Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 17 February 2022

The cover image is based on the Research Article One-pot synthesis of SnS2 Nanosheets supported on g-C3N4 as high capacity and stable cycling anode for sodium-ion batteries by Ha Tran Huu et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7377.
Cover Image
- Page: ii
- First Published: 17 February 2022

The cover image is based on the Research Article Methane storage in clathrate hydrates containing water-miscible oxirane promoters by Jiwoong Seol., https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7378.
Issue Information
- Pages: 2087-2092
- First Published: 17 February 2022
Recent developments in layered double hydroxide structures with their role in promoting photocatalytic hydrogen production: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 2093-2140
- First Published: 05 October 2021
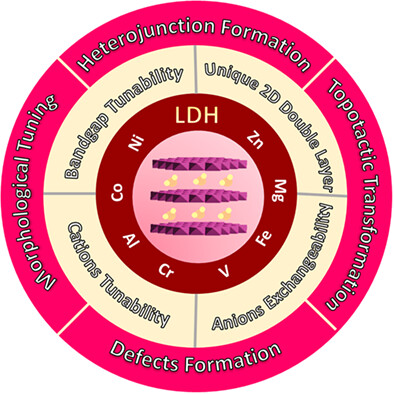
This review highlights the current advancements of Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The classification of LDH based on the divalent and trivalent cationic elements with their role to promote photocatalytic activity is reviewed. Next, the efficiency enhancement of metal-based LDH through engineering modifications is systematically discussed.
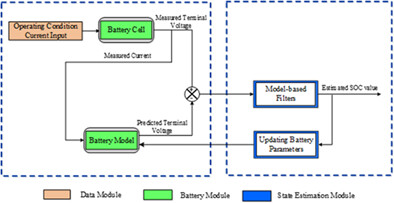
Modeling, state of charge estimation, and charging of lithium-ion battery in electric vehicle: A review
- Pages: 2141-2165
- First Published: 05 October 2021

The battery modeling, state of charge estimation, charging method of Li-ion cell on fault diagnosis and cell balancing of BMS in EV are reviewed. Selection of a suitable model type and parameter identification algorithm is required in battery modeling. Based on the review of SoC estimation, it is stated that an adaptive filter-based estimation and computer intelligence-based estimation may provide reliable results based on the selection of battery model, parameter type, parameter identification algorithm and training algorithm.
Ionic liquid-modified materials as polymer electrolyte membrane and electrocatalyst in fuel cell application: An update
- Pages: 2166-2211
- First Published: 25 October 2021
Materials development and prospective for protonic ceramic fuel cells
- Pages: 2212-2240
- First Published: 19 October 2021
The review article presents a detailed exposition of the material developmental strategies for the electrolyte, cathode, and anode of PCFCs. The states-of-the-art synthesis and fabrication techniques as well as prospective and scale-up possibilities of PCFCs were thoughtfully and logically presented.
Recent developments on transition metal–based electrocatalysts for application in anion exchange membrane water electrolysis
- Pages: 2241-2276
- First Published: 21 October 2021
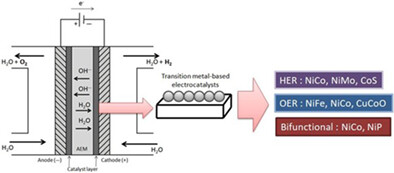
The recent advancement on transition metal–based electrocatalysts used in the actual operation of anion exchange water electrolysis (AEMWE) process is reviewed. The promising candidates for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and bifunctional water splitting catalysts are identified based on the overall performance and stability.
A survey of wearable energy harvesting systems
- Pages: 2277-2329
- First Published: 26 October 2021
When energy meets blockchain: A systematic exposition of policies, research hotspots, applications, and prospects
- Pages: 2330-2360
- First Published: 28 October 2021
In the present energy field, there have been such challenges as increasing complexity in controlling energy development and balancing supply and demand, severe overcapacity, redundant energy circulation process, nontransparent data, and difficult energy measurement process with long periods. To tackle such issues, blockchain technology is highly compatible with the energy sector thanks to its features including decentralization, openness, independence, security, and anonymity. The previous research on “blockchain + energy” is limited for the lack of systematic methods and models, with focuses on smart grid, micro grid, energy transaction, energy measurement, etc. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods, this article employs scientific cartography to conduct an in-depth literature analysis on “blockchain + energy,” so as to offer a panoramic understanding of the policies and regulations, research collaborations, research differences, application progress, and development trends in this field. Furthermore, policy suggestions are put forward from two perspectives: the external environment and internal technology, which count as reference for future research and application model innovation of blockchain as well as relevant decision-makers.
Structural, electronic, and optical properties of the pressure-driven novel polymorphs of gallium nitride: first-principles investigations
- Pages: 2361-2372
- First Published: 23 September 2021
Self-doping porous carbon materials synthesis from bio-wastes sodium lignosulfonate with high performance for supercapacitors
- Pages: 2373-2384
- First Published: 07 October 2021
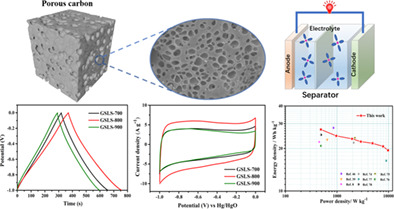
- An innovative method for synthesis of O/N/S porous carbon by lyophilisation and one-step carbonization from bio-wastes sodium lignosulfonate (SLS) for supercapacitor.
- The GSLS-800 exhibits excellent specific capacitance and cycle stability.
- The symmetric supercapacitor assembled by GSLS-800 achieves an ascendant balance in energy and power density.
Experimental study of effects of exhaust gas recirculation and combustion mode on combustion, emission, and performance of DME-methanol-fueled turbocharged common-rail engine
- Pages: 2385-2402
- First Published: 10 October 2021
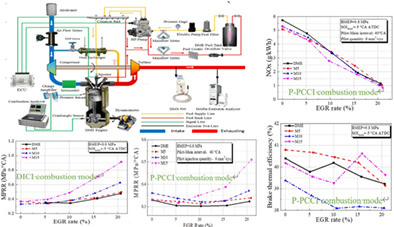
- Effects of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) and combustion mode on the combustion, performance, and emission of a six-cylinder turbocharged common-rail dimethyl ether (DME) engine with methanol blends are experimentally investigated.
- The premixed charge compression ignition (P-PCCI) mode effectively decreases the maximum pressure rise rate, and the upper limit of methanol proportion can be well increased.
- M5 (5 wt% methanol and 95 wt% DME) shows the highest brake thermal efficiency for both the P-PCCI and DICI modes.
Natural convection of water and nano-emulsion phase change material inside a square enclosure to cool the electronic components
- Pages: 2403-2417
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Operational hosting capacity-based sustainable energy management and enhancement
- Pages: 2418-2437
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Synthesis of a graphene oxide/ZnFe2O4/polyaniline nanocomposite and its structural and electrochemical characterization for supercapacitor application
- Pages: 2438-2445
- First Published: 06 October 2021
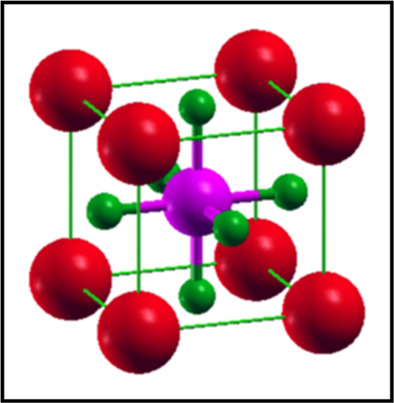
Structural, electronic, elastic, and magnetic properties of NaQF3 (Q = ag, Pb, Rh, and Ru) flouroperovskites: A first-principle outcomes
- Pages: 2446-2453
- First Published: 26 September 2021
Performance investigation and evaluation of an engine operating on a modified dual cycle
- Pages: 2454-2466
- First Published: 22 September 2021
Density functional theory based study of the physical properties of cesium based cubic halide perovskites CsHgX3 (X═F and Cl)
- Pages: 2467-2476
- First Published: 26 September 2021
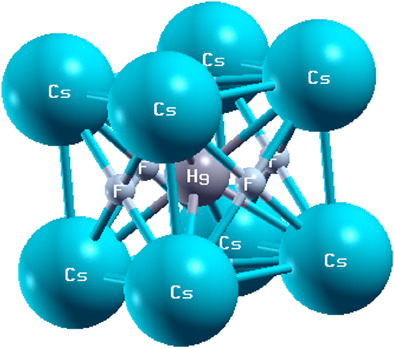
Structural, elastic, electronic, and optical properties of Cs-based halide perovskite compounds CsHgX3 (X=F and Cl) are computed in the framework of density functional theory. The obtained optimized lattice parameters are found to agree with available experimental and other theoretical data. Elastic parameters such as anisotropic factor, bulk modulus, elastic constants, Pugh ratio, and Poisson ratio are predicted. It is observed from the elastic properties measurements that these compounds are ductile, anisotropic, and mechanically stable. Band structures and DOS are performed for the computation of electronic properties and it is found that the calculated band-gap of CsHgF3 is of an indirect and semi-conductive nature, while CsHgCl3 reveals metallic nature. For more clarification of electronic properties, the DOS presents the different contributions of valence states to valence and conduction bands.
A novel mathematical approach for the optical efficiency optimization of solar tower power plant technology
- Pages: 2477-2499
- First Published: 15 October 2021
Synthesis of MnSe@C yolk-shell nanospheres via a water vapor-assisted strategy for use as anode in sodium-ion batteries
- Pages: 2500-2511
- First Published: 26 September 2021
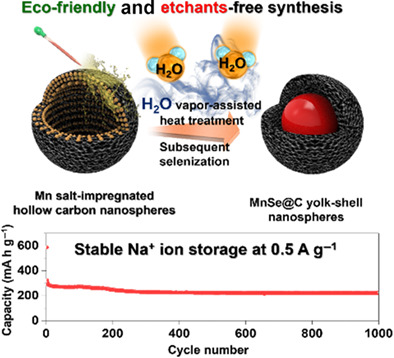
In this study, a novel H2O-vapor-assisted strategy for the formation of MnSe@C yolk-shell nanospheres is introduced. The prepared material is applied as anode for sodium-ion batteries, where the electrochemical conversion reaction mechanism is investigated by in- and ex-situ analyses. Successful encapsulation of active material in carbon shell enables stable cycle performance up to 1000 cycles at 0.5 A g−1.
Experimental study on flameless combustion and NO emission with hydrogen-containing fuels
- Pages: 2512-2528
- First Published: 30 September 2021
Hydrogen-rich syngas production from bi-reforming of greenhouse gases over zirconia modified Ni/MgO catalyst
- Pages: 2529-2545
- First Published: 01 October 2021
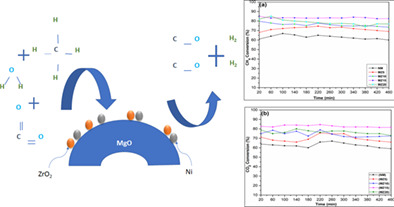
In the present study, the influence of ZrO2 modifications on the activity and stability of MgO-supported Ni catalyst in the BRM reaction was investigated. Although utilization of MgO and ZrO2 as support for individual catalysts has attracted huge attention, there is a need to investigate the application of mixed oxide ZrO2-MgO supported Ni catalysts for BRM. Till date, no research has been undertaken in BRM reaction for the suggested metal system that is, Ni/MgO-ZrO2.
Comparative study of heat pipes and liquid-cooling systems with thermoelectric generators for heat recovery from chimneys
- Pages: 2546-2557
- First Published: 30 September 2021
Study of ultrathin-film amorphous silicon solar cell performance using photonic and plasmonic nanostructure
- Pages: 2558-2566
- First Published: 29 September 2021
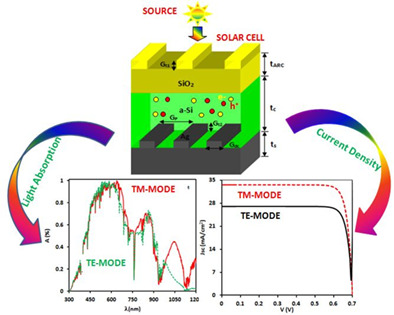
- Nanostructures are holding great promises for better photovoltaic performance by yielding the highest light-harvesting photons within the few nanometer absorber regions.
- Here, we have investigated ultrathin film amorphous silicon solar cell performance which was integrated by top-SiO2 and bottom-Ag nanogratings as a backside reflector.
- With the influence of optimization parameters, the highest current density of 27.03 and 33.53 mA/cm2 obtained from transverse electric and transverse magnetic polarization conditions.
Sandwich assembly of sulfonated poly (ether sulfone) with sulfonated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an efficient architecture for enhanced electrolyte performance in H2/O2 fuel cells
- Pages: 2567-2584
- First Published: 29 September 2021
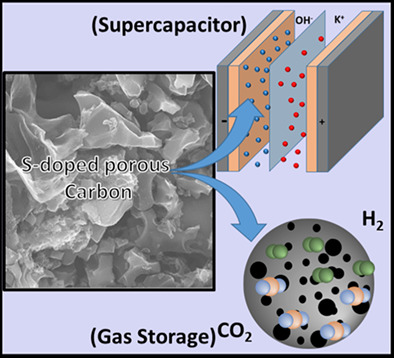
Synthesis of sulfur-doped porous carbon for supercapacitor and gas adsorption applications
- Pages: 2585-2600
- First Published: 29 September 2021
Combustion characteristics of butanol-Jet A-1 fuel blends in a swirl-stabilized combustor under the influence of preheated swirling air
- Pages: 2601-2616
- First Published: 06 October 2021
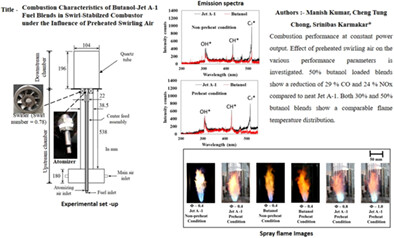
To understand the feasibility of butanol as potential fuel, the combustion characteristics of butanol and butanol/Jet A-1 blends are examined in a lab-scale swirl stabilized burner, with an emphasis on the effect of preheating of inlet air temperature on the performance characteristics. A 50% butanol-loaded blends show a reduction of 29% CO and 24% NOx compared to neat Jet A-1 whereas 30% loading follows a similar trend, and the pollutant emission is slightly higher than the 50% blend case.
Synthesis of (Gly)3PMo12O40@MnFe2O4 organic/inorganic hybrid nanocomposite as an efficient and magnetically recoverable catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of liquid fuels
- Pages: 2617-2632
- First Published: 29 September 2021

We report on the preparation of a new hybrid nanocomposite comprised of the glycine-modified polyoxomolybdate (Gly)3PMo12O40) and manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles. The nanocomposite was successfully synthesized under mild ultrasound irradiation and characterized by PXRD, FT-IR, FESEM, EDX, and VSM techniques. To explore the (Gly)3PMo12O40@MnFe2O4 applicability, it was used in catalytic oxidative desulfurization (Cat-ODS) reactions. The sulfur removal of model fuel could reach up to 95% at 35 °C, the ambient pressure, and the contact time of 1 hour.
Estimation of NCM111/graphite acoustic properties under different lithium stoichiometry based on nondestructive acoustic in situ testing
- Pages: 2633-2654
- First Published: 11 October 2021
A multi-period optimization model for power sector with CO2 emission considerations
- Pages: 2655-2673
- First Published: 05 October 2021
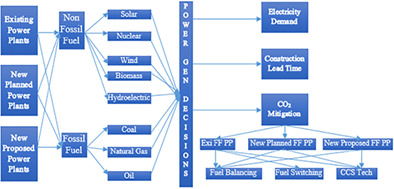
The main novelties of this research work include the incorporation of low, normal, and high GDP-based energy demands for summer and winter separately, fuel balancing, and carbon capture and sequestration as mitigation techniques, capacity expansion in addition to the already planned power plants, variable transmission and distribution losses, and retirement plan for the existing power plants in the optimization model. The complex problem of energy planning was solved using economic and operation-related data specific to the case study chosen for realistic results.
Catalytic co-pyrolysis of macroalgal components with lignocellulosic biomass for enhanced biofuels and high-valued chemicals
- Pages: 2674-2697
- First Published: 06 October 2021
Performance evaluation of a thermoelectric generator-coupled composite phase change material for intermittent aerodynamic heat sources
- Pages: 2698-2708
- First Published: 28 September 2021
Comparison of the advanced machine learning methods for better prediction accuracy of solar radiation using only temperature data: A case study
- Pages: 2709-2736
- First Published: 02 October 2021
Three-dimensional, porous, highly active α-MnO2/prGO hybrid nanocomposites as cathode of non-aqueous Li-O2 batteries
- Pages: 2737-2747
- First Published: 07 October 2021
Heterogeneous design and mechanical analysis of HELIAS 5-B helium-cooled pebble bed breeding blanket concept
- Pages: 2748-2770
- First Published: 13 October 2021
A multi-module equalization system for lithium-ion battery packs
- Pages: 2771-2782
- First Published: 27 October 2021
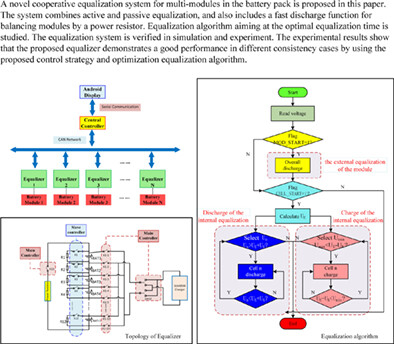
A novel cooperative equalization system for multi-modules in the battery pack is proposed in this paper. The system combines active and passive equalization, and also includes a fast discharge function for studied. The equalization system is verified in simulation and experiment. The experimental results show that the proposed equalizer demonstrates a good performance in different consistency cases by using the proposed control strategy and optimization equalization algorithm.
Performance assessment of hybrid active filtering technique to enhance the hosting capacity of distorted grids for renewable energy systems
- Pages: 2783-2809
- First Published: 24 October 2021
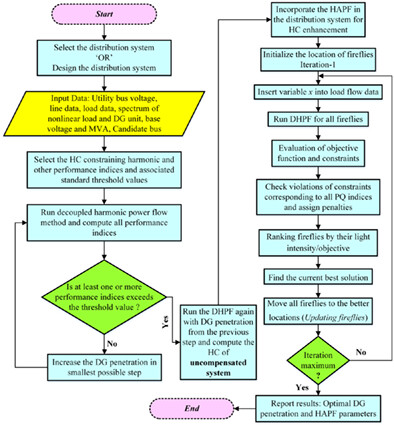
Hybrid harmonic filtering is investigated for enhancing the harmonic-constrained hosting capacity of distributed generation in distorted grid conditions. Along with increasing the penetration level of distributed generation the harmonic distortion is also substantially reduced instead of being at the verge of the standard limit. Furthermore, the other benefits of deploying HAPF, for HC-HC enhancement, are studied by simulating the system under changing utility-side's BVD and load-side’s NLL conditions.
Study on the reaction performance of Ce-doped NiFe2O4 oxygen carriers in the process of chemical looping hydrogen production
- Pages: 2810-2825
- First Published: 07 October 2021
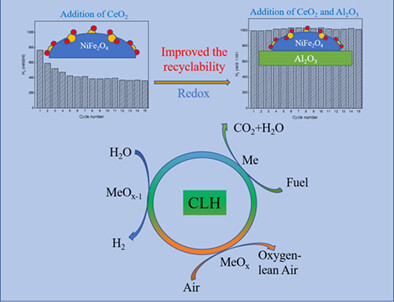
- The effects on different doping amount of Ce were compared.
- The introduction of Ce in NiFe2O4 enhanced the oxygen release capacity and hydrogen production capacity.
- 6 wt% Ce-NiFe2O4 exhibited the best hydrogen production and redox reactivity.
- The load of Al2O3 improved the reaction stability of the oxygen carrier.
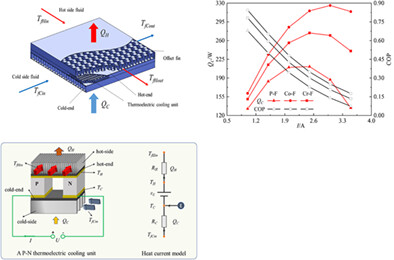
Optimal flow layout and current allocation for improving the thermoelectric refrigeration system based on heat current method
- Pages: 2826-2839
- First Published: 01 October 2021
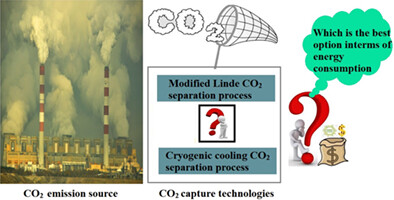
A comparative study of modified Linde and cryogenic cooling for CO2 separation
- Pages: 2840-2857
- First Published: 11 October 2021
Smart energy hub optimization in presence of stochastically modeled renewables and loads
- Pages: 2858-2875
- First Published: 07 October 2021
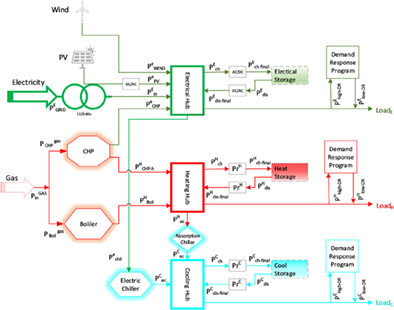
- A novel model of energy hub is proposed, mathematically modeled, and optimized which comprehensively includes all the entities of a modern EH.
- Stochastic modeling along with the scenario generation and reduction method for uncertain parameters like wind speed, solar irradiance, and load demands make the program faster without compromising on the accuracy of results.
- Reduction in cost of SEH by the inclusion of DRPs for electric, heating, and as well as cooling loads.
A variable multi-time-scale based dual estimation framework for state-of-energy and maximum available energy of lithium-ion battery
- Pages: 2876-2892
- First Published: 12 October 2021
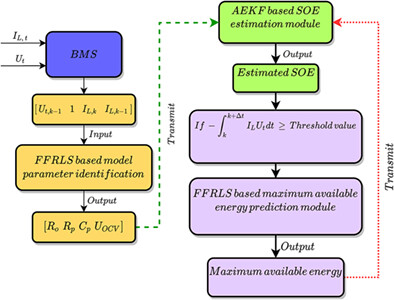
Highlights
- A variable multi-time-scale based dual estimation framework is proposed.
- A novel multi-objective decision method is presented to select macro time-scale.
- Various operating temperature of the battery is considered in this work.
- Robustness ability of the proposed dual estimation framework is validated.
- The superiority of presented algorithm on comprehensive performance is verified.
The detailed implementation flow of the proposed variable multi-time-scale based dual estimation framework.
H2 storage using Zr-CMK-3 developed by a new synthesis method
- Pages: 2893-2903
- First Published: 05 October 2021
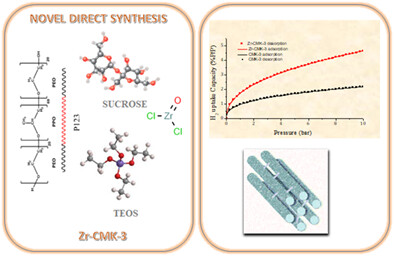
This work addresses a new direct synthesis technique used to obtain a novel mesoporous carbon (CMK3) modified with zirconium oxide. This novel material shows promise for hydrogen adsorption and storage application for energy harvesting. A Hydrogen uptake mechanistic approach was proposed and the role of the Zr+4 cation in hydrogen adsorption was discussed.
Life cycle assessment of bioethanol production from Pennisetum sp. using fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation at high solid loadings
- Pages: 2904-2922
- First Published: 11 October 2021
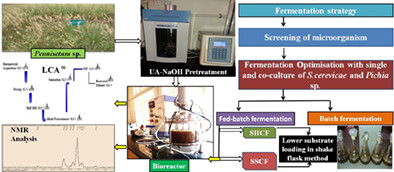
Fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation is an efficient process for bioethanol production from high solid loadings of the two Pennisetum sp i.e. Denannath and Hybrid Napier grass. NMR analysis of the residual biomass obtained after the production of ethanol in the bioreactor revealed efficiency of the fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation. Further, life cycle assessment for the process of bioethanol production revealed the competence of the Denannath grass as compared to Hybrid Napier grass.
Effect of CH4-H2 mixture on the combustion characteristics in a stabilized swirl burner
- Pages: 2923-2933
- First Published: 13 October 2021
A first-principles prediction of thermophysical and thermoelectric performances of SrCeO3 perovskite
- Pages: 2934-2946
- First Published: 05 October 2021
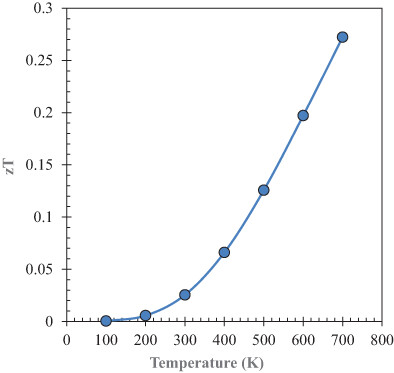
Strontium cerate (SrCeO3) has been studied for the first time with respect to its thermophysical and thermoelectric properties. It is found that SrCeO3 is a good thermoelectric material and can be used as an alternative source of energy owing to its thermoelectric performance indicators like Seebeck coefficient, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and power factor. Interestingly, SrCeO3 displays a figure of merit value of 0.27 at 700 K which suggests that this compound has the potential to be used in the thermoelectric device sector.
Performance analysis of a single cell-ultra-high concentration photovoltaic thermal module based on pin-fins cooling microchannel
- Pages: 2947-2969
- First Published: 12 October 2021
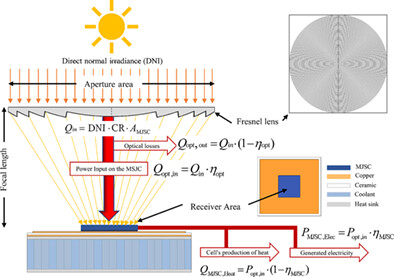
The current article entitled “Performance analysis of a single cell-ultra-high concentration Photovoltaic Thermal (HCPV/T) module Based on pin-fins cooling microchannel” is carrying out the performance investigation of an actively cooled Fresnel-based single-cell ultra-high concentration photovoltaic/thermal (UHCPV/T) system under concentration ratios (CR)s ranged between 500× and 2500×. Four cooling finned heat sink designs have been studied, that is, the in-line cylindrical pin fins (ICY), staggered cylindrical pin fins (SCY), in-line conical pin fins (ICO), and staggered conical pin fins (SCO). The analysis was carried out to study and optimize the maximum operating MJSC temperature, coolant flow outlet temperature, pressure drop across, and the thermal, electrical, and overall efficiency enhancement of the whole Fresnel-based UHCVP/T system. The numerical model has been first validated and then used to simulate the impact on the concentration ratio and Reynolds number on the limitations and records of each cooling finned design of the UHCPV/T. It was found that even though the aluminum-based ICO pin fins heat sink can achieve the optimum overall efficiency of 80.20% under 2000× and Re of 428, yet the aluminum-based ICY is the most appropriate pin-fins heat sink design for desalination purposes since it corresponds to the highest water outlet temperature of 66.16°C with a second-ranked overall efficiency of 72.5% under the same operating conditions.
Numerical investigation of a vertical triplex-tube latent heat storage/exchanger to achieve flexible operation of nuclear power plants
- Pages: 2970-2987
- First Published: 07 October 2021
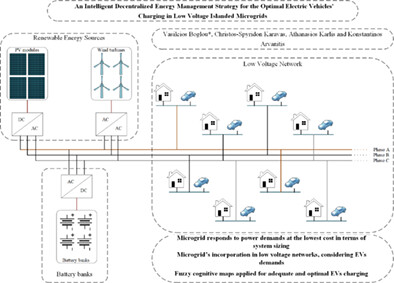
An intelligent decentralized energy management strategy for the optimal electric vehicles' charging in low-voltage islanded microgrids
- Pages: 2988-3016
- First Published: 11 October 2021
An integrated experimental and modeling study of the effect of solid electrolyte interphase formation and Cu dissolution on CuCo2O4-based Li-ion batteries
- Pages: 3017-3033
- First Published: 11 October 2021
Stacked bidirectional LSTM RNN to evaluate the remaining useful life of supercapacitor
- Pages: 3034-3043
- First Published: 14 October 2021
Water distribution and carbon corrosion under high current density in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell
- Pages: 3044-3056
- First Published: 13 October 2021
Methanol steam reforming over Cu supported on SiO2, amorphous SiO2-Al2O3, and Al2O3 catalysts: Influence of support nature
- Pages: 3057-3071
- First Published: 06 October 2021
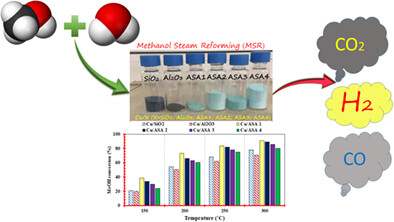
SiO2-, Al2O3-, and SiO2-AlsO3-based catalysts containing different Si/Al ratios have been prepared to study the effect of the support nature on the methanol steam reforming process catalyst. SiO2-Al2O3-based catalysts showed better performance compared to SiO2- and Al2O3-based catalysts due to their high surface area and pore volume. In addition, the γ-Al2O3 based catalyst produced a relatively large amount of CO, whereas those supported on amorphous SiO2-Al2O3 yielded much less CO.
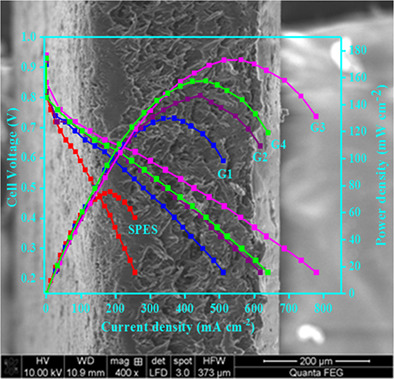
Synthesis of highly water-absorbing chromium oxyhydroxide as a dopant in a hybrid proton-conducting membrane
- Pages: 3072-3079
- First Published: 05 October 2021
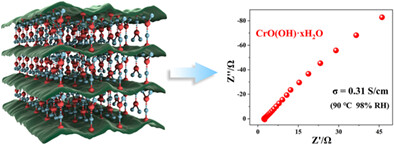
- Chromium oxyhydroxide (CrO(OH) xH2O) with proton conductivity (0.31 S cm−1) is synthesized by a simple and environmental friendly sol-gel method.
- CrO(OH) xH2O exhibits a high water absorption capacity of 450 mg g−1, contributing to the formation of a hydrogen bond network, and promoting the rapid transmission of protons.
- SPEAK-3% CrO(OH) membrane shows a proton conductivity (0.17 S cm−1) comparable to Nafion.
A study of Co-Mn phosphate supported with graphene foam as promising electrode materials for future electrochemical capacitors
- Pages: 3080-3094
- First Published: 11 October 2021
Enhancing power in a grid-connected system using unified power quality conditioner with black widow optimization-based floating photovoltaic system
- Pages: 3095-3114
- First Published: 29 October 2021
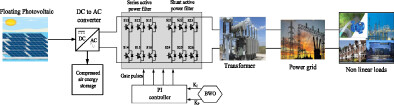
The proposed method shows that the PV is floating in the sea, pools, reservoir, and so on. The temperature of the water does not affect the floating PV panel but it provides some advantage for the system and improves the system efficiency. The major advantage of the floating PV system is the absence of shadows, so there are no barriers present in power generation. The structure of the floating PV is based on the raft supportive model. Raft contain drums or plastic blocks which are used for the purpose of floating the PV panel above the water surface. The PV-generated power is a direct current (DC) that is collected in the combiner boxes, after that the direct current is changed into an alternate current (AC) with the help of an inverter. The disadvantage of the floating PV system is power generation variation and control which is mitigated via a proper energy storage device. Generally, batteries are preferred for solar PV systems since battery energy storage systems are easy to mounted on the solar system, as well batteries are completely established for industrial purposes and more accurate to perform. Although, batteries have an imperfect lifetime and are more expensive, and the major issue is waste removal or reusing at that moment of the last life cycle. Compared to lifetime and cost, compressed air energy storage system (CAESS) have more advantage than the battery, that store electrical energy in underground caves or above the ground by the form of compressed atmosphere air. Need for an excess amount of electrical energy, the compressed air storage released the forced air to heat and passed over the turbine to generate electrical energy. The compressor produces high-pressure air in the form of molecular potential energy that was stored in the air storage subsystem. Because high-pressure air diminishes the necessary strength for control high-pressure air and cost.
Thermophysical properties and thermal performance evaluation of multiwalled carbon nanotube-based organic phase change materials using T-History method
- Pages: 3115-3131
- First Published: 21 October 2021
Automatically adaptive cooling of hotspots by a fractal microchannel heat sink embedded with thermo-responsive hydrogels
- Pages: 3132-3144
- First Published: 14 October 2021
(Fe, Ni, Co)9S8@CS catalyst decorated on N-doped carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction
- Pages: 3145-3154
- First Published: 10 October 2021
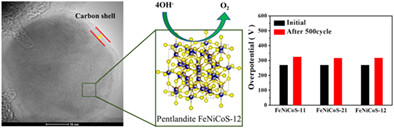
Trimetallic pentrladite sulfide of Fe, Ni and Co enwrapped with carbon layer was successfully synthesized by a solid-state copolymerization and a follwoing pyrolysis. It was revealed that electrochemical activity of (Fe, Ni, Co)9S8 depends on structural parameters not elemental composition and that carbon shell is effective for protecting the catalyst. The catalyst showed the overpotential of 260 mV at 10 mA cm-2 for oxygen evolution reaction and demonstrated the stability over 500 cyclic voltammetry cycles.
Thermoeconomic assessment and multiobjective optimization of a CCHP and MED hybrid system based on IR-SOFC/MGT
- Pages: 3155-3172
- First Published: 12 October 2021
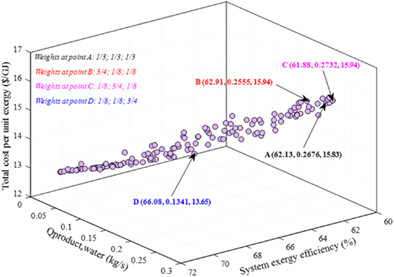
- A CCHP and multi-effect desalination (MED) hypbrid system combined with IR-SOFC and MGT is invetigated.
- Thermoeconomic analysis and multi-objective optimization are conducted to obtain optimal system design parameters and overall performance.
- It is validated that the system exergy efficiency and the system total cost per unit exergy are conflicted with the freshwater production.
Optimal dispatching of renewable energy-based urban microgrids using a deep learning approach for electrical load and wind power forecasting
- Pages: 3173-3188
- First Published: 20 October 2021
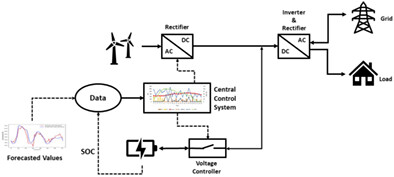
This research will discuss optimum operating strategies for an urban microgrid, including PV panels, wind turbines, and battery storage system. To remove the uncertainties and developing a robust model for operating control scenarios, hybrid forecasting models with a minimum error are proposed for electrical load demand and wind speed forecasting.
Integration of machine learning to increase steam turbine condenser vacuum and efficiency through gasket resealing and higher heat extraction into the atmosphere
- Pages: 3189-3212
- First Published: 13 October 2021
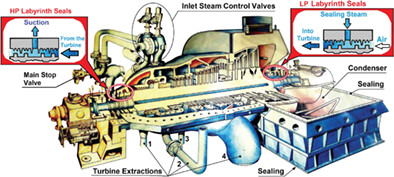
The increase in the turbine condenser vacuum is achieved by resealing the moving and fixed points of the steam turbine and turbine condenser and increasing the cooling water flow through the turbine condenser. The steam turbine low-pressure cylinder generates more power and consequently increases the useful efficiency of the process by as much as 2.48 %. The disadvantage of the increased vacuum in the turbine condenser lies in the increased cavitation load of the last stages of the stator and rotor blades.
An energy-efficiency evaluation method for high-sulfur natural gas purification system using artificial neural networks and particle swarm optimization
- Pages: 3213-3232
- First Published: 12 October 2021

The novelties of this paper are summarized as follows:
- A universal approach was proposed for evaluating the energy consumption performance of the high sulfur natural gas purification system.
- A system is established for hierarchical energy consumption indicators while presenting the detailed definition of evaluation indicators for process, unit, and device. And a solution of process energy consumption benchmark based on ANN and PSO is proposed.
- A case study of natural gas purification plant in China is given to illustrate the computational process of energy consumption benchmark in detail.
One-pot synthesis of SnS2 Nanosheets supported on g-C3N4 as high capacity and stable cycling anode for sodium-ion batteries
- Pages: 3233-3248
- First Published: 14 October 2021
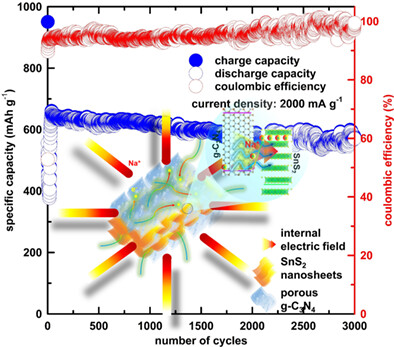
The composites constructed from SnS2 nanosheets in porous g-C3N4 matrix were synthesized via one-step solid state reaction. The enhancement in electrochemical performance of these composites was demonstrated as promising anode for sodium ions batteries in both half- and full-cell configuration which is contributed to the good accommodation of g-C3N4 to volume change of SnS2 along with the self-induced internal electric field formed at the heterointerface of the components.
Methane storage in clathrate hydrates containing water-miscible oxirane promoters
- Pages: 3249-3259
- First Published: 19 October 2021
Simple fabrication of Ni nanodots decorated Ni/Ketjen black composite for sulfur host in lithium-sulfur battery
- Pages: 3260-3271
- First Published: 14 October 2021
Smart contract formation enabling energy-as-a-service in a virtual power plant
- Pages: 3272-3294
- First Published: 22 October 2021
Analytical study of over-voltages in alkaline electrolysis and their parametric dependencies through a multi-physical model
- Pages: 3295-3323
- First Published: 19 October 2021
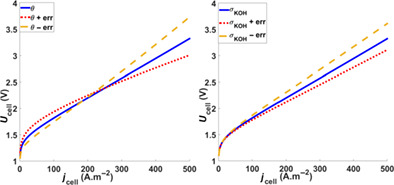
In this paper, the authors compare the AEM and conventional electrolysis technologies within a unique analytical model. Several electrolytes are tested under several conditions to be as general as possible, and not linked to a particular device at it is usually done. Finally, the path to 3D AEM modelling is explored, as the author thinks it is a good way for electrolysis performance improvement for those who do not have access to electrolyser devices.
Boost performance of porous electrode for microfluidic fuel cells: electrochemical modification or structure optimization?
- Pages: 3324-3334
- First Published: 18 October 2021
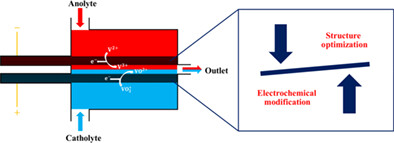
Parametric analyses are performed to identify and compare the effects of two different optimization methods, electrochemical modification, and structure optimization, on the performance of porous electrodes in microfluidic fuel cell (MFC). Useful guidance is given for the fabrication of high-performance porous electrode in the future development of MFCs.
Design and development of a novel additively manufactured geothermal heat exchanger
- Pages: 3335-3348
- First Published: 25 October 2021
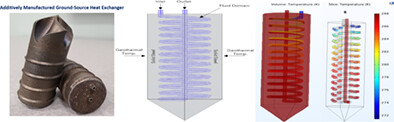
An additively manufactured geothermal heat exchanger was designed and developed via Direct-Metal-Laser-Sintering technique to demonstrate an innovative approach of utilizing geothermal energy. The geothermal heat exchanger developed here eliminates the current need to excavate the soil and install the long piping as conventionally required for the common geothermal systems, while the modular design allows it for easy scaling to meet different thermal loads. A detailed cost analysis was conducted to estimate the total cost per part for this prototype.
A facile strategy to construct layered membranes with high and stable proton conductivity based on sulfonated graphene oxide
- Pages: 3349-3361
- First Published: 15 October 2021
Aqueous organic redox flow batteries using naphthoquinone and iodide maintaining pH of electrolytes desirably by adoption of carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube catalyst
- Pages: 3362-3375
- First Published: 13 October 2021
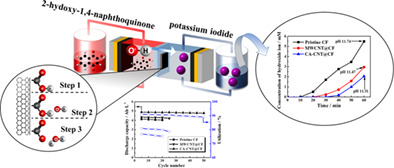
Herein we present an aqueous organic redox flow battery (AORFB) using 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (NQ-OH) and potassium iodide (KI) as redox couple. With the use of carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube doped carbon felt (CA-CNT@CF) and the control of KI concentration to suppress the side reaction of KI and occurrence of polyiodide, the stable performance of AORFB was achieved.
The study of optoelectronic and thermoelectric properties of Tl2PdX6 (X = Cl, Br, I) for energy harvesting
- Pages: 3376-3383
- First Published: 25 October 2021
Mesoporous carbon-supported CO3O4 derived from Zif-67 metal organic framework (MOF) for hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic and alkaline medium
- Pages: 3384-3395
- First Published: 21 October 2021
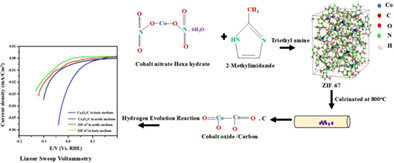
The Co3O4/C derived from ZIF-67 is investigated towards the electrocatalytic activity of HER.
Results shows Co3O4/C has a low Tafel slope of 69.37 mV/dec and a low charge transfer resistance of 2.05 ω.
Reaction follows Volmer-Heyrvosky mechanism with electrochemical desorption of hydrogen as rate limiting step.
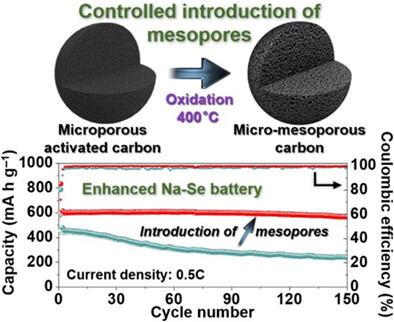
Deliberate introduction of mesopores into microporous activated carbon toward efficient Se cathode of Na−Se batteries
- Pages: 3396-3408
- First Published: 15 October 2021
Novel mechanical vapor recompression-assisted evaporation process for improving energy efficiency in pulp and paper industry
- Pages: 3409-3427
- First Published: 15 October 2021
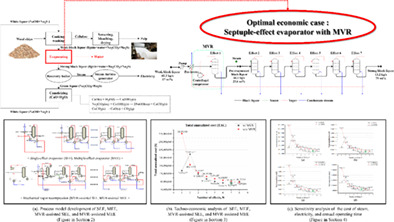
First, process models using SEE, MEE, MVR-assisted SEE, and MVR-assisted MEE were developed to predict the energy consumption of the evaporation process, and the simulation result was comparatively analyzed to verify the energy efficiency of the suggested MVR-assisted MEE. Second, the economic evaluation was conducted to derive optimal economic MVR-assisted MEE configuration. Finally, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to examine the effect of the main economic parameters on the optimal economic MVR-assisted MEE configuration.
The multi-objective optimization of an axial cyclone separator in the gas turbine
- Pages: 3428-3442
- First Published: 15 October 2021
Electrodeposition as a facile way for the preparation of piezoelectric ultrathin silk film–based flexible nanogenerators
- Pages: 3443-3457
- First Published: 28 October 2021
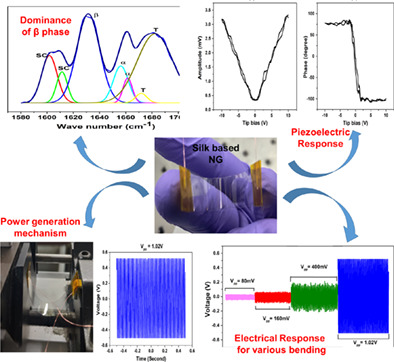
Our present work provides a significant contribution in the electrodeposition process to deposit ultra-smooth, thin silk film by decreasing the required voltage for deposition. Along with that the innate piezoelectric property of the as prepared film is studied well with the fabrication of highly reliable and stable silk-based flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator.
Balanced structural optimization of air-cooling battery module with single-layer sleeved heat spreader plate
- Pages: 3458-3475
- First Published: 21 October 2021
Greener process for syngas cogeneration: Bi-reforming of methane coupled with chemical looping combustion
- Pages: 3476-3489
- First Published: 01 November 2021
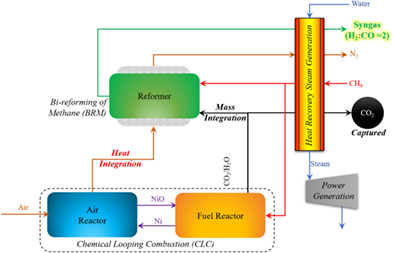
Current work proposes an integrated scheme of chemical looping combustion (CLC) and bi-reforming process for syngas production with a syngas ratio of 2 and without CO2 emissions. The proposed scheme can meet the pure “CO2 demand” as a co-feed and “heat demand” of the highly endothermic bi-reforming process by thermal and mass integration with CLC process.
Three-dimensional mesostructured single crystalline Fe3O4 for ultrafast electrochemical capacitor electrode with AC line filtering performance
- Pages: 3490-3501
- First Published: 21 October 2021
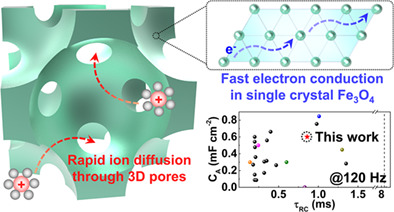
A new route based on 3D mesostructuring of a single crystalline half-metallic oxide is demonstrated to achieve the ultrafast electrochemical capacitor electrodes. The 3D mesostructured single crystalline Fe3O4 electrode fabricated by heteroepitaxial electrodeposition through self-assembled templates shows excellent AC line filtering performances, benefitting from high crystalline matrix with low defect density and 3D interconnected periodic pores.
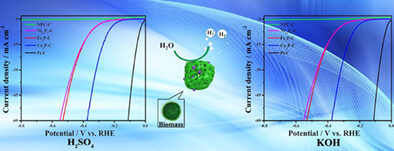
Biomass-based transition metal phosphides supported on carbon matrix as efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction
- Pages: 3502-3511
- First Published: 05 November 2021
A noise-immune model identification method for lithium-ion battery using two-swarm cooperative particle swarm optimization algorithm based on adaptive dynamic sliding window
- Pages: 3512-3528
- First Published: 05 November 2021
Lithium-ion battery state-of-charge estimation of an order-reduced physics-based model in electric vehicles considering erroneous initialization
- Pages: 3529-3538
- First Published: 22 October 2021
Double-shell and yolk-shell structured ZnSe-carbon nanospheres as anode materials for high-performance potassium-ion batteries
- Pages: 3539-3553
- First Published: 28 October 2021
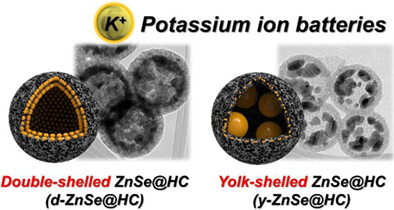
In this study, hollow carbon nanospheres encapsulating ZnSe crystals are synthesized via drop-and-dry process, followed by subsequent selenization. The acquired composite exerts excellent electrochemical properties including cycle and rate performances, demonstrating the effects of managing the size and position of ZnSe crystals upon hollow carbon nanospheres.
Identification of surrogate fluids for molten salt coolants used in energy systems applications including concentrated solar and nuclear power plants
- Pages: 3554-3571
- First Published: 29 October 2021
Hydrogen separation using palladium-based membranes: Assessment of H2 separation in a catalytic plasma membrane reactor
- Pages: 3572-3587
- First Published: 09 November 2021
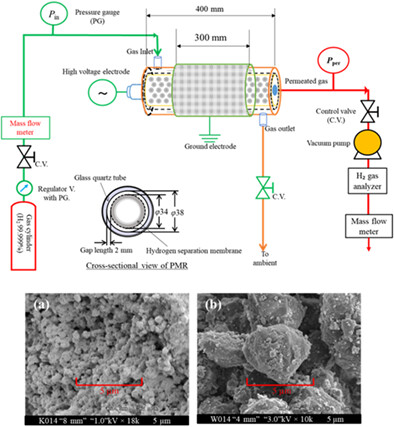
1. The fundamentals of the H2 permeation technique through palladium-based membranes were investigated. 2. The H2 permeability of the plasma-catalyst system reaches 100% in most input gas flow rates. 3. The H2 permeability results of the zeolite type SA-600A were higher than zeolite type 330-HUDIA. 4. The DBD plasma with zeolite materials showed a future potential to induce hydrogen separation.
Bioaugmented polyaniline decorated polylactic acid nanofiber electrode by electrospinning technique for real wastewater-fed MFC application
- Pages: 3588-3601
- First Published: 03 November 2021
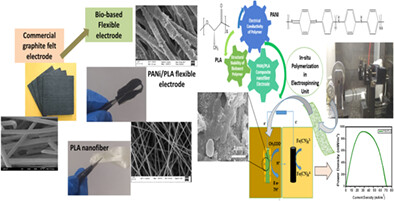
- Significant enhancement in MFCs performance using novel bio-based PANI/PLA anode.
- Demonstration of next-generation sustainable anode fabrication using electrospinning.
- Bio-synergistic of wastewater-borne microbial consortia and composite electrode.
- Practical application of mediator-less dual-chambered MFCs in wastewater treatment.
Improved covariance matching—electrical equivalent modeling for accurate internal state characterization of packing lithium-ion batteries
- Pages: 3602-3620
- First Published: 08 November 2021
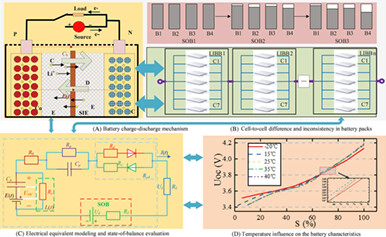
Covariance matching - electrical equivalent circuit modeling for lithium-ion battery packs. (a) Battery charge-discharge mechanism. (b) Cell-to-cell difference and inconsistency in battery packs. (c) Electrical equivalent modeling and state-of-balance evaluation. (d) Temperature influence on the battery characteristics
Effect of a direct current electric field on CO2 bubble evolution in a direct methanol fuel cell
- Pages: 3621-3633
- First Published: 29 October 2021
Waste tire derived char supported Ni-Fe catalyst for catalytic thermochemical conversion of wet municipal solid waste
- Pages: 3634-3646
- First Published: 28 October 2021
Experimental investigation of a parabolic greenhouse dryer improved with copper oxide nano-enhanced latent heat thermal energy storage unit
- Pages: 3647-3662
- First Published: 28 October 2021
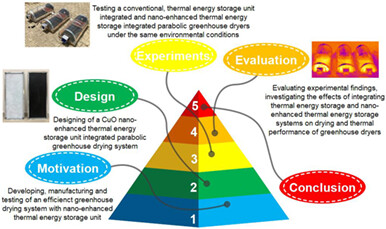
In this research, three different active greenhouse dryers, which are grouped in direct solar drying systems, have been designed, fabricated, and experimentally analyzed. An experimental investigation on nano-embedded thermal storage-assisted greenhouse drying system is performed. The impact of utilizing nano-enhanced thermal energy storage unit on the performance of a greenhouse dryer is studied.
Study on HHV prediction of municipal solid wastes: A machine learning approach
- Pages: 3663-3673
- First Published: 07 October 2021
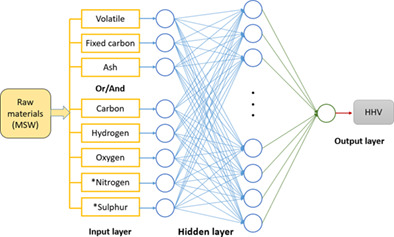
In this work, artificial neural network (ANN) models and particle swarm optimization (PSO) models based on machine learning were built to predict the HHVs of MSW quickly. Four kinds of BP ANN models and two PSO models were built using proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of 33 MSW samples as input variables. As a comparison, three classical linear empirical models employed from publications were also used.
Strategy to utilize amorphous phase of semiconductor toward excellent and reliable photochemical water splitting performance: Roles of interface dipole moment and reaction parallelization
- Pages: 3674-3685
- First Published: 28 September 2021
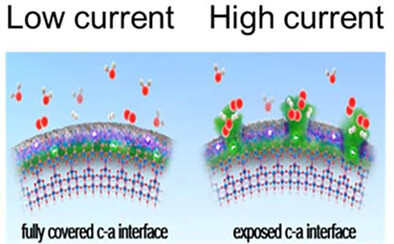
Photocatalytic water splitting activities of c-a junctioned TiO2 are largely affected by interface electric fields phase boundary exposed to the surface. This work successfully demonstrated two new important factors in the design of photoactive semiconductors: interface electric field and surface parallelization.
Suppressing the formation of double-layer in Cu2ZnSnSe4(CZTSe) absorber layer by facile heating process through nontoxic selenium atmosphere
- Pages: 3686-3696
- First Published: 03 October 2021
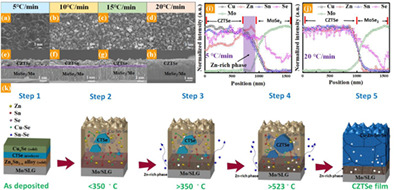
In Cu2ZnSnSe4 (CZTSe) thin films prepared by selenizing metallic precursors, there is double-layer distribution that can degrade the performance of the solar cell. Therefore, this study aims to reduce the number of air holes and alleviate double-layer distribution in the CZTSe absorber by using a simple method with adjusting the heating rate during selenization. By adjusting the heating rates, crystal quality was greatly improved, and the method led to the improvement in the conversion efficiency of CZTSe solar cells.
Selection of waste thermoplastics for shape stabilized phase change materials using multicriteria techniques
- Pages: 3697-3706
- First Published: 05 October 2021
Concentration-dependent excess Cu doping behavior and influence on thermoelectric properties in Bi2Te3
- Pages: 3707-3713
- First Published: 11 October 2021
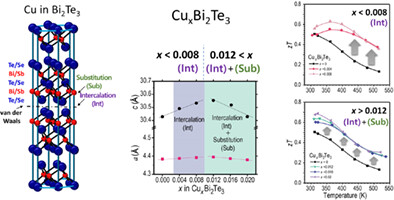
Cu doping behavior in a binary Bi2Te3 prepared by a conventional melt-solidification process was demonstrated, and corresponding changes in electronic and thermal transport properties were investigated. At low Cu concentrations (x ≤ 0.008 in CuxBi2Te3), interlayer intercalation of Cu optimizes electron concentration and increases the effective mass. At higher Cu concentrations (0.012 ≤ x ≤ 0.02), power factor enhancement is due to the substituted Cu at Bi-site, which increases the weighted mobility ratio.
A theoretical study of aluminium doping in silicon anode based lithium-ion batteries using ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulation
- Pages: 3714-3724
- First Published: 27 October 2021
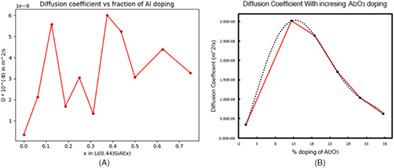
- ReaxFF interatomic potential and MD simulations were conducted to study the kinetic behavior of aluminium doped amorphous lithiated silicon (a-LixSiAly) compounds in silicon anode based LIBs.
- The results show that the specific amount of alumina can improve diffusivity but is not as significant as in the case of aluminium.
- Doping of aluminium and its amphoteric oxide can increase the diffusion coefficient of Li in LiSi batteries.
- Progressively this can improve the capacity and cycle performance of batteries.
Optoelectronic properties of thermally coated tin selenide thin films for photovoltaics
- Pages: 3725-3731
- First Published: 29 October 2021