Pulsed-UV illumination on graphene oxide: A new strategy in photocatalytic synthesis of electrocatalysts to control the structural and electrochemical properties
Navid Haghmoradi
Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorZahide Tuğba Sarı
Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering “Giulio Natta”, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorEmre Utku Öztürk
Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorSiddhartha Peri
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, Illinois, USA
Search for more papers by this authorSina Abdolhosseinzadeh
Laboratory for Functional Polymers, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa), Dübendorf, Switzerland
Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorBegüm Yarar Kaplan
Sabanci University SUNUM Nanotechnology Research Centre, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Selmiye Alkan Gürsel
Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey
Sabanci University SUNUM Nanotechnology Research Centre, Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence
Selmiye Alkan Gürsel, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul 34956, Turkey.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorNavid Haghmoradi
Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorZahide Tuğba Sarı
Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering “Giulio Natta”, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorEmre Utku Öztürk
Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorSiddhartha Peri
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, Illinois, USA
Search for more papers by this authorSina Abdolhosseinzadeh
Laboratory for Functional Polymers, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa), Dübendorf, Switzerland
Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorBegüm Yarar Kaplan
Sabanci University SUNUM Nanotechnology Research Centre, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Selmiye Alkan Gürsel
Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey
Sabanci University SUNUM Nanotechnology Research Centre, Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence
Selmiye Alkan Gürsel, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Istanbul 34956, Turkey.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Summary
This study demonstrated the capability of a novel method in controlling the structural and electrochemical properties of electrocatalysts, utilizing a pulsed-ultraviolet (UV) setup for the synthesis procedure. A hand-made reactor provided a new set of parameters. The variation of UVon and UVoff periods resulted in samples with a range of different structures, compositions, and activities. Graphene/Pt was prepared with varying forms of illumination pulse, and its hydrogen oxidation and oxygen reduction reaction performances were evaluated. Controlling the reduction degree of Pt ions on partially reduced graphene oxide was achieved by manipulating the setup design. The results revealed a dominant growth and agglomeration phase of Pt particles, mostly with metallic states, by increasing both UVon and Uoff time spontaneously. Long UVon without adequate UVoff did not result in promising electrocatalytic activities. In other words, different structures, compositions, and activities of samples suggested that not just the illumination is the crucial factor, it is also the resting time or UVoff which determines the surface adsorption kinetics, nucleation sites, and growth mechanism of nanoparticles. Further chemical reduction by highly concentrated ascorbic acid was used to confirm the proposed mechanisms, which lead to samples even with more metallic Pt (Pt0).
REFERENCES
- 1Tian XL, Xu YY, Zhang W, Wu T, Xia BY, Wang X. Unsupported platinum-based Electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Energy Lett. 2017; 2: 2035-2043. doi:10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00593
- 2Marinkas A, Arena F, Mitzel J, et al. Graphene as catalyst support: the influences of carbon additives and catalyst preparation methods on the performance of PEM fuel cells. Carbon. 2013; 58: 139-150. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.02.043
- 3Wan CH, Zhuang QH. Novel layer wise anode structure with improved CO-tolerance capability for PEM fuel cell. Electrochim Acta. 2007; 52: 4111-4123. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2006.11.045
- 4Tour JM. Rice group shows graphene quantum dots beat Pt catalyst. Fuel Cells Bull. 2014; 12: P13. doi:10.1016/S1464-2859(14)70355-4
10.1016/S1464?2859(14)70355?4 Google Scholar
- 5Li Y, Li Y, Zhu E, et al. Stabilization of high-performance oxygen reduction reaction Pt Electrocatalyst supported on reduced Graphene oxide/carbon black composite. J Am Chem Soc. 2012; 134: 12326-12329. doi:10.1021/ja3031449
- 6Ma J, Habrioux A, Alonso-Vante N. Enhanced HER and ORR behavior on photodeposited Pt nanoparticles onto oxide-carbon composite. J Solid State Electrochem. 2013; 17: 1913-1921. doi:10.1007/s10008-013-2046-y
- 7Yarar Kaplan B, Haghmoradi N, Jamil E, Merino C, Alkan Gürsel S. Platinum nanoparticles decorated carbon nanofiber hybrids as highly active electrocatalysts for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Int J Energy Res. 2020; 44: 10251-10261.
- 8Srivastava SK, Pionteck J. Recent advances in preparation, structure, properties and applications of graphite oxide. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015; 15: 1984-2000. doi:10.1166/jnn.2015.10047
- 9Velasco-Soto MA, Pérez-García SA, Alvarez-Quintana J, Cao Y, Nyborg L, Licea-Jiménez L. Selective band gap manipulation of graphene oxide by its reduction with mild reagents. Carbon. 2015; 93: 967-973. doi:10.1016/J.CARBON.2015.06.013
- 10Iqbal MZ, Rehman AU, Siddique S. Prospects and challenges of graphene based fuel cells. J Energy Chem. 2019; 39: 217-234. doi:10.1016/J.JECHEM.2019.02.009
- 11Zhu C, Liu P, Mathew AP. Self-assembled TEMPO cellulose nanofibers: graphene oxide-based biohybrids for water purification. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2017; 9: 21048-21058. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b06358
- 12Shen J, Zhu Y, Yang X, Li C. Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices, Chem. Commun. 2012; 48: 3686-3699. doi:10.1039/c2cc00110a
- 13Mahmood N, Zhang C, Yin H, Hou Y. Graphene-based nanocomposites for energy storage and conversion in lithium batteries, supercapacitors and fuel cells. J Mater Chem A. 2014; 2: 15-32. doi:10.1039/c3ta13033a
- 14Dreyer DR, Park S, Bielawski W, Ruoff RS. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem SocRev. 2010; 39: 228-240. doi:10.1039/b917103g
- 15Eda G, Chhowalla M. Chemically derived Graphene oxide: towards large-area thin-film electronics and optoelectronics. Adv Mater. 2010; 22: 2392-2415. doi:10.1002/adma.200903689
- 16Chua CK, Sofer Z, Pumera M. Graphite oxides: effects of permanganate and chlorate oxidants on the oxygen composition. Chem A Eur J. 2012; 18: 13453-13459. doi:10.1002/chem.201202320
- 17Jeong HK, Jin MH, So KP, Lim SC, Lee YH. Tailoring the characteristics of graphite oxides by different oxidation times. J Phys D. 2009; 42:065418. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/42/6/065418
- 18Shen Y, Yang S, Zhou P, et al. Evolution of the band-gap and optical properties of graphene oxide with controllable reduction level. Carbon. 2013; 62: 157-164. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.06.007
- 19Shin BH, Kim KK, Benayad A, et al. Efficient reduction of graphite oxide by sodium borohydride and its effect on electrical conductance, Adv. Funct Mater. 2009; 19: 1987-1992. doi:10.1002/adfm.200900167
- 20Zhu C, Guo S, Fang Y, Dong S. Reducing sugar: new functional molecules for the green synthesis of Graphene Nanosheets. ACS Nano. 2010; 4: 2429-2437. doi:10.1021/nn1002387
- 21Abdolhosseinzadeh S, Sadighikia S, Gürsel SA. Scalable synthesis of sub-Nanosized platinum-reduced Graphene oxide composite by an ultraprecise photocatalytic method. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2018; 6: 3773-3782. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04148
- 22Abdolhosseinzadeh S, Mousavi M, Haghmoradi N, Gürsel SA. A continuous-flow photocatalytic reactor for the precisely controlled deposition of metallic nanoparticles. J Vis Exp. 2019; 146:e58883. doi:10.3791/58883
- 23P. Sheath, M. Majumder, A Comparative Review of Graphene Oxide and Titanium Dioxide As Photocatalysts in Photocatalytic Systems, Chemeca 2011: Engineering a Better World, Sydney Hilton Hotel, NSW, Australia, 18–21 September (2011), 2346–2357.
- 24Kamat PV. Graphene-based nanoarchitectures: anchoring semiconductor and metal nanoparticles on a two-dimensional carbon support. J Phys Chem Lett. 2010; 1: 520-527. doi:10.1021/jz900265j
- 25Thanh NTK, Maclean N, Mahiddine S. Mechanisms of nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in solution. Chem Rev. 2014; 114: 7610-7630. doi:10.1021/cr400544s
- 26Wenderich K, Han K, Mul G. The effect of methanol on the Photodeposition of Pt nanoparticles on tungsten oxide. Part Part Syst Charact. 2018; 35: 1-8. doi:10.1002/ppsc.201700250
- 27Albiter E, Valenzuela MA, Alfaro S, Valverde-Aguilar G, Martínez-Pallares FM. photocatalytic deposition of ag nanoparticles on TiO2: metal precursor effect on the structural and photoactivity properties. J Saudi Chem Soc. 2015; 19: 563-573. doi:10.1016/j.jscs.2015.05.009
- 28Cao S, Chan TS, Lu YR, et al. Photocatalytic pure water splitting with high efficiency and value by Pt/porous brookite TiO2 nanoflutes. Nano Energy. 2020; 67:104287. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104287
- 29Sliem MA, Hikov T, Li ZA, et al. Interfacial cu/ZnO contact by selective photodeposition of copper onto the surface of small ZnO nanoparticles in non-aqueous colloidal solution. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2010; 12: 9858-9866. doi:10.1039/c003861j
- 30Lashgari M, Ghanimati M. A highly efficient nanostructured quinary photocatalyst for hydrogen production. Int J Energy Res. 2015; 39: 516-523. doi:10.1002/er.3265
- 31Srisawang N, Chaiyasat A, Ngernchuklin P, Chaiyasat P. Novel reusable pH-responsive photocatalyst polymeric microcapsules for dye treatment. Int J Energy Res. 2021; 45: 7535-7548. doi:10.1002/er.6335
- 32Zhang Z, Yi G, Li P, et al. Engineering approach toward catalyst design for solar photocatalytic CO2 reduction: a critical review. Int J Energy Res. 2021; 45: 9895-9913. doi:10.1002/er.6603
- 33Nandakumar DK, Vaghasiya JV, Yang L, Zhang Y, Tan SC. A solar cell that breathes in moisture for energy generation. Nano Energy. 2020; 68:104263. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104263
- 34Luo J, Bai X, Li Q, et al. Band structure engineering of bioinspired Fe doped SrMoO4 for enhanced photocatalytic nitrogen reduction performance. Nano Energy. 2019; 66:104187. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104187
- 35Foster NS, Lancaster AN, Noble RD, Koval CA. Effect of organics on the photodeposition of copper in titanium dioxide aqueous suspensions. Ind Eng Chem Res. 1995; 34: 3865-3871. doi:10.1021/ie00038a025
- 36Xi C, Chen Z, Li Q, Jin Z. Effects of H+, cl− and CH3COOH on the photocatalytic conversion of
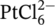 in aqueous TiO2 dispersion. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 1995; 87: 249-255. doi:10.1016/1010-6030(94)03983-2
in aqueous TiO2 dispersion. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 1995; 87: 249-255. doi:10.1016/1010-6030(94)03983-2
- 37Yeh T, Syu J, Cheng C, Chang T, Teng H. Graphite oxide as a Photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water, Adv. Funct Mater. 2010; 20: 2255-2262. doi:10.1002/adfm.201000274
- 38Xiong Z, Zhang L, Ma J, Zhao XS. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene–gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Chem Commun. 2010; 46: 6099-6101. doi:10.1039/c0cc01259a
- 39Xiong Z, Zhang LL, Song XS. Visible-light-induced dye degradation over copper-modified reduced, Chem. Eur J. 2011; 17: 2428-2434. doi:10.1002/chem.201002906
- 40Yarar Kaplan B, Haghmoradi N, Biçer E, Merino C, Gürsel SA. High performance electrocatalysts supported on graphene based hybrids for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2018; 43: 23221-23230. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.222
- 41Şanlı LI, Bayram V, Ghobadi S, Düzen N, Gürsel SA. Engineered catalyst layer design with graphene-carbon black hybrid supports for enhanced platinum utilization in PEM fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2017; 42: 1085-1092. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.210
- 42Quesnel E, Roux F, Emieux F, et al. Graphene-based technologies for energy applications, challenges and perspectives. 2D Mater. 2015; 2: 30204. doi:10.1088/2053-1583/2/3/030204
10.1088/2053?1583/2/3/030204 Google Scholar
- 43Ghosh A, Subrahmanyam KS, Krishna KS, et al. Uptake of H2 and CO2 by Graphene, J. Phys Chem C. 2008; 112: 15704-15707. doi:10.1021/jp805802w
- 44Mizukoshi Y, Takagi E, Okuno H, Oshima R, Maeda Y, Nagata Y. Preparation of platinum nanoparticles by sonochemical reduction of the Pt(IV) ions: role of surfactants. Ultrason Sonochem. 2001; 8: 1-6. doi:10.1016/S1350-4177(00)00027-4
- 45Ferrari AC, Robertson J. interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys Rev B. 2000; 61: 14095-14107. doi:10.1007/BF02543692
- 46Kim HJ, Ruqia B, Kang MS, et al. Shape-controlled Pt nanocubes directly grown on carbon supports and their electrocatalytic activity toward methanol oxidation. Sci Bull. 2017; 62: 943-949. doi:10.1016/j.scib.2017.05.029
- 47Chandrasekaran S, Ma D, Ge Y, et al. Electronic structure engineering on two-dimensional (2d) electrocatalytic materials for oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution, and hydrogen evolution reactions. Nano Energy. 2020; 77:105080. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105080




