Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Interleukin 27 deficiency drives dilated cardiomyopathy by ferroptosis
- First Published: 21 March 2025
An in-depth benchmark framework for evaluating single cell RNA-seq dropout imputation methods and the development of an improved algorithm afMF
- First Published: 22 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A myeloid IFN gamma response gene signature correlates with cancer prognosis
- First Published: 31 March 2025
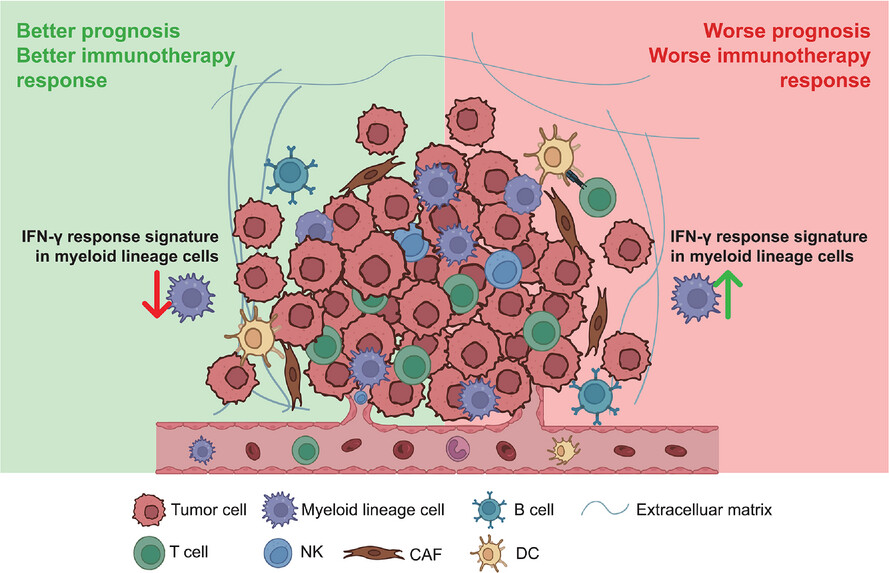
- IFGRNS score is a novel prognostic biomarker upregulated in myeloid lineage cells.
- IFGRNS score correlates with survival outcomes across multiple cancer types.
- IFGRNS score is associated with tumour pathology and immune microenvironment.
- IFGRNS score predicts immunotherapy response, with potential for clinical application.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
KMT2C/D mutations in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia: Clinical features, genetic co-occurrences and prognostic significance
- First Published: 26 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The antiprotease Spink7 promotes inflammation resolution by modulating multiple proteases activities during wound healing
- First Published: 27 March 2025
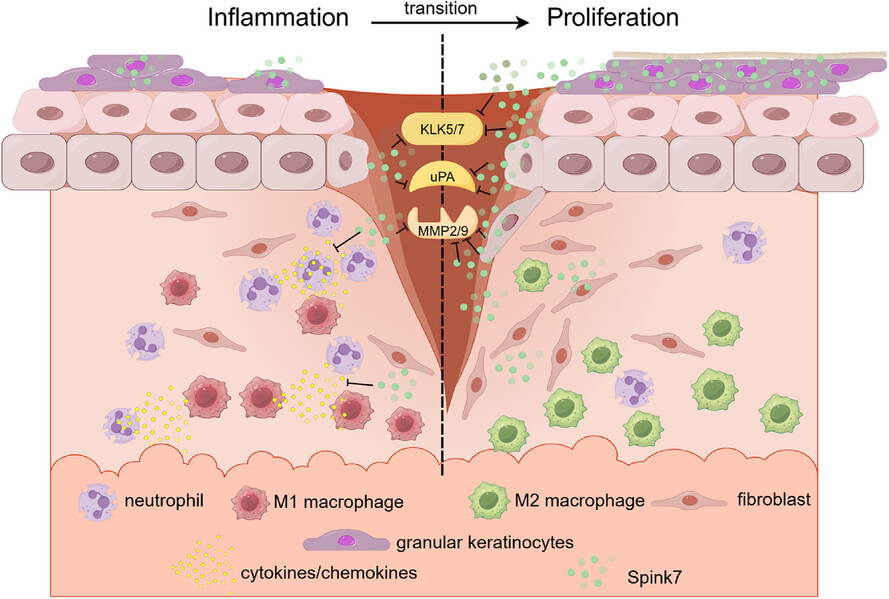
• Spink7, which originates from differentiated epidermal granular keratinocytes of proliferative phase, plays a crucial role during skin wound healing.
• Spink7 promotes inflammation resolution by suppressing multiple proteases activities including uPA, MMP2/9, and KLK5/7 during skin wound healing.
• Spink7 promotes the transition from inflammation to proliferation through inhibiting production of cytokines/chemokines and modulating M2 polarization of macrophage.
• Modulating Spink7 levels by siRNAs in wounds of radiation combined injury facilitates healing by enhancing inflammation.
SETD2 loss of function is a recurrent event in advanced-phase chronic myeloid leukemia and contributes to genomic instability: SETD2 loss in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- First Published: 24 April 2025
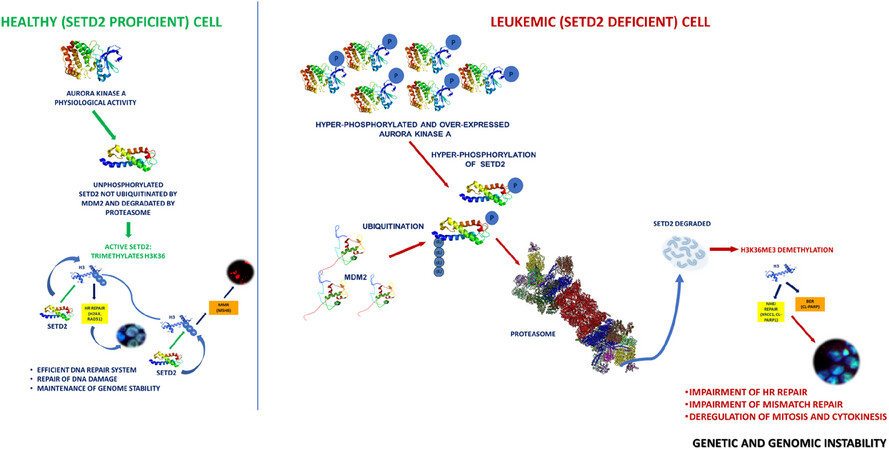
Virtually all CML patients in blast crisis display SETD2 loss of function
SETD2 loss seems to be accomplished at the posttranslational level rather than being the result of genetic/genomic hits or transcriptional repression
Phosphorylation by Aurora kinase A and ubiquitination by MDM2 contribute to SETD2 proteasome-mediated degradation in blast crisis CML patients
Loss of SETD2 results in increased DNA damage
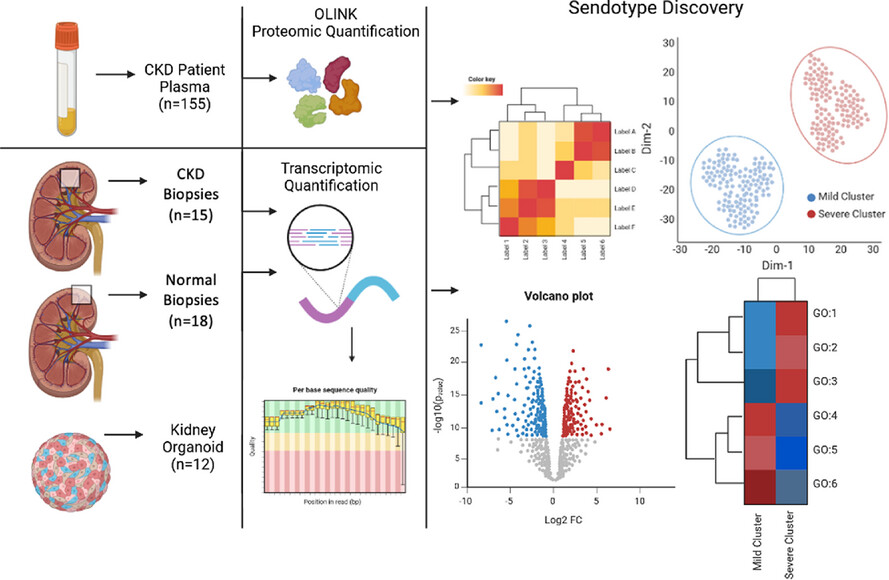
Sendotypes predict worsening renal function in chronic kidney disease patients
- First Published: 27 March 2025
REVIEW
Spatial omics strategies for investigating human carotid atherosclerotic disease
- First Published: 28 March 2025
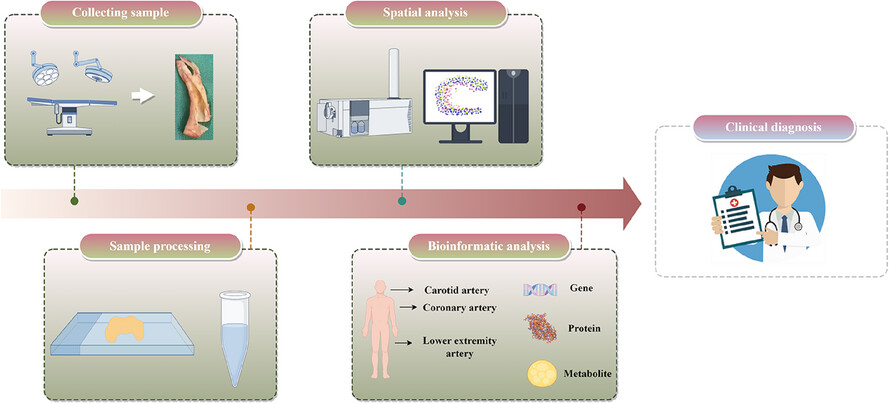
Spatial omics, by facilitating visualised precision medicine and accomplishing the spatial localisation of microscopic substances, is poised to emerge as a crucial tool in future research areas, including the exploration of molecular pathways, the implementation of precision targeted therapies and the refinement of disease diagnostic techniques.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
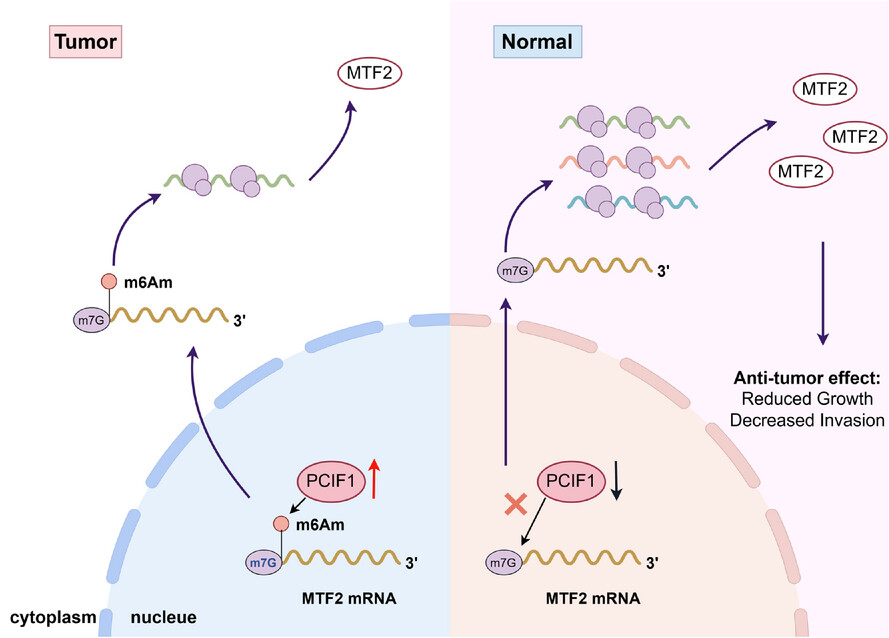
PCIF1 drives oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via m6Am-mediated suppression of MTF2 translation
- First Published: 28 March 2025
INVITED LETTER
GDF-15 blockade: A multi-directional approach to potentiate cancer immunotherapy and alleviate cancer cachexia
- First Published: 30 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
NSUN2 promotes colorectal cancer progression and increases lapatinib sensitivity by enhancing CUL4B/ErbB-STAT3 signalling in a non-m5C manner
- First Published: 28 March 2025
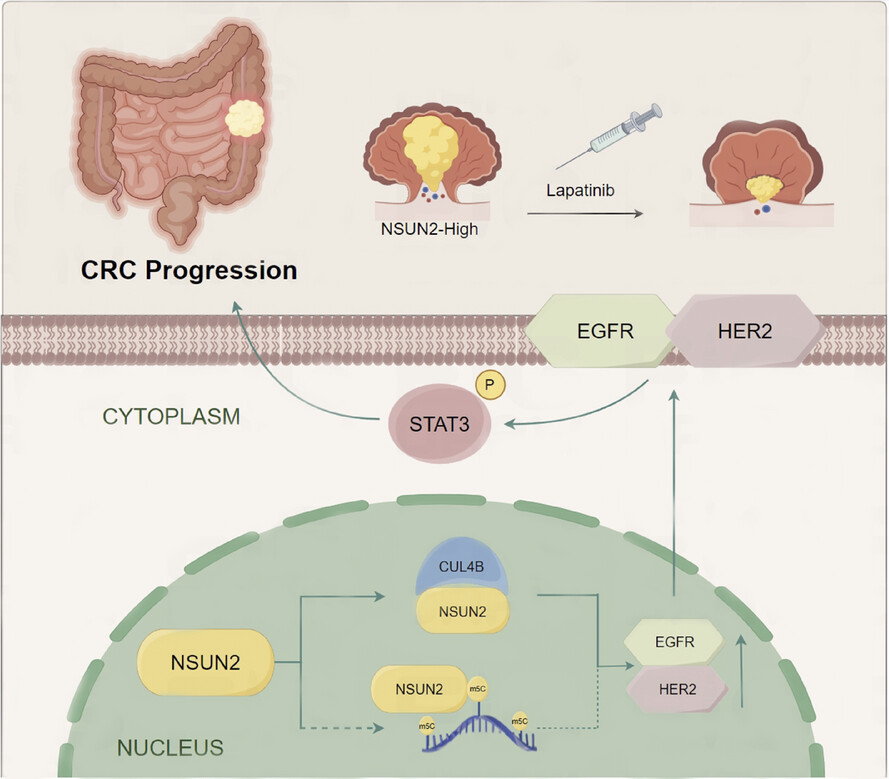
- NSUN2 is upregulated in CRC and associated with poor prognosis of CRC patients.
- NSUN2 promotes CRC malignancy independently of its m5C-enzymatic activity, a mechanism that has not been previously reported.
- The non-m5C carcinogenic roles of NSUN2 may be mediated through interactions with CUL4B, thereby activating the ErbB-STAT3 signalling pathway.
- NSUN2-mediated upregulation of ErbB-STAT3 pathway enhances the sensitivity of CRC to lapatinib treatment.
INVITED LETTER
The FBP1-TP53-NRF2 metabolic switch in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis-hepatocellular carcinoma progression and senescence reversal
- First Published: 30 March 2025
EDITORIAL
The role of metabolite sensors in metabolism-immune interaction: New targets for immune modulation
- First Published: 30 March 2025
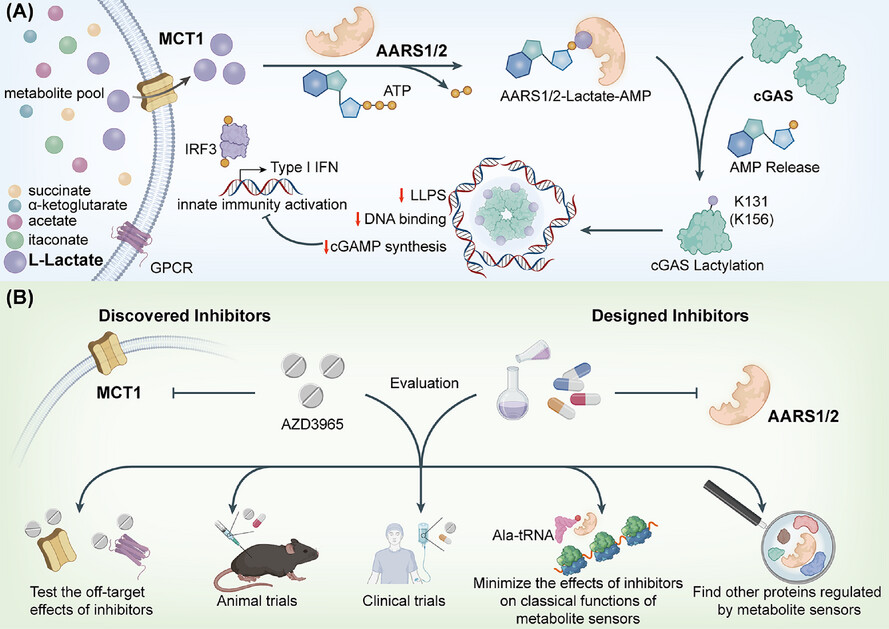
- Metabolites such as lactate, succinate, and itaconate modulate immune functions through specific sensors.
- AARS1 and AARS2 are identified as key lactate sensors, regulating immune responses via lactylation of cGAS.
- Targeting metabolite sensors holds potential for improving cancer immunotherapies and treating autoimmune diseases.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Transitional CXCL14+ cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance tumour metastasis and confer resistance to EGFR-TKIs, revealing therapeutic vulnerability to filgotinib in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 31 March 2025
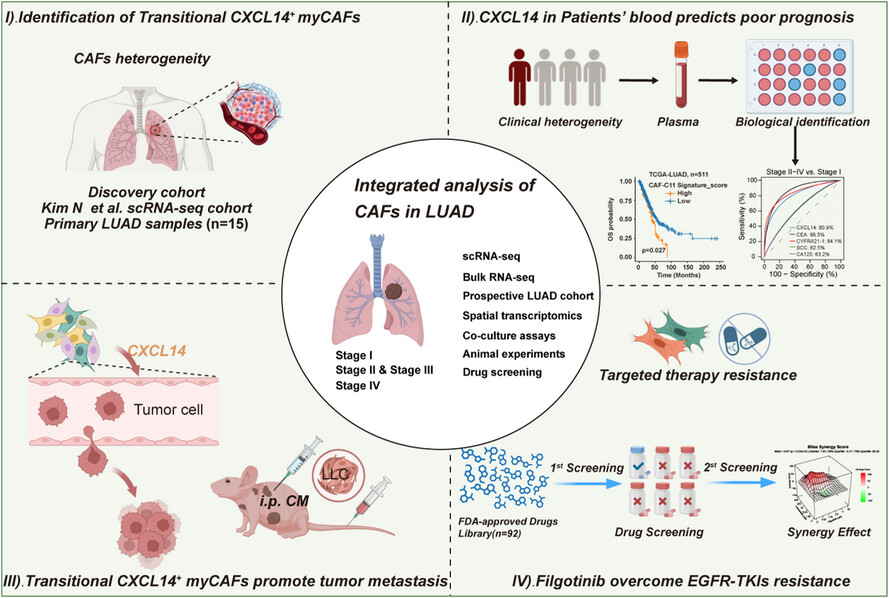
- Single-cell analysis identifies transitional CXCL14+ myofibroblastic cancer-associated fibroblasts (myCAFs) predominantly exist in the advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
- Transitional CXCL14+ myCAFs fuel metastasis by promoting epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and angiogenesis on the spatial level.
- CXCL14 is a potential diagnostic marker for LUAD patients and predict the occurrence of metastasis.
- Transitional CXCL14+ myCAFs induce the resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and JAK1 inhibitor, filgotinib could reverse the effect.
ATG16L1 restrains macrophage NLRP3 activation and alveolar epithelial cell injury during septic lung injury
- First Published: 11 April 2025
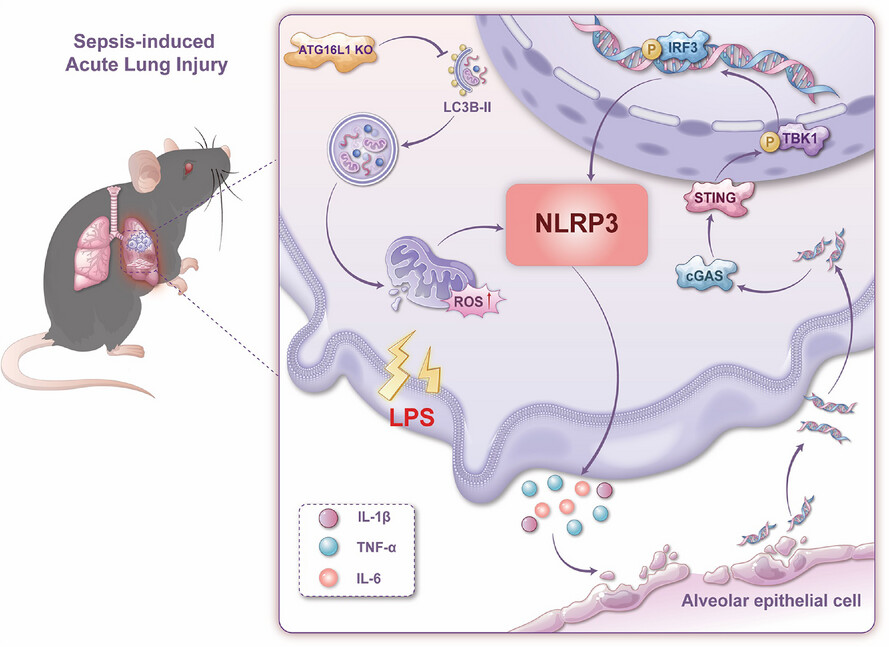
-
ATG16L1-deficient macrophages exhibited impaired LC3B lipidation and accumulation of ROS, resulting in the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
-
Overactivated ATG16L1-deficient macrophages aggravated the damage of alveolar epithelial cells, and increased the release of dsDNA.
-
Released dsDNA activated the STING‒NLRP3 signalling pathway, leading to positive feedback activation of macrophage NLRP3 signalling in macrophages.
INVITED LETTER
Targeting biomolecular condensates to inhibit breast cancer
- First Published: 01 April 2025
EDITORIAL
Towards a unified framework for single-cell -omics-based disease prediction through AI
- First Published: 01 April 2025
ERRATUM
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Clinical implement of Probe-Capture Metagenomics in sepsis patients: A multicentre and prospective study
- First Published: 03 April 2025
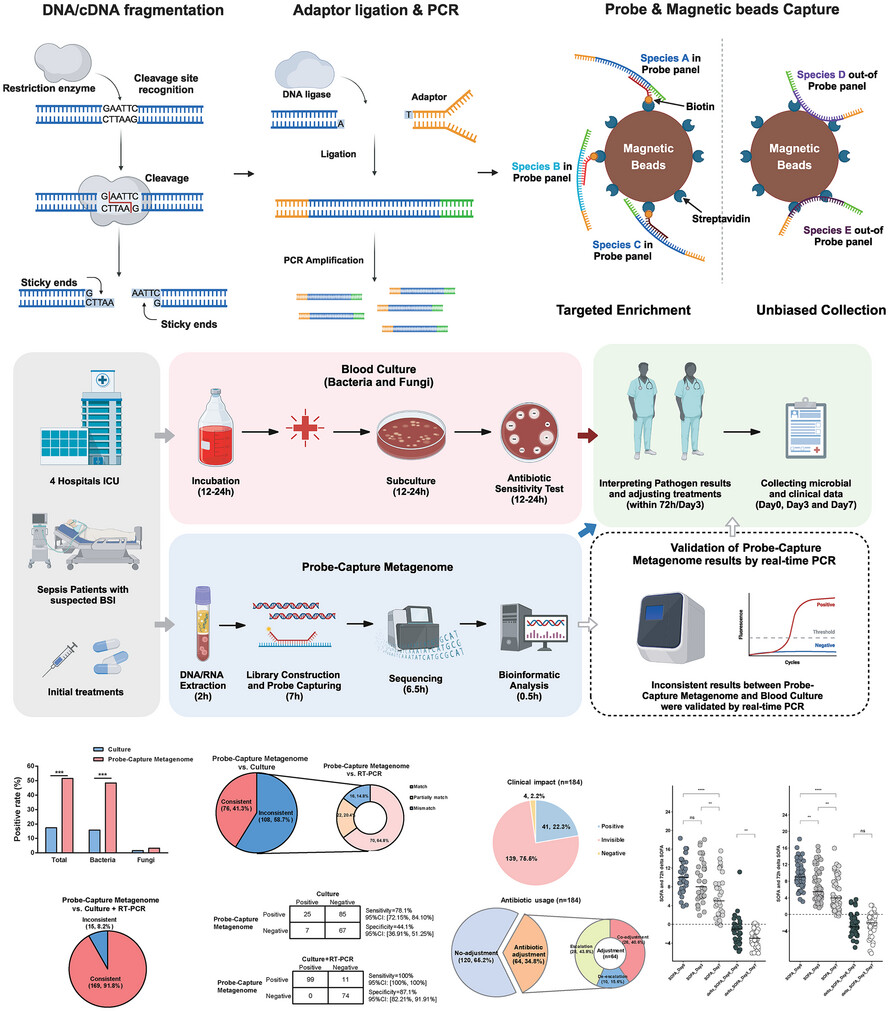
-
Probe-Capture Metagenome had a significantly higher positive rate than blood culture (51.6% vs. 17.4%, p < .001).
-
Combining blood culture and RT-PCR results, Probe-Capture Metagenome achieved a consistency rate of 91.8%.
-
Antibiotics were adjusted in 34.8% of patients based on Probe-Capture Metagenome results, and 22.3% of patients experienced a more than 2-point decrease in SOFA score.
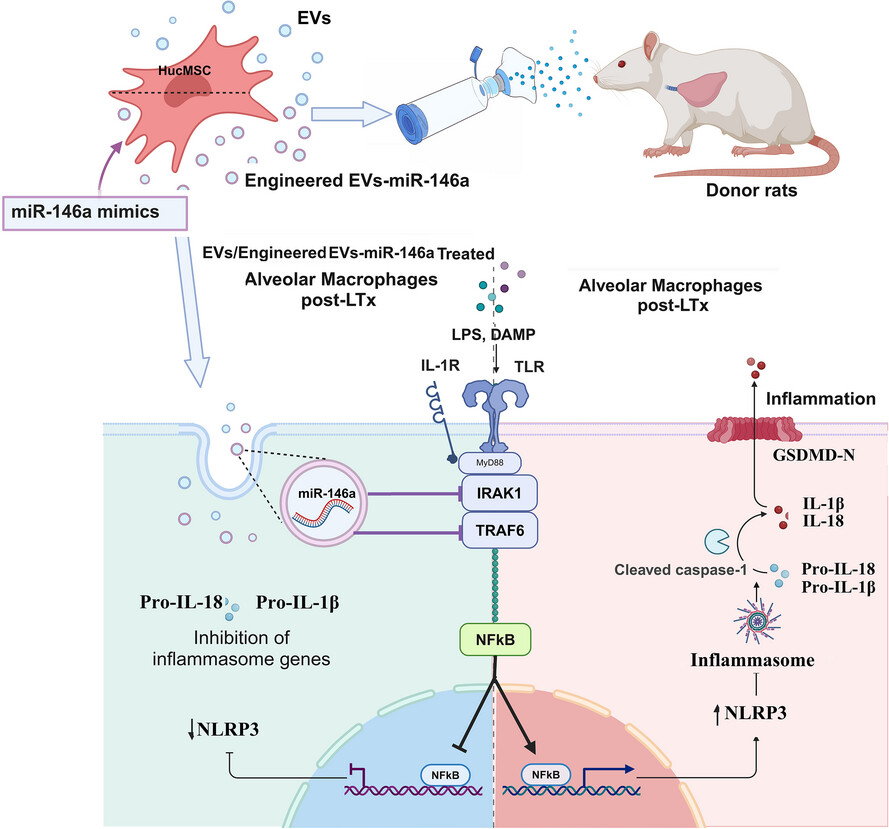
MiR-146a engineered extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells more potently attenuate ischaemia–reperfusion injury in lung transplantation
- First Published: 07 April 2025
REVIEW
The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumour microenvironment of urinary system
- First Published: 07 April 2025
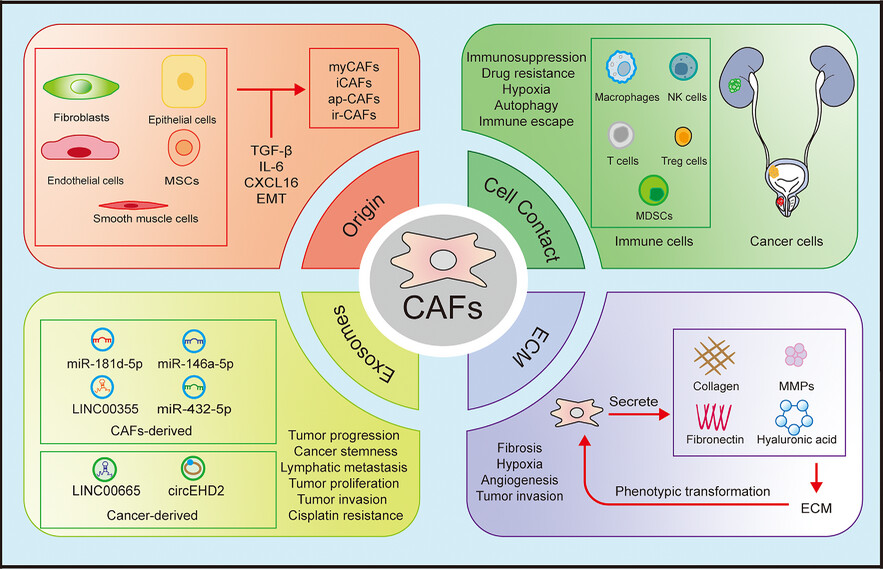
We summarised the role of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in urological tumours, including their origin, exosomes and extracellular matrix (ECM). CAFs are derived from various precursor cells and can communicate with other cells to form a hypoxic and immunosuppressive microenvironment. Additionally, CAFs can interact with tumour cells through various exosomes and exert a tumour-promoting effect .
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Severe SARS-CoV-2 infection in diabetes was rescued in mice supplemented with metformin and/or αKG, and patients taking metformin, via HIF1α-IFN axis
- First Published: 08 April 2025
REVIEW
Diverse potential of chimeric antigen receptor-engineered cell therapy: Beyond cancer
- First Published: 09 April 2025
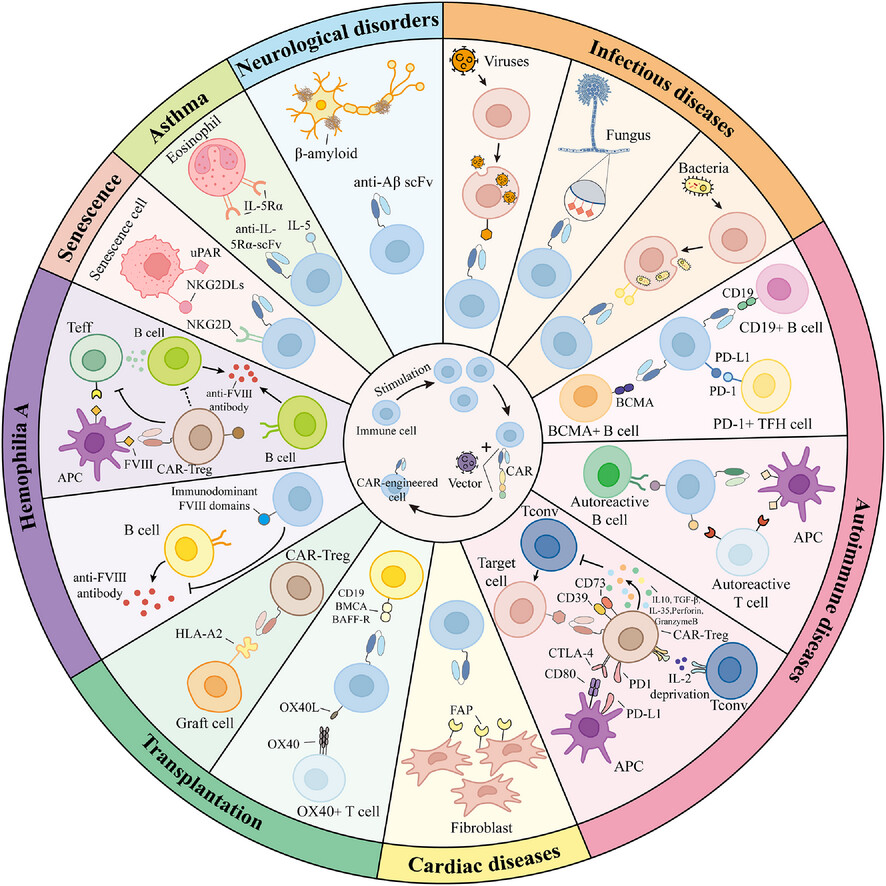
1. In theory, CAR-engineering therapy can achieve therapeutic effects by targeting cells expressing specific antigens and thereby eliminating or regulating disease-related cell subpopulations.
2. Although CAR-engineering therapy is currently only approved for the treatment of cancer, it has also shown potential in non-tumour diseases.
3. Immune cells from different sources expand the potential applications of CAR-engineering therapy.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Transcriptomic miRNA and mRNA signatures in primary prostate cancer that are associated with lymph-node invasion
- First Published: 11 April 2025
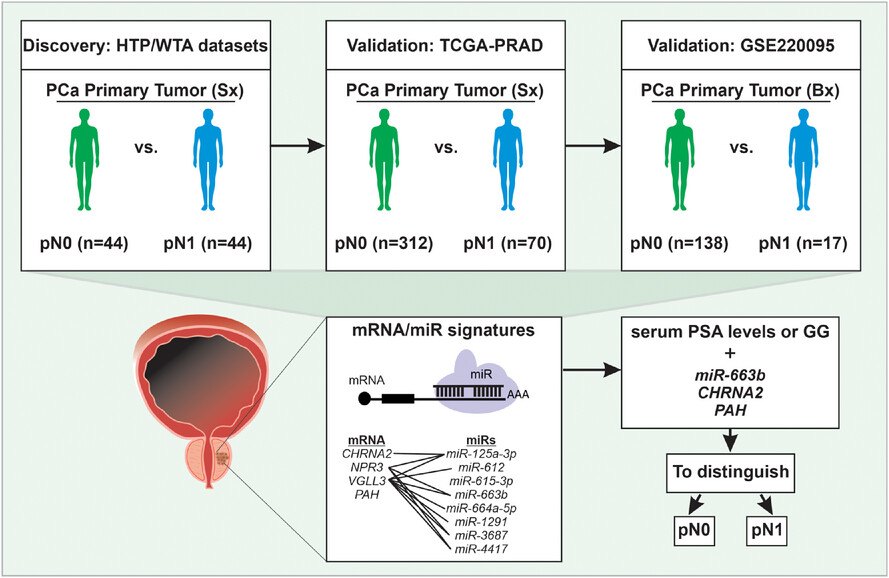
- Primary prostate cancer (PCa) tumours from patients pathologically diagnosed as N0 (pN0) or N1 (pN1) were dually assessed for microRNA (miRs) and mRNA levels using an NGS-based assay.
- A four-mRNA and an eight-miRNA signatures were found.
- The mRNA signatures were further validated using two datasets.
- The combination of serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels or Grade Group with the miR/mRNA signatures separate pN1 from pN0 PCa patients.
EDITORIAL
An important step to translate single-cell measurement into clinical practice: Stereoscopic cells
- First Published: 14 April 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Fruquintinib as first-line or second-line treatment in unresectable or metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma: A prospective, single-arm phase II study
- First Published: 15 April 2025
MS-based multi-dimensional metabolomics reveals protective effect of Polygalae Radix against metabolic disturbances in Alzheimer's disease mice
- First Published: 15 April 2025
EDITORIAL
Clinical marine biomedicine: An emerging area in clinical and translational medicine
- First Published: 20 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Ad-E6/7-HR vaccine improves the prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy in HPV-associated cancers
- First Published: 23 April 2025
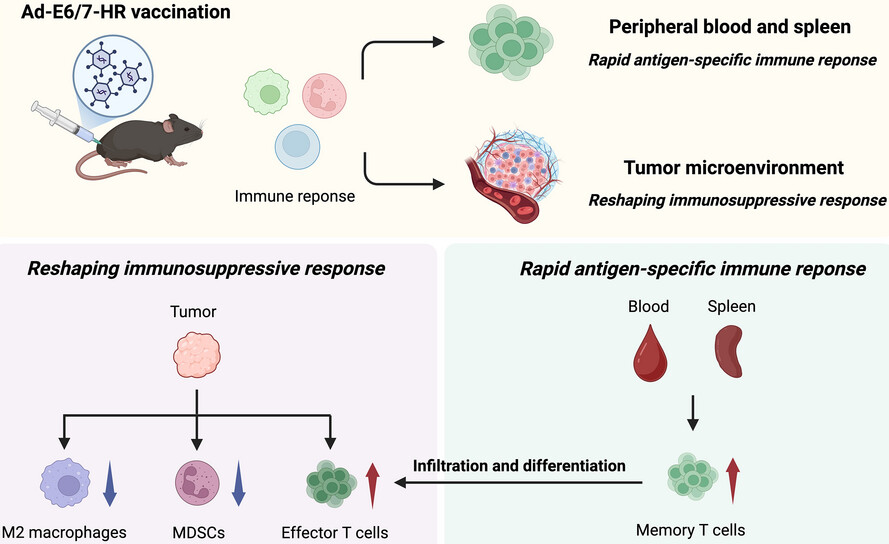
Ad-E6/7-HR activates HPV16-specific CD8+ T cells in the blood and spleen with enhanced IFN-γ/TNF-α secretion. Ad-E6/7-HR provides both preventative and therapeutic effects for HPV-associated cancers. Ad-E6/7-HR reprograms TME via increased CD8+ T-cell infiltration and reduced immunosuppressive MDSCs and M2 macrophages.
INVITED LETTER
Harnessing the power of ionising radiation to enhance cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 23 April 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Response-adapted zanubrutinib and tislelizumab as a potential strategy to enhance CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma: A retrospective observational study
- First Published: 23 April 2025
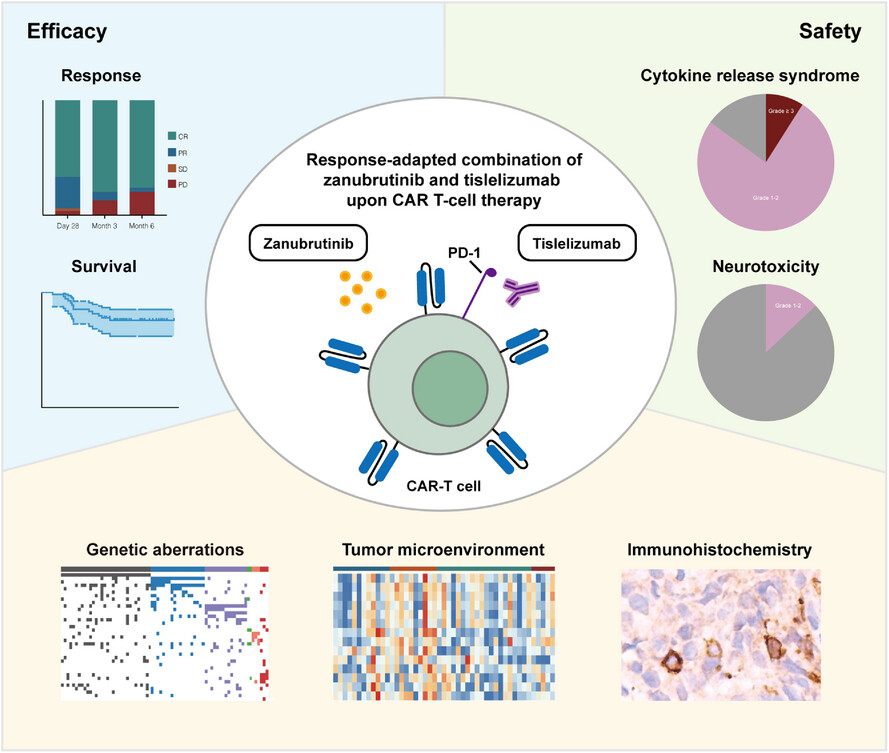
-
Response-adapted zanubrutinib plus tislelizumab potentially enhances the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy for R/R LBCL with acceptable safety profile.
-
This regimen functions independently of genetic subtypes, rendering it more applicable for clinical practice with CAR T-cell therapy.
-
This regimen effectively abrogates T-cell exhaustion, but fails to overcome the immunosuppressive effects of M2 macrophages, providing a rationale for remodelling TME to optimise CAR T-cell therapy.
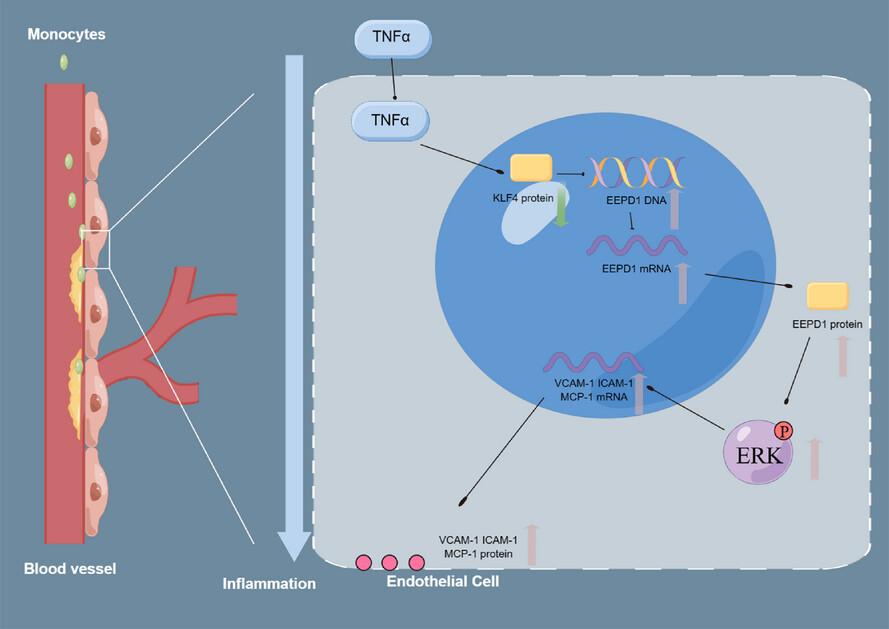
EEPD1 regulates inflammation and endothelial apoptosis in atherosclerosis through KLF4-EEPD1-ERK axis
- First Published: 23 April 2025
REVIEW
Angiogenesis and targeted therapy in the tumour microenvironment: From basic to clinical practice
- First Published: 23 April 2025
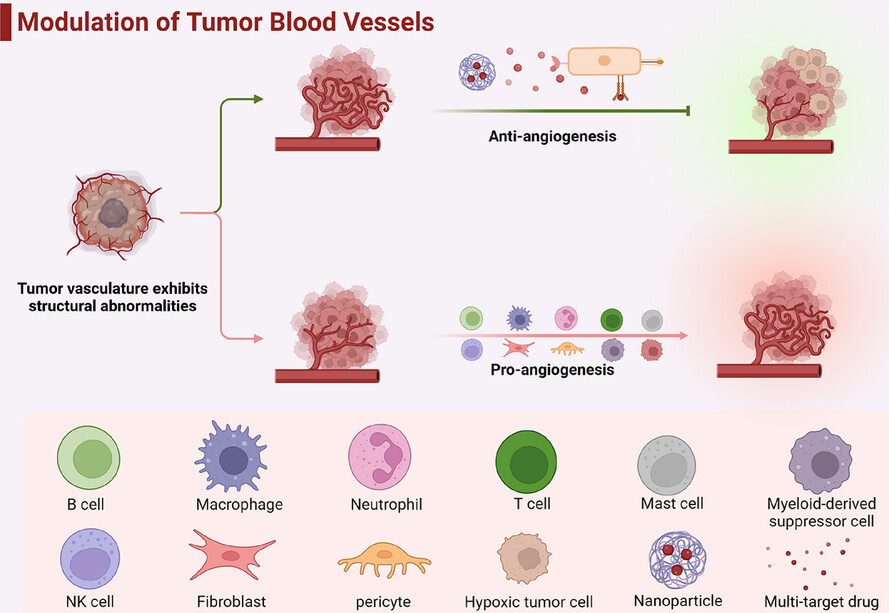
- Angiogenesis plays a key role in tumour progression, invasion and metastasis, so strategies targeting angiogenesis are gradually becoming an important direction in cancer therapy.
- Interactions between endothelial cells and stromal cells and immune cells in the tumour microenvironment are significant in angiogenesis.
- The application of antiangiogenic immunotherapy and nanotechnology in antiangiogenic therapy provides a vital strategy for prolonging the survival of cancer patients.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Skeletal muscle effects of antisense oligonucleotides targeting glycogen synthase 1 in a mouse model of Pompe disease
- First Published: 23 April 2025
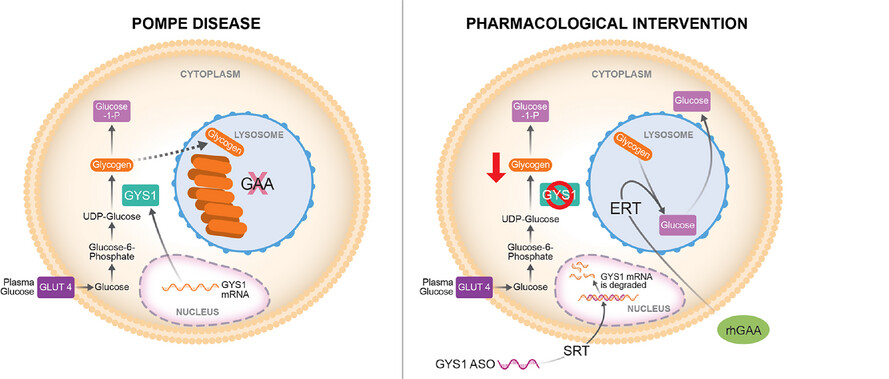
-
Antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) treatment in a mouse model of Pompe disease achieves robust knockdown of glycogen synthase (GYS1).
-
ASO treatment reduces glycogen content in skeletal muscle.
-
Combination of ASO and enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) further improves motor performance compared to ASO alone in a mouse model of Pompe disease.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Exploring glomeruli and renal tubules transcriptomic data: Crucial role of the AASS gene in membranous nephropathy
- First Published: 23 April 2025