Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Sodium Cholate-Based Active Delipidation for Rapid and Efficient Clearing and Immunostaining of Deep Biological Samples (Small Methods 1/2022)
- First Published: 18 January 2022

Front Cover
In article number 2100943, Chang and co-workers developed a novel sodium cholate-mediated tissue clearing method, called SCARF. By adopting an ion-conductive film as the separation barrier, SCARF renders orders of magnitude faster tissue transparency and better immunostaining capability than conventional SDS-based methods. Thus, SCARF would greatly facilitate the 3D structural mapping of biological tissues in various clearing regimes.
Inside Front Cover
Ultrahigh Resolution Pixelated Top-Emitting Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by Color-Converting Cavities (Small Methods 1/2022)
- First Published: 18 January 2022

Inside Front Cover
In article number 2101090, Chen and co-workers have developed the photopatternable color-converting cavity to realize ultrahigh resolution pixelated red, green, and blue quantum-dot (QD) LED arrays. By simply photopatterning the indium-zinc-oxide phase tuning layers, the cavity can selectively convert the unpatterned QD white emission as color-saturated and color-stable red, green, and blue emission with a resolution of ≈1700 pixel-per-inch and a color gamut of 111% NTSC. The demonstrated architecture could find potential applications in various displays ranging from cell phone to emerging virtual reality and augmented reality displays.
Inside Back Cover
Spray-Drying and Atomic Layer Deposition: Complementary Tools toward Fully Orthogonal Control of Bulk Composition and Surface Identity of Multifunctional Supraparticles (Small Methods 1/2022)
- First Published: 18 January 2022

Inside Back Cover
In article number 2101296, Thommes, Barr, Mandel, and co-workers used spray-drying as a scalable process that enables one to assemble freely chosen nanoparticles into supraparticles, i.e., microparticles with adjustable nanostructure, in combination with atomic layer deposition to deposit controlled thin films of different materials onto and within supraparticles. The combination of these two techniques allows for the independent adjustment of properties determined by bulk and surface composition.
Back Cover
Engineering CXCL12 Biomimetic Decoy-Integrated Versatile Immunosuppressive Nanoparticle for Ischemic Stroke Therapy with Management of Overactivated Brain Immune Microenvironment (Small Methods 1/2022)
- First Published: 18 January 2022

Back Cover
In article number 2101158, Shi, Yang, and co-workers report an engineering CXCL12 biomimetic decoy-integrated versatile immunosuppressive nanoparticle (VIN). VIN integrates inflammation tropism, peripherally inflammatory cells filtrate, brain-resident activated microglia polarization, as well as ROS scavenging. As a result, the VIN can promote outstanding therapeutic effects on ameliorating the mortality, reducing the infarct volume and protecting neurons post-stroke.
Masthead
Reviews
Recent Advances in Flexible Zn–Air Batteries: Materials for Electrodes and Electrolytes
- First Published: 19 November 2021
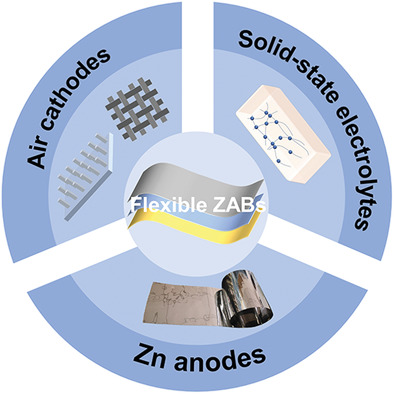
Flexible Zn–air batteries (ZABs) show applications on wearable electronical devices. The research on air cathodes, electrolytes, and Zn anodes of flexible ZABs is summarized in this review. This review further discusses the opportunities and challenges faced by the cathodes, electrolytes, anodes, and packaging technologies of flexible ZABs, and puts forward some personal perspectives on the development of flexible ZABs in the future.
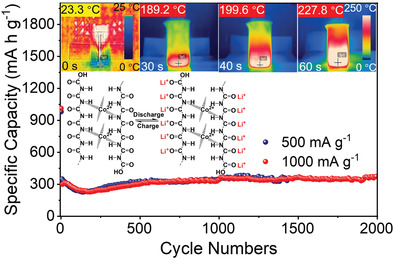
Li2O2 Formation Electrochemistry and Its Influence on Oxygen Reduction/Evolution Reaction Kinetics in Aprotic Li–O2 Batteries
- First Published: 21 November 2021
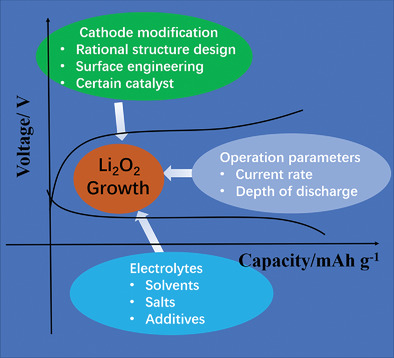
This review demonstrates the latest progress in understanding the Li2O2 electrochemistry and the recent advances in regulating the Li2O2 growth pathway, including operation parameters, rational cathode structure design, catalyst surface engineering, electrolyte components, and so on. Further prospects of the solutions in developing advanced Li–O2 batteries by control of favorable Li2O2 formation are highlighted.
Moiré Fringe Method via Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
- First Published: 25 November 2021
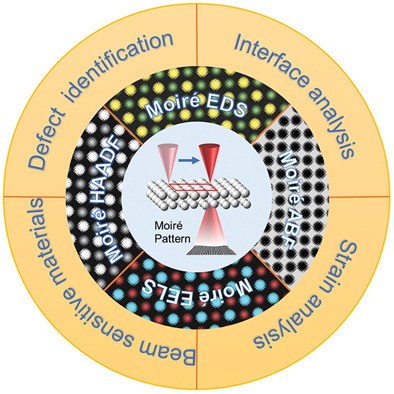
Moiré fringe is a commonly observed phenomenon in physics, optics, and materials science. Creating moiré fringe via scanning transmission electron microscopy has been developed to image materials’ structures. In this review, the principle of this method is introduced, and its applications on investigation of strain, defects, 2D materials, and beam-sensitive materials are discussed.
An Overview for the Nanoparticles-Based Quantitative Lateral Flow Assay
- First Published: 02 December 2021
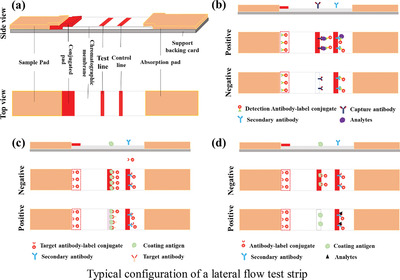
The lateral flow assay (LFA) has received much attention in both academia and industry because of their user friendliness, low cost, and easy operation. Here, the progress achieved of quantitative LFA during the last decade is summarized, and a helpful reference for solving the problems encountered in the development of quantitative LFA devices is provided.
Research Articles
Sodium Cholate-Based Active Delipidation for Rapid and Efficient Clearing and Immunostaining of Deep Biological Samples
- First Published: 05 November 2021
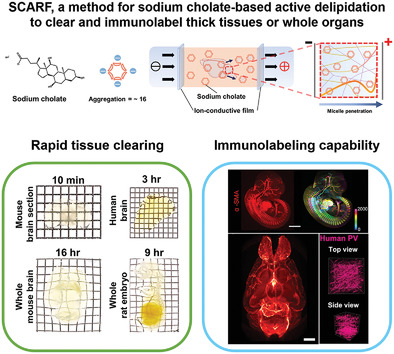
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) remains the first choice for active delipidation in tissue clearing methodologies. Detergents that form smaller micelles and higher critical micelle concentration should perform better but these remain unexplored due to technical limitations. By combining sodium cholate and an ion-conductive film, SCARF overcomes these limitations, providing remarkably faster, superior tissue clearing and immunolabeling than SDS-based methods.
Editor's Choice
Ultrahigh Resolution Pixelated Top-Emitting Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by Color-Converting Cavities
- First Published: 28 November 2021
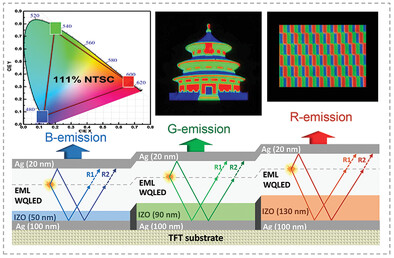
The photopatternable color-converting cavity is developed to realize ultrahigh resolution pixelated red, green, and blue quantum-dot (QD) light-emitting diode arrays. By simply photopatterning the IZO phase tuning layers, the cavity can selectively convert the unpatterned QD white emission as color-saturated and color-stable red, green, and blue emission with a resolution of ≈1700 pixel-per-inch and a color gamut of 111% national television system committee.
Spray-Drying and Atomic Layer Deposition: Complementary Tools toward Fully Orthogonal Control of Bulk Composition and Surface Identity of Multifunctional Supraparticles
- First Published: 21 November 2021
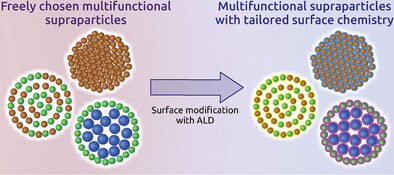
Spray-drying is a scalable process that enables one to assemble freely chosen nanoparticles into supraparticles, i.e., microparticles with adjustable nanostructure. Atomic layer deposition is used to deposit controlled thin films of different materials onto and within supraparticles. The combination of these two techniques demonstrated in this work allows for the independent adjustment of properties determined by bulk and surface composition.
Engineering CXCL12 Biomimetic Decoy-Integrated Versatile Immunosuppressive Nanoparticle for Ischemic Stroke Therapy with Management of Overactivated Brain Immune Microenvironment
- First Published: 10 November 2021
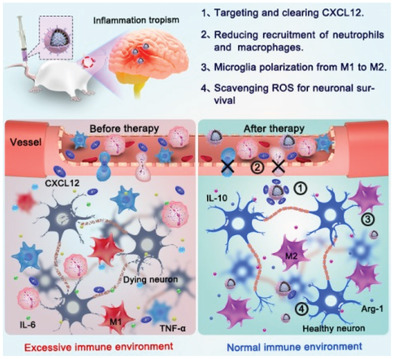
An engineering CXCL12 biomimetic decoy-integrated versatile immunosuppressive nanoparticle (VIN) is reported. VIN integrates inflammation tropism, peripherally inflammatory cells filtrate, brain-resident activated microglia polarization, as well as, ROS scavenging. As a result, the VIN can promote outstanding therapeutic effects on ameliorating the mortality, reducing the infarct volume, and protecting neurons post-stroke.
Frontispiece
Synthesis of Uniform Polymer Encapsulated Organic Nanocrystals through Ouzo Nanocrystallization (Small Methods 1/2022)
- First Published: 18 January 2022

Ouzo Nanocrystallization
In article number 2100808, Liu and co-workers report the simple and novel approach of ouzo nanocrystallization for the synthesis of small and highly uniform organic nanocrystals with photoluminescent properties. The process of ouzo nanocrystallization helps in bringing the unique properties of organic dyes to real biomedical applications.
Research Articles
Synthesis of Uniform Polymer Encapsulated Organic Nanocrystals through Ouzo Nanocrystallization
- First Published: 10 November 2021
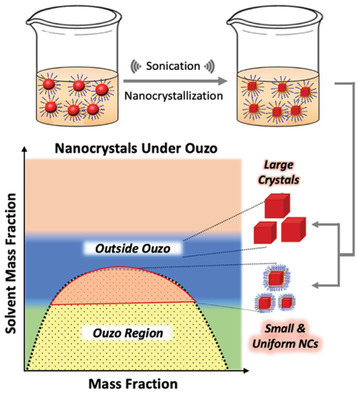
Nanocrystals have shown tremendous progress and great promises in biomedical, photocatalytic, and optoelectronic applications. Till now, methods available for the synthesis of polymer encapsulated nanocrystals are slow, lack controllability, and are not generic. In this study, we present the method of ouzo crystallization for fast, systematic, and controlled synthesis of small organic NCs (<100 nm) with high uniformity (PDI~0.1).
Frontispiece
Monitoring Retinoblastoma by Machine Learning of Aqueous Humor Metabolic Fingerprinting (Small Methods 1/2022)
- First Published: 18 January 2022

Advanced Metabolic Analysis
In article number 2101220, Qian, Fan, Jia, and co-workers have developed a nanoparticle enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry platform to record aqueous humor metabolic fingerprinting (AH-MF) of retinoblastoma (RB) with high performance. Early and advanced RB patients are differentiated by machine learning of AH-MF and identified biomarkers with area-under-the-curve over 0.9 and accuracy over 80%. This work will contribute to advanced metabolic analysis of eye diseases.
Research Articles
Monitoring Retinoblastoma by Machine Learning of Aqueous Humor Metabolic Fingerprinting
- First Published: 02 December 2021

This work develops a nanoparticle enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry platform to record aqueous humor metabolic fingerprinting (AH-MF) of retinoblastoma (RB) with high performance. Early and advanced RB patients are differentiated by machine learning of AH-MF and identified biomarkers with area-under-the-curve over 0.9 and accuracy over 80%. This work would contribute to advanced metabolic analysis of eye diseases.
Supramolecular Polymer Network Membranes with Molecular-Sieving Nanocavities for Efficient Pre-Combustion CO2 Capture
- First Published: 01 December 2021
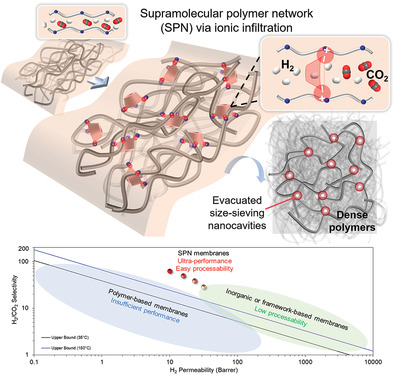
Current large-scale H2 production requires robust and scalable size-sieving membrane materials for efficient CO2 capture from syngas. This work innovatively utilizes the supramolecular polymer network structure with precise nanocavities in nanocomposite membrane design. It provides a seamless integration of the versatile processability and robust properties of amorphous polymers with sharp molecular-sieving abilities of porous nanoarchitectures for superior H2/CO2 separation.
Accurate and Real-Time Detection Method for the Exothermic Behavior of Enzymatic Nano-Microregions Using Temperature-Sensitive Amino-AgInS2 Quantum Dots
- First Published: 10 November 2021

Temperature-sensitive amino-AgInS2 quantum dots (QDs) are grafted onto lipase via glutaraldehyde to form lipase-QD conjugates. With the addition of the substrate in lipase-QDs solution, the heat generated by the substrate decomposition in nanoscale is detected in real-time by the QDs, accompanied by a decrease in photoluminescence intensity, demonstrating the nano-microregions exothermic behavior of the enzymatic reaction in real time.
Local Surface Chemistry Dynamically Monitored by Quantitative Phase Microscopy
- First Published: 17 November 2021
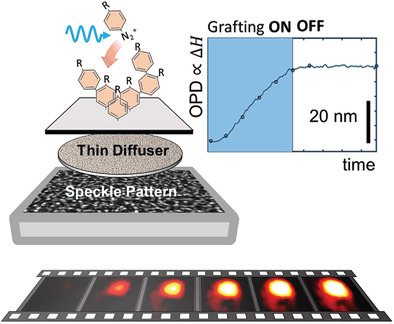
Herein, diffuser-based phase sensing and imaging, a quantitative phase imaging method for monitoring the advancement of surface modification reactions with sub-nanometric to nanometric precision is introduced. Its capacity to analyze grafting reactions is illustrated by performing and in-depth analysis of the photografting of aryldiazonium salts onto glass, revealing grafting regimes and extracting elusive physical and chemical parameters.
Mn-Dopant Differentiating the Ru and Ir Oxidation States in Catalytic Oxides Toward Durable Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Acidic Electrolyte
- First Published: 17 November 2021
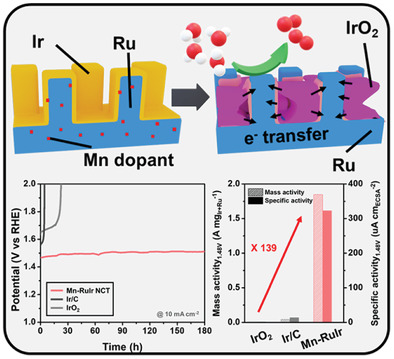
Unique cactus-like Ru/IrO2 heterostructures achieved high activity and long-term stability toward the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which is not feasible with a simple alloy of Ru- and Ir-based electrocatalysts. The electron flow from the robust rutile IrO2 to the highly active Ru effectively restrained the overoxidation of the Ru species into soluble species during the OER, leading to robust OER catalysts.
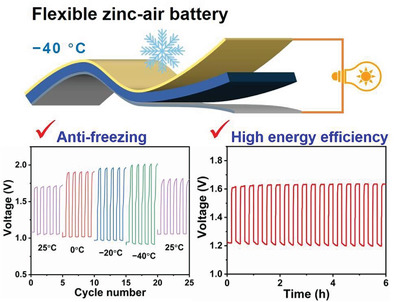
Flexible Zinc–Air Battery with High Energy Efficiency and Freezing Tolerance Enabled by DMSO-Based Organohydrogel Electrolyte
- First Published: 21 November 2021
Ultrafast Universal Fabrication of Metal-Organic Complex Nanosheets by Joule Heating Engineering
- First Published: 25 November 2021
Hierarchical Structure of CuO Nanowires Decorated with Ni(OH)2 Supported on Cu Foam for Hydrogen Production via Urea Electrocatalysis
- First Published: 28 November 2021
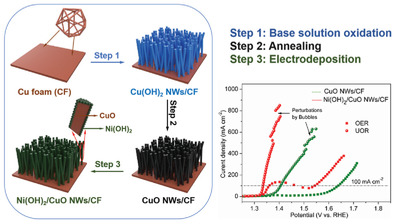
Combined theoretical and experimental analyses demonstrate the high reactivity and selectivity of CuO and Ni(OH)2 toward the urea oxidation reaction (UOR) instead of the oxygen evolution reaction. The hierarchical structure creates a synergistic effect between the two highly active sites, enabling an exceptional UOR activity, which significantly advances energy-saving hydrogen production.
Quenching as a Route to Defect-Rich Ru-Pyrochlore Electrocatalysts toward the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 25 November 2021
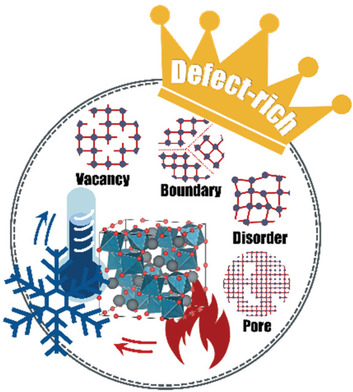
The defect-rich yttrium ruthenate oxides Y2Ru2O7−δ (denoted Drich-YRO) are fabricated by the liquid nitrogen (<−196 °C) quenching of Y2Ru2O7−δ produced by calcination at 1100 °C. Rich defects—including oxygen vacancies, grain boundaries, pores, and surficial disorder—resulting from the instantaneous cooling process, are preserved in room temperature material and act as electrocatalytic active sites for oxygen evolution.
Hydroprinting Technology to Transfer Ultrathin, Transparent, and Double-Sided Conductive Nanomembranes for Multiscale 3D Conformal Electronics
- First Published: 02 December 2021
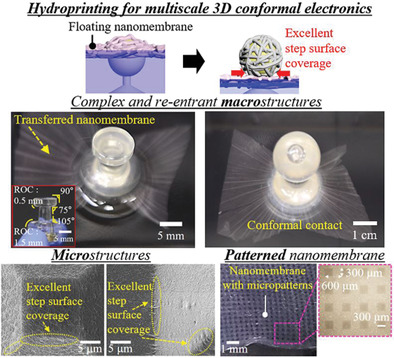
Novel hydroprinting technology to transfer ultrathin, transparent, and double-sided conductive/patterned nanomembranes for multiscale 3D conformal electronics is demonstrated via the fabrication of a functional film. The nanomembrane enables conformal contact with excellent step surface coverage of complex macro- and microstructures. The double-sided conductive nanomembrane enables wiring and layer-by-layer assembly regardless of the transfer direction of the surface.
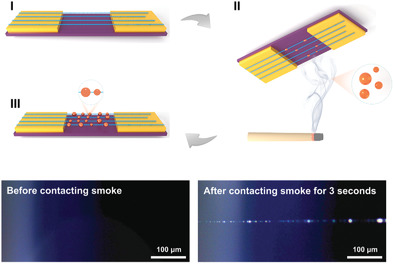
Fast In-Situ Optical Visualization of Carbon Nanotubes Assisted by Smoke
- First Published: 02 December 2021
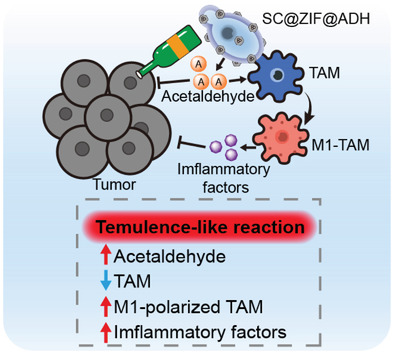
Temulence Therapy to Orthotopic Colorectal Tumor via Oral Administration of Fungi-Based Acetaldehyde Generator
- First Published: 02 December 2021
Flame-Assisted Synthesis of O-Coordinated Single-Atom Catalysts for Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction and Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 02 December 2021
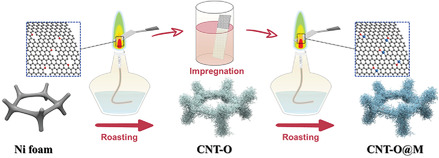
Well-defined O-coordinated single-atom catalysts on integrated carbon nanotube arrays (CNT-O@M, M = Co, Pt) are synthesized by facial flame-assisted method, which shows excellent activities for ORR and HER with utilization of active site as high as 75.7%. The methodology and concept proposed in this work could be extended to the synthesis of a variety of integrated single-atom catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis.
Interfacial Microenvironment Modulation Enhancing Catalytic Kinetics of Binary Metal Sulfides Heterostructures for Advanced Water Splitting Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 04 December 2021
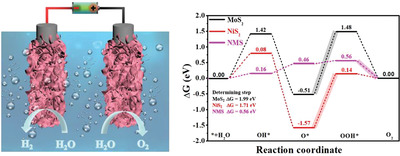
The defect-rich NiS2/MoS2 nanoflakes (NMS NFs) have been successfully synthesized by a simple method. The NMS NFs present remarkable electrocatalytic performances, including the small overpotentials for the oxygen evolution reaction (270 mV at 10 mA cm−2) and hydrogen evolution reaction (90 mV at 10 mA cm−2), as well as a low voltage for overall water splitting (1.60 V at 10 mA cm−2).
Binder-Free and High-Loading Cathode Realized by Hierarchical Structure for Potassium–Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 04 December 2021
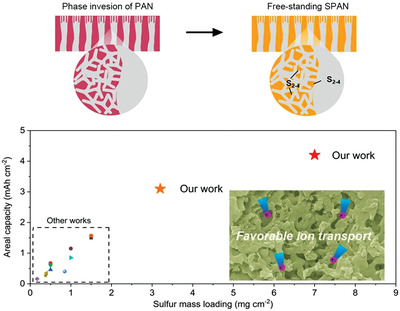
A binder-free and high-loading sulfur cathode is developed via facile phase inversion and sulfurization for application in potassium–sulfur batteries without using a current collector. The hierarchical structure of the cathode enables favorable ionic transport; therefore, a high areal capacity is successfully exerted even at high loadings. Moreover, the porous structure buffers the volume change, and good cycling stability is achieved.
3D Nanoscale Morphology Characterization of Ternary Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 07 December 2021
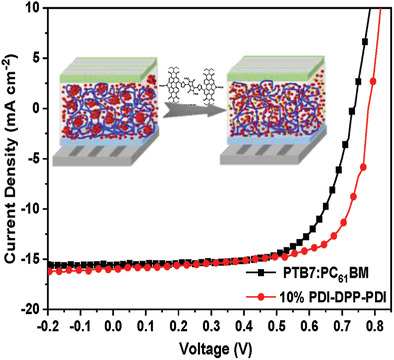
Ternary organic solar cells are fabricated by rationally selecting and incorporating the perylenediimide (PDI)-based nonfullerene acceptor, PDI-diketopyrrolopyrrole-PDI, as the third component into a model solar cell and their 3D morphology is qualitatively and quantitatively explored at the nanoscale by developing the new use of advanced characterization tools in the field of photovoltaics.
A Cascaded Droplet Microfluidic Platform Enables High-Throughput Single Cell Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing at Scale
- First Published: 08 December 2021
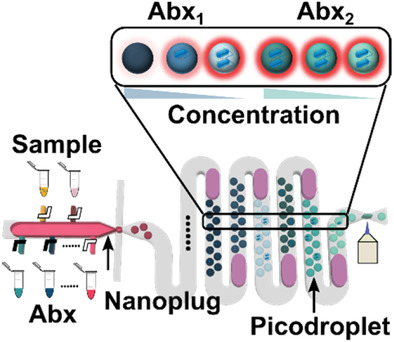
Single-cell antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) technologies have demonstrated unprecedented speed, but their clinical utility remains limited as most use devices that test only one concentration of one antibiotic. Here, a cascaded, assembly line-like droplet microfluidic platform is developed to perform single-cell AST against multiple antibiotics at the clinically relevant scale, thereby bringing single-cell AST technologies a step closer to clinical settings.
Epidermis-Inspired Wearable Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Using Reduced Graphene Oxide Self-Wrapped Copper Nanowire Networks
- First Published: 15 December 2021
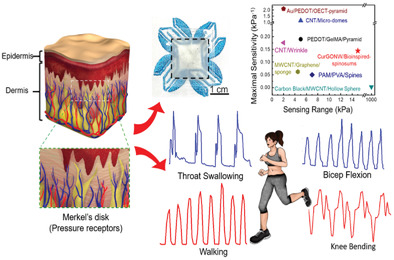
A epidermis-inspired wearable piezoresistive pressure sensors using reduced graphene oxide self-wrapped copper nanowire networks (CurGONW-SMPS) exhibit a high sensitivity, extensive sensing range, and good long-term stability. This CurGONW-SMPS can be used for real-time monitoring of human motions and subtle physiological signals.
Surface-Engineered Homostructure for Enhancing Proton Transport
- First Published: 08 December 2021
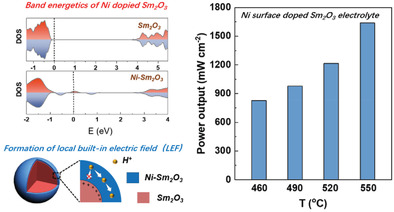
An advanced Sm2O3/Ni-Sm2O3 core-shell homostructure material with high proton conductivity is developed for a low-temperature solid oxide fuel cell. The local electrical field created by the interface confines the proton migration on the surface layer with accelerated ion transmission and promoted proton diffusion kinetics. This presents a new understanding for proton transport in rare-earth metal oxides semiconductor materials.