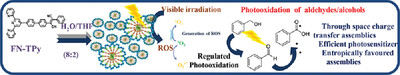
4. Stimulus-Responsive Materials
Recommended by Prof. Gen-ichi Konishi
Stimulus-responsive materials can display remarkable changes in the properties with a slight change in environmental conditions such as light, pH, temperature, moisture, electricity, and so forth, which provide enormous potential in the bio-/chemo-sensors, actuators, drug delivery, and artificial muscles. In this collection, recent advances of stimulus-responsive materials published in Aggregate are included.
2024
Organic cocrystals: From high‐performance molecular materials to multi‐functional applications
Graphical Abstract
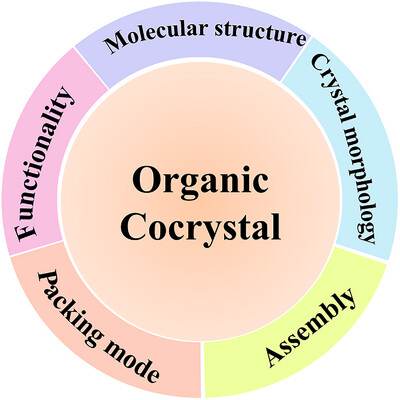
This review provides a comprehensive exploration of organic cocrystal engineering, focusing on the mechanism of cocrystal formation, stacking modes, driving forces behind cocrystal synthesis, innovative growth techniques, and the multifunctional properties of organic cocrystals, which offers guidelines for engineering high-performance molecular materials and expanding the applications of organic cocrystals in optoelectronic, photothermal, and energy storage and conversion fields.
Stimuli‐responsive photoluminescent copper(I) halides for scintillation, anticounterfeiting, and light‐emitting diode applications
Graphical Abstract
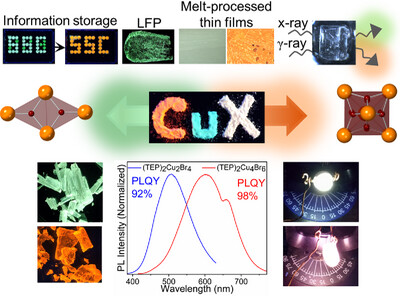
Green emitting (TEP)2Cu2Br4 and orange emitting (TEP)2Cu4Br6 are reported. Due to their photoluminescence efficiencies approaching 100%, these materials are promising for solid-state lighting, and X- and γ-rays scintillation applications. Furthermore, (TEP)2Cu2Br4 and (TEP)2Cu4Br6 are sensitive to external stimuli, which enables their use in high-level anti-counterfeiting and information storage applications.
Au···I coinage bonds: Boosting photoluminescence efficiency and solid‐state molecular motion
Graphical Abstract
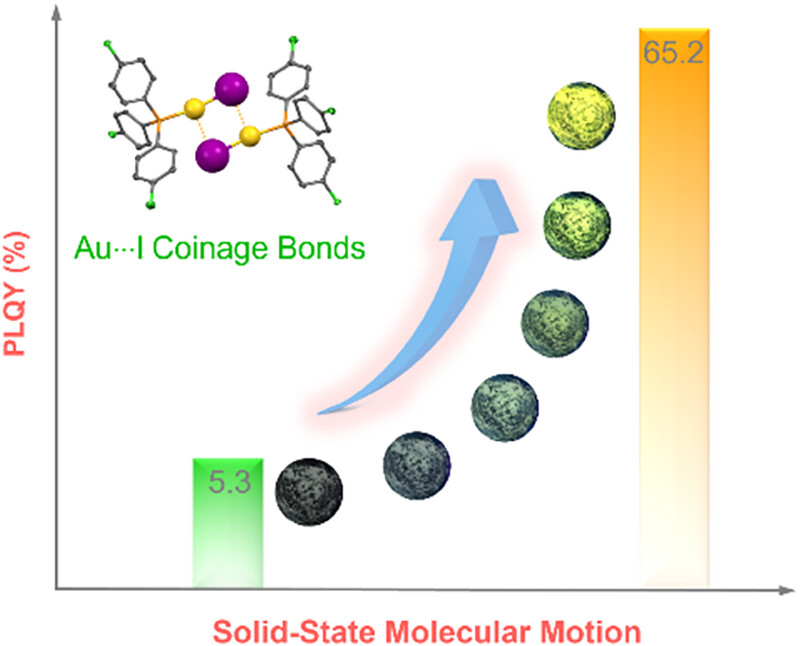
This study explores Au···I coinage bonds in an aggregation-induced emission (AIE)-active Au(I) complex, revealing multiswitchable luminescence behavior and solid-state molecular motion. The findings highlight the potential of these bonds in enhancing photoluminescence and developing smart, stimuli-responsive materials.
Dynamic color‐tunable ultra‐long room temperature phosphorescence polymers with photo‐chromism and water‐stimuli response for multilevel anti‐counterfeiting
Graphical Abstract
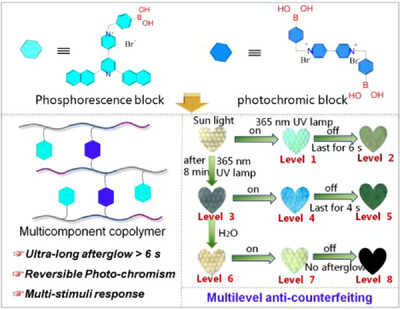
Dynamic color-tunable ultra-long room temperature phosphorescence (URTP) polymers with the ultra-long afterglow of over 6 s, photo-chromism, and water-stimuli response are exploited by integrating multicolor phosphorescence functional block and photo-chromic functional block into polyvinyl alcohol matrix. Also, their dynamic multilevel anti-counterfeiting applications are demonstrated. These results pave the way to develop smarter multifunctional URTP materials for anti-counterfeiting and optical sensing.
Stimuli‐responsive enaminitrile molecular switches as tunable AIEgens covering the chromaticity space, operating out‐of‐equilibrium, and acting as vapor sensors
Graphical Abstract
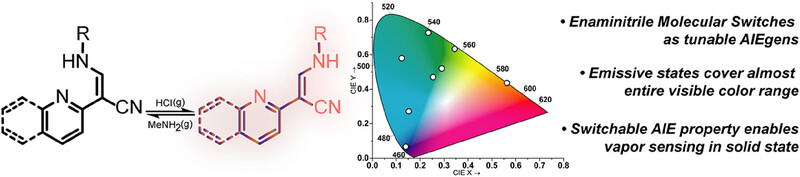
Responsive enaminitrile molecular switches showing tunable turn-on fluorescence upon switching and aggregation are presented. The switches were emissive over the visible color range and responsive aggregation-induced emission could be recorded. When applied as solid-state chemosensors, the switches could be used to detect acidic and basic vapors while displaying “off-on-off”.
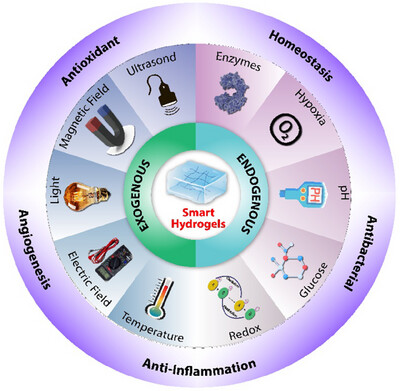
Endogenous/exogenous stimuli‐responsive smart hydrogels for diabetic wound healing
Graphical Abstract
Boosting disassembly of π–π stacked supramolecular nanodrugs under tumor microenvironment by introducing stimuli‐responsive drug‐mates
Graphical Abstract
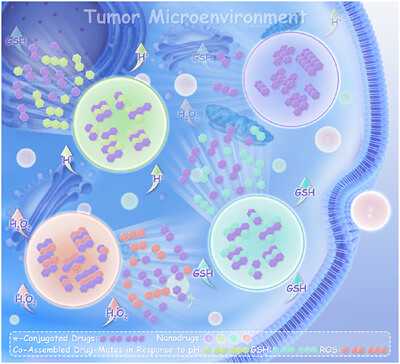
A concept of stimuli-responsive drug-mates is proposed for boosting the disassembly of π–π stacked supramolecular nanodrugs under tumor microenvironment (TME), in which π-conjugated drugs are foremost co-assembled with additional drug molecules that possess relatively weak π–π interaction but high TME responsiveness. The co-assembled drug-mates significantly lower the disassembly activation energy and accelerate the release of drug payloads.
Biomarker‐induced gold aggregates enable activatable near‐infrared‐II photoacoustic image‐guided radiosensitization
Graphical Abstract
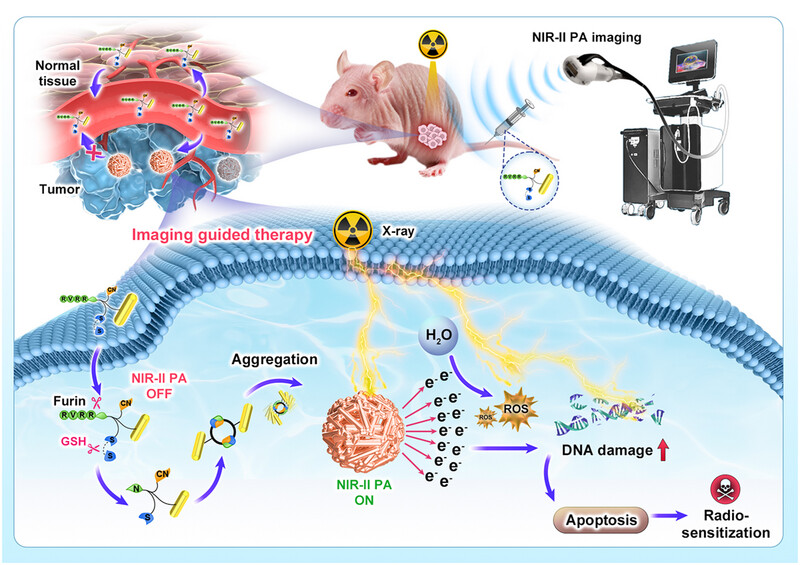
The RVRR peptide sequence of the AuNR@Peptide probe is cleaved by furin, triggering the aggregation of gold nanorods (AuNRs) into larger aggregates. This results in “Turn-On” near-infrared-II photoacoustic signals and enhanced tumor retention by preventing migration and backflow of AuNRs, thus achieving activatable imaging-guided sensitizing radiotherapy.
Spatiotemporal responsive hydrogel microspheres for the treatment of gastric cancer
Graphical Abstract
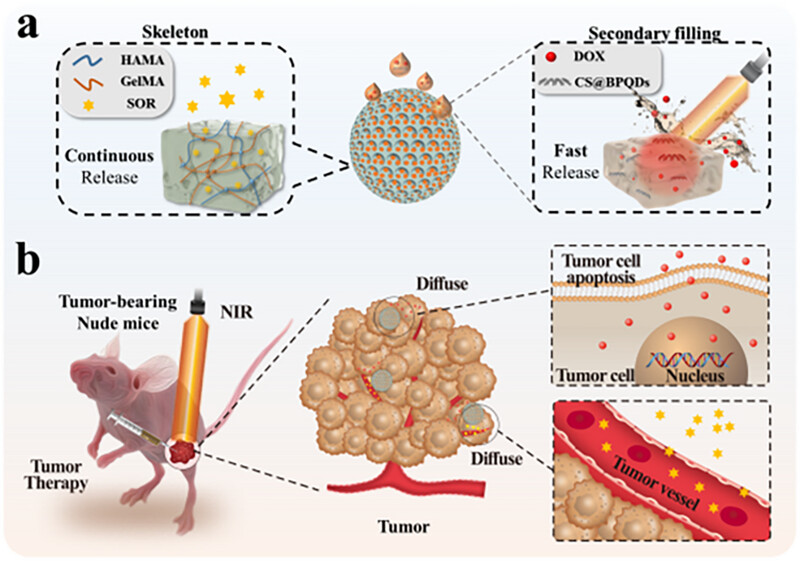
Spatiotemporal responsive microspheres are an innovative drug delivery system possessing exceptional spatiotemporal responsiveness behaviors and thus achieving two different drug release profiles. Such microspheres can significantly reduce tumor cell viability and enhance the efficiency in treating gastric cancer, indicating a promising stratagem in the field of drug delivery and tumor therapy.
Smart multi‐functional aggregates reoxygenate tumor microenvironment through a two‐pronged strategy to revitalize cancer immunotherapy
Graphical Abstract
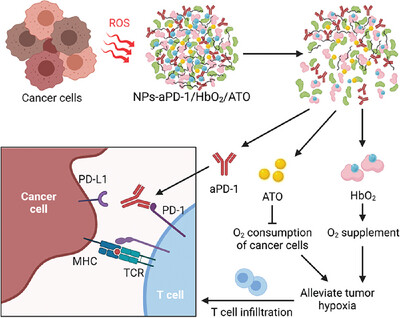
Here, a smart aggregate (NPs-aPD-1/HbO2/ATO) comprised of PD-1 antibody (aPD-1), hemoglobin (Hb), atovaquone (ATO) and an ROS-responsive cross-linker is presented. Tumor ROS disrupts the linkers, releasing Hb and ATO to alleviate hypoxia via an open-source and reduce-expenditure strategy, respectively, and assisting the released aPD-1 to fight against the cancer. This approach overcomes the side effects of systemic administration of the components and profoundly advances cancer immunotherapy.
Schiff base flexible organic crystals toward multifunctional applications
Graphical Abstract

This review provides an overview on the development of Schiff base flexible organic crystals (including elastic organic crystals, plastic organic crystals, and flexible organic crystals integrating elasticity and plasticity) from serendipitous discovery to design strategies and versatile applications such as stimuli responses, optical waveguides, optoelectronic devices, biomimetic soft robots, and organic photonic integrated circuits.
Aggregation‐based analytical chemistry in point‐of‐care nanosensors
Graphical Abstract
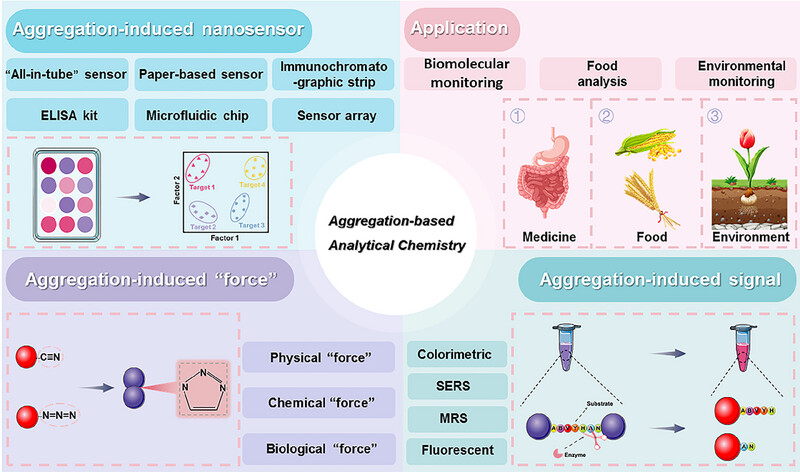
This review summarizes the recent progress of aggregation-based analytical chemistry in POC nanosensors. After reviewing the aggregation-induced “forces” for nanoprobes, the aggregation-induced signal transductions and POC nanosensors are discussed. Subsequently, the application of aggregation-based analytical chemistry-driven POC nanosensors in medicine, food, and environment are reviewed. This review is expected to provide new insights into the fabrication of POC nanosensors through aggregation-based analytical chemistry and promote the development of aggregation-based analytical chemistry with high speed.
Dynamic response and discrimination of gaseous sarin using a boron‐difluoride complex film‐based fluorescence sensor
Graphical Abstract
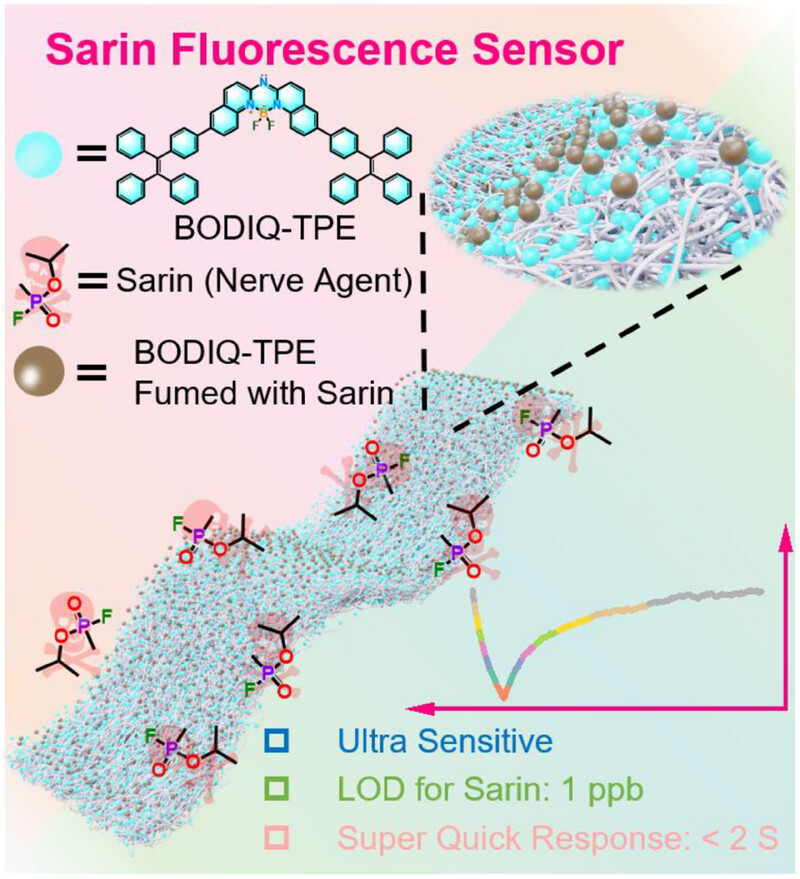
Designing sensors for detecting real nerve agents presents significant challenges, particularly in achieving high sensitivity and selectivity. This study employs film-based fluorescent sensors that leverage the high environmental sensitivity of fluorescent films. Utilizing an independently designed sensing platform, we achieve highly sensitive and selective detection of the nerve agent sarin. Additionally, we distinguish acidic interfering gases through sensing kinetics curves.
2023
Wide‐range color‐tunable afterglow emission by the modulation of triplet exciton transition processes based on buckybowl structure
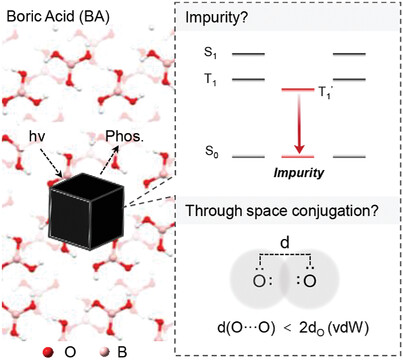
Unusual phosphorescence of boric acid: From impurity or clusterization‐triggered emission?
Supramolecular photoresponsive polyurethane with movable crosslinks based on photoisomerization of azobenzene
Graphical Abstract
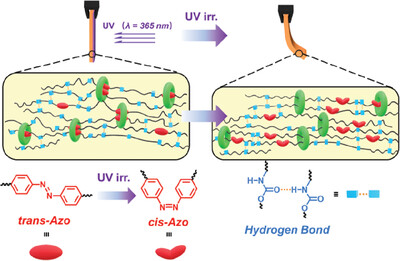
Supramolecular photoresponsive polyurethane (CD-Azo-PU) with movable crosslinks between azobenzene (Azo) and γ-cyclodextrins (CD) exhibits rapid photoresponsive actuation irradiated by UV light (λ = 365 nm). The films of CD-Azo-PU bend towards the light source. Photostimuli increase crystallinity via the formation of hydrogen-bond driven by the dissociation of the CD/Azo complexes.
Light‐controlled molecular tweezers capture specific amyloid oligomers
Graphical Abstract
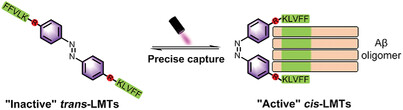
Here, we show a general method for precisely capturing specific Aβ oligomers using light-controlled molecular tweezers (LMTs), which can be activated to form a tweezer-like cis configuration that preferentially binds to specific oligomers matching the space of the tweezers via multivalent interactions of KLVFF motifs.
Aromatic compounds‐mediated synthesis of anatase‐free hierarchical TS‐1 zeolite: Exploring design strategies via machine learning and enhanced catalytic performance
Graphical Abstract

Anatase-free hierarchical TS-1 zeolites with high catalytic performance for olefins are prepared by an aromatic-compounds mediated synthesis method. The fabricated process is simple and avoids post-treatment. The state of Ti species and mesopore width are regulated by aromatic compounds, which improves the accessibility of substrates to active sites and promotes the transfer of products.
A simple strategy to simultaneously improve the lifetime and activity of classical iridium complex for photocatalytic water‐splitting
Graphical Abstract
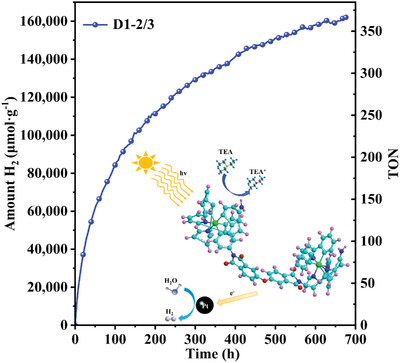
The oligomeric Ir photosensitizer is designed and synthesized, which simultaneously exhibits a long lifetime of 676 h and a high hydrogen evolution of 162055.1 μmol·g-1. The oligomer chain acts as a large steric hindrance to reduce the decomposition of photosensitizer and prolong its lifetime. The possible coupling of adjacent Ir complexes promotes electron transfer to improve photocatalytic activity.
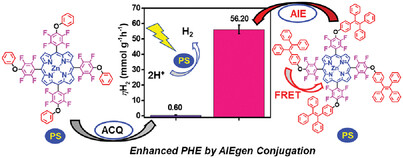
Design of AIEgen‐based porphyrin for efficient heterogeneous photocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Graphical Abstract
Aggregation induced edge sites actuation of 3D MoSe2/rGO electrocatalyst for high-performing water splitting system
Graphical Abstract
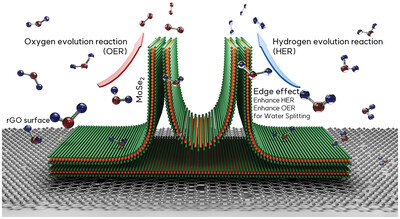
MoSe2/rGO heterostructure provides activated edge sites for electrochemical reactions. The interfacial covalent bond between MoSe2 and rGO improves stability and lowers the overpotential, leading to improved HER and OER with high current density for water splitting. The electrocatalyst is stable for over 70 h, making it a promising and cost-effective option for hydrogen fuel production.
Biomimetic Fe7S8/Carbon electrocatalyst from [FeFe]-Hydrogenase for improving pH-Universal electrocatalytic hydrogen production
Graphical Abstract
![Biomimetic Fe7S8/Carbon electrocatalyst from [FeFe]-Hydrogenase for improving pH-Universal electrocatalytic hydrogen production Issue 1, 2024](/cms/asset/2fea410d-7044-45f2-abed-350ee46e94f2/agt2444-gra-0001-m.jpg)
The present work enlightens the readers with coherent knowledge of the mechanism of hydrogen evolution reaction on hydrogenase structure Fe7S8/C. The developed iron-sulfide cluster surrounded by a carbon matrix acts as an efficient electrocatalyst for electrochemical water splitting under a wide pH range. The low overpotential of the electrocatalyst (45.9 mV under neutral pH) makes it a promising and cost-effective option for hydrogen fuel production.
Ligand‐dependent aggregation‐enhanced photoacoustic of atomically precise metal nanocluster
Graphical Abstract
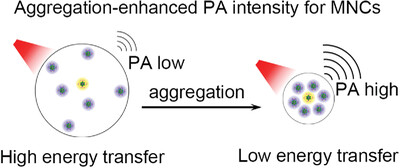
Hydrophilic Au25SR18 (SR = thiolate) exhibits photoacoustic (PA) signal intensity enhancement under weakly polar solvent induces aggregation, with the PA intensity and PA conversion efficiency highly dependent on the aggregation degree, while the aggregation-enhanced PA intensity (AEPA) positively correlates to the protected ligands. Further experiments show that the increased energy of AEPA originates from the aggregation inhibiting the intermolecular energy transfer from excited Au NCs to their surrounding medium molecules, rather than restricting radiative relaxations.
Realizing efficient emission and triple‐mode photoluminescence switching in air‐stable tin(IV)‐based metal halides via antimony doping and rational structural modulation
Graphical Abstract
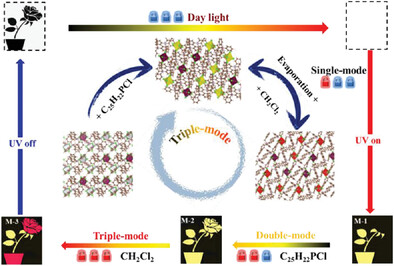
Three homologous compounds of Sb3+-doped zero-dimensional Sn(IV)-based metal halides with different crystal structures were synthesized, and they show different optical properties. Particularly, the nonemitting Sb3+−1 can be converted into yellow-emitting Sb3+−2α, and further turn into red-emitting Sb3+−2β under the treatment of C25H22PCl and CH2Cl2 solution, respectively. Thus, a triple-mode PL switching of off–onI–onII was constructed in Sb3+-doped Sn(IV)-based metal halides.
2022
Polarity‐triggered anti‐Kasha system for high‐contrast cell imaging and classification
Graphical Abstract
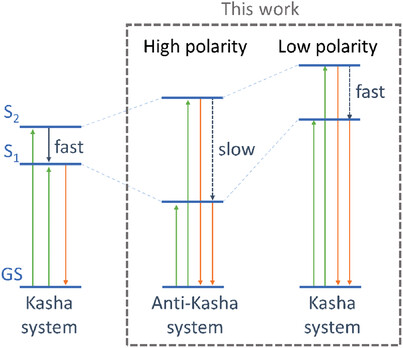
This paper provided a paradigm of an integrated chain to realize, design, synthesize, analyze, tune and utilize a system with anti-Kasha behavior. Anti-Kasha system in this work displayed not only academic and theoretical uniqueness, but also usefulness in cell-imaging with high contrast. Our work will make the anti-Kasha system more practical than theoretical, to unleash the power of infinite excited states.
Ratiometric hypoxia detection by bright organic room temperature phosphorescence of uniformed silica nanoparticles in water
Graphical Abstract
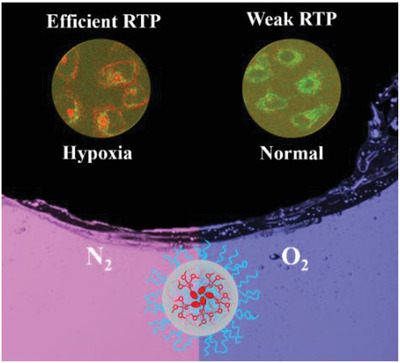
Incorporating organic phosphors to silica nanoparticles by covalent bonds shows high phosphorescence quantum yields (up to 22%) and long lifetimes (up to 3.5 ms) in aqueous phase. The dual fluorescence/phosphorescence of the monochromophore within the porous SiNPs successfully realized ratiometric hypoxia detection with ultrasensitivity (KSV = 449.3 bar−1).
Solid‐phase molecular self‐assembly facilitated supramolecular films with alternative hydrophobic/hydrophilic domains for skin moisture detection
Graphical Abstract
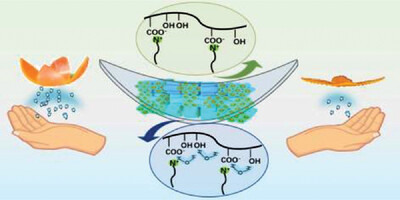
Upon pressing the precipitates formed with surfactants and oppositely charged polyelectrolytes, scaling up fabrication of macroscopic supramolecular films is possible. The hydrophobic mesophases composed of surfactant chains will greatly retard water diffusion inside the film, so that the film will bend upward automatically in touch with moisture environment. This can be utilized to create portable power-free skin moisture sensor.
Accurate and sensitive probing of onset of micellization based on absolute aggregation‐caused quenching effect
Graphical Abstract
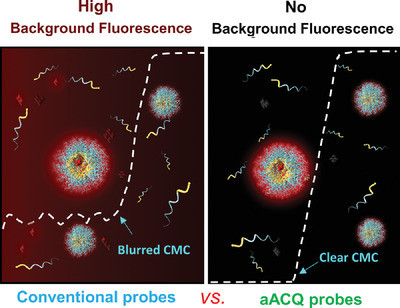
A novel method based on absolute aggregation-caused quenching (aACQ) probes is reported for critical micelle concentration (CMC) determination. These probes show absolutely no emission before micellization owing to molecular π–π stacking, while abruptly emit high and stable fluorescence upon micellization. Fast fluorescence “off/on” switching upon micellization/demicellization and background-free property make them outperform common probes for accurate and sensitive determination of ultralow CMCs.
An AIEgen/graphene oxide nanocomposite (AIEgen@GO)‐based two‐stage “turn‐on” nucleic acid biosensor for rapid detection of SARS‐CoV‐2 viral sequence
Graphical Abstract
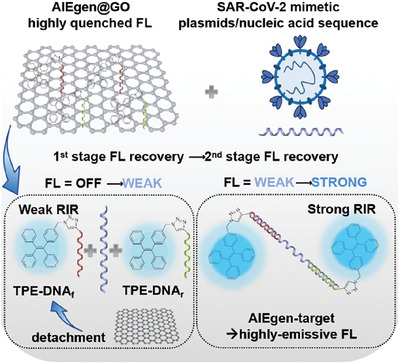
An AIEgen-graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposite-based assay is designed for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acids. The sensing mechanism is based on two-stage fluorescence signal recovery due to fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) effect by detaching AIEgen from GO surface and restricted intramolecular rotation (RIR) effect by formation of nucleic acid duplexes.
A fluorescent film sensor for high-performance detection of Listeria monocytogenes via vapor sampling
Graphical Abstract

A newly designed AIEgen-based fluorescent film sensor is developed and used successfully, for the first time, to detect gaseous 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, a biomarker of Listeria monocytogenes. The sensor depicts fast, sensitive, selective, and fully reversible sensing performance toward the analyte, as evidenced by the reliable finding of the foodborne pathogen at the very early stage.
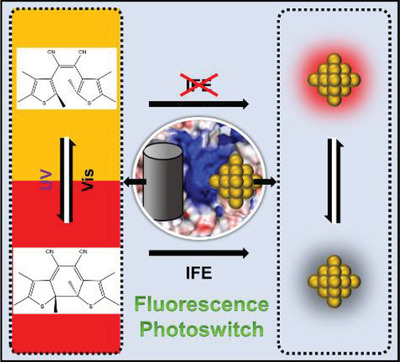
Site‐specific fabrication of gold nanocluster‐based fluorescence photoswitch enabled by the dual roles of albumin proteins
Graphical Abstract
2021
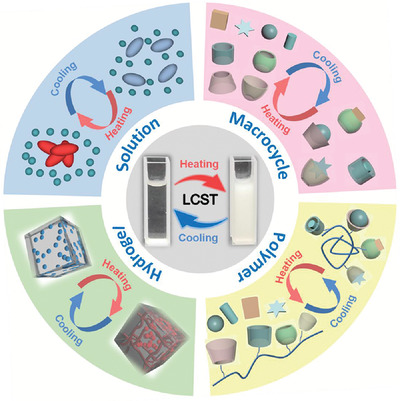
Supramolecular control over thermo‐responsive systems with lower critical solution temperature behavior
- Aggregate
- 35-47
- 10.1002/agt2.12
Luminescence anti‐counterfeiting: From elementary to advanced
- Aggregate
- 20-34
- 10.1002/agt2.15
Graphical Abstract
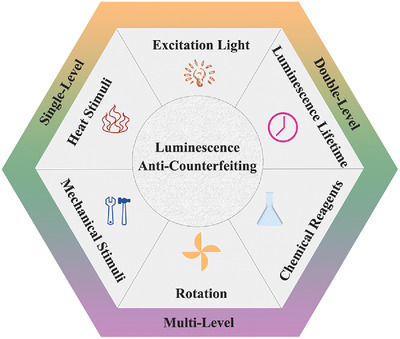
The luminescence of anti-counterfeiting labels can be triggered or changed by excitation light, luminescence lifetime, chemical reagents, heat, mechanical force, or rotation. In this review, according to the numbers of changes of anti-counterfeiting labels under various regulation conditions, anti-counterfeiting strategies are classified into three levels: single-level, double-level, and multilevel anti-counterfeiting, and the state-of-the-art research on luminescence anti-counterfeiting are presented.
Recent advances in AIEgen‐based crystalline porous materials for chemical sensing
Graphical Abstract
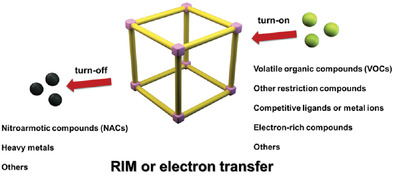
AIEgen-based crystalline porous materials were widely studied as chemical sensors with promising sensitivity and selectivity, short response time, and excellent recyclability. Two different sensing modes (“turn on” and “turn off”) were explored for monitoring various analytes, including hazardous wastes (NACs, heavy metals, and VOCs) and biomolecules (amino acids and drug). Chemical sensing behavior of AIE-active crystalline porous materials was summarized and some guidance for further development was provided.
Stereodefined tetraarylethylenes: Synthesis and applications
Graphical Abstract
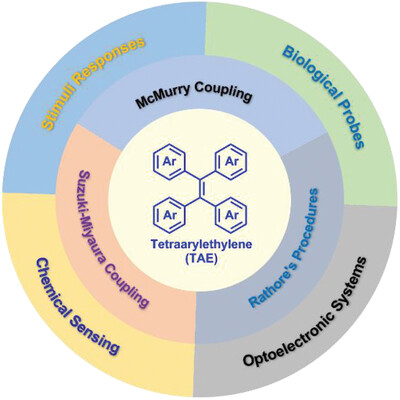
Among various luminogens, tetraarylethylenes attract considerable attentions due to their widespread applications in chemo-/biosensing and optoelectronic devices. The structural diversity of tetraarylethylenes constructs a powerful platform for exploring their distinguished high-tech applications. A variety of synthetic protocols for the preparation of stereodefined tetraarylethylenes are summarized, and differences in properties and applications of TAEs stereoisomers are also discussed.
Rational design for thermochromic luminescence in amorphous polystyrene films with bis-o-carborane-substituted enhanced conjugated molecule having aggregation-induced luminochromism
Graphical Abstract
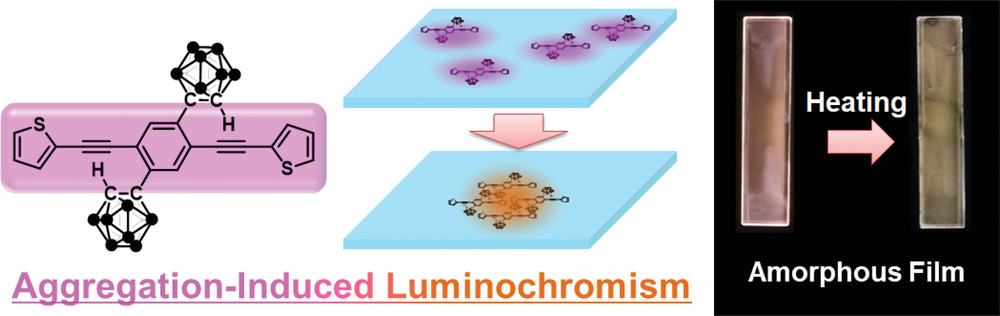
To realize aggregation-induced luminochromism in polystyrene, we designed bis-o-carborane-substituted conjugated triad. By loading the electron-rich unit, thiophene, onto the aggregation-induced emission-active skeleton, luminochromic behaviors by heating, followed by thermochromic luminescence, were obtained.
Optical nature of non‐substituted triphenylmethyl cation: Crystalline state emission, thermochromism, and phosphorescence
Graphical Abstract

The optical nature of non-substituted trityl hexafluorophosphate (PF6) in the crystalline state has been investigated. Trityl PF6 exists as two crystal polymorphs including yellow and orange crystals, and the crystals display different color emissions. Further investigation revealed that the orange crystal undergoes a color change to yellow upon cooling, and both crystals display phosphorescence.
Flexible sensors based on assembled carbon nanotubes
Graphical Abstract
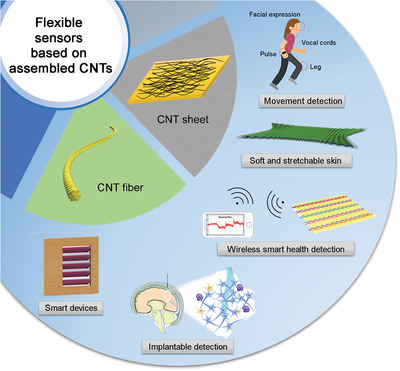
The recent advance of flexible sensors based on carbon nanotube assemblies as electrodes or functional materials has been carefully discussed, with an emphasis on understanding the working mechanism for their high sensing properties. The remaining challenges are finally highlighted to offer some insights for future study.