Enzymatic Cascade Catalysis for the Synthesis of Multiblock and Ultrahigh-Molecular-Weight Polymers with Oxygen Tolerance
Zhifen Liu
Institute of Nanochemistry and Nanobiology, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYue Lv
Institute of Nanochemistry and Nanobiology, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zesheng An
Institute of Nanochemistry and Nanobiology, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhifen Liu
Institute of Nanochemistry and Nanobiology, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYue Lv
Institute of Nanochemistry and Nanobiology, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zesheng An
Institute of Nanochemistry and Nanobiology, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
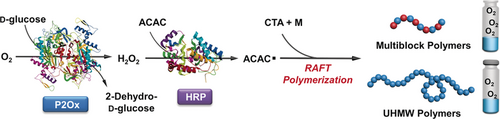
Ultrahigh: Enzymatic cascade catalysis enables the synthesis of multiblock (up to 10 blocks) copolymers and ultrahigh-molecular-weight polymers (UHMW; up to 2.3×106 g mol−1). The reaction employs a P2Ox-HRP system and can be run in vessels open to air, thus highlighting the oxygen tolerance of the process. P2Ox=pyranose oxidase, HRP=horseradish peroxidase, ACAC=acetylacetone, RAFT=reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer.
Abstract
Synthesis of well-defined multiblock and ultrahigh-molecular-weight (UHMW) polymers has been a perceived challenge for reversible-deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP). An even more formidable task is to synthesize these extreme polymers in the presence of oxygen. A novel methodology involving enzymatic cascade catalysis is developed for the unprecedented synthesis of multiblock polymers in open vessels with direct exposure to air and UHMW polymers in closed vessels without prior degassing. The success of this methodology relies on the extraordinary deoxygenation capability of pyranose oxidase (P2Ox) and the mild yet efficient radical generation by horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The facile and green synthesis of multiblock and UHMW polymers using biorenewable enzymes under environmentally benign and scalable conditions provides a new pathway for developing advanced polymer materials.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201707993-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf604.4 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aG. Moad, E. Rizzardo, S. H. Thang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1133–1142;
- 1bB. M. Rosen, V. Percec, Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5069–5119;
- 1cF. A. Leibfarth, K. M. Mattson, B. P. Fors, H. A. Collins, C. J. Hawker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 199–210; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 210–222;
- 1dK. Matyjaszewski, N. V. Tsarevsky, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6513–6533;
- 1eA. Anastasaki, V. Nikolaou, G. Nurumbetov, P. Wilson, K. Kempe, J. F. Quinn, T. P. Davis, M. R. Whittaker, D. M. Haddleton, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 835–877;
- 1fC. Boyer, N. A. Corrigan, K. Jung, N. Diep, N. Thuy-Khanh, N. N. M. Adnan, S. Oliver, S. Shanmugam, J. Yeow, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1803–1949;
- 1gM. Chen, M. Zhong, J. A. Johnson, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10167–10211;
- 1hM. Ouchi, M. Sawamoto, Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2603–2614.
- 2M. R. Hill, R. N. Carmean, B. S. Sumerlin, Macromolecules 2015, 48, 5459–5469.
- 3
- 3aL. Hartmann, H. G. Börner, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3425–3431;
- 3bM. Ouchi, N. Badi, J.-F. Lutz, M. Sawamoto, Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 917–924;
- 3cJ.-F. Lutz, M. Ouchi, D. R. Liu, M. Sawamoto, Science 2013, 341, 1238149;
- 3dB. V. K. J. Schmidt, C. Barner-Kowollik, Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 990–992;
- 3eQ. Zhang, J. Collins, A. Anastasaki, R. Wallis, D. A. Mitchell, C. R. Becer, D. M. Haddleton, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4435–4439; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4531–4535.
- 4
- 4aA. H. Soeriyadi, C. Boyer, F. Nyström, P. B. Zetterlund, M. R. Whittaker, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11128–11131;
- 4bG. Gody, T. Maschmeyer, P. B. Zetterlund, S. Perrier, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2505;
- 4cY.-M. Chuang, A. Ethirajan, T. Junkers, ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 732–737;
- 4dG. Gody, T. Maschmeyer, P. B. Zetterlund, S. Perrier, Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3451–3460;
- 4eJ. Xu, K. Jung, A. Atme, S. Shanmugam, C. Boyer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5508–5519;
- 4fN. G. Engelis, A. Anastasaki, G. Nurumbetov, N. P. Truong, V. Nikolaou, A. Shegiwal, M. R. Whittaker, T. P. Davis, D. M. Haddleton, Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 171–178;
- 4gL. Shen, Q. Lu, A. Zhu, X. Lv, Z. An, ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 625–631.
- 5
- 5aL. Despax, J. Fitremann, M. Destarac, S. Harrisson, Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 3375–3377;
- 5bJ. K. D. Mapas, T. Thomay, A. N. Cartwright, J. Ilavsky, J. Rzayev, Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3733–3738.
- 6
- 6aJ. Rzayev, J. Penelle, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1691–1694; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 1723–1726;
- 6bV. Percec, T. Guliashvili, J. S. Ladislaw, A. Wistrand, A. Stjerndahl, M. J. Sienkowska, M. J. Monteiro, S. Sahoo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14156–14165;
- 6cR. W. Simms, M. F. Cunningham, Macromolecules 2007, 40, 860–866;
- 6dP. Kwiatkowski, J. Jurczak, J. Pietrasik, W. Jakubowski, L. Mueller, K. Matyjaszewski, Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1067–1069;
- 6eE. Read, A. Guinaudeau, D. James Wilson, A. Cadix, F. Violleau, M. Destarac, Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 2202–2207;
- 6fN. P. Truong, M. V. Dussert, M. R. Whittaker, J. F. Quinn, T. P. Davis, Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3865–3874;
- 6gR. N. Carmean, T. E. Becker, M. B. Sims, B. S. Sumerlin, Chem 2017, 2, 93–101.
- 7J. Xu, K. Jung, C. Boyer, Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4217–4229.
- 8
- 8aK. Matyjaszewski, S. Coca, S. G. Gaynor, M. Wei, B. E. Woodworth, Macromolecules 1998, 31, 5967–5969;
- 8bR. Chapman, A. J. Gormley, K.-L. Herpoldt, M. M. Stevens, Macromolecules 2014, 47, 8541–8547;
- 8cS. Shanmugam, J. Xu, C. Boyer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9174–9185;
- 8dJ. Xu, S. Shanmugam, H. T. Duong, C. Boyer, Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 5615–5624;
- 8eR. Chapman, A. J. Gormley, M. H. Stenzel, M. M. Stevens, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4500–4503; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 4576–4579;
- 8fS. Shanmugam, J. Xu, C. Boyer, Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9345–9357;
- 8gJ. Wang, M. Rivero, A. Munoz Bonilla, J. Sanchez-Marcos, W. Xue, G. Chen, W. Zhang, X. Zhu, ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1278–1282;
- 8hQ. Yang, J. Lalevee, J. Poly, Macromolecules 2016, 49, 7653–7666;
- 8iQ. Fu, K. Xie, T. G. McKenzie, G. G. Qiao, Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 1519–1526;
- 8jS. Fleischmann, B. M. Rosen, V. Percec, J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2010, 48, 1190–1196;
- 8kN. H. Nguyen, V. Percec, J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2011, 49, 4756–4765;
- 8lN. H. Nguyen, X. Leng, H.-J. Sun, V. Percec, J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2013, 51, 3110–3122;
- 8mG. Lligadas, S. Grama, V. Percec, Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1039–1063.
- 9S.-i. Shoda, H. Uyama, J.-i. Kadokawa, S. Kimura, S. Kobayashi, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2307–2413.
- 10F. Giffhorn, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 727–740.
- 11
- 11aB. Zhang, X. Wang, A. Zhu, K. Ma, Y. Lv, X. Wang, Z. An, Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7792–7802;
- 11bA. P. Danielson, D. B. Van Kuren, M. E. Lucius, K. Makaroff, C. Williams, R. C. Page, J. A. Berberich, D. Konkolewicz, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 362–367.
- 12K. Decamps, I. J. Joye, D. Haltrich, J. Nicolas, C. M. Courtin, J. A. Delcour, Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1485–1492.