Comparative study of heat pipes and liquid-cooling systems with thermoelectric generators for heat recovery from chimneys
Summary
This article presents a comparative experimental study of three different cooling systems used with thermoelectric generators mounted on a chimney for waste heat recovery. The studied systems are heat pipes, closed-circuit liquid cooling, and open-circuit liquid cooling. The study considers the variation of the performance of each system at different operating conditions and their impact on the output thermoelectric generator power. The auxiliary power consumed by the cooling system itself is included. The heat pipes' system is studied at different fan speeds, while the liquid-cooling systems are studied at different water flow rates and fan speeds for the radiator (closed-circuit only). Also, the required surface area for each system is considered. The results show that for the heat pipes' system, the optimum system net power is achieved at medium fan speed at an operating voltage of 5.5 to  . The closed-circuit liquid-cooling system can generate up to
. The closed-circuit liquid-cooling system can generate up to  more power compared to the heat pipes' system, while the open circuit can generate up to
more power compared to the heat pipes' system, while the open circuit can generate up to 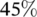 more power. When considering the occupied area, these numbers become
more power. When considering the occupied area, these numbers become 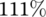 and
and 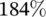 more power per unit area, respectively. The liquid-cooling system is a better option compared to the heat pipes' system, especially when considering the required surface area.
more power per unit area, respectively. The liquid-cooling system is a better option compared to the heat pipes' system, especially when considering the required surface area.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing not applicable-no new data generated.




