Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Laser Induced Coffee-Ring Structure through Solid-Liquid Transition for Color Printing (Small 6/2023)
- First Published: 08 February 2023

Coffee-Ring Structures
In article number 2205696, Jianfeng Yan and co-workers propose a strategy of laser induced transient solid-liquid transition to fabricate coffee-ring structures. Through modulating the transient state of metal from solid to liquid phase using ultrafast laser pulse train, the controllable fabrication of coffee-ring structures is achieved. The coffee-ring structure exhibit tunable structure color, which can be used for color printing.
Inside Front Cover
One-Pot Controllable Assembly of a Baicalin-Condensed Aptamer Nanodrug for Synergistic Anti-Obesity (Small 6/2023)
- First Published: 08 February 2023

Baicalin-Condensed Aptamer Nanodrugs
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-driven DNA micro-nano-flowers are used to construct a nanosized baicalin-compressed-aptamer-nanodrug (bcaND) via one-pot assembly. The tailored Adipo-8 (tAdi-8) overhang in the PCR amplicon, like an arrow, displays anti-obesity targeting activity, while the baicalin loaded in the bcaND plays a three-fold role as a lipid-lowering factor, bcaND size compressor, and uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1)-raised thermogenic activator. More details can be found in article number 2205933 by Wentao Xu and co-workers.
Inside Back Cover
High-Throughput Cellular Heterogeneity Analysis in Cell Migration at the Single-Cell Level (Small 6/2023)
- First Published: 08 February 2023

High-Throughput Cellular Heterogeneity
In article number 2206754, Yu-Chih Chen and co-workers present a microfluidic cell migration platform that coordinates robotic liquid handling and computer vision for rapidly quantifying individual cellular motility. The high-throughput single-cell screening experiments reveal that many compounds inhibit migration of most cells while leaving fast-moving subpopulations unaffected. They further investigate dynamic cell movement and discover synergistic drug combinations that overcome the resistance of fast-moving subpopulations.
Back Cover
Scalable Fabrication of MXene-PVDF Nanocomposite Triboelectric Fibers via Thermal Drawing (Small 6/2023)
- First Published: 08 February 2023

Nanocomposite Triboelectric Fibers
In article number 2206107, Mustafa Ordu and co-workers demonstrate the strategy for single-step scalable fabrication of MXene-polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanocomposite fibers. The thermal drawing process has the potential to fabricate fibers in kilometers of length necessary for textile and electronic industries. The triboelectric fibers are capable of energy harvesting and biomotion analysis.
Masthead
Correction
Correlated Study of Material Interaction between Capillary Printed Eutectic Gallium Alloys and Gold Electrodes
- First Published: 08 February 2023
Reviews
Solid-State Nanopore Array: Manufacturing and Applications
- First Published: 05 December 2022
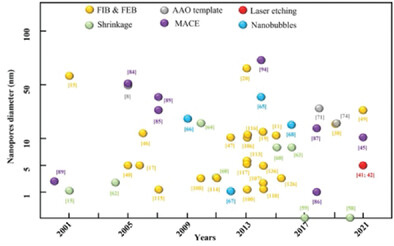
Nanopore brings extraordinary properties for a variety of potential applications, such as DNA/RNA sequencing, energy conversion and storage, water desalination, nanosensors, nanoreactors, and dialysis. However, the mass manufacturing of nanopores is still a global challenge. This review systematically summarizes the manufacturing methods for single nanopore and nanopore array, and presents some new possibilities for fabricating large area nanopore array.
Recent Nanotechnologies to Overcome the Bacterial Biofilm Matrix Barriers
- First Published: 05 December 2022
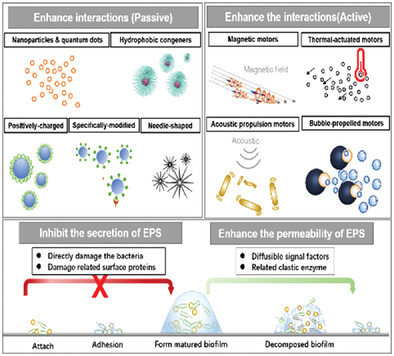
This review summarizes the current progress of nanotechnology methods to improve drug penetration against biofilm matrix obstacles. The mentioned strategies mainly include 1) regulating material morphology and surface properties, 2) utilizing the physical penetration of nano/micromotors or microneedle patches, and 3) equipping nanoparticles with extracellular polymeric substances degradation enzymes or signal molecules.
Frontispiece
A Multilayered Mesoporous Gold Nanoarchitecture for Ultraeffective Near-Infrared Light-Controlled Chemo/Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Guided by SERS Imaging (Small 6/2023)
- First Published: 08 February 2023

Chemo/Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Guided by SERS Imaging
In article number 2206762, Mo Yang, Siu Hong Dexter Wong, and co-workers develop a multilayered mesoporous gold nanoarchitecture labeled with Raman reporters for ultraeffective surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) imaging-guided synergistic therapy toward cancer. This nanoplatform enables efficient xenograft tumor model targeting with sensitive SERS imaging in vitro and in vivo for identifying the tumor cells and optimal therapeutic time point, thereby achieving the highest therapeutic outcome of noninvasive near-infrared triggered photothermal therapy and hyperthermia enhanced chemotherapy.
Research Articles
A Multilayered Mesoporous Gold Nanoarchitecture for Ultraeffective Near-Infrared Light-Controlled Chemo/Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Guided by SERS Imaging
- First Published: 02 January 2023
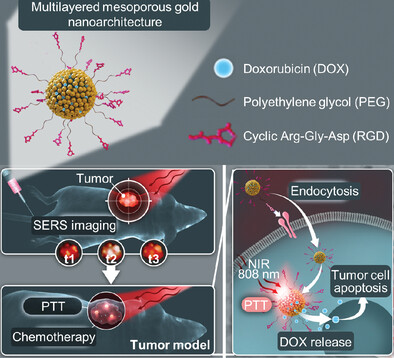
A multilayered mesoporous gold nanoarchitecture (RGD/DOX−pAS@AuNC) labeled with Raman reporters for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) imaging-guided synergistic therapy toward cancer is reported. This nanoplatform enables efficient xenograft tumor of HeLa cell targeting with ultraeffective SERS imaging for tumor site and optimal therapeutic time point identification, as well as near-infrared triggered photothermal therapy and hyperthermia enhanced chemotherapy.
Frontispiece
Spatial Control of Substitutional Dopants in Hexagonal Monolayer WS2: The Effect of Edge Termination (Small 6/2023)
- First Published: 08 February 2023
The Effect of Edge Termination
In article number 2205800, Humberto Terrones, Ana Laura Elías, Mauricio Terrones, and co-workers demonstrate the importance of atomic edge termination in determining the spatial distribution of substitutional dopants in 2D transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) hexagonal monolayers. Preferential iron and vanadium doping occurs on the sulfur-terminated edges of the hexagonal monolayers, causing a decrease in photoluminescence intensity and forming binary optical/electrical domains.
Research Articles
Spatial Control of Substitutional Dopants in Hexagonal Monolayer WS2: The Effect of Edge Termination
- First Published: 01 January 2023
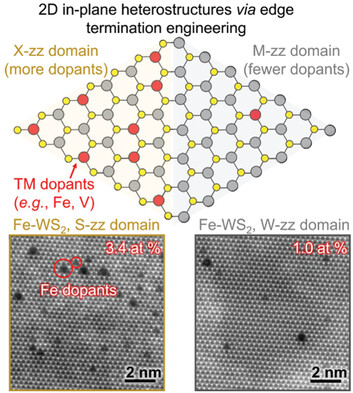
An edge-dependent dopant distribution effect (i.e., sulfur-zigzag edge terminated domains host a higher density of transition metal dopants) is demonstrated using examples of hexagonal Fe- and V-doped WS2 monolayers. This work highlights the important role of edge termination in tuning the spatial distribution of dopants, which constitutes a novel knob for creating in-plane hetero-/multi-junctions that locally display intriguing physicochemical properties.
Laser Induced Coffee-Ring Structure through Solid-Liquid Transition for Color Printing
- First Published: 20 November 2022

Ultrafast laser processing is an effective technology for functional micro/nano structures manufacture. This study proposes a novel strategy of laser induced transient solid-liquid transition to fabricate coffee-ring structures. The solid-liquid transition dynamics is revealed and controlled by modulating the ultrafast laser pulse train. Based on the laser-induced coffee-ring structure, color printing with different structure color is achieved.
One-Pot Controllable Assembly of a Baicalin-Condensed Aptamer Nanodrug for Synergistic Anti-Obesity
- First Published: 02 December 2022

Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)-driven DNA micro-nano-flowers are used to construct a nanosized baicalin-compressed-aptamer-NanoDrug (bcaND) via one-pot assembly. The tailored Adipo-8 (tAdi-8) overhang in the PCR amplicon, like an arrow, displays anti-obesity targeting activity, while the baicalin loaded in the bcaND plays a three-fold role as a lipid-lowering factor, bcaND size compressor, and uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1)-raised thermogenic activator.
High-Throughput Cellular Heterogeneity Analysis in Cell Migration at the Single-Cell Level
- First Published: 30 November 2022
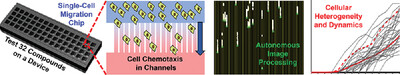
This work presents a high-throughput single-cell migration platform that coordinates robotic liquid handling and autonomous image processing for quantifying cellular heterogeneity and dynamics in migration. Using this innovative technology, this work has revealed a surprisingly low correlation between inhibition of cell migration and growth, and many compounds inhibited migration of most cells but not fast-moving subpopulations.
Scalable Fabrication of MXene-PVDF Nanocomposite Triboelectric Fibers via Thermal Drawing
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Chiral Transport in Nanochannel Based Artificial Drug Transporters
- First Published: 04 December 2022
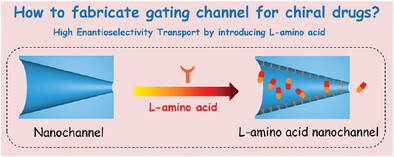
Herein, the L-amino acids are introduced through biomimetic strategy to fabricate the gated nanochannels for the chiral drugs. The gated transport effect of l-tyrosine nanochannels on propranolol enantiomers is found, which is not presented by other nanochannels. The research would provide a new idea for constructing artificial channels to regulate chiral drug delivery.
End Group Effect of Asymmetric Benzodithiophene-Based Donor with Liquid-Crystal State for Small-Molecule Binary Solar Cell
- First Published: 27 November 2022
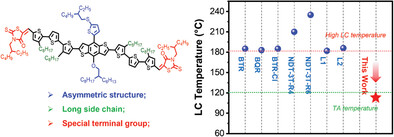
One new small molecule donor with the combination strategy of symmetry-breaking and liquid-crystal (LC) property is synthesized. The LC temperature (117 °C) of a-BTR-H4 coincides well with the thermal annealing temperature of Y6-based accepters, which is conducive to gaining more favored morphology, better light harvest as well as balanced carrier generation and transport in binary all-small-molecule-organic solar cells.
Phase Transition Induced via the Template Enabling Cocoon-like MoS2 an Exceptionally Electromagnetic Absorber
- First Published: 03 December 2022
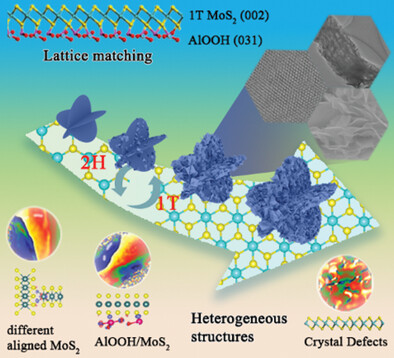
Phase transition of MoS2 is realized under the layered AlOOH template with high lattice matching degree, prompting the conductivity of materials. The purity of 1T phase is regulated through the tunable lattice mismatch, which also expands the absorbing bandwidth to 6.3 GHz. Diverse heterojunctions benefiting from numerous crystal defects and interfaces are constructed to trigger more polarization phenomenon.
Exsolution of Ru Nanoparticles on BaCe0.9Y0.1O3-δ Modifying Geometry and Electronic Structure of Ru for Ammonia Synthesis Reaction Under Mild Conditions
- First Published: 04 December 2022
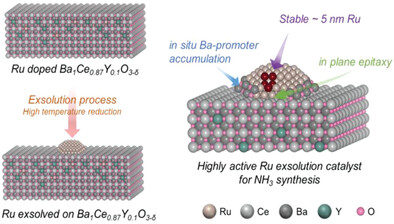
A highly active and stable ammonia synthesis catalyst is prepared by the exsolution of Ru nanoparticles from Ba1Ce0.9Y0.1O3-δ. The optimal nanoparticle size is maintained as the Ru nanoparticles are well-anchored to the support with in-plane epitaxy. The electronic structure of Ru is modified by in situ Ba promoter accumulation around the base of the Ru nanoparticles.
Robust Full-Spectral Color Tuning of Photonic Colloids
- First Published: 04 December 2022
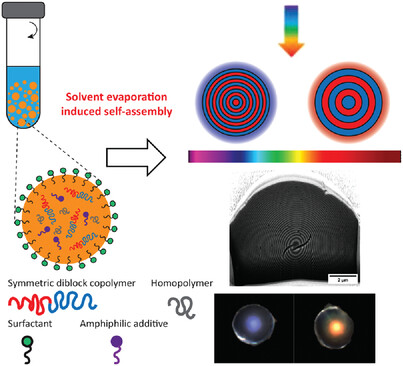
A methodology to create photonic pigments as dispersed and micrometer-scale particles based on highly ordered concentric lamellar microspheres made of block copolymers is presented. Color tuning of the Bragg interference-based reflection band across the entire visible spectrum is achieved by controlling the lamellar thickness by domain differential swelling. These photonic pigments find applications in inks, coatings, and displays.
Creating Highly Active Iron Sites in Electrochemical N2 Reduction by Fabricating Strongly-Coupled Interfaces
- First Published: 03 December 2022
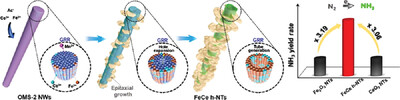
Hierarchical Fe2O3/Fe3O4-CeO2 nanotubes with remarkable electrochemical N2 reduction performance are fabricated through an unconventional galvanic replacement reaction, in which CeO2 is essential to stabilize Fe2+ species. The generation of Fe2O3-Fe3O4 interfaces is of great significance in boosting the hydrogenation of *N2 to *N*NH, thereby accelerating the reaction rate.
Hydrogen Storage in Partially Exfoliated Magnesium Diboride Multilayers
- First Published: 05 December 2022
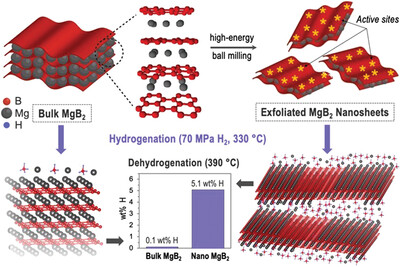
Ultrathin 4 nm magnesium diboride multilayers are synthesized using a simple mechanochemical approach and display enhanced reactivity toward dihydrogen at 70 MPa and 330 °C. Simulations and experiments reveal that exfoliation disrupts the stable boron–boron ring structure, while during hydrogenation it becomes energetically favorable to trade a small number of Mg vacancies in Mg(BH4)2 for greater surface Mg coverage in MgB2.
Enhancing Tungsten Oxide Gasochromism with Noble Metal Nanoparticles: The Importance of the Interface
- First Published: 04 December 2022
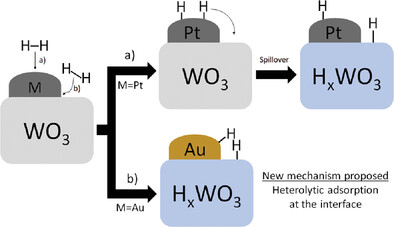
When functionalized with gold and/or platinum nanoparticles, tungsten trioxide thin films can serve as optical sensors for hydrogen detection. By means of experimental and computational investigations, we were able to assess the role the metal species and nanoparticle dimension have toward the device performances, proposing a novel mechanism for hydrogen sensing which highlight the fundamental importance of the metal-oxide interface.
En Route to High-Density Chiral Single-walled Carbon Nanotube Arrays using Solid Trojan Catalysts
- First Published: 03 December 2022
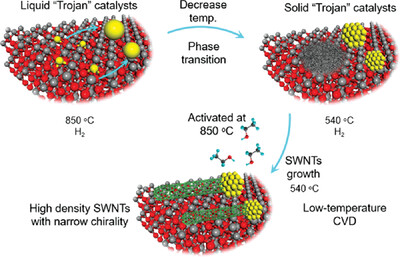
Herein, a method to grow chirality-enriched SWNT horizontal arrays is developed with high density using solid “Trojan” catalysts at very low temperature. In our method, high temperature “Trojan” catalyst formation process provides sufficient catalyst number to obtain high density. These liquid “Trojan” catalysts were cooled to solid state by adopting low growth temperature (≈540 °C). The solid “Trojan” catalysts can be good template to realize the chirality controlling of SWNTs with exposing six-fold symmetry face, (111). Finally, after optimizing the growth condition, (9, 6) and (13, 1) SWNTs enriched horizontal array with the purity of ≈90% and density of 4 tubes µm−1 are realized.
Partial Sulphidation to Regulate Coordination Structure of Single Nickel Atoms on Graphitic Carbon Nitride for Efficient Solar H2 Evolution
- First Published: 03 December 2022
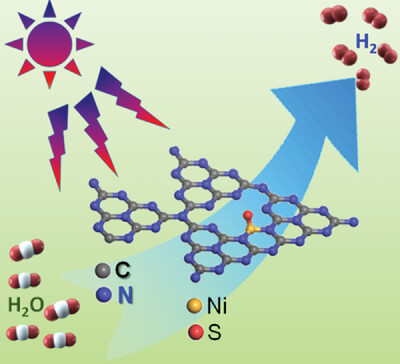
This work reports the unique single Ni sites (Ni1-N2S) on graphitic carbon nitride with unique local coordination structure featuring one Ni atom coordinated with two nitrogen atoms and one sulfur atom, acting as non-precious metal cocatalyt to efficiently promote H2 evolution from water splitting under visible light irradiation, ascribed to the unique electron structure of Ni1-N2S sites.
Triple Stimuli-Responsive Flexible Shape Memory Foams with Super-Amphiphilicity
- First Published: 03 December 2022
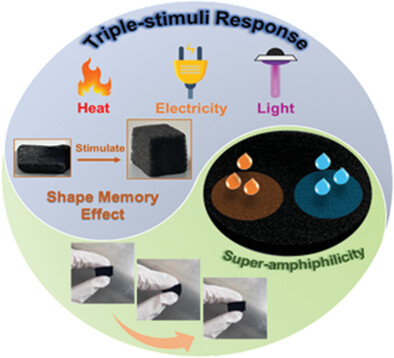
The thermo-, electro-, and photo-responsive composite foam is fabricated through in situ crosslinking polycaprolactone on the surface of carbon foam (CF). CF has robust elasticity and efficient electrothermal/photothermal conversions acting as the flexible supporting framework and continuous energy transition network. Combined with unique super-amphiphilicity, it's applied as a new type of sensor for leakage detection.
Functional CNTs@EMIM+-Br− Electrode Enabling Polysulfides Confining and Deposition Regulating for Solid-State Li-Sulfur Battery
- First Published: 26 November 2022
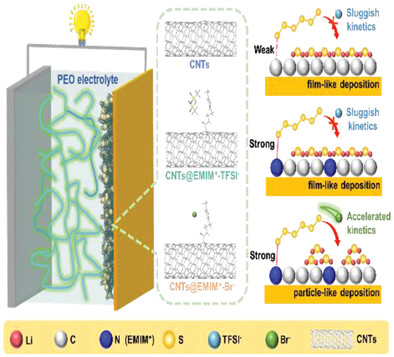
The novel CNTs@EMIM-Br host material is prepared as a dual-effect host material in solid-state Li-Sulfur battery. It not only inhibits the polysulfides shuttling by strong chemical interactions via imidazolium cation (EMIM+), but also facilitates the electrochemical kinetics for promoting the formation of 3D particulate Li2S through high donor anion (Br−).
Synergistic Effect of Surface p-Doping and Passivation Improves the Efficiency, Stability, and Reduces Lead Leakage in All-Inorganic CsPbIBr2-Based Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 02 December 2022
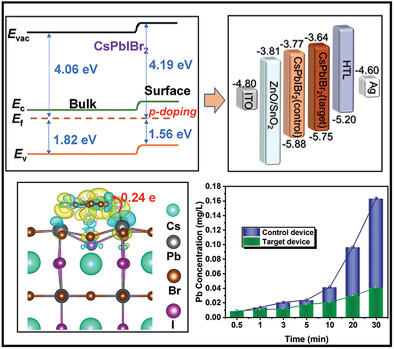
A synergistic effect of surface p-doping and passivation on the inorganic perovskite CsPbIBr2 is studied. The p-type doping treatment optimizes film quality, improves energy level alignment, and suppresses nonradiative recombination. Finally, the device achieves a high PCE of 11.02%, a Voc of 1.33 V, and a FF of 0.75. Lead leakage is well reduced within the safe range of human blood lead content.
Fabrication of a Cation Exchange Membrane with Largely Reduced Anion Permeability for Advanced Aqueous K-ion Battery in an Alkaline-Neutral Electrolyte Decoupling System
- First Published: 01 December 2022
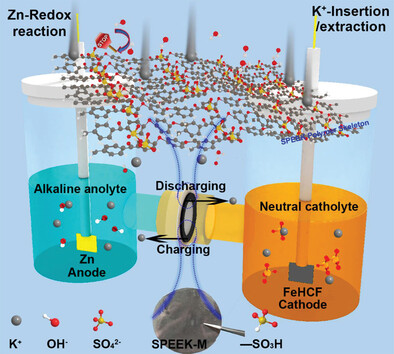
An efficient cation exchange membrane is prepared for an aqueous K-ion battery with decoupling electrolyte (zinc foil anode in alkaline electrolyte and Prussian blue cathode in neutral electrolyte). The electrolyte decoupling strategy maximizes the operating window of the system to 2.6 V and the membrane can effectively block anion shuttling and smoothly conduct cations to ensure long-term normal operation.
Maneuvering the Peroxidase-Like Activity of Palladium-Based Nanozymes by Alloying with Oxophilic Bismuth for Biosensing
- First Published: 03 December 2022
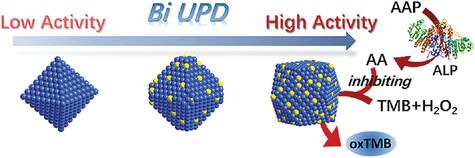
Incorporation of oxophilic bismuth by an underpotential deposition strategy endows Pd-based nanocrystals (NCs) with outstanding nanozyme properties. Mechanistic studies suggest that the oxophilicity of Bi contributes to the excellent peroxidase-like activity of the alloy NCs, and thus they can be utilized in biosensing with high sensitivity.
Lattice Distortions and Multiple Valence Band Convergence Contributing to High Thermoelectric Performance in MnTe
- First Published: 21 November 2022
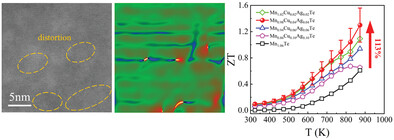
Dense lattice distortions were induced by Cu and Ag dopants possessing large differences in atom radius with host elements, resulting in extremely low lattice thermal conductivity in MnTe. Cu and Ag codoping enables multiple valence band convergence in its electronic structure, contributing to large Seebeck coefficient. Consequently, an outstanding ZT of 1.3 is achieved for Mn0.98Cu0.04Ag0.04Te by these synergistic effects.
Gradient-Structured Ceramics with High Energy Storage Performance and Excellent Stability
- First Published: 03 December 2022
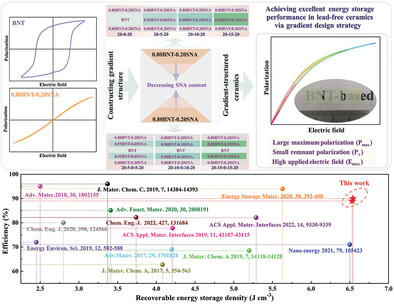
The lead-free ceramics with gradient structure are designed and prepared by the tape-casting method. After optimizing the composition and distribution of the gradient-structured ceramics, giving rise to slim P–E loops, large Pmax and high energy storage performance (Wrec > 6.5 J cm−3 and η ≥ 89%) along with excellent stability.
Remodeling Microenvironment for Endogenous Repair through Precise Modulation of Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans Following Spinal Cord Injury
- First Published: 18 November 2022
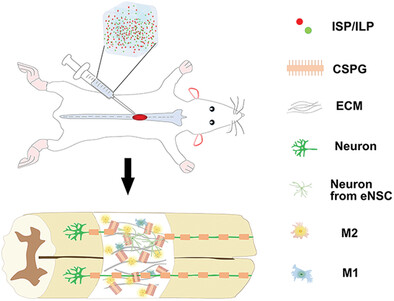
Injected functional self-assembling peptide hydrogel loaded with intracellular sigma peptide/LAR peptide might promote endogenous neural regeneration by modulating chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) after spinal cord injury (SCI). Local CSPG manipulation establishes an anti-inflammatory environment by inducing anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, which facilitates extracellular matrix remodeling for neuronal differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells and axon regrowth. The precise modulation of CSPGs will provide novel insights for the endogenous repair of SCI potentially.
Multiphase Molybdenum Carbide Doped Carbon Hollow Sphere Engineering: The Superiority of Unique Double-Shell Structure in Microwave Absorption
- First Published: 27 November 2022
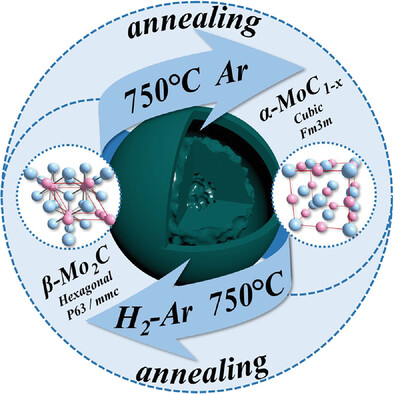
Molybdenum carbide doped carbon hollow spheres with different crystalline phases XX obtained by changing the heat treatment atmosphere. The prepared Mo-PDA double-shell hollow spheres XX heat treated in H2-Ar atmosphere to obtain β-phase Mo2C, which belongs to the P63/mmc space group and is a closely spaced hexagonal crystal system. And the α-phase MoC1-x XX obtained in Ar atmosphere, which is a face-centered cubic crystal system and belongs to the Fm3m space group.
Swarming Magnetic Microrobots for Pathogen Isolation from Milk
- First Published: 07 December 2022
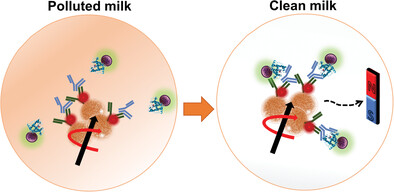
Magnetic microrobots (MagRobots) based on paramagnetic hybrid microstructures modified with anti-rabbit IgG produced in goat and IgG from rabbit serum, that can specifically bind and isolate S. aureus bacteria from milk using the protein A present on the bacteria cell wall for efficient bacteria removal as well as their specific determination.
SMART Silly Putty: Stretchable, Malleable, Adherable, Reusable, and Tear-Resistible Hydrogels
- First Published: 26 November 2022
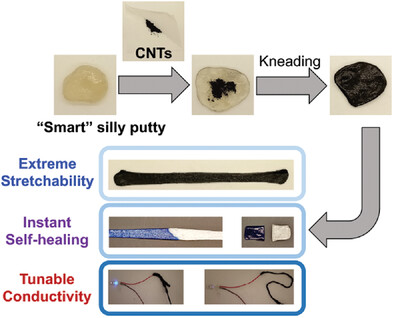
An extremely stretchable, malleable, adherable, reusable, and tear-resistible (SMART) hydrogel is synthesized from a double network of poly(vinyl alcohol)/boric acid and chitosan. The instant bond exchange of boronic ester dynamic covalent bonds leads to extreme stretchability and rapid self-healing and stress relaxation. Various water-dispersible additives can be readily incorporated in the hydrogels via hand kneading.






