Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 6/2020
- Page: 1023
- First Published: 19 May 2020

BIWIC 2019 – 26. International Workshop on Industrial Crystallization. Copyright: Adrian Flood
Crystallization is a vital process for the modern chemical industry. The International Workshop on Industrial Crystallization (BIWIC) promotes the international exchange and collaboration in industrial crystallization research. This cover illuminates the meaning behind the conference's dodecahedral logo (top right). Top left: Morphology of a hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) crystal with HMT molecules shown based on data from L. N. Becka et al., Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1997, A273, 435–454. The image was produced using Mercury (C. F. Macrae et al., J. Appl. Cryst. 2020, 53, 226–235). Top right: The logo for BIWIC is a rhombic dodecahedron, such as the structure of HMT. Bottom left: SEM image of a typical HMT crystal (courtesy of P. Pantaraks). Bottom right: An interesting feature of HMT is its retrograde solubility. Displayed data shows the solubility in water (L. Wang et al., J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 2907–2909).
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 6/2020
- Page: 1024
- First Published: 19 May 2020
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 6/2020
- Page: 1025
- First Published: 19 May 2020
Highlights
Editorial
Industrial Crystallization: A Vital Process for the Modern Chemical Industry
- Page: 1028
- First Published: 19 May 2020
Research Articles
Modeling of Mixing-Precipitation Processes: Agglomeration
- Pages: 1029-1039
- First Published: 09 December 2019
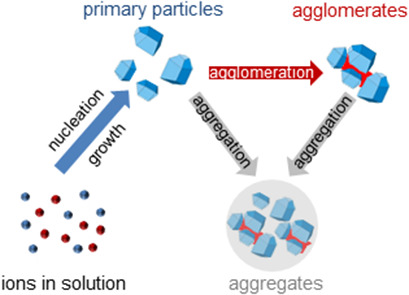
By applying a rigorous approach, a comprehensive description of the barium sulfate precipitation process in a wide range of supersaturations was achieved. Using carefully designed experiments, a model describing the process was validated. The proposed model has proven to express the experiments with a high degree of accuracy in the whole range of supersaturations investigated.
Ice Crystal Growth in Sucrose Solutions Containing Kappa- and Iota-Carrageenans
- Pages: 1040-1047
- First Published: 21 February 2020
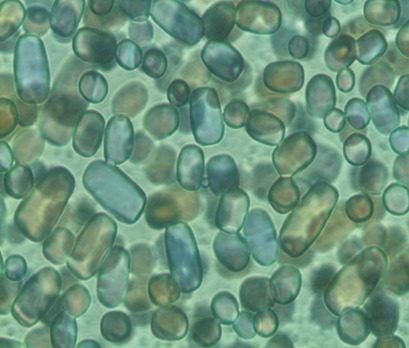
The ice recrystallization inhibition (IRI) and thermal hysteresis (TH) activities of κ- and ι-carrageenans were measured in sucrose solution. Both carrageenans have high IRI activity but no TH activity. The habit modifications were observed based on the interaction of carrageenans with ice crystals. Both carrageenans proved to be suitable as novel cryoprotectants in cryopreservation applications.
Evaluation of Scale and Corrosion Inhibition of Modified Polyaspartic Acid
- Pages: 1048-1058
- First Published: 25 February 2020
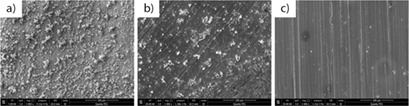
Formation of calcium scale is a serious problem in, e.g., industrial circulating cooling water and seawater desalination, and causes major economic losses. Herein, modified polyaspartic acid inhibitors were synthesized, and their scale inhibition properties were studied theoretically and experimentally. A mechanism by which they inhibit scaling in the presence of calcium ions is proposed.
Effect of Anti-Encrustation Additives on Zirconium Molybdate Hydrate
- Pages: 1059-1064
- First Published: 12 March 2020

Encrustation is a serious issue in numerous industrial processes. Encrustation of zirconium molybdate hydrate containing tellurium can be prevented or minimized by addition of molybdate trioxide hemihydrate as anti-encrustation reagent, having a large specific surface area and high supersaturation. The presence of tellurium with high adhesion potential affected the encrustation amount.
Partial Seeding Policy for Controlling the Crystal Quality in Batch Cooling Crystallization
- Pages: 1065-1071
- First Published: 12 March 2020
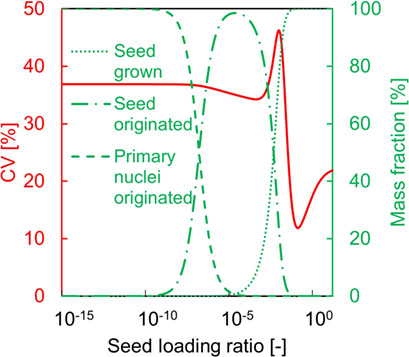
Partial seeding, in which the nuclei originating from seed crystals grow to yield the product crystals, was simulated and optimized for the crystallization of L-arginine. The optimum seed loading amount and the resulting product quality were correlated with the seed crystal size and the cooling rate. The simulated values were compared to the measured ones.
Crystallization and Purification of 4,4′-Diaminodiphenyl Ether
- Pages: 1072-1078
- First Published: 12 March 2020
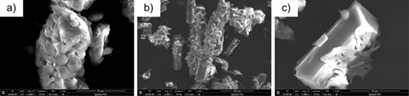
The purification of 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl ether (ODA) containing impurities was investigated. Crystals with appropriate crystal morphology and particle size distribution were obtained by the combination of sublimation and anti-solvent crystallization. In this way, the original samples were reprocessed to prepare ODA with good color, uniform particle size distribution, and reasonable crystal shape.
Experiments and Correlations of the Solubility of γ-DL-Methionine in Binary Solvent Mixtures
- Pages: 1079-1086
- First Published: 20 March 2020
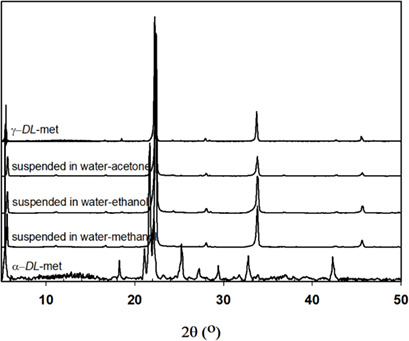
The solubility of γ-DL-methionine in binary solvent mixtures was measured by the gravimetric method. The solubility increased with higher temperature and decreased with higher mass fraction of antisolvent. The solubility was lowest when using acetone as the antisolvent. The thermodynamic properties based on the experimental data indicated that the solubility process is endothermic and entropy-driven.
Analysis of Morphological Changes in Monosodium Urate Monohydrate Crystals for Gout Treatment
- Pages: 1087-1092
- First Published: 20 March 2020
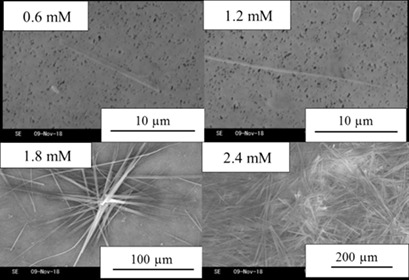
In static experiments, granular monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) crystals were observed to disappear when needle-like crystals were formed, suggesting that the granular crystals are consumed by the growth of the needle-like crystals. Thus, gout, which is induced by MSU crystals, may be treated by suppressing the nucleation of granular crystals and controlling the morphology change from granular to needle-like.
Resolution by Preferential Crystallization of Proxyphylline by Using Its Salicylic Acid Monohydrate Co-Crystal
- Pages: 1093-1098
- First Published: 20 March 2020
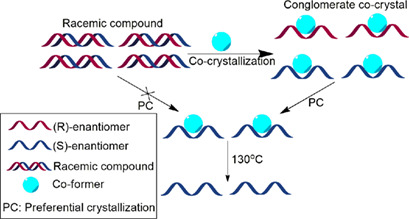
Production of pure enantiomers is of high interest in the pharmaceutical industries. Preferential crystallization is a very efficient technique designed to separate enantiomers forming a conglomerate system. The first example of applying this method to a conglomerate co-crystal of a racemic compound is highlighted, showing the high productivity and high yield of the process.
Effect of Ultrasonic Irradiation on the Probability of Primary Nucleation of L-Arginine Hydrochloride
- Pages: 1099-1104
- First Published: 20 March 2020
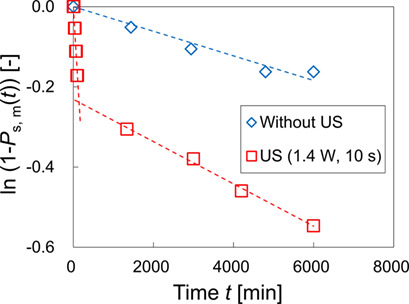
Amino acids are utilized as medical raw materials and food additives. As most of the amino acids show polymorphism and since polymorph control is required in crystallization process, nucleation of L-arginine hydrochloride by ultrasonication was investigated, revealing that ultrasonication may be a feasible method to induce significant nucleation of a particular polymorph.
Effect of Crystallization Conditions on the Metastable Zone Width and Nucleation Kinetics of p-Aminobenzoic Acid in Ethanol
- Pages: 1105-1114
- First Published: 08 April 2020
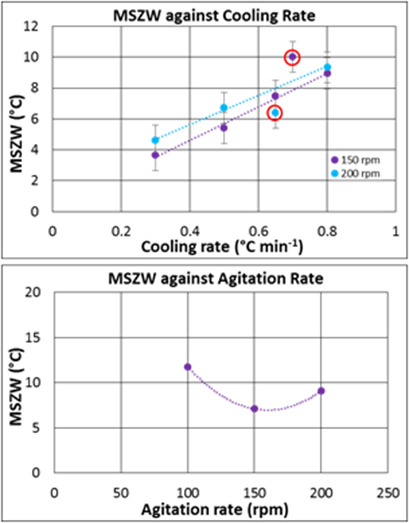
Information on the metastable zone width and nucleation kinetics as functions of cooling rates and agitation rates is essential for the design of batch cooling crystallization processes. Crystallization and dissolution temperatures were measured as a function of cooling rate and impeller speed for the batch cooling crystallization of p-aminobenzoic acid in ethanol.
Solid Solubilities of Sulfonamides and Use of Rapid Expansion of Supercritical Solutions for Microparticle Production
- Pages: 1115-1123
- First Published: 08 April 2020
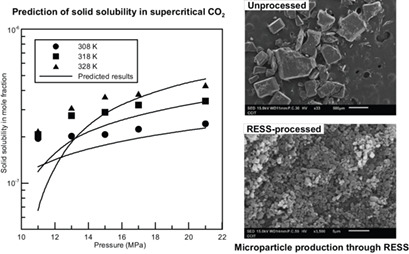
A predictive solution model was developed to predict the solid solubility of sulfonamides in supercritical CO2. Microparticles of p-toluenesulfonamide, an anticancer drug, with a mean size of 1.09 μm were successfully produced through an organic solvent-free rapid expansion of supercritical solutions process. The effects of rapid expansion of supercritical solutions process parameters were evaluated.
Thermodynamic Models and Central Composite Design for Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Solubility
- Pages: 1124-1136
- First Published: 21 April 2020
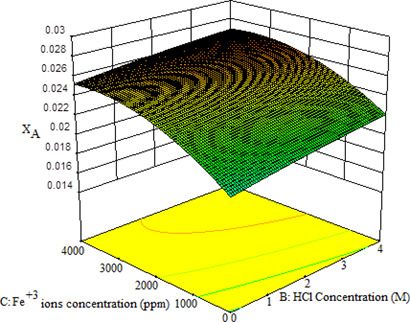
The solubility of gypsum was determined in the presence of Cr3+ and Fe3+ ions at various temperatures in HCl solutions. Modified Apelblat and Buchowski-Kiazczak models were applied and the effect of three variables on solubility was evaluated by central composite design. The results help improving the gypsum production processes and reducing the scale formation based on the relative insolubility of gypsum.
Additive-Induced Selective Crystallization of the Elusive Form-II of γ-Aminobutyric Acid
- Pages: 1137-1143
- First Published: 16 April 2020
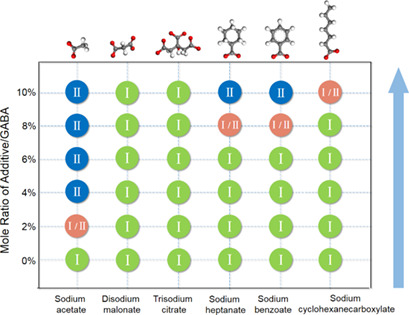
The strategy of additive-induced polymorphs was applied to achieve selective crystallization of the elusive Form-II of γ-aminobutyric acid. The effect of two structural factors of sodium carboxylate additives on their ability to induce such selective crystallization in terms of the number of –COO− groups and the types of the R group, i.e., chain alkyl, cyclic alkyl or phenyl, was evaluated.
Multidimensional Population Balance Modeling for Pathological Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystals in the Presence of Amino Acids
- Pages: 1144-1151
- First Published: 16 April 2020
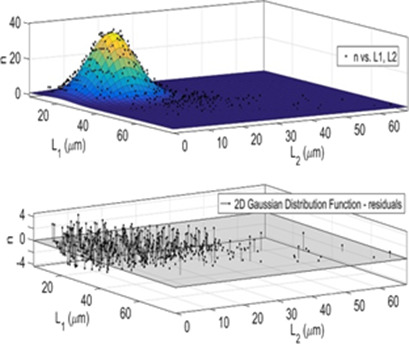
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate is a pathological crystal of great importance for medical research. In order to suppress the growth of such crystals, L-Lys and L-Thr were applied as potential inhibitors. A two-directional population balance equation was established and numerically solved involving agglomeration and breakage effects. L-Thr had a remarkable inhibition effect on such crystals.
Computational Analysis of the Solid-State and Solvation Properties of Carbamazepine in Relation to its Polymorphism
- Pages: 1152-1159
- First Published: 08 April 2020
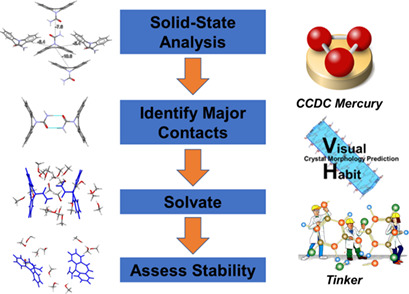
A molecular modeling workflow is applied to uncover details of the solution chemistry which drives the unusual carbamazepine polymorphic crystallization in a range of polar and apolar solvents. The usability of this workflow is assessed, with respect to how it could be diversely applied to a range of pharmaceutical compounds for identifying solvents to obtain a desired crystal polymorph.
Membrane Distillation of Butanol from Aqueous Solution with Polytetrafluoroethylene Membrane
- Pages: 1160-1166
- First Published: 25 February 2020
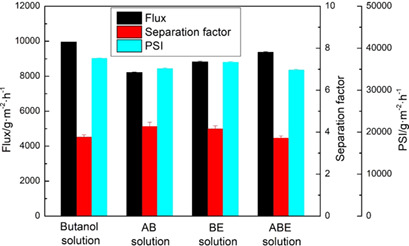
Separation of acetone, butanol, and ethanol from aqueous solution was carried out by vacuum membrane distillation with polytetrafluoroethylene membrane using mechanical vapor compression. Membrane distillation with permeate vapor fractional condensation was found to be more energy-efficient than conventional procedures and cost-effective due to about 50 % lower energy consumption.
Highly Accurate Prediction Method for Thermophysical Properties of Cryogenic Phase Change Materials
- Pages: 1167-1175
- First Published: 17 February 2020
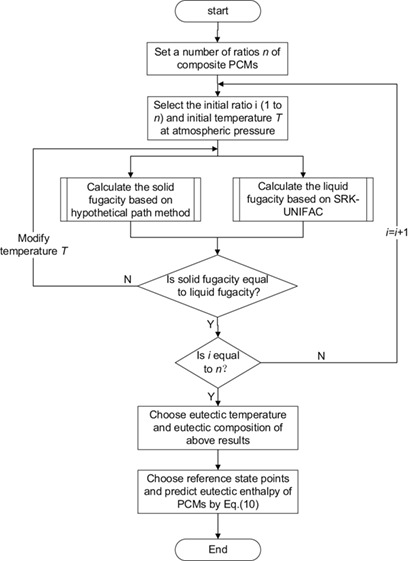
In view of the limitations of experimental studies on thermophysical properties of cryogenic phase change materials, a highly accurate approach to predict these properties was developed. The method was adopted for material selection and design for a cold storage unit with high efficiency, providing a theoretical reference for selecting such materials for liquid natural gas cold storage engineering.
Flow Characteristics in a Honeycomb Structure to Design Nanobubble Generating Apparatus
- Pages: 1176-1185
- First Published: 17 January 2020
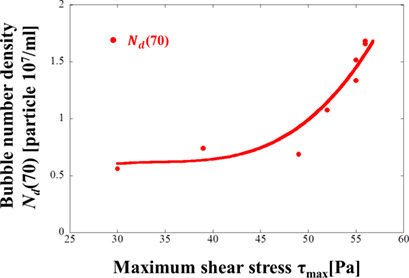
The mechanism of nanobubble generation and generation ability are studied for a small and a large apparatus using different honeycomb structures based on the results of experiments and computational fluid dynamics/population balance model analysis. The maximum shear stress appearing repeatedly around honeycomb cell corners controls the nanobubble generation.
Micronization of Three Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Using the Rapid Expansion of Supercritical Solution Technology
- Pages: 1186-1193
- First Published: 08 January 2020
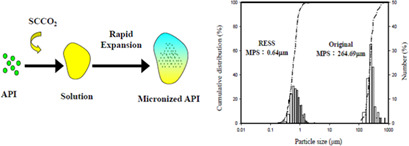
Three active pharmaceutical ingredients of monobenzone, ethylparaben, and kojic acid were recrystallized and micronized employing the rapid expansion of supercritical solution (RESS) technology. The mean particle sizes of these ingredients were micronized down to submicron level. Enhanced dissolution behavior was observed for the RESS-processed active pharmaceutical substances.
Cost-Saving Opportunities in the Energy Management of Papermaking Processes
- Pages: 1194-1204
- First Published: 27 January 2020
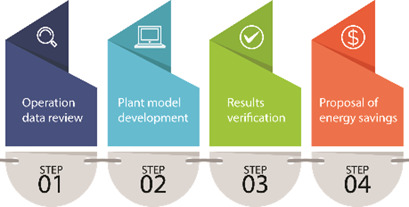
A complex methodology from operation data review through mathematical model development based on mass and energy balances for proposing of cost-saving measures in energy management of a paper machine is presented. Four energy-saving measures targeting paper stock pumping and paper drying operation are recommended and partially verified in real-time operation.
Polymer Film Heat Transfer Surfaces in Seawater Desalination: Fouling Layer Formation and Technology
- Pages: 1205-1213
- First Published: 27 January 2020
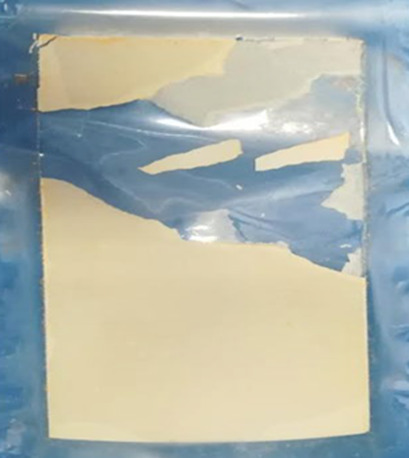

Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) films can be applied as future heat exchanger materials in seawater thermal desalination processes. The fouling layer formed on the pure PEEK film is brittle, detachable, and adaptable to in-situ cleaning by hydrodynamic methods such as pulsed washing. Applying pure PEEK polymer material in seawater desalination will reduce the costs of maintenance anti-scaling chemicals.
Polyacrylonitrile/α-Fe2O3 Hybrid Photocatalytic Composite Adsorbents for Enhanced Dye Removal
- Pages: 1214-1223
- First Published: 20 March 2020
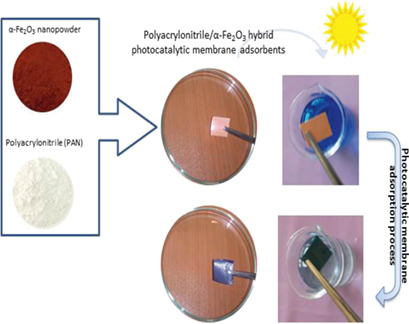
A novel hybrid photocatalytic composite adsorbent was fabricated by dispersing an α-Fe2O3 nanophotocatalyst on the surface of polyacrylonitrile (PAN). The hybrid film shows an excellent efficacy for degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution. After adsorption, the film can be easily collected from the solution. The PAN/α-Fe2O3 hybrid film is an efficient solution for degradation of toxic dyes.
Applying Reaction Kinetics to Pseudohomogeneous Methanation Modeling in Fixed-Bed Reactors
- Pages: 1224-1233
- First Published: 20 March 2020
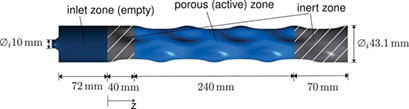
Complex interactions between chemical and physical processes make simulating catalytic fixed-bed reactors challenging. Various microkinetic models of pseudohomogeneous CO and CO2 methanation at elevated temperatures were evaluated. The best kinetic model was fitted to the operating conditions and validated by CFD simulations. The simulations match experimental data for various operating conditions.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 6/2020
- Page: 1234
- First Published: 19 May 2020










