Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 16 March 2022
The cover image is based on the Short Communication Construction of hierarchical nickel cobalt sulfide@manganese oxide nanoarrays@nanosheets core-shell electrodes for high-performance electrochemical asymmetric supercapacitor by Vinayak G. Parale et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7413.
Maintenance cost minimization models for offshore wind farms: A systematic and critical review
- Pages: 3739-3765
- First Published: 08 November 2021
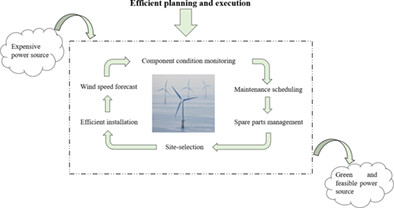
All the models related to offshore maintenance were classified into four (04) major categories: opportunistic maintenance, condition-based maintenance, risk-based uncertainty management, cost and task breakdown models. Most cost-efficient opportunistic maintenance model produced 48.2% less cost than corrective maintenance. However, the best CBM strategy was 44.42% less expensive than traditional preventive replacement policy. On the other hand, best risk and reliability-based model illustrated 23% annual cost reduction.
A review of bipolar plates materials and graphene coating degradation mechanism in proton exchange membrane fuel cell
- Pages: 3766-3781
- First Published: 02 November 2021
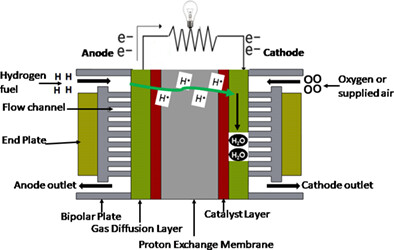
In this review, the proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) parts have been identified and role of carbon support and its material properties summarized. The degradation process and mechanism of carbon in the PEMFC environment are highlighted. The failure modes associated with the PEMFC degradation due to corrosion are discussed and recommendation provided for addressing the carbon degradation and improving the performance of the PEMFC.
Biomass-based heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 3782-3809
- First Published: 05 November 2021
Factors influencing the performance of PEM fuel cells: A review on performance parameters, water management, and cooling techniques
- Pages: 3810-3842
- First Published: 02 November 2021
Li-ion battery modeling and characterization: An experimental overview on NMC battery
- Pages: 3843-3859
- First Published: 03 November 2021
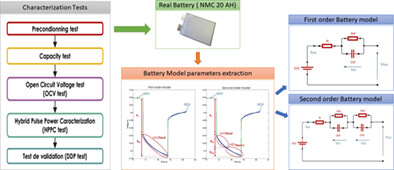
This article provides an overview of the modeling and characterization of Li-ion batteries in EV applications, so all characterization tests have been accurately described. These tests were applied on a 20 Ah NMC Li-ion battery for the development of the two models of Thevenin of the first and second order. This validation proves the effectiveness of the considered characterization protocol by recording a model error around 1%.
Biolubricant production via esterification and transesterification processes: Current updates and perspectives
- Pages: 3860-3890
- First Published: 11 December 2021
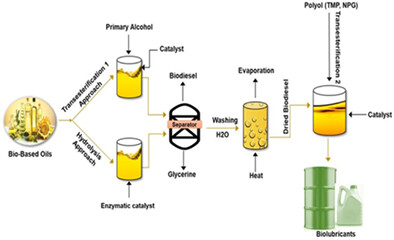
In this review paper, we report the most updated literature and prospects pertaining to the synthesis of biolubricants via esterification and transesterification process from bio-based oils. The esterification and transesterification chemical modification pathway has enhanced the lubrication properties (ie, thermo-oxidative stability, cold-flow properties, etc) of the synthesized biolubricants. The tribological performance of biolubricants has increased notably with the addition of ionic liquids and special additives under this same chemical modification pathway.
Recovery of actinides and fission products from spent nuclear fuel via electrolytic reduction: Thematic overview
- Pages: 3891-3905
- First Published: 26 November 2021
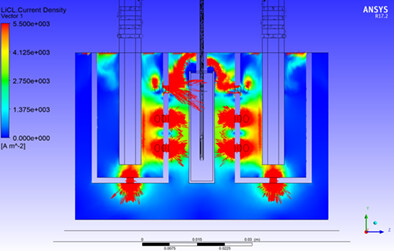
Current density distribution in a LiCl + 2 wt.% Li2O melt during electrolytic reduction of SNF in a laboratory electrolyzer. The cathode with the basket for the loaded SNF is located in the center of the electrolyzer, and the anodes, protected by ceramic sheaths, are located on the left and right. The maximum current density is found near the small holes in the sheaths and at the top of the cathode.
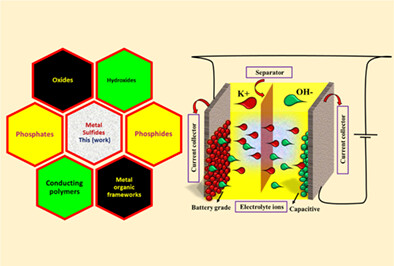
Recent progress of battery grade metal sulfides for hybrid energy storage devices
- Pages: 3906-3938
- First Published: 11 December 2021
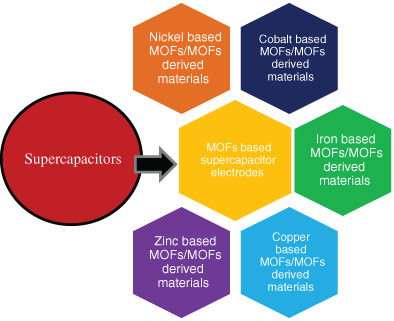
An overview of supercapacitors electrode materials based on metal organic frameworks and future perspectives
- Pages: 3939-3982
- First Published: 24 November 2021
An overview on the use of metal vanadium oxides and vanadates in supercapacitors and rechargeable batteries
- Pages: 3983-4000
- First Published: 19 November 2021

The versatile group of metal vanadium oxides and vanadates has emerged as a promising electrode material for rechargeable batteries and supercapacitors. This group of materials possesses high theoretical capacitance and multiple redox states, which help in reducing the activation energy for redox reactions. A detailed investigation regarding the influence of morphology developed during synthesis of these materials on the electrochemical properties of the electrode has been presented here, along with the prospects and challenges associated with their commercialization.
A review on converting plastic wastes into clean hydrogen via gasification for better sustainability
- Pages: 4001-4032
- First Published: 02 December 2021
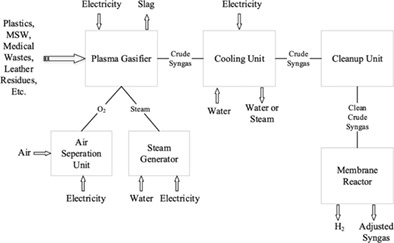
Plasma co-gasification is recommended as an important environmentally benign technological solution for clean hydrogen production from plastic wastes. Also, it is suggested that plasma co-gasification of plastics wastes with coal, municipal solid wastes, and biomass should be applied to increase the gas production performance and to offer a promising conversion opportunity to the municipalities, hospitals, and pandemic wastes. It is concluded by a performed case study for plastic gasification process, exergetic sustainability index and exergetic efficiency decrease and environmental impact factor and waste exergy ratio increase while energy efficiency rise.
A review on carbon nanomaterials for K-ion battery anode: Progress and perspectives
- Pages: 4033-4070
- First Published: 28 November 2021
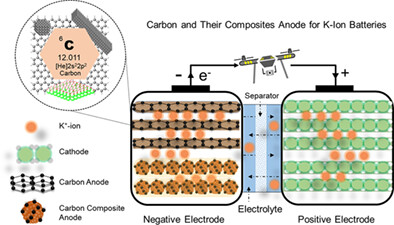
As a potential alternative to commercial Li-ion batteries, K-ion batteries (KIBs) have received great interest because of the abundance of K resources and superior properties. This review comprehensively summarizes and discusses the recent developments with future perspectives in carbon materials as anode for KIBs.
Recent progress of transparent conductive electrodes in the construction of efficient flexible organic solar cells
- Pages: 4071-4087
- First Published: 01 December 2021
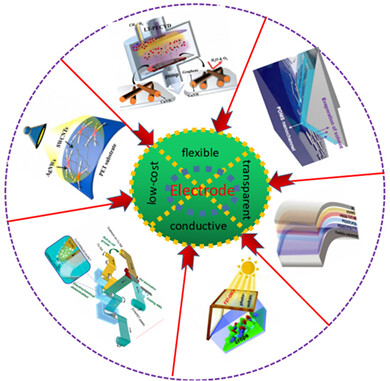
Around the structure design of flexible solar cells and the development of new transparent conductive electrodes, metal oxides, metals, carbon materials, polymers, and the composite materials were designed successively to obtain flexible transparent conductive electrodes with high conductivity, high transmission, and low surface roughness.
A comprehensive review on applications of multicriteria decision-making methods in power and energy systems
- Pages: 4088-4118
- First Published: 12 December 2021
Spinel-type Ni2GeO4 electrocatalyst for electrochemical ammonia synthesis via nitrogen reduction reaction under ambient conditions
- Pages: 4119-4129
- First Published: 28 October 2021
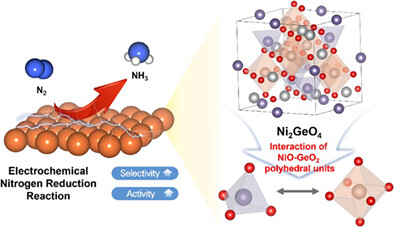
The electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction for ammonia synthesis under ambient conditions is recognized as an environmental-friendly strategy compared to the conventional Haber-Bosh process. In this work, Ni2GeO4 nanoparticles synthesized via a facile hydrothermal method were investigated as a novel electrocatalyst for nitrogen electroreduction. Notably, the Ni2GeO4 electrocatalyst achieved an excellent Faradaic efficiency of 3.38% and an ammonia yield rate of 2.66 μg h−1 cm−2 at −0.1 V vs RHE, owing to the enhanced charge transfer and chemical activity caused by charge polarization between the polyhedral units.
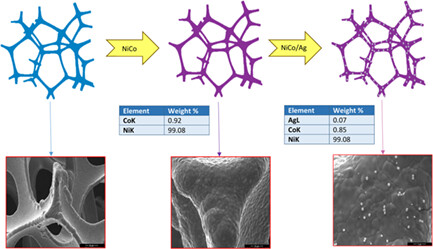
Production of NF/NiCo/Ag catalyst for hydrogen generation in alkaline medium
- Pages: 4130-4141
- First Published: 25 October 2021
High temperature-induced myoglobin-mimic catalytic structure having high axial ligand content for one-compartment hydrogen peroxide fuel cells
- Pages: 4142-4155
- First Published: 28 October 2021
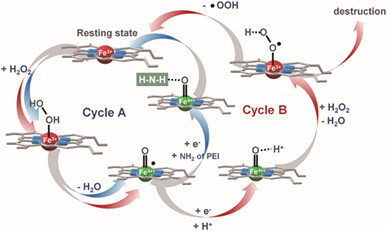
We introduce a facile and inexpensive method of fabricating a myoglobin-mimic nanostructure-based anodic catalyst for use in hydrogen peroxide fuel cells (HPFC). Due to the high content of axial ligand coordination between CoPc and PEI, the maximum power density reaches 129.0 μW cm−2 with 0.340 V of open-circuit voltage in the polarization curves measured using a 3D printed membraneless flow-type fuel cell, which offers the best performance for hydrogen peroxide fuel cells under physiological conditions.
Investigation of hydrogen production from sodium borohydride by carbon nano tube-graphene supported PdRu bimetallic catalyst for PEM fuel cell application
- Pages: 4156-4173
- First Published: 29 October 2021
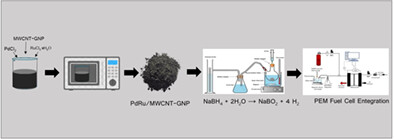
PdRu/MWCNT-GNP bimetallic catalyst was used in NaBH4 hydrolysis for hydrogen production. PdRu/MWCNT-GNP bimetallic catalyst was synthesized via microwave synthesis method. Synergetic interaction between Pd and Ru enhanced catalytic activity of PdRu/MWCNT-GNP. NaBH4 based hydrogen generation system is integrated to a PEM fuel cell.
Development and performance analysis of polybenzimidazole/boron nitride composite membranes for high-temperature PEM fuel cells
- Pages: 4174-4186
- First Published: 02 November 2021
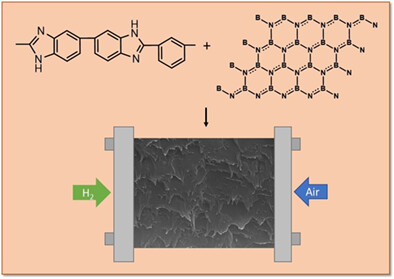
- Boron Nitride emerged as an effective filler for a composite membrane for application in HT-PEMFC.
- PBI/BN membranes were found to show improved electrochemical properties compared with pure PBI.
- 2.5 wt% PBI/BN composite membrane was found to be superior membrane properties and membrane performance in HT-PEMFC.
Simulation and experimentation study on the performance of metal hydride storage vessels
- Pages: 4187-4203
- First Published: 03 November 2021
Study of annual performance and capacity of data center passive cooling mode
- Pages: 4204-4221
- First Published: 29 October 2021
Enhancement of photovoltaic power farms using a new power prediction approach
- Pages: 4222-4246
- First Published: 29 October 2021
Study on the optimum orientation of bifacial photovoltaic module
- Pages: 4247-4266
- First Published: 16 November 2021
Scalable, colloidal synthesis of SnSb nanoalloy-decorated mesoporous 3D NiO microspheres as a sodium-ion battery anode
- Pages: 4267-4278
- First Published: 28 October 2021
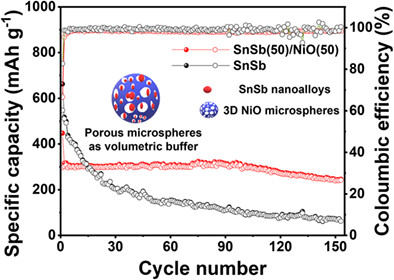
In this study, porous SnSb/NiO microsphere is synthesized via a facile, scalable colloidal route and employed as a sodium-ion battery anode. Formation of SnSb nanoalloy leads to fast electrode kinetics by shortening the diffusion path, and mesoporous NiO enables nanoconfinement of SnSb and prevents self-agglomeration. The resultant SnSb/NiO microsphere exhibits high sodiation/desodiation reversibility with good cycling and rate performance.
Sinc and discrete singular convolution for analysis of three-layer composite of perovskite solar cell
- Pages: 4279-4300
- First Published: 02 November 2021
A swarm intelligence approach for energy management of grid-connected microgrids with flexible load demand response
- Pages: 4301-4319
- First Published: 29 October 2021
Oxygen-enriched flameless combustion of CH4/H2/CO mixtures
- Pages: 4320-4338
- First Published: 29 October 2021
A facile one-step synthesis of bio-inspired porous graphitic carbon sheets for improved lithium-sulfur battery performance
- Pages: 4339-4351
- First Published: 29 October 2021
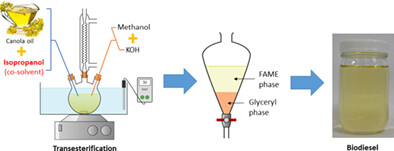
Transesterification using isopropanol as a co-solvent for the production of green biodiesel fuel
- Pages: 4352-4361
- First Published: 29 October 2021
A novel rule-based computational strategy for a fast and reliable energy management in isolated microgrids
- Pages: 4362-4379
- First Published: 01 November 2021
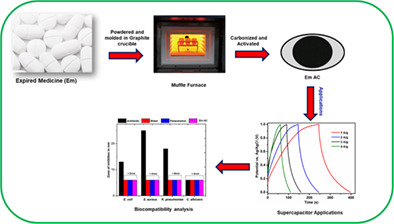
A simple conversion of expired medicines into nontoxic activated carbon for energy storage applications
- Pages: 4380-4392
- First Published: 29 October 2021
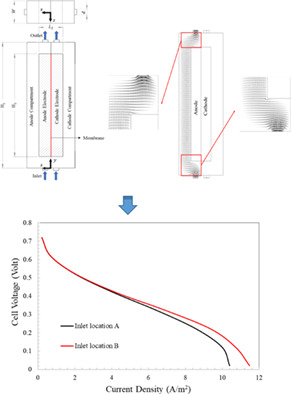
Effect of adjusting inlet/outlet location on the power performance of a continuous type of microbial fuel cells
- Pages: 4393-4404
- First Published: 07 November 2021
Understanding the role of lithium bonds in doped graphene nanoribbons as cathode hosts for Li-S batteries: A first-principles study
- Pages: 4405-4416
- First Published: 13 November 2021
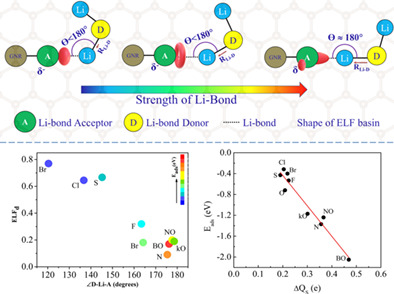
The lithium bond between the lithium polysulfides and doped GNRs is found to be analogous to a hydrogen bond with unique directional properties. Shape of the lone pair basins and value of Electron localization function at the position of dopant are identified to reveal the adsorption strength. Employing good hydrogen bond acceptors as suitable dopants for graphene-based cathode hosts is a promising strategy in the design of lithium sulfur batteries.
Experimental study on the static and dynamic performances of gas foil bearings for the centrifugal air compressor used in fuel cell vehicles
- Pages: 4417-4433
- First Published: 08 November 2021
Specific capacitance behavior of Co-Co3O4 nanocomposite thin films synthesized via different electrodeposition modes
- Pages: 4434-4444
- First Published: 01 November 2021
Application of new hybrid models based on artificial neural networks for modeling pyrolysis yields of Atriplex nitens S.
- Pages: 4445-4461
- First Published: 01 November 2021
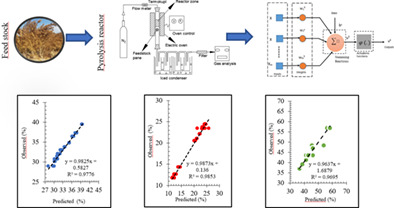
- Biochar, bio-oil, and synthesis gas yields obtained from the Atriplex nitens S. plant at the end of the pyrolysis process were modeled using artificial neural networks and hybrid models.
- Multiple linear regression, artificial neural networks, principal component analysis + multiple linear regression, and principal component analysis + artificial neural network models were used. In addition, 48 different network architectures in artificial neural networks were tested.
- The best prediction results of biochar, bio-oil, and synthesis gas were obtained from the ANN 35, ANN 17, and ANN 44 artificial neural network architecture, respectively.
A multiobjective planning framework for EV charging stations assisted by solar photovoltaic and battery energy storage system in coupled power and transportation network
- Pages: 4462-4493
- First Published: 09 November 2021
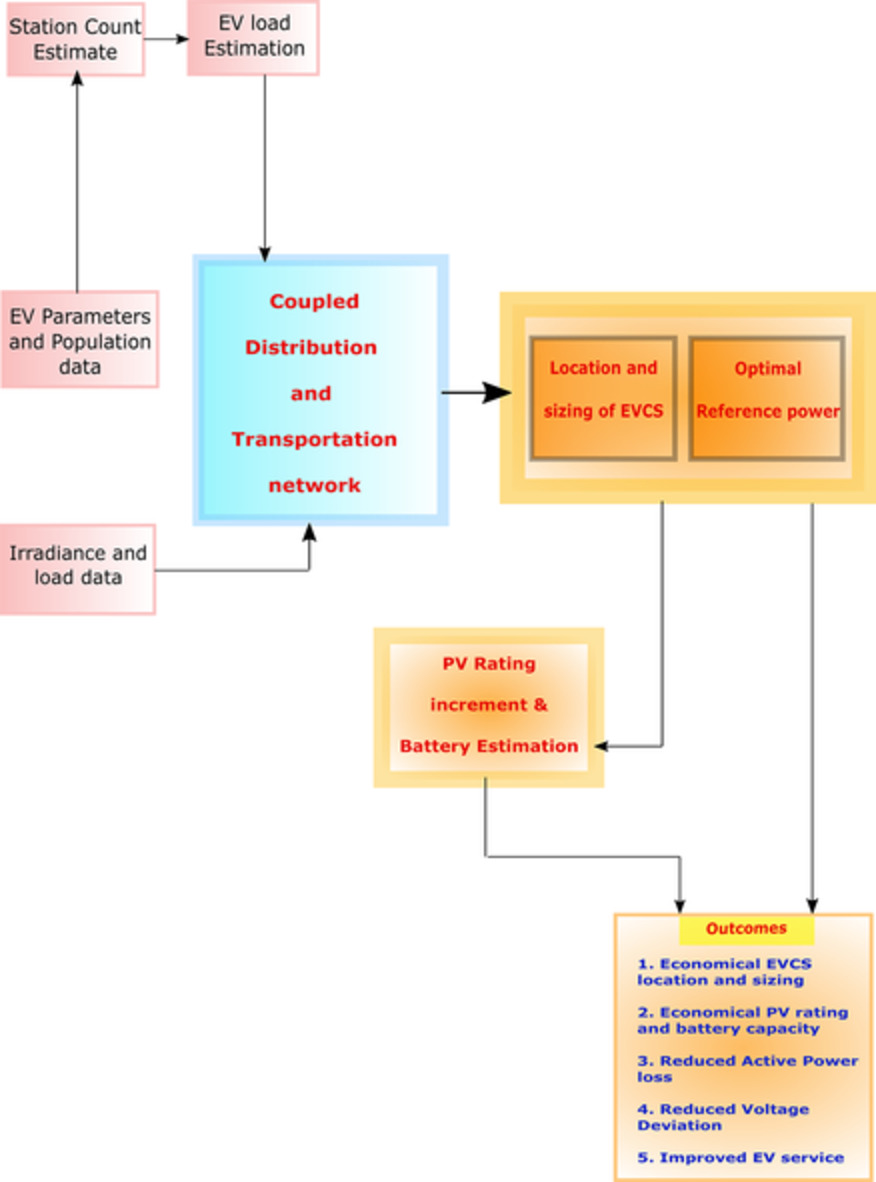
- A two-stage multi-objective planning framework is designed to determine optimal placements and sizing of FCEVS, Photovoltaic (PV) facilities, and Battery Energy Storage Systems incorporating seasonal variations for the generation and weekly patterns for traffic flow.
- A mathematical model for the optimal planning of solar-powered EVCS is developed, with multiple objectives for (i) reduced power loss, (ii) improved voltage profile, (iii) minimization of total cost associated with EVCS, and (iv) increased EV served flow as the objective function. MOGWO and fuzzy techniques are further used for optimizing the above planning problem.
MnO2/Co3O4 with N and S co-doped graphene oxide bimetallic nanocomposite for hybrid supercapacitor and photosensor applications
- Pages: 4494-4505
- First Published: 01 November 2021
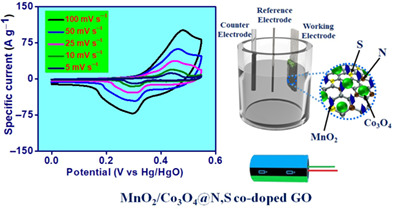
Hydrothermally synthesized MnO2/Co3O4@N, S co-doped GO hybrid composite is studied for energy storage and photosensing applications. Dual N and S doping has been achieved using single reagent thiourea. This synthesized composite showed 614 F.g−1 specific capacitance at 1 A.g−1 with above 95% retention up to 10000 cycles. Good photosensing with one order of current increase under visible light has been obtained.
Polydopamine and Nafion bi-layer passivation modified CdS photoanode for photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution
- Pages: 4506-4515
- First Published: 06 November 2021
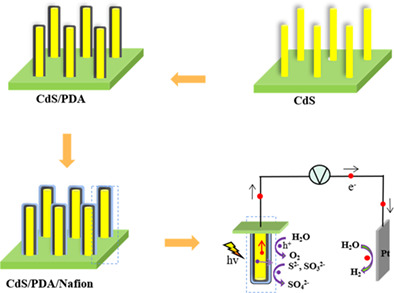
To reduce the rate of photogenerated carriers' recombination and chemically corrosion of CdS photoanode, a composite component surface state passivation layer was introduced. The PDA and Nafion co-modified CdS nanorods were successfully prepared by simple electropolymerization and dipping methods. The steady-state and time-resolved photoluminescence spectra and electron paramagnetic resonance were mainly used to analyze the mechanism of the PDA/Nafion bi-layer passivation towards CdS. The optimized CdS/PDA/Nafion photoanode exhibits highly improved photoelectrochemical water splitting activity and stability under visible light.
Optimal electric vehicles charging scheduling for energy and reserve markets considering wind uncertainty and generator contingency
- Pages: 4516-4539
- First Published: 10 November 2021
Capacity factor characteristics for a multi-tubular sensible energy storage system with wire coil inserts
- Pages: 4540-4549
- First Published: 05 November 2021
The potential of deep learning to reduce complexity in energy system modeling
- Pages: 4550-4571
- First Published: 22 November 2021
Optimized modeling and experimental investigation on the thermal/electrical characteristics of MWCNT nanofluid for effective solar thermal applications
- Pages: 4572-4587
- First Published: 08 November 2021
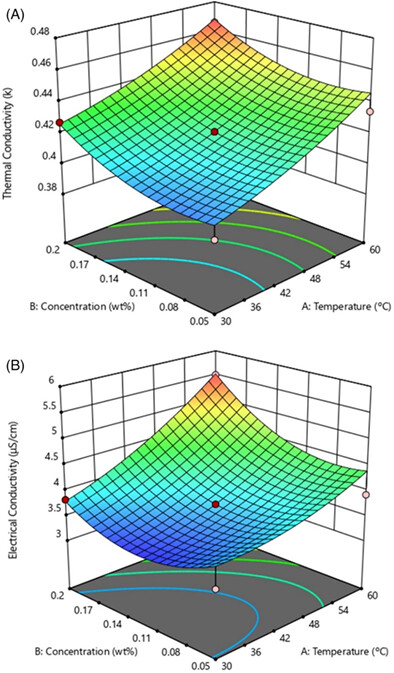
Response surface methodology was utilized to determine the optimum thermal and electrical conductivity characteristics of a solar glycol (SG)-water (H2O) (50:50) blend nanofluid with multiwall carbon nanotube for efficient solar thermal applications. A three-level factorial optimization design and experimentation were performed to evaluate the effects of volumetric concentration and operating temperature. Optimum conditions for maximum thermal and electrical conductivities included an operational temperature of 66.2°C and MWCNT volume concentration of 0.125% in SG-H2O base fluid.
Parametric study of a metal hydride reactor with phase change materials and heat pipes
- Pages: 4588-4598
- First Published: 08 November 2021
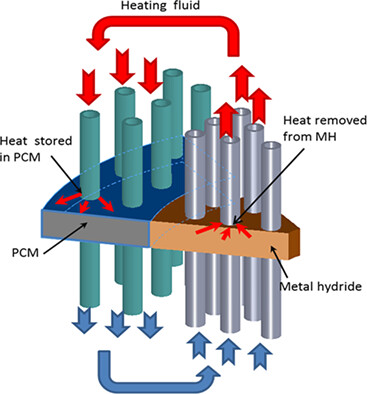
The hydriding rate, the hydrogen storage capacity, and the melted fraction are strongly affected by the MH bed and PCM thermal conductivity, the melting temperature, the number of heat pipes in the system, and the convective heat transfer coefficient between the MH bed/heat pipe and the PCM/heat pipe walls.
Sustainable hydrothermal synthesis of cobalt-nickel nanomaterial for supercapacitor using green stabilizing agents
- Pages: 4599-4608
- First Published: 08 November 2021
Operating performance of multi-modular water-phase change material tanks for emergency cooling in an underground shelter
- Pages: 4609-4629
- First Published: 15 November 2021
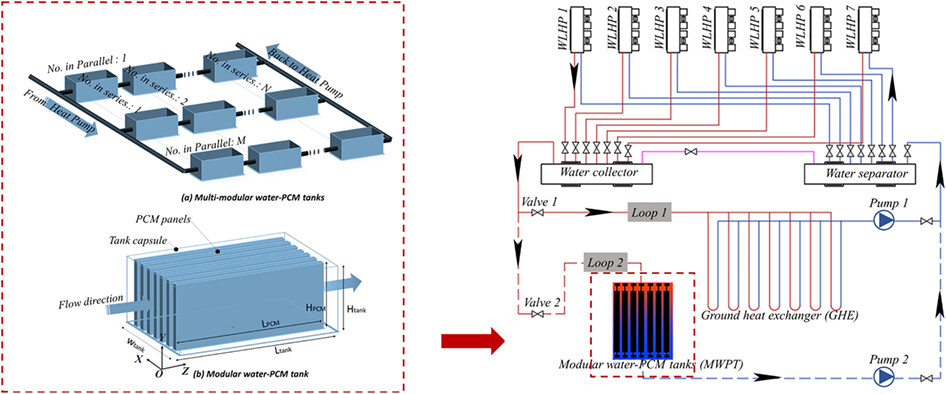
Latent heat thermal energy storage can not only alleviate the mismatch between supply and demand but also improve the performance and dependability of the energy system. Unfortunately, previous research achieves a specific engineering load shifting using a single water-phase change material (PCM) tank, the volume of which is tailored to the specific cooling or heating load. This paper proposes the concept of multi-modular water-PCM tanks (MMWPT), which offer flexibility and are simple to be mass-produced, as thermal storage in an underground shelter's emergency mode. The thermal inertia of the geothermal energy is used to keep the PCM solid at first and to naturally cool the tank once they are melted. The mathematical model is created in MATLAB and validated by experiment with an NMBE of less than ±10% and RMSE of less than 30%. In addition, the MMWPT's thermal performance in various matrixes was investigated in an underground shelter where the peak load occurs suddenly and with low frequency. This research is planned to give references for using the MMWPT in underground shelters to shift loads.
An evaluation of activation energy, surface area, and catalytic activity relationship of the developed nonmetal alloy decorated Schiff's base based conjugated conductive polymer composite electrodes for fuel cell applications
- Pages: 4630-4644
- First Published: 14 November 2021
Upcycling waste tires to affordable catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
- Pages: 4645-4654
- First Published: 07 November 2021
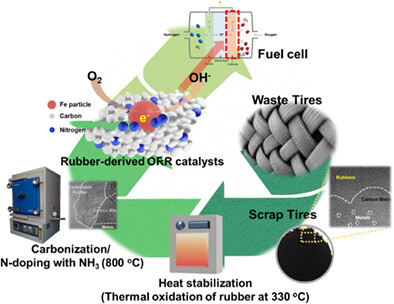
We demonstrated a new upcycling method to effectively manage the waste tires without abandoning any contents such as carbon black, rubbers, and metal particles. Under thermal oxidation, rubbers were transformed into stable structures and subsequently converted to carbonized rubbers on further heat treatment. Furthermore, heat treatment in NH3 atmosphere provided abundant nitrogen functional groups on the waste tire-derived catalysts. Our N-doped catalysts with Fe exhibited oxygen reduction reaction activity comparable to that of commercial Pt/C catalyst.
Adjusting the pinch point of heat transfer to improve the thermal performance of the organic Rankine cycle
- Pages: 4655-4670
- First Published: 15 November 2021
Using conductive carbon fabric to fabricate binder-free Ni-rich cathodes for Li-ion batteries
- Pages: 4671-4679
- First Published: 11 November 2021
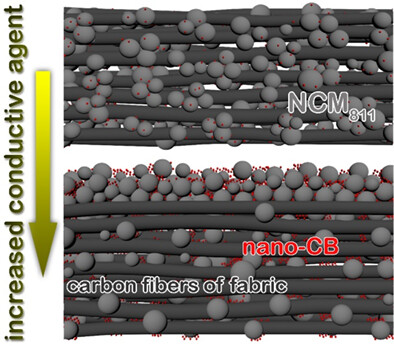
Carbon fabric is adopted as a conductive matrix to solve the corrosion problem of conventional Al current collector when fabricating electrodes using alkaline water-processed NCM811 slurries. The flexible and robust interlaced fabric structure provides strong support for the electrode materials without using any insulating binder. The mass ratio of the conductive agent determines the distribution uniformity of NCM811 electrode materials in the carbon fabric.
Graphite felt modified with WO3, SnO2, and binary WO3/SnO2-mixtures as novel positive electrodes for cerium-based redox flow batteries
- Pages: 4680-4698
- First Published: 14 November 2021
Exploratory studies on wet oxidation grown ternary hafnium tantalum oxide for metal-oxide semiconductor application
- Pages: 4699-4711
- First Published: 14 November 2021
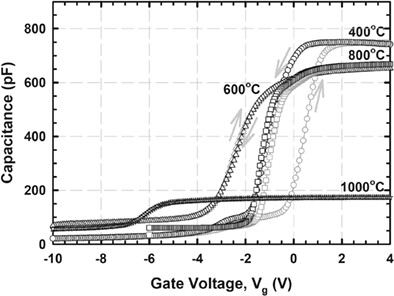
The present work innovates the research by co-sputtering HfO2 and Ta targets in an argon ambient, followed by a wet oxidation to transform the as-sputtered film to Hf-doped Ta2O5. In contrast to the previous work that introduced either thermal oxidation or postdeposition annealing in O2 or N2 ambient to yield the oxide, wet oxidation could provide a combination of oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen environment. It was anticipated that the wet oxidation would trigger a triple functions, which can be described as a simultaneous oxidation of the HfO-Ta film by the oxygen, a passivation of interface defects between Hf-doped Ta2O5 and Si substrate by the hydrogen and a nitridation of the Si surface by the nitrogen. Thus far, none of the previous studies have reported about wet oxidation for Hf-doped Ta2O5. Hence, it is of interest to perform a preliminary investigation on this aspect by studying the effects of wet oxidation temperature (400°C, 600°C, 800°C, and 1000°C) onto structural and morphological characteristics of the oxide as well as performance of the oxide as a high dielectric constant passivation layer in a functional MOS structure.
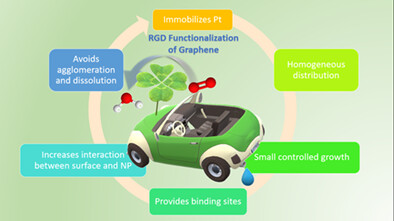
Arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD) peptide-modified graphene as efficient support material for Pt electrocatalyst in proton exchange membrane fuel cells
- Pages: 4712-4725
- First Published: 22 November 2021
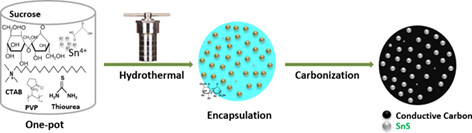
Carbon microsphere encapsulated SnS for use as an anode material in full-cell sodium-ion battery
- Pages: 4726-4738
- First Published: 15 November 2021
Reliability improvement of wind power frequency modulation based on look-ahead control strategy and stage of charge optimization of energy storage
- Pages: 4739-4753
- First Published: 14 November 2021
The role and impact of costing method in the decision-making of energy project: A comparative assessment between levelized cost of energy and benefit-to-cost ratio analysis
- Pages: 4754-4769
- First Published: 15 November 2021
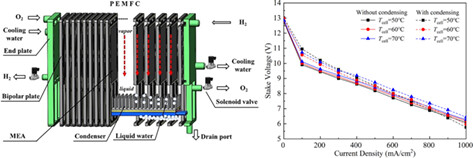
Effect of cathode moisture condensation on temperature distribution characteristics of dead-ended proton-exchange membrane fuel cell stack
- Pages: 4770-4780
- First Published: 15 November 2021
Ultrahigh-areal-capacitance aqueous supercapacitors enabled by soft biomass-derived porous carbon membrane
- Pages: 4781-4793
- First Published: 14 November 2021
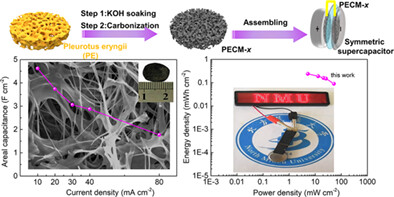
A heteroatom-doped porous carbon membrane (PECM) is fabricated via direct pyrolysis of Pleurotus eryngii (PE) using KOH as an activator and directly used as a self-supported electrode for assembling an aqueous supercapacitor. The PECM possesses a hierarchically porous structure, high graphitization degree, excellent mechanical strength, and superior electrolyte wettability. The symmetric aqueous supercapacitor based on PECM exhibits ultrahigh areal capacitance of 4.6 F cm−2 at 10 mA cm−2 and a maximum energy density of 0.24 mWh cm−2 at a power density of 5.20 mW cm−2.
Enhanced performance of high-temperature proton exchange membrane by introducing 1,2,4-triazole-functionalized graphene oxide into polybenzimidazole
- Pages: 4794-4807
- First Published: 17 November 2021
Generalized penalties and standard efficiencies of carbon capture and storage processes
- Pages: 4808-4824
- First Published: 17 November 2021
Energy saving and performance analysis of air-cooled photovoltaic panels
- Pages: 4825-4834
- First Published: 16 November 2021
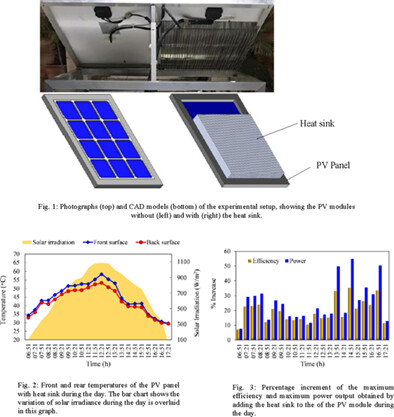
- An optimized heat sink was used to reduce the surface temperature and improve the efficiency and power output of the PV panel.
- The suggested cooling system is expected to be more beneficial and attractive in regions like southern Australia and the southern USA.
- The proposed design may be used in building integrated photovoltaic for zero-emission buildings.
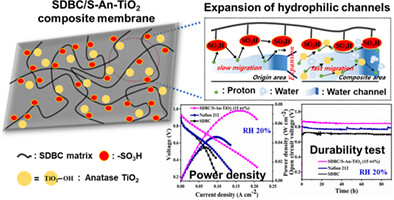
Enhanced performance and durability of composite membranes containing anatase titanium oxide for fuel cells operating under low relative humidity
- Pages: 4835-4851
- First Published: 21 November 2021
Comparison of neutronic aspects in high-temperature gas-cooled reactor using ZrC and SiC Triso particle with 50 and 100 MWt power
- Pages: 4852-4868
- First Published: 22 November 2021
An adaptive fractional-order extended Kalman filtering for state of charge estimation of high-capacity lithium-ion battery
- Pages: 4869-4878
- First Published: 15 November 2021
A capacity efficient power distribution network supported by battery swapping station
- Pages: 4879-4894
- First Published: 15 November 2021
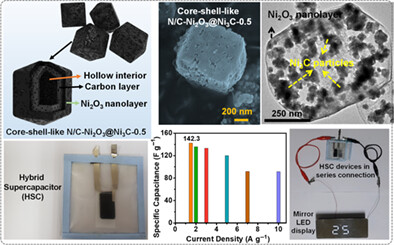
Nitrogen- and carbon-rich Ni2O3 nanolayer shielded Ni3C elongated square bipyramidal-like nanostructures for hybrid supercapacitors
- Pages: 4895-4907
- First Published: 21 November 2021
Enhanced thermophysical properties in spinel CuFe2O4-based nanofluids for concentrated solar power
- Pages: 4908-4918
- First Published: 21 November 2021
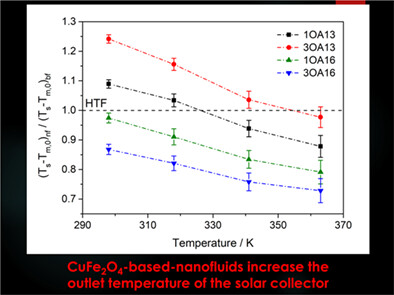
This manuscript reports the preparation of nanofluids based on spinel CuFe2O4 nanoparticles in a base fluid that is a heat transfer fluid commonly used in concentrating solar power (CSP) plants. The nanofluids prepared showed dramatically enhanced thermal properties, that is, the thermal conductivity increased up to 68.5%. So, the efficiency of these nanofluids was analysed considering the possible application in CSP plants. An enhancement of up to 35% in efficiency was found.
A novel hybrid parameter estimation technique of solar PV
- Pages: 4919-4934
- First Published: 16 November 2021
Mesoporous carbon hollow sphere with dandelion-like radial-hierarchy for high-performance supercapacitors
- Pages: 4935-4946
- First Published: 15 November 2021
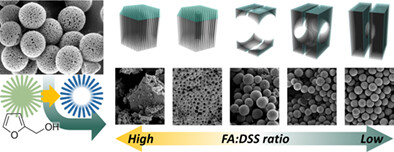
We synthesized mesoporous carbon hollow spheres (MCHSs) with a “Dual-templating method.” The radial and hierarchical pores in the sphere provide a large surface area, short diffusion path, and open-pore that facilitate ion transfer to any direction. Simultaneously, the hollow sphere carved in the center of the MCHSs allows space for the improvement of ion mobility and electrolyte retention.
Performance investigation and energy production of a novel horizontal axis wind turbine with winglet
- Pages: 4947-4964
- First Published: 21 November 2021
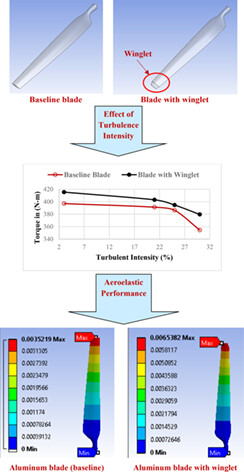
This paper aims to investigate the turbulence effect on a horizontal axis wind turbine blade without and with a winglet at the tip using numerical analysis. The results found that The overall performance of the wind turbine can be influenced depending upon the turbulence intensity. Furthermore, adding a winglet at the tip of the blade increases the weight of the wind turbine system and aeroelastic instability.
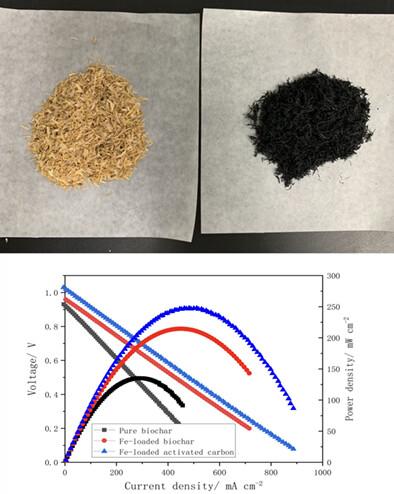
Direct carbon solid oxide fuel cells powered by rice husk biochar
- Pages: 4965-4974
- First Published: 21 November 2021
Minimum loads of coal-fired power plants and the potential suitability for energy storage using the example of Germany
- Pages: 4975-4993
- First Published: 06 December 2021
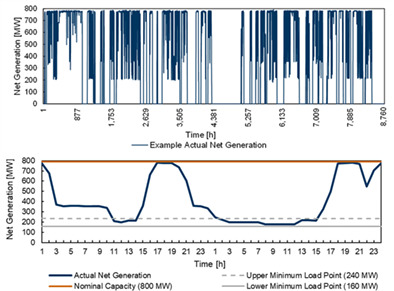
In this manuscript, we show the occurrence of minimum loads and their durations of selected hard coal– and lignite-fired power plants in all transmission system areas in Germany from 2016 to 2018. Besides analyzing and discussing the development of these minimum loads in Germany, we also give a short insight into how energy storage systems could resolve the plant-design restrictions and enlarge the overall bandwidth of operation of power plants by using energy storage systems during minimum loads.
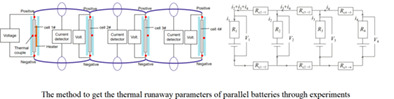
Experimental study on thermal runaway characteristic parameters of parallel battery modules
- Pages: 4994-5005
- First Published: 14 December 2021
Decentralized approach for security enhancement of wind-integrated energy systems coordinated with energy storages
- Pages: 5006-5027
- First Published: 25 November 2021
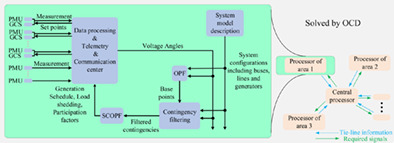
The SCOPF model is decentralized based on OCD algorithm to enhance the security of multi-area energy systems associate with ESS-coordinated wind energy sources in response to rapid changes of wind speed by ESS units. In addition to the low number of iterations needed for convergence of the problem by OCD algorithm, contingency filtering is employed to lower the computational burden. Furthermore, unlike the conventional participation factor in literatures, it is modified to face with the capacity constraints of generating units.
Influence of pretreatment conditions on the catalytic behavior and structure of Fe-Co-Mn/MgO FTS nanocatalyst: Modeling and optimization using RSM
- Pages: 5028-5049
- First Published: 03 December 2021
Effect of glass cover on the energy and exergy performance of a combined system including a building integrated photovoltaic/thermal system and a sensible rotary heat exchanger
- Pages: 5050-5066
- First Published: 25 November 2021
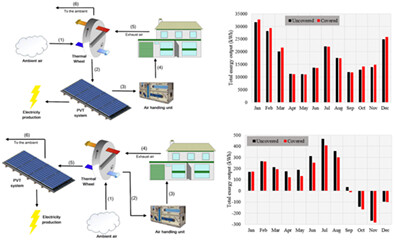
The effect of setting a glass cover on the photovoltaic panels belonging to a building integrated photovoltaic thermal system on the energy and exergy performances of a hybrid system consisting of a building integrated photovoltaic/thermal system and a sensible rotary heat exchanger is investigated numerically. The outcomes are compared with those of the hybrid system incorporating an uncovered building integrated photovoltaic/thermal system. For this purpose, the multi-objective optimization is used to determine the optimal energy and exergy performances of the covered and uncovered hybrid systems, then the performances of optimal units are compared for climate of Kermanshah, Iran. Glass cover has a considerable effect on the energy and exergy performances of hybrid system, and when designing the hybrid system, its impact must definitely be considered.
Creating membrane-air-liquid interface through a rough hierarchy structure for membrane gas absorption to remove CO2
- Pages: 5067-5082
- First Published: 28 November 2021
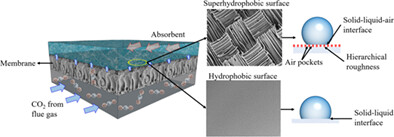
Since there is no literature discussing on rough hierarchical membrane surface structure in contact with corrosive liquid amine absorbent in the membrane gas absorption (MGA) process, the fundamentals of their dynamic interaction remain unclear. This work evaluated the wetting tendency of membrane through the macroscopic understanding of the membrane-liquid-air interface. The successful transformation of the membrane from a hydrophilic solid-liquid interface to a superhydrophobic solid-air-liquid interface and the improvement of CO2 absorption in MGA are the novelties of this work.
Experimental and theoretical study: Design and implementation of a floating photovoltaic system for hydrogen production
- Pages: 5083-5098
- First Published: 24 November 2021
Constructing a novel supercritical carbon dioxide power cycle with the capacity of process switching for the waste heat recovery
- Pages: 5099-5118
- First Published: 26 November 2021
High-voltage performance of P2-NaxMn0.5Co0.5O2 layered cathode material
- Pages: 5119-5133
- First Published: 02 December 2021
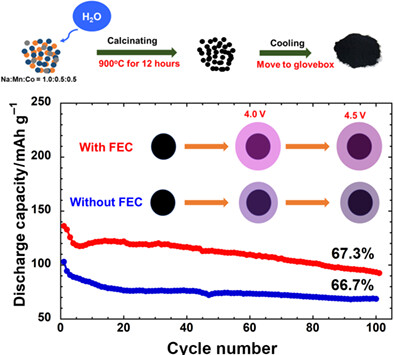
Recent work reports on evaluating the electrochemical performance of cathode material P2-NaxMn0.5Co0.5O2 synthesized by solid state reaction. The focus is on the performance in wide operating voltage and in the electrolyte with and without adding FEC. Our investigations revealed that the high rate capability with good capacity retention was contribued to the suppression of Co4+/Co3+ redox couple at high rates. The FEC exclusion would destroy the performance of the electrode. Additionally, the change of structure and electrod surface were in the two electrolytes were explored by X-ray diffraction, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy.
A novel state of charge estimation method of lithium-ion batteries based on the IWOA-AdaBoost-Elman algorithm
- Pages: 5134-5151
- First Published: 11 December 2021
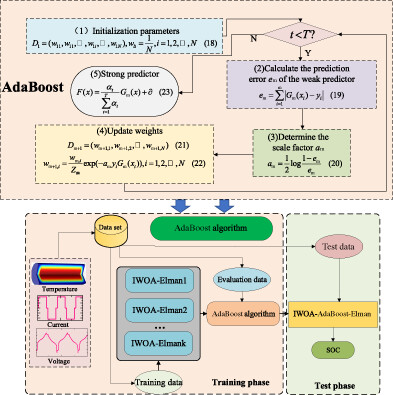
An IWOA-AdaBoost-Elman algorithm-based SOC estimation method for Li-ion batteries is proposed, the method can overcome the effects of different discharge multipliers, different ambient temperatures, and different aging cycles on SOC estimation. Both theoretical and experimental results show that the IWOA-AdaBoost-Elman algorithm provides a new way for the SOC estimation of Li-ion batteries.
Fissile utilization of uranium, thorium, and plutonium fuels for a 60 MWt block-type high-temperature gas-cooled reactor
- Pages: 5152-5164
- First Published: 25 November 2021

The utilization of fissile material becomes an important parameter in High-Temperature Gas Reactor technology because of the use of layered particle-type fuel that makes it challenging to reprocess. This research aims to compare and optimize the fissile utilization of HTGR 60 MWt using uranium, thorium, and plutonium fuels. Analysis was performed to find the optimal configuration of fuel enrichment and the number of coated fuel particles to give the best values of infinite multiplication factor, conversion ratio, and utilization of fissile material while achieving the reactor operation target.
Influence of Nafion loading in the anode catalyst layer on the performance of anion-exchange membrane direct formate fuel cells
- Pages: 5165-5176
- First Published: 28 November 2021
Poly(dopamine) surface-modified polyethylene separator with electrolyte-philic characteristics for enhancing the performance of sodium-ion batteries
- Pages: 5177-5188
- First Published: 26 November 2021
The development of novel cost-effective bio-electrolyte with glycerol host for carbon-based flexible supercapacitor applications
- Pages: 5189-5199
- First Published: 29 November 2021
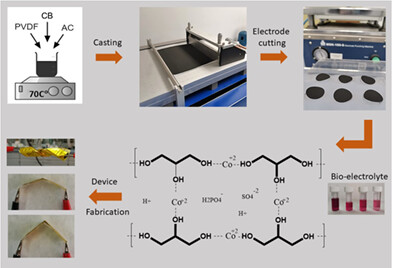
Cost effective and eco-friendly supercapacitors were fabricated using Glycerol-H3PO4 (GlyP) bio-based electrolyte with cobalt ions as a redox mediator. The flexible supercapacitor device showed a maximum specific capacitance of 349 F g−1 with an excellent specific energy of 47 Wh kg−1. The same device showed almost 99% improved specific capacitance when compared to Co-free system. A light-emitting diode (LED) was successfully powered when the same device (dimensions: 1-4 cm) was charged up to 2.7 V.
Pulsed-UV illumination on graphene oxide: A new strategy in photocatalytic synthesis of electrocatalysts to control the structural and electrochemical properties
- Pages: 5200-5214
- First Published: 30 November 2021
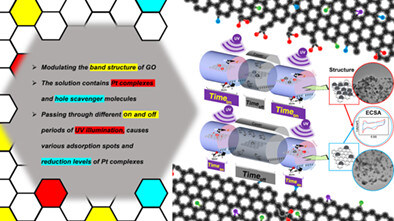
- New perspective to electrocatalysts synthesis: Pulsed illumination on graphene oxide.
- Pulsed ultraviolet (UV) light as a distinctive strategy in the controlled photoreduction of Pt ions.
- Precise manipulation of Pt4+ → Pt2+ → Pt0 by merely adapting the setup design.
- Significant variations in the performance of precisely engineered electrocatalysts.
- Calling attention to the significant role of O-functional groups of partially reduced graphene oxide in ORR.
Aerosol-assisted synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticle-loaded bamboo-like N-doped carbon nanotubes as an efficient bifunctional oxygen catalyst for Zn-air batteries
- Pages: 5215-5225
- First Published: 26 November 2021
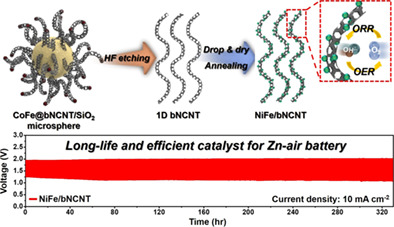
One-dimensional bamboo-like N-doped CNTs were prepared by spray pyrolysis and subsequent post-treatment. To improve the insufficient OER properties, NiFe nanoparticles were spread on the prepared bNCNTs by drop-and-dry method. Due to the synergistic effect of highly dispersed NiFe nanoparticles and bNCNTs, NiFe/bNCNT exhibited superior electrocatalytic performances for ORR and OER, as well as excellent Zn-air battery performances.
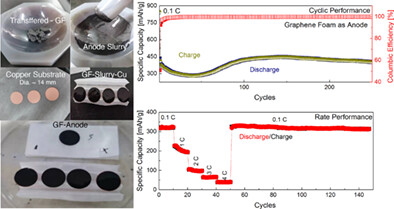
Graphene foam as a stable anode material in lithium-ion batteries
- Pages: 5226-5234
- First Published: 25 November 2021
Integration of biodiesel internal combustion engines and transcritical organic Rankine cycles for waste-heat recovery in small-scale applications
- Pages: 5235-5249
- First Published: 28 November 2021
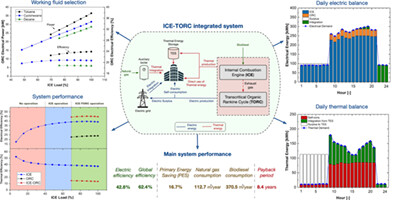
The work investigates a novel integrated energy system for small-scale combined heat and power (CHP) generation in design and off-design conditions. The system consists of a topping biodiesel-fired internal combustion engine (ICE) and a bottoming transcritical organic Rankine cycle (TORC) for waste-heat recovery. To the authors' best knowledge, no investigation on biodiesel-fuelled ICE-TORC combined systems is present in the literature, even though these apparatuses represent an effective option to promote sustainable energy production and the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
Construction of hierarchical nickel cobalt sulfide@manganese oxide nanoarrays@nanosheets core-shell electrodes for high-performance electrochemical asymmetric supercapacitor
- Pages: 5250-5259
- First Published: 27 October 2021
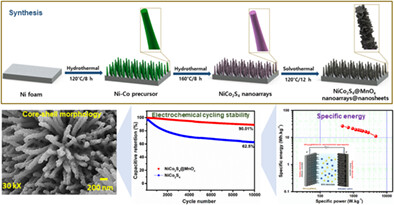
Hierarchical NiCo2S4@MnOx nanoarrays@nanosheets are prepared by simple hydrothermal and solvothermal methods with high electrode capacitance and excellent electrochemical cyclic stability for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors. No previous study reported including amorphous MnOx synthesis using the proposed synthesis method, which acts as a protective layer to enhance NiCo2S4 electrochemical performance. Electrode specific energy and potential window can be widened by fabricating a core-shell structure with battery-like NiCo2S4 and pseudocapacitive MnOx.
Concentrated perovskite photovoltaics enable minimization of energy loss below 0.5 eV under artificial light-emitting diode illumination
- Pages: 5260-5268
- First Published: 02 November 2021
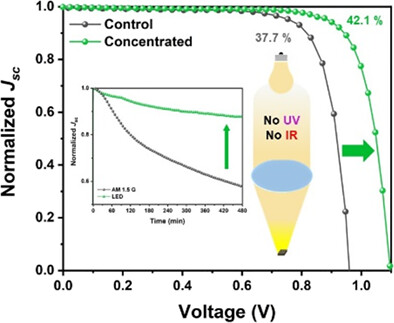
Perovskite artificial light cell (PALC) with high efficiency over 40% and low energy loss below 0.5 eV was demonstrated by optimizing the perovskite absorber and concentrating LED light. PALC also maintained high stability under concentrated LED light due to the absences of ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths.
Electrodeposited bimetallic microporous MnCu oxide electrode as a highly stable electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction
- Pages: 5269-5279
- First Published: 13 November 2021
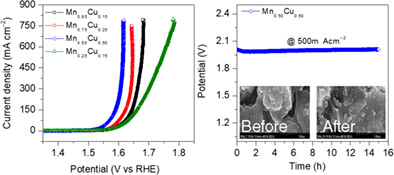
In this work, we fabricated bimetallic Mn1−xCux oxide (0.15 ≤ x ≤ 0.75) thin-film electrodes via the electrodeposition method, which is one of the easy and simple routes, and they were investigated for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalyst for electrochemical water splitting. The best performing electrode exhibits an overpotential of 291 mV (vs RHE) to attain a current density of 10 mA cm−2 and the lower Tafel slope of 54.6 mV dec−1, which reveals the most favorable catalytic kinetics for mass and electron transport during the OER reaction.
Potential pathways for syngas transformation towards kerosene range hydrocarbons in a dual Fischer-Tropsch-zeolite bed
- Pages: 5280-5287
- First Published: 10 November 2021
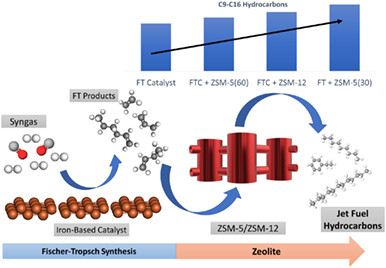
In this work, the effect of combining H-ZSM-5 and H-ZSM-12 zeolites and a Fischer-Tropsch catalyst on a stacked bed to enhance the production of jet fuel range hydrocarbons has been studied. The combination of a potassium-cobalt-promoted iron catalyst with an H-ZSM-5 zeolite (Si/Al = 30) or an H-ZSM-12 zeolite (Si/Al = 60) on a stacked bed produces more kerosene range hydrocarbons (C9-C16) than when using only the FT catalyst in a single bed. Considering the results obtained in this and previous works, a reaction network has been proposed to explain the transformations of Fischer-Tropsch products inside the zeolites channels.
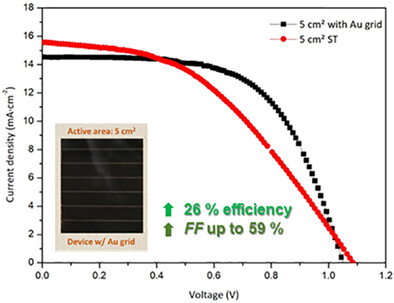
Embedded current collectors for efficient large area perovskite solar cells
- Pages: 5288-5295
- First Published: 15 November 2021
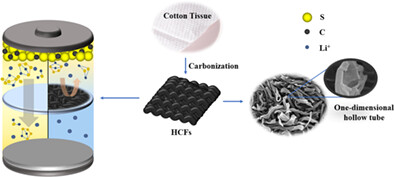
Lightweight freestanding hollow carbon fiber interlayer for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries
- Pages: 5296-5305
- First Published: 16 November 2021
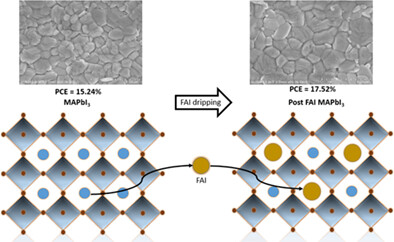
Formamidinium post-dripping on methylammonium lead iodide to achieve stable and efficient perovskite solar cells
- Pages: 5306-5314
- First Published: 25 November 2021
Ion-exchange synthesis of microporous Co3S4 for enhanced electrochemical energy storage
- Pages: 5315-5329
- First Published: 24 November 2021
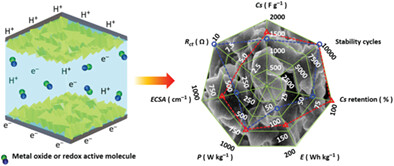
Ion-exchange synthesis of polyhedral Co3S4 on the three-dimensional architecture of Ni foam with a desirable microporous morphology is reported along with its impressive electrochemical energy storage performance in alkaline KOH medium. The fabricated symmetric supercapacitor cell exhibits an outstanding supercapacitive performance due to the enhanced conductivity (resistivity ~10−4 Ω), low electronegativity, and efficient electron transport endowed with flexible material structure of Co3S4 than its oxide counterpart.
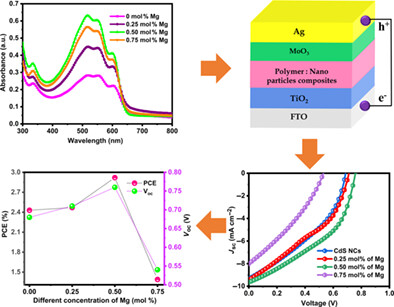
Studying the impact of Mg doping on the physical properties of CdS nanocrystals for the fabrication of hybrid solar cells–based organic P3HT:PCBM polymers and inorganic Mg-doped CdS nanocrystals
- Pages: 5330-5341
- First Published: 29 November 2021
A novel scaly N-doped carbon/Mo-doped TiO2 composite to regulate polysulfides for excellent-performance lithium-sulfur batteries
- Pages: 5342-5349
- First Published: 27 October 2021
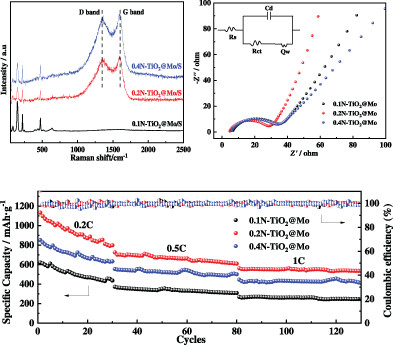
Novel scaly N-doped carbon/Modoped TiO2 composite as sulfur wrapping host for lithium-sulfur batteries is designed. This host not only can physically adsorb polysulfides due to the unique scaly carbon structure with a rough surface, but also chemically adsorb polysulfides which effectively inhibit the shuttle effect from Ti-O bond. In addition, N-TiO2@Mo cathode display a high-capacity maintenance and low capacity degradation.
South Koreans' acceptance of hydrogen production using nuclear energy
- Pages: 5350-5361
- First Published: 15 November 2021
Feasibility analysis of applying Taguchi method to fuel cell simulation
- Pages: 5362-5366
- First Published: 25 November 2021
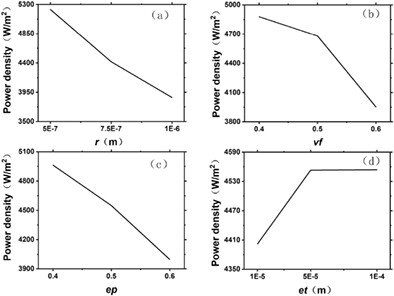
To verify the feasibility of applying Taguchi method to fuel cell simulation, a cathode optimization experiment is purposely designed based on a validated solid oxide fuel cell model. It is found that (a) the optimal results with the Taguchi method are reliable, and (b) the use of the Taguchi method may lead to deviations in conclusions related to less influential factors.