Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
CD73 alleviates GSDMD-mediated microglia pyroptosis in spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling
- First Published: 31 December 2020
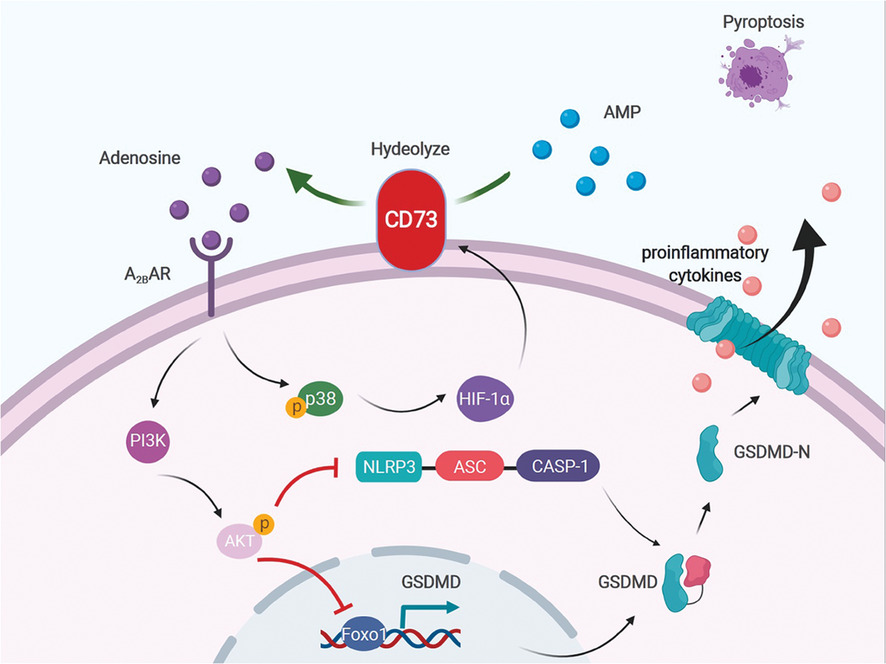
Inflammatory programmed cell death pyroptosis executed by the pore-forming protein gasdermin D (GSDMD) is an essential step of neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury. We demonstrated that CD73, a widely accepted immunosuppressive molecule, can inhibit pyroptosis via mediating GSDMD through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling.
Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of using human menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in treating severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: An exploratory clinical trial
- First Published: 27 January 2021
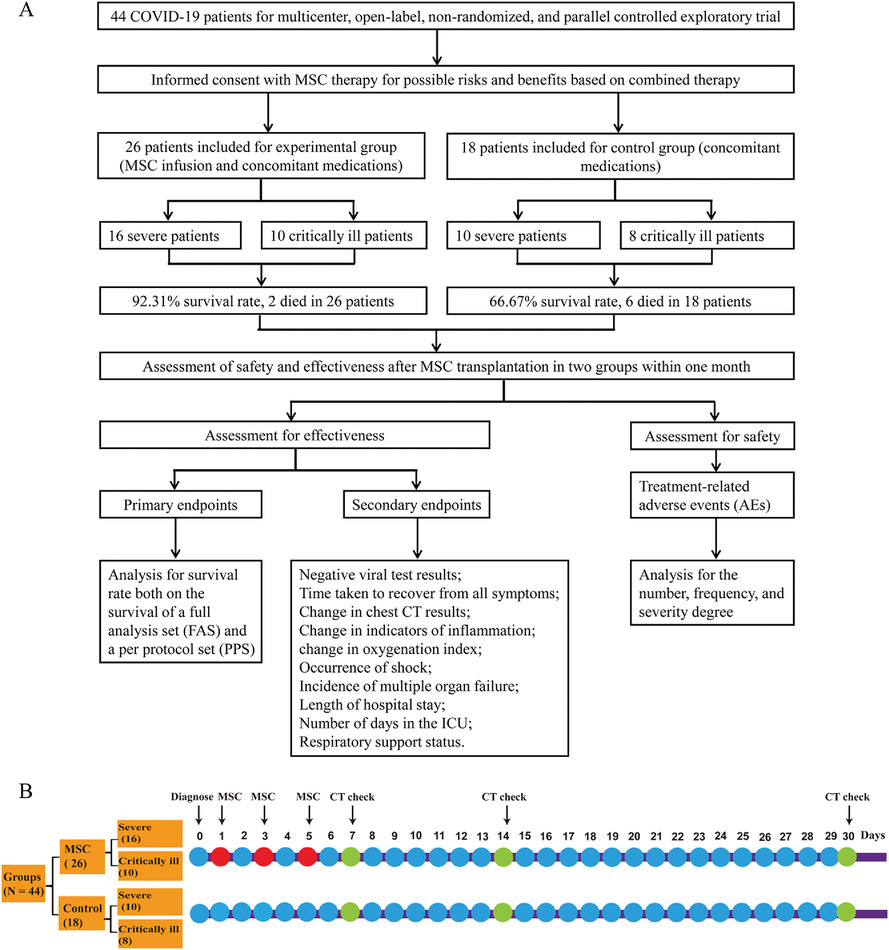
Menstrual blood-derived MSC transplantation significantly lowers the mortality of severe and critical SARS-CoV-2-induced COVID-19.
This prospective and systematic report assessed the ability of menstrual blood-derived MSCs to treat both severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients.
MSC-based therapy may serve in future clinical applications as an alternative way for the treatment of COVID-19
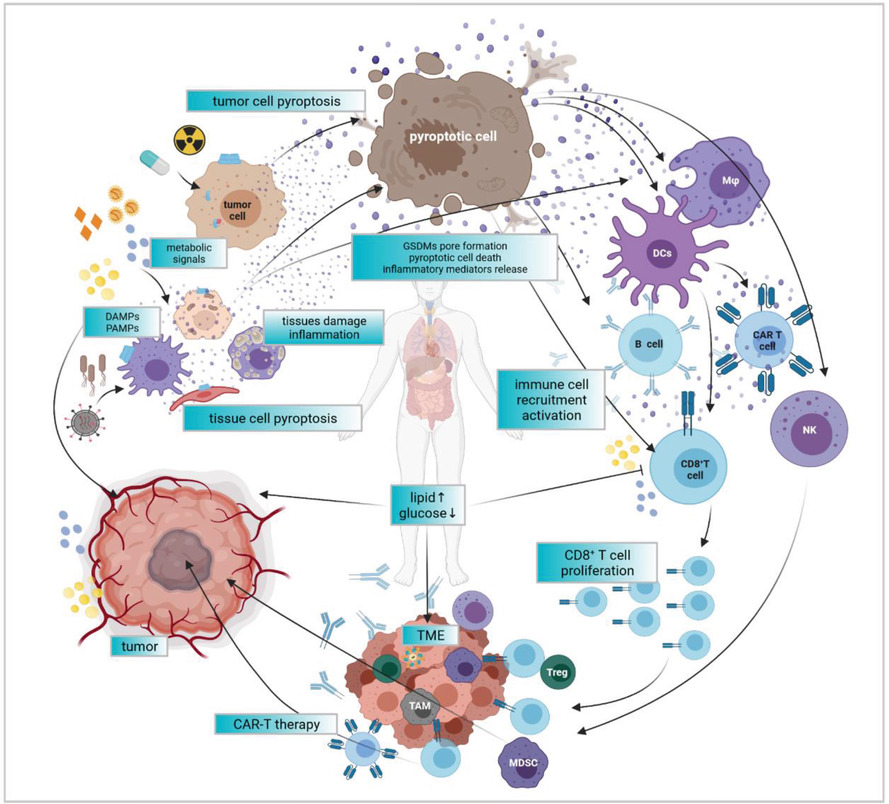
Pyroptosis, metabolism, and tumor immune microenvironment
- First Published: 03 August 2021
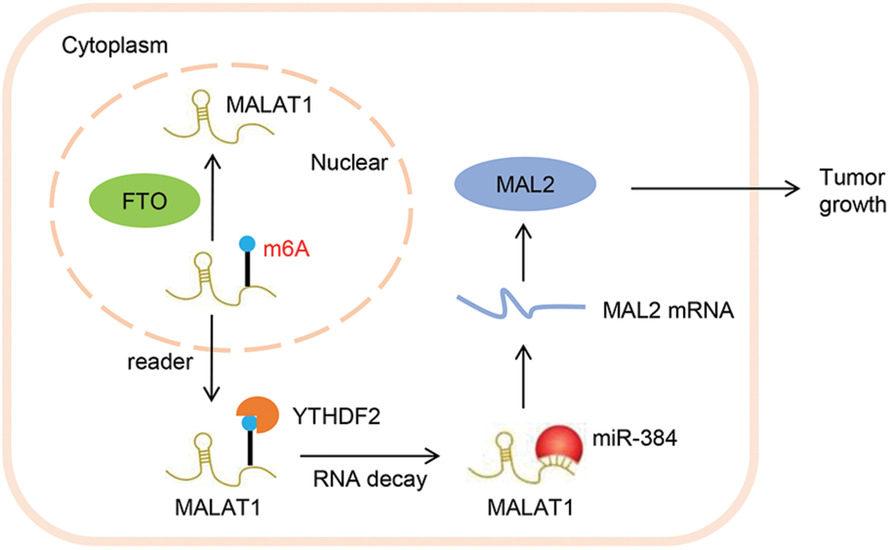
FTO modifies the m6A level of MALAT and promotes bladder cancer progression
- First Published: 01 February 2021
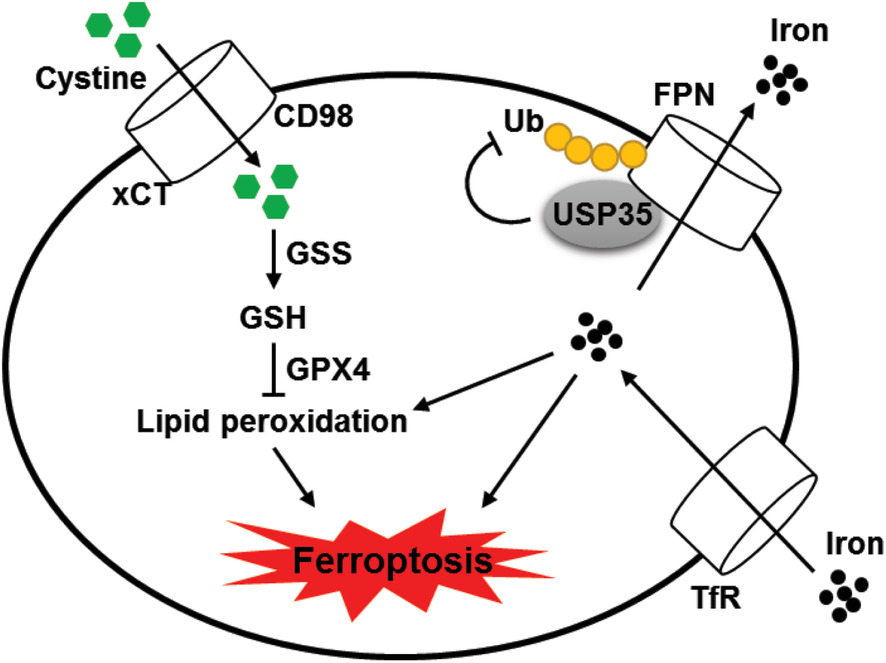
Deubiquitinase USP35 modulates ferroptosis in lung cancer via targeting ferroportin
- First Published: 01 May 2021
METTL1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis via m7G tRNA modification-dependent translation control
- First Published: 12 December 2021
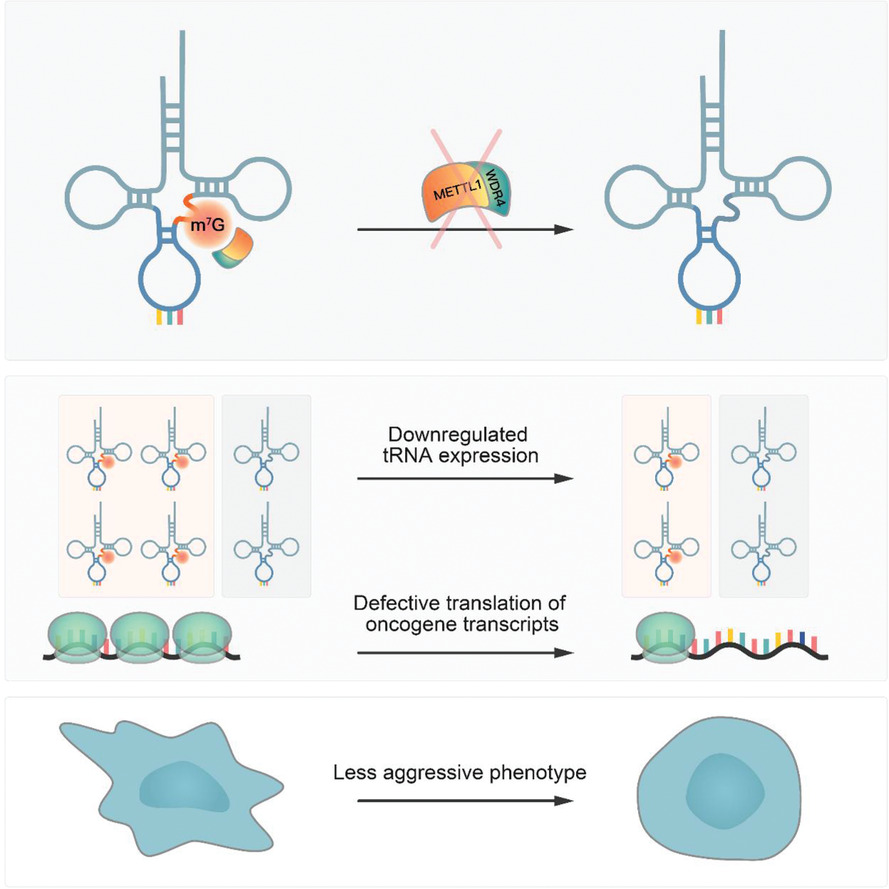
- m7G tRNA modification and its catalytic enzyme METTL1 are elevated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and associated with poor HCC prognosis.
- The m7G tRNAs are essential for tRNA expression and mRNA translation.
- Overactive m7G tRNA expression promotes hepatocarcinogenesis in vitro and in hydrodynamic transfection HCC mouse models.
Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 27 June 2021
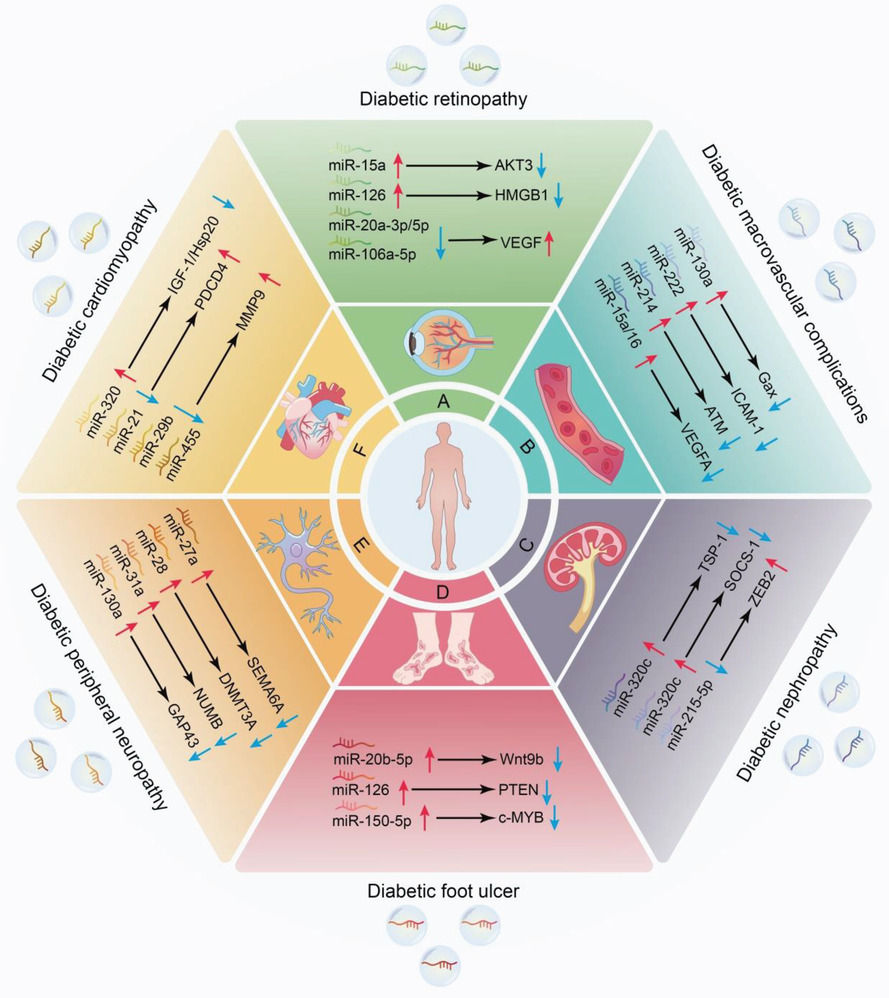
Recent studies have closely associated exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) with various human diseases, including diabetes mellitus (DM), which is a complex multifactorial metabolic disorder disease. In the diabetic condition, exosomal miRNAs are taken up by recipient cells, where they exert their biological function and thereby modulate the progression of DM-associated complications, including diabetic retinopathy (DR), diabetic macrovascular complications (DMCs), diabetic nephropathy (DN), diabetic foot ulcer (DFU), diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), and diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM).
Vaccine-breakthrough infection by the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant elicits broadly cross-reactive immune responses
- First Published: 26 January 2022
Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and applications: A brief overview
- First Published: 29 March 2022
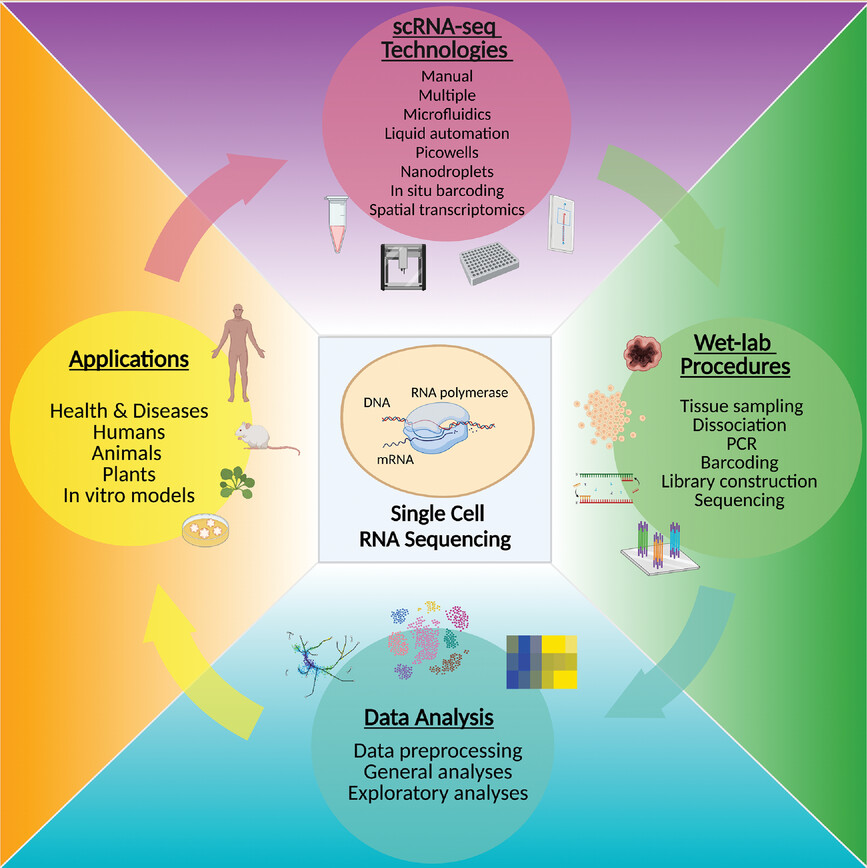
- This review provides a concise summary of the single-cell RNA sequencing technologies.
- Overview and guidelines for planning experimental procedures are presented.
- Bioinformatics tools for scRNA-seq data analysis are thoroughly discussed.
- Applications and further development of scRNA-seq technology are highlighted.
Spatial omics: Navigating to the golden era of cancer research
- First Published: 18 January 2022
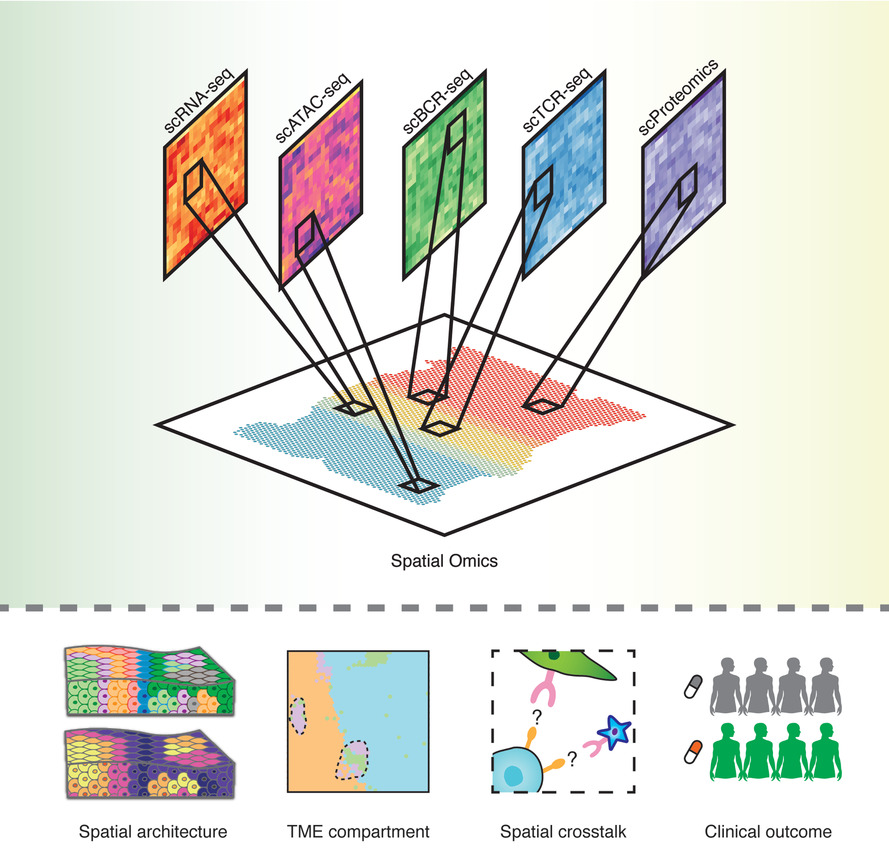
-
Spatial omics is transforming our understanding of the cancer ecosystem at the systemic level.
-
The integration of spatial omics and single-cell omics can fundamentally improve our understanding of tumourigenesis and cancer microenvironment.
-
Generating the spatial atlas of human cancers across multiple omics and timescales will potentially pioneer the revolution of spatiotemporal molecular medicine.
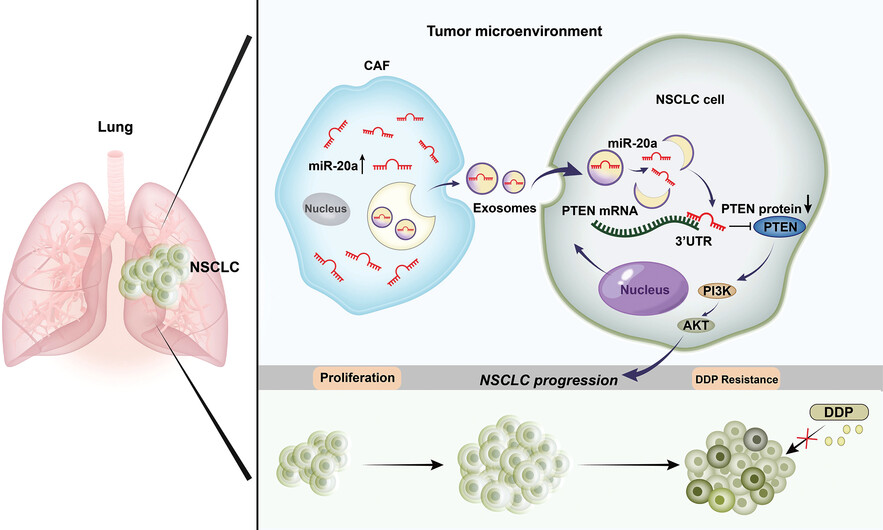
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-20a suppresses the PTEN/PI3K-AKT pathway to promote the progression and chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 20 July 2022
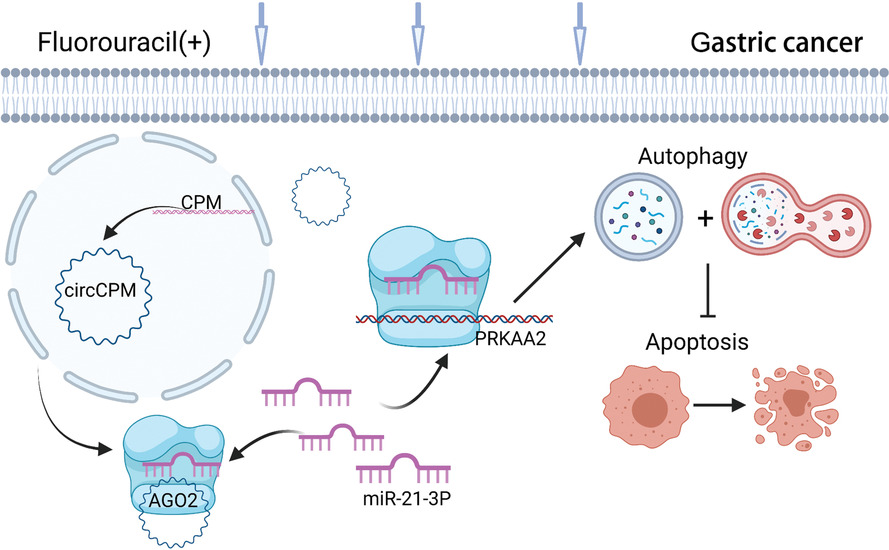
Circular CPM promotes chemoresistance of gastric cancer via activating PRKAA2-mediated autophagy
- First Published: 24 January 2022
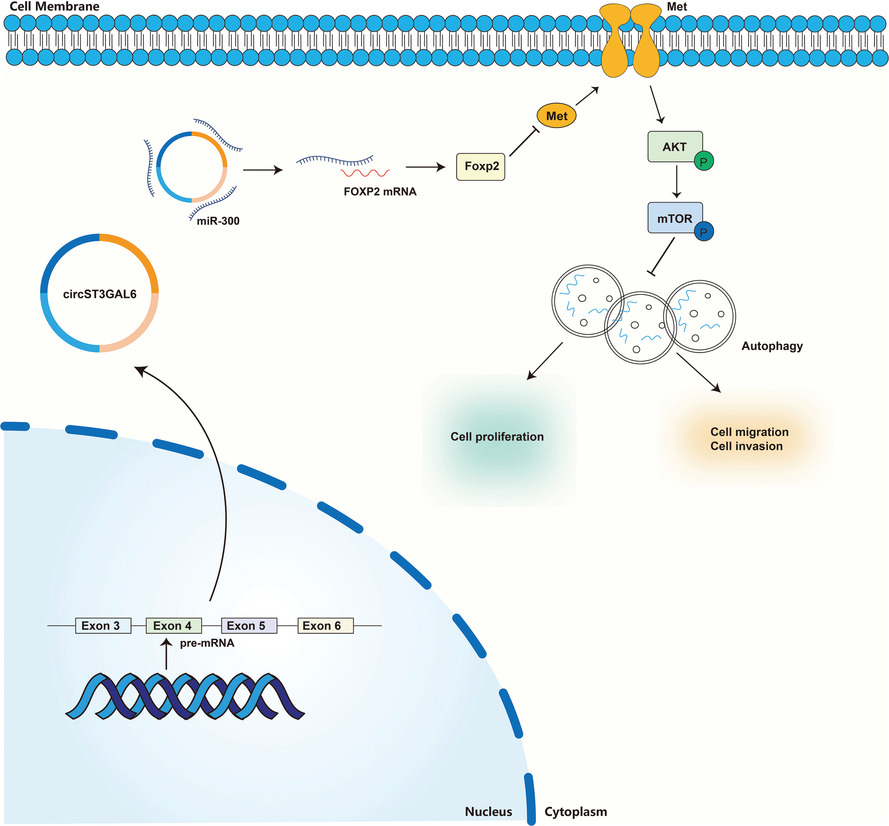
The novel role of circular RNA ST3GAL6 on blocking gastric cancer malignant behaviours through autophagy regulated by the FOXP2/MET/mTOR axis
- First Published: 21 January 2022
The role of cell-penetrating peptides in potential anti-cancer therapy
- First Published: 20 May 2022
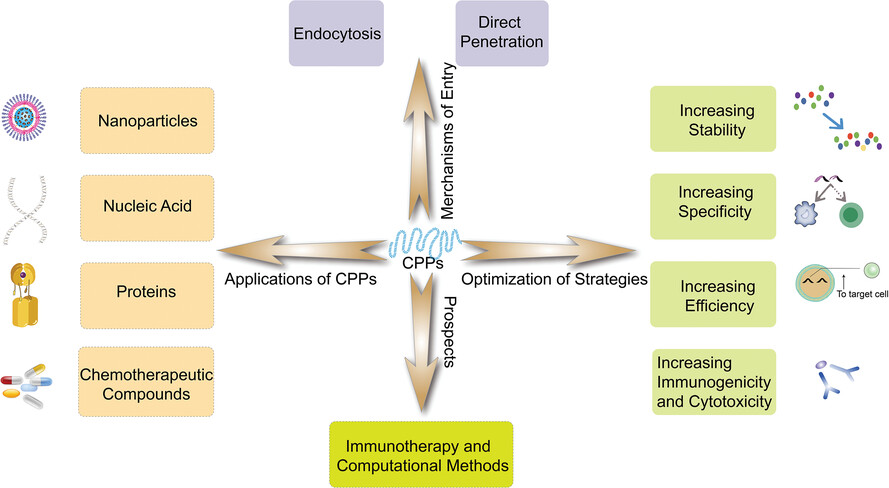
-
CPPs are amino acid sequences that can induce uptake processes by the cells.
-
CPPs can facilitate the intracellular delivery of a variety of anti-cancer therapeutic moleculars.
-
The mechanisms of the CPPs uptake can be generally categorised into energy-dependent and direct penetration.
-
The optimisation of CPPs' defects will promote their clinical applications as drug delivery vehicles.
Multi-omic landscaping of human midbrains identifies disease-relevant molecular targets and pathways in advanced-stage Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 28 January 2022
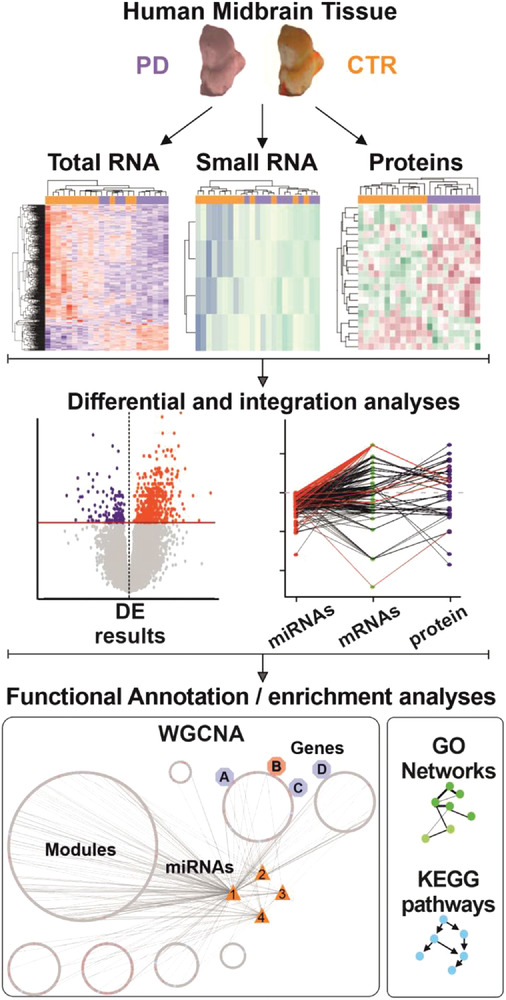
Midbrain samples of Parkinson's disease (PD) and control (CTR) patients were subjected to a multi-omic analysis. The expression of miRNAs, transcripts and proteins was explored, followed by data integration and functional analyses. This comprehensive assessment of PD-affected and CTR human midbrains revealed multiple molecular targets and networks that are relevant to the disease mechanism of advanced PD.




2001-1326.top-cited-2021-2022.cover.gif)