Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
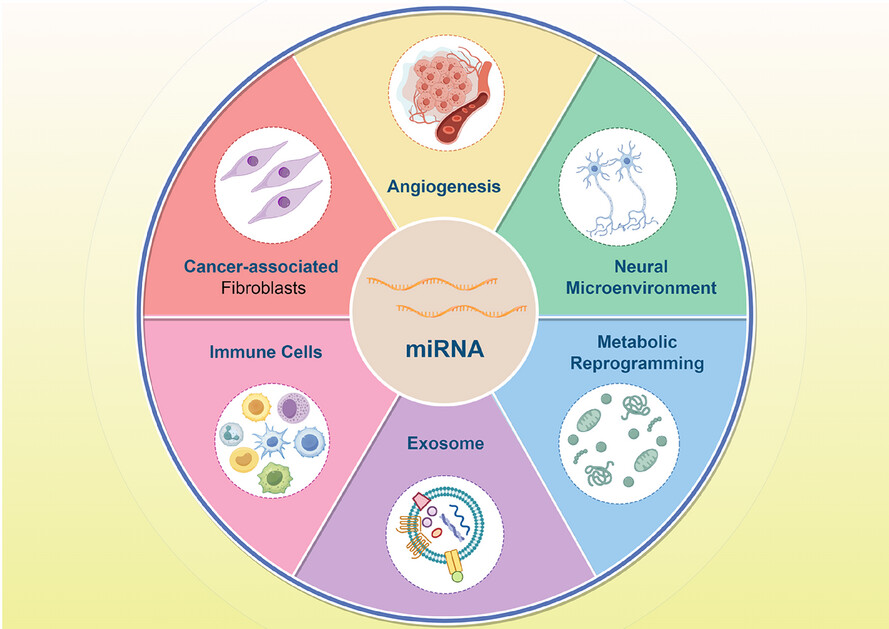
Decoding the pancreatic cancer microenvironment: The multifaceted regulation of microRNAs
- First Published: 27 June 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
T-cell differentiation stage block bias confers hypermethylation and mediastinal preference in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma
- First Published: 27 June 2025
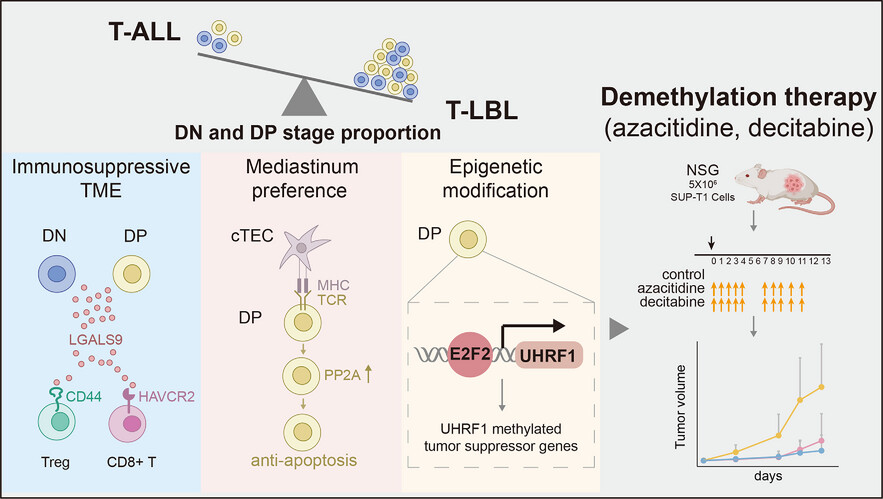
- Malignant T cells in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) are predominantly blocked in double negative (DN) and double positive (DP) stages.
- Block bias induces an immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment (TME) and mediastinal preference.
- Block bias upregulates UHRF1 leading to hypermethylation of tumour suppressor genes.
- Demethylation therapy exhibits potential in the treatment of T-LBL.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
tRF-59:76-Arg-ACG-1-M2 is upregulated during colorectal carcinogenesis and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion
- First Published: 30 June 2025
COMMENTARY
Clinical translation potential of self-inspired live-cell super-resolution microscopy
- First Published: 01 July 2025
INVITED LETTER
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Clinical implementation of a multidisciplinary pipeline for genome sequencing in rare diseases: A prospective, multicenter, observational cohort study
- First Published: 10 July 2025
COMMENTARY
Neuromorphic electronic tactile system for human-level tactile feedback
- First Published: 10 July 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
RESEARCH ARTICLE
FTO-mediated m6A demethylation regulates IGFBP3 expression and AKT activation through IMP3-dependent P-body re-localisation in lung cancer
- First Published: 07 July 2025
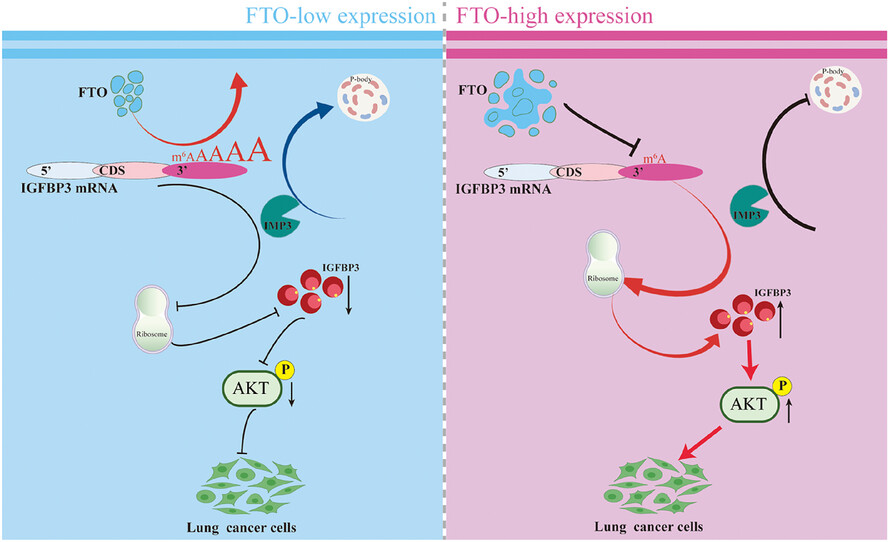
- FTO regulates the translation of IGFBP3 by demethylating m6A sites in the 3′-untranslated region of IGFBP3 mRNA.
- Binding of the m6A reader protein IMP3 to 3′UTR m6A sites in IGFBP3 mRNA promoted its localisation and sequestration in cellular organelles known as to P-bodies, thereby suppressing IGFBP3 mRNA translation.
- IGFBP3 regulates activation of the AKT signalling pathway, and that FTO-mediated regulation of IGFBP3 influences LUAD malignant behaviours.
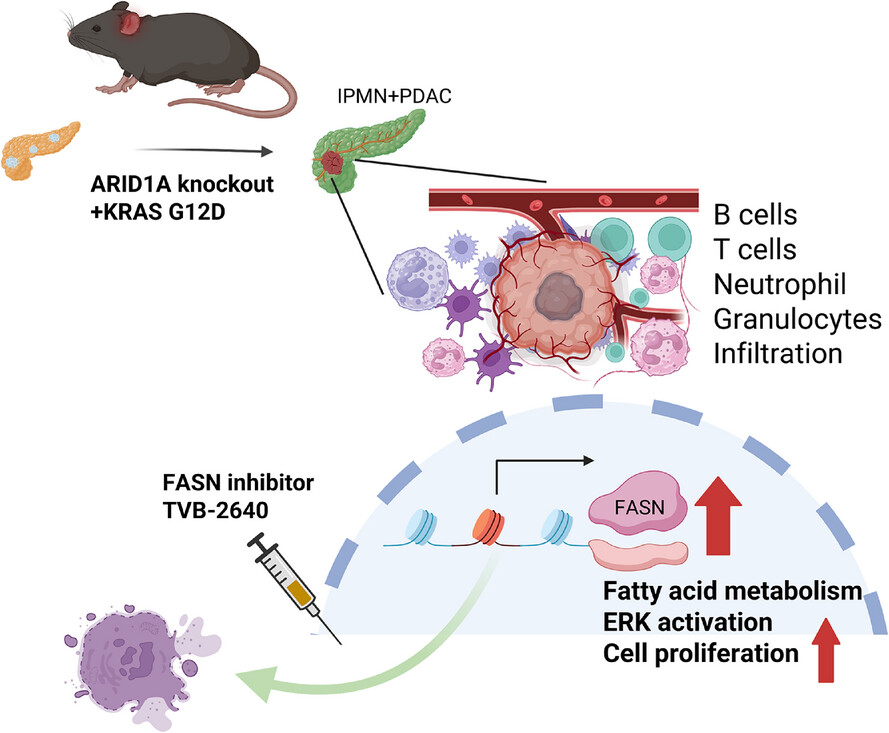
Arid1a deficiency sensitises pancreatic cancer to fatty acid synthase inhibition
- First Published: 07 July 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
The utility of automated artificial intelligence-assisted digital cytomorphology for bone marrow analysis in diagnostic haemato-oncology
- First Published: 09 July 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
IGF2BP2 binding to CPSF6 facilitates m6A-mediated alternative polyadenylation of PUM2 and promotes malignant progression in ovarian cancer
- First Published: 09 July 2025
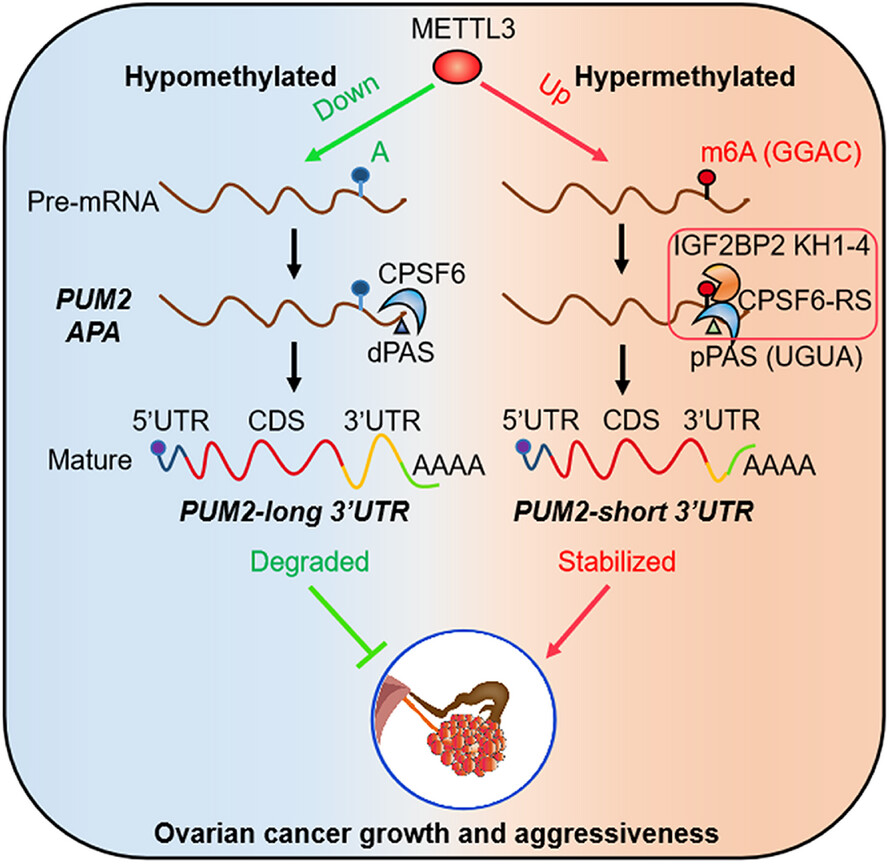
-
The interaction between m6A and APA is mediated by the m6A regulator IGF2BP2 and the APA factor CPSF6
-
The transcripts harbouring m6A modification tend to use the proximal polyadenylation signal (PAS) in ovarian cancer (OC)
-
PUM2 promotes the malignant progression of OC through its m6A methylation and APA processing
MiRNA-501-3p and MiRNA-502-3p: A promising biomarker panel for Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 09 July 2025
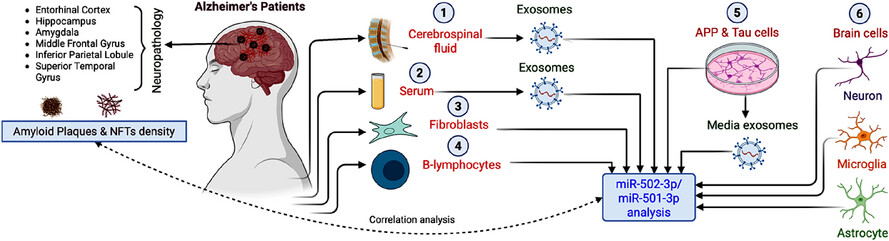
-
MiR-501-3p and miR-502-3p expression is elevated in AD CSF exosomes, AD serum exosomes, AD B-lymphocytes and Aβ- and Tau-treated cells.
-
MiR-501-3p and miR-502-3p are correlated with amyloid plaque and NFT tangle density in specific brain regions.
-
MiR-501-3p and miR-502-3p are highly expressed in neurons and astrocytes, suggesting that these cells are the source of miRNA secretion.
-
MiR-501-3p and miR-502-3p could be a promising biomarker panel for AD.
REVIEW
CD70: An emerging target for integrated cancer diagnosis and therapy
- First Published: 09 July 2025
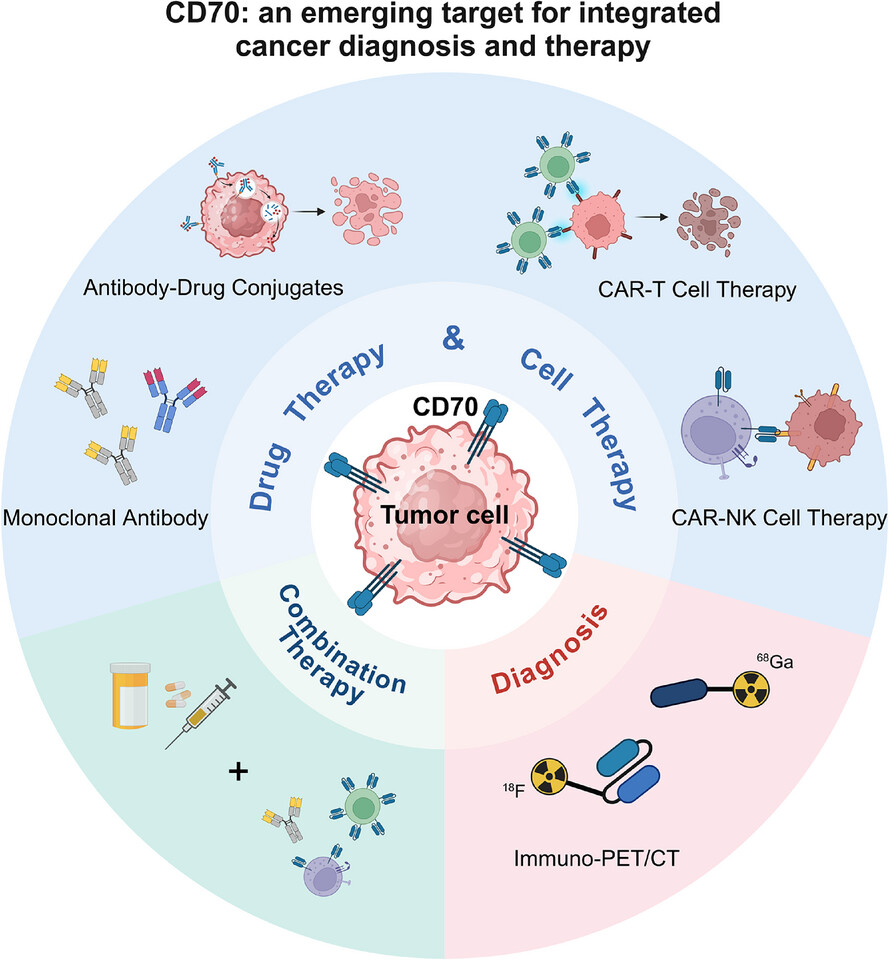
CD70 is aberrantly overexpressed in diverse tumours with limited normal tissue expression, making it a compelling diagnostic and therapeutic target. Immuno-PET/CT facilitates tumour detection, staging, and treatment monitoring. Multiple CD70-targeted therapies are under early evaluation. Rational combination strategies are emerging to enhance antitumor efficacy.
COMMENTARY
Unlocking oncoembryonic programs for clinical advances in cancer therapy
- First Published: 11 July 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Advancing immune profiling in colon cancer through enhanced lipidomics of low-input samples
- First Published: 11 July 2025
COMMENTARY
The coming of age of DNA-based catalysts for therapeutic applications
- First Published: 14 July 2025
EDITORIAL
Adaptive evolution of koala retrovirus transcription silencing and what it means for conservation
- First Published: 15 July 2025
REVIEW
Cancer therapy resistance from a spatial-omics perspective
- First Published: 17 July 2025
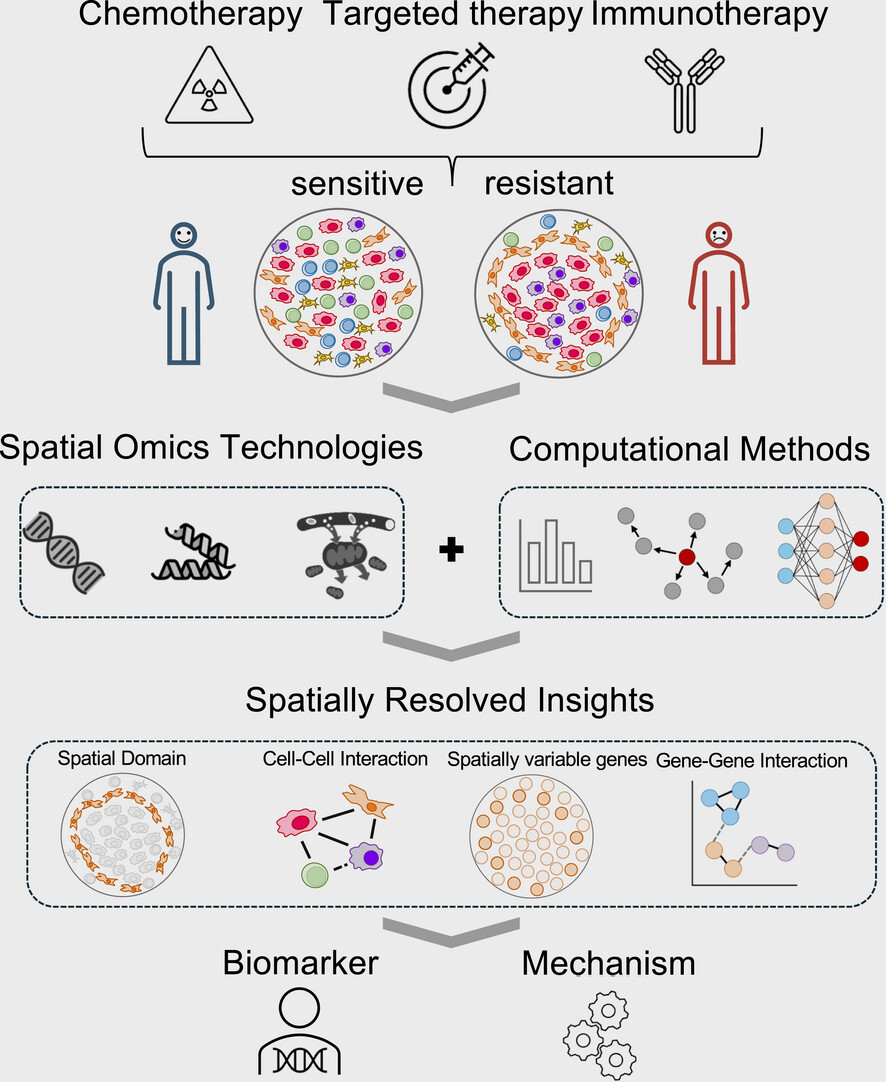
Spatial omics technologies reveal unprecedented insights into cancer therapy resistance (CTR) by resolving spatial heterogeneity of tumour and microenvironment. This review highlights cutting-edge spatial omics and computational technologies, showcasing their transformative potential in deciphering CTR mechanisms and uncovering novel diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities.
Cancer stem cells: Bridging microenvironmental interactions and clinical therapy
- First Published: 15 July 2025
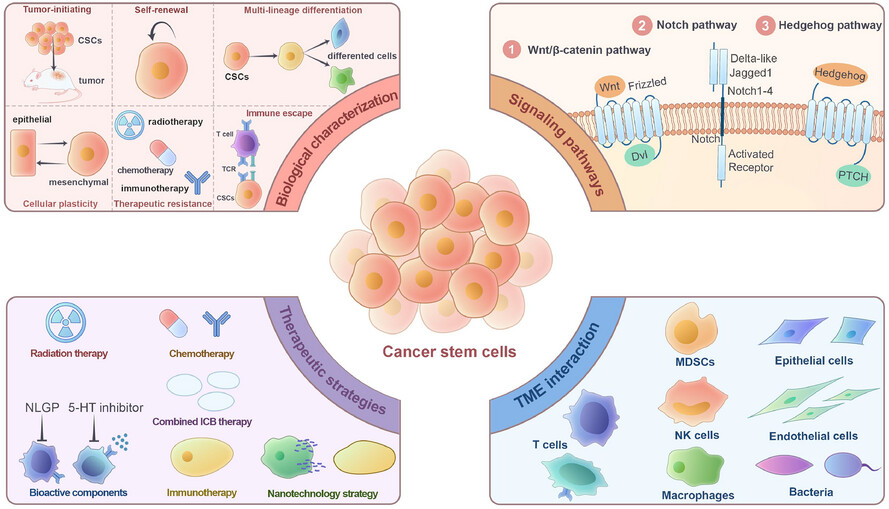
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) drive tumor progression through their dynamic self-renewal capacity, epigenetic plasticity, and drug resistance. These cells interact bi-directionally with the tumor ecosystem to promote immunosuppressive reprogramming and metastatic spread. We systematically evaluated current targeting of CSC-specific markers, signaling pathways and tumor microenvironment interactions, and clinical therapeutic strategies.
COMMENTARY
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Asymmetric bilayer dressings with spatiotemporal sequence loaded with IL-24 and GCDs for the treatment of diabetic wounds
- First Published: 16 July 2025
REVIEW
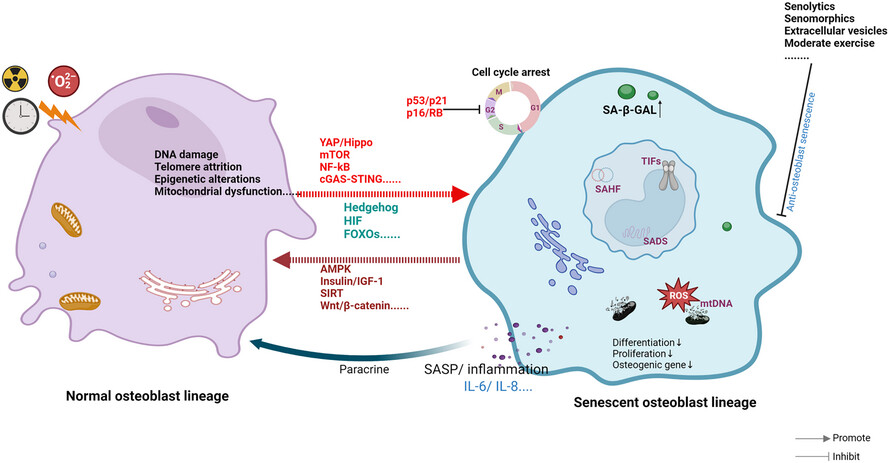
Addressing osteoblast senescence: Molecular pathways and the frontier of anti-ageing treatments
- First Published: 18 July 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Interleukin-11 promotes lung adenocarcinoma tumourigenesis and immune evasion
- First Published: 17 July 2025
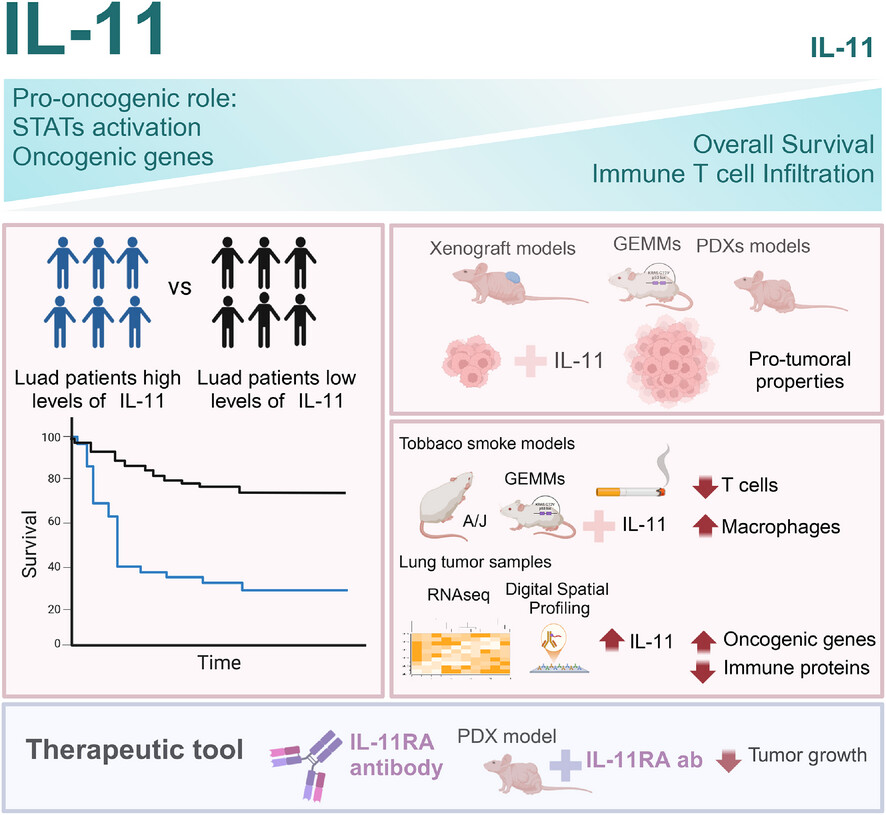
IL-11 drives tumour progression and is linked to poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients, as well as an immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment. Antibody targeting of the IL-11 receptor (IL-11RA) shows significant anti-tumour effects in a patient-derived xenograft model highlighting IL-11 as a compelling therapeutic target.
INVITED LETTER
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of ATR inhibitors: Advances, challenges, and opportunities in cancer therapy
- First Published: 17 July 2025
REVIEW
Decoding MHC loss: Molecular mechanisms and implications for immune resistance in cancer
- First Published: 17 July 2025
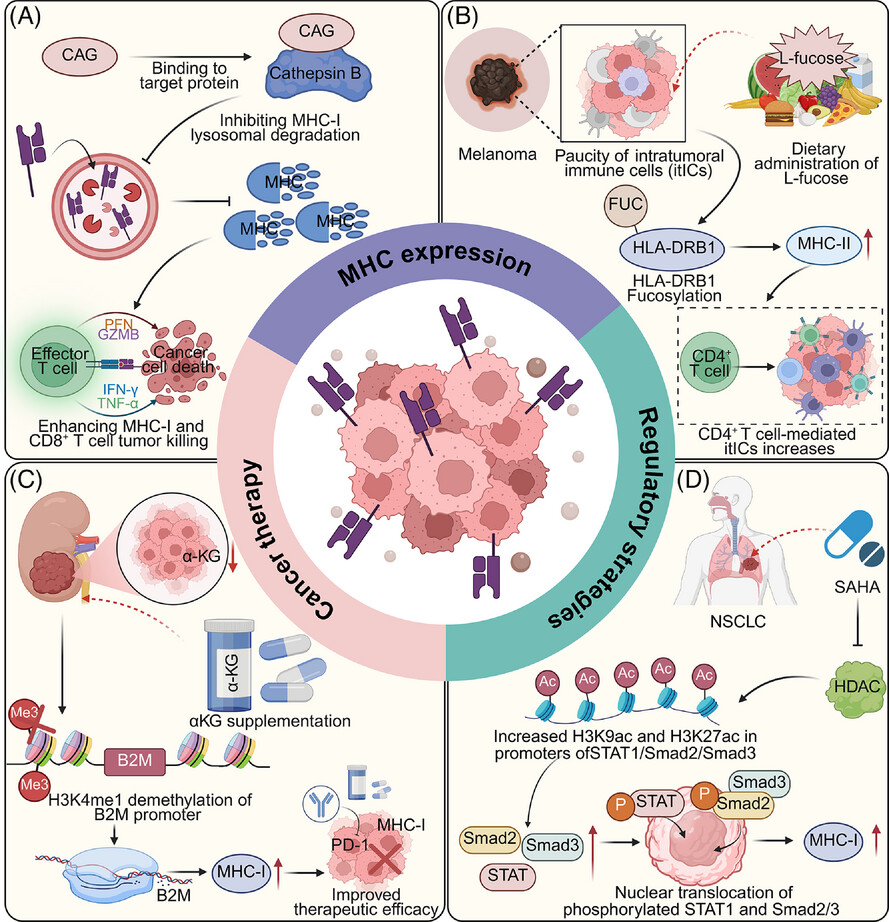
-
Tumour cells evade immune surveillance by downregulating MHC expression through transcriptional repression, lysosomal degradation and post-translational modifications.
-
Pharmacological agents interventing epigenetic and metabolic can upregulate MHC expression and improve T cell activation.
-
Combination strategies potentiate immunotherapy efficacy by reinvigorating tumour immunogenicity.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
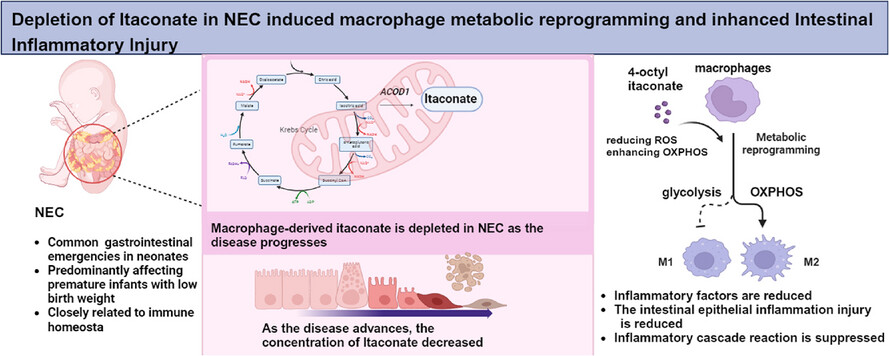
Itaconate suppresses neonatal intestinal inflammation via metabolic reprogramming of M1 macrophage
- First Published: 17 July 2025
PDK4 and nutrient responses explain muscle specific manifestation in mitochondrial disease
- First Published: 18 July 2025
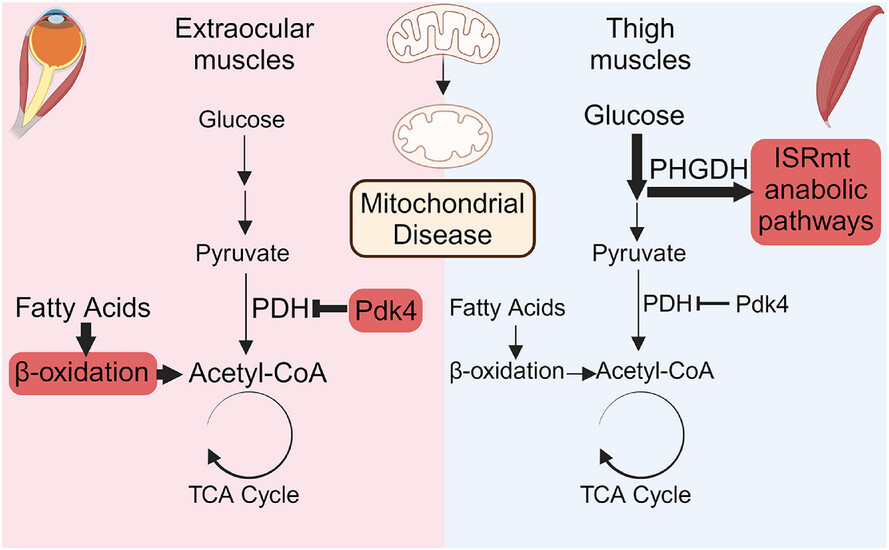
Mitochondrial disease triggers opposite responses in different muscles. Mitochondrial integrated stress response (ISRmt) and aerobic glycolysis characterize large muscles. Eye muscles show no ISRmt but activate PDK4—inhibitor of glucose oxidation—thereby upregulating beta-oxidation, which is non-optimal in mitochondrial disease and can explain eye muscle atrophy in mitochondrial disease.
YOD1 regulates oxidative damage of dopamine neurons in Parkinson's disease by deubiquitinating PKM2
- First Published: 18 July 2025
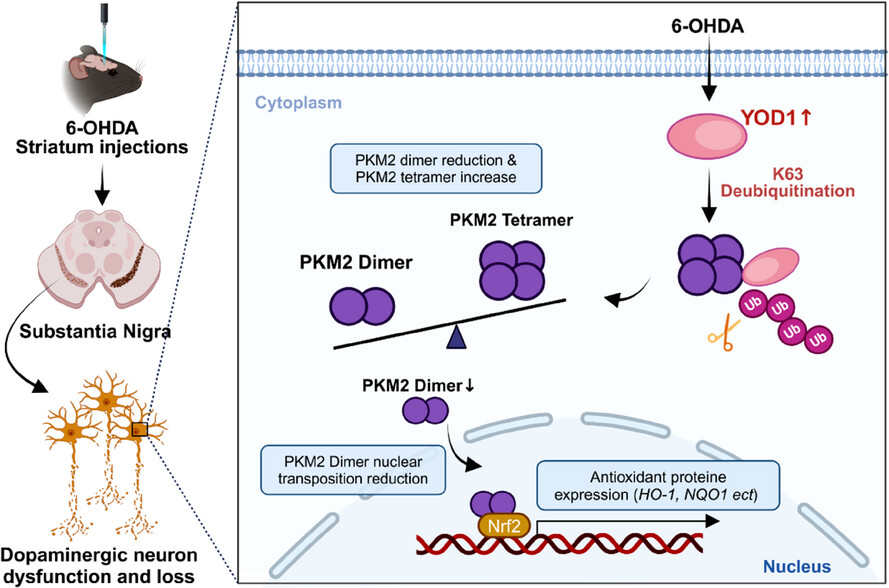
YOD1 binds to PKM2 and reduces its ubiquitination level by removing the K63 ubiquitin chain of PKM2, thereby increasing the tetramer level and reducing the dimer level of PKM2. It then inhibited dimerized PKM2 entry into the nucleus and activated the Nrf2 signaling pathway, thus promoting oxidative stress.
INVITED LETTER
Glutamate as a therapeutic strategy to promote liver regeneration
- First Published: 21 July 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Spatially resolved proteomics surveys the chemo-refractory proteins related to high-grade serous ovarian cancer
- First Published: 23 July 2025
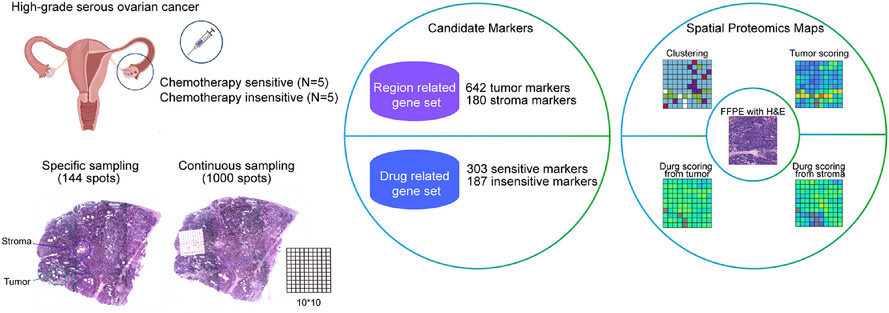
-
HGSC intra-tumour heterogeneity is predominantly driven by stroma, as revealed by spatial proteomic compartmentalization (tumour/stroma).
-
Spatial proteomics expands the therapeutic target database, enabling prediction of platinum-based chemotherapy response.
-
Chemo-resistant patients exhibit pre-treatment metabolic activation rather than proliferative signatures.
-
TFRC (iron transport) and PDLIM3 (cytoskeletal remodelling) are spatially validated as chemo-response biomarkers.
COMMENTARY
Precision treatment in breast cancer: Leveraging genetic interactions
- First Published: 23 July 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Early molecular changes predict cancer cachexia in LKB1-deleted mouse models of NSCLC
- First Published: 23 July 2025