Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
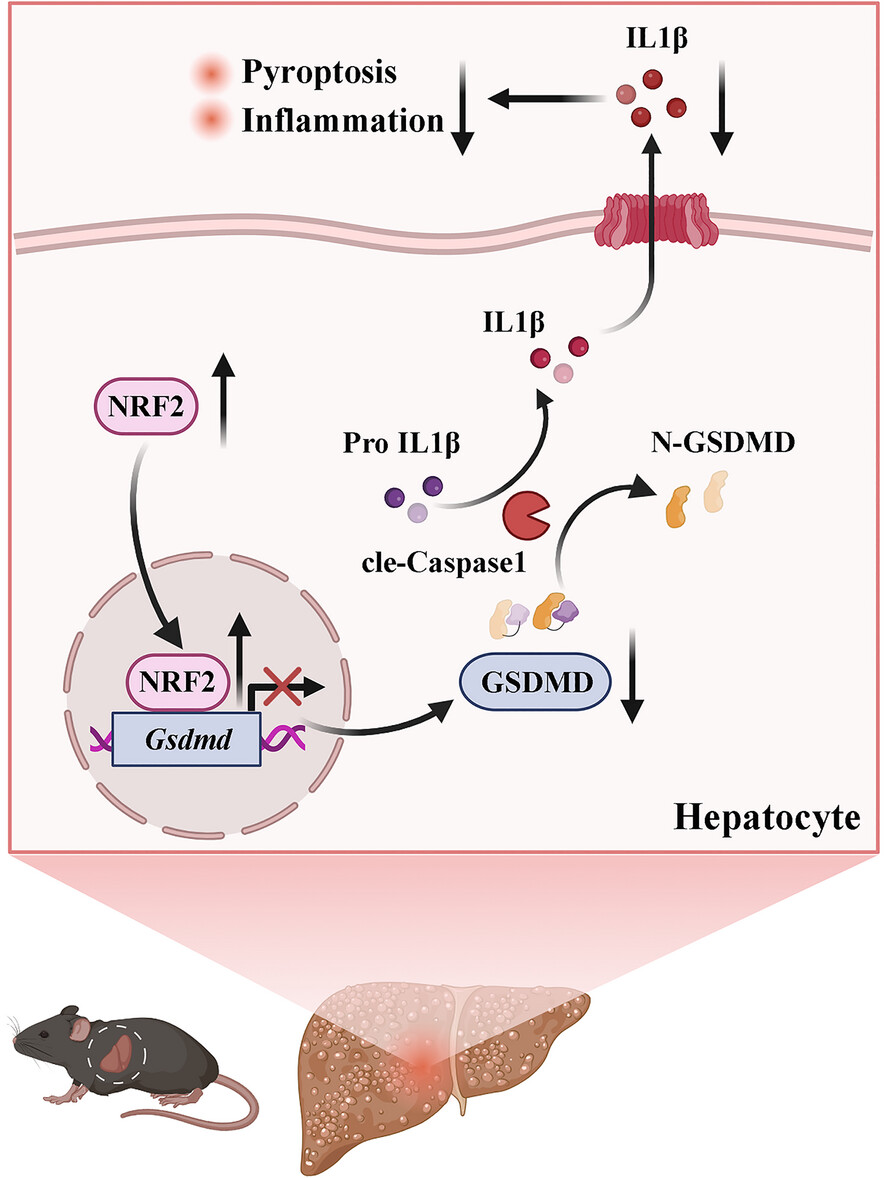
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 ameliorates disordered glucose and lipid metabolism in liver: Involvement of gasdermin D in regulating pyroptosis
- First Published: 24 February 2025
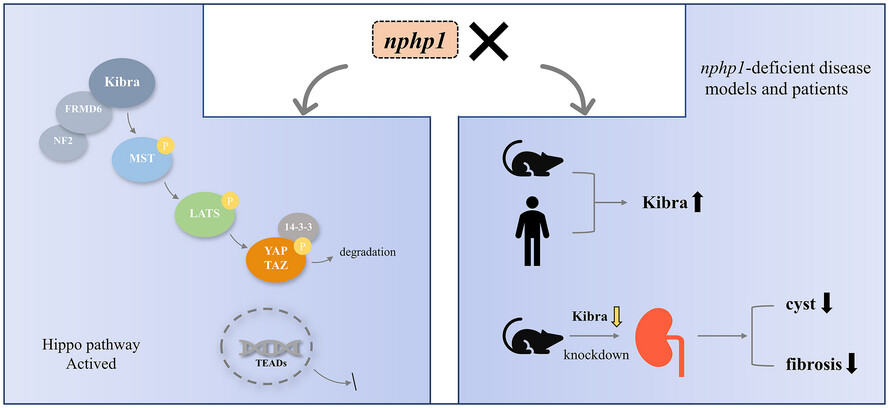
Kibra knockdown inhibits the aberrant Hippo pathway, suppresses renal cyst formation and ameliorates renal fibrosis in nphp1KO mice
- First Published: 24 February 2025
Comprehensive transcriptome, miRNA and kinome profiling identifies new treatment options for personalized lung cancer therapy
- First Published: 24 February 2025
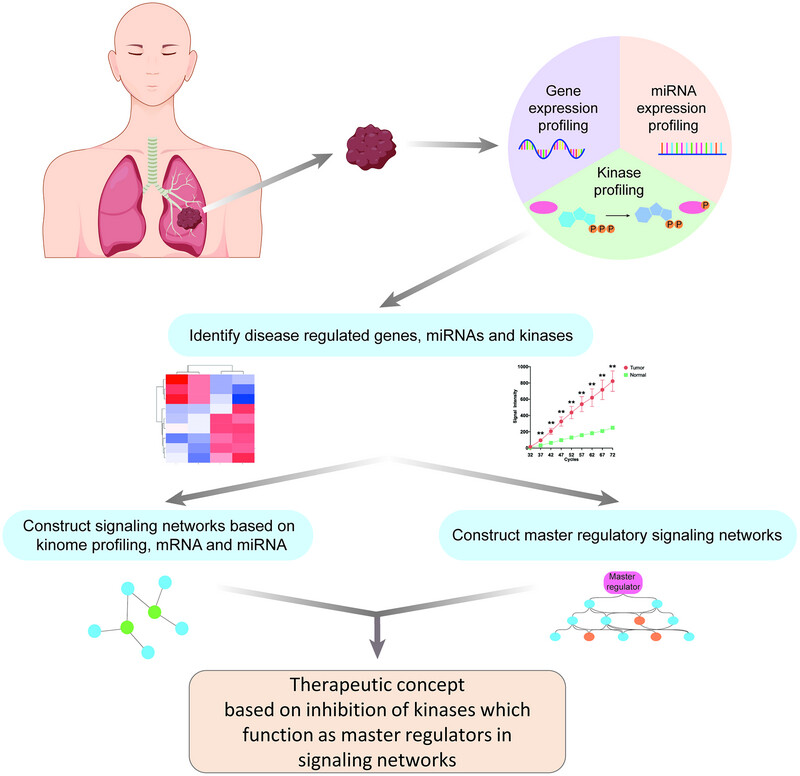
Kinase inhibition–based therapies are recommended for a small subset of LC patients with driver mutations. Through enabling technologies and bioinformatics, we demonstrate the potential of KI-based therapies based on the patient specific needs. Thus, most LC patients become eligible for such treatment algorithms.
Genome-wide profiling of N6-methyladenosine-modified pseudogene-derived long noncoding RNAs reveals the tumour-promoting and innate immune-restraining function of RPS15AP12 in ovarian cancer
- First Published: 25 February 2025
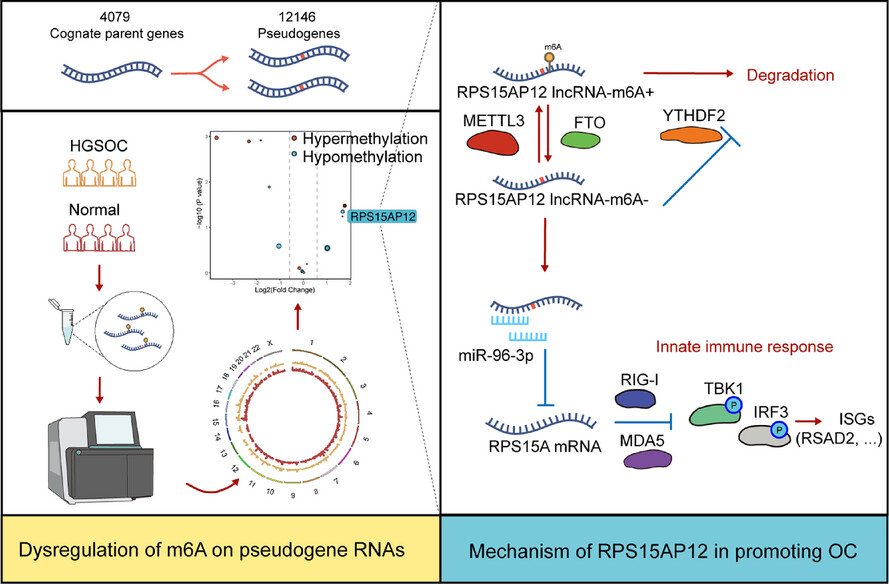
Genome-wide profiling reveals the redistribution of m6A modification on pseudogene-derived lncRNAs and m6A redistribution-relevant dysregulation of pseudogenes in HGSOC. RPS15AP12, as a representative processed pseudogene, is up-regulated by FTO-mediated demethylation and acts as a miRNA sponge to promote RPS15A expression via competitively binding to miR-96-3p. The RPS15AP12/ RPS15A axis exhibits an anti-tumour effect via inhibiting innate immune response in ovarian cancer.
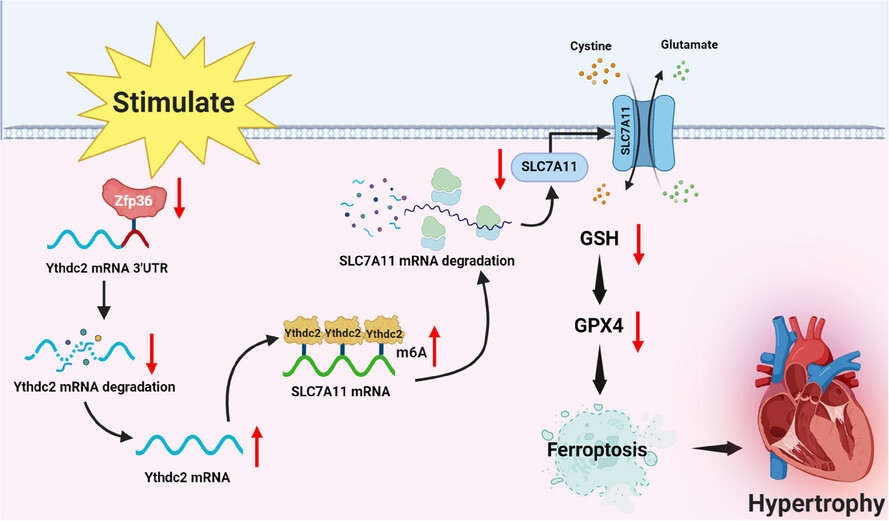
Targeting Zfp36 to combat cardiac hypertrophy: Insights into ferroptosis pathways
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Predictive circulating biomarkers of the response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in advanced HER2 negative breast cancer
- First Published: 25 February 2025
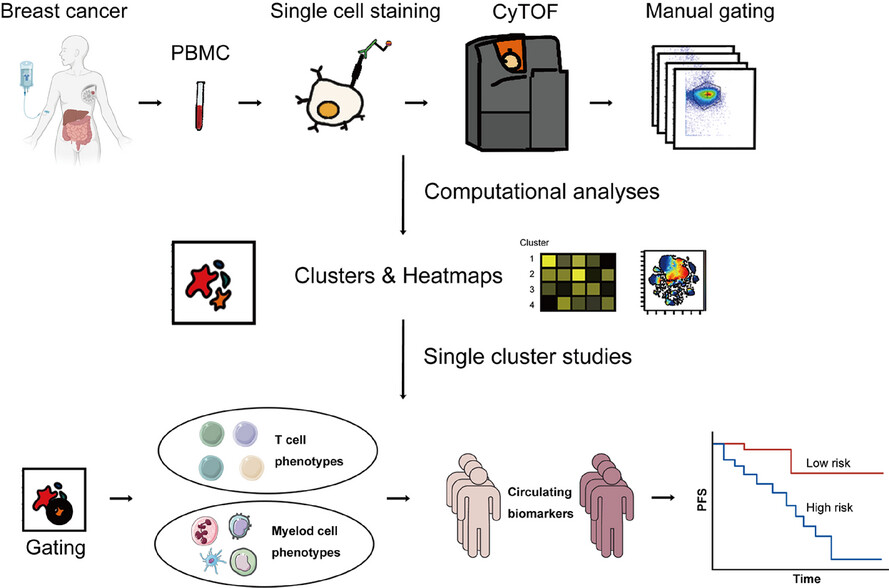
Our study identified that the proportions of CD39+ Tregs and moDCs in the peripheral blood were correlated with the response to immunotherapy in patients with advanced breast cancer. These two subpopulations are potential predictive biomarkers for determining patient prognosis, offering valuable guidance for treatment strategies.
An adoptive cell therapy with TREM2-overexpressing macrophages mitigates the transition from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease
- First Published: 25 February 2025
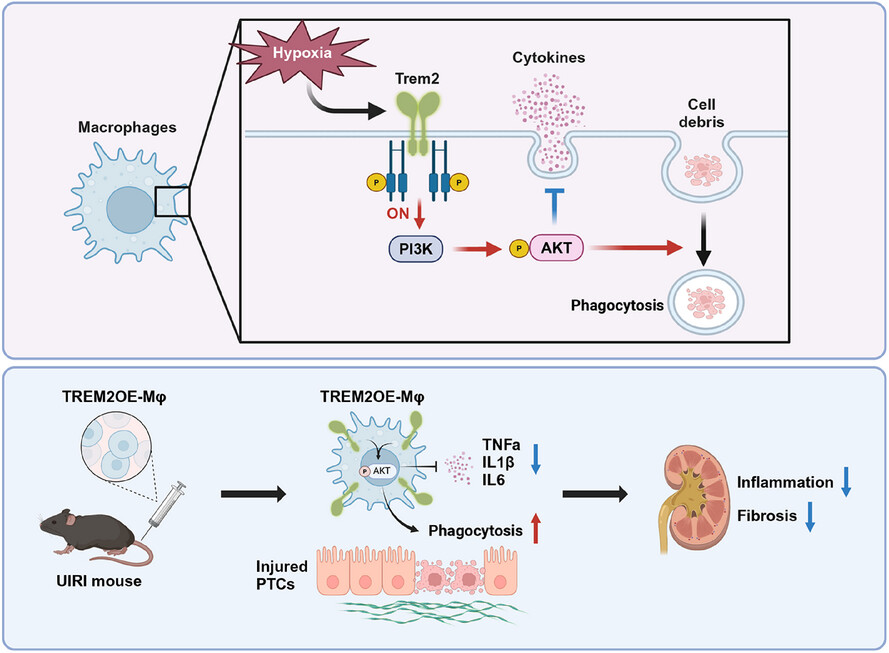
In unilateral ischaemia–reperfusion injury (UIRI), Trem2 expression is upregulated by hypoxia via HIF-1α in macrophages, and the activation of Trem2 enhances phagocytosis and reduces cytokine production through the PI3K-AKT pathway in macrophages. An adoptive cell therapy using Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells 2 (TREM2)-overexpressing macrophages effectively mitigates the transition from acute kidney injury (AKI) to chronic kidney disease (CKD) in UIRI animals.
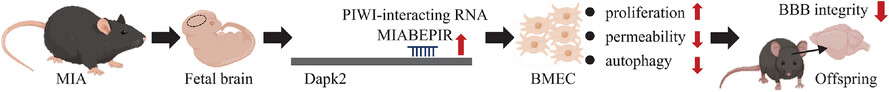
PIWI-interacting RNA MIABEPIR regulates cerebral endothelial cell function via DAPK2 pathway in offspring following maternal immune activation
- First Published: 25 February 2025
LINC01088 prevents ferroptosis in glioblastoma by enhancing SLC7A11 via HLTF/USP7 axis
- First Published: 25 February 2025
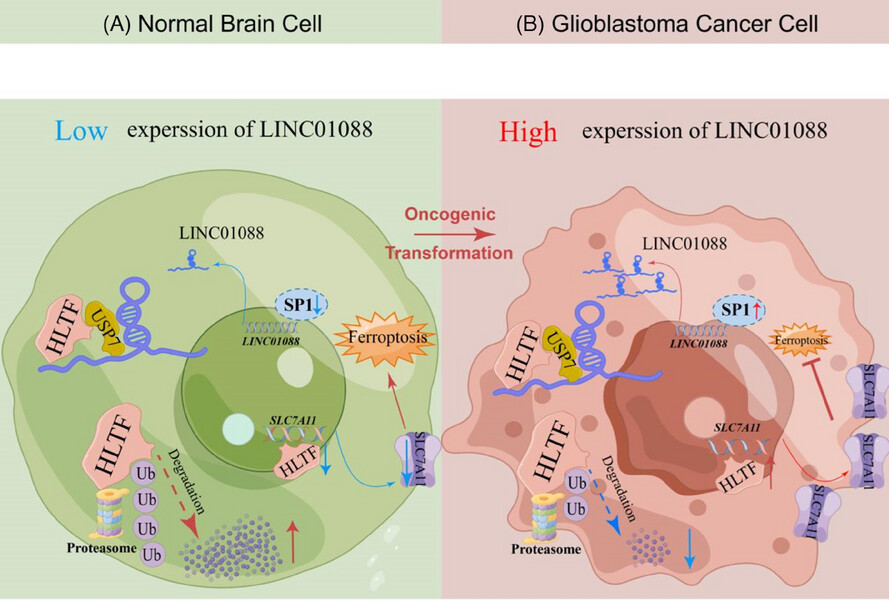
Schematic model detailing the molecular mechanisms of LINC01088 in normal brain cells and GBM cells.
LINC01088 is transcriptionally upregulated by SP1.
LINC01088 acts as a scaffold platform to bind USP7 and HLTF.
USP7, as a deubiquitinating enzyme of HLTF, participates in inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of HLTF.
HLTF transcriptionally upregates the expression of downstream SLC7A11, and ferroptosis of GBM cells was inhibited.
Enhanced human adipose-derived stem cells with VEGFA and bFGF mRNA promote stable vascular regeneration and improve cardiac function following myocardial infarction
- First Published: 26 February 2025
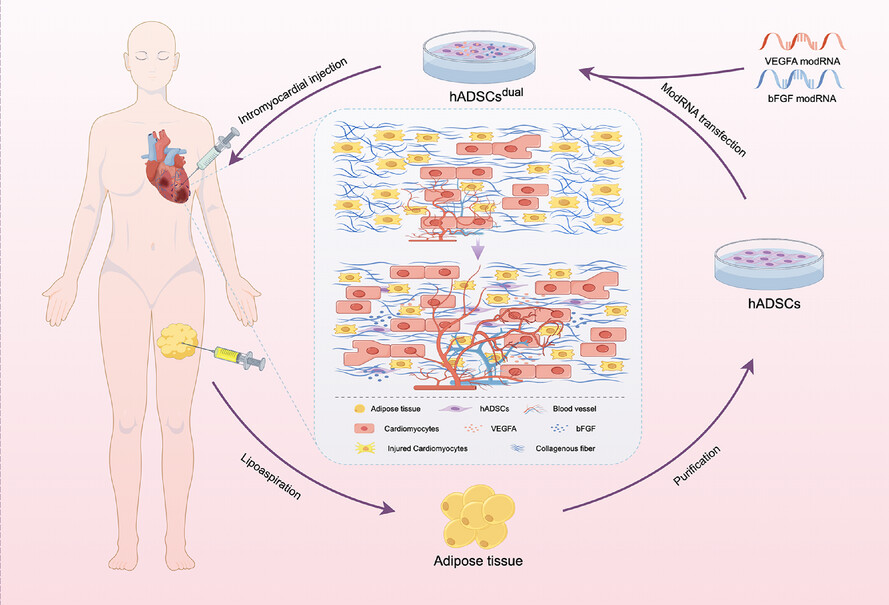
- ModRNAs-transfected hADSCs exhibit pulsed and transient expression, enabling efficient production of functional VEGFA and bFGF proteins.
- Intracardiac injection of these engineered hADSCs leads to the enhancement of cardiac function and the improvement of electrical conduction.
- The hADSCsdual mainly exerts its effect on myocardial infarction by promoting stable vascular regeneration and suppressing cell apoptosis.
REVIEW
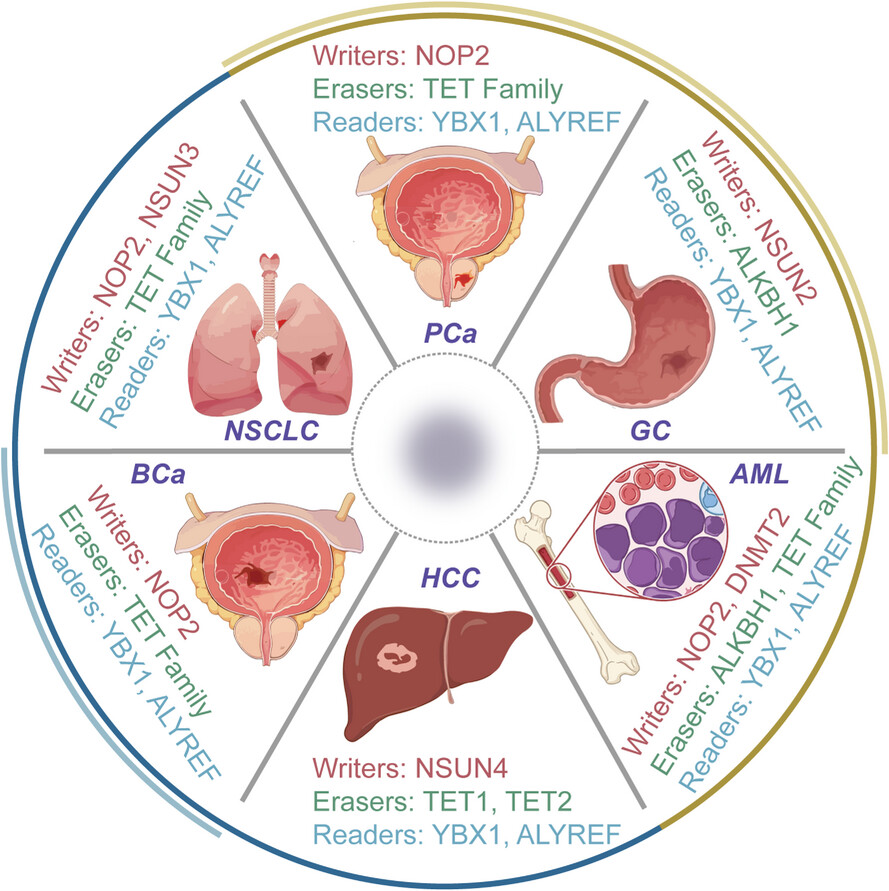
Detection, molecular function and mechanisms of m5C in cancer
- First Published: 26 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
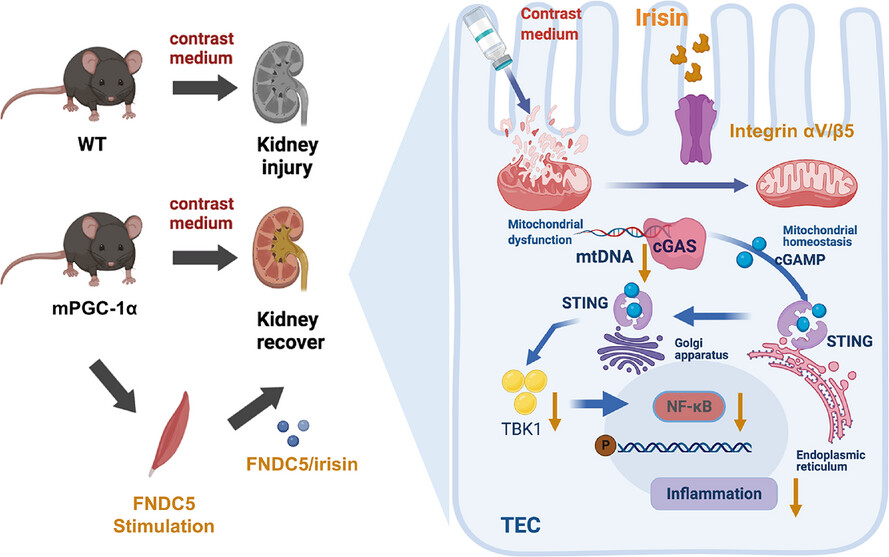
Irisin-mediated muscle-renal crosstalk as a protective mechanism against contrast-induced acute kidney injury via cGAS-STING signalling inhibition
- First Published: 26 February 2025
INVITED LETTER
Long-term impact of obesity: Unraveling adipose epigenetic memory
- First Published: 04 March 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
RESEARCH ARTICLE
SH3GL1-activated FTH1 inhibits ferroptosis and confers doxorubicin resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- First Published: 04 March 2025
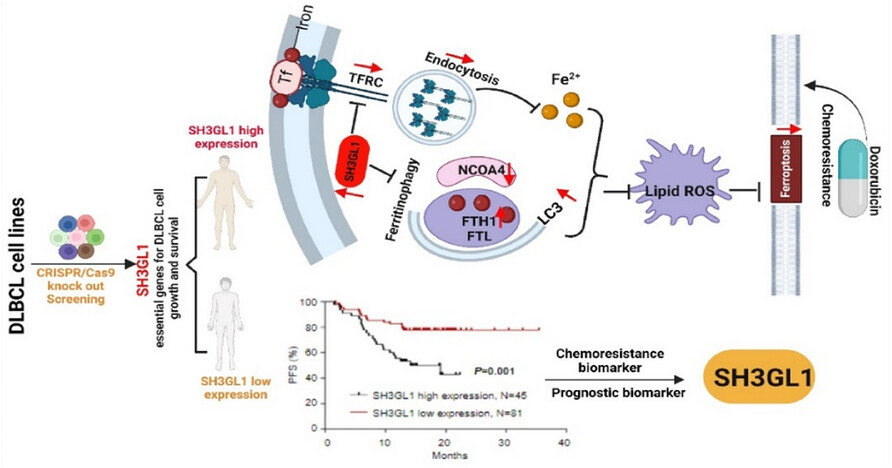
Elevated expression levels of SH3GL1 in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) was associated with poor prognostic outcomes.
SH3GL1 plays an important role in promoting DLBCL cell survival through the regulation of ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1)-mediated ferroptosis and doxorubicin resistance.
SH3GL1 can be a valuable prognostic biomarker and a potential target for anti-DLBCL intervention in the future .
REVIEW
Deciphering the epigenetic role of long non-coding RNAs in mood disorders: Focus on human brain studies
- First Published: 04 March 2025
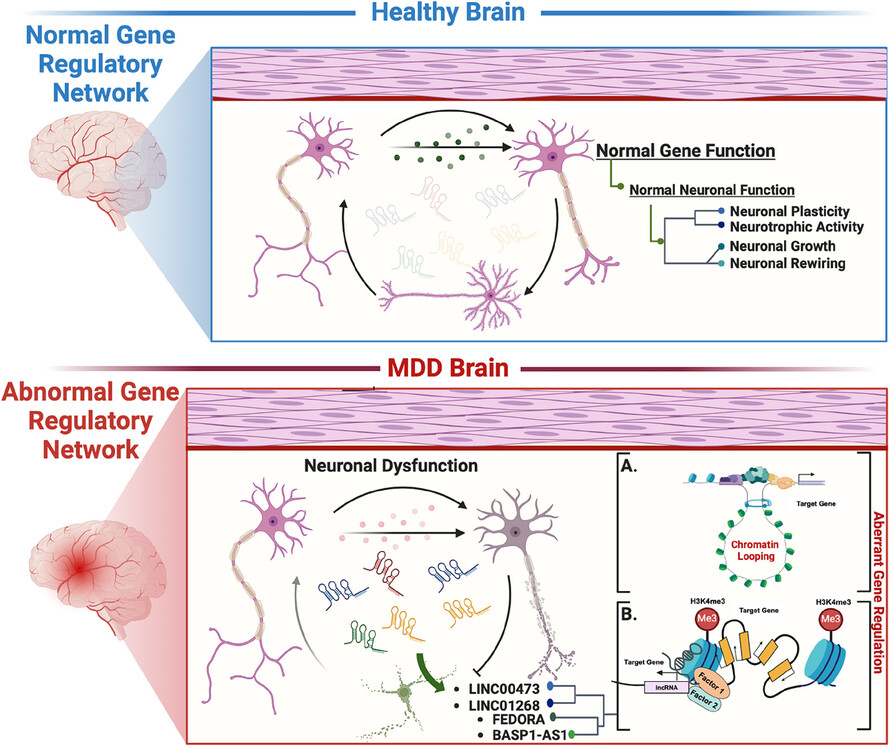
- Brain-centric lncRNAs regulate gene networks, and their disruption is linked to MDD.
- In MDD, altered lncRNAs disrupt gene regulation by changing chromatin looping or modifying chromatin accessibility.
- These changes lead to neuronal dysfunction, affecting neural circuitry and synaptic plasticity.
- The result is impaired brain function, contributing to the symptoms of MDD.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Topical TYK2 inhibitor ameliorates psoriasis-like dermatitis via the AKT-SP1-NGFR-AP1 pathway in keratinocytes
- First Published: 04 March 2025
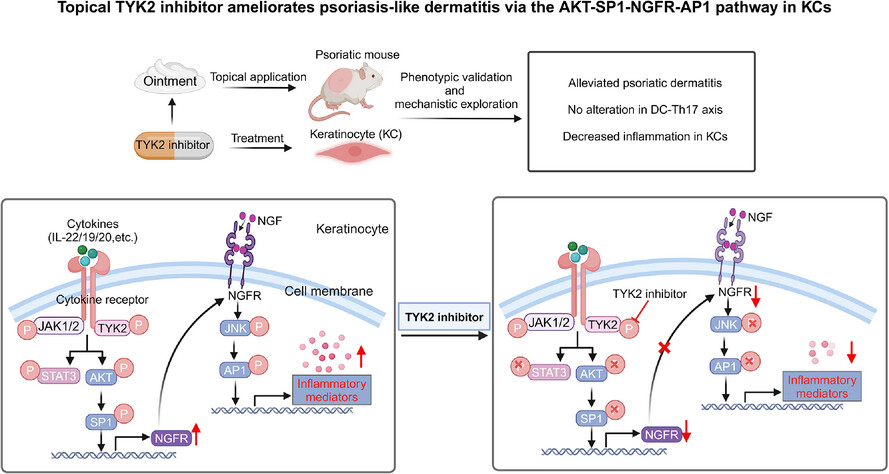
- Topical tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor alleviates psoriasis-like dermatitis.
- Topical TYK2 inhibitor reduces psoriasis progression through restraining the inflammatory responses of keratinocytes.
- The inhibition of TYK2 regulates the inflammatory response of keratinocytes through AKT-SP1-NGFR-AP1 pathway.
REVIEW
Ferroptosis of T cell in inflammation and tumour immunity
- First Published: 05 March 2025
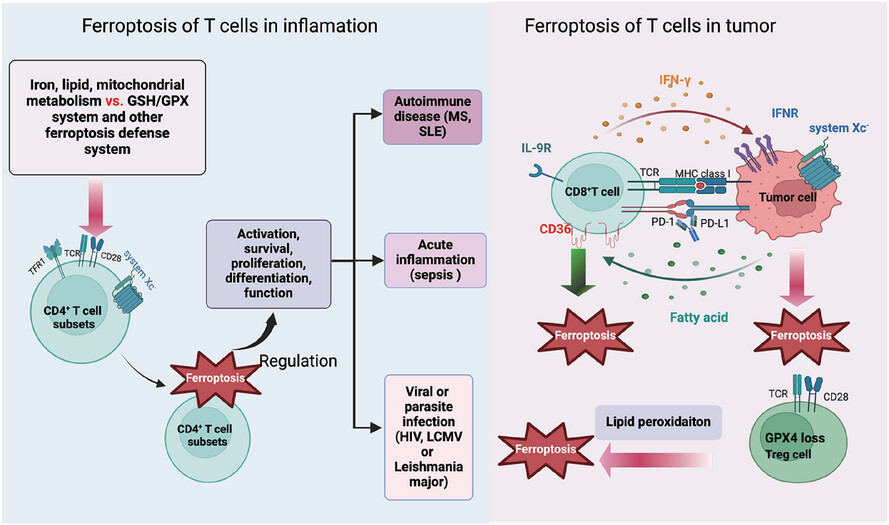
- Ferroptosis-related mechanisms significantly affect the biology of CD4+ T-cell subsets and are further involved in inflammatory diseases.
- Crosstalk between CD8+ T cells and tumour cells induces ferroptosis in the tumour microenvironment.
- Glutathione peroxidase 4 loss promotes regulatory T-cell ferroptosis to enhance anti-tumour immunity.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The novel GSDMD inhibitor GI-Y2 exerts antipyroptotic effects to reduce atherosclerosis
- First Published: 05 March 2025
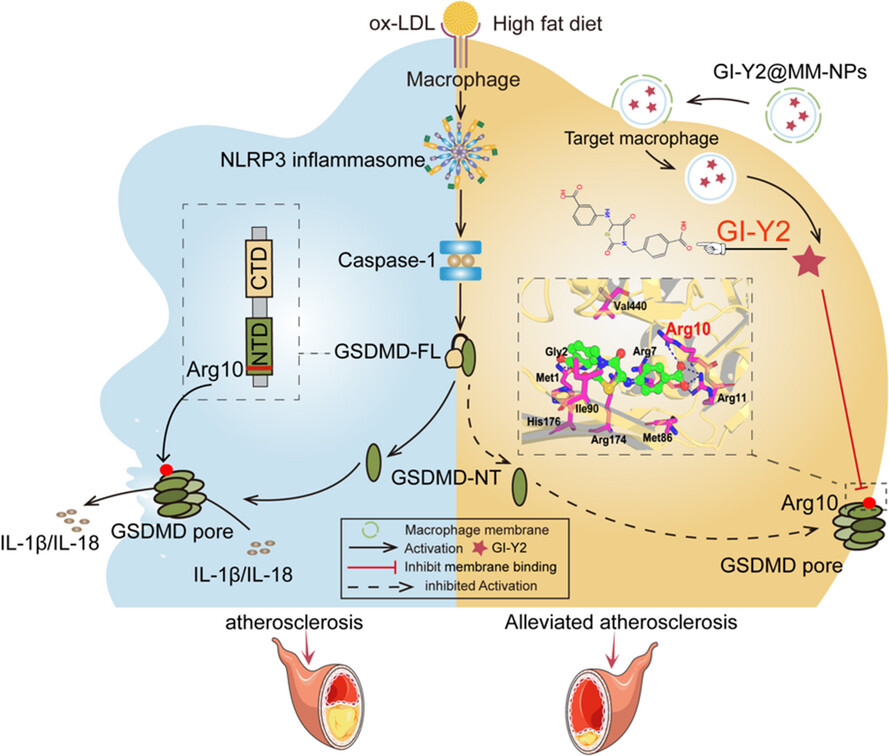
We confirmed GI-Y2 as a novel inhibitor of GSDMD. GI-Y2 directly interacts with the Arg10 residue of GSDMD and reduces the membrane binding of GSDMD-N. We constructed macrophage membrane-coated GI-Y2 nanoparticles to enhance the targeting of GI-Y2 to macrophages in atheromatous plaques and demonstrated its vascular protective effect.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy based on stem cell-like memory T cells enhances anti-tumour effects in multiple myeloma
- First Published: 05 March 2025
REVIEW
Vascularised organoids: Recent advances and applications in cancer research
- First Published: 05 March 2025
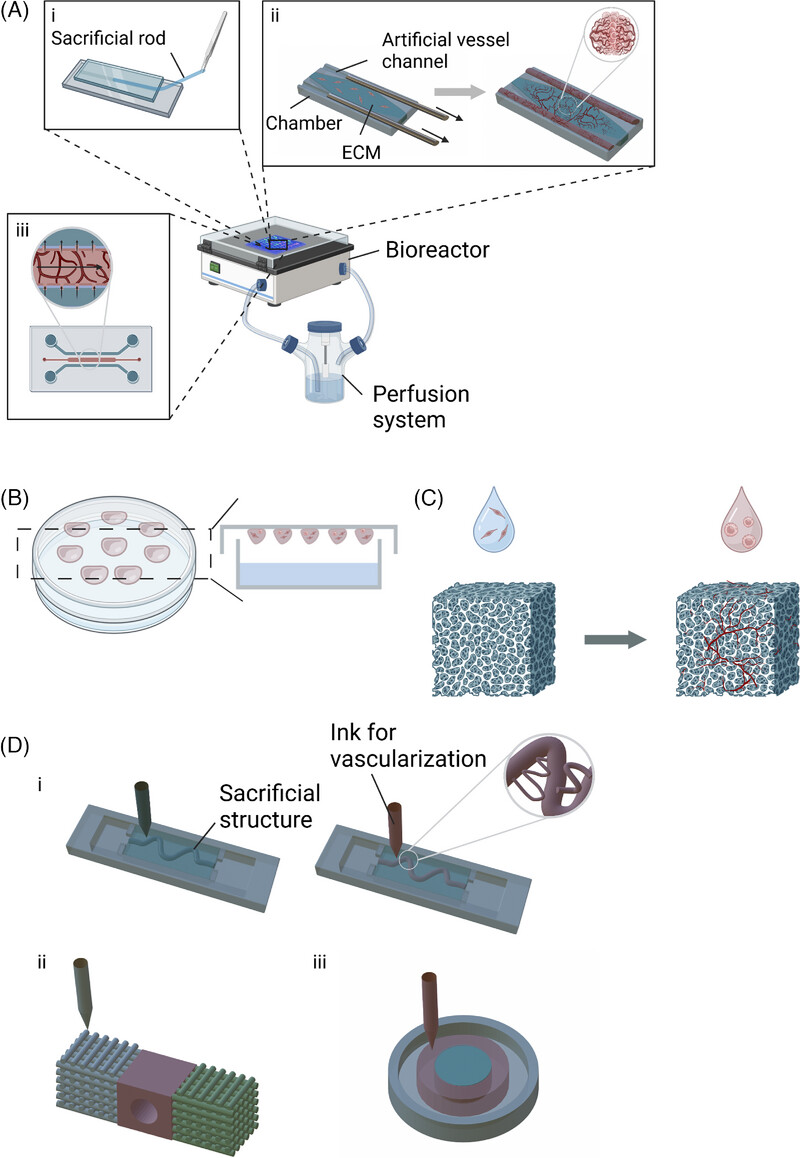
This review explores vascularised organoids in oncology, highlighting their advantages over 2D cultures and animal models in replicating the tumour microenvironment. It examines fabrication methods, vascularisation techniques and advancements in biomaterials, emphasising their applications in studying vasculature–cancer interactions, drug screening and advancing cancer research and clinical practice.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
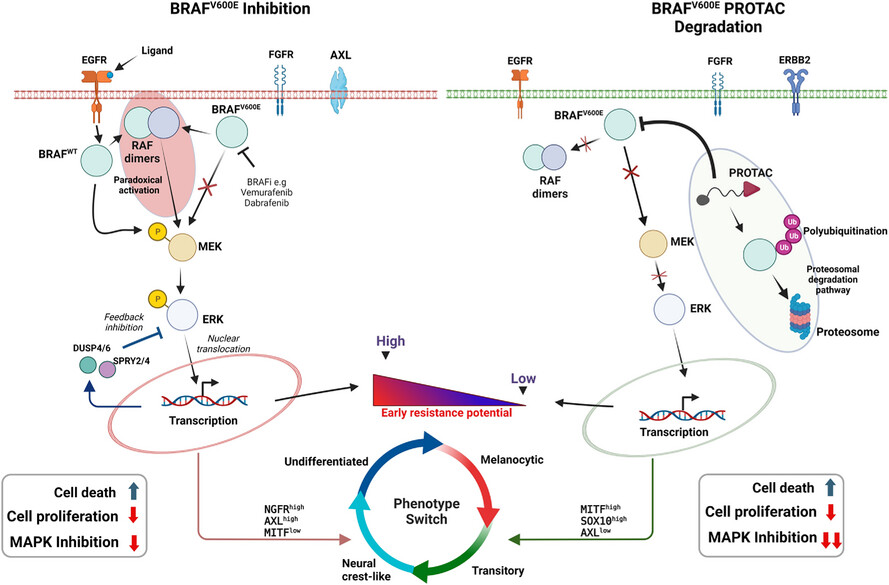
BRAFV600E-PROTAC versus inhibitors in melanoma cells: Deep transcriptomic characterization
- First Published: 05 March 2025
Exon junction complexes regulate osteoclast-induced bone resorption by influencing the NFATc1 m6A distribution through the “shield effect”
- First Published: 06 March 2025
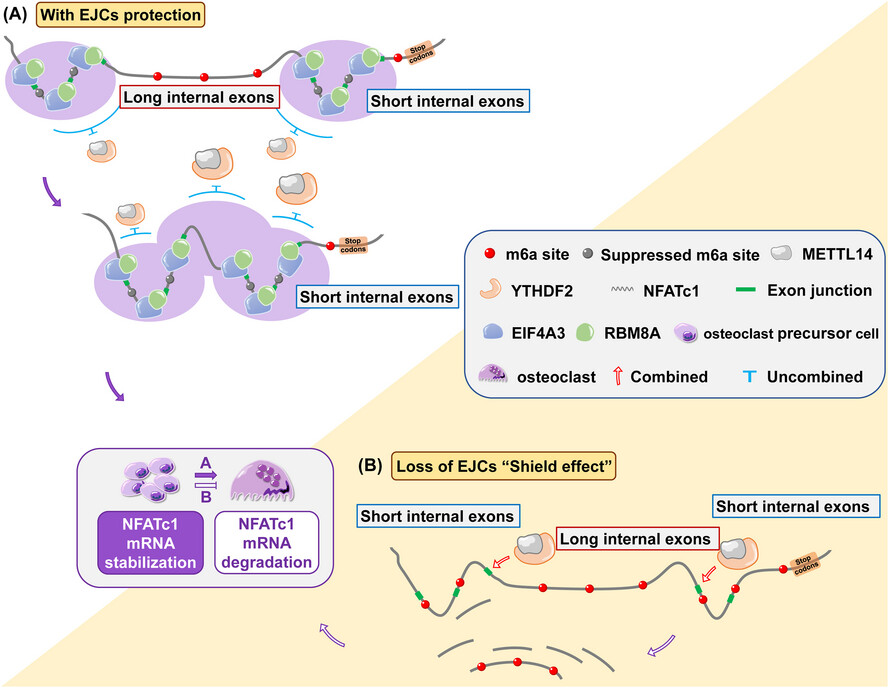
EJCs protected the methylation sites of the NFATc1 gene (located in the inner exon fragment of 50–200 nt) from hypermethylation and degradation, and the “shields” disappeared when the exon fragment was extended to 300 nt. Downstream, YTHDF2 induced the degradation of NFATc1 transcripts without site restriction. EJCs act as “shields” to regulate the m6A region selectivity of the NFATc1 gene, thereby determining the characteristics of the m6A distribution in this gene.
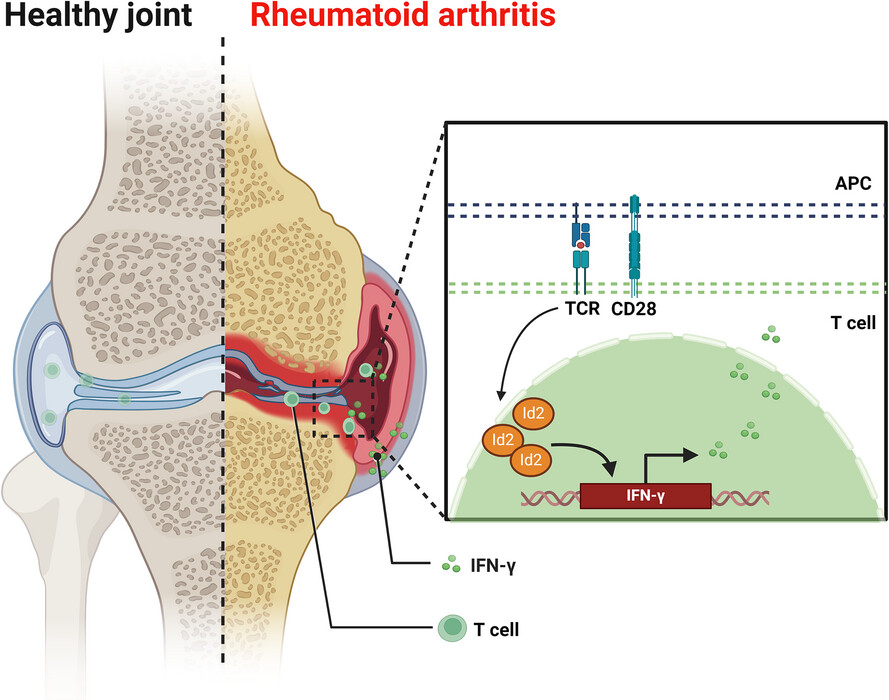
Id2 exacerbates the development of rheumatoid arthritis by increasing IFN-γ production in CD4+ T cells
- First Published: 06 March 2025
Integrated spatial multi-omics profiling of Fusobacterium nucleatum in breast cancer unveils its role in tumour microenvironment modulation and cancer progression
- First Published: 11 March 2025
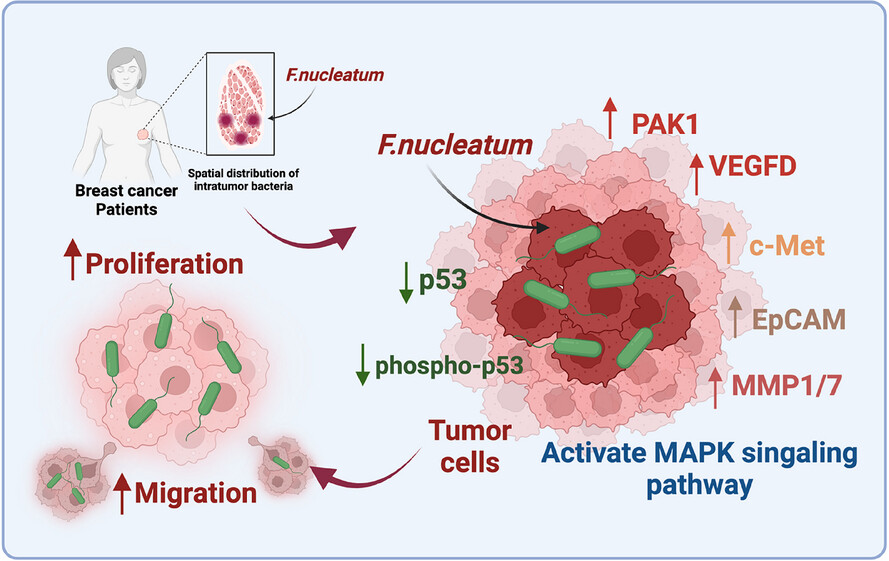
- Intratumoral Fusobacterium nucleatum exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity within breast cancer tissues.
- F. nucleatum colonization alters the expression of key proteins involved in tumour progression and migration.
- The MAPK signalling pathway is a critical mediator of F. nucleatum-induced breast cancer cell proliferation and migration.
- VEGFD and PAK1 are potential therapeutic targets to mitigate F. nucleatum-induced tumour progression.
Aberrant DNA methylation of genes regulating CD4+ T cell HIV-1 reservoir in women with HIV
- First Published: 11 March 2025
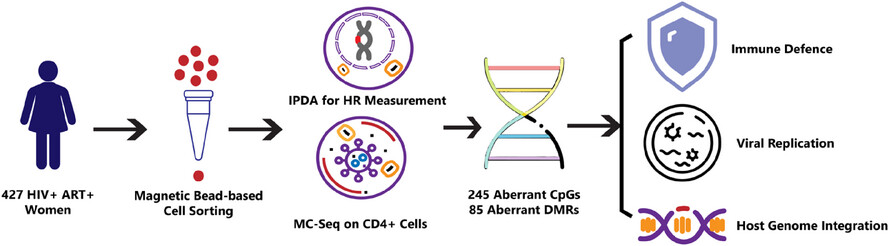
- Study involved 427 women with HIV.
- Identified 245 aberrant DNA methylation sites and 85 methylation regions in CD4+ T cells linked to the HIV-1 reservoir.
- Highlighted genes are involved in viral replication, immune defence, and host genome integration.
- Findings suggest potential molecular targets for eradication strategies.
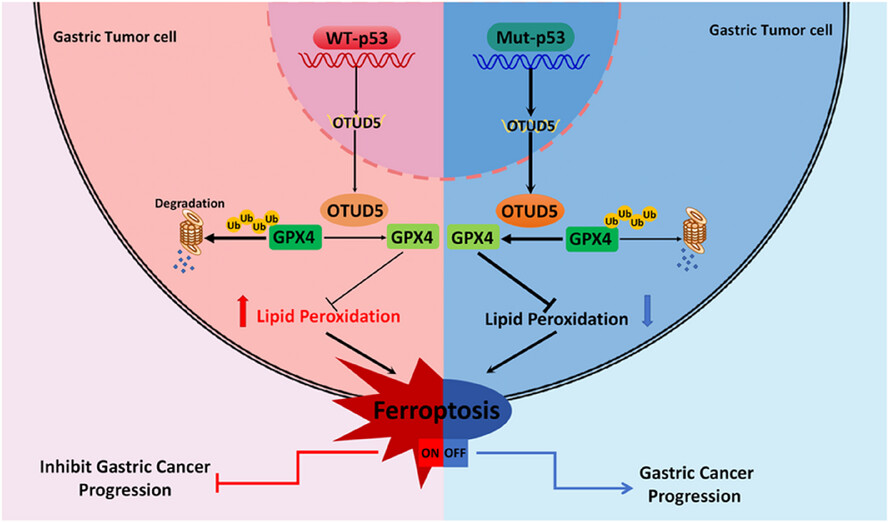
p53 inhibits OTUD5 transcription to promote GPX4 degradation and induce ferroptosis in gastric cancer
- First Published: 11 March 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Exploring targets in oropharyngeal cancer – association with immune markers and AI-scoring of B7-H3 expression
- First Published: 12 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
PADI4 facilitates stem-like properties and cisplatin resistance through upregulating PRMT2/IDs family in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 13 March 2025
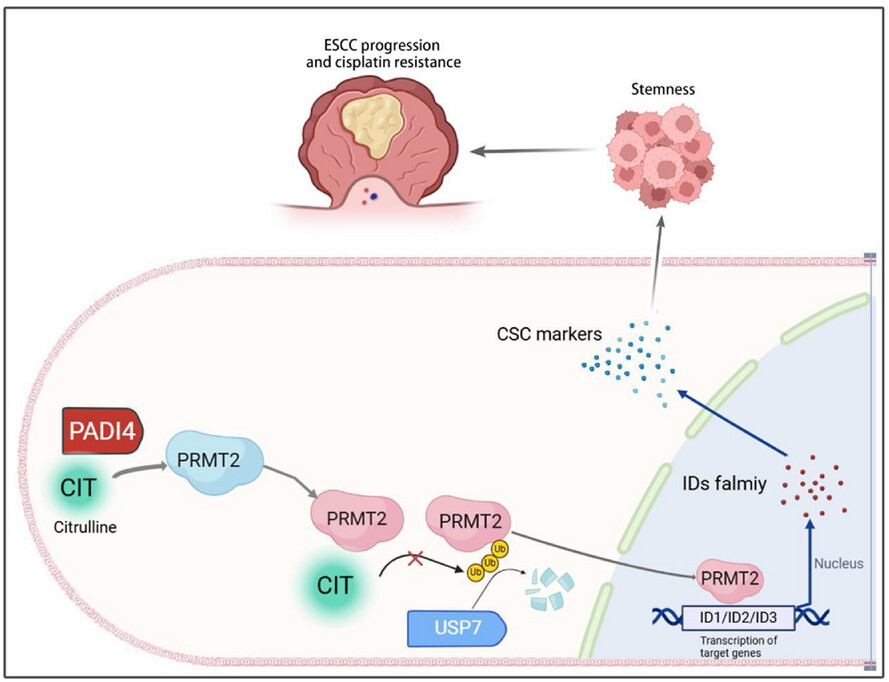
Citrullinization is a post-translational modification that has rarely been studied. Our research found that enzyme peptididylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) facilitates the citrullination of protein arginine methyltransferase 2 (PRMT2), a process essential for the stabilization of PRMT2 expression and the enhancement of its function in promoting the transcription of IDs family (ID1 and ID2) via histone arginine methylation. This mechanism subsequently increases cancer stem cells (CSCs) stemness and contributes to the cisplatin resistance observed in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Mutations at the R312 site or inhibition by GSK484 can attenuate stemness in OSCC, thereby reducing cisplatin resistance.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Targeting YBX1-m5C mediates RNF115 mRNA circularisation and translation to enhance vulnerability of ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 15 March 2025
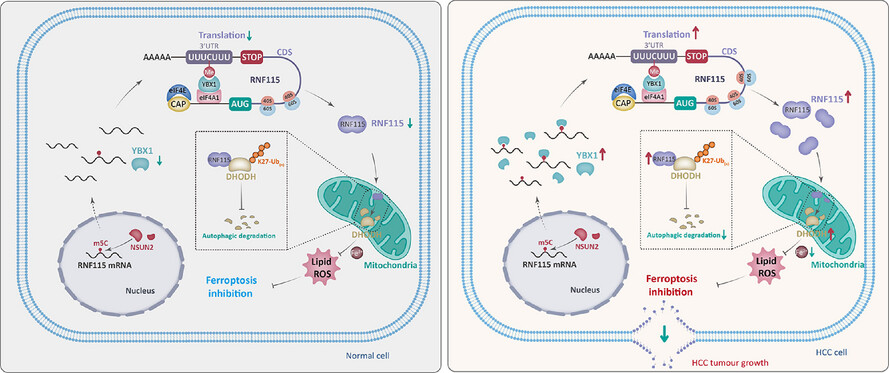
NOP2/Sun RNA methyltransferase 2 (NSUN2) promotes 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification of Ring Finger Protein 115 (RNF115) mRNA, which is subsequently bound by YBX1. Then, YBX1 interacts with Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4A1 (EIF4A1) to promote RNF115 mRNA looping and translation. Subsequently, RNF115 interacts with dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) to promote its K27 ubiquitination and inhibit the autophagic degradation of DHODH to resist ferroptosis and promote hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Single-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- First Published: 17 March 2025
Interferon regulatory factor 5 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by inducing GATA2 expression in colorectal cancer
- First Published: 20 March 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Preclinical B cell depletion and safety profile of a brain-shuttled crystallizable fragment-silenced CD20 antibody
- First Published: 21 March 2025
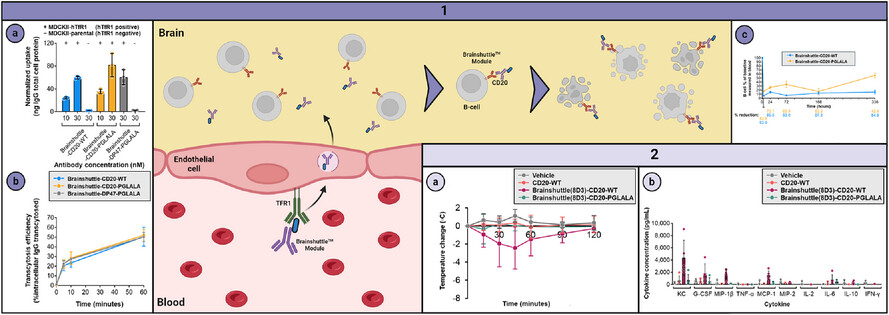
The BBB hinders mAb-based brain disorder therapies.
A brain-targeted B-cell-depleting mAb for MS that efficiently crosses the BBB via hTfR1 was developed using Brainshuttle technology (1A and 1B).
The Brainshuttle-CD20 mAb was well tolerated (2A and 2B) and displayed B-cell-killing properties (1C), paving the way for future development and clinical translation of TfR1-targeting therapies for increased brain penetration.
HIF-1α-induced long noncoding RNA LINC02776 promotes drug resistance of ovarian cancer by increasing polyADP-ribosylation
- First Published: 21 March 2025
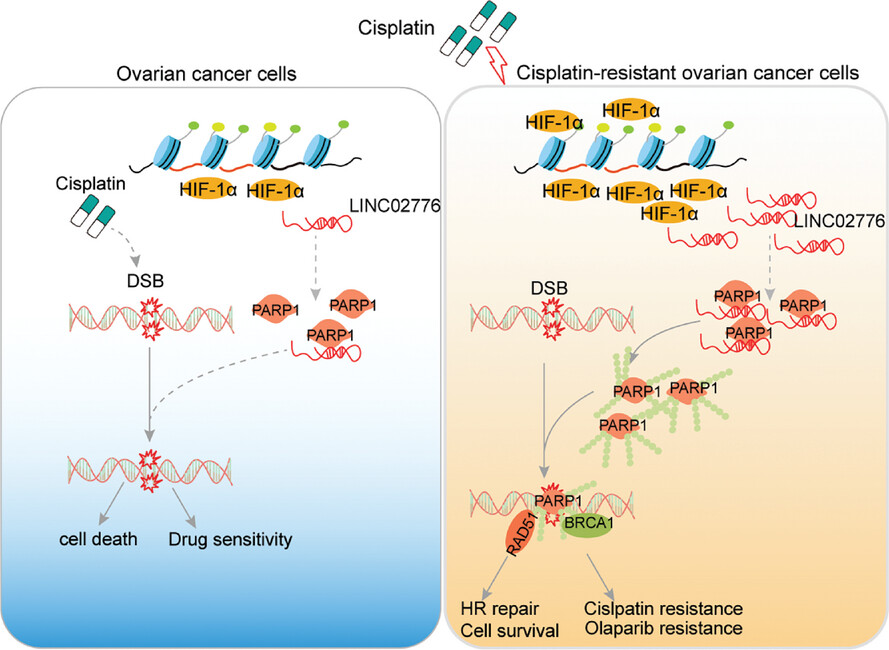
LINC02776 was significantly upregulated in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer (OC) patients compared to those sensitive to platinum therapy. LINC02776 directly binds catalytic domain of PARP1 to enhance PARP1-dependent polyADP-ribosylation, thereby promoting homologous recombination (HR) restoration.