on electrochemical performance promises to provide new insights for the design of materials with exceptional cycle stability.
Frontispiece
Dome-Structure Array from Pre-Strained Extendable Mesh for Tactile Sensing Without Crosstalk and Lateral Strain Interference (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Tactile Sensors
The frontispiece illustration presents a strain-insensitive, tactile sensor array that eliminates crosstalk effects through a highly stretchable mesh design. This unique structure ensures that each sensing cell remains electrically isolated, allowing accurate pressure measurements without cell-to-cell crosstalk. The illustration depicts the strain-insensitive stretchable sensor functioning despite arm joint movement, monitoring sustained pressure on the elbow. More in article number 2401730, Kim and co-workers.
Research Article
Dome-Structure Array from Pre-Strained Extendable Mesh for Tactile Sensing Without Crosstalk and Lateral Strain Interference
- First Published: 16 January 2025
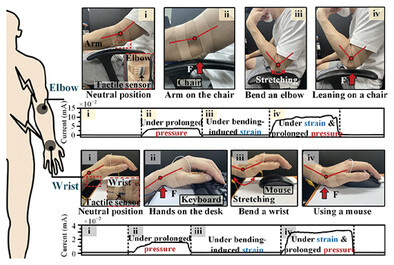
A tactile sensor based on CNT–PDMS clogged in a stretchable mesh is presented. The sensor exhibits negligible changes in sensing performance under lateral stretching of up to 100%. The advantages of sensitivity, sensing range, and repeatability enable the sensor to be used in various applications. Furthermore, prolonged pressure on the wrist and elbow is successfully monitored using the sensor.
Frontispiece
A Chemogenetic Toolkit for Inducible, Cell Type-Specific Actin Disassembly (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Actin Disassembly
In article number 2401522, Zhou, Zuchero, and co-workers develop “ChiActs,” first-in-class chemogenetic tools to induce actin disassembly in living cells. These tools will allow researchers to study the diverse cellular roles of actin filament assembly and dynamics across eukaryotic model systems. The image shows molecularly-accurate actin filaments being disassembled into actin monomers by ChiActs, which are depicted as a wrecking ball. Image credit: Dr. Janet Iwasa, University of Utah.
Research Article
A Chemogenetic Toolkit for Inducible, Cell Type-Specific Actin Disassembly
- First Published: 31 January 2025
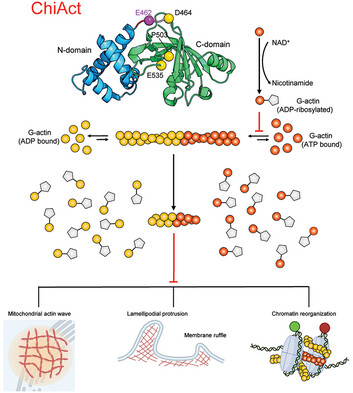
ChiActs are novel actin-perturbing genetic tools that can be rapidly activated by chemical actuators and optogenetically targeted to distinct subcellular locations using light. ChiActs rapidly induce actin disassembly in several model cell types and are able to perturb actin-dependent nano-assembly and cellular functions, including inhibition of lamellipodial protrusions and membrane ruffling, remodeling of mitochondrial morphology, and chromatin reorganization.
Frontispiece
Ultrafast Synthesis of Hard Carbon Anodes for Sodium-ion Batteries: An Intense-Pulsed-Light-Assisted Approach to Photothermal Carbonization of Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Composite Films (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Sodium-Ion Batteries
In article number 2401801, Lee, Jeong, Park, and co-workers demonstrate the ultrafast preparation of hard carbon anodes using intense-pulsed-light-assisted photothermal carbonization. The successive irradiation of intense pulsed lights enables the high-temperature carbonization of the polymer/SWCNT composite films in just one minute, providing a sustainable method for the large-scale, time-efficient, and energy-saving production of hard carbon anodes for future sodium-ion battery technologies.
Research Article
Ultrafast Synthesis of Hard Carbon Anodes for Sodium-ion Batteries: An Intense-Pulsed-Light-Assisted Approach to Photothermal Carbonization of Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Composite Films
- First Published: 15 January 2025
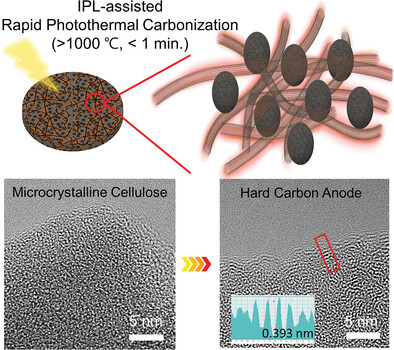
The ultrafast (<1 min) synthesis of hard carbon (HC) anodes using an intense pulsed light (IPL)-assisted photothermal carbonization process has been demonstrated. This research highlights IPL-assisted photothermal carbonization as a viable, time-efficient, and energy-saving alternative to conventional methods, offering a sustainable pathway for large-scale production of HC anodes for future sodium-ion battery technologies.
Frontispiece
Tailorable Thermal Conduction and Thermal Energy Storage Behaviors in 3D Printed Hierarchical Cellular Structure-Based Phase Change Materials (Small Methods 7/2025)
- First Published: 23 July 2025

Phase Change Materials
In article number 2402089, Qiu, Feng, and co-workers develop a framework of multiscale topology optimization for cellular structures assembled by periodic base cells. The optimized structure renders the minimum thermal compliance, showing the best heat dissipation performance. The findings are expected to provide higher storage and release rates of heat energy to achieve high-efficiency solar power generation.
Research Article
Tailorable Thermal Conduction and Thermal Energy Storage Behaviors in 3D Printed Hierarchical Cellular Structure-Based Phase Change Materials
- First Published: 21 February 2025
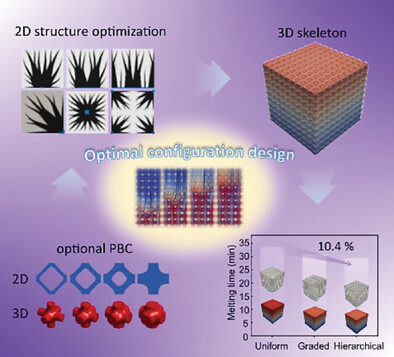
This work develops a framework of multiscale topology optimization for cellular structures, which can find out the optimal configuration and optimal density distribution for PBCs. The optimized topology structure turns out to be tree-like. The optimized cellular structure renders the minimum thermal compliance under a given constraint condition, and thus shows the best heat dissipation performance.
Spatial-Temporal Scanning Kelvin Probe Microscopy for Evaluating Ionic Velocity in Solid-State Electrolytes
- First Published: 17 June 2025
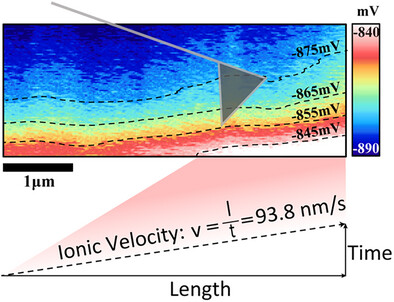
A simple yet effective approach is developed for in situ measurement of microscopic ionic velocity in solid-state electrolytes (SSEs). The ionic conductivity calculated from the spatiotemporal trajectory of ionic motion under an electric field is closely aligned with the result of macroscopic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy tests. This method, validated on LiZr2(PO4)3 and Li1.05Zr1.95Fe0.05(PO4)3, can be further extended to other SSEs.
Low-Temperature Single-Step Inkjet-Printed Metallic Patterns With Self-Regulated Vertical Compositional Gradient
- First Published: 15 May 2025
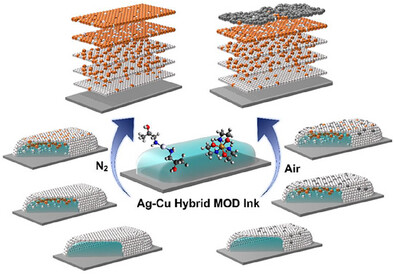
This study combines analysis of DFT modelling of complex structure decomposition studies with hybrid ink formulation resulting in inkjet printing of a range of useful electronic materials. The formulated hybrid MOD ink is exploited to form self-regulated layered pattern structures with vertical compositional gradient at low temperature.
Perspective
Synthetic Biology-Based Strategy for Nanomedicine Design
- First Published: 03 March 2025
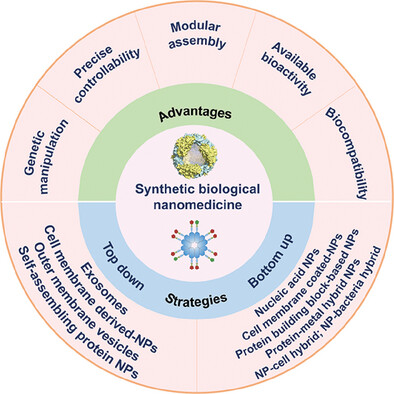
This Perspective provides an overview of the fundamental concepts of synthetic biological nanomedicine, defined as the application of gene-engineering strategies in the design and development of nanomedicines. It highlights two primary approaches in this field: top-down and bottom-up strategies. The Perspective explores recent advancements in leveraging these strategies for nanomedicine design and concludes with an analysis of the potential benefits and challenges associated with this rapidly evolving discipline.
Review
Electrochemical In Situ Characterization Techniques in the Field of Energy Conversion
- First Published: 09 January 2025
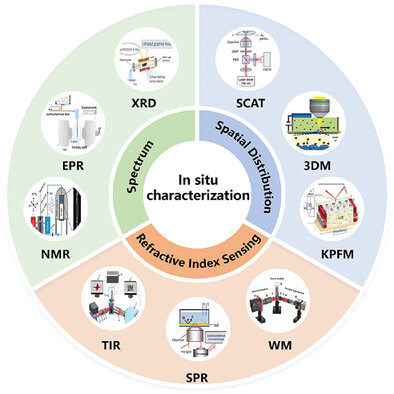
This paper comprehensively reviews electrochemical in-situ characterization techniques in the field of energy conversion from three perspectives: spectral characterization techniques of electrochemical reactions, characterization techniques for the spatial distribution of electrochemical reactions, and surface refractive index optical characterization techniques for the spatial analysis of electrochemical reactions.
MXene-Based Nanocomposites for Supercapacitors: Fundamentals and Applications
- First Published: 29 April 2025

MXene-based nanocomposites with 2D materials like transition metal oxides, transition metal chalcogenides, and layered double hydroxides improve supercapacitor performance. Here it reviews how these composites facilitate high capacitance, power density, and cycling stability, advancing next-generation energy storage.
Defects in MOFs for Photocatalytic Water Reduction to Hydrogen Generation: From Fundamental Understanding to State-of-Art Materials
- First Published: 30 November 2024
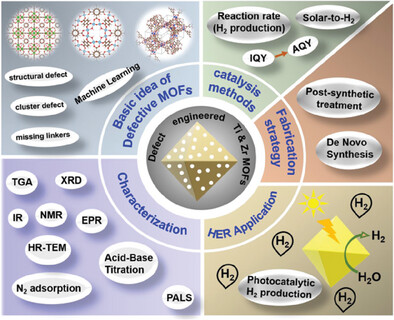
This review focuses on defect-engineered Ti and Zr based MOFs with tunable optoelectronic properties as promising approaches for solar-driven hydrogen production. It examines the impact of defect-induced structural and electronic modifications on charge transfer processes, alongside discussing innovative synthesis methods and advanced characterization techniques aimed at enhancing photocatalytic performance. The review also outlines key design principles and innovative strategies, addressing existing challenges, and emphasizing the role of machine learning (ML) in accelerating material design for efficient energy conversions.
Nanoarchitecturing of Bimetallic Metal‒Organic Frameworks for Emerging Applications in Quartz Crystal Microbalance Gas Sensors
- First Published: 12 May 2025
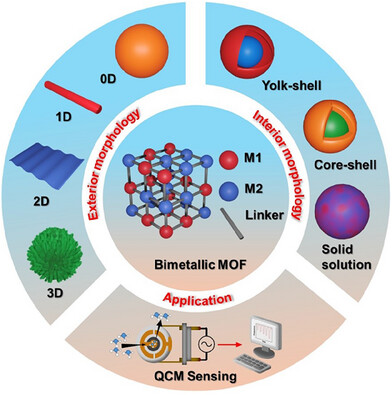
This review summarizes recent progress in the design and nanoarchitectural control of bimetallic metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and their applications in quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensors for the detection of various gases. It also discusses the underlying sensing mechanisms of bimetallic MOFs and concludes with challenges and future directions for advancing the synthesis and practical use of bimetallic MOFs in QCM-based sensing technologies.
Progress in Experimental Methods Using Model Electrodes for the Development of Noble-Metal-Based Oxygen Electrocatalysts in Fuel Cells and Water Electrolyzers
- First Published: 31 January 2025
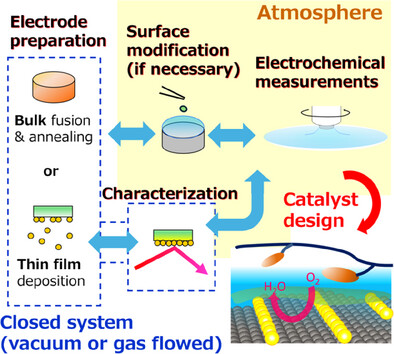
Electrochemical experimental studies using single-crystal electrodes as model catalysts, with controlled elemental distribution, microstructure, and modification patterns, provide valuable insights into reaction and degradation mechanisms as well as catalyst development strategies. This paper reviews these studies, focusing on electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions and oxygen evolution reactions, which are relevant to fuel cells and water electrolyzers.
Metal Halide Perovskite Single-Crystal Thin Films: From Films Growth to Light-Emitting Application
- First Published: 05 March 2025
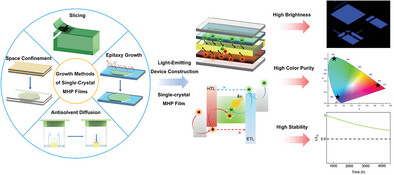
This review summarizes a general overview from perovskite single-crystal (SC) film growth to light-emitting applications and strategies to optimize SC perovskite light-emitting diodes (SC-PeLEDs) performance. Challenges and perspectives are proposed further to facilitate performance improvement and practical application of SC-PeLEDs. This review will help researchers develop a new perspective on SC-PeLEDs.
Advancements in 2D Titanium Carbide (MXene) for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption: Mechanisms, Methods, Enhancements, and Applications
- First Published: 28 January 2025
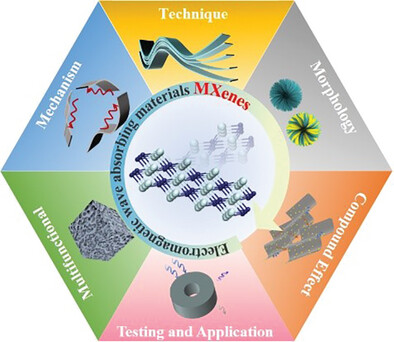
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the recent progress in MXene-based electromagnetic wave-absorbing materials, with a focus on the mechanisms, synthetic methods, performance improvements, and applications. Specifically, the challenges and opportunities of improving absorption performance and achieving multifunctional applications of materials through various preparations are discussed, aiming to provide insightful guidance for researchers in this rapidly growing field.
Recent Advances for Cation-Anion Aggregates in Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Mechanism, Strategies, and Applications
- First Published: 13 March 2025
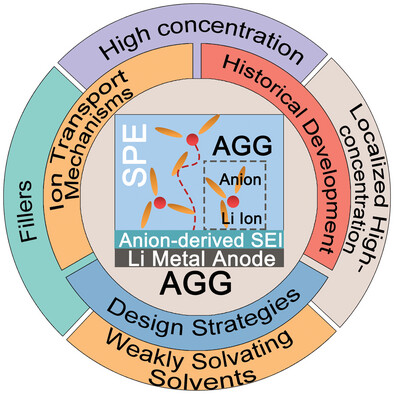
Cation-anion aggregates in SPEs facilitate Li ion transport and construct anion-driven solid electrolyte interphase for high-performance solid-state batteries. This review traces the evolution of cation-anion aggregates, discusses their ion transport mechanisms, summarizes design strategies, and outlines future prospects and challenges for their further applications in solid polymer electrolyte.
3D Printing of Solid Electrolyte and the Application in All-Solid-State Batteries
- First Published: 06 February 2025
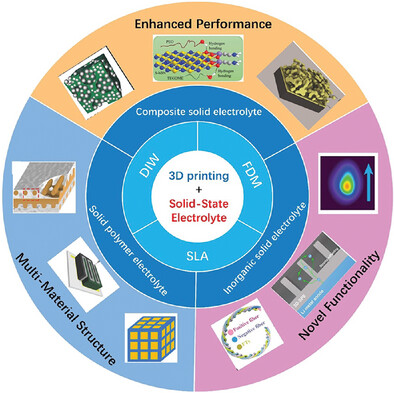
This review mainly introduces the application of 3D printing technology in solid electrolyte manufacturing. Through detailed case studies, the distinctive capabilities of additive manufacturing in solid electrolyte fabrication are demonstrated while pointing out current technological challenges and limitations. This work aims to guide future research efforts toward addressing these identified challenges, thereby advancing the development of solid electrolyte manufacturing technologies.
Magnetic Field-Assisted Photocatalysis: Mechanisms, Devices, and Applications
- First Published: 09 February 2025
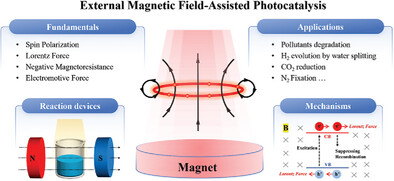
This paper reviews recent advancements in magnetic field-assisted photocatalysis, focusing on the following aspects: 1) the fundamentals explaining how magnetic fields influence photocatalysis; 2) the classification and demonstration of magnetic field-assisted photocatalytic devices; 3) performance data of magnetic field-enhanced photocatalysts in specific applications; and 4) the interpretation of the mechanisms underlying magnetic field-enhanced photocatalysis, supported by specific research data.
Porphyrin-Based Metal-Organic Framework Photocatalysts: Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- First Published: 05 January 2025

This review summarized the research progress of PMOF photocatalysts in the last ten years and analyzed the effects of the spatial structure, porphyrin ligands, porphyrin central metals, and metal nodes of PMOF on the photocatalytic performance. The applications of PMOF-based photocatalysts in H2 production, CO2 reduction, pollutant degradation, and sterilization are reviewed. In addition, the mechanism of these processes are described in detail. Finally, some suggestions on the development of PMOF photocatalysts are put forward.
The Role of Fluorine in Polyanionic Cathode Materials for Sodium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 05 February 2025
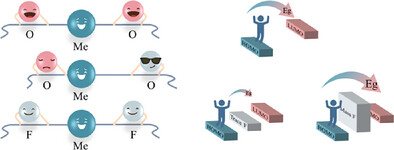
In this perspective, the research status of fluorine introduction in the cathode materials of polyanionic sodium-ion batteries is reviewed, and the effects of fluorine introduction on the structure, dynamics, and electrochemistry of the materials are discussed. The effect and mechanism of different fluorine content are analyzed in depth, including trace fluorine doping and mass fluorine substitution. It also discusses the challenges faced by the practical application of fluorine introduction materials and proposes corresponding solutions.
Research Article
Imaging Bias-Driven Domain Wall Motion With Scanning Oscillator Piezoresponse Force Microscopy
- First Published: 10 January 2025
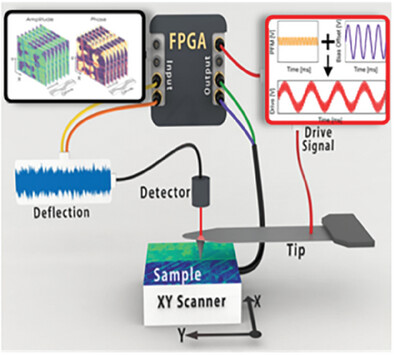
Scanning Oscillator Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (SO-PFM) is introduced as a novel technique for visualizing domain wall dynamics at the nanoscale under sub-coercive electric fields. By resolving electrostatic artifacts, SO-PFM reveals thermally activated flow and creep-like regimes, providing unprecedented insights into reversible domain wall motion and its coupling to local material properties.
Collapsing Carbon Nanotube Enhances Its Phonon Transport
- First Published: 04 June 2025
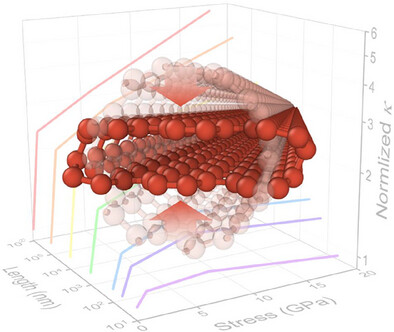
Radial compression, a common phenomenon at carbon nanotube (CNT) contacts, has been found to significantly enhance thermal conductivity (κ), as demonstrated using the phonon Boltzmann transport equation. An optimal stress level exists for maximizing the κ in CNTs, but is strongly dependent on CNT length. These findings provide a promising strategy for optimizing thermal management in CNT-based electronic devices.
Introducing an Experimental Route to Identify and Unify Lab-Scale Redox-Flow Battery Cell Performances via Molar Fluxes and Cell Constants
- First Published: 28 May 2025
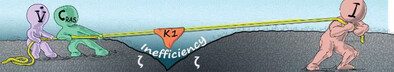
Introducing an experimental route to identify optimal lab-scale redox flow batteries (RFB) operating parameters between electrolyte flow rate, redox-active species concentration and applied current for aqueous and nonaqueous calibration electrolytes via a molar flux concept. K1critical as an RFB-setup performance evaluating, ζ as an RFB cell-constant, and K2 as an cell-architecture independent performance characteristic number are introduced to improve comparability between lab-scale RFB architectures.
Fabrication of Multifarious Nanoparticles Inside a TEM: An In Situ Evaporation and Deposition Method
- First Published: 25 April 2025
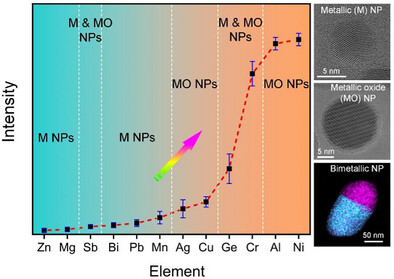
A method by which nanoparticles with ultra-clean surfaces can be controllably fabricated inside TEM is developed. 12 types of materials are used as precursors, respectively, and different kinds of products are found. This work deepens the understanding of the interaction between electron beam and precursors, and provides a novel strategy to unveil the property and behavior of delicate nanoparticles.
Fabrication of QLED Devices with Designable Patterns via Regulating the Carrier Transport Behavior
- First Published: 11 February 2025
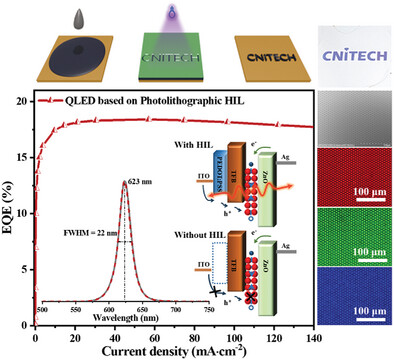
Based on direct photolithography, a novel strategy is proposed to regulate the carrier injection behavior by modifying the energy level alignment regions. As proof of concept, QLED devices with a resolution exceeding 3,300 DPI (dot per inch) are achieved utilizing the pixelated hole injection layer. In addition, the external quantum efficiency of the QLED devices has been improved from 17.2% to 18.4%.
Mitigating Passivation Layer Damage and Lowering Contact Resistivity of TOPcon Solar Cells Through Low PbO Content Ag Paste
- First Published: 23 December 2024
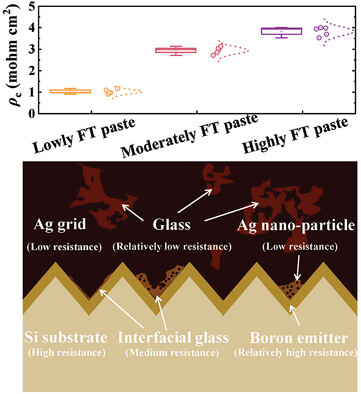
The application potential of Ag-Al paste with low Al content suitable for high sheet resistance emitters by modulating the Ag-Si interface structure is demonstrated. The coupling between microstructure and device performance is elucidated. Additionally, an innovative approach for mitigating the contact resistivity of high sheet resistance solar cells to ≈1 mΩ cm2 is proposed.
Precursor-Induced Growth of Highly-Oriented Nanowire Arrays
- First Published: 31 January 2025
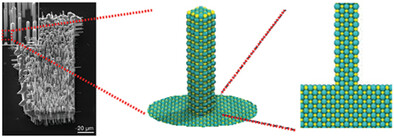
A general strategy for growing nanowire arrays based on homogeneous precursor can be obtained through both calculations and experiments. It is demonstrated that using a self-assembly micro-platform in advance facilitates epitaxial growth via chemical vapor deposition to achieve highly oriented nanowire arrays of SnTe, which is attributed to changes in crystallographic disregistry and adhesion energy.
Tuning Self-Assembly of Hole-Selective Monolayers for Reproducible Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cells
- First Published: 25 February 2025
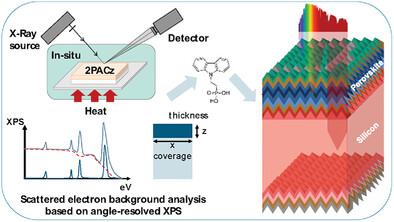
This study investigates how annealing temperature affects the formation of hole-selective self-assembled monolayers. Advanced in situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy uncovers that increasing the annealing temperature beyond the conventional 100°C reduces the thickness of 2PACz from a multilayer stack of ∼5 nm to a monolayer at 150°C and improves its packing density. Consequently, fully-textured perovskite silicon tandem solar cells achieve ∼30% PCE.
Phase Tailoring of In2Se3 Toward van der Waals Vertical Heterostructures via Selenization of γ-InSe Semiconductor
- First Published: 26 November 2024
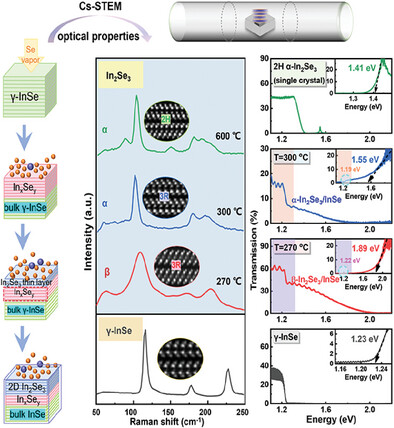
In2Se3/InSe vertical heterojunctions are prepared with specific phases by optimizing the growth conditions using 2D InSe as the seeding material. Meanwhile, the microstructural mechanism for the temperature-dependent phase evolution of β-In2Se3, 3R α-In2Se3, and 2H α-In2Se3 is revealed by using the state-of-the-art Cs-STEM technique. It has been found that β-In2Se3 is the intermediate state for the phase transition between different In2Se3 polymorphs.
Droplet-Based EPR Spectroscopy for Real-Time Monitoring of Liquid-Phase Catalytic Reactions
- First Published: 15 January 2025
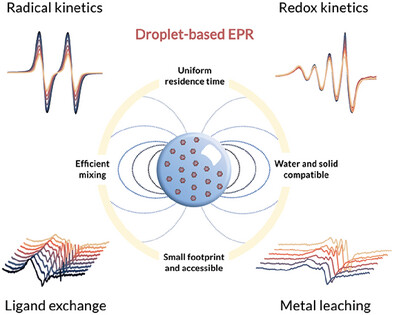
Current electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy methods for in situ liquid-phase catalytic reactions are limited by scale, mass transport control, solid and water applicability, and accessibility. This droplet-based microfluidic platform addresses these challenges, enabling real-time monitoring of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalytic systems, and advancing in situ EPR spectroscopy capabilities for kinetic and mechanistic studies.
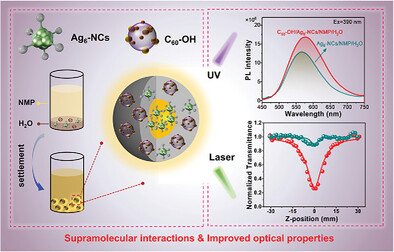
Co-assemblies of Silver Nanoclusters and Fullerenols With Enhanced Third-Order Nonlinear Optical Response
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Imidazopyridinium-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient Gold Recovery
- First Published: 01 December 2024
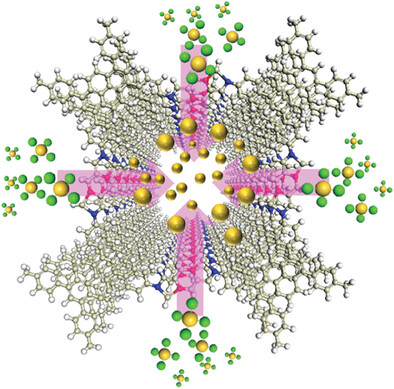
Imidazopyridinium-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are synthesized through the modification of pyridine nitrogen and imine bonds. Both experimental and theoretical results indicate that these charged COFs are advantageous for adsorbing AuCl4−, exhibiting high adsorption performance and rapid kinetics.
Oxygen Vacancy Engineering of TiNb2O7 Modified PE Separator Toward Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Battery
- First Published: 22 November 2024
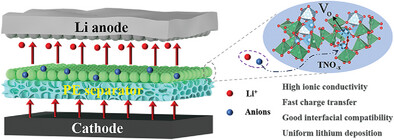
The conductivity of TiNb2O7 is improved by regulating its oxygen vacancies via calcination at argon atmosphere, which could provide more lithium-ion transmission channels. Furthermore, the introduction of oxygen vacancy can also enhance the charge transfer ability of the material and absorbing anions, guiding the uniform distribution of lithium-ion flux and inhibiting growth of Li dendrite in lithium metal batteries.
Characterization of the Dynamic Flow Response in Microfluidic Devices
- First Published: 26 November 2024
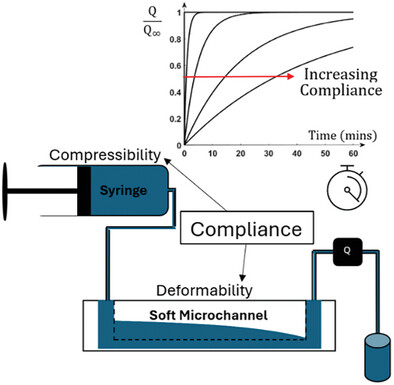
The effect of liquid compressibility on flow delays in syringe-pump driven applications is fully characterized experimentally. Long time delays, up to tens of minutes, can be experienced depending on the syringe volume, microchannel resistance and liquid type. The effect of flexibility of the polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) channels is also considered and a lumped-electric circuit model is presented to simplify the analysis.
3D-Printed Nanocarbon Polymer Conductive Structures for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding
- First Published: 16 March 2025
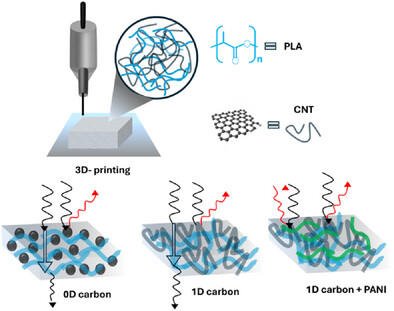
This study introduces EMI shielding bricks by 3D printing PLA composites with carbon-based fillers such as carbon black and carbon nanotubes, followed by polyaniline coating. It examines how 0D and 1D carbon fillers influence electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency and how this can be further improved by electrodepositing with conductive polyaniline.
Low-Impedance Hybrid Carbon Structures on SiOX: A Sequential Gas-Phase Coating Approach
- First Published: 16 January 2025
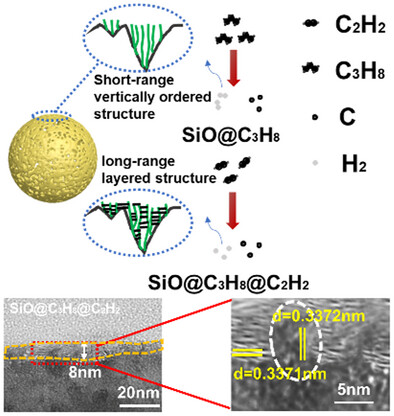
This article develops a low-impedance hybrid carbon structure on the surface of SiOX, where C3H8 is first deposited to create a short-range, vertically ordered carbon architecture, followed by C2H2 to establish a long-range, layered structure, effectively filling the gaps. This dense hybrid carbon layer is characterized by minimal defects, high crystallinity, and excellent electronic conductivity.
Silylated Carbon Nanofiber/Polydimethylsiloxane Based Printable Electrorheological and Sensor Inks for Flexible Electronics
- First Published: 08 December 2024
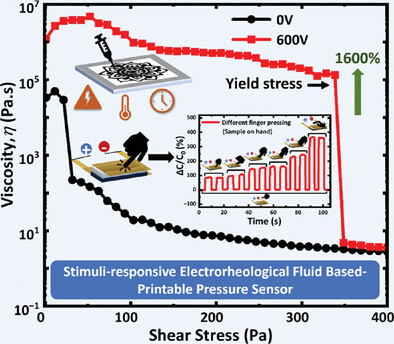
An Electrorheological fluid (ERF) based printable capacitive pressure sensor is devised using silylated carbon nanofiber and polydimethylsiloxane, exhibiting excellent pressure-sensing capability (6.3%/kPa) and repeatability over multiple cycles. The yield stress increased by 1600% (at E = 600 V mm−1. The long-term behavior of the ink is predicted using the time-temperature and the time-waiting time superposition.
Mechanically Robust 3D Flexible Electrodes via Embedding Conductive Nanomaterials in the Surface of Polymer Networks
- First Published: 02 February 2025
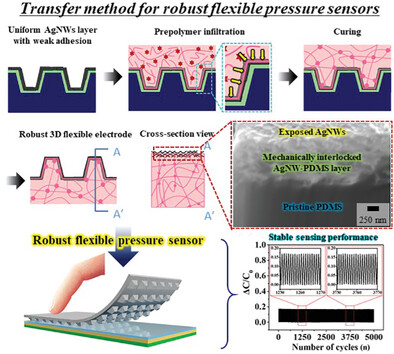
The proposed transfer method utilizes optimal surface energy control to embed conductive nanomaterials into the surface of polymer networks. This approach enables the fabrication of mechanically robust 3D flexible electrodes of various shapes and scales and contributes to the development of reliable and flexible pressure sensors with diverse characteristics, such as high sensitivity and a wide dynamic range.
Innovative Method for Reliable Measurement of PEM Water Electrolyzer Component Resistances
- First Published: 24 January 2025
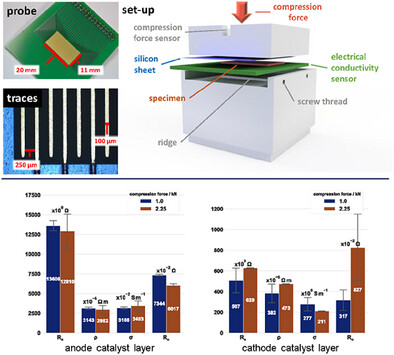
Accurate sheet resistance measurements are essential for optimizing porous electrode design in polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzers. The authors present a reliable method using a novel probe concept based on industrial printed circuit board technology. Furthermore, the authors use image processing to extract the thickness distribution of the catalyst layer, which is discussed in relation to the in-plane electrical resistivity.
Tetragonal Tungsten Oxide for Supercapacitor Electrodes: Study of Phase-Driven Charge Storage Mechanism and Work Function Control
- First Published: 26 December 2024
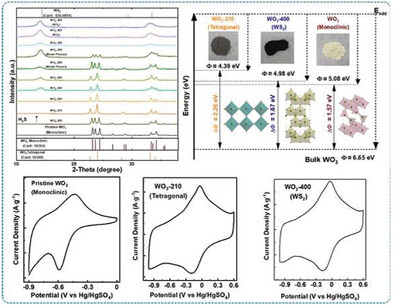
A novel synthetic route successfully explores the tetragonal phase of WO3, demonstrating its superiority as a supercapacitor electrode with an extended potential window. A phase-dependent charge storage mechanism is proposed, supported by in situ Raman studies that provide real-time insights into the underlying processes and improved electrochemical results.
Supramolecular Interface Buffer Layer for Stable Zinc Anode
- First Published: 19 January 2025
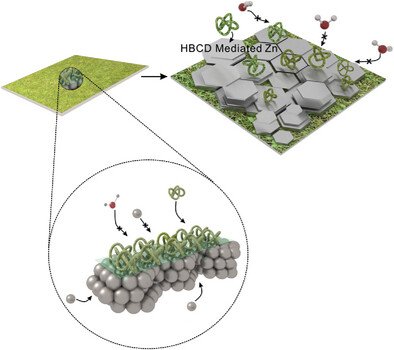
In this paper, a supramolecular interface buffer layer is proposed. The (2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin (HBCD) prefers to chemical adsorb onto Zn (002) planes and barriers the interfacially active waters, which lead to expanded voltage window and stable anode surface. This endows both of the button and pouch batteries with high capacity and durable service life.
Stress Release of Zincophilic N-Doped Carbon@Sn Composite on High-Curvature Surface of Zinc Foam for Dendrite-Free 3D Zinc Anode
- First Published: 15 January 2025
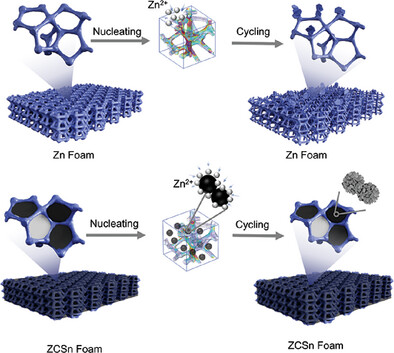
We employed zincophilic N-doped carbon@Sn composites (N-C@Sn) as nano-fillings to effectively release the local stress of high curvature surface of 3D Zn foams toward dendrite-free anode in aqueous zinc ion battery (AZIB). These electronegative and conductive N-C@Sn nano-fillings as supporters can provide a highly zincophilic channel for initial Zn nucleation and reduce local current density for regulating Zn deposition.
In-Situ Monitoring the Magnetotransport Signature of Topological Transitions in a Chiral Magnet
- First Published: 12 February 2025
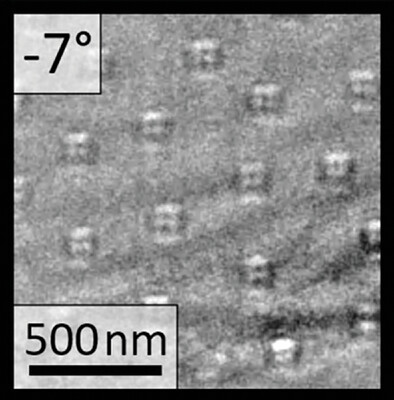
The connection between magnetotransport and high-resolution magnetic imaging is established by simultaneously monitoring magnetotransport properties and conducting in-situ Lorentz Transmission Electron Microscopy. Ex-situ approaches necessitated separate specimens, resulting in ambiguous correlations due to sample differences. A new direction for the field of magnetotransport is enabled, advancing its state-of-the-art.
Highly Sensitive Linear Triaxial Force Sensor Based on Multimodal Sensing for 3D Pose Reconstruction
- First Published: 02 January 2025
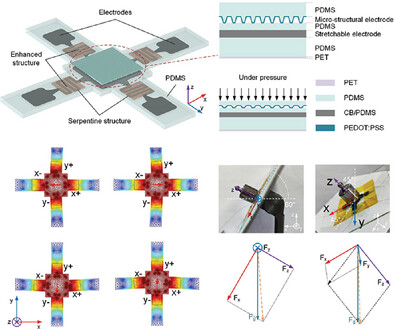
Based on the principle of multimode sensing, the triaxial force sensor consists of a capacitive sensing unit and four resistive sensing units for the detection of pressure and shear forces, respectively. The triaxial force sensor can realize the 3D reconstruction of the object pose according to the mechanical analysis.
Development of Electrostatic Dual-Carbon-Fiber Microgrippers for Precise 2D Patterning and 3D Stacking of Single Microparticles
- First Published: 17 March 2025

This study develops electrostatic dual-carbon-fiber microgrippers for the precise manipulation of SiO2 microparticles. Theoretical and FEA simulations demonstrate that a non-uniform electric field induces dielectrophoresis for pick-and-place manipulation. Particle release occurs due to van der Waals forces after the voltage is turned off, eliminating the need for corona discharge or vibrational separators. This enables accurate 2D patterning and 3D stacking.
N,O Co-Doped Carbon Spheres Enable Stable Anode-Less Sodium Metal Batteries
- First Published: 05 January 2025
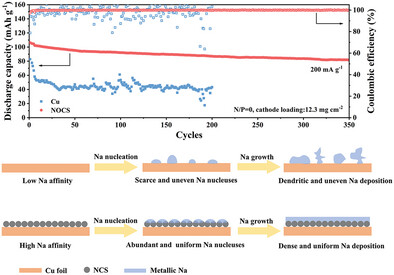
N,O co-doped carbon spheres (NOCS), which are synthesized via a scalable polymerization and pyrolysis method, are coated on the conventional Cu foil current collector as a sodiophilic nucleation layer. The assembled anode-less NOCS||NVP full-cell shows a high energy density of 281.7 Wh kg−1 and superior cycling stability with a capacity retention of 79.0% after 350 cycles at 200 mA g−1.
Trivalent Ionic Molecular Bridges as Efficient Charge-Trapping Method for All-Solid-State Organic Synaptic Transistors toward Neuromorphic Signal Processing Applications
- First Published: 15 December 2024
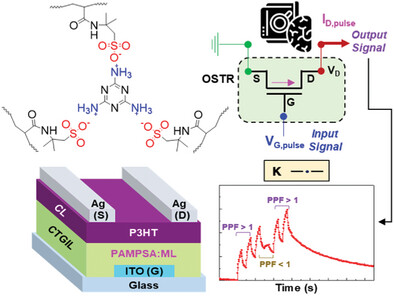
Trivalent ionic molecular bridges generated in water-processable polymeric films play an efficient charge-trapping role in achieving all-solid-state organic synaptic transistors (OSTRs), which can be operated at low voltages (≤5 V) and act as neuromorphic processors with high recognition accuracy of >95%, for promising next-generation computing applications.
Gold Flake-Enabled Miniature Capacitive Picobalances
- First Published: 10 December 2024
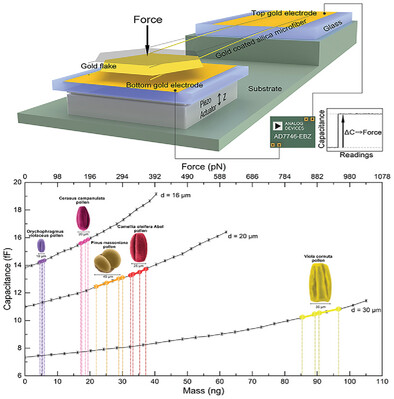
Miniature capacitive picobalances are constructed by using freestanding gold flakes with high reflectivity (≈98% at 980 nm) as the sample tray and silica microfibers with extremely low spring constant (≈0.05 mN m−1) as the cantilever beams. The performance of picobalances can be precisely calibrated by exerting radiation pressure on the gold flake with a laser, showing a detection limit of ≈6.9 pN. As a demonstration, various types of pollens with masses down to 4.6 ng are measured at single-particle level.
Regularized Gradient Statistics Improve Generative Deep Learning Models of Super Resolution Microscopy
- First Published: 02 June 2025
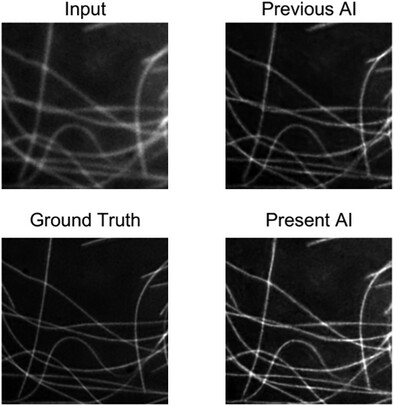
A generative AI model for super-resolution microscopy images is presented. Super-resolution microscopy provides high spatial detail at the expense of lower time resolution. Using it for live samples requires computational image reconstruction. It is unclear what good priors and metrics for AI-generated super-resolution images are. Here, a perceptive metric accounting for the human visual system provides clues.
Decoding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Insights from Multi-Fluid Metabolomic Analysis
- First Published: 02 February 2025
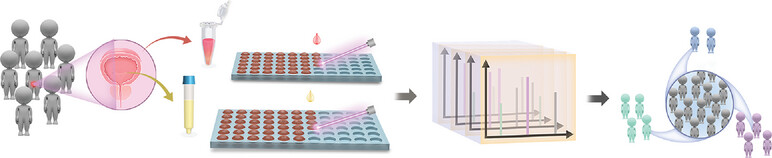
This study develops a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS) metabolomic detection platform utilizing urine and serum samples to identify biomarkers for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The platform facilitates rapid analysis and effectively differentiates BPH patients from those experiencing lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), achieving an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.830.
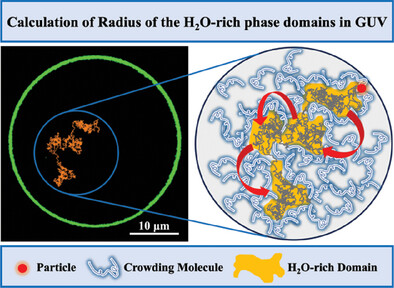
Elucidating Local Confinement in Crowded Polymer Solutions Within Giant Unilamellar Vesicles (GUVs) Through Single Particle Tracking Toward Deeper Understanding of Cells
- First Published: 17 February 2025
Selective Photocatalytic C─H Oxidation Using All-Inorganic Perovskite Quantum Dots Encapsulated in UiO-Series MOFs
- First Published: 16 December 2024
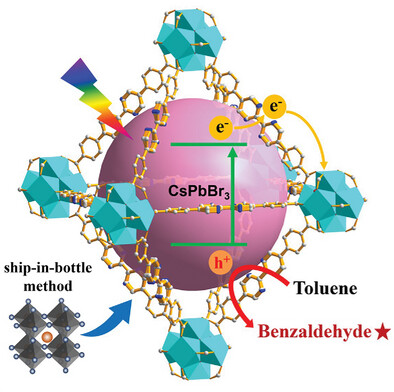
CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots are assembled in the cages of UiO-series metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) through in situ method to construct the photocatalytic system. Benefiting from efficient photogenerated electron–hole separation within heterostructure, the CsPbBr3@MOF hybrid exhibit exceptionally high selectivity and stability for toluene oxidation under visible light irradiation.
Dual-Induced Directed Deposition Mechanism Based on Anionic Surfactants Enables Long Cycle Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries
- First Published: 28 January 2025

By preferential adsorption of anionic surfactants on the Zn(100) and Zn(101) crystal surfaces, the Zn(002) crystal surface becomes a nucleation site for Zn2+ ions, while the presence of a large number of amide groups in the additives can form a fast ion channel, inducing rapid and uniform deposition of Zn to ensure a long cycling life.
Lego-Inspired Splicing of Modularized Vascular Channels
- First Published: 29 May 2025
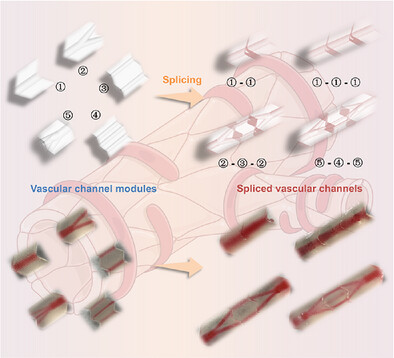
This study presents a Lego-inspired modular strategy to construct hierarchical perfusable vascular channels in hydrogels. Customized modules with diverse architectures are assembled into multi-dimensional constructs, to validate the flexibility and scalability of the splicing technique. Functionalized models mimic vascular barriers and support endothelial cell viability under flow, providing a valuable platform for advancing research under both physiological and pathological conditions.
Impact of Geometry on Chemical Analysis Exemplified for Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Black Silicon
- First Published: 23 March 2025
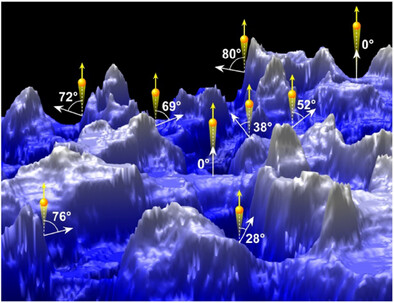
This study describes how layer thicknesses of nano-rough surfaces, here black silicon, can be determined by combining spectroscopic and topographical data. Angular integrated spectroscopic data (XPS) of nano-rough surfaces are least-square fitted to angular resolved data from an ultra-flat surface, here Si wafer, after weighting the latter by the inclination distribution of the topography as determined from AFM data.
Fabrication of a Mechanically Robust Solid-Electrolyte Interphase on Sodium-Metal Anodes by Anion Modulation for Ambient Sodium-Air Batteries
- First Published: 30 April 2025
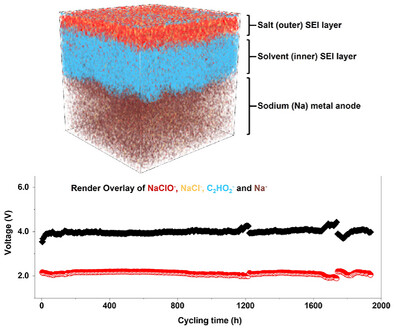
A robust SEI is designed by modulating competitive reactions between metallic-Na anodes and anion/solvent molecules. The SEI consists of a salt-derived outer layer and a solvent-derived inner layer. Thanks to the water balance between inorganic-absorbing and organic-blocking in the solvent-rich inner layer, which prevents Na corrosion from atmospheric moisture, the metallic Na anode can be used directly in opened batteries.
Single Extracellular Vesicle Profiling to Define Brain Specific Traumatic Brain Injury Induced Neuro-Inflammation
- First Published: 19 May 2025
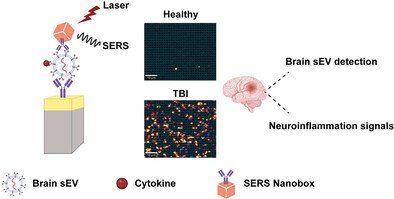
A highly innovative and implementable diagnostic tool for profiling microenvironmental perturbations in TBI patients by analyzing sEVs derived from glial cells circulating in the blood. This device provides a window into the injured brain and identifies neuroinflammatory signals, potentially serving as a platform for detecting highly specific brain biomarkers following TBI.
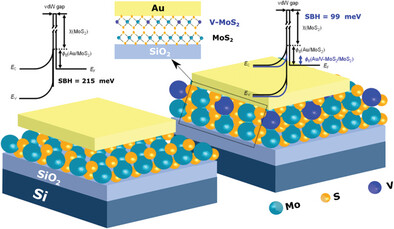
Interfacial Engineering of Degenerately Doped V0.25Mo0.75S2 for Improved Contacts in MoS2 Field Effect Transistors
- First Published: 29 December 2024
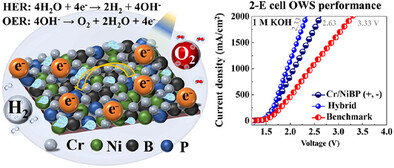
Chromium-Doped NiBP Micro-Sphere Electrocatalysts for Green Hydrogen Production under Industrial Operational Conditions
- First Published: 19 January 2025
Amino Acids-Enabled Fast-Restore of Triplet-Triplet Annihilation Upconversion Luminescence for Background-Free Sensing of Herbicides
- First Published: 14 February 2025
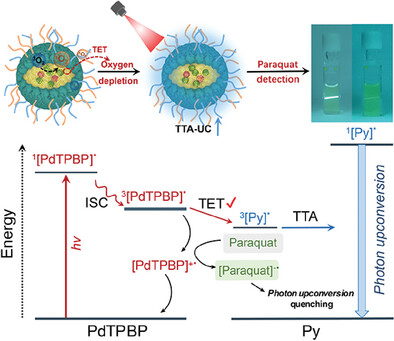
The photooxidation of methionine quickly scavenges the oxygen-mediated triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion luminescence quenching, resulting in a rapid recovery of upconversion emission. Further, a new mechanism of photoinduced electron transfer is proposed to enable highly sensitive, extremely specific, rapid detection of paraquat in real lake water in a background-free manner.
Graphene Oxide Foam-Based Floating Actuators Manipulated via Dual-Marangoni-Effect Propulsion and Magnetic-Field-Guided Navigation
- First Published: 19 January 2025
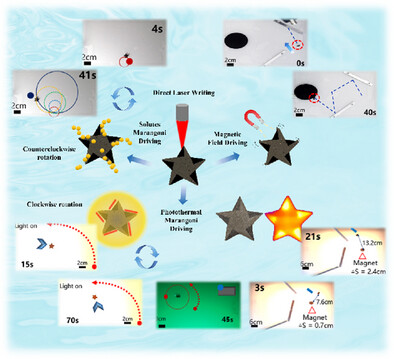
A dual-Marangoni-effect actuator based on graphene oxide foam and direct laser writing is reported. The actuator can compensate for the inability to sustain motion caused by chemical Marangoni effect and slow start-up caused by photothermal Marangoni effect. Under the control of magnetic field, the actuator can achieve intelligent acceleration and deceleration movements.
High-throughput Photoactive Magnetic Microrobots for Food Quality Control
- First Published: 11 March 2025

Magneto-photocatalytic Bi₂O₂CO₃@Fe₃O₄ microrobots enable automated antioxidant detection in food. Under UV light, they generate reactive oxygen species that oxidize a colorless dye into a green radical cation, with antioxidants inhibiting dye oxidation. A rotating magnetic field steers these microrobots across a custom 3D-printed platform, providing high-throughput, cost-effective, and accurate food quality assessments—offering a significant advance in automated food safety technology.
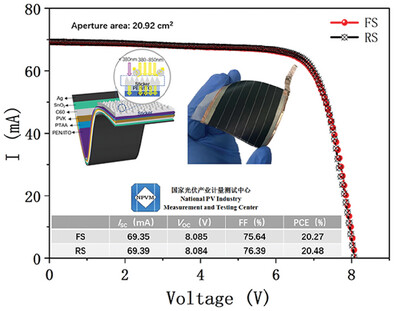
Enhancing Flexible Perovskite Photovoltaic Cells and Modules Through Light-Trapping and Light-Shifting Strategies
- First Published: 15 January 2025
An Integrated, Portable, and Automatic Digital Detection System for Hepatitis B Virus Using Hybrid Magnetic System
- First Published: 02 January 2025
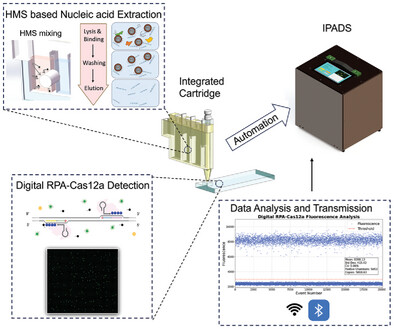
The integrated portable and automatic digital detection system (IPADS) consists of an automation platform and a disposable integrated cartridge. The cartridge combines novel hybrid magnetic system (HMS)-based nucleic acid extraction with digital RPA-Cas12a detection, enabling rapid, fully automated, “sample-in to digital-answer-out” detection. IPADS demonstrates outstanding efficiency and sensitivity with HBV DNA samples, offering a new solution for point-of-care testing.
Stable Electrochemical Lithium Extraction Using LiMn2O4 Coated With Lithiated Nafion
- First Published: 19 January 2025
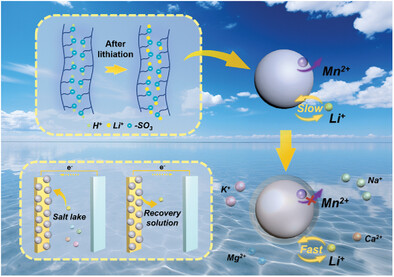
The schematic of LMO@Li-Nafion for electrochemical lithium extraction in brine. Through discharge and charging, using LMO as the working electrode and Ag as the counter electrode, the separate extraction of Li⁺ in the salt lake and its enrichment in the recovery solution are achieved respectively. The surface wettability, structural stability, and Li+ diffusion kinetics of LMO are enhanced by coating lithiated Nafion.
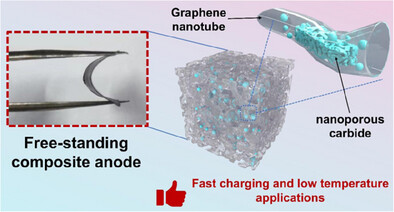
Nanoporous Graphene with Encapsulated Multicomponent Carbide as High-Performance Binder-Free Lithium-Ion Battery Anodes
- First Published: 13 March 2025
Battery Cathode Recycling With Superior Dissolution Kinetics by Laser Augmentation
- First Published: 16 February 2025
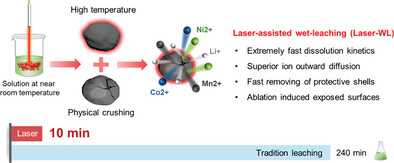
A laser-assisted wet leaching (Laser-WL) method is introduced for efficient recycling of lithium-ion battery cathodes. By decoupling particle and solution temperatures, Laser-WL achieves rapid metal dissolution (95.6% in 15 min) while reducing acid and water consumption by 87% and 27%, respectively. This sustainable approach enhances leaching kinetics, offering a promising solution for circular battery economies.
Tunable NiSe-Ni3Se2 Heterojunction for Energy-Efficient Hydrogen Production by Coupling Urea Degradation
- First Published: 07 January 2025
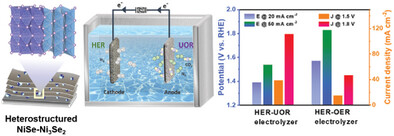
A simple and feasible method is reported to fabricate NiSe-Ni3Se2 heterojunction with tunable NiSe-to-Ni3Se2 ratio on graphene-coated nickel foam skeleton (NiSe-Ni3Se2/GNF). The two-electrode UOR-HER electrolyzer using optimized NiSe-Ni3Se2/GNF as both cathode and anode shows much lower cell voltage than that for the OER-HER electrolyzer, providing a new viable paradigm for energy-saving H2 production.
Atomic Layer Thickness Modulated the Catalytic Activity of Platinum for Oxygen Reduction and Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction
- First Published: 19 March 2025
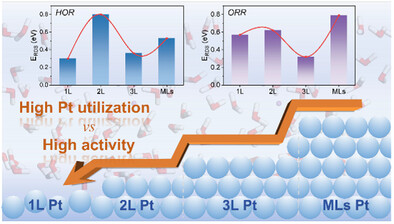
The TOC summarizes the energy barriers corresponding to the rate-determining steps in the catalytic HOR and ORR for 1L, 2L, 3L, and MLs Pt-H2O structures. Compared to MLs Pt, few-layered Pt structures not only significantly enhance Pt utilization but also reduce the reaction energy barriers for catalytic HOR or ORR to varying degrees, thus improving their catalytic activity.
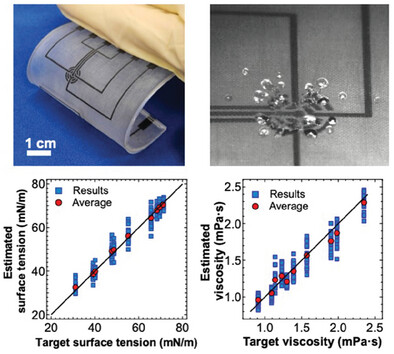
Simultaneous Measurement of Surface Tension and Viscosity Using a Liquid Dynamics Sensor
- First Published: 18 February 2025
POCALI: Prediction and Insight on CAncer LncRNAs by Integrating Multi-Omics Data with Machine Learning
- First Published: 23 May 2025
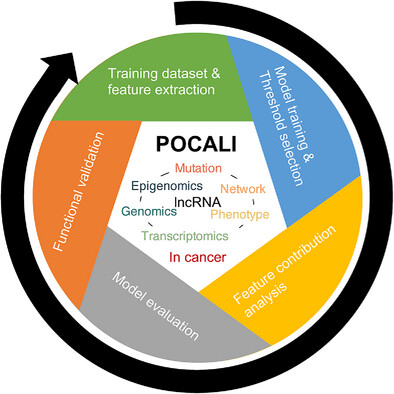
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are receiving increasing attention as biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and therapy, highlighting the urgent need for computational methods to accelerate their comprehensive discovery. Here, to better predict and provide functional insight into cancer lncRNAs, a novel interpretable machine-learning method (POCALI) is developed by leveraging 44 multi-omics features in six categories.
Controllable Synthesis of Monodispersed Zirconia Submicrospheres Based on Oligomer Aggregation Mechanism for Enhanced Scattering Manipulation
- First Published: 04 March 2025
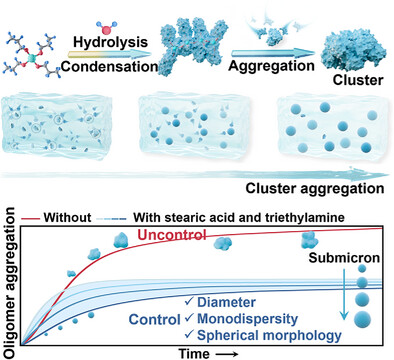
A nonclassical mechanism of oligomer aggregation is proposed for the controllable synthesis of monodispersed ZrO2 submicrospheres. By introducing alkanoic acids and amines to precisely regulate homogeneous oligomer formation and aggregation, the controls over the spherical morphology, monodispersity, and diameter are achieved. The resulting ZrO2 submicrospheres, ranging from 0.263 to 1.295 µm, exhibit enhanced and tunable scattering performance for photonic applications.
Programmable Biporphyrin-G-Quadruplex Nanoflowers for Simultaneous Tumor Cell Recognition and Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy
- First Published: 06 July 2025
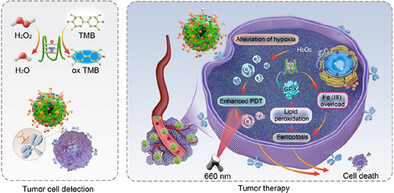
This nanotechnology-driven strategy enables precise control of AS1411 aptamers and G- quadruplex within RCA nanoflowers. Hemin integration with G4 structure confers peroxidase-like activity, enabling tumor cell detection via hydrogen peroxide generation. The biporphyrin-loaded RCA nanoflowers serve as a multifunctional platform, integrating tumor detection with photodynamic therapy.
Glycan-Anchored Fluorescence Labeling of Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Investigating Their Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Fate
- First Published: 25 February 2025
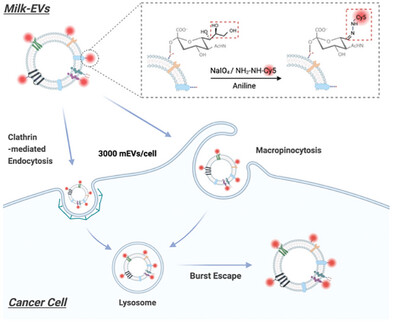
A glycan-anchored fluorescence labeling strategy enables precise tracking of the cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of milk-derived extracellular vesicles (mEVs). This method surpasses traditional membrane dyes, achieving high labeling efficiency without compromising mEV integrity or causing dye leakage. Quantitative analyses identify clathrin-mediated endocytosis and lysosomal escape as key pathways, highlighting its potential for drug delivery and intracellular studies.
Influence of Magnetic Field on the Kinetics of Ho(III) Solvent Extraction Using D2EHPA: A Comprehensive Study
- First Published: 04 March 2025
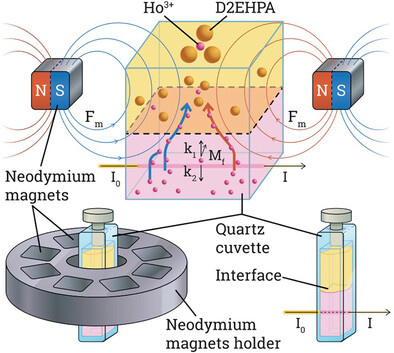
The study explores how a magnetic field influences the extraction of holmium (Ho(III)) ions using D2EHPA. Researchers find that the field alters the extraction rate, increases activation energy, and impacts the formation of a magnetic precipitate at the phase boundary. These findings provide new insights into magnetically controlled solvent extraction processes, potentially improving rare earth separation techniques.
Polarization Induced by Chlorine Defect Engineering in High-Entropy Halide Perovskite to Promote CO2 Photomethanation
- First Published: 13 March 2025
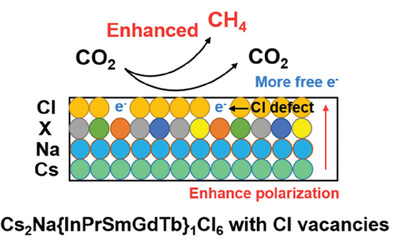
Regulating polarization in Cs2Na{InPrSmGdTb}1Cl6 perovskite material via chlorine defect engineering results in an enhanced internal polarization electric field for promoting the separation of charge carriers, thus achieving an enhanced CO2 photomethanation activity with improved product selectivity.
Lobelia-Inspired Photothermal Storage Flexible Film for Efficient Deicing
- First Published: 26 January 2025
An AI-Powered Methodology for Atomic-Scale Analysis of Heterogenized Correlated Single-Atom Catalysts
- First Published: 09 May 2025
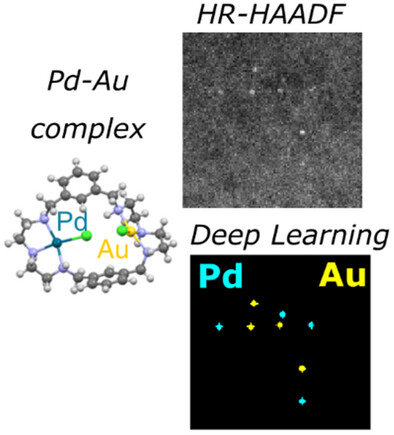
An advanced methodology, combining machine learning and mathematical optimization techniques, is developed to detect and quantify metal–metal interactions in heterobinuclear Au(III)-Pd(II) complexes using HAADF-STEM images. The results provide key insights into the stability and bonding dynamics of these complexes, revealing robust Au–Pd interactions even after deposition on an amorphous carbon substrate and exposure to electron beam irradiation.
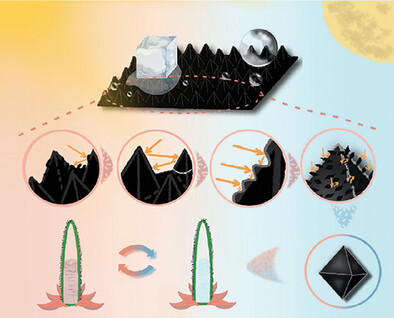
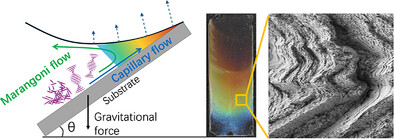
Marangoni Flow-Driven Angular Self-Assembly of Cellulose Nanocrystals: The Tale of Tilted Tactoids and Folded Domains
- First Published: 19 May 2025
Growth Pathway and Phase Transition From Quasi-layered Pt5Se4 to Layered PtSe2 Nanocrystals
- First Published: 02 February 2025
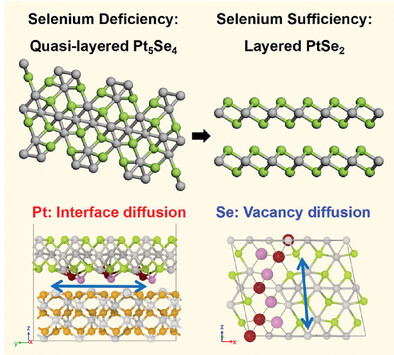
The synthesis of Pt5Se4 and PtSe2 nanocrystals is achieved by controlling the degree of selenization. A two-step growth pathway of PtSe2 and the growth mechanisms of Pt─Se compounds are revealed. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate diffusion paths of Pt atoms with interface diffusion and Se atoms with vacancy diffusion, proving the phase transition from quasi-layered Pt5Se4 to layered PtSe2.
Graphene Oxide Pre-Installed with a Covalent Adaptable Network Resulted in a “Nacre-Like” and “Self-Healable” Multi-Layered Interface in Carbon Fiber Laminates
- First Published: 10 April 2025
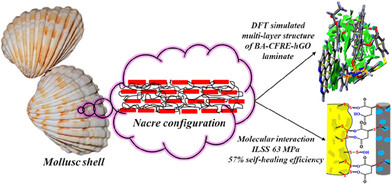
An epoxy/carbon fiber laminate reinforces with functional graphene oxide (hGO) and polyetherimide-based sizing agent (BA) with dynamic disulfide bonds to improve interfacial adhesion. The laminate shows higher mechanical properties, including 37% increase in interlaminar shear strength, 38% increase in flexural strength, and 190% improvement in storage modulus. It also exhibits self-healing, EMI shielding, Joule heating, and deicing properties.
Electrosynthesis of Ru (II)-Polypyridyl Oligomeric Films on ITO Electrode for Two Terminal Non-Volatile Memory Devices and Neuromorphic Computing
- First Published: 23 January 2025
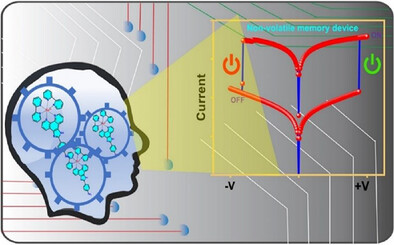
Redox-active oligomeric films are prepared on ITO electrodes using an electrochemical grafting method that yields covalent interfaces between molecules and ITO working electrodes. Molecular junctions of varied thickness are exploited in charge transport studies including non-volatile memory and logic-in memory IMPY operation.
Branched Hierarchical Porous Carbon Enables Ultrasensitive Detection of Serum Glycans for Comprehensive Assessment of Urological Cancers
- First Published: 27 February 2025
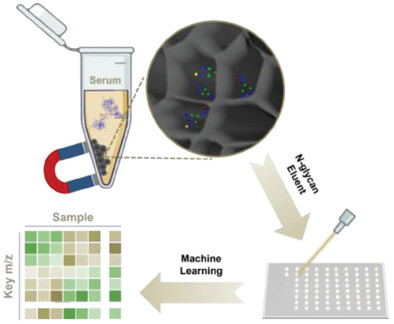
This study integrated high-specific-surface magnetic hierarchical porous carbon (HPC-Ce/Fe), high-throughput mass spectrometry, and machine learning modeling to identify key N-glycans associated with urological cancers, enabling effective differentiation between healthy controls and cancers, as well as among different cancer types.
Rational Design and Characterization of 2D Metal-Semiconductor Junctions for Optoelectronics by Combining Quantum Transport and Excited State Carrier Dynamics Simulations: Case of 2H-WTe2 Based Junctions
- First Published: 27 March 2025
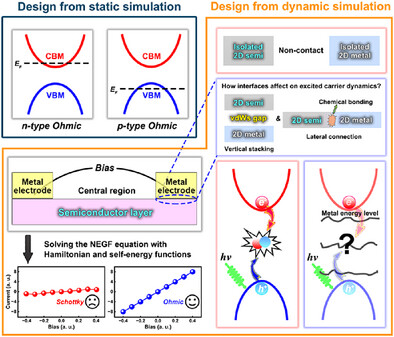
This work evaluates the performance of 2H-WTe2-based vertical and lateral metal-semiconductor junctions (MSJs) by considering both ground and excited states. It highlights the limitations of static electronic structures for determining Ohmic contacts. Quantum transport and non-adiabatic molecular dynamics simulations reveal the influence of interfaces on carrier lifetime and transport, providing insights for optimizing MSJ design in optoelectronic devices.
Selective Nitrogen Doping at Hole Edges of Holey Graphene: Enhancing Ionic Transport Mechanisms for High-Performance Supercapacitors
- First Published: 24 March 2025
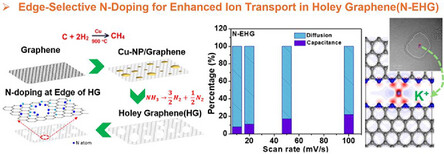
Selective edge N-doping in holey graphene enhances ionic transport, conductivity, and charge storage. A two-step process enables precise doping, significantly improving surface area, capacitance, and stability. Compared to untreated graphene, N-doped variants exhibit superior ion diffusion. DFT calculations confirm lower diffusion barriers and strong K⁺ adsorption, demonstrating its potential for high-performance energy storage applications.
Synergistic Effect of Solvent and Component Engineering for High-Efficiency Carbon-Based Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 04 March 2025
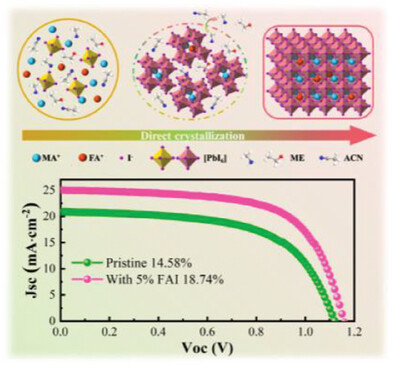
Perovskite films are designed using a mixture solvent of methylamine ethanol solution (MA-EtOH sol) and acetonitrile (ACN) (MA-EtOH-ACN), doped with formamidinium iodide (FAI). This eliminates the high-temperature annealing process while FAI retards crystallization, yielding dense films. Synergistic solvent and component engineering reduce defects, boost absorption, and enhance stability. The resulting ITO/SnO2/FA0.05MA0.95PbI3/carbon device achieves 18.74% efficiency.
Chemo-Mechanical Due-Biomimetic Approach for Ultra-Stable Adsorption Across Multiple Scenarios
- First Published: 26 January 2025

As suction cups are extremely important in the fields of medicine and engineering, they often exhibit weak adhesion on rough surfaces. Here, an ultra-stable suction cup is constructed through dual biomimicry of the leech's mouthparts and mucus. Although it has a large diameter of 5 cm, it can be compatible with various surfaces, achieving universal ultra-stable adhesion.
Highly Selective Ethylene/Ethane Separation in MOF Composites through Pore Contraction and Particle Size Enlargement Strategy
- First Published: 05 February 2025
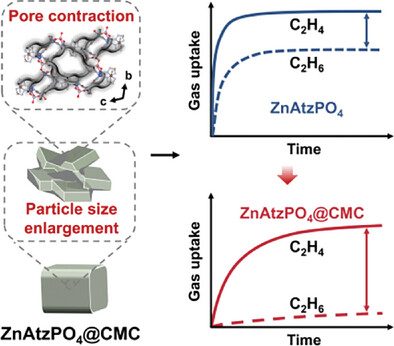
The pore contraction ascribing to carboxymethyl (CMC) modification and particle size enlargement through shaping synergistically amplify the diffusion difference between ethylene and ethane in ZnAtzPO4@CMC composites. ZnAtzPO4@CMC thereby realizes the quasi-exclusion of ethane from ethylene. The ethylene/ethane kinetic selectivity of ZnAtzPO4@CMC increases significantly from 13.06 (ZnAtzPO4) to 34.67 at 298 K, superior to the most reported kinetically selective adsorbents.
Circular Single-Stranded DNA-Based Artificial Nanoviruses Mitigate Colorectal Cancer Development
- First Published: 21 January 2025
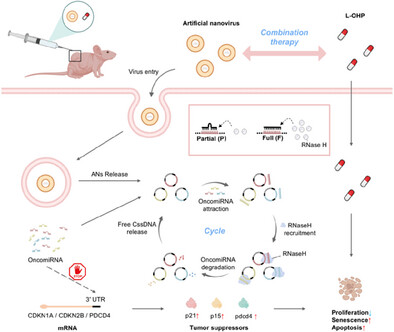
Inspired by the cooperative mechanisms of plant nanovirus, which employ multiple circular single-stranded DNA genomes, artificial nanoviruses (ANs) containing multiple CssDNA are developed to target a variety of oncomiRs. In addition, it is also found that ANs can increase the oxaliplatin sensitivity and inhibit CRC malignant progression. These results confirm the significant therapeutic potential of ANs in anti-cancer treatment.
Growth of Highly-Ordered-Crystalline Indium-Gallium-Oxide Thin-Film via Plasma-Enhanced ALD for High Performance Top-Gate Field-Effect Transistors
- First Published: 30 December 2024
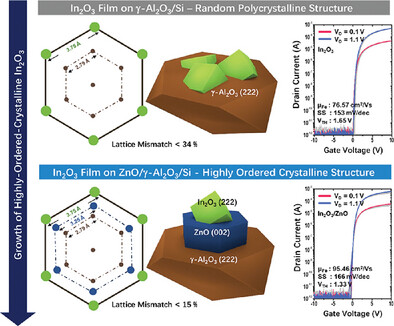
This study presents a novel method for growing highly ordered crystalline (ho) indium-gallium-oxide (IGO) thin films using dual seed layers (Al2O3 and ZnO) to reduce lattice mismatch. This approach enables controlled growth of high-quality In2-xGaxO3 with adjustable In/Ga ratios, while the absence of seed layers results in random polycrystalline (rp) IGO. ho-IGO transistors show significantly enhanced performance over rp-IGO.
Disulfide Bonds Reinforced Self-Assembly of Cellulosic Wastes Toward N/S-Enriched 3D Carbon Foams with Starfish-Like Networks for High-Performance Supercapacitors
- First Published: 24 February 2025
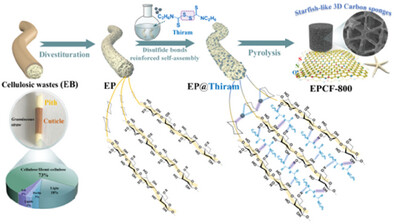
A disulfide bond reinforced self-assembly of cellulosic wastes strategy is pioneeringly proposed to fabricate N/S-enriched starfish-like skeleton connected 3D carbon foams (EPCF-800) with high-level of N/S codoping, hierarchical porous structure, and excellent compression resilience. The resultant EPCF-800 electrode achieves high capacitance and excellent rate capability, and the assembled flexible supercapacitors could provide high energy density and long cycle performance.
High-Uniformity, Shape-Controlled Silicon Nanowires for Enhanced Performance in Optoelectronic Devices
- First Published: 19 January 2025
A novel fabrication approach combines nanoimprint lithography, nanotransfer printing, and metal-assisted chemical etching to produce highly uniform, shape-controlled silicon nanowire (Si NW) arrays. The method achieves Si NWs of various diameters (100, 200, and 400 nm) on 6-inch wafers with high uniformity, confirmed by statistical and surface reflection analyses. Titanium nitride coating enables broadband absorption (75% from 250 to 2500 nm), demonstrating potential for advanced optoelectronic devices.
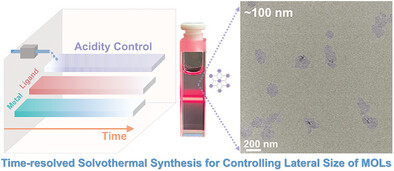
Time-resolved Solvothermal Synthesis for Controlling Lateral Size of 2D Metal–Organic Layers
- First Published: 16 February 2025
Thermal Imaging for Quality Control in Thin Silicon-Based Coatings for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Defect Detection, Drying Dynamics, and Machine Learning-Based Mass Loading Estimation
- First Published: 14 April 2025
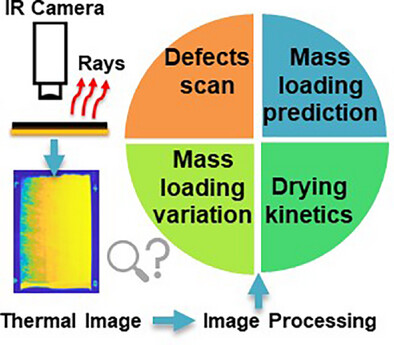
Thermal imaging offers a non-destructive approach to quality control in silicon-based lithium-ion battery electrodes, enabling the detection of defects, variations in mass loading, and the monitoring of drying dynamics. This study introduces an automated defect-detection-algorithm and a machine learning-based Random Forest model to estimate mass loading from thermal imaging data. While applied in a batch process, these methods could be adapted for inline quality control in future studies.
Diatomite-Based Hybrid Electrolyte for Improving Reversibility of Cathode/Anode Interface Reaction in Zn-MnO2 Batteries
- First Published: 23 January 2025
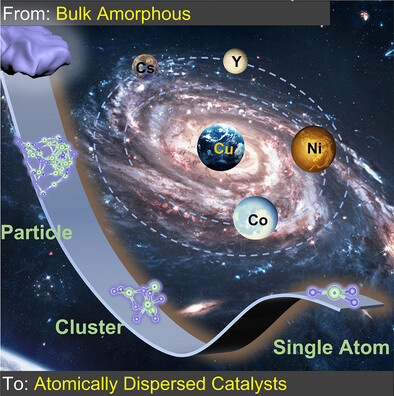
Amorphous-to-Crystalline Transformation for Tunable Synthesis of Single Atom, Cluster, and Nanoparticle Catalysts: Dispersion of Metal Elements (Cu, Co, Ni, Y, Cs) on Holey 2D Ultra-Thin Al2O3 Nanosheets
- First Published: 10 April 2025
Biomimetic Nanoplatform-Mediated Protective Autophagy Blockage Enhancing Sonodynamic and Ca2+-Overload Combined Therapy for Colon Cancer
- First Published: 26 January 2025
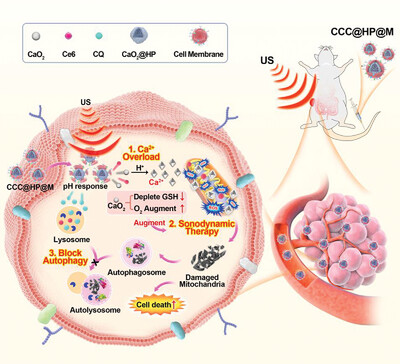
This study synthesized biomimetic hollow polydopamine nanoparticles (CCC@HP@M) that encapsulate CaO2 nanoparticles and co-load chloroquin (CQ) along with Ce6. The CCC@HP@M nanoparticles are delivered directly to the tumor through intravenous injection. The blockage of autophagy enhanced the efficacy of combined sonodynamic therapy and calcium overload therapy for colon cancer.
High-Resolution 3D Printing of Stretchable Granular Hydrogel Filaments for Fabricating Robust and Durable Tissue Phantoms with Tunable Mechanical Strength
- First Published: 20 May 2025
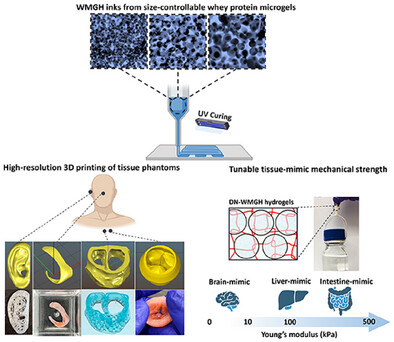
A novel whey protein microgels-based granular hydrogel (WMGH) consisting of size-controllable microgels allows high-resolution 3D printing of intricate tissue phantoms. Incorporating a polyacrylamide second network transforms WMGH into robust, durable double-network hydrogels (DN-WMGH). Controlling microgel size provides a new approach to widely tailor mechanical strength from brain (<10 kPa) to intestine (≈300 kPa), the idea for tissue-mimicking applications.
Rational Design and Visualization of Multifunctional Phenothiazine-Based Self-Assembled Monolayers for Better Interface Contact in High-Efficiency and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 02 February 2025
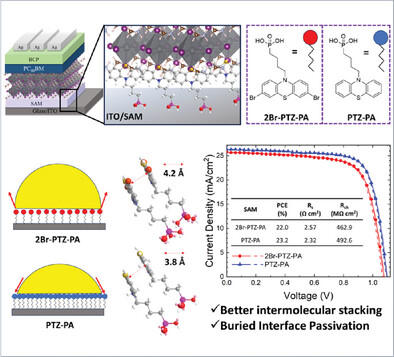
The rational design and visualization of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) based on phenothiazine for perovskite solar cells are investigated. Introducing, a novel SAM namely PTZ-PA as a hole transport layer in p-i-n PSCs, ensures uniform film coverage, addresses non-wetting issues, and provides effective buried interface passivation. PTZ-PA shows superior performance due to its compatibility with perovskite and optimal intermolecular stacking distance.
Nanolaminate Nano-Optoelectrodes Enable Dual-Channel Plasmon-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Electrochemistry
- First Published: 11 February 2025
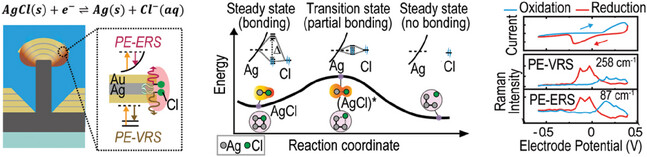
This study unveils a dual-channel electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (EC-SERS) strategy using nanolaminate Au/Ag/Ag nano-optoelectrodes. It concurrently monitors plasmon-enhanced vibrational and electronic Raman scattering, revealing distinct signatures of the (AgCl)* transition state during redox reactions. This approach differentiates interfacial reactions based on electronic and vibrational characteristics, offering insights into short-lived transition state dynamics.
3D Vector Piezoresponse Imaging with Interferometric Atomic Force Microscopy
- First Published: 02 May 2025
Colloidal Synthesis of Na2Fe2(SO4)3 Nanocrystals as the Cathode Toward High-Rate Capability and High-Energy Density Sodium-ion Batteries
- First Published: 09 January 2025
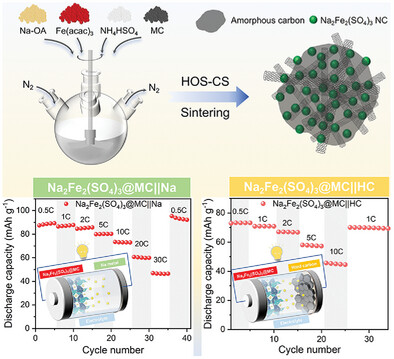
A facile strategy is developed to construct carbon nanotubes-modified Na2Fe2(SO4)3 nanocrystals as a cathode material of sodium-ion batteries. The unique architecture of nanoscale Na2Fe2(SO4)3 wrapped by carbon network endows it with favorable high-rate capability and cyclic stability both in half-cell and full-cell configurations. This work offers a promising polyanionic cathode for fast-charging applications.
SpaDCN: Deciphering Spatial Functional Landscape from Spatially Resolved Transcriptomics by Aligning Cell–Cell Communications
- First Published: 17 February 2025
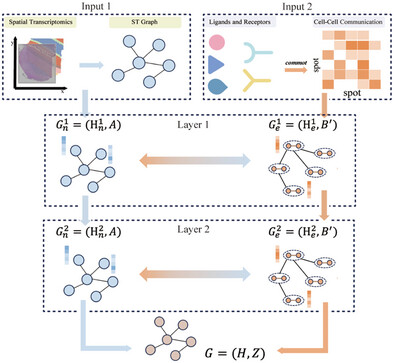
SpaDCN integrates ligand–receptor interactions and dynamic graph convolutions, alternating node (gene expression), and edge (cell communication) layers to resolve spatial sparsity/noise and static GCN over-smoothing. This biologically informed design enhances spatial domain detection, data denoising, and prognostic marker identification in cancer, achieving robust performance across platforms/species with high ARI scores, and advancing precision in spatial transcriptomic analysis.
Imaging of Recombination Rates and Lifetime in Perovskite Thin Film Processing
- First Published: 16 February 2025
Achieving consistent, homogeneous layer quality in perovskite thin films is a critical challenge for large-scale processing. This study introduces relative photoluminescence quantum yield (rPLQY)-imaging, a novel, non-invasive imaging technique that enables spatially resolved characterization of fundamental optoelectronic characteristics. This method provides valuable insights into recombination processes and enhances optimization potential across various sample configurations.
Controllable Growth of Thick-Layer Graphene or Graphite on Copper by Tuning Silicon Additives
- First Published: 21 February 2025
The low carbon solubility and self-limiting phenomenon result in the formation of nonuniform few layers on the copper substrate via the chemical vapor deposition method. In this study, it is demonstrated that a Cu-Si layer on the copper surface can facilitate the transition of graphene growth from a nonuniform few layers to a uniform thick layer by synchronous growth.