Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
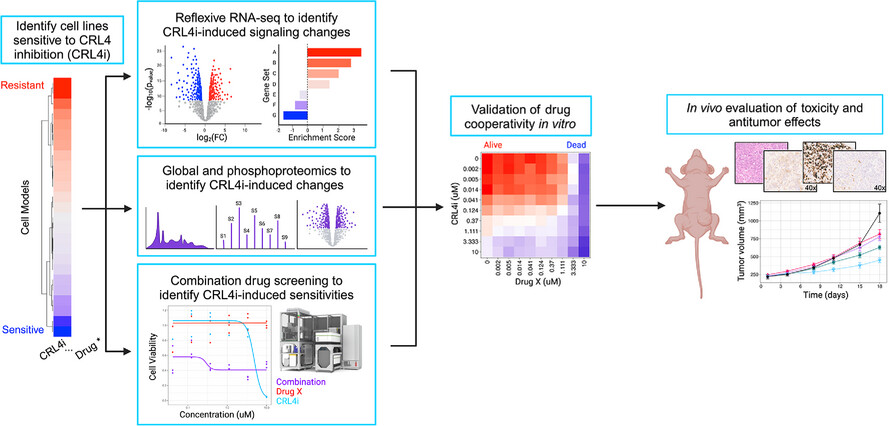
Functional genomics pipeline identifies CRL4 inhibition for the treatment of ovarian cancer
- First Published: 24 January 2025
-
A precision medicine pipeline identifies ovarian cancer sensitivity to CRL4 inhibitors.
-
CRL4 inhibition induces activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling as identified by RNA sequencing, proteomics, and phosphoproteomics.
-
Inhibitor combinations that target both CRL4 and this CRL4 inhibitor-induced survival signalling enhance ovarian cancer sensitivity to treatment.
COMMENTARY
Engineering the future of medicine: Natural products, synthetic biology and artificial intelligence for next-generation therapeutics
- First Published: 24 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Spatial distribution of immune cells and their proximity to STING+ cells are associated with survival in glioblastoma
- First Published: 24 January 2025
Transcriptome profiles of human preimplantation blastocysts related to mosaicism, developmental speed and competence
- First Published: 24 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
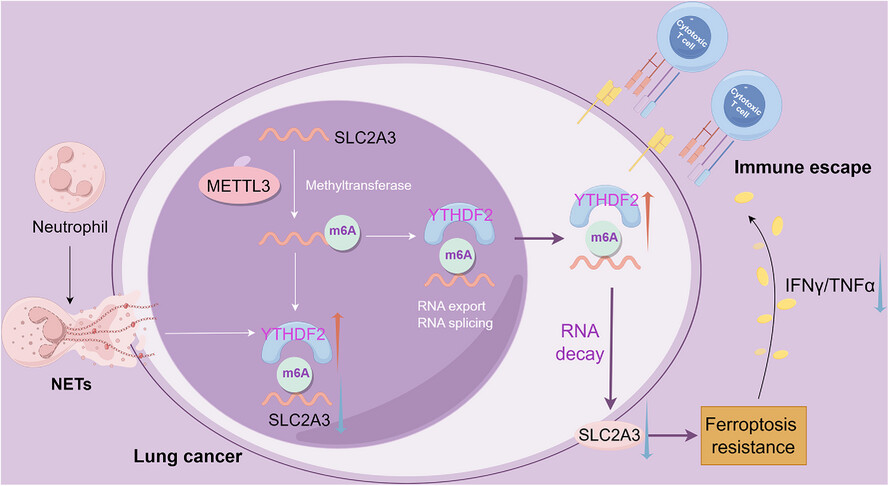
Neutrophil extracellular traps promote growth of lung adenocarcinoma by mediating the stability of m6A-mediated SLC2A3 mRNA-induced ferroptosis resistance and CD8(+) T cell inhibition
- First Published: 26 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Proteomic profiling of the serum of patients with COVID-19 reveals key factors in the path to clinical improvement
- First Published: 27 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Oestrogen suppresses the adipogenesis of fibro/adipogenic progenitors through reactivating the METTL3–ESR1-mediated loop in post-menopausal females
- First Published: 28 January 2025
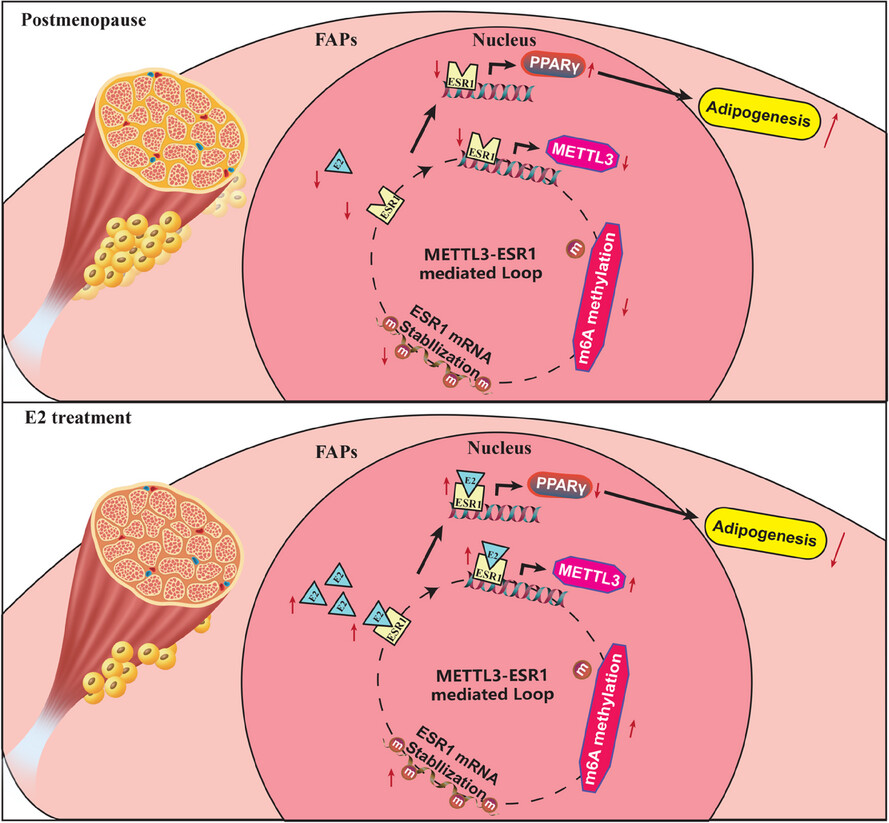
Excessive muscular fatty infiltration in post-menopausal women arose from the disruption of the methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)–oestrogen receptor 1 (ESR1)-mediated loop of fibro/adipogenic progenitors (FAPs) due to oestrogen deficiency. Reactivation of the METTL3–ESR1-mediated loop by oestrogen alleviated excessive adipogenesis in FAPs, thereby ameliorating muscular fatty infiltration and improving locomotor function in ovariectomy (OVX) mice.
INVITED LETTER
Artificial metabzyme-driven metabolic reprogramming and precision oncology
- First Published: 30 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
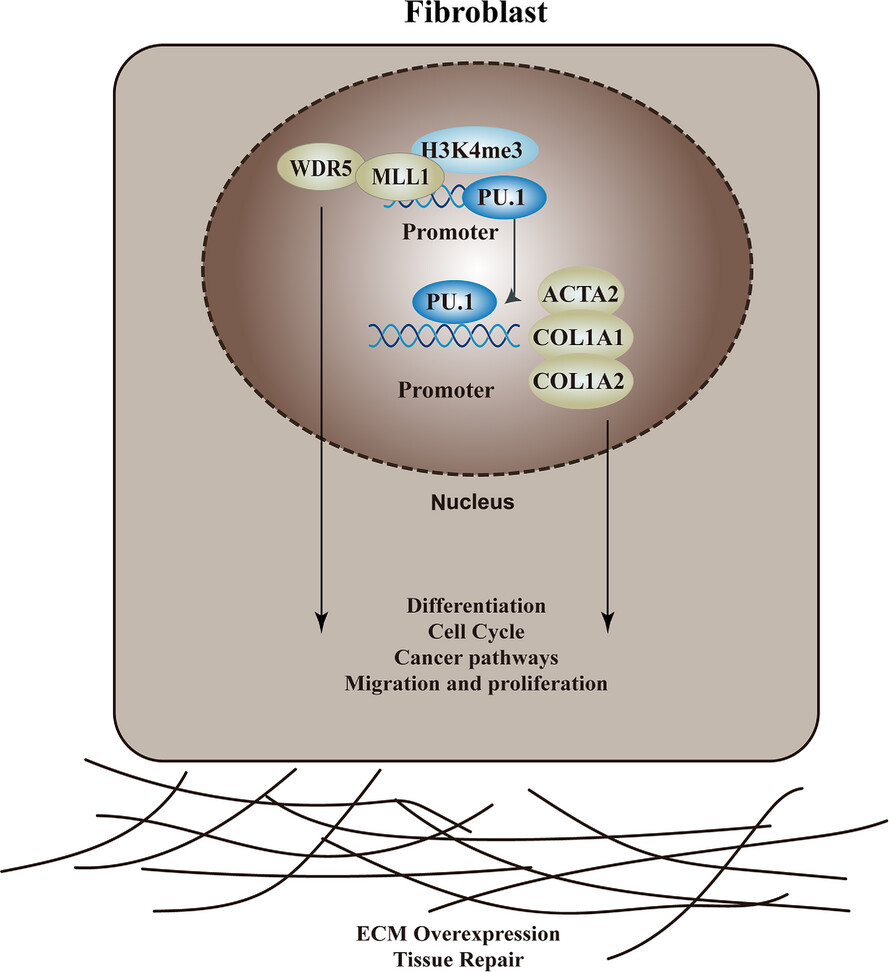
Histone methyltransferase KMT2A promotes pulmonary fibrogenesis via targeting pro-fibrotic factor PU.1 in fibroblasts
- First Published: 30 January 2025
ERRATUM
Erratum for the “S100A7 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma promotes M2 macrophage infiltration and angiogenesis” by Zhiliang Lu et al.
- First Published: 03 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Sodium pump subunit NKAα1 protects against diabetic endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting ferroptosis through the autophagy-lysosome degradation of ACSL4
- First Published: 04 February 2025
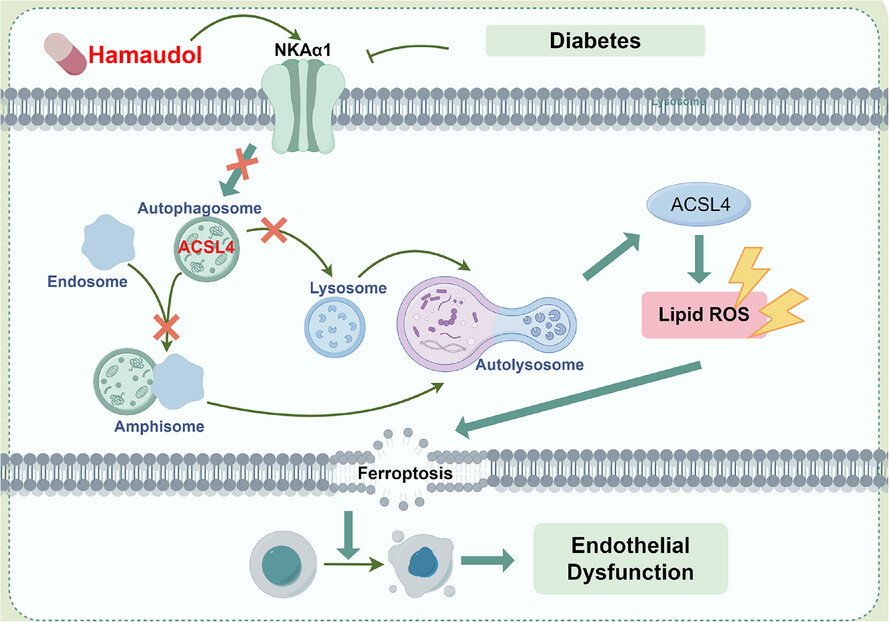
• NKAα1 downregulation impairs endothelial function in diabetes by promoting oxidative/nitrative stress and ferroptosis.
• NKAα1 supports lysosomal degradation of ACSL4 via autophagy, preventing lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis.
• Hamaudol, an activator of NKAα1, restores endothelial relaxation in diabetic mice by inhibiting NKAα1 phosphorylation and endocytosis.
COMMENTARY
The utilisation of ctDNA approaches for residual disease detection during neoadjuvant and perioperative immunotherapy in oesophagogastric cancers
- First Published: 04 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Monocyte–macrophage dynamics as key in disparate lung and peripheral immune responses in severe anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis-related interstitial lung disease
- First Published: 04 February 2025
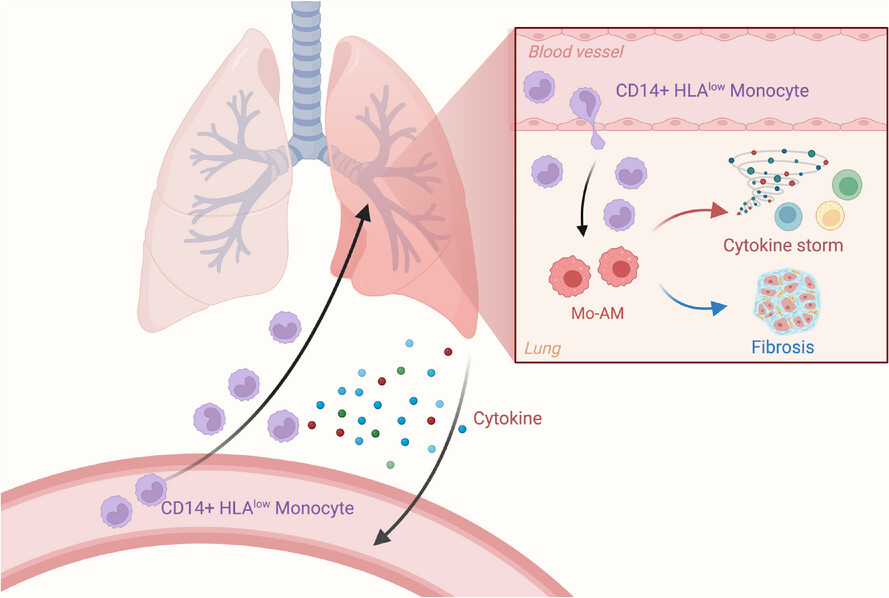
• Peripheral immune suppression and pulmonary immune hyperactivation characterise the distinct immune landscapes in anti-MDA5+DM with RP-ILD.
• Circulating monocytes transition from an immunosuppressive phenotype in the periphery to proinflammatory and profibrotic Mo-AMs in the lungs.
• Chemokines produced by Mo-AMs drive monocyte and other immune cell recruitment to the lungs, amplifying pulmonary inflammation.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Single-cell transcriptomics and metabolomic analysis reveal adenosine-derived metabolites over-representation in pseudohypoxic neuroendocrine tumours
- First Published: 04 February 2025
Multi-organ transcriptomic atlas reveals hallmarks of labour
- First Published: 04 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Cell-free epigenomes enhanced fragmentomics-based model for early detection of lung cancer
- First Published: 05 February 2025
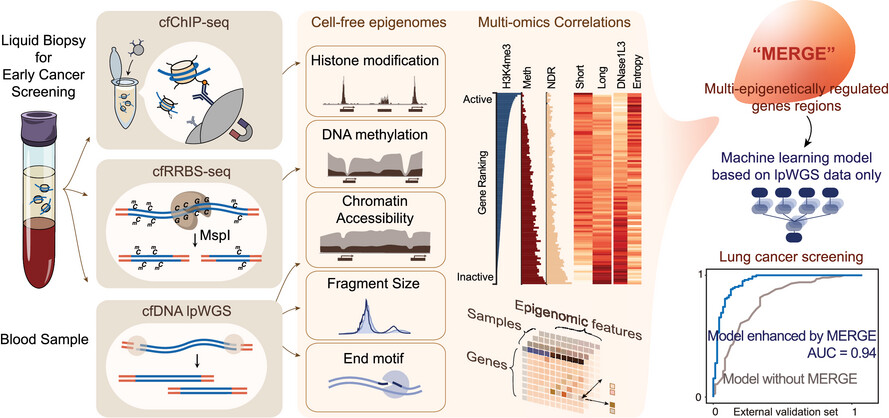
Lung cancer-related changes in fragmentomic features were unevenly distributed across the genome, showing significant enrichment in epigenetically regulated regions of specific genes.
The cfDNA fragmentomics-based model demonstrated superior detection capability, especially for early-stage lung cancer.
This study offers novel insights into cfDNA biology and paves new avenues for the accurate and cost-effective early detection of lung cancer.
RNF31 induces paclitaxel resistance by sustaining ALYREF cytoplasmic–nuclear shuttling in human triple-negative breast cancer
- First Published: 06 February 2025
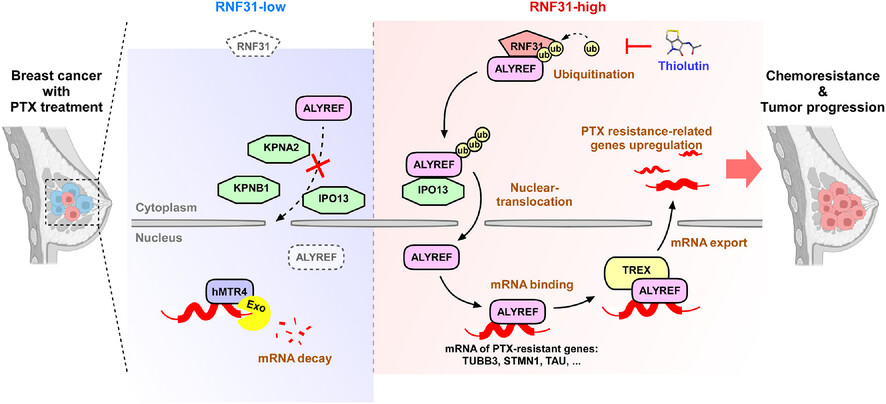
An overview of the paclitaxel resistance mechanism induced by RNF31-mediated ALYREF subcellular distribution. RNF31 promoted the linear ubiquitination of ALYREF, subsequently enhancing ALYREF nuclear transport via IPO13 upon PTX treatment. In addition, RNF31-mediated ubiquitination of ALYREF facilitated ALYREF binding and export of PTX resistance-related factors, including TUBB3, STMN1, and TAU, ultimately leading to PTX resistance in TNBC. Thiolutin, an inhibitor of RNF31, enhanced PTX sensitivity in TNBC.
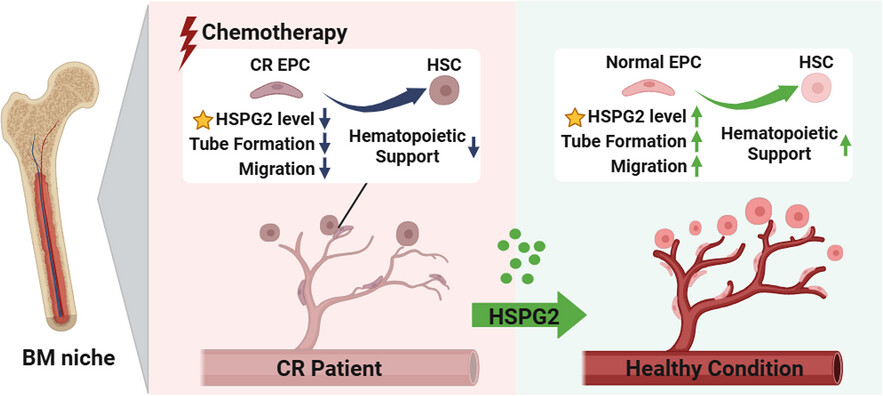
HSPG2 could promote normal haematopoiesis in acute myeloid leukaemia patients after complete remission by repairing bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells
- First Published: 06 February 2025
N6-Methyladenosine modification mediated by METTL3 promotes DNA-PKcs expression to induce anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma
- First Published: 09 February 2025
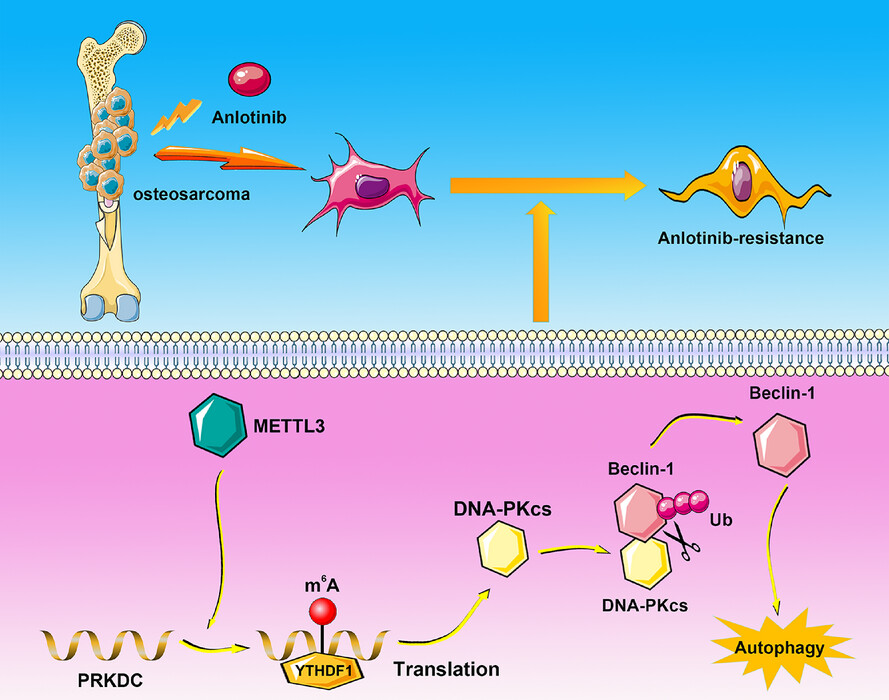
DNA-PKcs knockdown heightens osteosarcoma sensitivity to anlotinib.
DNA-PKcs modulates anlotinib-induced protective autophagy through interacts with Beclin-1 and regulates its ubiquitination.
m6A modification of OLE_LINK82PRKDC mRNA induced by METTL3 contributes to anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma.
m6A methylation of PRKDC mRNA recognised by YTHDF1 amplifies the expression of DNA-PKcs.
INVITED LETTER
Paclitaxel biological synthesis promotes the innovation of anti-cancer drugs
- First Published: 09 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Role of the FOXM1/CMA/ER stress axis in regulating the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- First Published: 09 February 2025
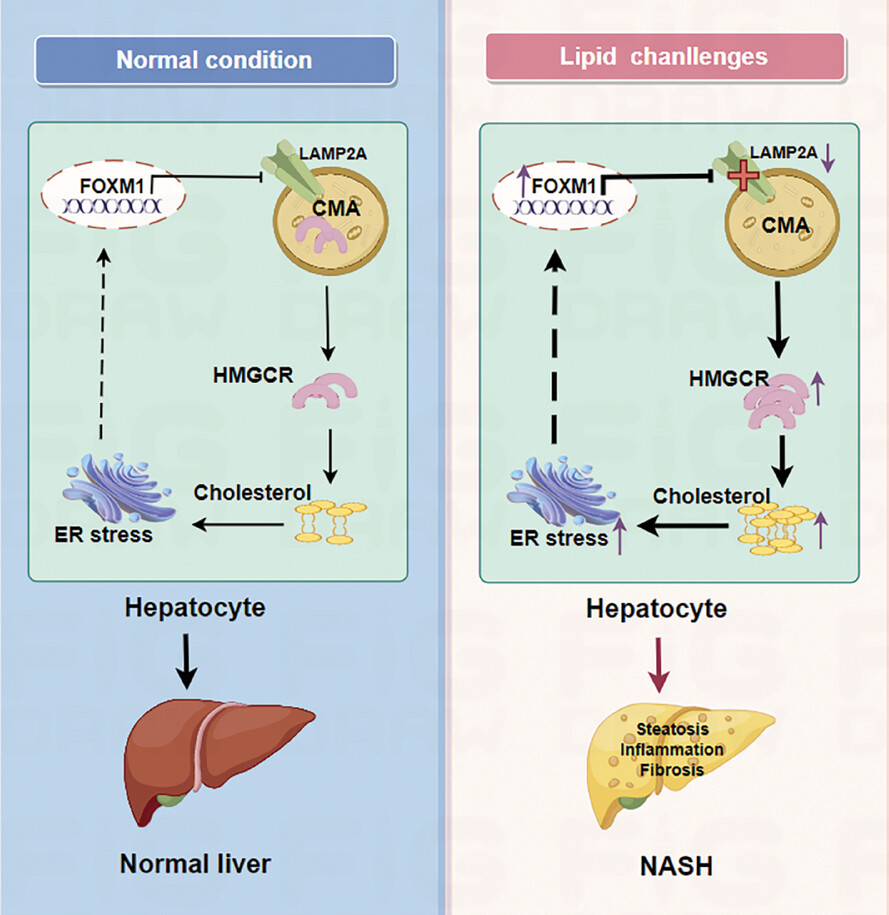
Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) deficiency in hepatocytes promotes hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) by inducing cholesterol accumulation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress.
Upregulated FOXM1 impairs CMA by suppressing the transcription of lysosome-associated membrane protein 2A (LAMP2A), a rate-limiting component of CMA.
ER stress increases FOXM1 expression and cholesterol accumulation.
FOXM1/CMA/ER stress axis forms a vicious circle and promotes the development of NASH.
REVIEW
Spatial‒temporal heterogeneities of liver cancer and the discovery of the invasive zone
- First Published: 09 February 2025
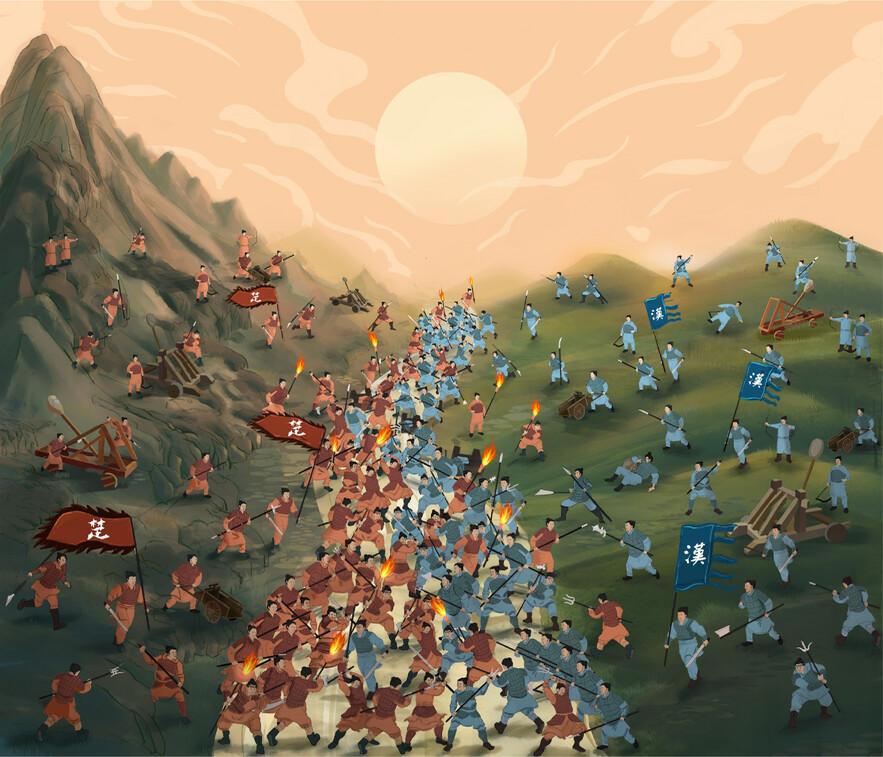

Solid tumours are complex ecosystems characterised by significant heterogeneity in both their component composition and spatial‒temporal organisation. This complexity contributes to challenges in accurate stratification, as well as in the development of drug resistance and early relapse. Our study maps the transcriptional architecture of human liver cancer using high-resolution Stereo-seq and single-cell RNA sequencing across various tissue types, and we identified a 500 µm-wide zone centred around the tumour border in patients with liver cancer, referred to as ‘invasive zone’. We detected strong immunosuppression, metabolic reprogramming and severely damaged hepatocytes in this zone. Similarly, the invasive zone between tumour tissues and paratumoural tissues of solid tumours resembled the border area of the two opposing powers, namely, ‘Chu’ and ‘Han’ Dynasties in fighting for hegemony in the late Qin Dynasty. The most intense heavy fighting and complex mutual interactions were found around the battlefronts of the two powers, which was called ‘Honggou’, namely, the wide chasm in the history like ‘invasive zone’. Furthermore, when the smoke of war gradually dissipated in the long river of history, the border area between Chu and Han Dynasties was forever fixed on the Chinese chess board and represented the balance between offense and defense.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A comparative genomic study across 396 liver biopsies provides deep insight into FGF21 mode of action as a therapeutic agent in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
- First Published: 17 February 2025
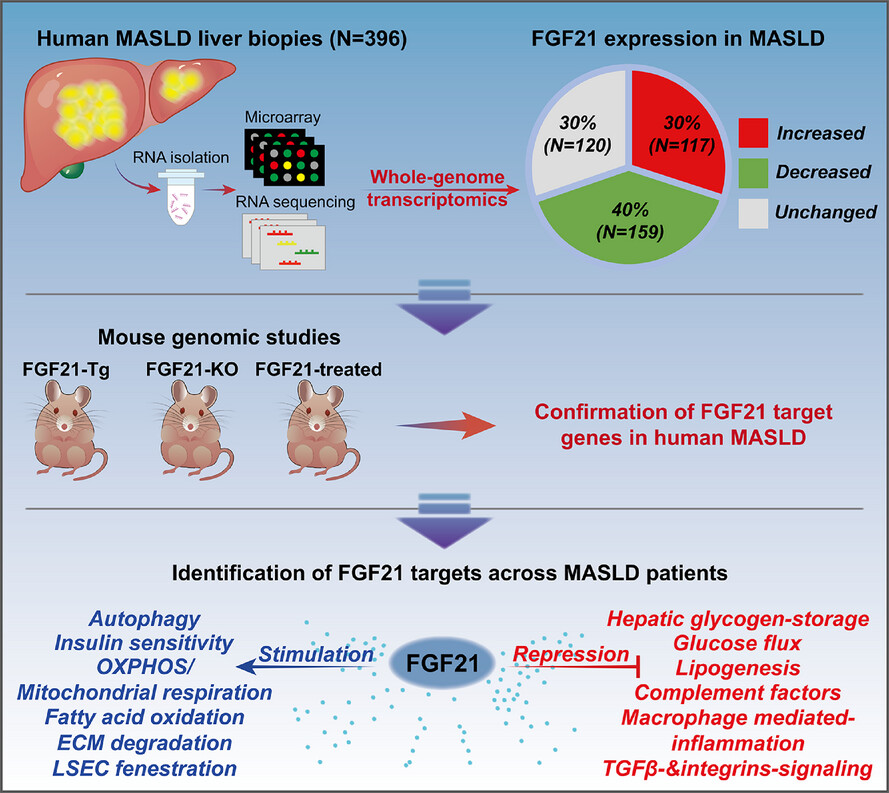
Performed comprehensive genomics across liver biopsies of 396 MASLD patients and identified patients with increased, decreased and unchanged FGF21 expression.
Used genomic data from FGF21 transgenic, knock-out and animal MASLD models treated with synthetic FGF21 analogues to identify FGF21-mode-of-action and metabolic networks in human MASLD.
Given the significant heterogeneity in FGF21 expression, not all patients will benefit from FGF21-based therapies.
Immune profiling of the macroenvironment in colorectal cancer unveils systemic dysfunction and plasticity of immune cells
- First Published: 11 February 2025
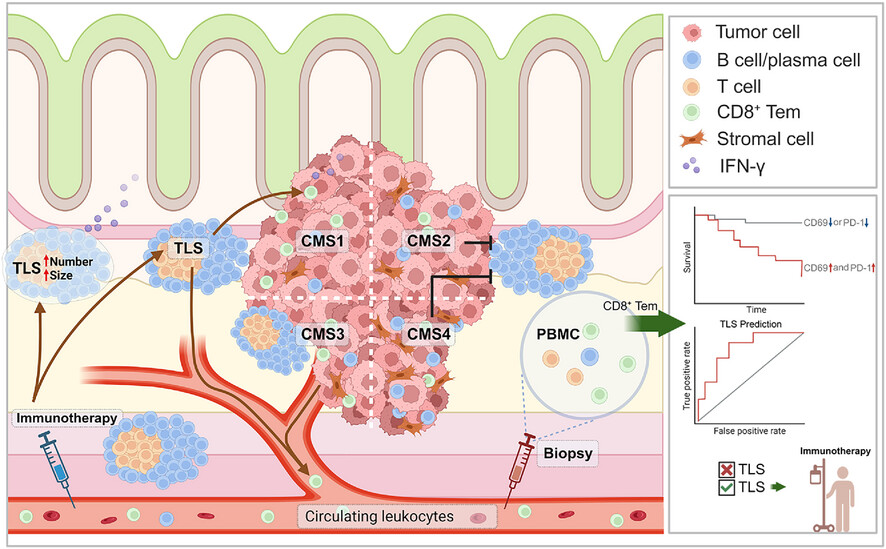
- Distinct immunotypes are identified in the CRC macroenvironment.
- TLS and immunotherapy exert influence on the immune macroenvironment.
- TLS presence correlates with patient survival, CMS and therapeutic efficacy of ICI.
- PD-1 and CD69 expressed in CD8+ Tem from blood can predict TLS presence in the CRC macroenvironment.
INVITED LETTER
Large-scale cluster randomised trial reveals effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori eradication for gastric cancer prevention
- First Published: 12 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
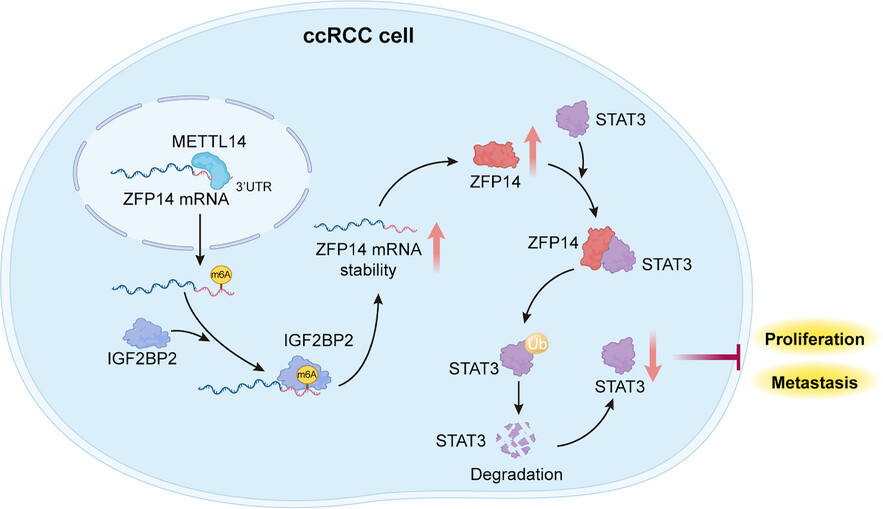
METTL14-mediated m6A modification of ZFP14 inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression via promoting STAT3 ubiquitination
- First Published: 12 February 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
EpCAM deficiency causes the premature ageing of intestinal stem cells via EGFR/SP1/mTORC1 pathway
- First Published: 12 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
5-hydroxymethylcytosine features of portal venous blood predict metachronous liver metastases of colorectal cancer and reveal phosphodiesterase 4 as a therapeutic target
- First Published: 16 February 2025
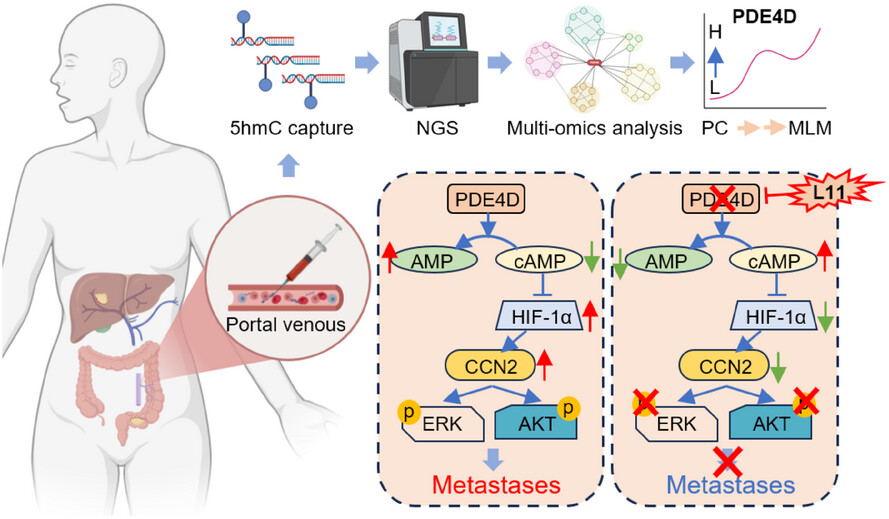
- 5hmC epigenetic markers derived from portal venous blood could accurately predict metachronous metastasis of colorectal cancer.
- PDE4D was a key metastasis-driven target that promoted metachronous metastasis via the HIF-1α-CCN2 pathway.
- The newly synthesised compound L11 could specifically inhibit PDE4D and abolish metachronous metastasis of colorectal cancer without obvious toxic side effects.
ERRATUM
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
RESEARCH ARTICLE
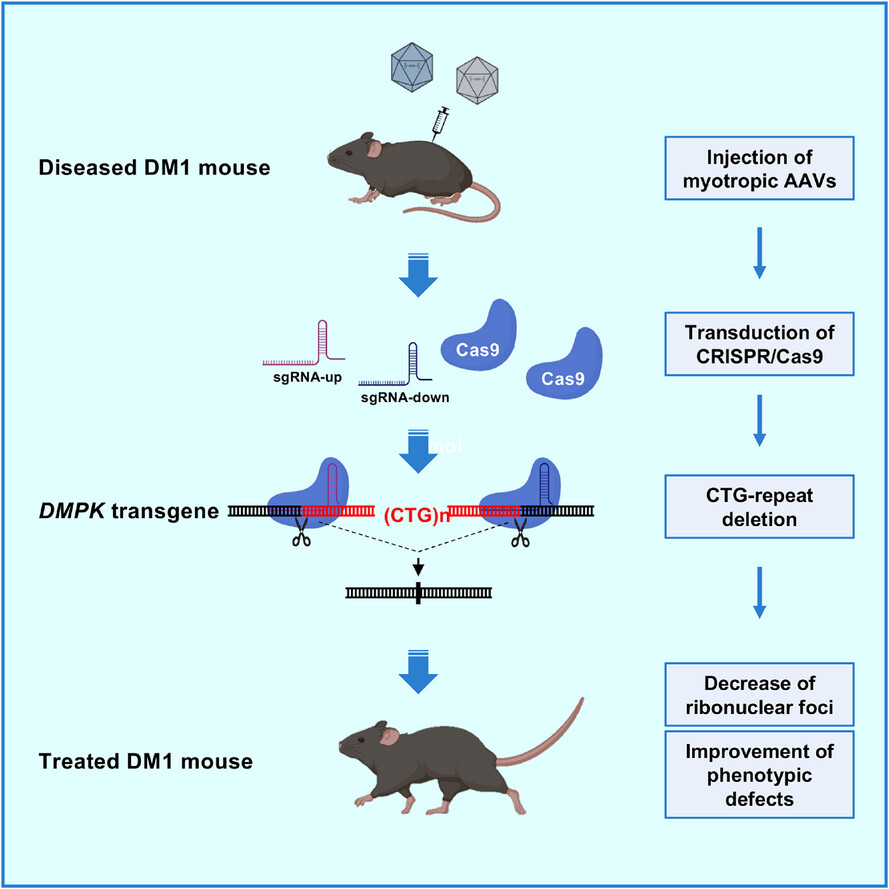
Muscle-specific gene editing improves molecular and phenotypic defects in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy type 1
- First Published: 16 February 2025
E2F1/CDK5/DRP1 axis mediates microglial mitochondrial division and autophagy in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
- First Published: 19 February 2025
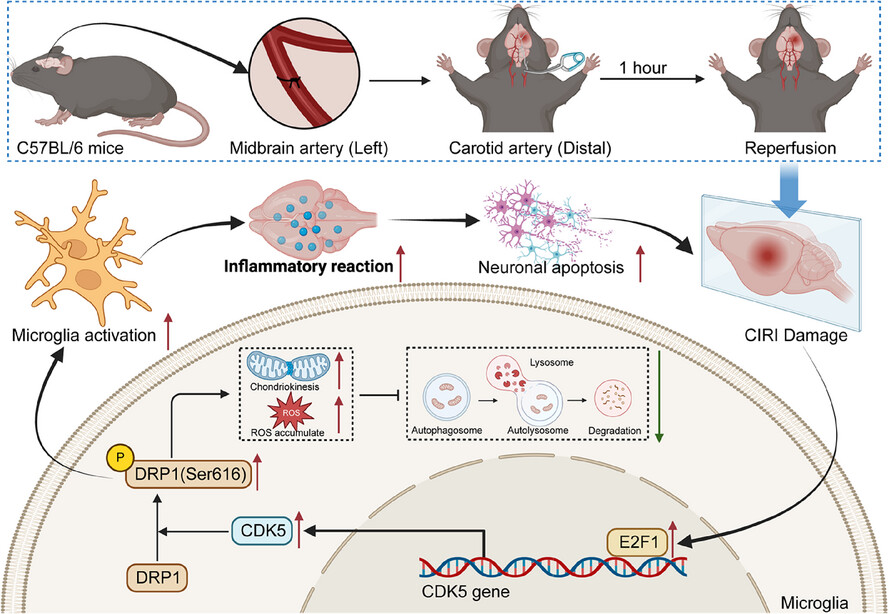
- E2F1-mediated CDK5 activation drives mitochondrial dysfunction in microglia, exacerbating CIRI damage.
- Mitochondrial fission and impaired mitophagy are key processes influenced by E2F1-CDK5 signalling in CIRI.
- Targeting the E2F1-CDK5-DRP1 axis offers novel therapeutic strategies for mitigating CIRI-induced brain injury.
Single-cell transcriptomic atlas of different endometriosis indicating that an interaction between endometriosis-associated mesothelial cells (EAMCs) and ectopic stromal cells may influence progesterone resistance
- First Published: 19 February 2025
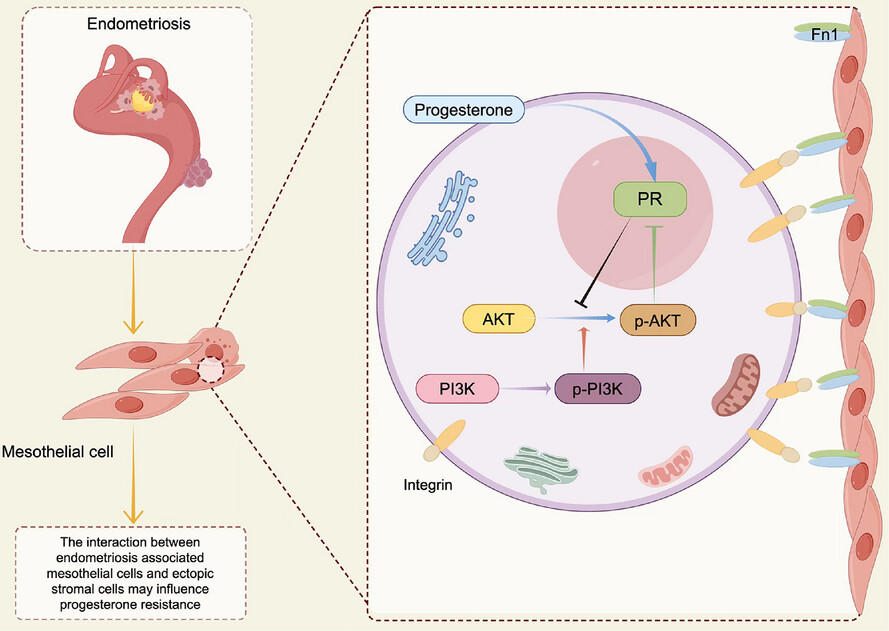
- Single-cell RNA (ScRNA) atlas across types of endometriosis is established.
- Mesothelial cells are founded in ovarian endometriosis.
- Endometriosis-associated mesothelial cells (EAMCs) experience various level of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in different subtypes.
- EAMCs may exert an influence on progesterone resistance in stromal cells through intercellular communication mediated by the FN1-AKT pathway.
Adipose tissue deficiency impairs transient lipid accumulation and delays liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy in male Seipin knockout mice
- First Published: 20 February 2025
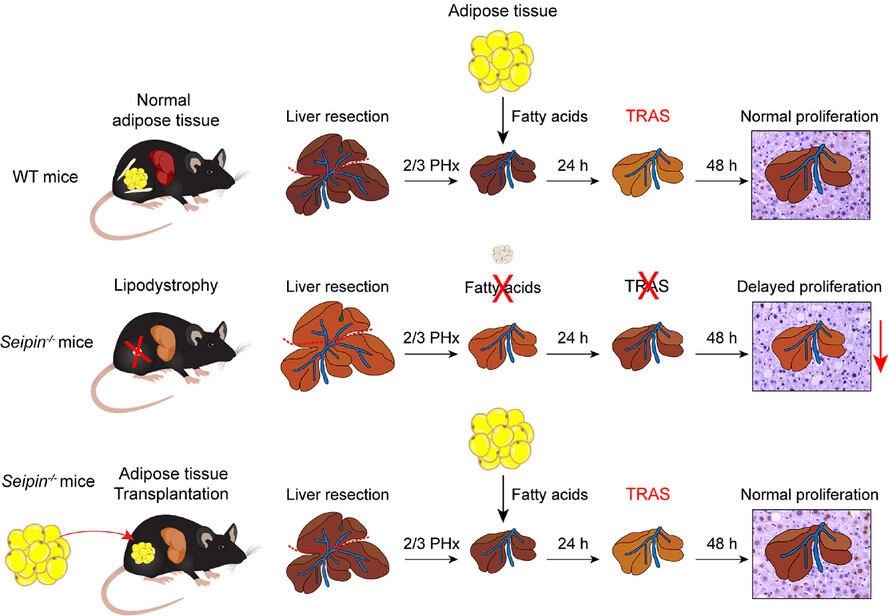
- Seipin−/− mice, which lack adipose tissue, exhibit significantly impaired TRAS and delayed liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy.
- Transplantation of normal adipose tissue into Seipin−/− mice restores TRAS and enhances liver regeneration, highlighting the essential role of adipose tissue in these processes.
- Liver-specific overexpression of Seipin has no effect on TRAS and liver regeneration in Seipin−/− mice.
REVIEW
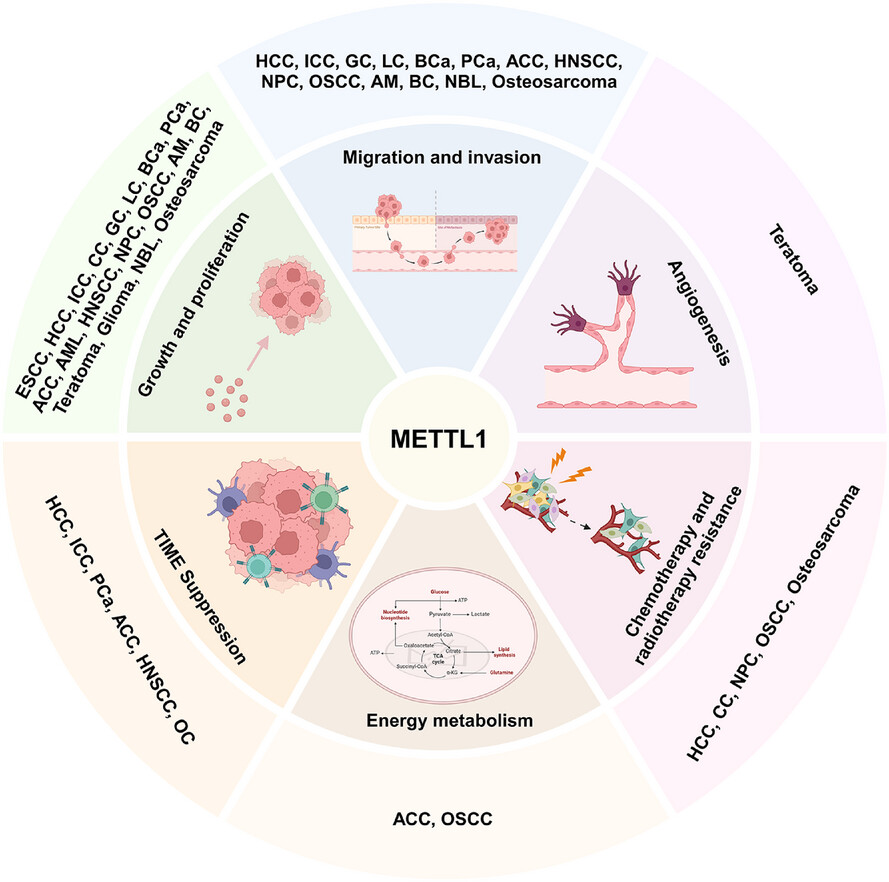
Deciphering the secret codes in N7-methylguanosine modification: Context-dependent function of methyltransferase-like 1 in human diseases
- First Published: 20 February 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
SHP2 inhibition and adjuvant therapy synergistically target KIT-mutant GISTs via ERK1/2-regulated GSK3β/cyclin D1 pathway
- First Published: 21 February 2025
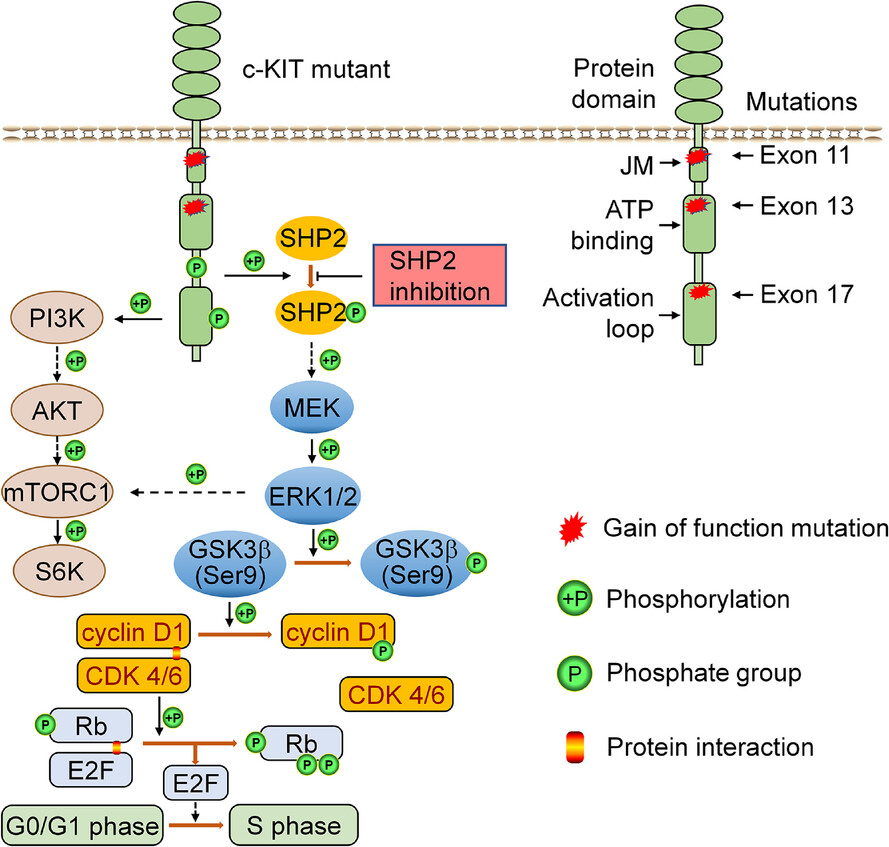
- SHP2 plays a pivotal role as a signal transducer in the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.
- SHP2 controls the cell cycle via the GSK3β/cyclin D1/Rb pathway in oncogenic KIT-driven GIST.
- Inhibition of SHP2 synergizes with adjuvant therapy drugs in inhibiting KIT-driven GIST with primary and secondary mutations both in vitro and in vivo.
INVITED LETTER
Spatial genomics uncovers cytokines promoting ovarian tumour heterogeneity and immunotherapy resistance
- First Published: 23 February 2025