Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Atezolizumab, bevacizumab, pemetrexed and platinum for EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients after EGFR TKI failure: A phase II study with immune cell profile analysis
- First Published: 23 December 2024
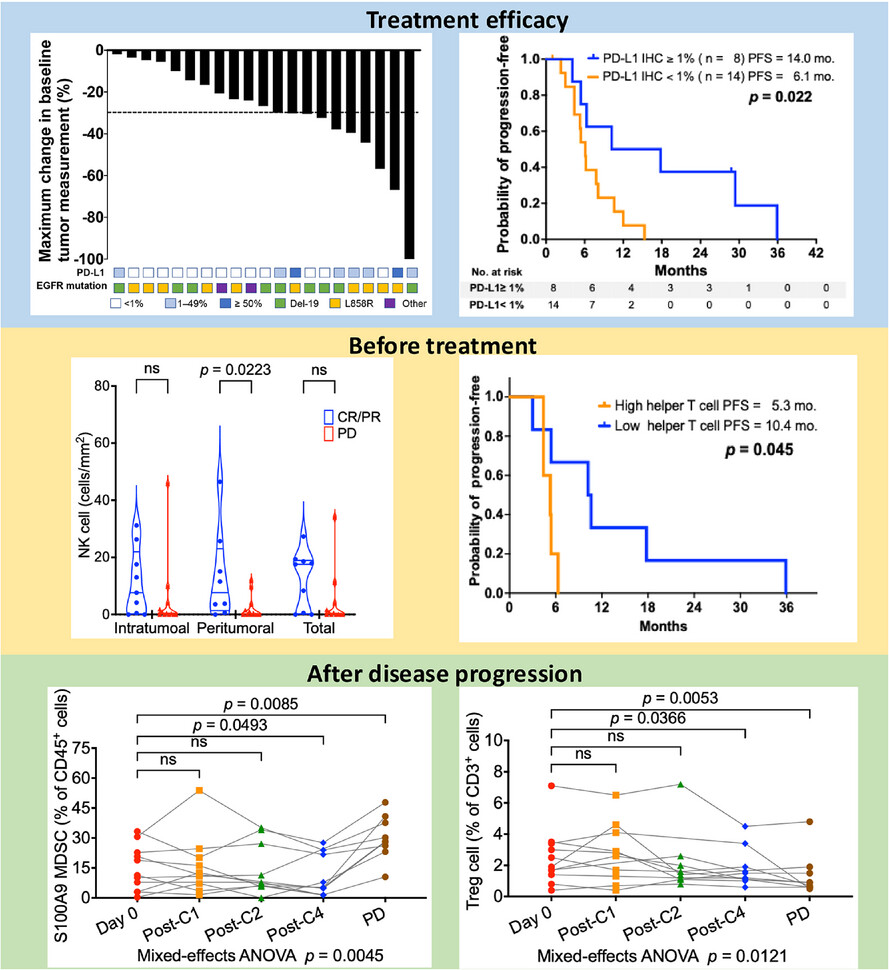
- The combination regimen yielded promising efficacy in NSCLC patients after EGFR-TKI resistance, particularly those with PD-L1-positive tumours.
- Higher peritumour NK cell and lower peripheral helper T cell were associated with favourable ORR and longer PFS, respectively.
- After disease progression, the proportion of S100A9+ MDSC increased, but Treg cells decreased.
ZSH-2208: A novel retinoid with potent anti-tumour effects on ESCC stem cells via RARγ–TNFAIP3 axis
- First Published: 26 December 2024
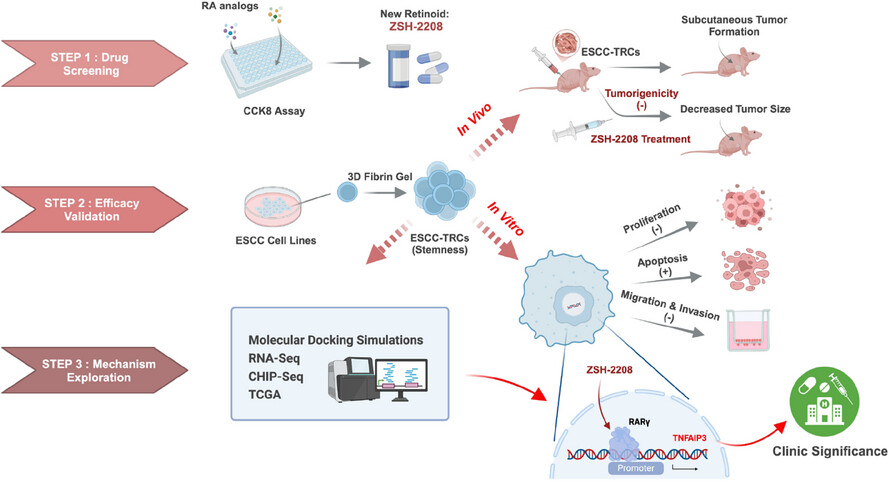
-
The ESCC-TRCs replicates the characteristics of ESCC stem cells, which are inhibited by ZSH-2208.
- In vivo and in vitro experiments demonstrated that ZSH-2208, a novel RA analogue, effectively inhibits the growth of ESCC-TRCs through the RARγ–TNFAIP3 axis.
-
Low levels of TNFIP3 protein may be associated with improved survival probability in ESCC patients.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
The impact of homologous recombination deficiency on the prognosis of epithelial ovarian cancer
- First Published: 26 December 2024
REVIEW
Intestinal oxygen utilisation and cellular adaptation during intestinal ischaemia–reperfusion injury
- First Published: 26 December 2024
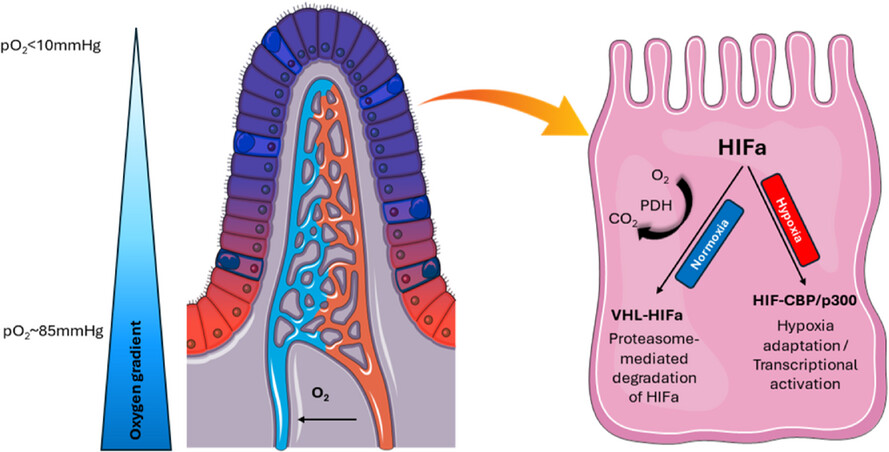
During intestinal ischaemia, mitochondrial oxygen uptake is reduced when cellular oxygen partial pressure decreases to below the threshold required to maintain normal oxidative metabolism.
Upon reperfusion, intestinal hypoxia may persist because microcirculatory flow remains impaired and/or because available oxygen is consumed by enzymes, intestinal cells and neutrophils.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Concurrent DNA hypomethylation and epigenomic reprogramming driven by androgen receptor binding in bladder cancer oncogenesis
- First Published: 27 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Revealing the heterogeneity of treatment resistance in less-defined subtype diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients by integrating programmed cell death patterns and liquid biopsy
- First Published: 27 December 2024
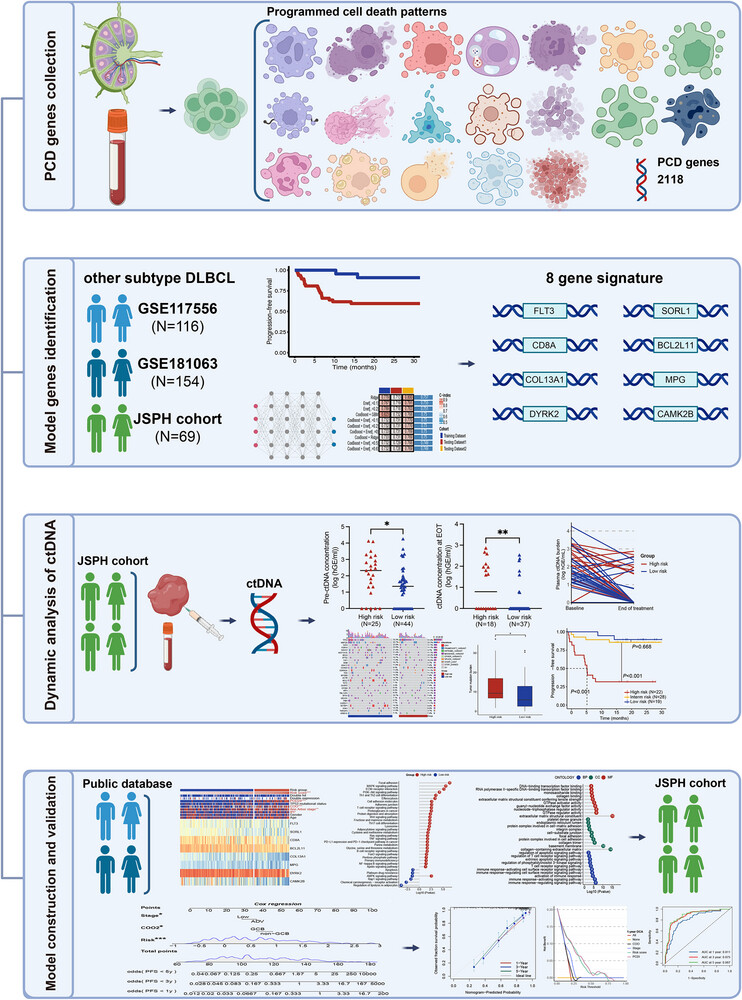
1. Developing the Programmed Cell Death Index (PCDI) utilizing multiple machine learning algorithms for patients with less-defined subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
2. The difference in clinical characteristics, circulating tumour DNA burden and immune profiling between patients with distinct PCDI groups.
3. A potentially effective regimen was speculated for patients with high PCDI scores who tend to exhibit worse progression-free survival.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Erratum for the research article “The suppressive efficacy of THZ1 depends on KRAS mutation subtype and is associated with super-enhancer activity and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A hypothesis-generating study” by Huang et al
- First Published: 27 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Deficiency of ATF3 facilitates both angiotensin II-induced and spontaneously formed aortic aneurysm and dissection development by activating cGAS–STING pathway
- First Published: 27 December 2024
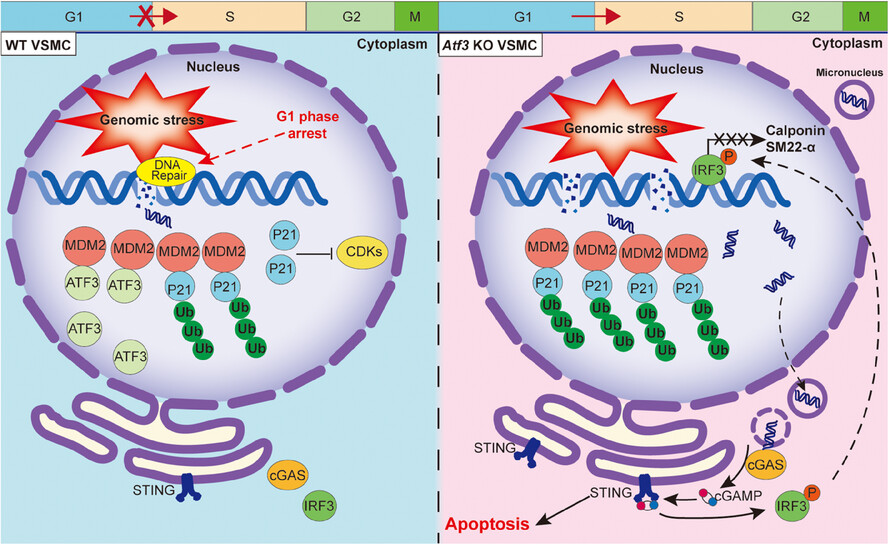
-
ATF3 deficiency led to degradation of P21 through ubiquitination, which abolished the G1 phase arrest.
-
VSMCs had no time window to repair the damaged DNA, leading to generation of micronuclei in cytoplasm.
-
Cytoplasmic micronuclei facilitating the activation of cGAS–STING pathway, thus inducing the phenotypic switch and apoptosis of VSMCs
The antiarthritic effect of CBR-470-1 in hypoxic environment is to increase the level of NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 ubiquitination by decreasing phosphoglycerate kinase 1 activity
- First Published: 27 December 2024
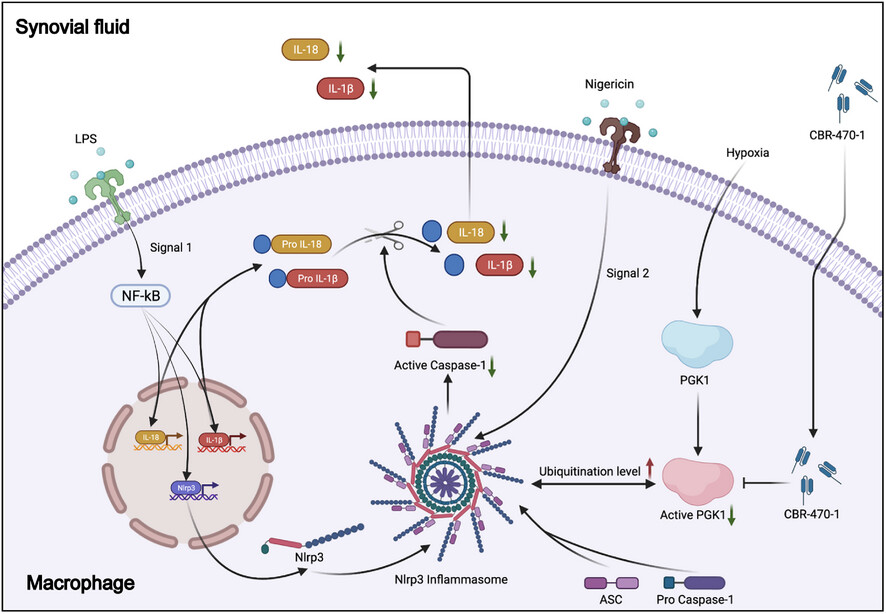
Hypoxia plays a pro-inflammatory role by increasing phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) activity and reducing the binding of the deubiquitinating enzyme ubiquitin-specific peptidase 14 to NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), thereby reducing the ubiquitination level of NLRP3. CBR-470-1, a specific inhibitor of PGK1, can reduce PGK1 activity to reverse the role of hypoxia in the progression of osteoarthritis.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 modulation of pyroptosis pathway in traumatic brain injury: A potential therapeutic target
- First Published: 31 December 2024
COMMENTARY
A new paradigm for cancer immunotherapy: Orchestrating type 1 and type 2 immunity for curative response
- First Published: 31 December 2024
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Single-cell sequencing analysis reveals cetuximab resistance mechanism and salvage strategy in colorectal cancer
- First Published: 31 December 2024
COMMENTARY
Mesoscopic connectome enters the new age of single-neuron projectome
- First Published: 30 December 2024
From general to specific: Tailoring large language models for real-world medical communications
- First Published: 31 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Titin gene mutations enhance radiotherapy efficacy via modulation of tumour immune microenvironment in rectum adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 02 January 2025
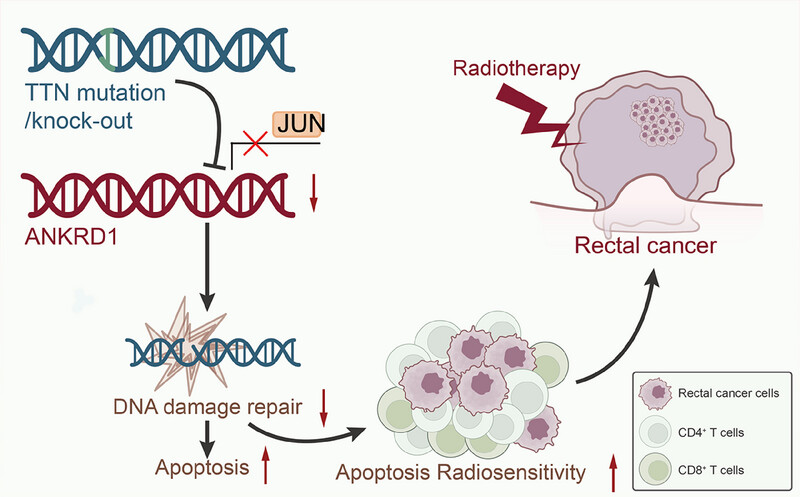
(1) TTN knockout results in decreased ANKRD1 expression, impairing DNA damage repair.
(2) Impaired DNA repair increases apoptosis and enhances radiosensitivity in rectal cancer cells.
(3) Radiotherapy in TTN-deficient cancer cells induces immune cell infiltration, including CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
(4) Apoptosis and immune modulation contribute to improved radiotherapy outcomes in rectal cancer.
Exosome-derived long non-coding RNA AC010789.1 modified by FTO and hnRNPA2B1 accelerates growth of hair follicle stem cells against androgen alopecia by activating S100A8/Wnt/β-catenin signalling
- First Published: 02 January 2025
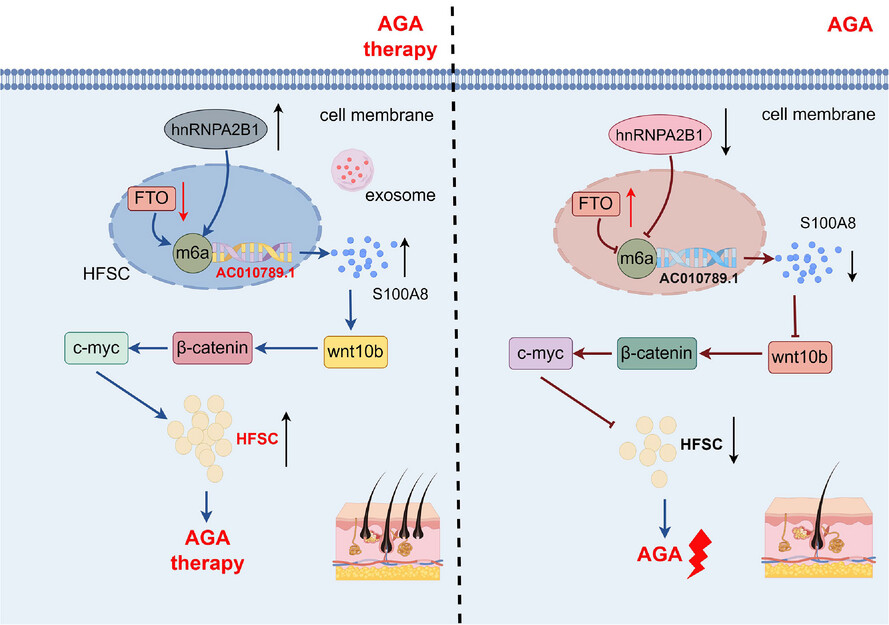
- Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) AC010789.1 was downregulated in hair follicle tissues from androgenic alopecia (AGA) and upregulated in hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs).
- LncRNA AC010789.1 promoted the proliferation and migration of HFSCs.
- FTO/hnRNPA2B1-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA AC010789.1 promoted HFSCs growth by activating S100A8/Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
- Exosome-derived AC010789.1 accelerated HFSCs proliferation.
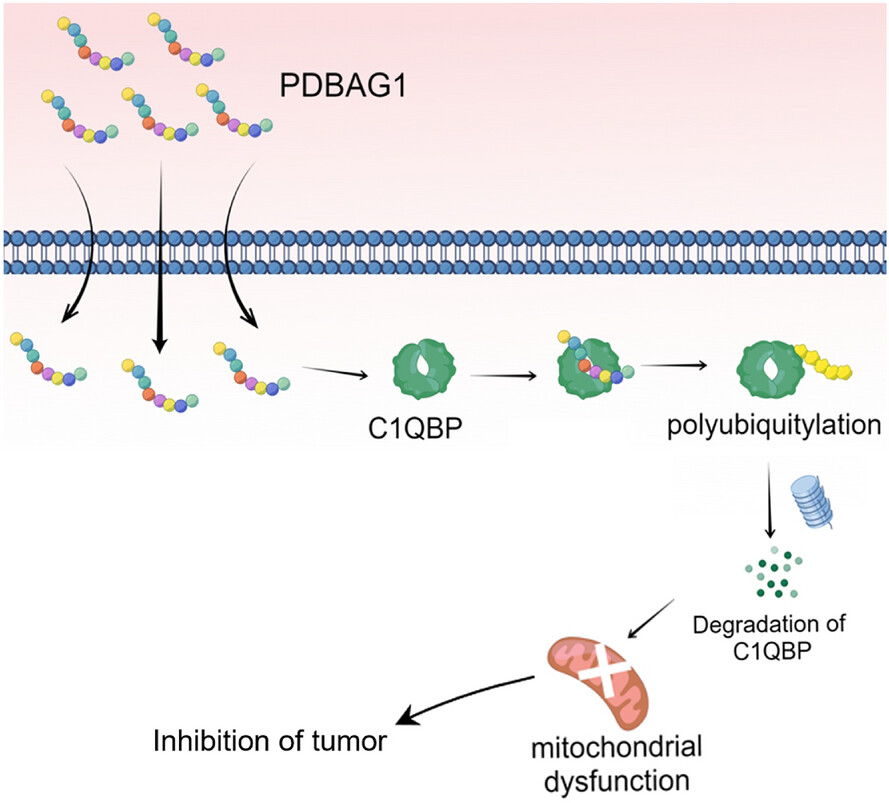
A new peptide inhibitor of C1QBP exhibits potent anti-tumour activity against triple negative breast cancer by impairing mitochondrial function and suppressing homologous recombination repair
- First Published: 02 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Identification of taste cells and reduced taste-related proteins in saliva correlate with the impaired taste sensitivity in long-coronavirus disease
- First Published: 02 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Disrupting EDEM3-induced M2-like macrophage trafficking by glucose restriction overcomes resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade
- First Published: 03 January 2025
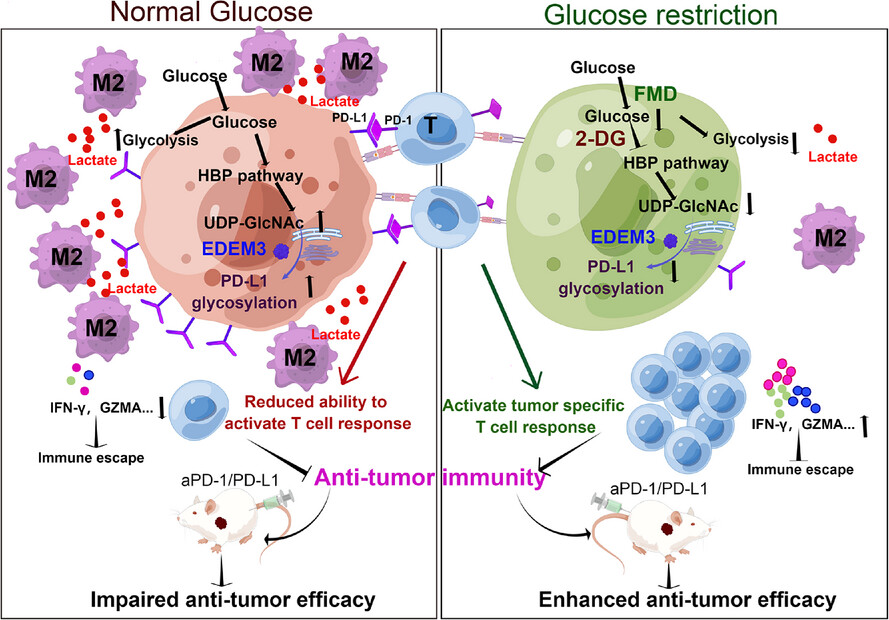
- Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) can enhance PD-L1 glycosylation through the glycosyltransferase EDEM3, contributing to immune evasion during tumour progression.
- EDEM3 predominantly activates the recruit M2-like macrophages via a glucose metabolism-dependent mechanism.
- Blocking glucose utilization antagonizes recruiting and polarizing M2-like macrophages synergistically with PD-1 antibody to improve anticancer immunity.
Unravelling the prognostic and operative role of intratumoural microbiota in non-small cell lung cancer: Insights from 16S rRNA and RNA sequencing
- First Published: 03 January 2025
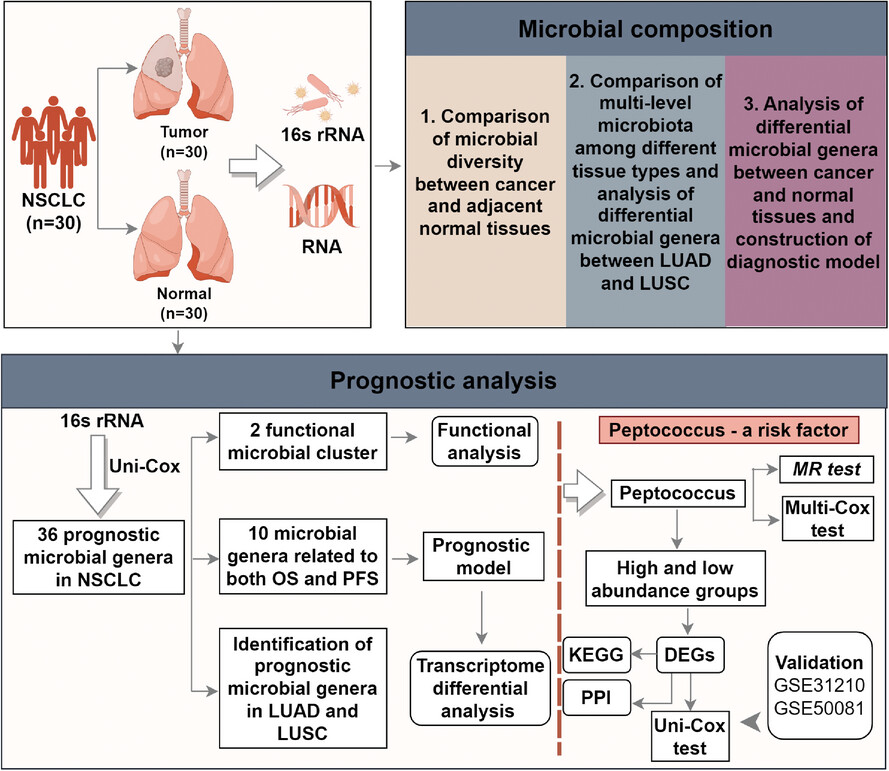
- Four phyla, five classes, nine orders, 17 families and 36 genera have been found associated with NSCLC prognosis.
- We identified a protective microbial cluster associated with delayed recurrence and a harmful microbial cluster related to shorter survival and earlier recurrence.
- We identified Peptococcus as an independent, detrimental prognostic factor for NSCLC, potentially impacting prognosis via TNF signalling.
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with unresectable or metastatic mucosal melanoma: 3-year survival update and multi-omics analysis
- First Published: 05 January 2025
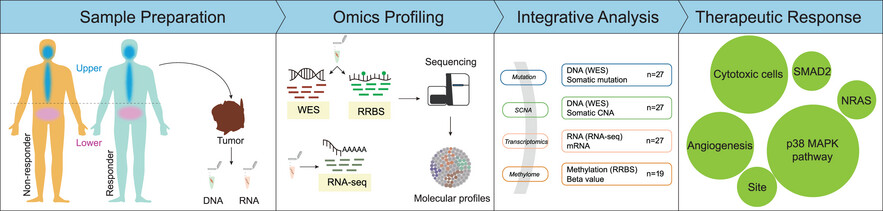
-
After a 3-year follow-up, this study further confirms that the combination therapy of atezolizumab and bevacizumab has long-term efficacy in mucosal melanoma.
-
Patients with upper site melanoma and NRAS mutation exhibited a more favourable response to this combination treatment.
-
Inflammatory cell infiltration, angiogenic status and activation of the SMAD2 and p38 MAPK pathways may be prognostic indicators.
EHMT2-mediated R-loop formation promotes the malignant progression of prostate cancer via activating Aurora B
- First Published: 06 January 2025
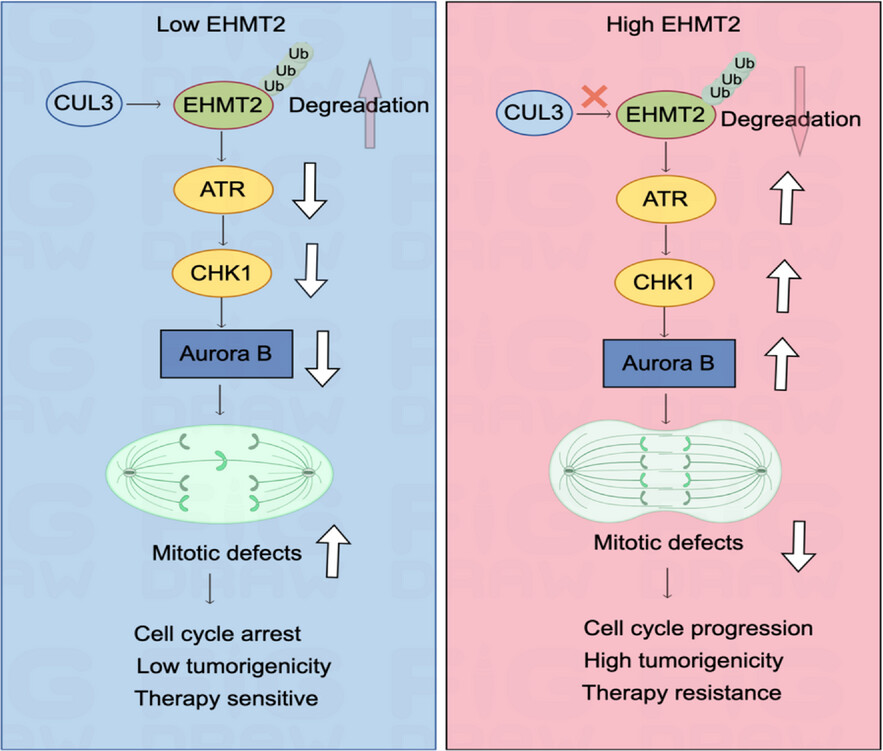
-
Euchromatic histone lysine methyltransferase 2 (EHMT2) is overexpressed in advanced prostate cancer, restraining catastrophic chromosomal instability (CIN) and enhancing cell fitness.
-
EHMT2 functions via the centromeric R-loop-driven ATR–CHK1–Aurora B pathway to promote chromosomal stability.
-
EHMT2 confers enzalutamide resistance via activating Aurora B.
-
Cullin 3 (CUL3) promotes EHMT2 destabilisation via deubiquitination.
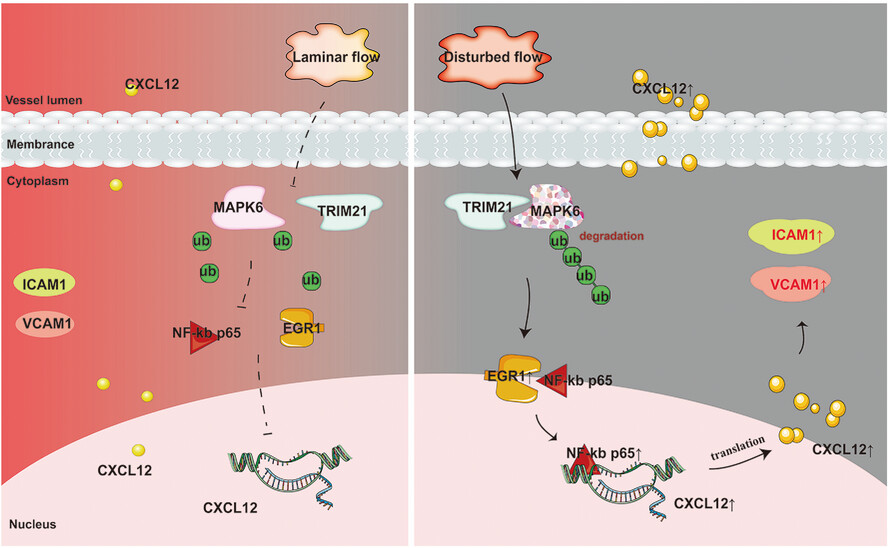
Disturbed shear stress promotes atherosclerosis through TRIM21-regulated MAPK6 degradation and consequent endothelial inflammation
- First Published: 06 January 2025
PINK1 modulates Prdx2 to reduce lipotoxicity-induced apoptosis and attenuate cardiac dysfunction in heart failure mice with a preserved ejection fraction
- First Published: 06 January 2025
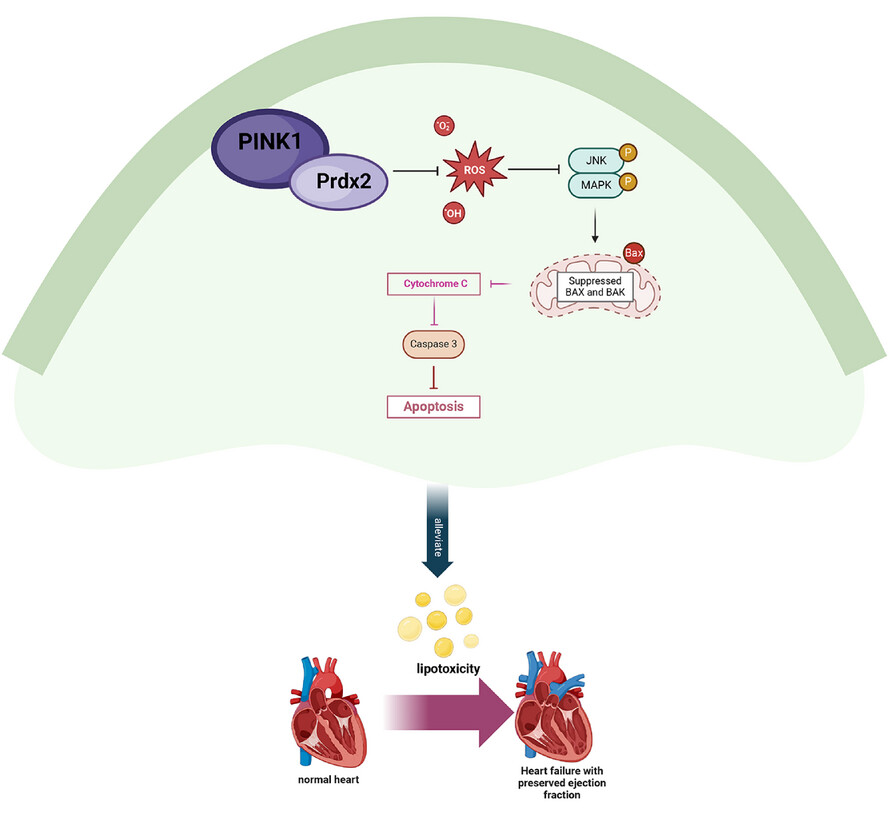
Our investigation discloses a pivotal relationship between PINK1 and Prdx2 in the context of HFpEF.
Notably, PINK1, in addition to its role in mitochondrial autophagy, can increase Prdx2 expression, effectively remove ROS and attenuate cardiomyocyte apoptosis by modulating the JNK and p38 pathways, thereby alleviating myocardial lipotoxicity and improving HFpEF cardiac function.
Our studies offer valuable insights, opening avenues for the development of innovative therapeutic strategies in the prevention and treatment of HFpEF .
Enhancement of anti-sarcoma immunity by NK cells engineered with mRNA for expression of a EphA2-targeted CAR
- First Published: 06 January 2025
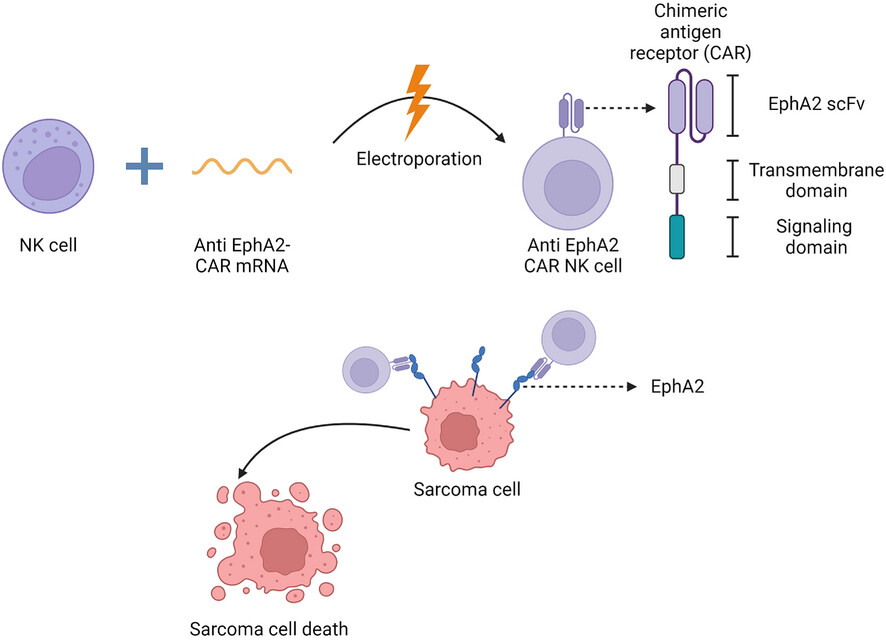
-
Human NK cells can be efficiently transfected with mRNA to safely express an EphA2-CAR without genomic alterations.
-
EphA2-targeted CAR-NK cells exhibit enhanced cytotoxicity against paediatric sarcomas, including rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma and osteosarcoma.
-
This study demonstrate the potential of CAR-NK cell therapies to improve outcomes in hard-to-cure paediatric sarcomas and provides a foundation for their clinical evaluation.
COMMENTARY
Transforming precision medicine: The potential of the clinical artificial intelligent single-cell framework
- First Published: 06 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
The N1-methyladenosine methyltransferase TRMT61A promotes bladder cancer progression and is targetable by small molecule compounds
- First Published: 06 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
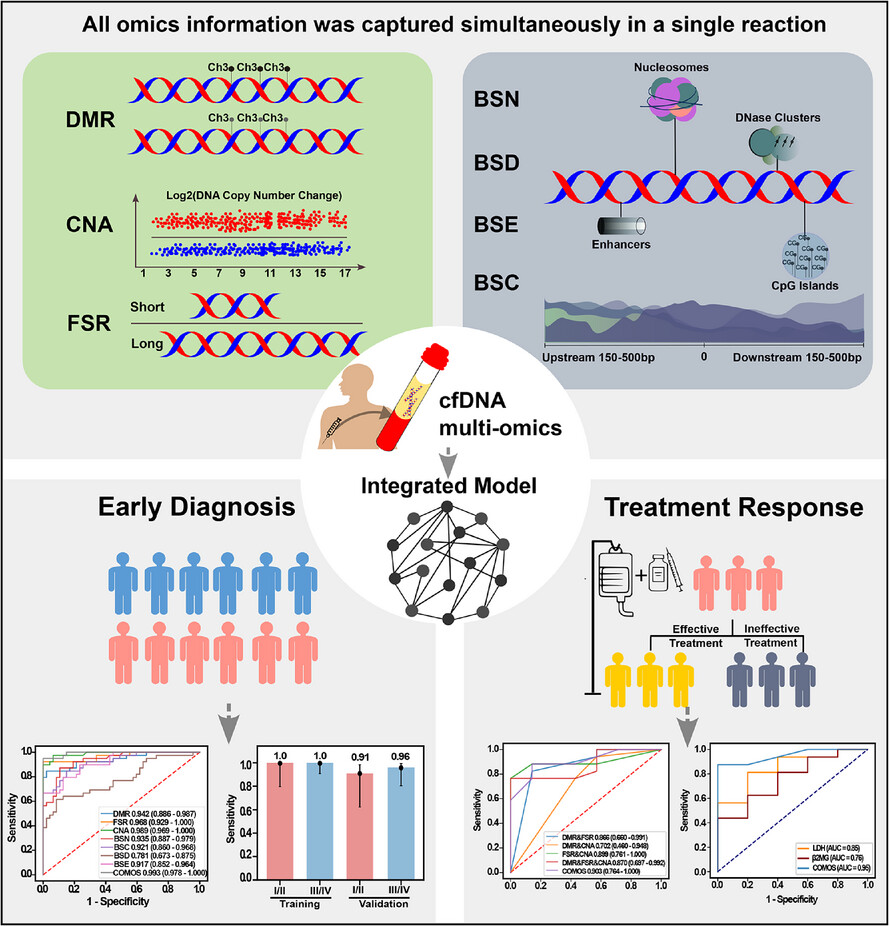
Integrating multi-omics features enables non-invasive early diagnosis and treatment response prediction of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- First Published: 07 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Somatic mutation correlation with lymph node metastasis and prognosis in T1/2 stage colorectal cancer patients: A propensity score matching analysis
- First Published: 07 January 2025
REVIEW
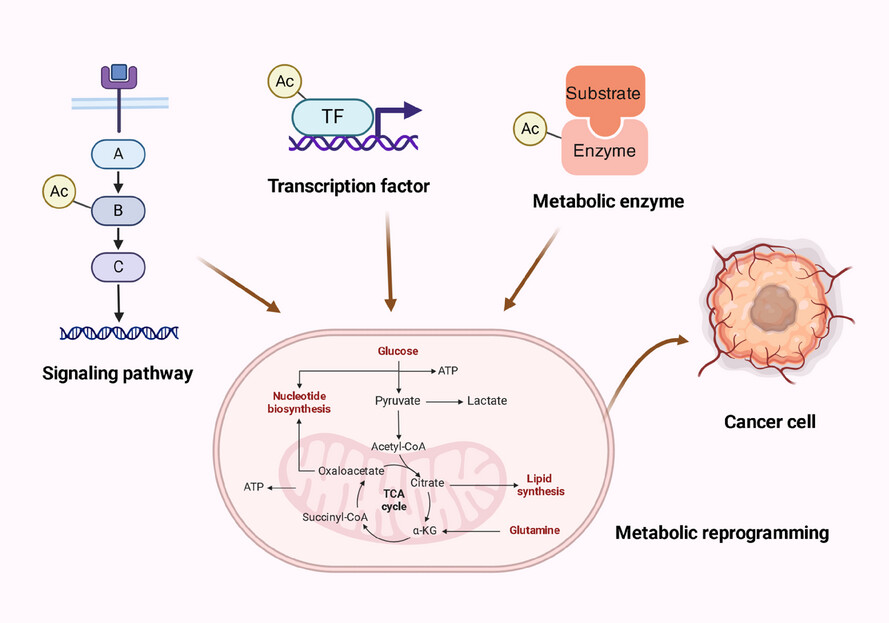
The role of acetylation and deacetylation in cancer metabolism
- First Published: 07 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
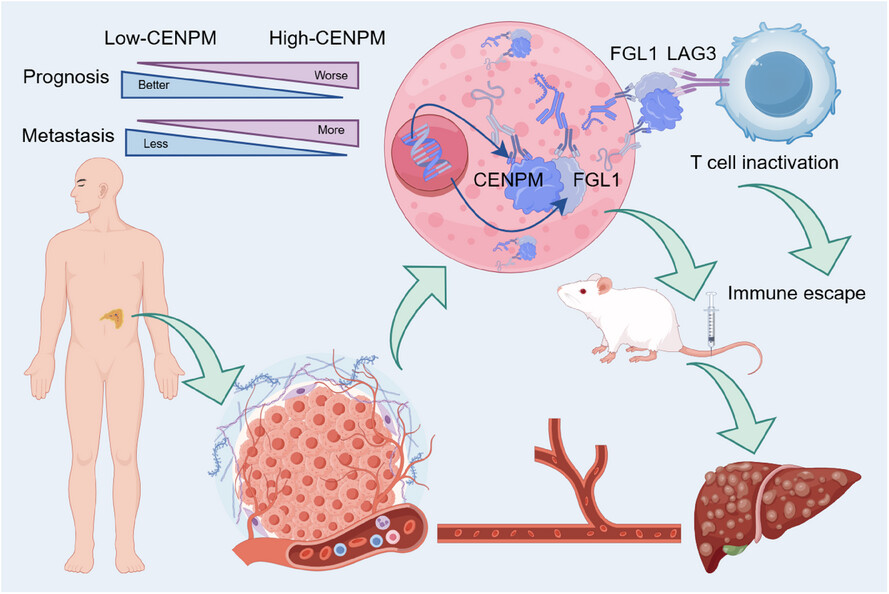
Identification of CENPM as a key gene driving adrenocortical carcinoma metastasis via physical interaction with immune checkpoint ligand FGL1
- First Published: 08 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
iDICss robustly predicts melanoma immunotherapy response by synergizing genomic and transcriptomic knowledge via independent component analysis
- First Published: 08 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Immunoregulatory programs in anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis identified by single-cell multi-omics analysis
- First Published: 08 January 2025
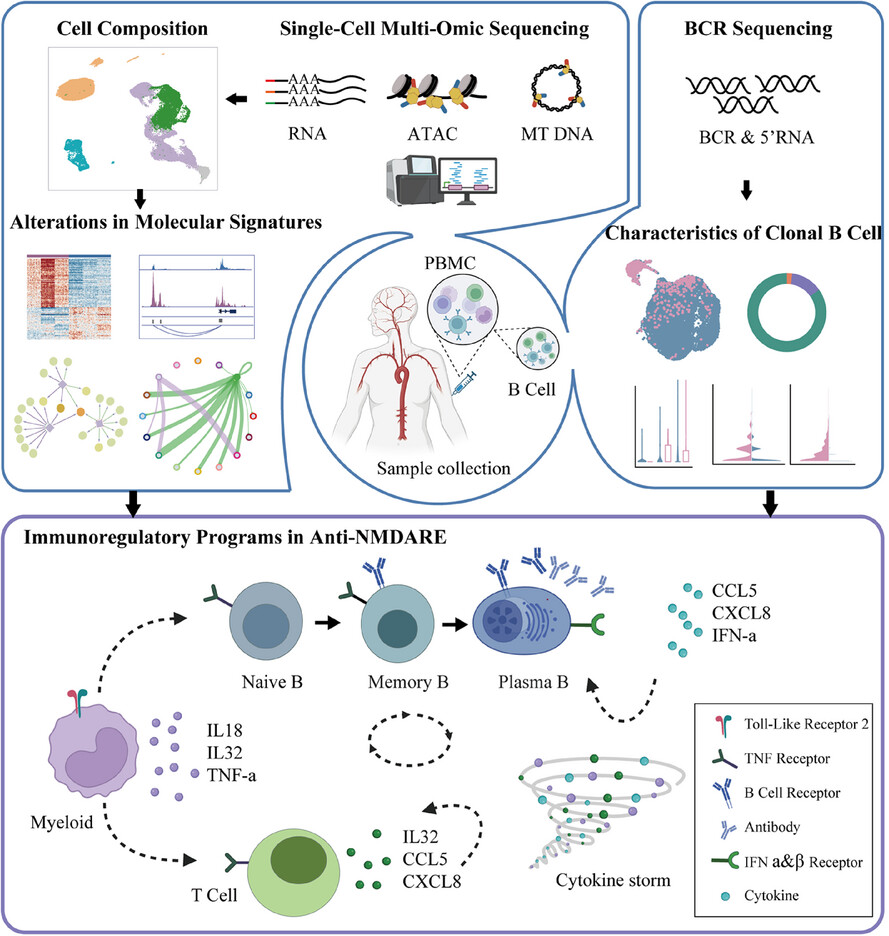
- Single-cell multi-omics analysis revealed distinct immune cell populations and their functional states in anti-NMDARE.
- Systematical analysis identified key immunoregulation programs involved in disease progression.
- Interactions via cytokines among immune cells may intensify the inflammatory response and disease activity, providing therapeutic implications.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Cannabinoid receptor 2 facilitates the Schwann cells-dependent peripheral nerve regeneration
- First Published: 08 January 2025
COMMENTARY
Commentary: Molecular responses in pig heart to human xenotransplantation unveiled by longitudinal multi-omic profiling
- First Published: 08 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Machine learning-based multi-omics models for diagnostic classification and risk stratification in diabetic kidney disease
- First Published: 08 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Nanopore adaptive sampling accurately detects nucleotide variants and improves the characterization of large-scale rearrangement for the diagnosis of cancer predisposition
- First Published: 09 January 2025
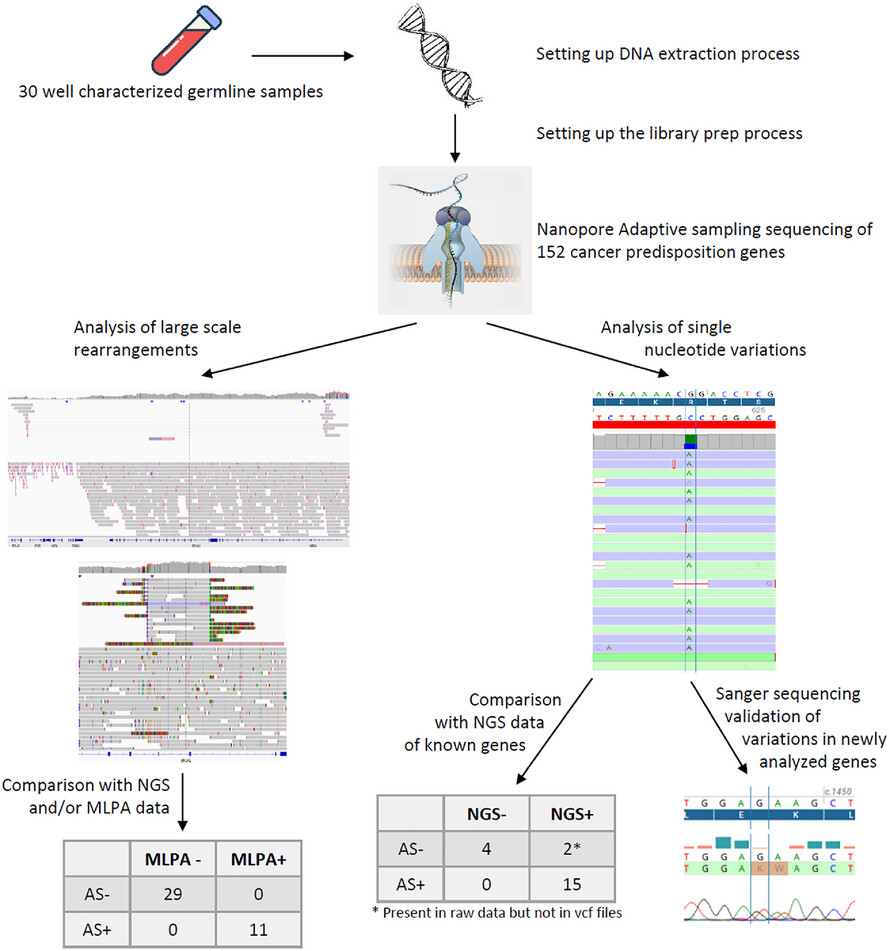
1. Nanopore adaptive sampling sequencing is reliable for the analysis of germline alterations by improving the characterization of LSR and detecting SNV even at low coverage.
2. The protocol we set up can be immediately used in routine molecular diagnosis labs for the characterization of large-scale rearrangements.
LcProt: Proteomics-based identification of plasma biomarkers for lung cancer multievent, a multicentre study
- First Published: 09 January 2025
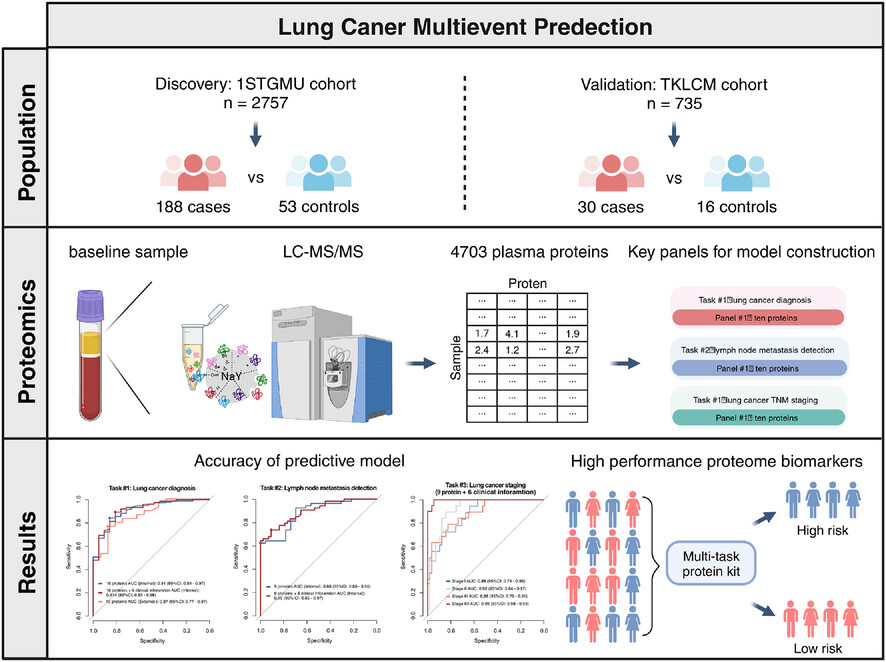
•NaY-based proteomics enables cost-effective and efficient plasma proteome screening.
•Prospective cohorts uncover plasma protein dynamics across benign and malignant nodules and different cancer stages.
•Machine learning models achieve high-accuracy lung cancer diagnosis from plasma profiles.
•A minimal biomarker panel identified via NaY-based proteomics enables low-cost, multitasking capabilities for diagnosis and staging.
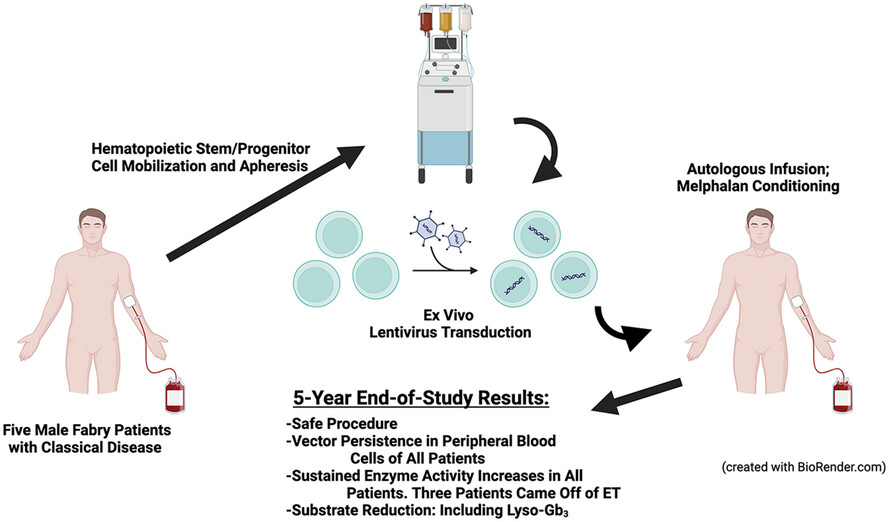
Lentivirus-mediated gene therapy for Fabry disease: 5-year End-of-Study results from the Canadian FACTs trial
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Lower respiratory tract microbiome dysbiosis impairs clinical responses to immune checkpoint blockade in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 10 January 2025
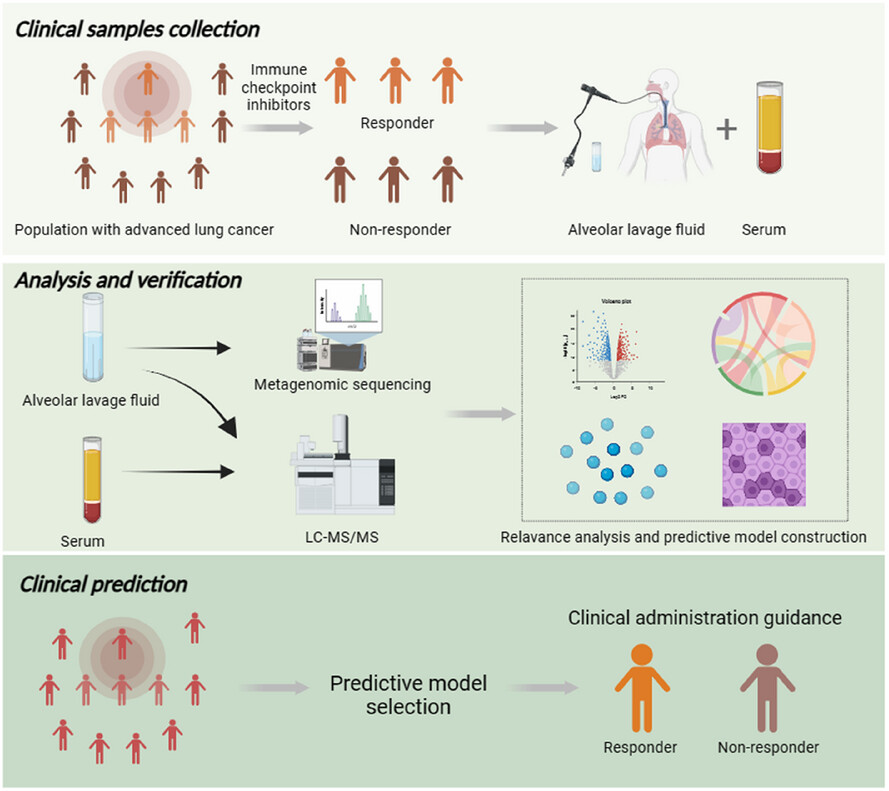
- Alterations of the lower respiratory tract microbiome indicate different clinical responses to ICB within advanced NSCLC.
- Reduced microbial diversity of lower respiratory tracts impairs anti-tumoral performances.
- Microbe-derived metabolites perform as a dominant regulator to remodify the microecological environment in lower respiratory tracts.
- Multi-omics sequencings of the lower respiratory tract possess the potential to predict the long-term clinical responses to ICB among advanced NSCLC.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Predictive nomogram integrating radiomics and multi-omics for improved prognosis-model in cholangiocarcinoma
- First Published: 12 January 2025
INVITED LETTER
Breakthroughs in deep tumour penetrating nano-phototheranostics for tumour ablation
- First Published: 12 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
CMPK2 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation via mtDNA-STING pathway in house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis
- First Published: 12 January 2025
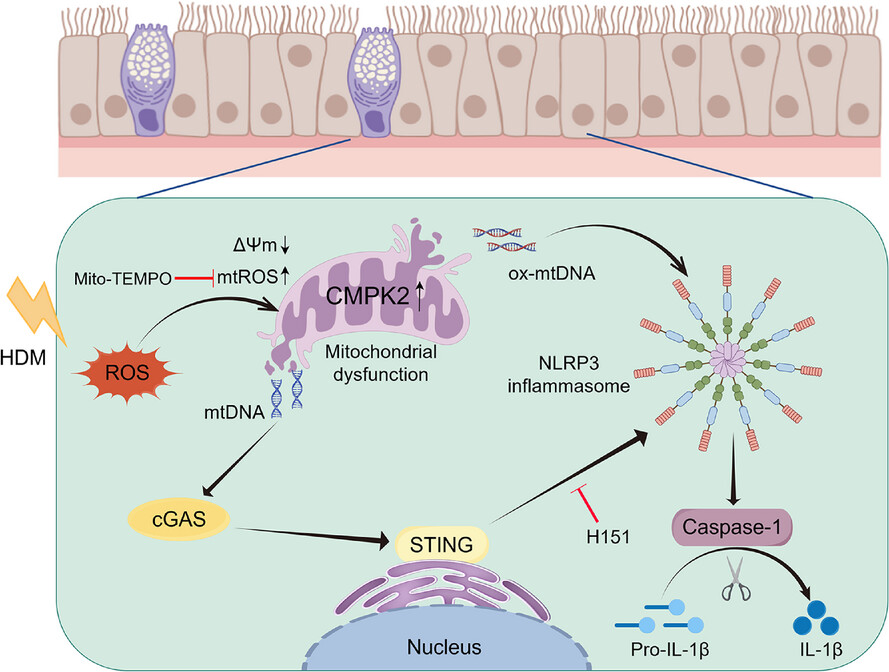
-
Cytidine/uridine monophosphate kinase 2 (CMPK2) expression is up-regulated in the nasal mucosa of patients and mice with allergic rhinitis (AR).
-
CMPK2 caused NLRP3 inflammasome activation via mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)-STING pathway.
-
Blocking CMPK2 or STING signalling significantly reduced the activation of NLRP3 in house dust mite (HDM)-challenged mice and human nasal epithelial cells (HNEPCs).
EDITORIAL
Translational inhalable extracellular vesicle-based mRNA therapy for the treatment of lung cancer
- First Published: 12 January 2025
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Major cell types in the coronary thrombosis of acute myocardial infarction patients revealed by scRNA-seq
- First Published: 13 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
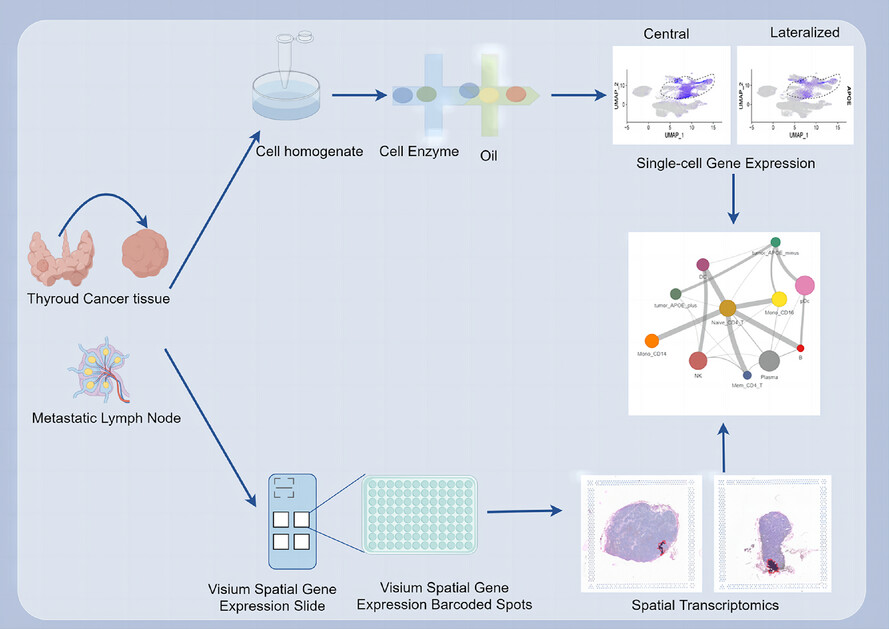
Single-cell RNA-sequencing and spatial transcriptomic analysis reveal a distinct population of APOE− cells yielding pathological lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer
- First Published: 15 January 2025
RECQL4 affects MHC class II-mediated signalling and favours an immune-evasive signature that limits response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with malignant melanoma
- First Published: 15 January 2025
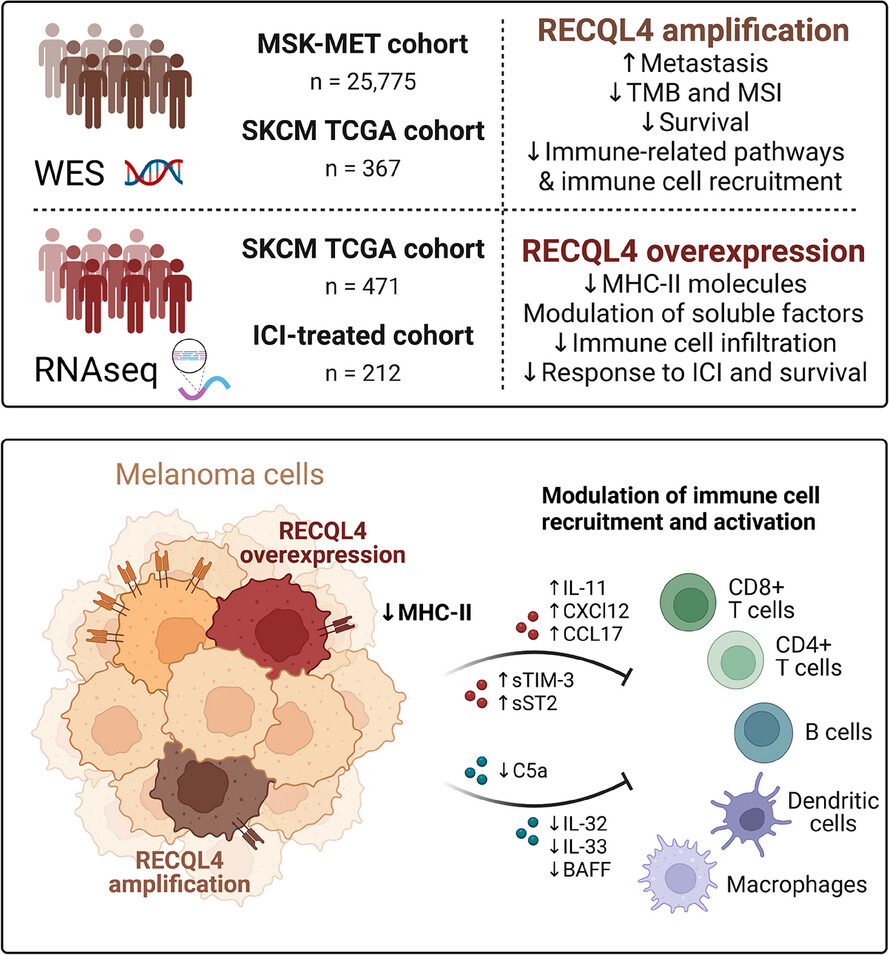
-
High RECQL4 expression limits survival and can act as an independent prognostic factor in melanoma patients.
-
RECQL4 has the potential to act as a negative feedback mediator of immune checkpoint-targeted therapy by limiting signatures associated with therapeutic efficacy.
-
RECQL4 favours an immune-evasive phenotype by downregulating major histocompatibility complex class II molecules.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Advanced mutant receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand development with low affinity for osteoprotegerin
- First Published: 17 January 2025
COMMENTARY
REVIEW
Deciphering the pseudouridine nucleobase modification in human diseases: From molecular mechanisms to clinical perspectives
- First Published: 20 January 2025
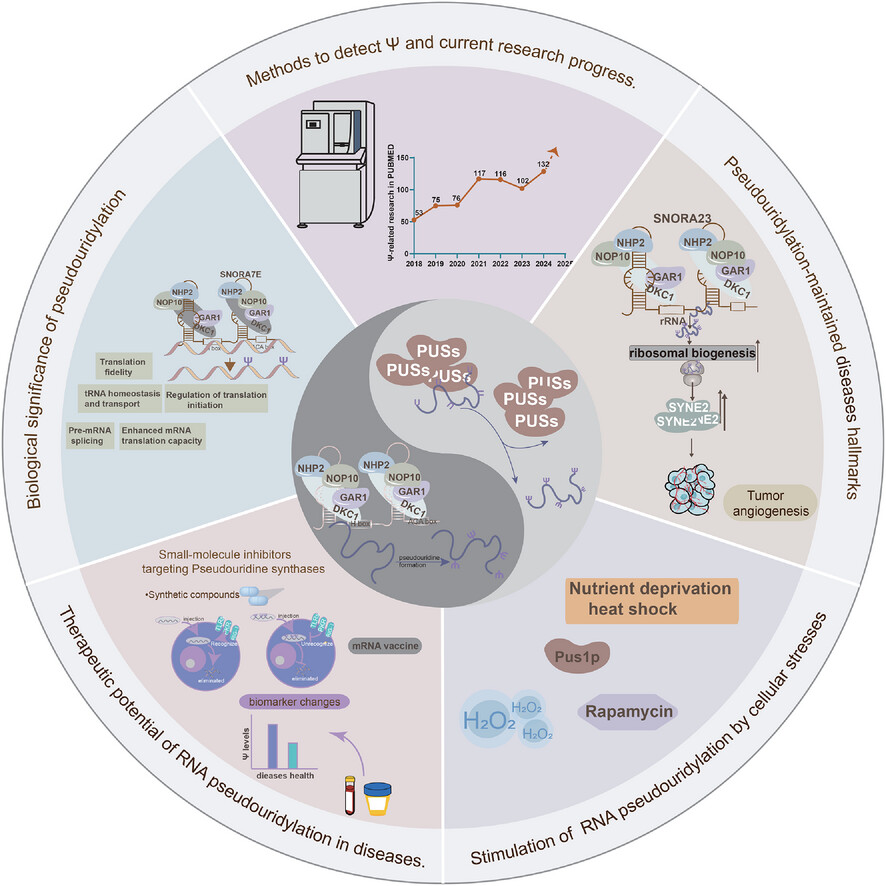
This review discusses the regulatory mechanisms and pathological significance of pseudouridylation in human diseases, with a special emphasis on its involvement in tumourigenesis. Furthermore, the potential therapeutic advantages of targeting pseudouridylation are explored, offering novel strategies for disease treatment.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
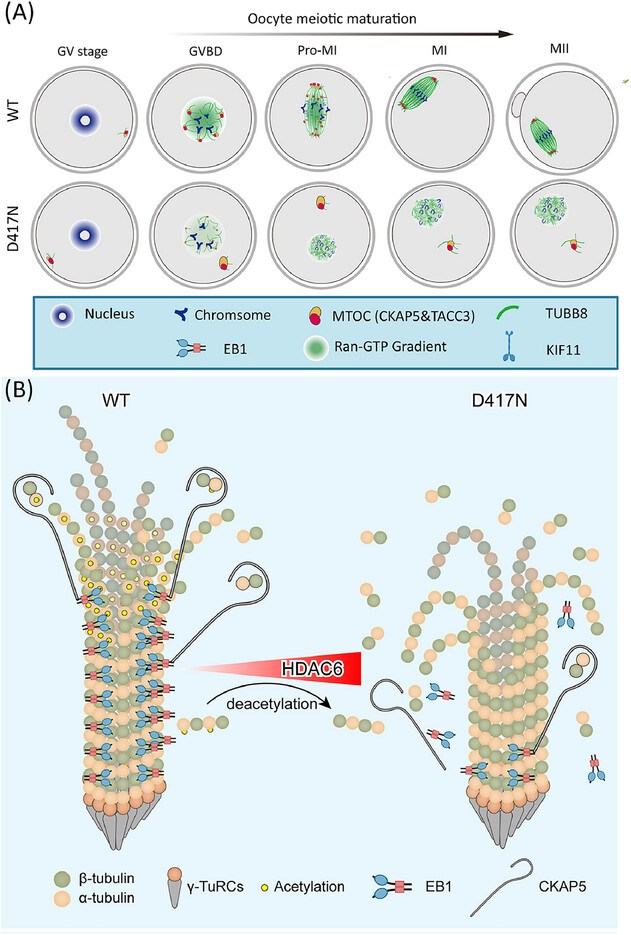
Pathogenic variants of TUBB8 cause oocyte spindle defects by disrupting with EB1/CAKP5 interactions and potential treatment targeting microtubule acetylation through HDAC6 inhibition
- First Published: 20 January 2025
Single-cell landscape of the intrahepatic ecosystem in alcohol-related liver disease
- First Published: 20 January 2025
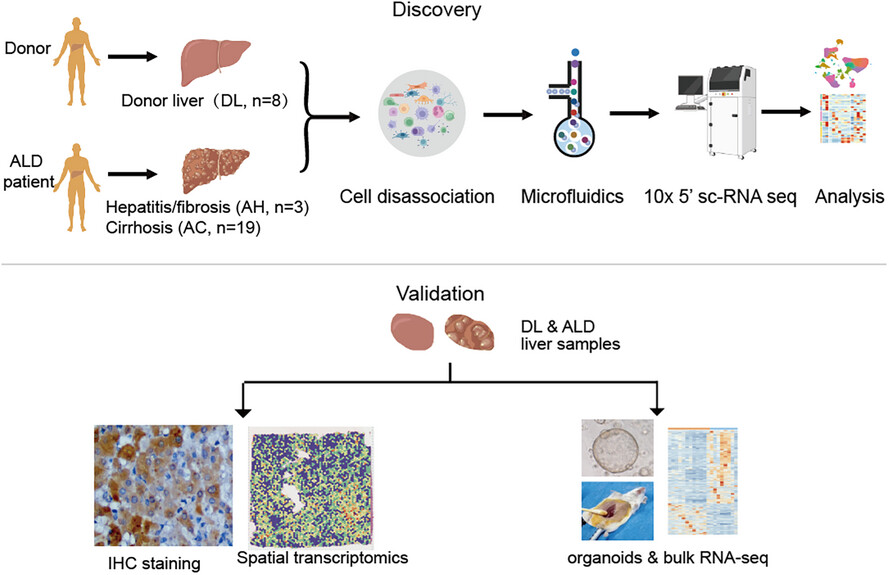
- This study provides single-cell landscape of human liver samples across different ALD stages.
- The ALB+ KRT7+ epithelium were enriched in ALD patients, and the function of this epithelial population varied significantly across ALD stages.
- ALB+KRT7+ epithelium from advanced alcohol-related cirrhosis had malignant transformation potential and tumour promotion activity.
- The comprehensive changes of parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells in the ALD livers lay a hidden danger for the further malignant progression.
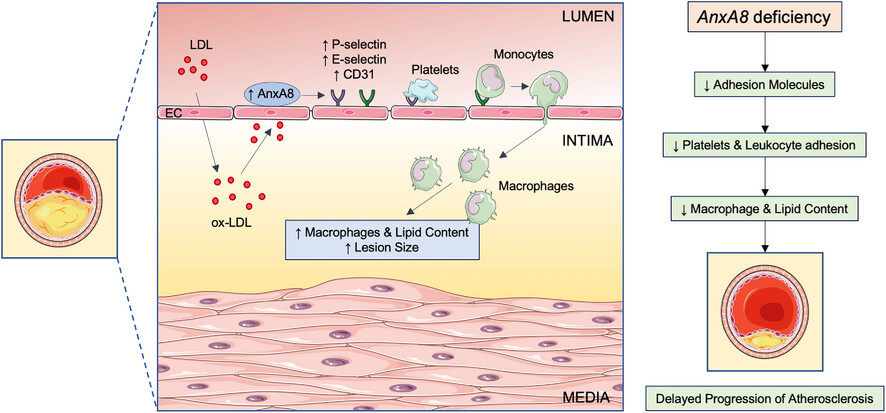
Annexin A8 deficiency delays atherosclerosis progression
- First Published: 21 January 2025
Our work demonstrates a pathogenic role of endothelial Annexin A8 in atherosclerosis. The upregulation of AnxA8 in both human and mice atherosclerotic plaques strongly suggest that AnxA8 promotes disease progression through regulation of adhesion molecules expression and influx of immune cells to the intima. Therapeutic interventions to reduce AnxA8 expression in endothelial cells may delay atherosclerosis progression.