Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Machine-learning analysis identifies “elite” viral controllers with increased survival and homeostatic responses in critical COVID-19
- First Published: 25 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Myeloid deficiency of Z-DNA binding protein 1 restricts septic cardiomyopathy via promoting macrophage polarisation towards the M2-subtype
- First Published: 27 April 2025
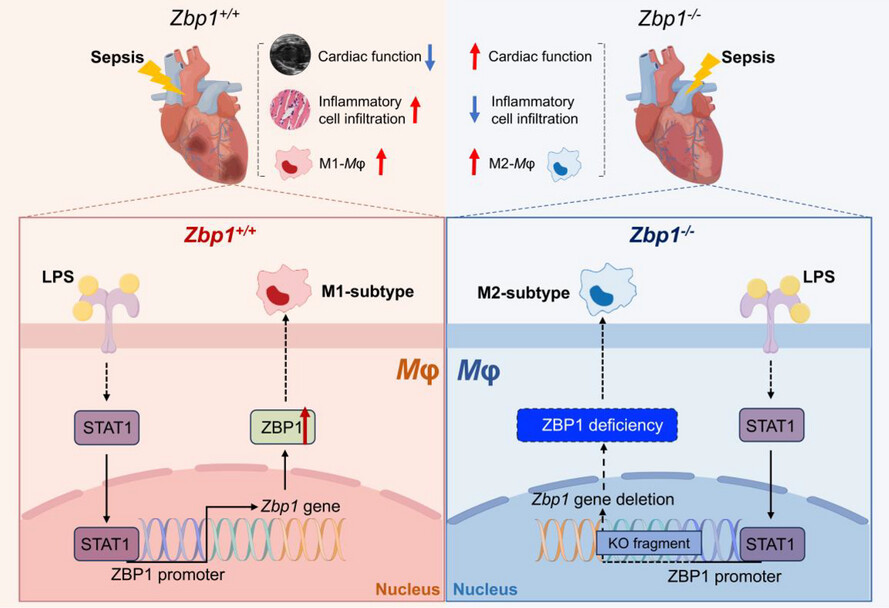
LPS induces the transcription and expression of ZBP1 via STAT1, driving macrophage polarisation towards the pro-inflammatory M1-subtype macrophage, which results in inflammatory cell infiltration and cardiac dysfunction. In contrast, myeloid-specific ZBP1 deficiency shifts macrophages towards the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, reducing inflammatory cell infiltration and alleviating cardiac dysfunction. These findings highlight the role of macrophage-derived ZBP1 in septic cardiomyopathy, suggesting that ZBP1 could be a potential therapeutic target for septic cardiomyopathy.
Mφ, macrophage. KO fragment, knockout fragment of Zbp1 gene.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Induction of HMOX1 by mesenchymal stem cell cytotherapy inhibits osteoclastogenesis and myeloma-induced bone disease
- First Published: 27 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
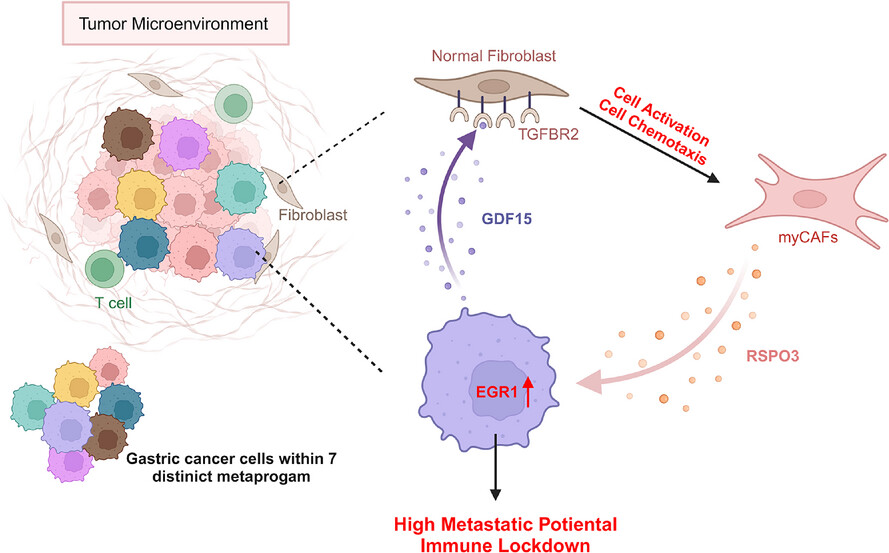
Deciphering of intra-tumoural heterogeneity and the interplay between metastasis-associated meta-program and myofibroblasts in gastric cancer
- First Published: 28 April 2025
cGAS/STING signalling in macrophages aggravates obliterative bronchiolitis via an IFN-α-dependent mechanism after orthotopic tracheal transplantation in mice
- First Published: 28 April 2025
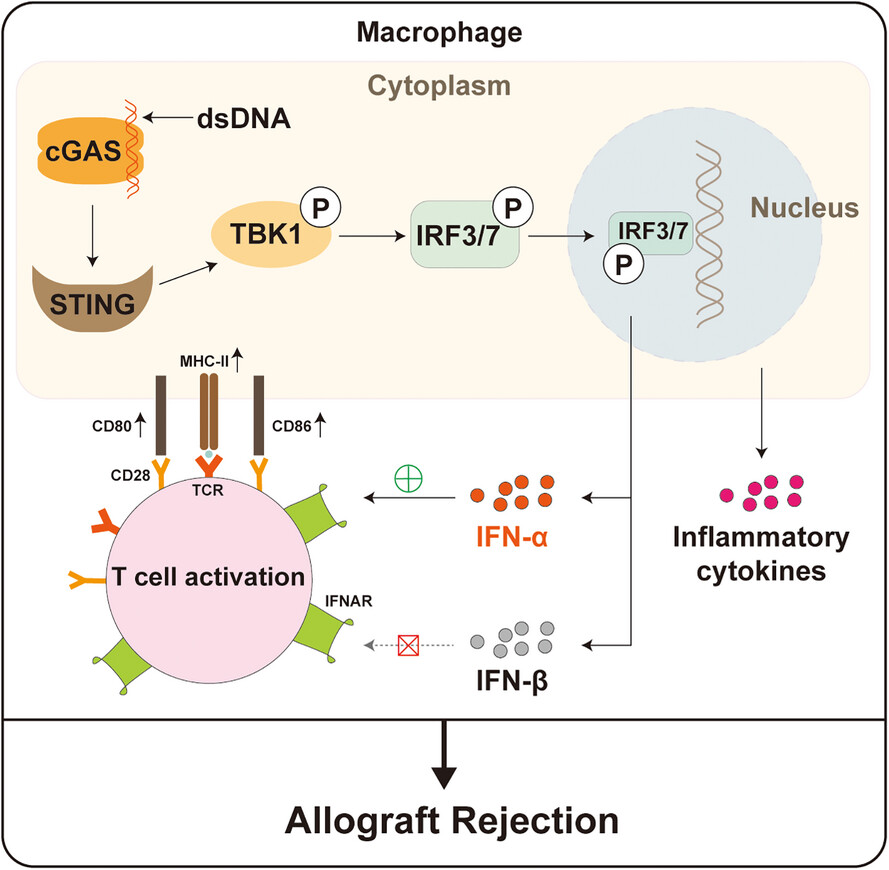
• cGAS/STING signalling pathway was activated in macrophages infiltrating allografts.
• cGAS/STING signalling pathway in macrophages exacerbated allograft rejection, promoted antigen-presenting ability of macrophages and enhanced alloreactive T-cell responses in an IFN-α2-dependent manner.
• STING inhibition potentiated the therapeutic efficacy of CTLA4-Ig in OB.
INVITED LETTER
Enhancing the safety and efficacy of cell therapy with programmed sense-and-respond function
- First Published: 28 April 2025
Tackling aggression: Translating preclinical insights into clinical relevance
- First Published: 02 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Targeting capacity, safety and efficacy of engineered extracellular vesicles delivered by transdermal microneedles to treat plasmacytoma in mice
- First Published: 02 May 2025
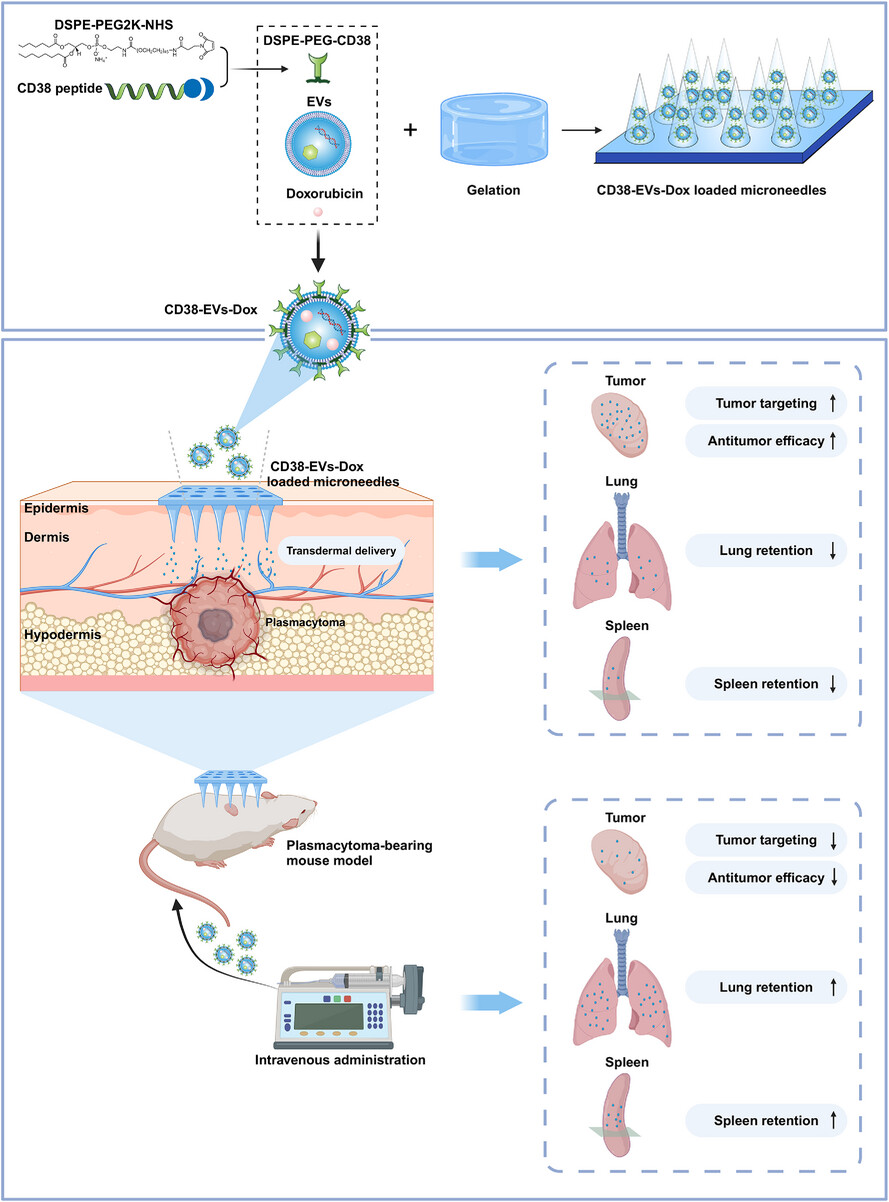
A schematic illustration of engineered EVs (CD38-EVs-Dox) delivered via MNs or intravenous administration for plasmacytoma treatment. CD38-EVs encapsulated within MNs effectively enhanced tumour cell targeting compared to standard EVs in MNs and intravenously administered CD38-EVs, with reduced lung and spleen distribution.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Abnormal lineage differentiation of peri-implantation aneuploid embryos revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing
- First Published: 07 May 2025
Fluorescence imaging assisted precise assessment of the depth of myometrial invasion in endometrial cancer lesions
- First Published: 07 May 2025
REVIEW
Obesity: Next game changer of allergic airway diseases?
- First Published: 07 May 2025
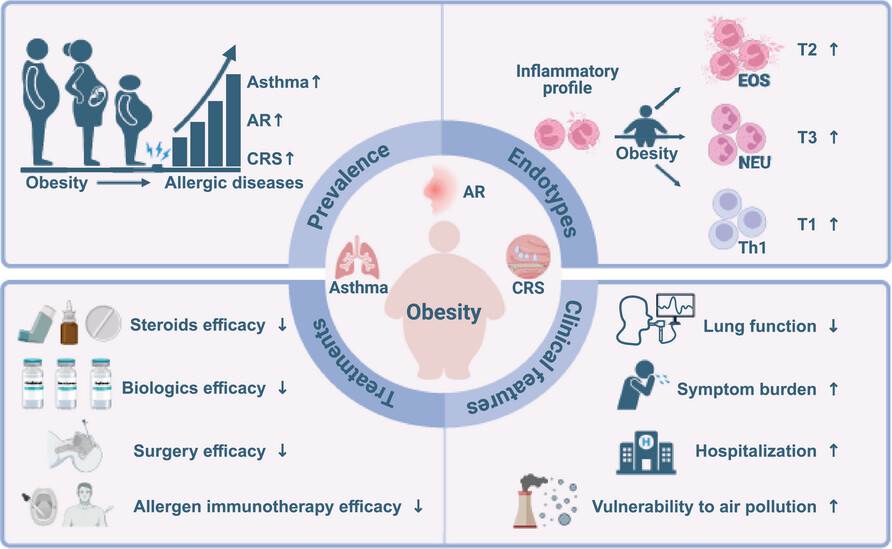
Obesity affects various aspects of allergic airway diseases, including prevalence, endotypes, clinical features and therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, obesity-related allergic airway diseases represent a unique class of endotypes and phenotypes, which need much more in-depth research for tailored treatment.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
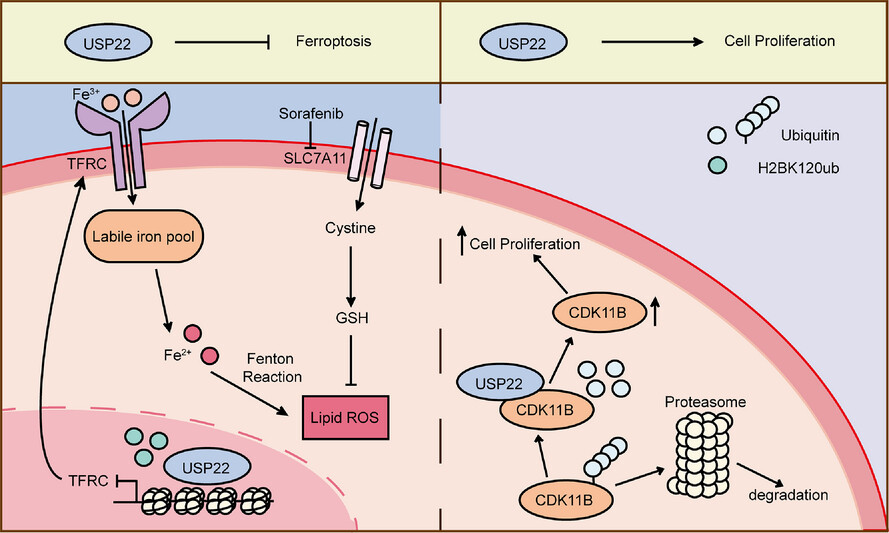
USP22 promotes the proliferation and Sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via its deubiquitinase activity
- First Published: 07 May 2025
Downregulation of SENP1 impairs nuclear condensation of MEF2C and deteriorates ischemic cardiomyopathy
- First Published: 07 May 2025
-
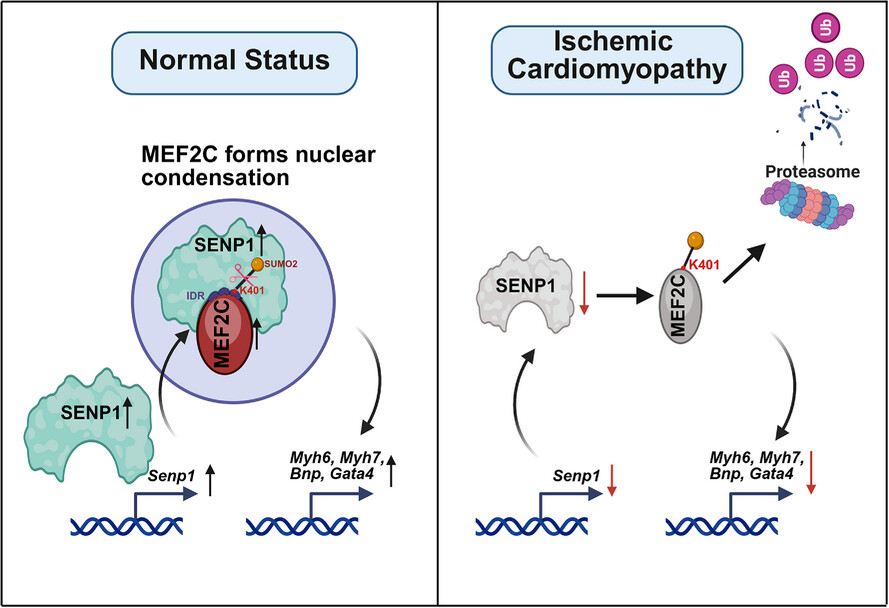
SNEP1 is downregulated in the cardiomyocyte of ICM mouse models and in patients.
-
SENP1 deSUMOylates the SUMO2-mediated modification of MEF2C at lysine 401 for protein stability.
-
The interaction with SENP1 controls the nuclear condensation of MEF2C to promote cardiomyocyte function.
-
Cardiac rescue of SENP1 alleviates ischemic heart injury in ICM mouse models by AAV9.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
CRISPRi screening identifies PIKfyve as a co-therapeutic target for obinutuzumab
- First Published: 07 May 2025
REVIEW
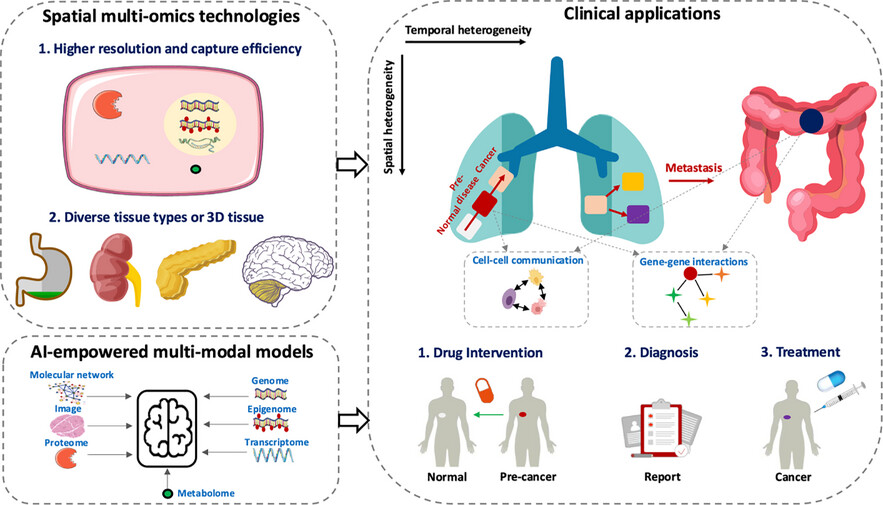
Unravelling tumour spatiotemporal heterogeneity using spatial multimodal data
- First Published: 07 May 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Changes in plasma lipid composition upon glucocorticoid treatment in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia
- First Published: 07 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 deletion reshapes tumour microenvironment to overcome acquired resistance to anti-programmed death 1 therapy in liver cancer
- First Published: 12 May 2025
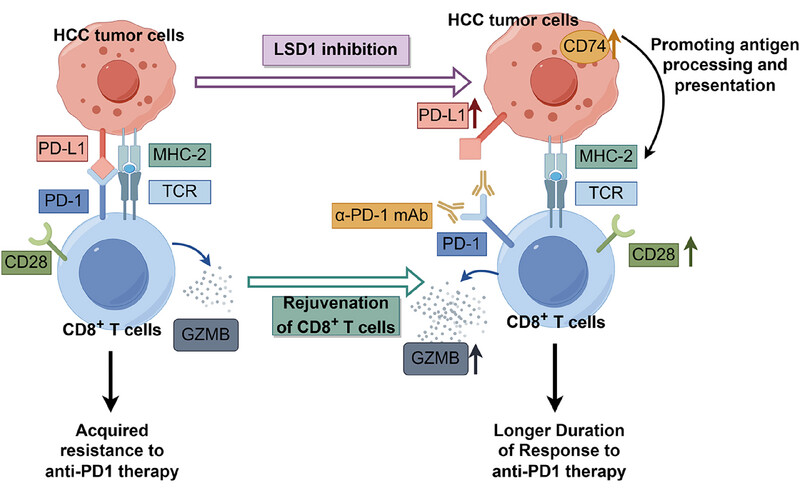
LSD1 deletion increased PD-L1 expression in tumor cells, rejuvenated effector CD8+ T cells, and enhanced antigen presentation. Combination therapy with an LSD1 inhibitor and anti-PD1 antibody remodeled the tumor microenvironment, reversing the acquired resistance and prolonging the duration of response to anti-PD1 therapy.
REVIEW
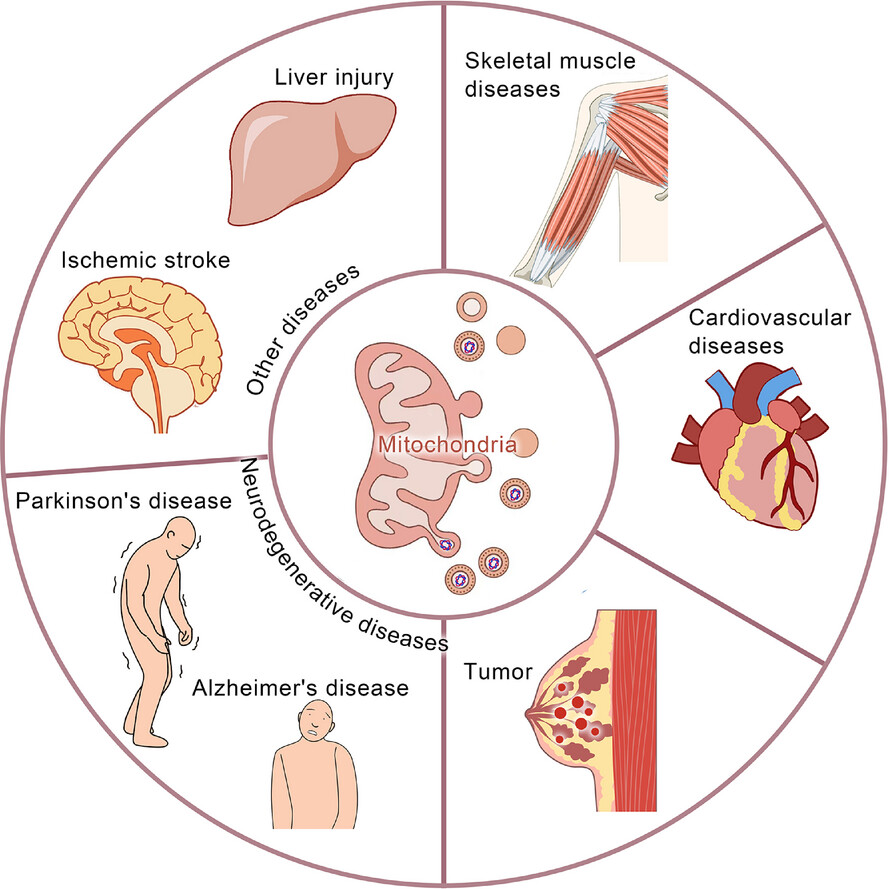
Mitochondria-derived vesicles: A promising and potential target for tumour therapy
- First Published: 12 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
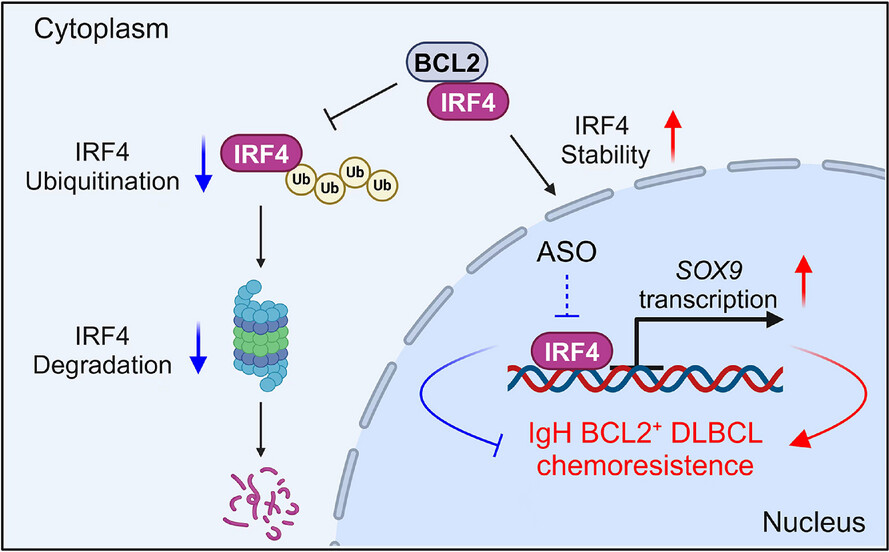
IRF4 contributes to chemoresistance in IGH::BCL2-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphomas by mediating BCL2-induced SOX9 expression
- First Published: 12 May 2025
Upregulated CEMIP promotes intervertebral disc degeneration via AP-1-mediated change in chromatin accessibility
- First Published: 21 May 2025
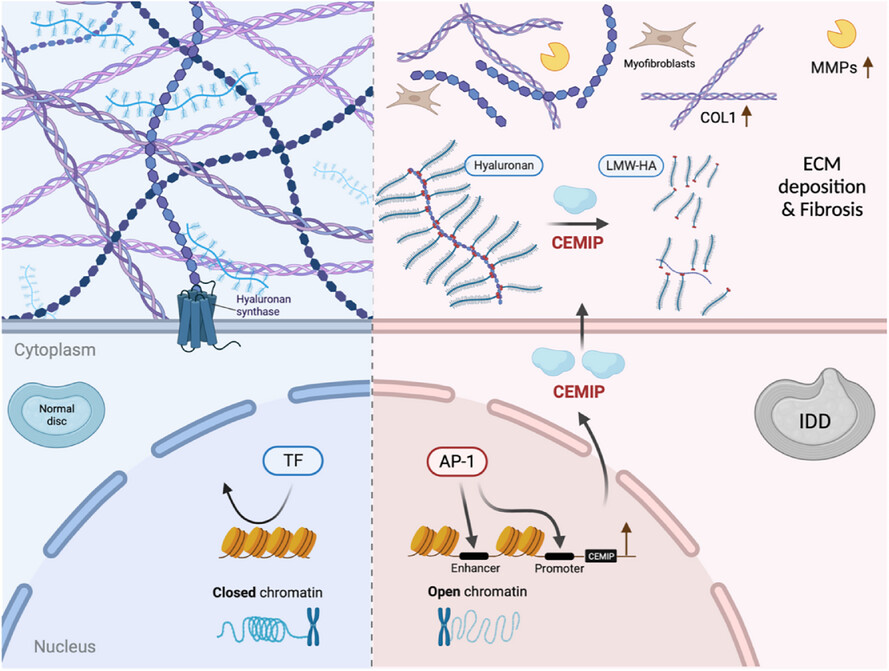
In degenerated NPCs, AP-1 activation increased the accessibility of chromatin to transcriptionally upregulate CEMIP, while CEMIP disrupted ECM homeostasis through its regulation of HMW-HA degradation, and its contribution to fibrotic changes within NP tissues. The AP-1/CEMIP axis emerges as a novel target for the prevention and treatment of IDD.
REVIEW
Neuroimmune interactions: The bridge between inflammatory bowel disease and the gut microbiota
- First Published: 21 May 2025
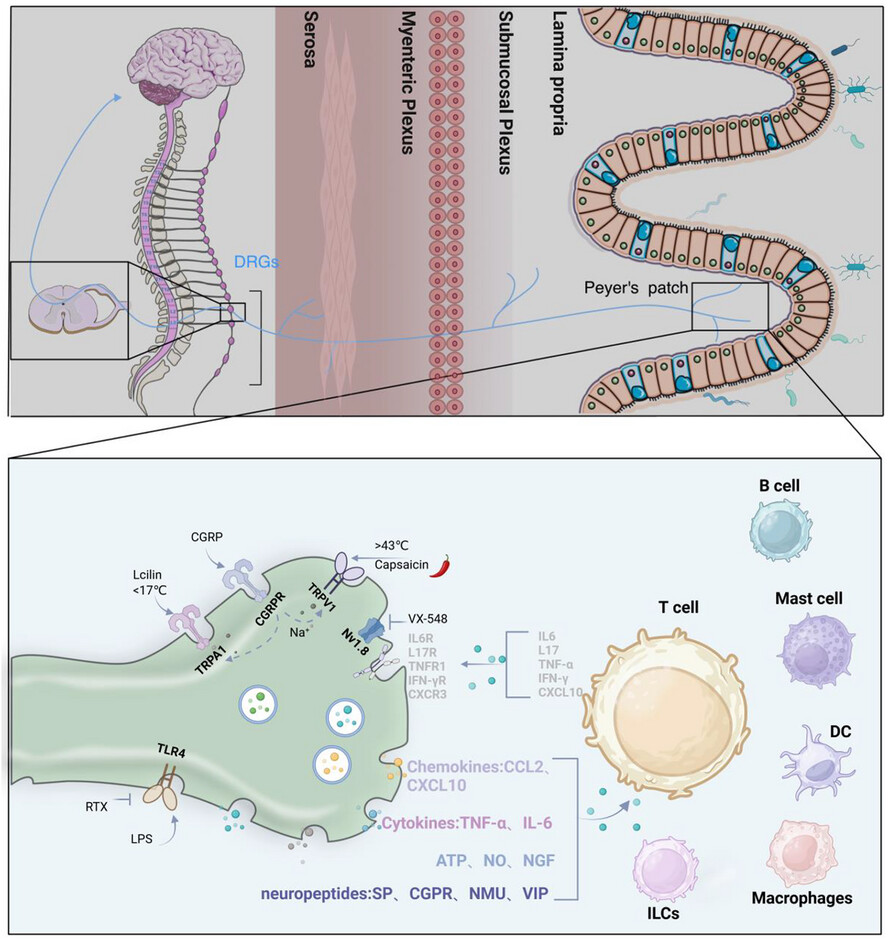
- The gut microbiota regulates the gut–brain–immune axis, modulating neuroimmune interactions in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Microbiota-derived metabolites influence immune cells, driving cytokine release that activates dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons.
- DRG neurons secrete mediators, enabling bidirectional neuroimmune communication essential for intestinal homeostasis.
- Disruptions contribute to IBD, offering therapeutic targets. Graphic created with BioRender.com (https://biorender.com).
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Comparative impact of proton versus photon irradiation on triple-negative breast cancer: Role of VEGFC in tumour aggressiveness
- First Published: 21 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
VSIG4 Promotes Tumour-Associated Macrophage M2 Polarization and Immune Escape in Colorectal Cancer via Fatty Acid Oxidation Pathway
- First Published: 22 May 2025
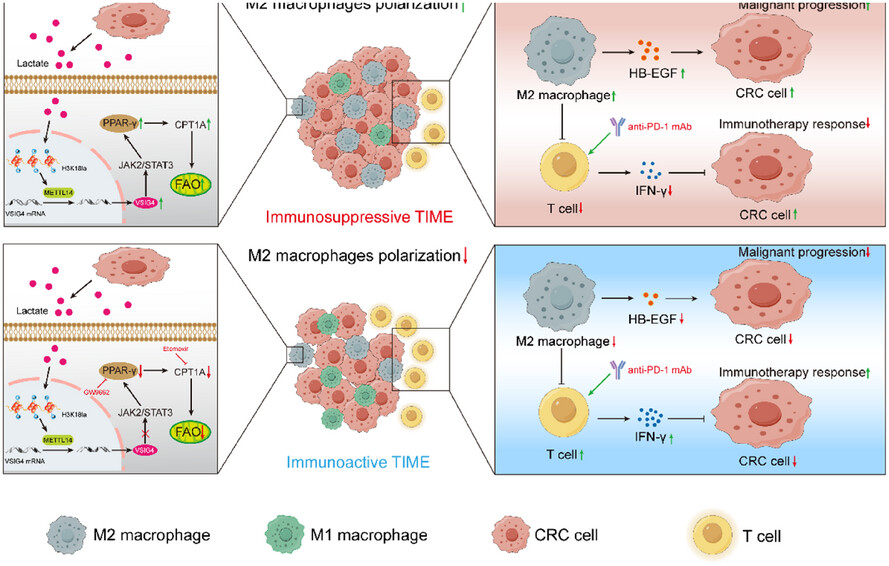
-
Colorectal cancer cells secrete lactate to upregulate VSIG4 in macrophages via the H3K18la-METTL14-m6A axis.
-
VSIG4 promotes fatty acid oxidation of macrophages and drives its M2-type polarization.
-
These VSIG4-expressing M2 macrophages promote tumour progression and an immunosuppressive microenvironment.
-
Inhibition of VSIG4 expression can synergistically enhance the therapeutic effect of anti-PD-1 antibody.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Macrophage C1q contributes to pulmonary fibrosis by disturbing the metabolism of alveolar epithelial cells
- First Published: 22 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Microbial metabolism mediates the deteriorative effects of sedentary behaviour on insulin resistance
- First Published: 24 May 2025
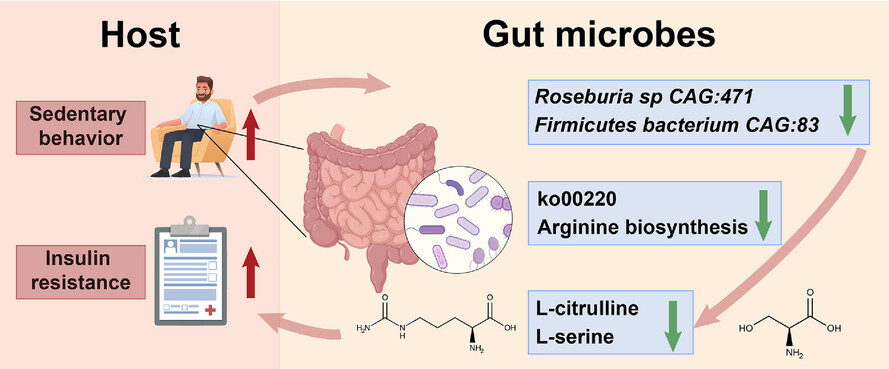
- Prolonged sedentary time leads to a depletion of Roseburia sp. CAG:471 and Firmicutes bacterium CAG:83, and suppresses arginine biosynthesis.
- Decreased L-citrulline and L-serine function as key microbial effectors mediating the adverse effect of sedentary time on insulin sensitivity.
- Targeting gut microbiota holds promise to combat insulin resistance induced by excessive sedentary time.
Screening of candidate analgesics using a patient-derived human iPSC model of nociception identifies putative compounds for therapeutic treatment
- First Published: 25 May 2025
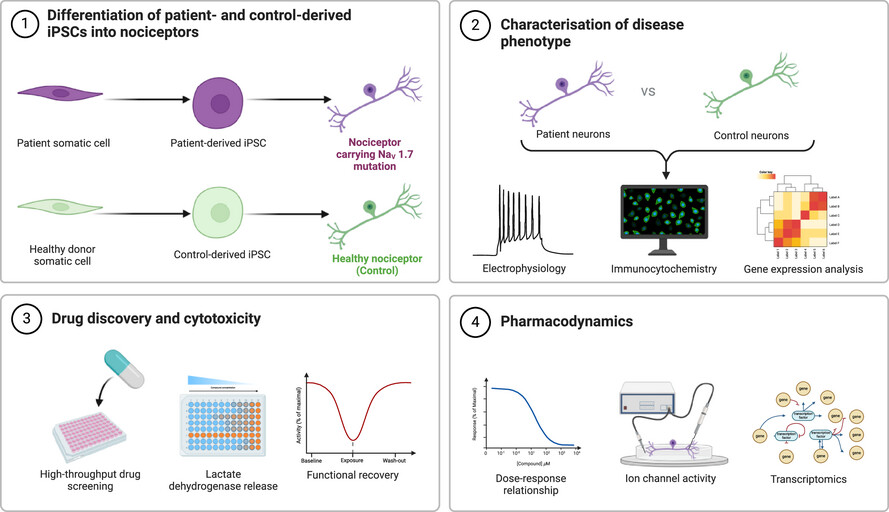
In this study, Thornton and colleagues utilised an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-based model of inherited erythromelalgia (IEM) to screen a library of 295 small molecules in search of potential pain-modulating compounds. Their screening identified four compounds that significantly reduced spontaneous firing in iPSC-derived nociceptor-like cells, with minimal associated toxicity .
REVIEW
Unravelling T cell exhaustion through co-inhibitory receptors and its transformative role in cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 25 May 2025
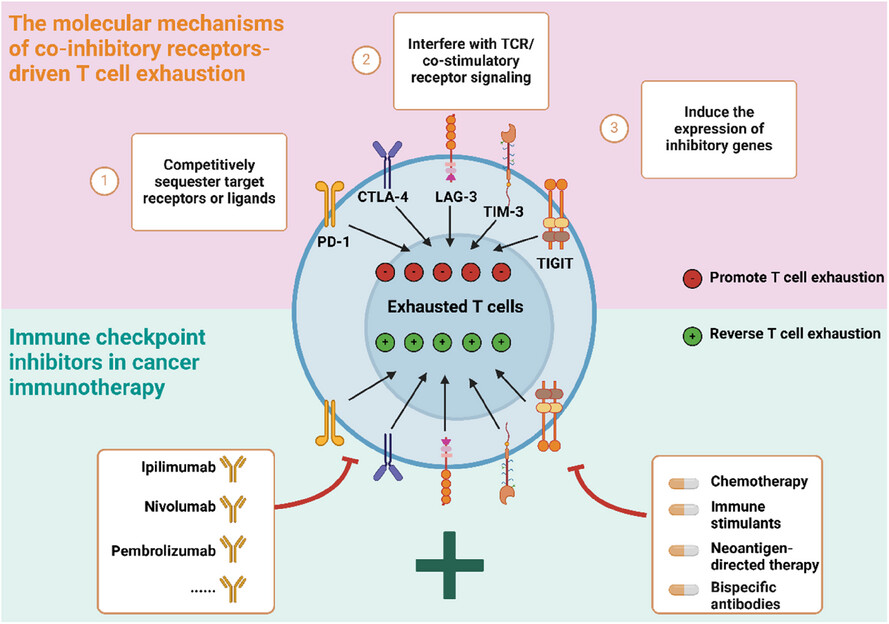
-
This review discusses five major co-inhibitory receptors (PD-1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, TIM-3 and TIGIT) and their related mechanisms of T cell exhaustion in the tumour environment.
-
We also discuss the clinical application of checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in cancer immunotherapy.
-
The potential of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) in cancer immunotherapy is highlighted.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
CD248 deficiency promotes angiotensin II-induced aortic lesion by attenuating receptor stability in smooth muscle cells
- First Published: 25 May 2025
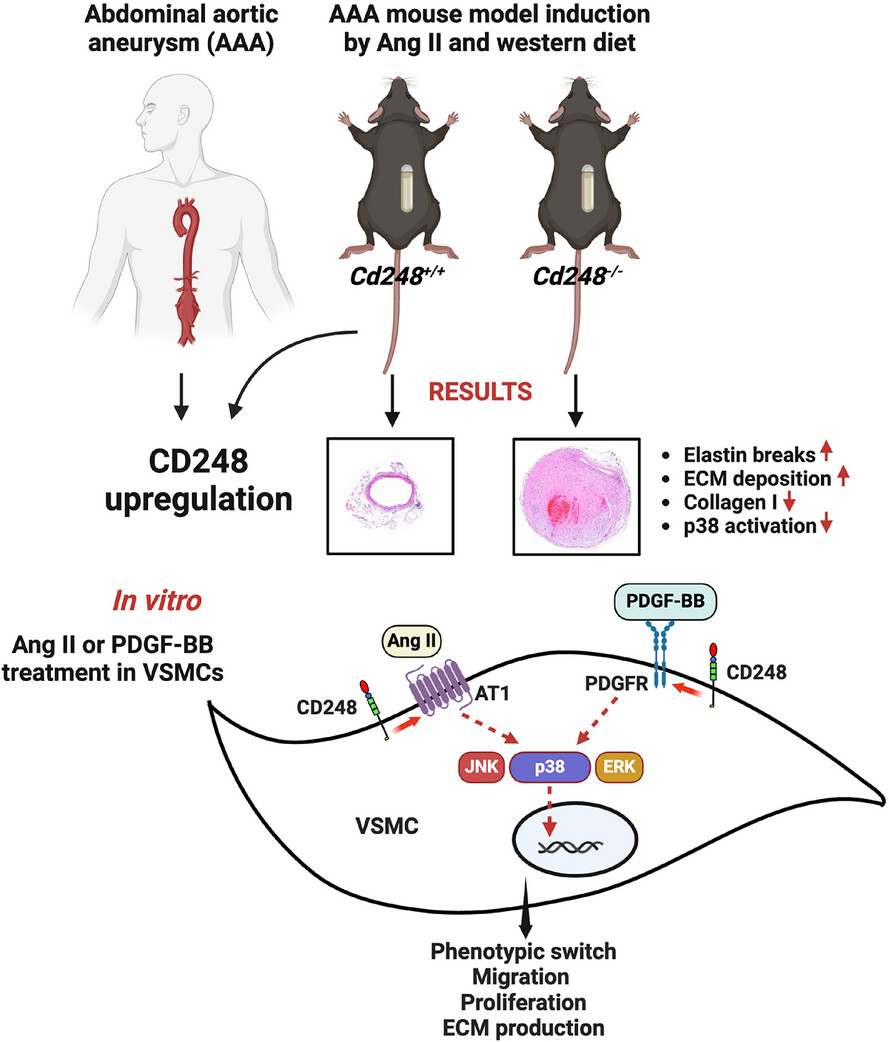
1. In the established angiotensin II-induced AAA model, CD248 deficiency exacerbated aortic lesion, accompanied by lower collagen I content and p38 activation.
2. Silencing CD248 in VSMCs led to reduced MAP kinase activation and ECM production.
3. Furthermore, loss of CD248 in VSMCs destabilizes membrane receptors for angiotensin II and PDGF, a phenomenon possibly mediated by its C-terminal cytoplasmic tail.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
PICH deficiency attenuates the progression of lung adenocarcinoma and disrupts the DNA damage response
- First Published: 29 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Responsiveness of different MET tumour alterations to type I and type II MET inhibitors
- First Published: 29 May 2025
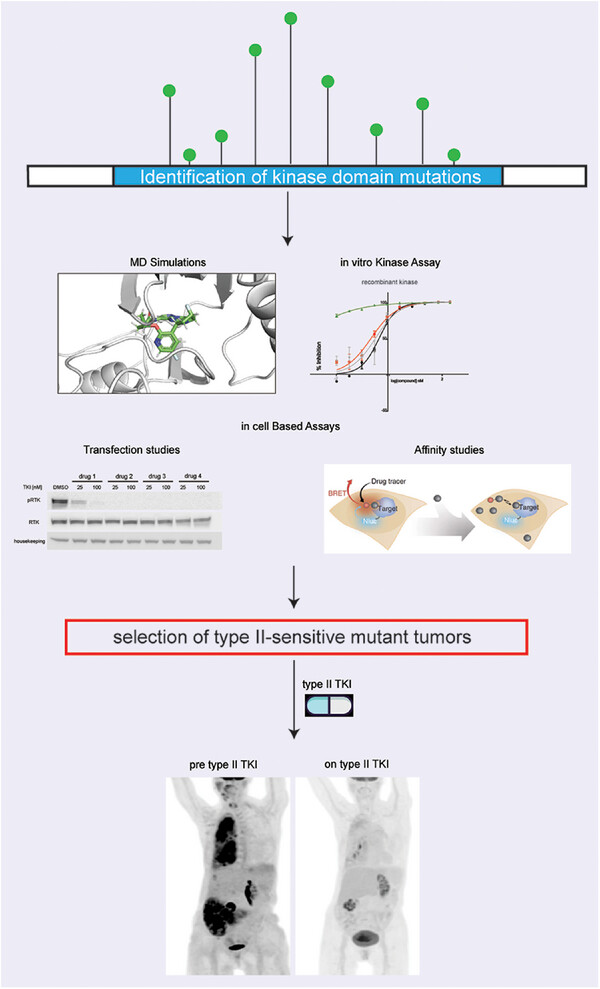
- Kinase mutations in RTKs are primary or secondary drivers in multiple cancer types
- Some of these mutations confer resistance to type I but not to type II inhibitors in preclinical samples and in patients
- The biochemical characterization of mutations in oncogenic kinases based on their sensitivity to type I and type II inhibitors is crucial to inform clinical intervention
INVITED LETTER
Bridging the bench-to-bedside divide in microbiome research
- First Published: 29 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Extracellular vesicle proteomics uncovers energy metabolism, complement system, and endoplasmic reticulum stress response dysregulation postexercise in males with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome
- First Published: 04 June 2025
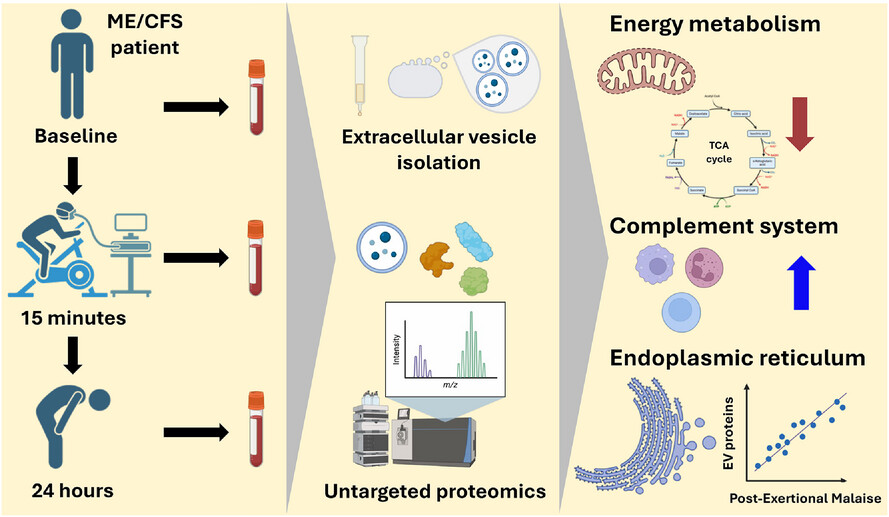
-
EVs were isolated from plasma of ME/CFS patients and healthy controls at baseline, and 15 min and 24 h postexercise.
-
Untargeted proteomics revealed dysregulation in energy metabolism, the complement system, and the endoplasmic reticulum stress response.
-
Changes in EV protein levels postexercise are associated with post-exertional malaise.
-
These findings suggest promising therapeutic targets for post-exertional malaise and ME/CFS pathophysiology.
The deubiquitinase OTUD3 plays a neuroprotective role by reducing ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischaemia reperfusion via stabilizing PLK1 via deubiquitination
- First Published: 03 June 2025
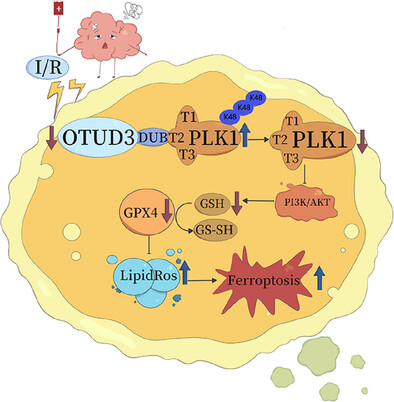
Ovarian tumour domain-containing protein 3 (OTUD3) modified PLK1 through deubiquitinating K48-linked ubiquitination in the amino acid sequence 35–305 of PLK1. Decreased expression of OTUD3 after cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion resulted in increased PLK1 ubiquitination and decreased PLK1 protein expression. In turn, this inhibited the activation of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway, reduced glutathione content, inhibited the activity of GPX4 and led to an increase in the generation of ROS, which ultimately contributed to the occurrence of ferroptosis in neuronal cells.
Coordination of SLC39A1 and DRP1 facilitates HCC recurrence by impairing mitochondrial quality control
- First Published: 03 June 2025