Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: A Pyrene-Linked Cavity within a β-Barrel Protein Promotes an Asymmetric Diels–Alder Reaction (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2017)
- Page: 13533
- First Published: 05 October 2017

A pyrene-linked protein cavity attracts two substrate molecules like the scent of a flower attracts butterflies. In their Communication on page 13618 ff., A. Onoda, T. Hayashi, and co-workers demonstrate that a polycyclic pyrene moiety linked within the rigid protein scaffold of the β-barrel of nitrobindin acts as a platform to provide an aromatic interaction with a substrate. An asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction between azachalcone and cyclopentadiene proceeds smoothly with high stereoselectivity within the reaction scaffold.
Inside Cover: Precisely Assembled Cyclic Gold Nanoparticle Frames by 2D Polymer Single-Crystal Templating (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2017)
- Page: 13534
- First Published: 05 October 2017

Free-standing frames can be prepared by a directed assembly method in which nanoparticles are precisely linked together by using polymer single crystals (PSCs) as a template. In their Communication on page 13645 ff., C. Y. Li and co-workers use preformed PSCs to direct the crystallization of block copolymers, which in turn direct gold NPs (AuNPs) to form precisely controlled AuNP frames. These AuNP frames topologically resemble nanoparticle rings and cyclic polymer chains, and show unique surface plasmon resonance behaviors.
Inside Back Cover: Olefins from Natural Gas by Oxychlorination (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2017)
- Page: 13899
- First Published: 05 October 2017

Turning myth into reality. Pérez-Ramírez et al. show in their Communication on page 13670 ff. the outstanding performance of EuOCl for the production of light olefins from ethane and propane by oxychlorination chemistry. The high activity, selectivity, and stability of the system are illustrated by the mythological princess Europa, who was carried from Asia to the Hellenic world by Zeus, who was disguised as a white bull. Both the continent of Europe and the element europium later took her name.
Back Cover: Potential-Cycling Synthesis of Single Platinum Atoms for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution in Neutral Media (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2017)
- Page: 13900
- First Published: 05 October 2017

Single Pt atoms can be synthesized on CoP-based nanotube arrays supported by Ni foams through potential cycling. In their Communication on page 13694 ff., X. J. Liu, J. Luo, and co-workers use this strategy to transfer single Pt atoms from a Pt source to a nanotube substrate in a neutral phosphate buffer solution (PBS). As an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in PBS, these single atoms exhibit a higher Pt-mass activity and a better stability than commercial Pt/CIn.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Because the Light is Better Here: Correlation-Time Analysis by NMR Spectroscopy
- First Published: 18 October 2017
NMR Spectroscopy In their Communication on page 13590, M. Ernst, B. H. Meier, and A. A. Smith examine potential pitfalls for the NMR analysis of protein dynamics and propose the use of dynamics detectors to characterize different ranges of correlation times.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2017
- Pages: 13537-13554
- First Published: 18 October 2017
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44/2017
- Pages: 13558-13561
- First Published: 19 July 2017
Author Profile
News
Highlights
Rearrangement Reactions
Enantioselective [2,3]-Sigmatropic Rearrangements: Metal-Bound or Free Ylides as Reaction Intermediates?
- Pages: 13566-13568
- First Published: 18 September 2017
Ribosomal Peptide Biosynthesis
Expanding the Structural Space of Ribosomal Peptides: Autocatalytic N-Methylation in Omphalotin Biosynthesis
- Pages: 13570-13572
- First Published: 26 September 2017
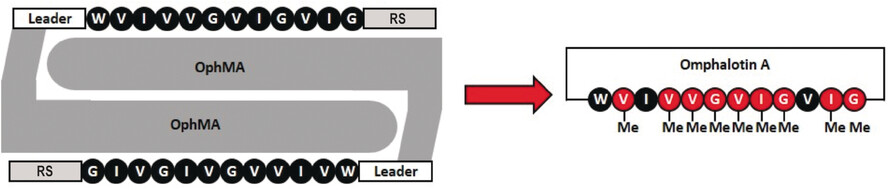
Tail-Me: The N-methylation of backbone amide bonds in peptide natural products was thought to be exclusive to non-ribosomal peptides. A newly discovered methylation mechanism now brings this structural feature into the world of ribosomal peptides, thereby significantly expanding the structural diversity of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs).
Reviews
Biotechnology
Cascades in Compartments: En Route to Machine-Assisted Biotechnology
- Pages: 13574-13589
- First Published: 10 July 2017
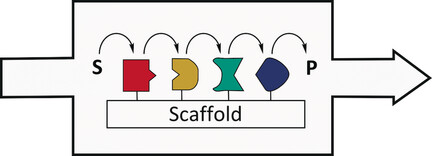
Machine-generated multienzyme cascades: The machine-assisted development of biomimetic compartments and catalytic cascades will pave the way towards a novel generation of biotechnological processes. Molecular scaffolds with small cross-linkers, proteins, nucleic acids, colloids, and patterned surfaces can be used to arrange the catalytic units. S: substrate, P: product.
Communications
Molecular Motion | Very Important Paper
Because the Light is Better Here: Correlation-Time Analysis by NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 13590-13595
- First Published: 30 August 2017
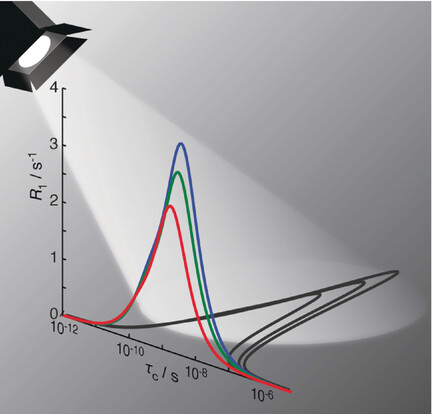
Fighting bias: NMR Dynamics data are more sensitive to some correlation times than to others. Models of the correlation function tend to be biased towards where the light is better, that is, where the experiment is more sensitive, thereby yielding an unreliable characterization of the motion. Replacing modeling by detectors that are sensitive to different ranges of correlation times could help to overcome this bias.
Catalyst Design | Very Important Paper
Enzyme Activity by Design: An Artificial Rhodium Hydroformylase for Linear Aldehydes
- Pages: 13596-13600
- First Published: 25 August 2017
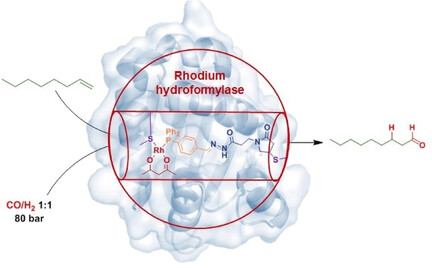
Artificial metalloenzymes are hybrid catalysts that offer a unique opportunity to combine the superior performance of natural protein structures with the unnatural reactivity of transition-metal catalytic centers. An artificial rhodium hydroformylase has been developed that displays remarkable activities and selectivities in the biphasic production of long-chain linear aldehydes.
Conjugated Systems
Regioselective Transformation of Long π-Conjugated Backbones: From Oligofurans to Oligoarenes
- Pages: 13601-13605
- First Published: 10 September 2017
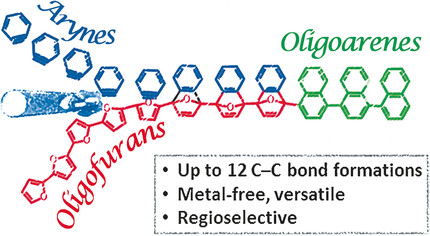
To cut a long story short: Oligofurans underwent sequential Diels–Alder reactions to provide oligoarenes in two chemical steps, regardless of the oligomer length (see picture). Different maleimide and benzyne dienophiles were also used to construct a range of substituted oligoarenes from a single oligofuran precursor in a highly regioselective manner.
Soft Materials
Manipulation of Biomolecule-Modified Liquid-Metal Blobs
- Pages: 13606-13611
- First Published: 06 September 2017
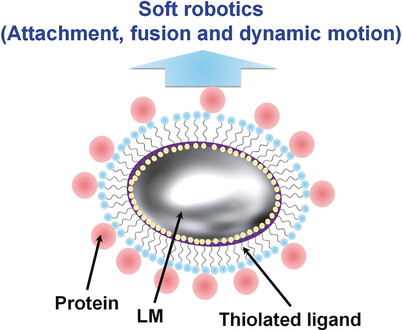
No interest in blobbing out: Biomolecule-functionalized liquid-metal (LM) blobs (see picture) were developed with macroscopic behavior promoted by molecular recognition, for example, through formation of the biotin–avidin complex. Bubble formation on the surface of enzyme-modified LM conjugates also enabled self-propelled dynamic motion. These behaviors could lead to efficient LM soft robots for operation in physiological environments.
Polymer Synthesis
Combining Orthogonal Chain-End Deprotections and Thiol–Maleimide Michael Coupling: Engineering Discrete Oligomers by an Iterative Growth Strategy
- Pages: 13612-13617
- First Published: 05 September 2017
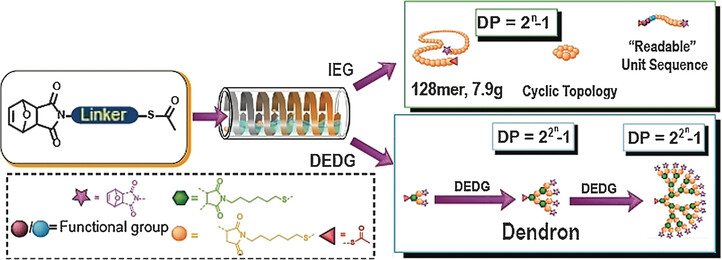
Discrete oligomers were fabricated by a versatile, efficient, and metal-free chemical process, which combines orthogonal deprotections of maleimide and thiol groups together with thiol–maleimide Michael coupling. Key: iterative exponential growth (IEG); double exponential dendrimer growth (DEDG); degree of polymerization (DP).
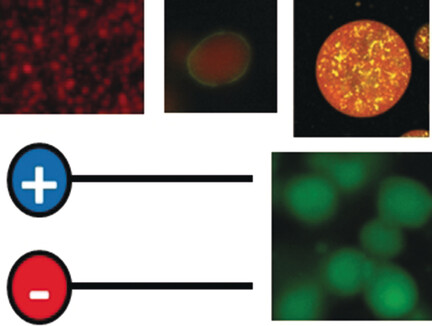
Protein Structures
A Pyrene-Linked Cavity within a β-Barrel Protein Promotes an Asymmetric Diels–Alder Reaction
- Pages: 13618-13622
- First Published: 09 August 2017
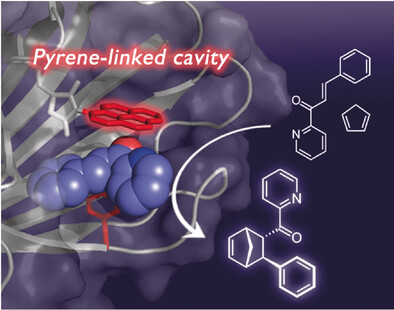
Selectivity by the barrel-load: A reaction cavity with a tethered polycyclic pyrene moiety, which acts as a platform to provide aromatic interactions, is constructed within the rigid scaffold of the β-barrel nitrobindin protein. An asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction between azachalcone and cyclopentadiene proceeds within the reaction cavity of the pyrene-linked nitrobindin with high stereoselectivity.
Separation Processes | Very Important Paper
Peristome-Mimetic Curved Surface for Spontaneous and Directional Separation of Micro Water-in-Oil Drops
- Pages: 13623-13628
- First Published: 05 September 2017
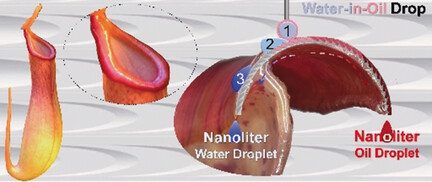
Keep 'em separated: A curved surface resembling the peristome, that is, the fringe of small projections around the opening of a capsule of a tropical pitcher plant is prepared. It enables the spontaneous separation of water and oil from micro-scale water-in-oil drops without energy input. The separation occurs within milliseconds and the separated liquids are spontaneously and uni-directionally transported in different directions.
Heterometallic Rings
An Extensive Family of Heterometallic Titanium(IV)–Metal(III) Rings with Structure Control through Templates
- Pages: 13629-13632
- First Published: 08 September 2017
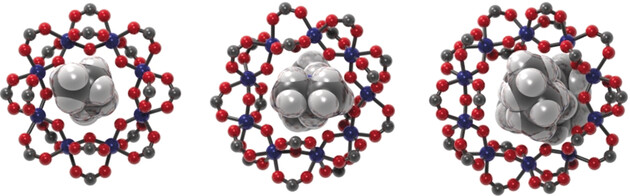
Size control: A family of heterometallic [Cat][TixMO(x+1)(O2C tBu)2x+2] rings is reported where Cat=a secondary or tertiary alkyl ammonium ion, x=7, 8 or 9, and M=Fe, Ga, Cr, In and Al. The structures are regular polygons with eight, nine or ten vertices with each edge bridged by an oxide and two pivalates. The size of the ring formed is controlled by the alkylammonium cation present.
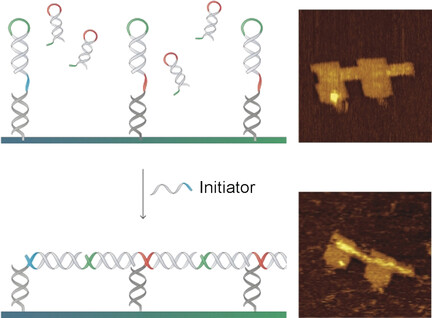
DNA Nanotechnology
AFM Imaging of Hybridization Chain Reaction Mediated Signal Transmission between Two DNA Origami Structures
- Pages: 13633-13636
- First Published: 03 September 2017
Whole-Cell Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Engineered Fluorine Metabolism and Fluoropolymer Production in Living Cells
- Pages: 13637-13640
- First Published: 31 August 2017
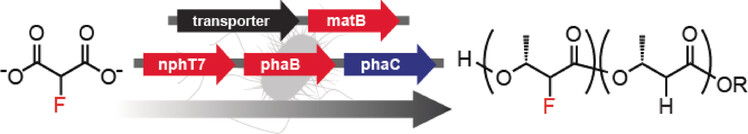
Live action: An engineered microbial host for organofluorine metabolism can produce a fluorinated diketide at around 50 % yield. The diketide can be used as a monomer to produce fluorinated poly(hydroxyalkanoate) bioplastics in vivo with fluorine substitution of up to 15 %. This system provides a platform to generate a broad range of fluorinated small-molecule targets in living cells.
Proteomics
Phosphate Transfer in Activated Protein Complexes Reveals Interaction Sites
- Pages: 13641-13644
- First Published: 04 September 2017
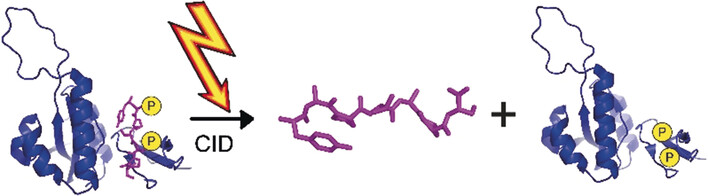
Pass the P: Phosphate groups can be transferred non-enzymatically from one interaction partner to the other during gas-phase activation. In high-affinity complexes, this phosphate transfer occurs within the binding site, thereby revealing the interaction interface within the protein/phosphopeptide complex.
Nanoparticle Assembly
Precisely Assembled Cyclic Gold Nanoparticle Frames by 2D Polymer Single-Crystal Templating
- Pages: 13645-13649
- First Published: 27 July 2017
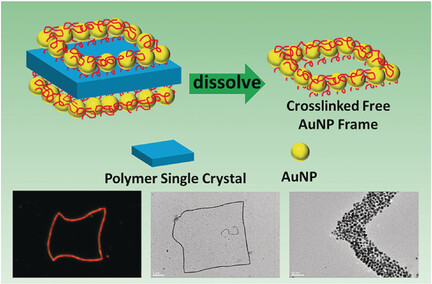
Frame: Free-standing gold nanoparticle (AuNP) frame structures are formed by directed assembly of AuNPs on polymer single-crystal templates. The size and width of the frames are precisely controllable and easily tunable. These frames resemble NP nanorings and 1D cyclic polymer chains, and have intriguing optical properties similar to Au nanorods.
Light-Emitting Diodes
High-Performance CsPb1−xSnxBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots for Light-Emitting Diodes
- Pages: 13650-13654
- First Published: 02 September 2017
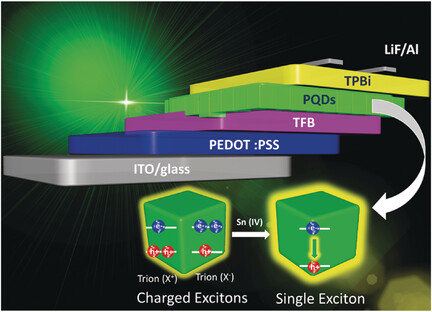
Suppressed trion formation: CsPb1−xSnxBr3 quantum dots (QDs) were synthesized by a hot-injection approach. As trion formation is suppressed by the SnIV substitution, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) based on these highly luminescent QDs performed very well, with the highest current efficiencies and external quantum efficiencies ever reported for such Sn-based systems.
Organic Radicals
Gas-Phase Synthesis of the Elusive Cyclooctatetraenyl Radical (C8H7) via Triplet Aromatic Cyclooctatetraene (C8H8) and Non-Aromatic Cyclooctatriene (C8H8) Intermediates
- Pages: 13655-13660
- First Published: 08 September 2017
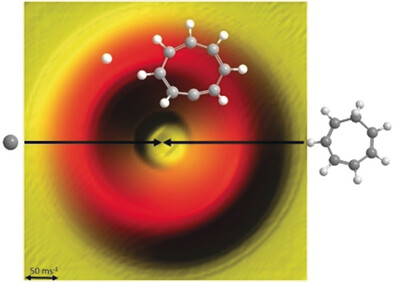
Carbon eight-ed: Gas-phase reaction of ground-state carbon atoms and cycloheptatriene (C7H8) under single-collision conditions leads to the production of the 1,2,4,7-cyclooctatetraenyl radical (C8H7). Ab initio electronic structure calculation shows the reaction proceeds via exotic triplet C8H8 reaction intermediates: the non-aromatic 2,4,6-cyclooctatriene and the aromatic 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene. The picture shows the flux contour map of the reaction.
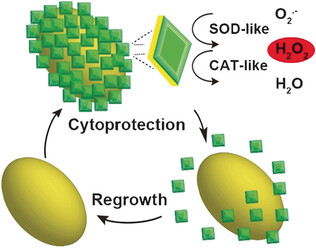
Cytoprotection
Manganese Dioxide Nanozymes as Responsive Cytoprotective Shells for Individual Living Cell Encapsulation
- Pages: 13661-13665
- First Published: 07 September 2017
Allylic Compounds
Regioselective Intermolecular Allylic C−H Amination of Disubstituted Olefins via Rhodium/π-Allyl Intermediates
- Pages: 13666-13669
- First Published: 14 September 2017
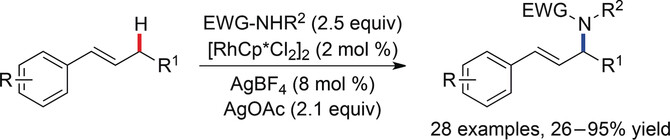
A method for catalytic intermolecular allylic C−H amination of trans-disubstituted olefins has been developed that is efficient for a range of common nitrogen nucleophiles bearing one electron-withdrawing group (EWG), and proceeds under mild reaction conditions. Good levels of regioselectivity are observed for a wide range of electronically diverse trans-β-alkyl styrene substrates.
Alkanes | Hot Paper
Olefins from Natural Gas by Oxychlorination
- Pages: 13670-13674
- First Published: 03 August 2017
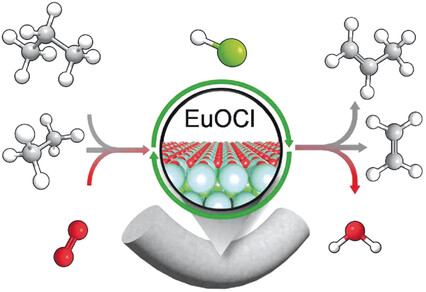
Gas up: Ethylene and propylene can be generated from ethane and propane, respectively, or from methane/ethane/propane mixtures, over a europium oxychloride catalyst. The reaction proceeds by oxychlorination with yields surpassing those of any existing technologies for alkene production. Its performance is preserved in technical form, and testifies to the practical relevance of this technology for the manufacture of light olefins.
Magnetic Properties | Very Important Paper
Molecular Dynamics of Hexamethylbenzene at Low Temperatures: Evidence of Unconventional Magnetism Based on Rotational Motion of Protons
- Pages: 13675-13678
- First Published: 17 August 2017
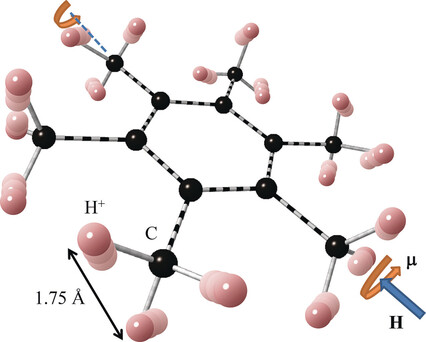
A strongly correlated system: A previously unidentified type of magnetism based on the rotational motion of protons within methyl groups is shown to occur in hexamethylbenzene. At lower temperatures spin–spin interactions exist between methyl groups aligned in a previously unclassified type of antiferromagnetic configuration.
Plasma Chemistry
One-Step Reforming of CO2 and CH4 into High-Value Liquid Chemicals and Fuels at Room Temperature by Plasma-Driven Catalysis
- Pages: 13679-13683
- First Published: 25 August 2017
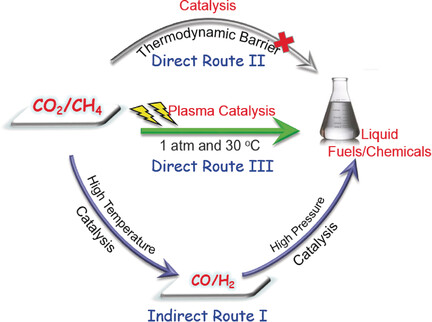
Liquid fuels and chemicals (e.g. acetic acid, methanol, ethanol, and formaldehyde) were synthesized in a one-step process from CO2 and CH4 at room temperature (30 °C) and atmospheric pressure for the first time by using a novel plasma reactor with a water electrode. The total selectivity to oxygenates was approximately 50–60 %, with acetic acid as the major component.
Anticancer Therapy
Black Pigment Gallstone Inspired Platinum-Chelated Bilirubin Nanoparticles for Combined Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Therapy of Cancers
- Pages: 13684-13688
- First Published: 04 September 2017
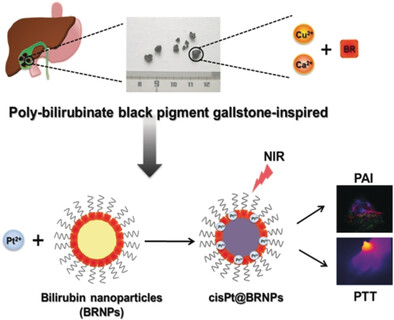
The gall of it: A new class of near infrared light-responsive photonic nanomaterial which is biodegradable and biocompatible is developed based on the inherent metal-chelating ability of bilirubin, a bile pigment found in gall stones. The resulting cisplatin-chelated bilirubin nanoparticles (cisPt@BRNPs) are promising for combined photoacoustic imaging (PAI) and photothermal therapy (PTT) of cancers.
Artificial Cell Models
Catanionic Coacervate Droplets as a Surfactant-Based Membrane-Free Protocell Model
- Pages: 13689-13693
- First Published: 13 September 2017
Hydrogen Evolution | Very Important Paper
Potential-Cycling Synthesis of Single Platinum Atoms for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution in Neutral Media
- Pages: 13694-13698
- First Published: 08 August 2017
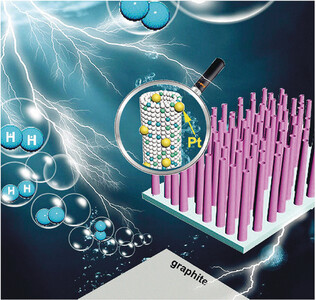
Singles suitable for HER: Large-area single Pt atoms on CoP-based nanotube arrays supported by Ni foams were synthesized by potential cycling. These binder-free electrocatalysts are centimeter-scale and can be scaled up further. They exhibit unparalleled performance when catalyzing the hydrogen evolution reaction in neutral media.
Noncovalent Interactions
Rotational Spectroscopy Probes Water Flipping by Full Fluorination of Benzene
- Pages: 13699-13703
- First Published: 05 September 2017
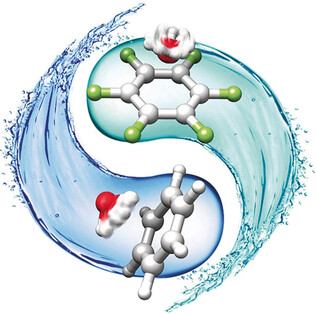
Flipping water: The prototype system for the lone-pair⋅⋅⋅π-hole interaction, hexafluorobenzene–water, has been investigated by rotational spectroscopy. Interesting chemical and dynamic features have been found: a) fluorine substitution flips the water bond with benzene, from O−H⋅⋅⋅π to O⋅⋅⋅π hole; b) water is almost freely rotating above the ring and the spectrum of the complex appears to be that of a symmetric top.
Fluorescent Probes
Specific and Direct Amplified Detection of MicroRNA with MicroRNA:Argonaute-2 Cleavage (miRACle) Beacons
- Pages: 13704-13708
- First Published: 04 September 2017
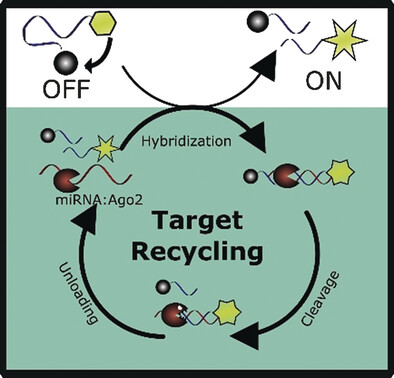
Simple sensors simulate substrate: MicroRNA detection with molecular beacons can be used for in situ genetic profiling. Beacons that are susceptible to the endogenous nuclease Argonaute-2 (Ago2) have now been developed. After purification of the complex by co-immunoprecipitation, microRNA:Ago2 cleavage (miRACle) beacons undergo site- and sequence-specific cleavage, and show a 13-fold fluorescence enhancement over traditional beacons.
Gene Delivery | Very Important Paper
Polyamine-Mediated Stoichiometric Assembly of Ribonucleoproteins for Enhanced mRNA Delivery
- Pages: 13709-13712
- First Published: 19 September 2017
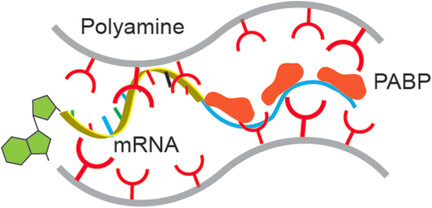
Although numerous carriers have been developed for mRNA delivery, the inefficient mRNA expression inside cells remains a major challenge. Inspired by the dependence of mRNA on 3′-terminal polyadenosine nucleotides (poly A) and poly A binding proteins (PABPs) for optimal expression, synthetic mRNA containing a poly A tail was complexed with PABPs in a stoichiometric manner.
Ultrafast Dynamics
Spin Changes Accompany Ultrafast Structural Interconversion in the Ground State of a Cobalt Nitrosyl Complex
- Pages: 13713-13716
- First Published: 04 September 2017
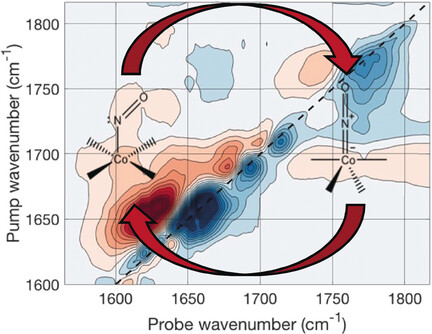
The ground state intersystem crossing of a cobalt nitrosyl complex is shown to occur on an ultrafast time scale. The electron spin changing dynamics can be observed with 2DIR spectroscopy by probing the nuclear vibrational frequencies associated with each electronic state. Comparison of the spin-state exchange rates in two halido-substituted complexes shows that inertial effects outweigh ligand spin–orbit coupling effects.
Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots Used for Boosting Light Harvesting in Organic Photovoltaics
- Pages: 13717-13721
- First Published: 11 September 2017
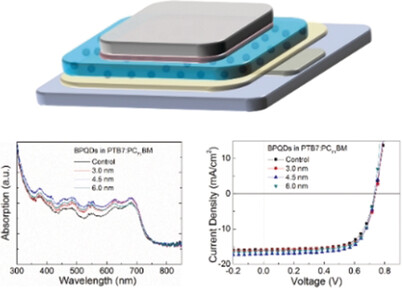
Strong light absorption: The power conversion efficiencies of organic photovoltaics have been improved by introducing black phosphorus quantum dots (BPQDs; 0.055 wt % relative to the donor polymers) due to the boosted light harvesting of the devices. The effect is attributed to the strong light absorption as well as the two-dimensional structure of the BPQDs. A pronounced size effect of BPQDs on the performance enhancement is observed.
Organocatalysis
Organocatalytic Intramolecular [4+2] Cycloaddition between In Situ Generated Vinylidene ortho-Quinone Methides and Benzofurans
- Pages: 13722-13726
- First Published: 04 September 2017
![Organocatalytic Intramolecular [4+2] Cycloaddition between In Situ Generated Vinylidene ortho-Quinone Methides and Benzofurans](/cms/asset/a7e45861-8ea2-4b61-92ea-588cc42570f0/anie201707523-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Triple play: The enantioselective construction of oxygen-containing [5-6-5] tricyclic heterocycles by a thiourea-catalyzed asymmetric [4+2] cycloaddition of vinylidene ortho-quinone methides (VQMs) and benzofurans is reported. A series of oxygen-containing [5-6-5] tricyclic heterocycles having various functional groups were synthesized with excellent enantio- and diastereoselectivities.
Polycycles
Extended Ladder-Type Benzo[k]tetraphene-Derived Oligomers
- Pages: 13727-13731
- First Published: 08 September 2017
Peptide Therapeutics
Bioactive Macrocyclic Inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint
- Pages: 13732-13735
- First Published: 07 September 2017
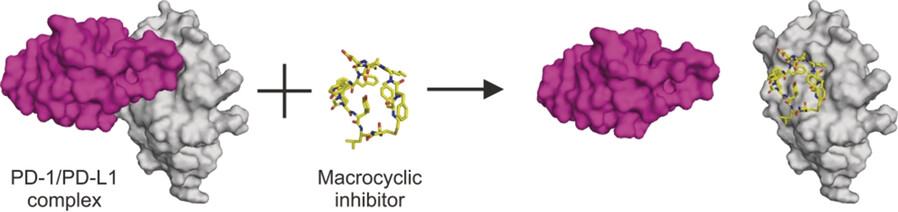
Circle of life: Macrocyclic peptide inhibitors can block the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway by directly binding to PD-L1 and, similarly to anti-PD-L1 antibodies, they can restore the function of T-cells. Structures of the macrocycle/PD-L1 interfaces provide a foundation for the design of small-molecule inhibitors with antitumor properties.
Nanobiotechnology
A Biomimetic Escape Strategy for Cytoplasm Invasion by Synthetic Particles
- Pages: 13736-13740
- First Published: 05 September 2017
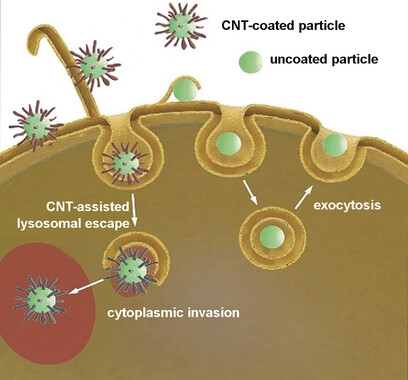
A clean getaway: An engineered nanocoating composed of carbon nanotubes enabled particles with nano/micrometer dimensions to break through lysosomal membranes and invade the intracellular realm (see picture). The coated materials resemble viruses in terms of their structure and reproduce the viral cell-invasive mechanisms of receptor-mediated endocytosis, endolysosomal escape, and cytosolic particle release with the preservation of cell viability.
Electrochemistry | Hot Paper
An Ultraflexible Silicon–Oxygen Battery Fiber with High Energy Density
- Pages: 13741-13746
- First Published: 21 September 2017

A silicon–oxygen battery fiber with high energy density and ultra-high flexibility has been created. The coaxial architecture of the fiber was obtained by using a lithiated silicon/carbon nanotube hybrid fiber as inner anode, a polymer gel as middle electrolyte and a carbon nanotube sheet as outer cathode.
Electron Transfer
Electron-Transfer and Hydride-Transfer Pathways in the Stoltz–Grubbs Reducing System (KOtBu/Et3SiH)
- Pages: 13747-13751
- First Published: 11 September 2017
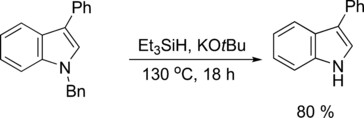
Transfers: Triethylsilane and potassium tert-butoxide react to form a highly attractive and versatile system. The work herein highlights the reductive transformations which lead to 1) C−N bond cleavage in N-benzyl- and N-allylindoles and 2) reduction of polycyclic arenes to their dihydro derivatives.
Photodynamic Therapy
H2S-Activable MOF Nanoparticle Photosensitizer for Effective Photodynamic Therapy against Cancer with Controllable Singlet-Oxygen Release
- Pages: 13752-13756
- First Published: 30 August 2017
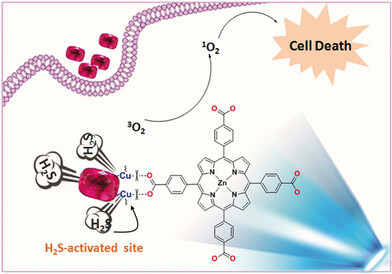
Selective cancer treatment: A mixed-metal metal–organic framework nanoparticle photosensitizer has been activated by a H2S-signaling molecule in a specific tumor microenvironment for photodynamic therapy of cancer using controllable singlet-oxygen release. The effective removal of tumors in vivo confirms the satisfactory treatment effect of the photosensitizer.
Organocatalysis
Selective C−O Bond Cleavage of Sugars with Hydrosilanes Catalyzed by Piers’ Borane Generated In Situ
- Pages: 13757-13761
- First Published: 12 September 2017
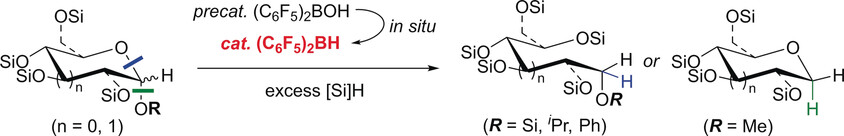
Piers’ borane [(C6F5)2BH], generated in situ, is demonstrated to promote the hydrosilylative reduction of sugars, thereby providing a series of linear or cyclic polyols with high chemo- and regioselectivities under mild conditions. Studies of catalytic reactivity and regioselectivity with regard to the C−O bond cleavage with hydrosilanes suggest an importance of the steric environment around the anomeric carbon center of the sugar.
High-Valent Transition Metals
Valence Interconversion of Octahedral Nickel(II/III/IV) Centers
- Pages: 13762-13766
- First Published: 28 August 2017
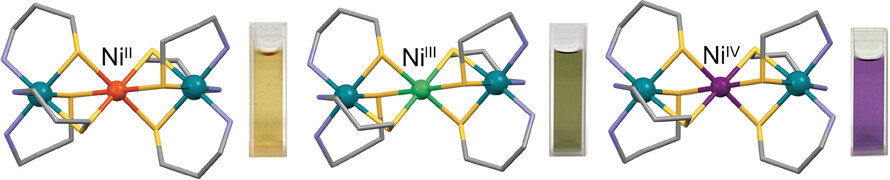
Bridge over troubled water: A series of S-bridged RhNiRh trinuclear complexes capable of supporting an octahedral nickel center in three different oxidation states (+2, +3, +4) have been isolated. Oxidation state interconversion is accompanied by changes in color, magnetism, and geometric Jahn–Teller distortions, with retention of the trinuclear structure.
Self-Assembly
Visualization of Stereoselective Supramolecular Polymers by Chirality-Controlled Energy Transfer
- Pages: 13767-13771
- First Published: 11 September 2017
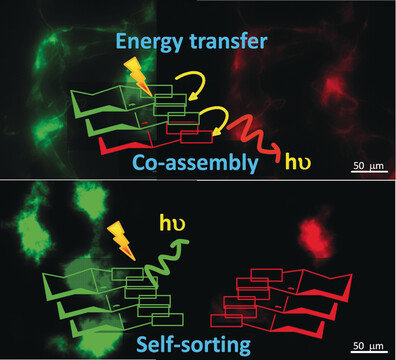
To the core: Presented herein are two fluorescent core-substituted naphthalene-diimide-based donor and acceptor molecules with minimal structural mismatch, and they comprise self-recognizing chiral motifs to facilitate the self-sorting process. Visual discrimination of the stereoselective self-sorted and co-assembled supramolecular polymers is presented by using chirality-controlled energy transfer.
Single-Molecule Imaging | Hot Paper
Single Turnover at Molecular Polymerization Catalysts Reveals Spatiotemporally Resolved Reactions
- Pages: 13772-13775
- First Published: 11 September 2017
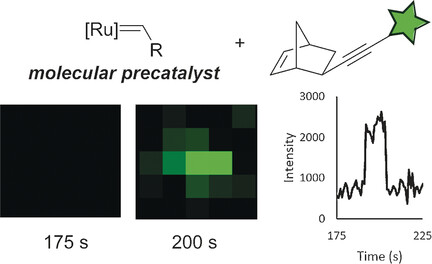
Singled out: Single-turnover detection has enabled the spatiotemporal resolution of individual reactions within growing polymers. The addition of a spectator fluorophore to the polymerization of norbornene enabled individual monomer reactions at an industrially important molecular ruthenium ring-opening metathesis polymerization catalyst to be observed as a bright-green point flash by fluorescence microscopy.
Natural Products
One-Step Multigram-Scale Biomimetic Synthesis of Psiguadial B
- Pages: 13776-13780
- First Published: 08 September 2017
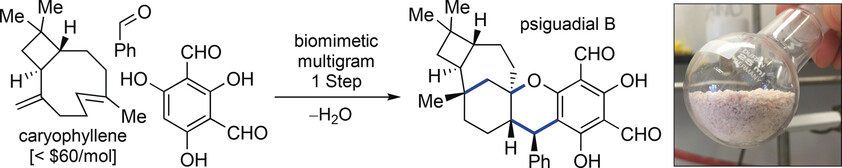
A one-step multigram-scale synthesis of psiguadial B has been achieved using a biomimetic three-component coupling, thus generating three C−C bonds, one C−O bond, two rings, and four stereocenters. Combined synthetic and computational experiments suggest the reaction proceeds by a Michael addition of caryophyllene to an in situ generated ortho-quinone methide, followed by two sequential cationic cyclization events.
Trifunctional Electrocatalysts
Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Architectures Derived from Surface-Mounted Metal–Organic Framework Membranes for Enhanced Electrocatalysis
- Pages: 13781-13785
- First Published: 04 September 2017
Burnt to a crisp: Surface-mounted metal–organic framework (MOF) membranes were pyrolyzed to produce electrocatalytic nanomaterials with 3D nanoarchitectures and abundant catalytic sites. Cobalt contained in the MOF thin-film has a dual function; it facilitates growth of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes and promotes oxygen reduction, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen evolution reactions.
Continuous-Flow Synthesis
Integration of Bromine and Cyanogen Bromide Generators for the Continuous-Flow Synthesis of Cyclic Guanidines
- Pages: 13786-13789
- First Published: 06 September 2017
Porous Materials | Very Important Paper
Mass Production and Pore Size Control of Holey Carbon Microcages
- Pages: 13790-13794
- First Published: 18 September 2017
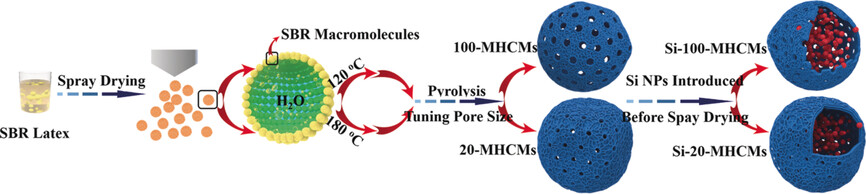
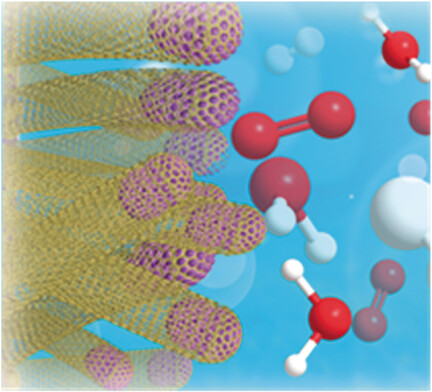
Holey controllable: Holey carbon microcages with controllable pore sizes are easily synthesized by a scalable spray-pyrolysis technique. Beyond energy storage, these porous, hollow carbon microcages can be further constructed into micro-containers for holding other functional materials with promising applications. Their lithium-ion storage ability for use in lithium-ion batteries is demonstrated.
Nanoparticles
Repairing Nanoparticle Surface Defects
- Pages: 13795-13799
- First Published: 03 September 2017
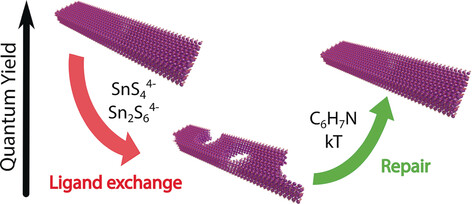
Solar devices based on semiconductor nanoparticles require the use of conductive ligands; however, the exchange of insulating ligands with conductive metal chalcogenide complexes introduces structural defects that act as traps for charge carriers. CdSe nanoplatelets were used as a model system to show that it is possible to minimize the formation of defects, as well as trigger surface healing, by a judicious choice of mild treatments.
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Synergistic Effects between Atomically Dispersed Fe−N−C and C−S−C for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Acidic Media
- Pages: 13800-13804
- First Published: 31 August 2017
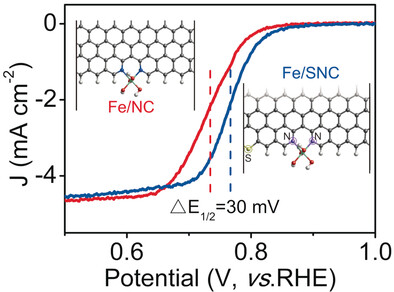
A sulfur-doped Fe/N/C catalyst with much better activity in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in 0.5 m H2SO4 solution than the sulfur-free variant was developed. The incorporated sulfur atoms reduce the electron localization around the iron centers, improve the interaction with oxygenated species, and therefore facilitate the complete 4 e− ORR in acidic solution.
Silver Catalysis
Silver-Catalyzed Stereoselective Aminosulfonylation of Alkynes
- Pages: 13805-13808
- First Published: 19 June 2017
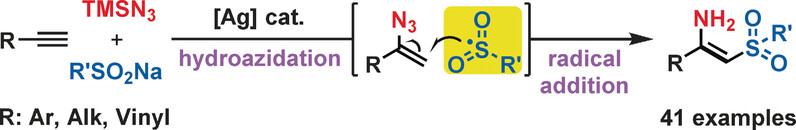
Controllable assembly: The first intermolecular aminosulfonylation of terminal alkynes with sodium sulfinates and TMSN3 is reported. This three-component coupling, which shows excellent functional group tolerance, proceeds through sequential hydroazidation of the terminal alkyne and addition of a sulfonyl radical to the resultant vinyl azide. This enables the stereoselective synthesis of a wide range of β-sulfonyl N-unprotected enamines.
Photocatalytic Rearrangement
Efficient Aryl Migration from an Aryl Ether to a Carboxylic Acid Group To Form an Ester by Visible-Light Photoredox Catalysis
- Pages: 13809-13813
- First Published: 28 August 2017

A great migration: In a retro-Smiles rearrangement under visible-light photoredox catalysis at ambient temperature, one aryl group of a diaryl ether migrated to the carboxy group to form an ester (see scheme). The transformation requires no transition metals and no stoichiometric oxidant or base and could be followed by saponification in a one-pot, two-step process enabling overall C−O cleavage of the aryl ether.
Synthetic Methods
Catalytic Asymmetric Mannich Reaction with N-Carbamoyl Imine Surrogates of Formaldehyde and Glyoxylate
- Pages: 13814-13818
- First Published: 09 September 2017
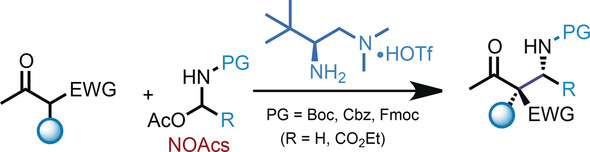
On the bench: N,O-acetals (NOAcs) were developed as bench-stable surrogates for N-carbamoyl (Boc, Cbz, Fmoc) formaldehyde and glyoxylate imines in asymmetric Mannich reactions. This reaction offers a straightforward approach for the asymmetric synthesis of α- or β-amino carbonyls bearing chiral quaternary centers in a practical and highly stereocontrolled manner. EWG=electron-withdrawing group, PG=protecting group.
Solar Cells
Formation of Stable Tin Perovskites Co-crystallized with Three Halides for Carbon-Based Mesoscopic Lead-Free Perovskite Solar Cells
- Pages: 13819-13823
- First Published: 05 September 2017
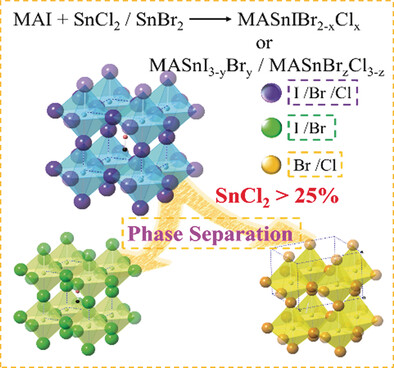
Tin in: Stable tin perovskites co-crystalized with three different halide elements (I, Br, and Cl) were produced by the reaction of methylammonium (MA) iodide with SnCl2/SnBr2 mixtures at ratios equal to or less than 25/75. The best device made of a carbon-based mesoscopic electrode and MASnIBr1.8Cl0.2 exhibited a PCE of 3.1 %.
Hydrogenation
Reductive Coupling of Acrylates with Ketones and Ketimines by a Nickel-Catalyzed Transfer-Hydrogenative Strategy
- Pages: 13824-13828
- First Published: 04 September 2017
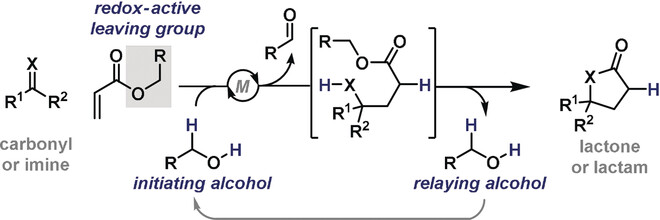
Catch and release: Nickel-catalyzed coupling of benzyl acrylates with activated ketones and imines provides a direct entry to γ-butyrolactones and lactams, respectively. The benzyl alcohol by-product released during the lactonization/lactamization event is relayed to the next cycle, where it then serves as the reductant for C−C bond formation.
Aromaticity
Benzodisilacyclobutadienes: 8π-Electron Systems with an Antiaromatic Silicon Ring
- Pages: 13829-13832
- First Published: 28 August 2017
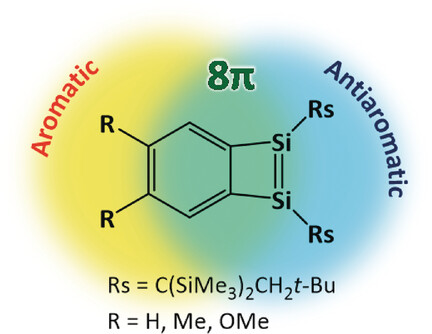
Slowing the flow: Benzodisilacyclobutadienes (see structure) were synthesized and isolated as blue and green crystalline solids. According to their solid-state structures, UV/Vis absorption and NMR spectra, and theoretical calculations, these benzodisilacyclobutadienes exist as 8π-electron systems that contain an antiaromatic 1,2-disilacyclobutadiene.
Natural Products
Bioinspired Total Synthesis of (−)-Vescalin: A Nonahydroxytriphenoylated C-Glucosidic Ellagitannin
- Pages: 13833-13837
- First Published: 30 August 2017
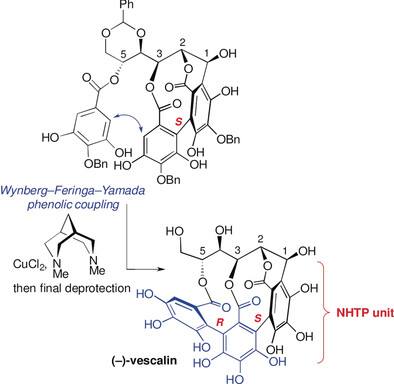
Catch a tan(nin): The total synthesis of a first member of the nonahydroxytriphenoylated (NHTP) C-glucosidic ellagitannins, (−)-vescalin, is described. The route is closely tailored to the commonly proposed sequence of events leading to its biogenesis. Its characteristic 2,3,5-(S,R)-NHTP unit was elaborated by a copper(II)-mediated Wynberg–Feringa–Yamada-type phenolic coupling using the achiral bicyclic diamine N,N′-dimethylbispidine.
Quantum Chemistry | Hot Paper
Correct Modeling of Cisplatin: a Paradigmatic Case
- Pages: 13838-13841
- First Published: 30 August 2017
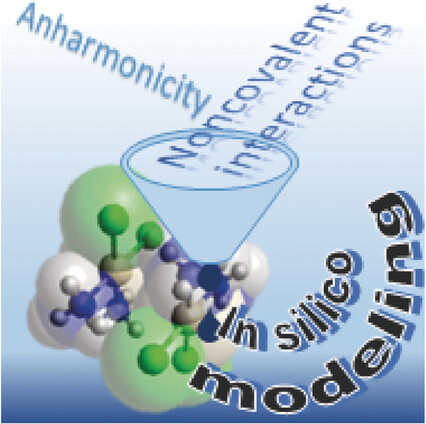
Two are needed for a valid prediction: A dimer of cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] as a quantum chemical model for cisplatin provides the first quantitative agreement with experiment for structural and vibrational properties. This result indicates that a reliable in silico drug design requires a model capturing the essential physical picture of the system and a proper theoretical protocol.
Organocatalysis
Organocatalytic Enantioselective Protonation for Photoreduction of Activated Ketones and Ketimines Induced by Visible Light
- Pages: 13842-13846
- First Published: 19 September 2017
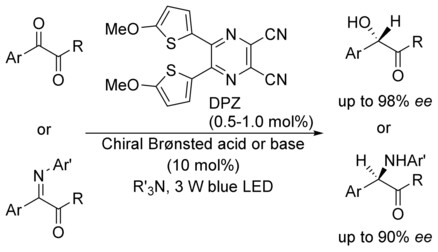
Enantioselective protonation: The first catalytic asymmetric photoreduction of 1,2-diketones and α-keto ketimines under visible light irradiation relies on a transition-metal-free cooperative catalysis platform that harnesses dicyanopyrazine-derived chromophore (DPZ) as the photoredox catalyst and a noncovalent chiral organocatalyst. A variety of chiral α-hydroxy ketones and α-amino ketones was obtained with high yields and enantioselectivities.
Amino Acids
Synthesis of Acylborons by Ozonolysis of Alkenylboronates: Preparation of an Enantioenriched Amino Acid Acylboronate
- Pages: 13847-13851
- First Published: 14 September 2017
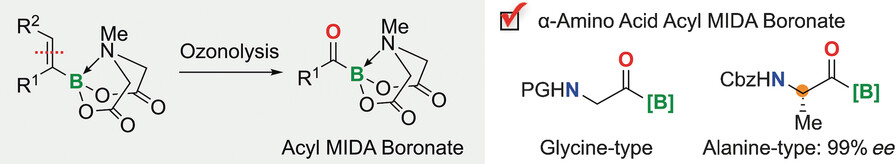
In the (o)zone: Highly functionalized acylborons are prepared by ozonolysis of alkenyl MIDA boronates. The first synthesis of α-amino acylborons, including the enantiopure alanine-type acylboron was achieved by using this method. The products are essential for protein–protein conjugation by potassium acyltrifluoroborate ligation. Oligopeptide synthesis using α-amino acylborons proceeded in dilute aqueous medium and the alanine-type acylboron is configurationally stable under ligation conditions.
Polymerization
Enzymatic Cascade Catalysis for the Synthesis of Multiblock and Ultrahigh-Molecular-Weight Polymers with Oxygen Tolerance
- Pages: 13852-13856
- First Published: 08 September 2017
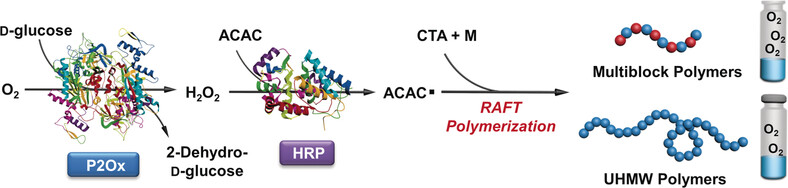
Ultrahigh: Enzymatic cascade catalysis enables the synthesis of multiblock (up to 10 blocks) copolymers and ultrahigh-molecular-weight polymers (UHMW; up to 2.3×106 g mol−1). The reaction employs a P2Ox-HRP system and can be run in vessels open to air, thus highlighting the oxygen tolerance of the process. P2Ox=pyranose oxidase, HRP=horseradish peroxidase, ACAC=acetylacetone, RAFT=reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer.
Biomimetic Synthesis | Very Important Paper
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (−)-Deoxoapodine
- Pages: 13857-13860
- First Published: 01 September 2017
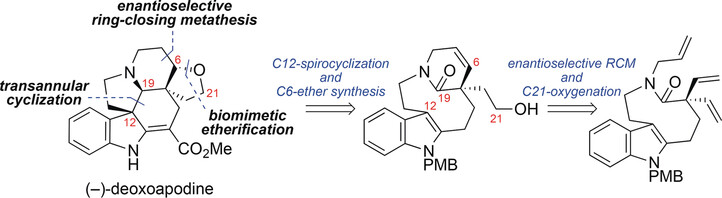
A molybdenum-catalyzed enantioselective ring-closing metathesis reaction for the desymmetrization of an advanced intermediate is one of the key steps of the total synthesis of (−)-deoxoapodine. After C21-oxygenation, the pentacyclic core was accessed through amide activation and transannular spirocyclization. A dehydrative C6-etherification introduced the F-ring and the fourth contiguous stereocenter.
Gold Complexes
Gold(III) Alkyne Complexes: Bonding and Reaction Pathways
- Pages: 13861-13865
- First Published: 11 September 2017
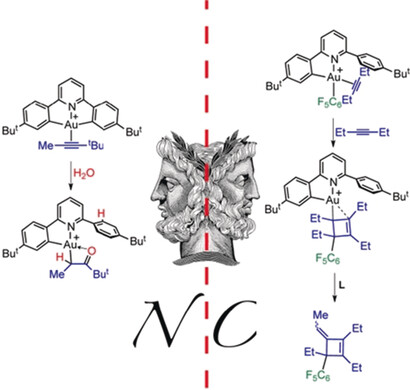
Good as gold: The synthesis of hitherto hypothetical gold(III) π-alkyne complexes highlights the differences between classical platinum alkyne complexes and their drastically more reactive AuIII congeners. Alkyne bonding in these complexes is subject to a strong trans influence, with ligands trans to a pyridine N atom being bound significantly more strongly than those trans to an anionic C donor.
Si4 Ring Compounds
Diradicaloid or Zwitterionic Character: The Non-Tetrahedral Unsaturated Compound [Si4{N(SiMe3)Dipp}4] with a Butterfly-type Si4 Substructure
- Pages: 13866-13871
- First Published: 23 August 2017
![Diradicaloid or Zwitterionic Character: The Non-Tetrahedral Unsaturated Compound [Si4{N(SiMe3)Dipp}4] with a Butterfly-type Si4 Substructure](/cms/asset/4939c5be-a00b-4e8a-bee8-851ae0c3f33d/anie201705787-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A change in structure: The unsaturated butterfly-shaped Si4 ring compound 1 ([Si4{N(SiMe3)Dipp}4]; Dipp=2,6-iPr2C6H3) was obtained by reduction of {N(SiMe3)Dipp}SiBr3. Compound 1 exhibits positively and negatively polarized three-coordinate Si atoms with flexible geometry, as determined by experimental and computational studies. Reactions of 1 with 5 or 8 equiv of sulfur afforded compound 2, a new amido-substituted Si4S3 cage compound.
Ring Opening
Transition-Metal-Free Ring-Opening Silylation of Indoles and Benzofurans with (Diphenyl-tert-butylsilyl)lithium
- Pages: 13872-13875
- First Published: 08 September 2017
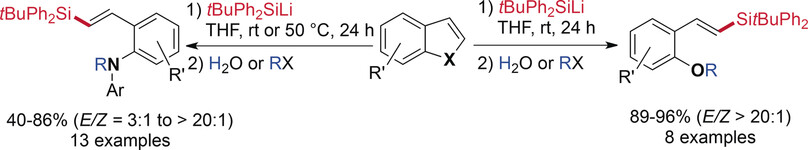
Open for business: Ring-opening silylation of various indoles and benzofurans using diphenyl-tert-butylsilyllithium affords ortho-β-silylvinyl anilines or phenols. Dearomatization of the heteroarene core proceeds in the absence of any transition-metal catalyst through addition of a silyl anion and a subsequent stereoselective β-elimination.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Conversion of Methane into Methanol and Ethanol over Nickel Oxide on Ceria–Zirconia Catalysts in a Single Reactor
- Pages: 13876-13881
- First Published: 08 August 2017
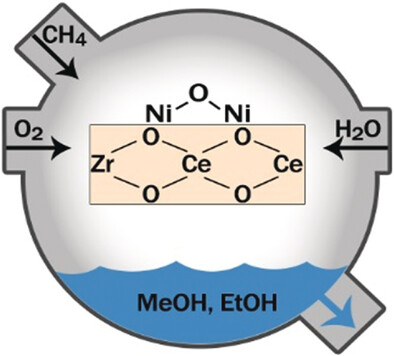
Controlled oxidation: Methanol and ethanol are produced continuously from methane and oxygen in a single reaction over a catalyst consisting of NiO clusters on ceria–zirconia. Oxygen is the abundantly available oxidant for this reaction and the presence of steam ensures the production of alcohols as opposed to products of the complete combustion of methane.
Light Harvesting
Highly Fluorescent Pyridinium Betaines for Light Harvesting
- Pages: 13882-13886
- First Published: 10 July 2017
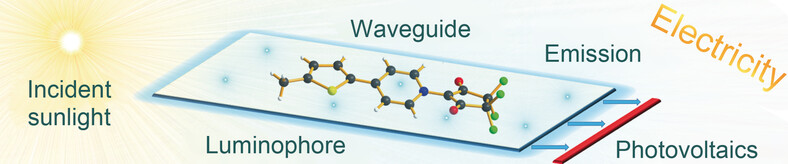
Experiment and theory: Pyridinium enolates and their potential utility in light-harvesting applications, such as in luminescent solar concentrators, were studied experimentally and theoretically. The synthesis, structures, photophysical properties, and wavefunction-based quantum-chemical studies of five cyclobetaines are presented.
Perovskite Nanowires
From Precursor Powders to CsPbX3 Perovskite Nanowires: One-Pot Synthesis, Growth Mechanism, and Oriented Self-Assembly
- Pages: 13887-13892
- First Published: 21 August 2017
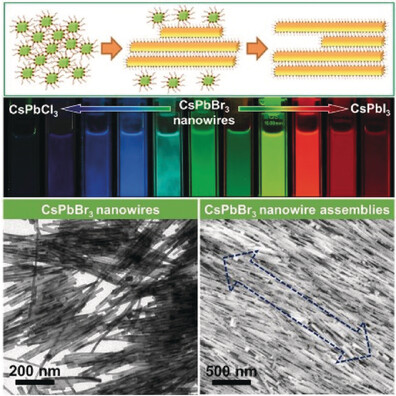
Cubes, wires, and assemblies: Single-crystalline perovskite nanowires were prepared directly from precursor powders in a single-step ligand-assisted process by ultrasonication. The nanowires likely resulted from the oriented attachment of nanocubes. Quasi-oriented self-assemblies of the perovskite nanowires were fabricated at air/liquid interfaces.
Biocatalysis
Regioselective para-Carboxylation of Catechols with a Prenylated Flavin Dependent Decarboxylase
- Pages: 13893-13897
- First Published: 30 August 2017
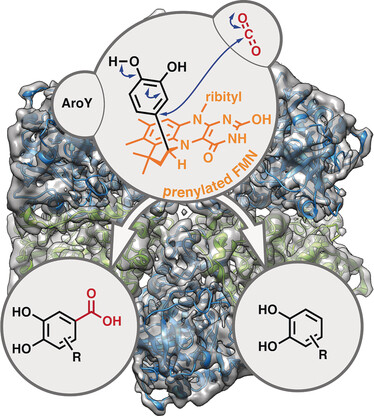
Biocatalytic CO2 fixation: 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid decarboxylases are shown to catalyze the regioselective para-carboxylation of the aromatic core of catechols under ambient conditions. The enzymes depend on the recently discovered prenylated FMN cofactor for catalysis, which is proposed to proceed via a monocovalently bound quinoid–cofactor intermediate.







![Enantioselective [2,3]-Sigmatropic Rearrangements: Metal-Bound or Free Ylides as Reaction Intermediates?](/cms/asset/8d012363-490e-449a-a456-e03186df1447/anie201707092-toc-0001-m.jpg)
![Extended Ladder-Type Benzo[k]tetraphene-Derived Oligomers](/cms/asset/333272b8-936e-40ce-a19a-c109d0c1bb63/anie201707595-toc-0001-m.jpg)



































