Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Articles
Pt/MnO2 Nanoflowers Anchored to Boron Nitride Aerogels for Highly Efficient Enrichment and Catalytic Oxidation of Formaldehyde at Room Temperature
- First Published: 20 December 2020
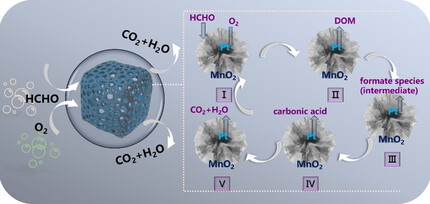
A three-dimensional monolithic Pt/MnO2-BN catalyst was prepared by anchoring Pt/MnO2 nanoflower on boron nitride (BN) aerogels. The as-formed porous aerogels catalyst offers a combination of adsorption and oxidation to efficiently remove formaldehyde at room temperature, as well as easier recycling and reuse in comparison with powdery catalysts.
A Superstrong and Reversible Ionic Crystal-Based Adhesive Inspired by Ice Adhesion
- First Published: 02 February 2021
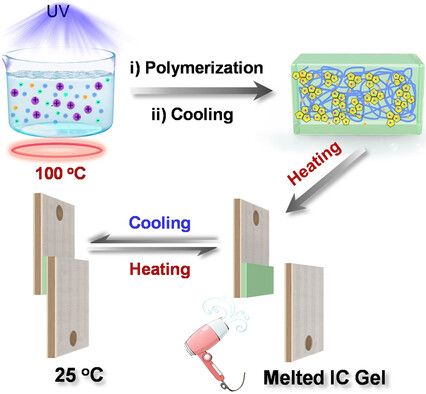
Inspired by reversible ice adhesion, a reversible ionic crystal (IC) based gel adhesive was prepared, which showed superstrong and reversible adhesion due to the phase transition of ICs. In addition, the reversible adhesion can be adjusted by heating and light, and be effectively monitored by resistance and capacitance.
Transfer, Amplification, Storage, and Complete Self-Recovery of Supramolecular Chirality in an Achiral Polymer System
- First Published: 22 June 2021
Controlling the Multiple Chiroptical Inversion in Biphasic Liquid-Crystalline Polymers
- First Published: 09 September 2021
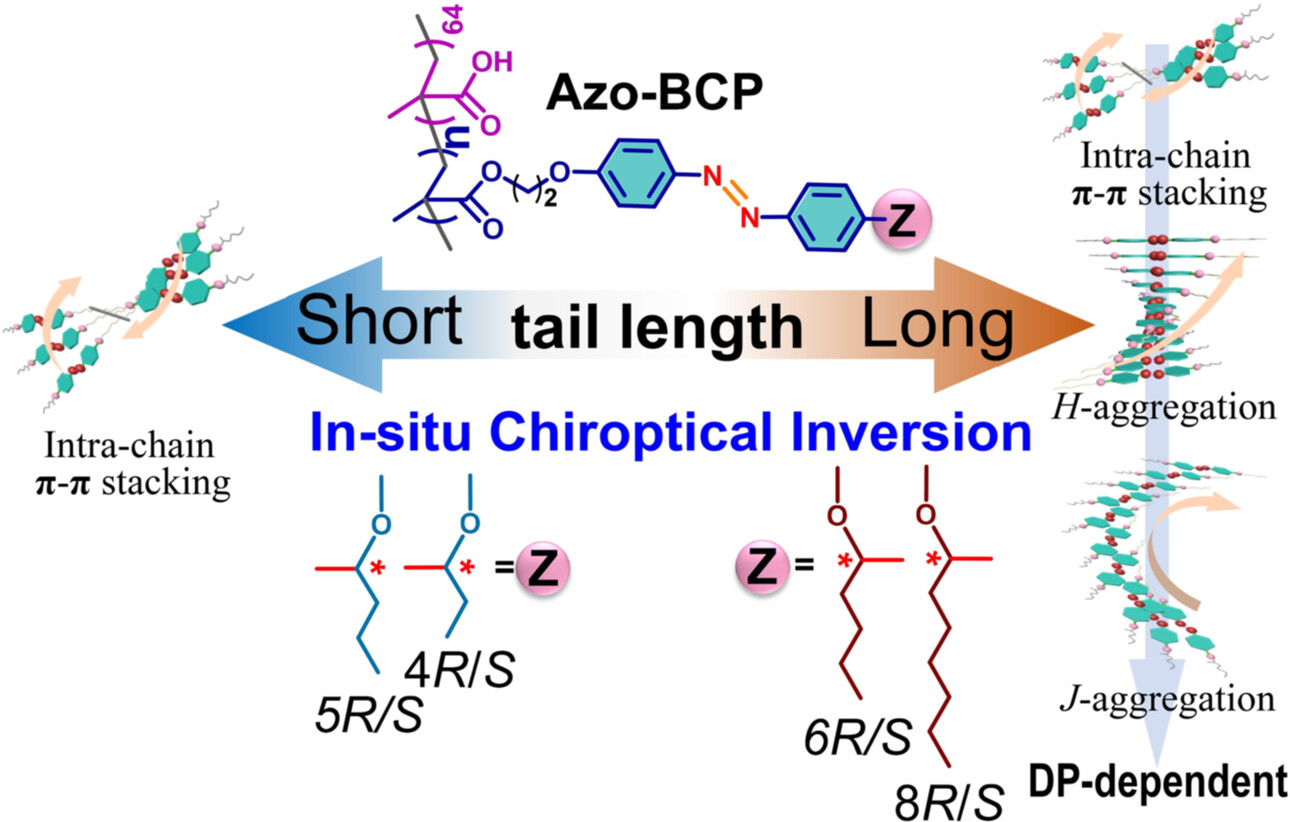
The multiple chiroptical inversion in Azo biphasic liquid-crystalline (LC) polymers is for the first time realized in situ through the tail length modification and degree of polymerization (DP) variation. The amorphous-to-LC phase transition and biphasic LC interconversion allow the transcription of three stacking modes, thereby controlling the dynamic reversal of supramolecular chirality.
Rhenium-Catalyzed Arylation–Acyl Cyclization between Enol Lactones and Organomagnesium Halides: Facile Synthesis of Indenones
- First Published: 28 April 2021
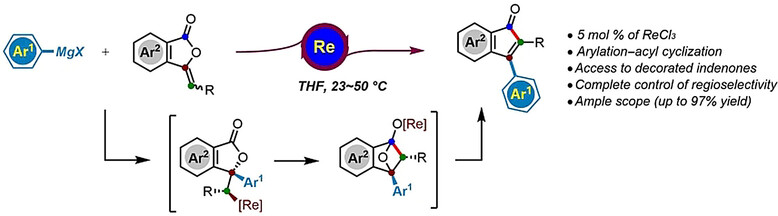
A range of functionalized organomagnesium halides and enol lactones underwent rhenium-catalyzed sequential arylation–acyl cyclization under mild reaction conditions, thus providing an expedient route to polyfunctionalized indenones with complete control of regioselectivity. This approach features a broad substrate scope, excellent functional group tolerance, and synthetic utility in the straightforward synthesis of biologically relevant molecules.
Built-in Electric Field Triggered Interfacial Accumulation Effect for Efficient Nitrate Removal at Ultra-Low Concentration and Electroreduction to Ammonia
- First Published: 25 August 2021
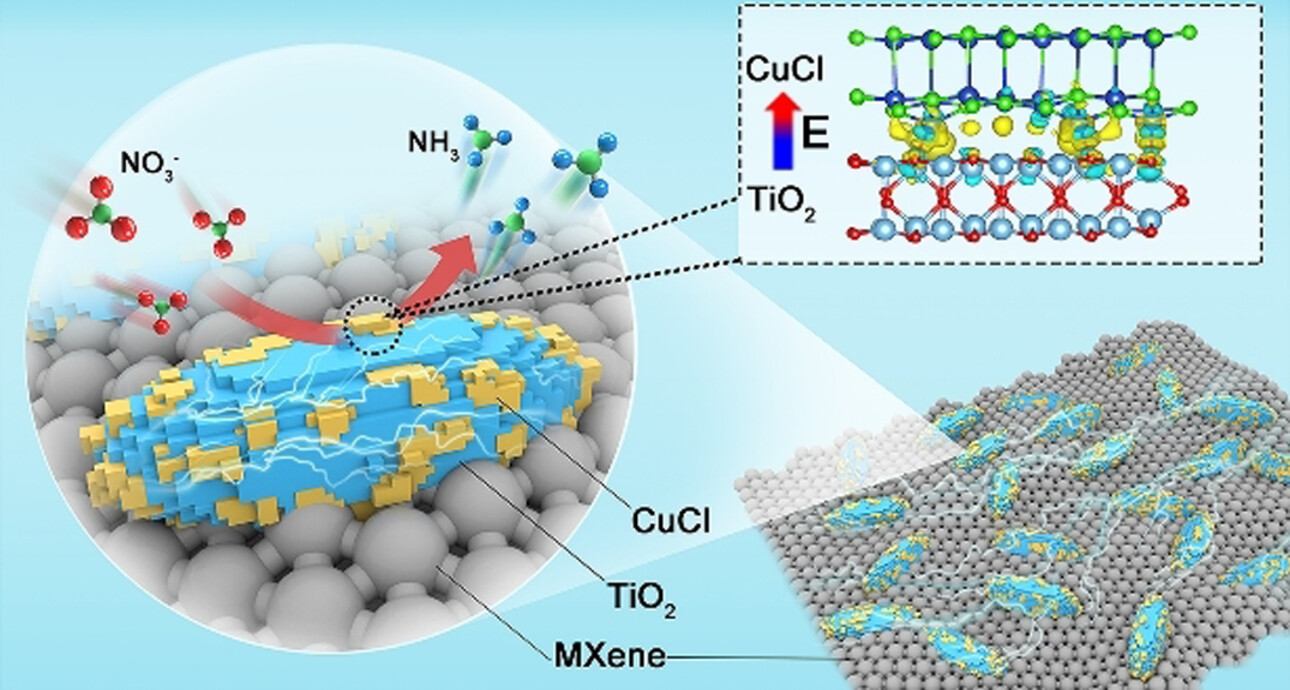
An electrocatalyst is created by stacking CuCl (111) and rutile TiO2 (110) layers together. A built-in electric field induced from the electron transfer from TiO2 to CuCl (CuCl_BEF) is thus formed, which triggers interfacial accumulation of NO3− ions around the electrocatalyst. A NH3 product selectivity of 98.6 %, a low NO2− production of <0.6 %, and mass-specific ammonia production rate of 64.4 h−1 is achieved.
Alkene Difunctionalization Triggered by a Stabilized Allenyl Radical: Concomitant Installation of Two Unsaturated C−C Bonds
- First Published: 20 June 2021
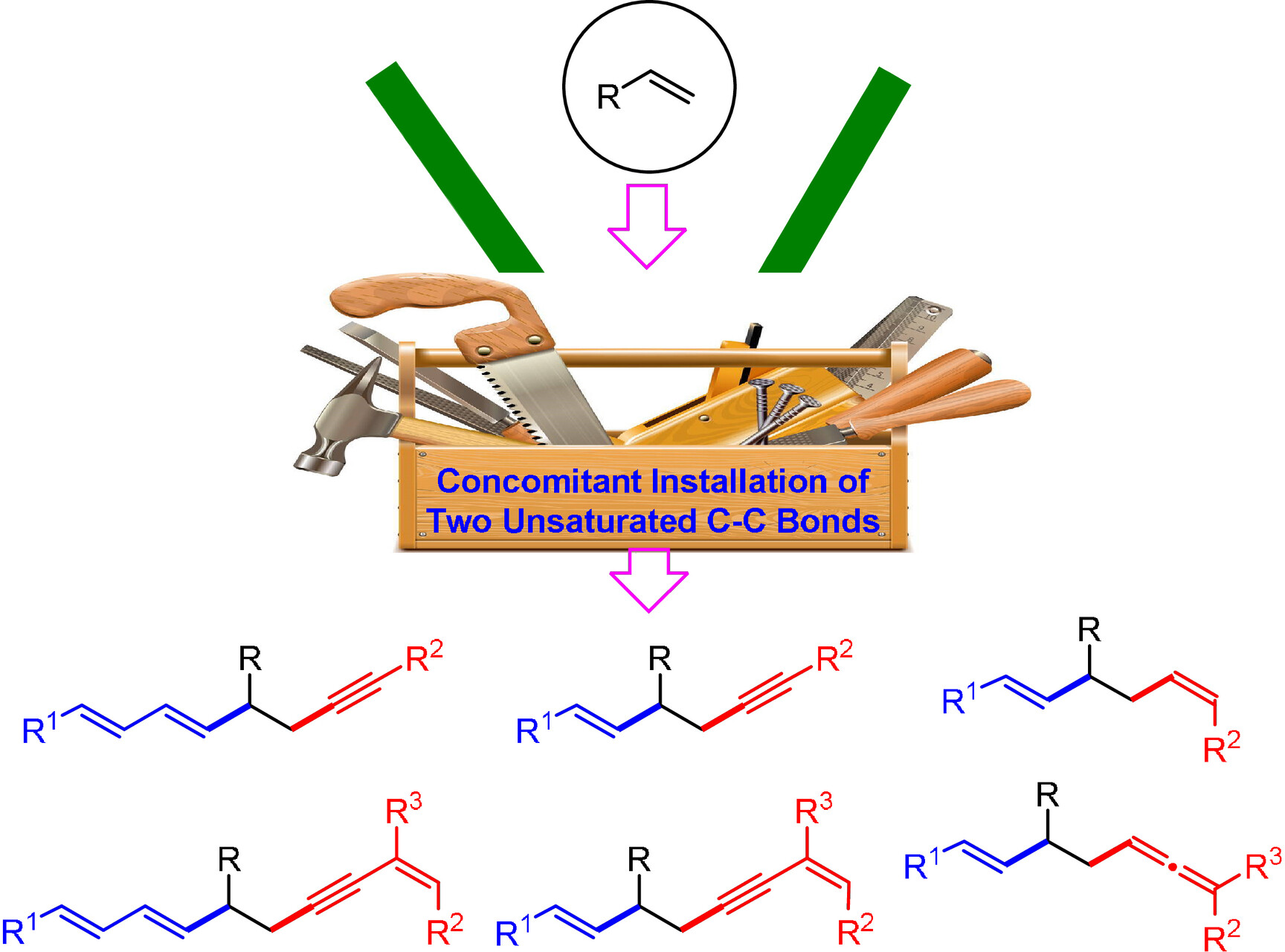
Disclosed herein for the first time is the photocatalytic 1,2-alkynylalkenylation and 1,2-enynylalkenylation of alkenes, triggered by the intermolecular addition of a stabilized allenyl radical to an alkene. A portfolio of strategically designed, easily accessible dual-function reagents are applied to a radical docking-migration cascade. The protocol has broad substrate scope and efficiently increases the degree of unsaturation.
Heterocyclization Reagents for Rapid Assembly of N-Fused Heteroarenes from Alkenes
- First Published: 02 November 2020
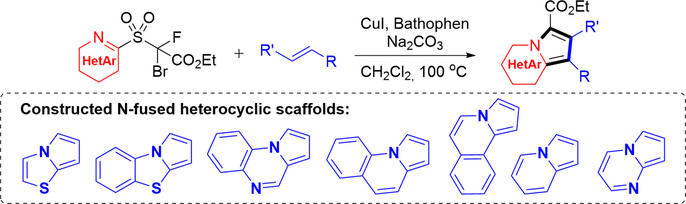
Described herein is a conceptually new approach for the synthesis of N-fused heteroarenes from alkenes. A portfolio of rationally designed heterocyclization reagents are readily prepared for the cascade reaction. A variety of N-fused heteroarenes involving seven types of heterocyclic core are accomplished.
Photoredox-Catalyst-Enabled para-Selective Trifluoromethylation of tert-Butyl Arylcarbamates
- First Published: 23 June 2021
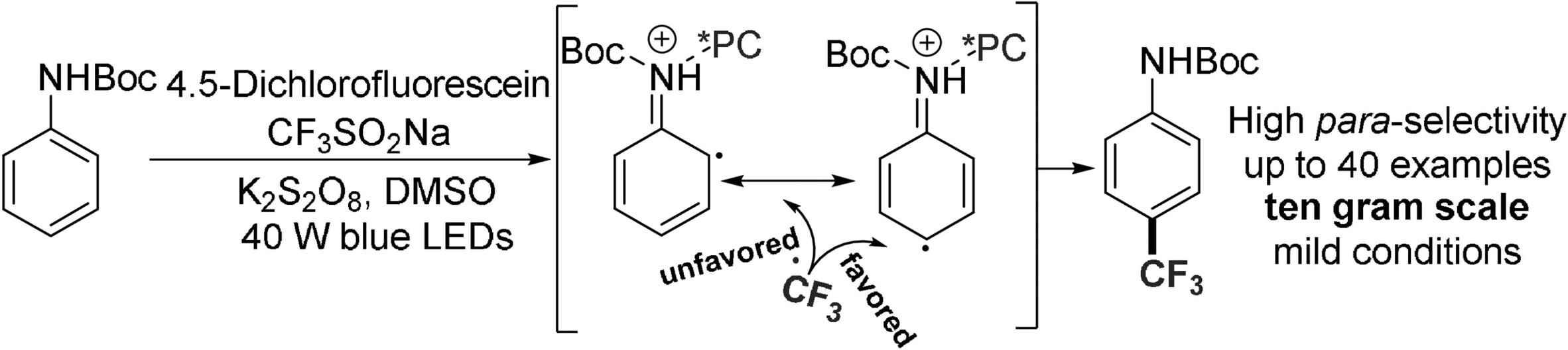
We report a light-promoted 4,5-dichlorofluorescein (DCFS)-enabled para-selective C−H trifluoromethylation of arylcarbamates using the Langlois reagent. Arylcarbamates, including the bioactive compound chlorzoxazone, vorinostat precursor, chlorpropham, and teriflunomide precursors, were suitable for this reaction, leading to the formation of the corresponding products in moderate to good yields.
An Ion-In-Conjugation-Boosted Organic Semiconductor Gas Sensor Operating at High Temperature and Immune to Moisture
- First Published: 22 April 2021
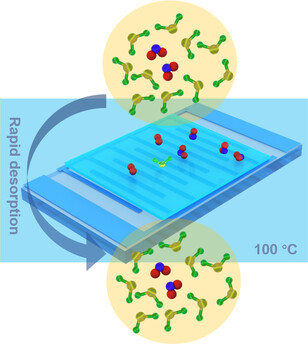
A robust NO2 sensor device based on an ion-in-conjugation structure maintained its performance at high temperature, which counteracted the effects of humidity (see picture; NO2 blue/red, H2O green/yellow). Charge transfer between NO2 and the chemiresistor was more efficient at 100 °C than at room temperature. The fabricated sensor had a parts-per-billion (ppb) NO2 detection limit and showed the highest sensitivity of all reported NO2 chemiresistive sensors.
A MOF-based Ultra-Strong Acetylene Nano-trap for Highly Efficient C2H2/CO2 Separation
- First Published: 06 January 2021
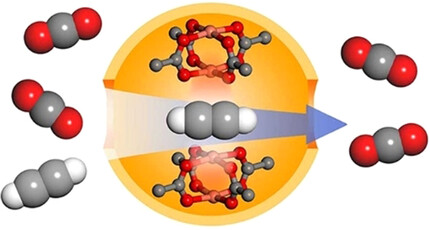
A new type of ultra-strong C2H2 nano-trap featuring the synergistic effect of multiple open metal sites has been proposed for separating C2H2/CO2 mixture gas. The unique C2H2 nano-trap shows the strongest binding interaction with C2H2 and a benchmark for C2H2/CO2 separation. The binding mechanism for C2H2 was studied through single-crystal X-ray diffraction experiments and molecular simulation studies.
Optimized Active Layer Morphologies via Ternary Copolymerization of Polymer Donors for 17.6 % Efficiency Organic Solar Cells with Enhanced Fill Factor
- First Published: 15 October 2020
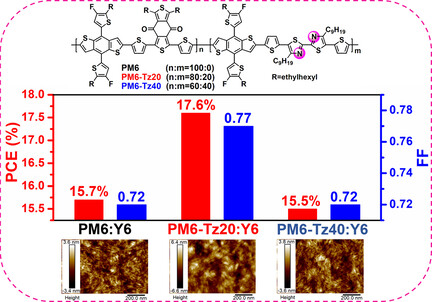
A terpolymer donor PM6-Tz20 was developed by incorporating the third 5,5′-dithienyl-2,2′-bithiazole (DTBTz) unit into the PM6 backbone. The introduction of DTBTz can tailor the molecular ordering, orientation, and aggregation properties, and then optimize the morphology and electrical properties of devices, ultimately improving fill factor (0.77) and thus device efficiency (17.6 %).
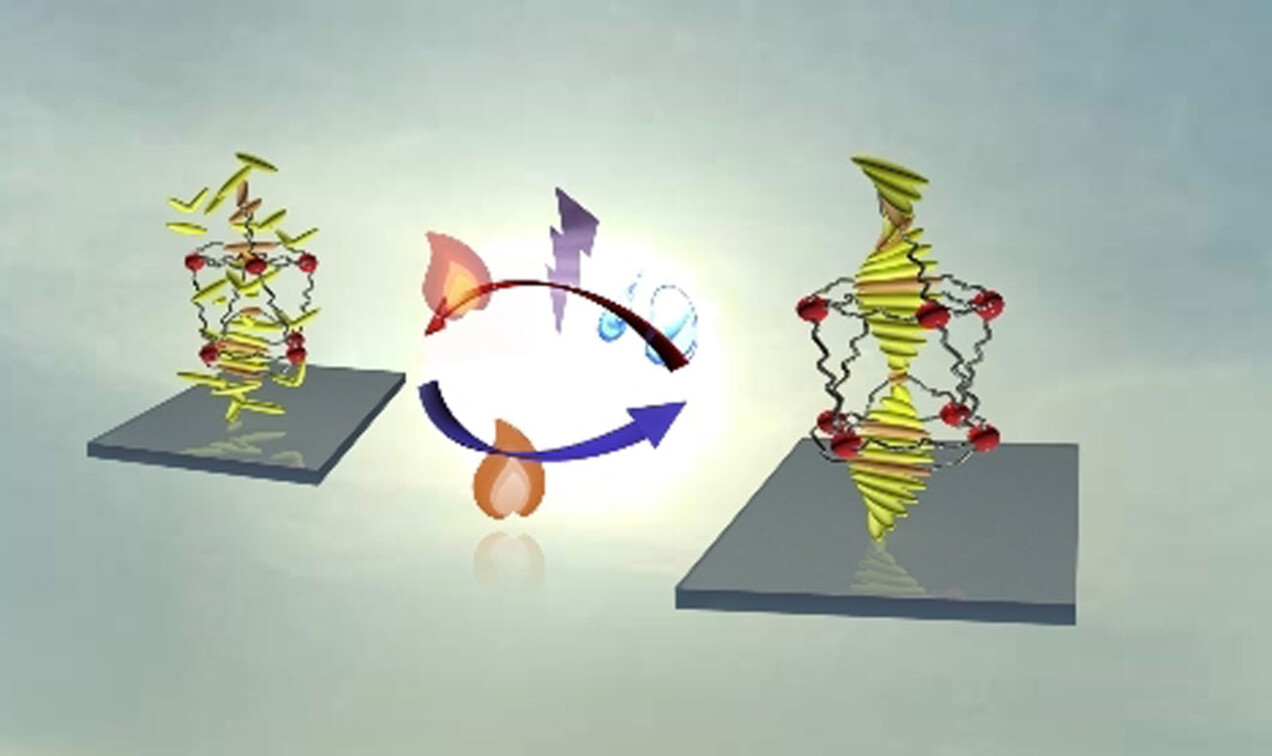
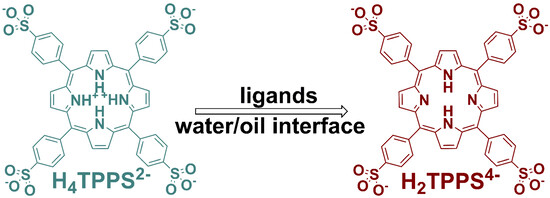
Surfactant-Induced Interfacial Aggregation of Porphyrins for Structuring Color-Tunable Liquids
- First Published: 28 October 2020
Yttrium-Catalyzed ortho-Selective C−H Borylation of Pyridines with Pinacolborane
- First Published: 09 March 2022
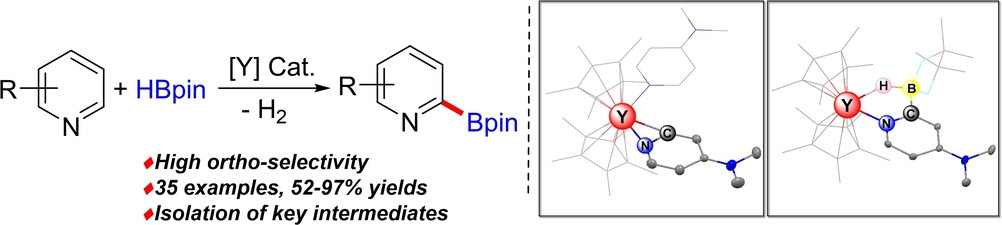
The ortho-selective C−H borylation of a wide range of pyridines using pinacolborane was achieved through yttrium catalysis. Notably, the possible hydroboration side reaction was effectively suppressed by using the proper ligand/metal combination. The resultant 2-pyridyl boronates were subjected to further transformations such as a Suzuki–Miyaura coupling or the Chan–Lam amination.
Salt-Stabilized Silylzinc Pivalates for Nickel-Catalyzed Carbosilylation of Alkenes
- First Published: 18 February 2022
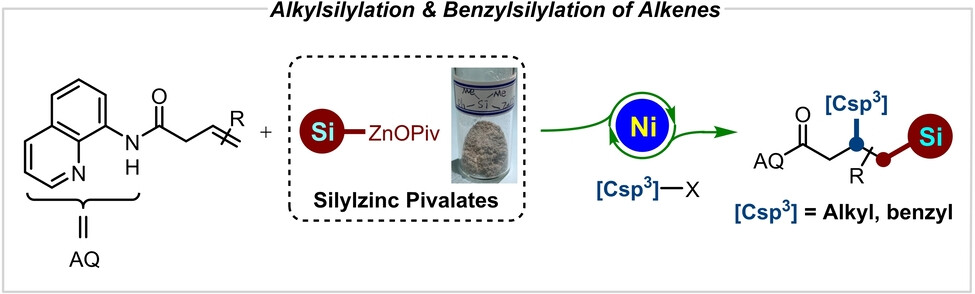
A new type of salt-stabilized solid silylzinc pivalate prepared from the silyllithium reagents via transmetalation with Zn(OPiv)2 is reported. These silylzinc pivalates showed enhanced air and moisture stability and unique reactivity in the nickel-catalyzed regioselective alkyl and benzylsilylation of alkenes. Kinetic experiments highlighted the crucial involvement of OPiv-coordination in improving the reactivity of silylzinc pivalates.
Construction of Perylene-based Amphiphilic Micelle and Its Efficient Adsorption and In Situ Photodegradation of Bisphenol A in Aqueous Solution
- First Published: 16 August 2022
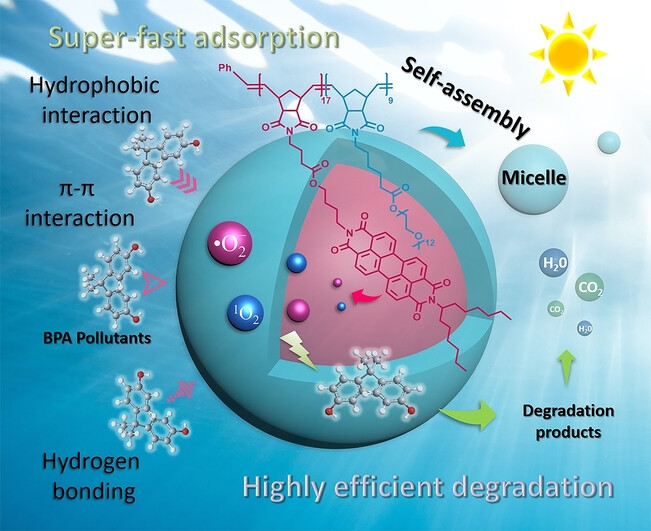
A new idea of designing self-assembled amphiphilic micelles containing photo-functional perylene blocks for “selective adsorption/catalytic degradation” of bisphenol A (BPA) has been put forward. The results show that the micelles possess high mass-transfer efficiency with ultrafast adsorption rate (within 10 s), high adsorption capacity (448 mg g−1), and high selectivity for BPA, which greatly improves the BPA photodegradation efficiency.
Organic Branched Heterostructures with Optical Interconnects for Photonic Barcodes
- First Published: 15 March 2022
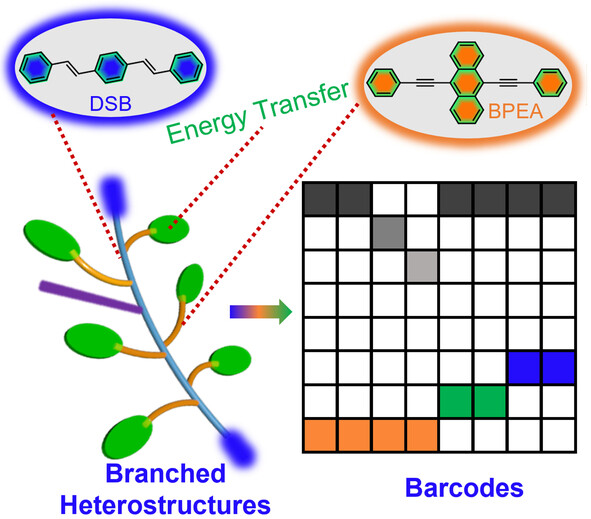
The precise synthesis of well-defined organic heterostructures toward active optoelectronic functions remains challenging. Optical interconnections based on organic branched heterostructures (OBHs) have been synthesized through a sequential self-assembly process. The accurate spatial organization has been applied to the generation of 2D barcodes.
Asymmetric Radical Cyclization of Alkenes by Stereospecific Homolytic Substitution of Sulfinamides
- First Published: 13 May 2022
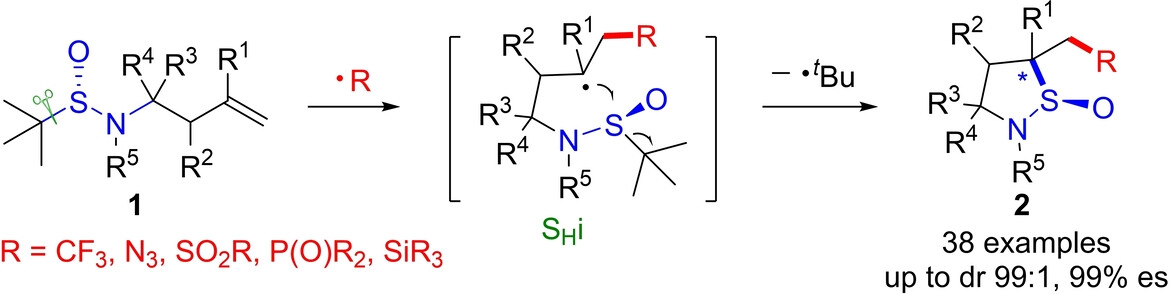
A novel asymmetric radical cyclization of alkenes via stereospecific homolytic substitution of sulfonamides was established, allowing ready access to a diversity of cyclic sulfinamides with excellent stereocontrol. The protocol offers a robust tool for the synthesis of chiral sulfinamides and their derivatives.
Molecular Self-Assembly Regulated Dopant-Free Hole Transport Materials for Efficient and Stable n-i-p Perovskite Solar Cells and Scalable Modules
- First Published: 05 September 2022
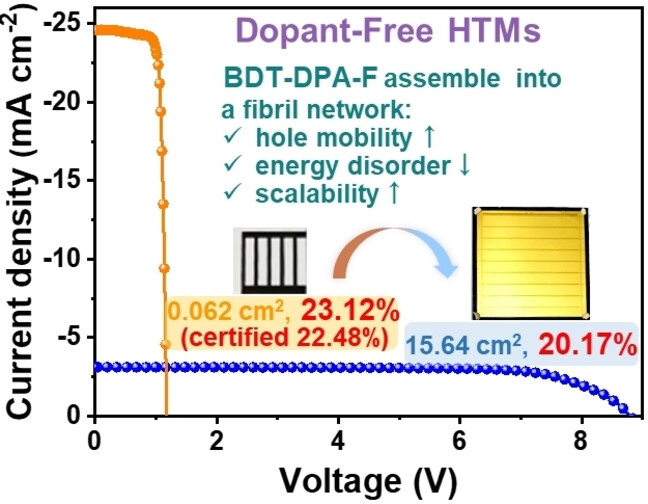
A hole transport material (BDT-DPA-F) is designed, and it can assemble into a fibril network, showing an obviously improved hole mobility, a decreased energy disorder and high scalability. The perovskite solar cells based on BDT-DPA-F without any dopant obtain promising power conversion efficiencies of 23.12 % (certified 22.48 %) for small-area devices (0.062 cm2) and 20.17 % for large-area modules (15.64 cm2).
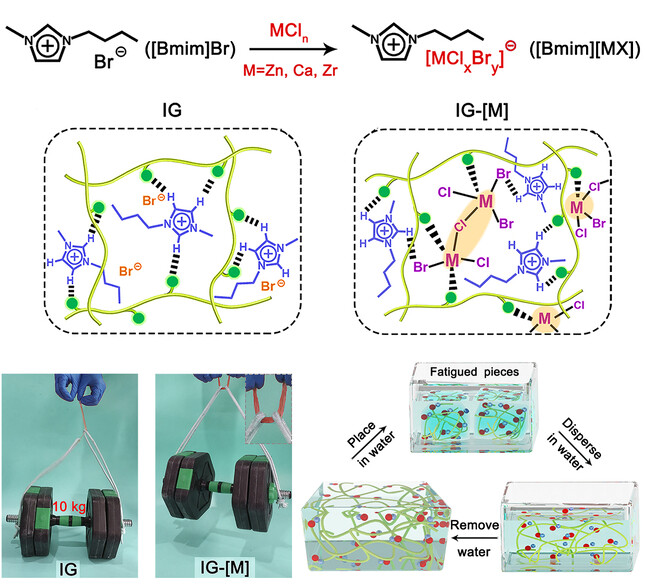
Ultra-Tough and Recyclable Ionogels Constructed by Coordinated Supramolecular Solvents
- First Published: 20 October 2022