Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
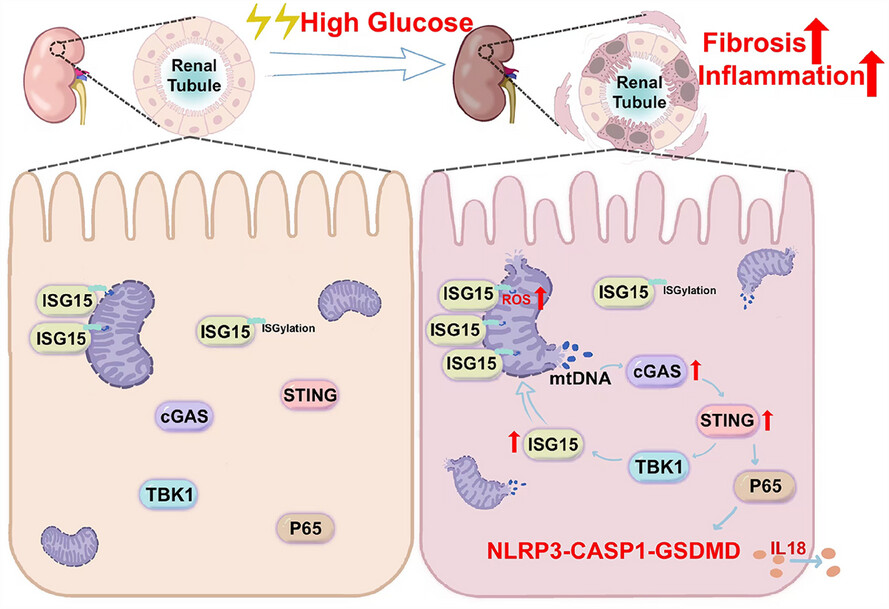
Elevation of ISG15 promotes diabetic kidney disease by modulating renal tubular epithelial cell pyroptosis
- First Published: 03 June 2025
Fibroblasts-specific p16INK4a exacerbates inflammageing-mediated post-infarction ventricular remodelling through interacting with STAT3 to regulate NLRP3 transcription
- First Published: 03 June 2025
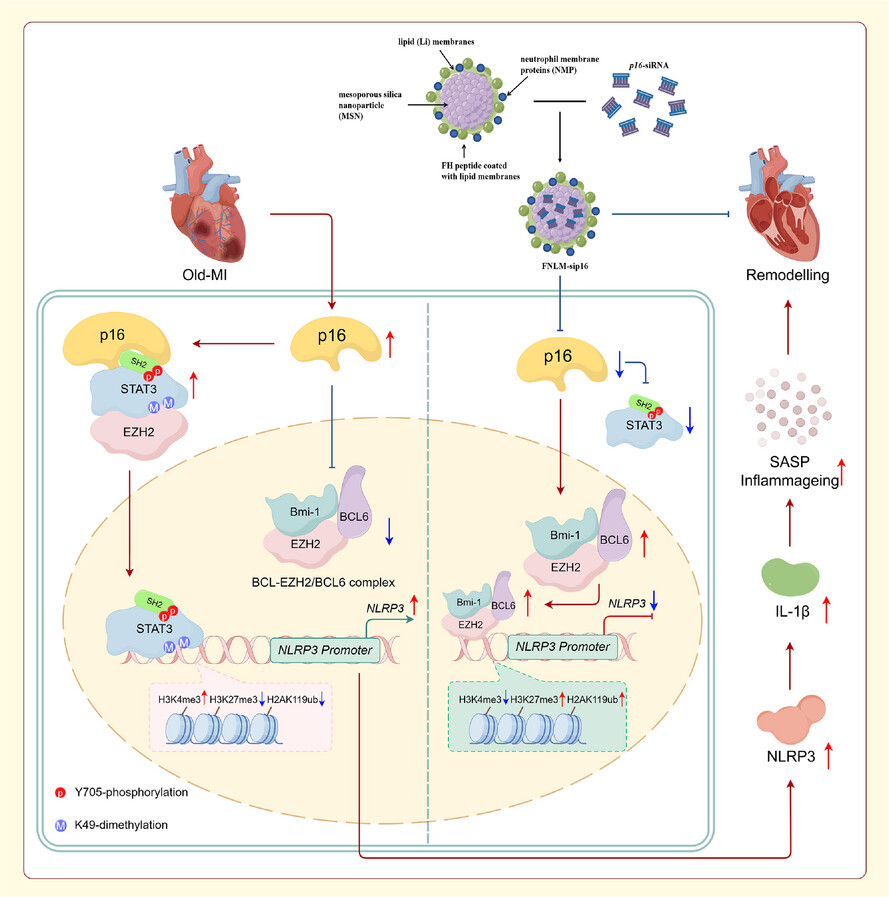
- In ageing fibroblasts, p16INK4a concurrently enhanced STAT3 di-methylation mediated by EZH2 and suppressed the assembly of Bmi-1-EZH2/BCL-6 complexes at the NLRP3 promoter region.
- These dual regulatory actions synergistically upregulated STAT3-dependent NLRP3 transcription, thereby exacerbating inflammageing-driven ventricular remodelling following myocardial infarction.
- FNLM-nanocaged p16INK4a-siRNA prevents post-infarction ventricular remodelling through inhibiting NLRP3 transcription in targeted cardiac fibroblasts.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
DNA methylation profiles reveals STAB1-mediated endothelial cell and immune cell interactions in Moyamoya disease
- First Published: 03 June 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Targeting the MDK/c-Myc complex to overcome temozolomide resistance in glioma
- First Published: 04 June 2025
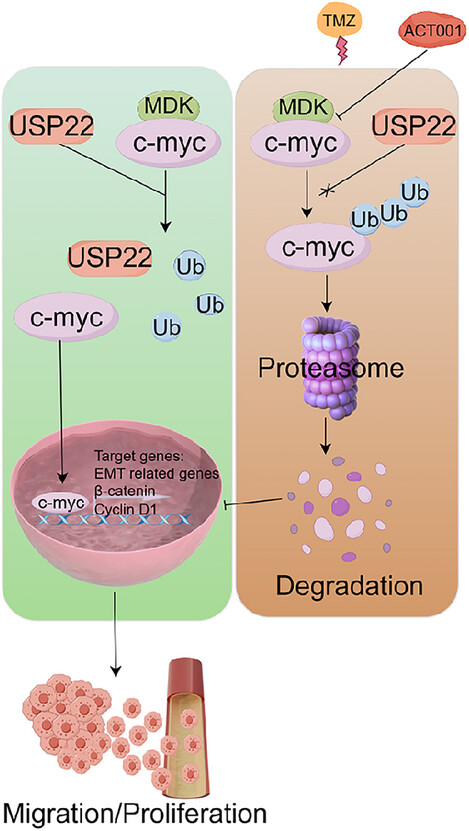
ACT001 disrupts the MDK/c-Myc complex, enhancing c-Myc ubiquitination and overcoming temozolomide resistance in glioma. Combining ACT001 with temozolomide synergistically inhibits tumour growth and progression, offering a promising therapeutic strategy for glioma patients, particularly those with high MDK expression.
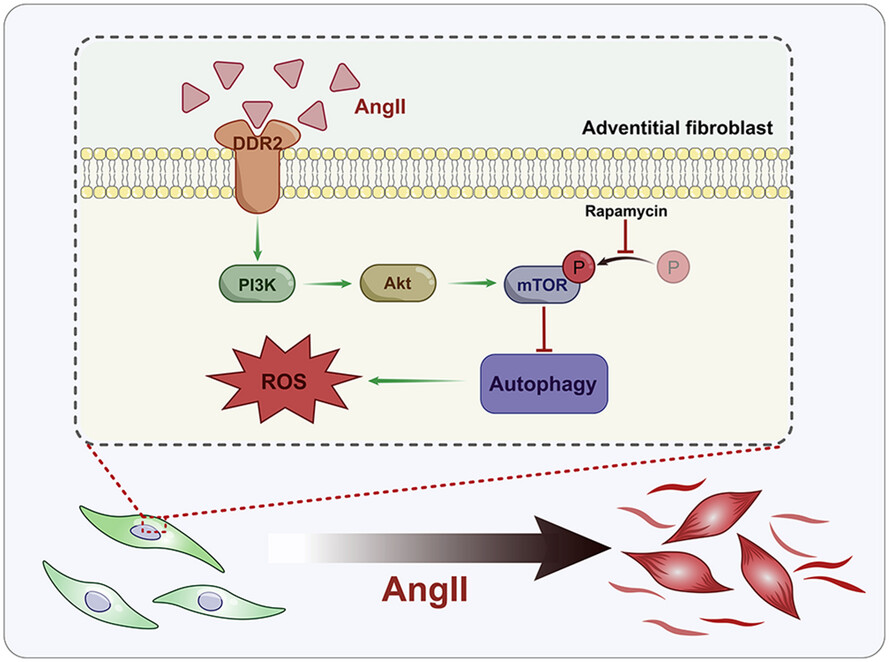
DDR2-mediated autophagy inhibition contributes to angiotensin II-induced adventitial remodeling
- First Published: 04 June 2025
LncRNA MIR503HG regulates NETs-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NSCLC metastasis by enhancing the ubiquitination of C/EBPβ
- First Published: 09 June 2025
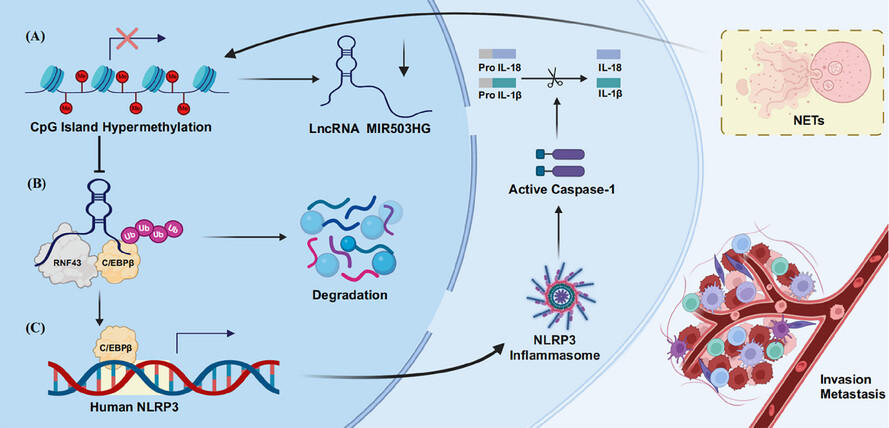
- NETs suppress the expression of MIR503HG by inducing promoter DNA methylation.
- C/EBPβ binds to the NLRP3 promoter to promote NLRP3 expression.
- MIR503HG inhibits the expression of C/EBPβ protein by promoting the interaction between C/EBPβ and the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF43, thereby repressing NLRP3 expression.
REVIEW
Antisenescence therapies for age-related bone loss: Target factors, medicines, biomedical materials
- First Published: 09 June 2025
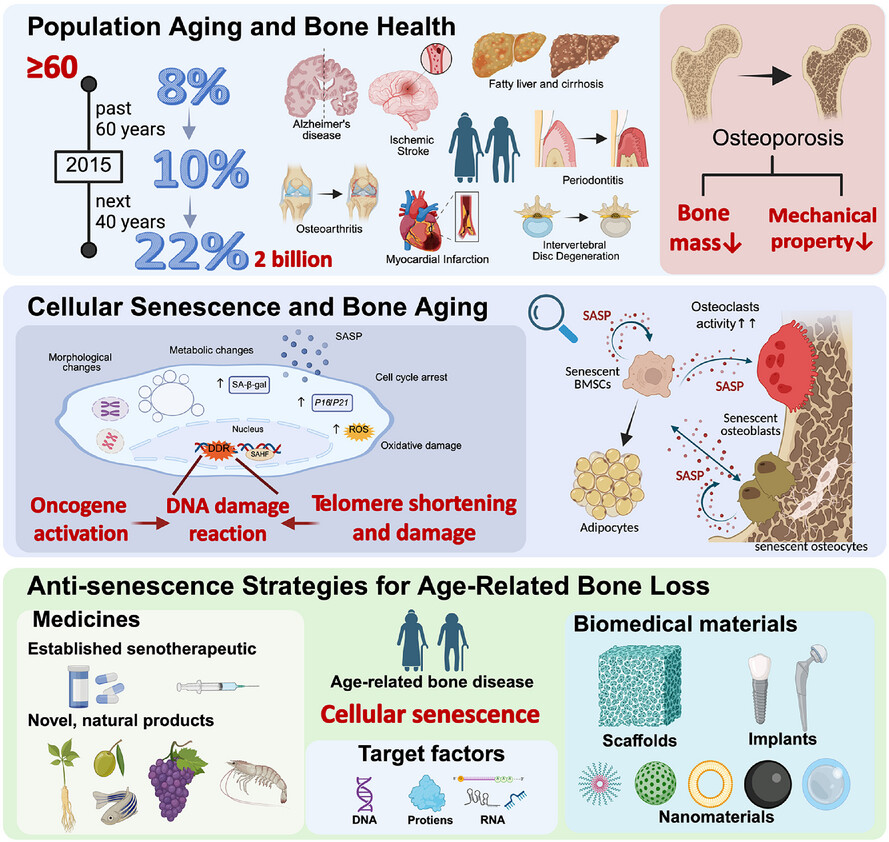
With extended lifespans causing population aging, bone aging has become a worldwide issue. Cellular senescence in the bone microenvironment causes bone degeneration and dysfunction. This review summarises targets in cellular senescence and bone aging while detailing potential therapeutic strategies, including novel medicines and innovative biomedical materials. https://BioRender.com/0wqyt7g
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
RESEARCH ARTICLE
MLKL‒OPTN axis regulates herpesvirus-induced neurological sequelae
- First Published: 09 June 2025
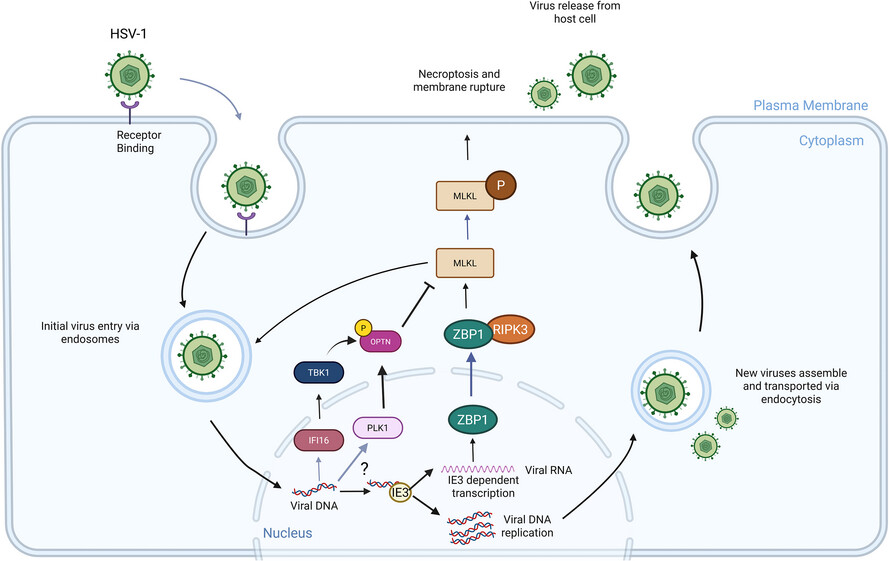
- MLKL plays a significant role in regulating endosomal transport of HSV-1 to nucleus during early stages of infection.
- Formation of p-MLKL bodies during HSV-1 infection leads to death of oligodendrocyte and subsequent demyelination.
- OPTN can negatively modulate MLKL levels to restrict infection and consequential oligodendrocyte death during HSV-1 infection.
INVITED LETTER
The new era of siRNA therapy: Advances in cancer treatment
- First Published: 09 June 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Targeting enabled homolog with daunorubicin inhibits ERK1/2/c-Fos pathway and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression
- First Published: 09 June 2025
REVIEW
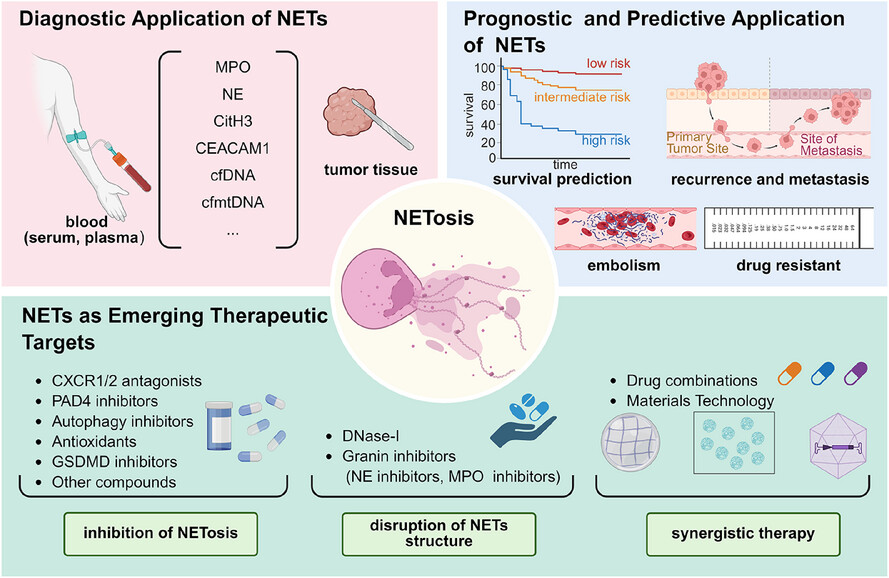
Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer: From mechanisms to treatments
- First Published: 13 June 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Integrating spatial transcriptomics and single-cell RNA-seq dissects immune microenvironment in fatty liver regeneration
- First Published: 13 June 2025
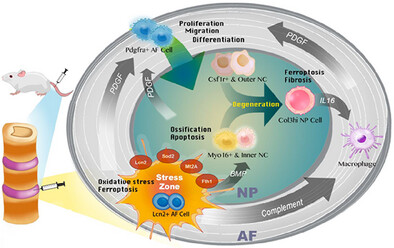
Klotho mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating autophagy and energy metabolism
- First Published: 13 June 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Single nuclear-spatial transcriptomic sequencing reveals distinct puncture-induced cell subpopulations in the intervertebral disc of a rat model
- First Published: 13 June 2025
INVITED LETTER
Multilayered precision regulation to induce robust CD8+ T-cell immune responses
- First Published: 18 June 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Hypoxia-induced PGK1 expression promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via stimulating MYH9-mediated GSK3β/β-catenin signalling
- First Published: 18 June 2025
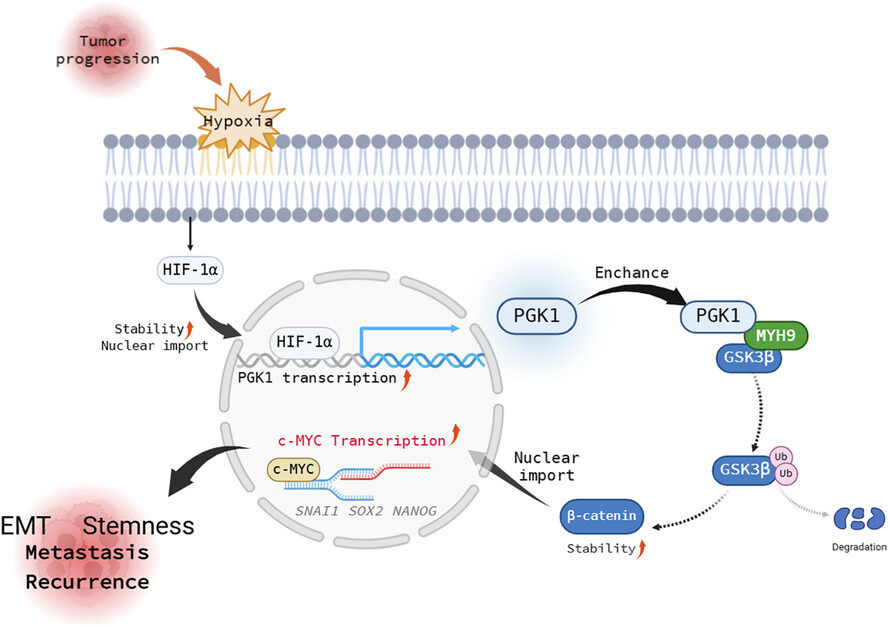
Under hypoxic conditions, elevated PGK1 interacts with MYH9, promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of GSK3β, which leads to β-catenin stabilisation and nuclear translocation. Activated β-catenin increases the transcription of c-Myc and downstream targets genes enhancing cancer stemness, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, and ESCC recurrence.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Long-term survival and association of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy in resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 18 June 2025
REVIEW
Splicing to keep splicing: A feedback system for cellular homeostasis and state transition
- First Published: 19 June 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Engineered small extracellular vesicles for targeted delivery of perlecan to stabilise the blood–spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury
- First Published: 19 June 2025
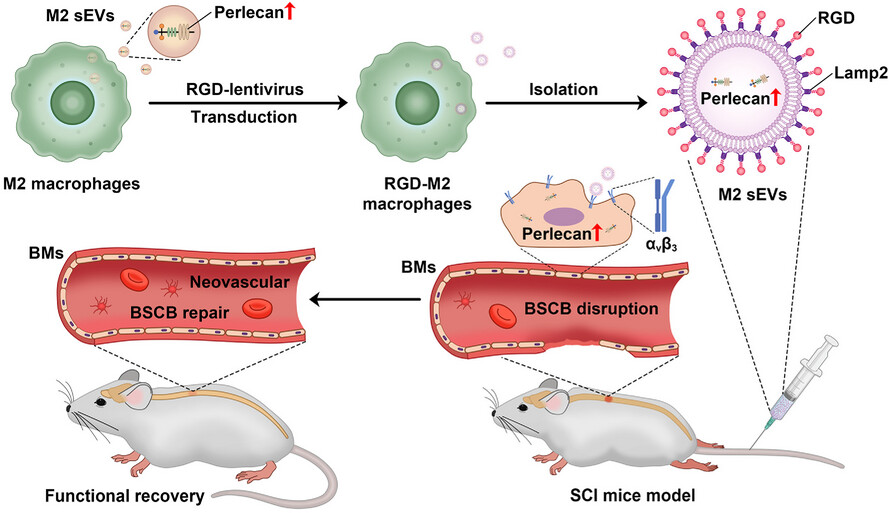
- Perlecan, a crucial component of basement membranes that plays a vital role in stabilising BSCB homeostasis and functions, was found to be upregulated in M2-sEVs.
- M2-sEVs decorated with RGD peptide can effectively target the neovascular endothelium surfaces at the injured spinal cord site.
- RGD-M2-sEVs promote BSCB restoration by transporting perlecan to neovascular endothelial cells, representing a potential strategy for SCI treatment.
INVITED LETTER
The discovery of Cas9's trans-cleavage activity: Unlocking new molecular diagnostic tools
- First Published: 19 June 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
INVITED LETTER
In vitro reconstitution of SPO11-mediated DNA cleavage reveals mechanistic and clinical insights into meiotic DNA double-strand break formation
- First Published: 22 June 2025
A sex- and gender-informed future for Parkinson's disease care
- First Published: 23 June 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
OXA1L deficiency causes mitochondrial myopathy via reactive oxygen species regulated nuclear factor kappa B signalling pathway
- First Published: 23 June 2025
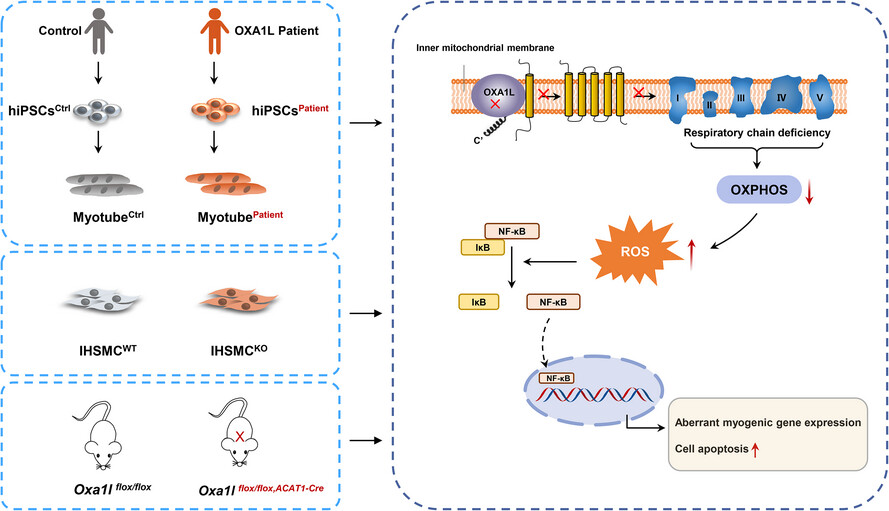
- OXA1L gene bi-allelic variants cause mitochondrial myopathy.
- OXA1L deficiency results in combined mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and OXPHOS impairments.
- OXA1L deficiency leads to elevated ROS production, which may activate the NF-κB signalling pathway, disturbing myogenic gene expression and triggering cell apoptosis.