Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
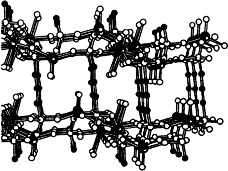
Cover Picture (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2/1995)
- First Published: February 3, 1995

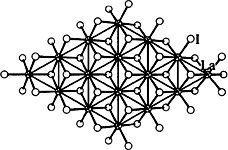
The cover picture shows the structure, generated by molecular mechanics calculations, of a chromophoric self-assembled superlattice with a very large second-order nonlinear optical response (blue, benzylic coupling layer; green: stilbazolium chromophore layer with high polarizability: violet and yellow: siloxane capping layer: white spheres: iodide counterions). The synthesis and properties of the associated real systems are one of the themes of the review by T. J. Marks and M. A. Ratner on molecule-based assemblies with nonlinear optical properties on pp. 155ff. This article complements excellently that by N. J. Long on the “organometallic route” to NLO materials in the previous issue.
Graphical Abstract (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2/1995)
- Pages: 131-137
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Reviews
Disulfide-Reductase Inhibitors as Chemotherapeutic Agents: The Design of Drugs for Trypanosomiasis and Malaria
- Pages: 141-154
- First Published: February 3, 1995
The designation “scourge of mankind” has been attached to parasitic infections such as Chagas' heart disease, sleeping sickness, and malaria. In many countries of the world they lead to human misery and massive socio-medical problems. Several approaches are possible for the design of chemotherapeutic agents that can interfere as enzyme inhibitors with the metabolism of parasites. For instance, structural motifs of an enzyme and its natural substrates can be expolited to control the kinetics of the enzyme–substrate interactions, and thus substrate analogues can influence the enzyme as inhibitors at various stages of the catalytic cycle. The results may be irreversible inhibition, destabilization of the enzyme's structure, or an alteration of its substrate specificity. Glutathione reductase and trypanothione reductase are target enzymes for this strategy of drug design in the fight against tropical diseases.
Design, Synthesis, and Properties of Molecule-Based Assemblies with Large Second-Order Optical Nonlinearities
- Pages: 155-173
- First Published: February 3, 1995
The rational construction of supramolecular assemblies with preordained collective properties is an important theme in many areas of contemporary chemistry. The advances made in this respect with regard to polymeric NLO materials, and what problems must still be addressed before technologically viable NLO building blocks become readily available, are surveyed by the authors of this review. Superlattices of the type shown schematically on the right should be among the most promising materials.
Highlights
Peptide Ligases—Tools for Peptide Synthesis
- Pages: 175-177
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Since the ligation of peptide fragments in vivo is meaningless, no natural enzyme is capable of replacing chemical coupling methods, which have the danger of racemization in segment condensation. Native proteases and those altered by protein design as well as catalytic antibodies may serve as peptide ligases, as demonstrated recently with subtiligase in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of R Nase A.
Catalytic Asymmetric CC Bond Formation: New Enolato- and Organolithium Chemistry
- Pages: 178-180
- First Published: February 3, 1995
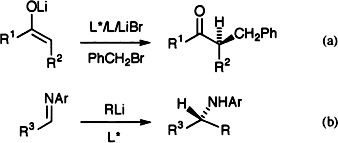
Catalytic and enantioselective are two new efficient processes for CC bond formation developed from fundamental reactions of organolithium compounds. Koga et al. have achieved the benzylation of Li enolates in the presence of both chiral (L*) and achiral (L) ligands [Eq.(a)], and Denmark et al. describe the addition of RLi to aryl imines [Eq. (b)] with very good selectivities, R Me, vinyl.
Communications
Trace Analysis of the Radionuclides 90Sr and 89Sr in Environmental Samples I: Laser Mass Spectrometry†
- Pages: 181-183
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Strontium-90 is one of the most poisonous radionuclides. Its toxicity results from its long half-life of 28.5 years and permanent deposition in the blood-forming bone system. Strontium-90 is formed in high yields during the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and plutonium-239. The classic analytical procedure for the determination of 90Sr, which relies on the β−-radiation of the daughter nuclide yttrium-90, necessitates the chemical removal of all accompanying nuclides. This method requires the Sr/Y ratio to be at equilibrium which takes about two to three weeks to achieve—far too long for the analysis of acute contaminations. Three communications deal with new procedures for ultra-trace analysis using complex physical detection methods (resonance ionization and accelerator mass spectrometry) and high-performance separation techniques (high-performance ion chromatography, HPIC) are presented. In accordance with the strategies of the German Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation, and Nuclear Safety, precision methods are described for the determination of the strontium-90 content in aerosols. These techniques yield data for calculations of the spread of contaminants, which in turn yield results that can be verified in various samples with the aid of the novel fast detection method (HPIC with on-line detectors). The three analytical procedures are set up in a modular manner and can therefore be utilized in variable combinations. They also indicate the high level of refinement achieved by modern ultra-trace analyses.
Trace Analysis of the Radionuclides 90Sr and 89Sr in Environmental Samples II: Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS)†
- Pages: 183-186
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Strontium-90 is one of the most poisonous radionuclides. Its toxicity results from its long half-life of 28.5 years and permanent deposition in the blood-forming bone system. Strontium-90 is formed in high yields during the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and plutonium-239. The classic analytical procedure for the determination of 90Sr, which relies on the β−-radiation of the daughter nuclide yttrium-90, necessitates the chemical removal of all accompanying nuclides. This method requires the Sr/Y ratio to be at equilibrium which takes about two to three weeks to achieve—far too long for the analysis of acute contaminations. Three communications deal with new procedures for ultra-trace analysis using complex physical detection methods (resonance ionization and accelerator mass spectrometry) and high-performance separation techniques (high-performance ion chromatography, HPIC) are presented. In accordance with the strategies of the German Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation, and Nuclear Safety, precision methods are described for the determination of the strontium-90 content in aerosols. These techniques yield data for calculations of the spread of contaminants, which in turn yield results that can be verified in various samples with the aid of the novel fast detection method (HPIC with on-line detectors). The three analytical procedures are set up in a modular manner and can therefore be utilized in variable combinations. They also indicate the high level of refinement achieved by modern ultra-trace analyses.
Trace Analysis of the Radionuclides 90Sr and 89Sr in Environmental Samples III: Development of a Fast Analytical Method†
- Pages: 186-189
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Strontium-90 is one of the most poisonous radionuclides. Its toxicity results from its long half-life of 28.5 years and permanent deposition in the blood-forming bone system. Strontium-90 is formed in high yields during the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and plutonium-239. The classic analytical procedure for the determination of 90Sr, which relies on the β−-radiation of the daughter nuclide yttrium-90, necessitates the chemical removal of all accompanying nuclides. This method requires the Sr/Y ratio to be at equilibrium which takes about two to three weeks to achieve—far too long for the analysis of acute contaminations. Three communications deal with new procedures for ultra-trace analysis using complex physical detection methods (resonance ionization and accelerator mass spectrometry) and high-performance separation techniques (high-performance ion chromatography, HPIC) are presented. In accordance with the strategies of the German Federal Ministry of the Environment, Nature Conservation, and Nuclear Safety, precision methods are described for the determination of the strontium-90 content in aerosols. These techniques yield data for calculations of the spread of contaminants, which in turn yield results that can be verified in various samples with the aid of the novel fast detection method (HPIC with on-line detectors). The three analytical procedures are set up in a modular manner and can therefore be utilized in variable combinations. They also indicate the high level of refinement achieved by modern ultra-trace analyses.
Diastereoselective Coupling of Anodically Generated Radicals Bearing Chiral Amide Groups†‡
- Pages: 189-191
- First Published: February 3, 1995
A Rhodium-Mediated, Stepwise Trimerization of an Alkyne That Does Not Lead to a Benzene but Selectively to a Hexadienyne Derivative†‡
- Pages: 191-194
- First Published: February 3, 1995
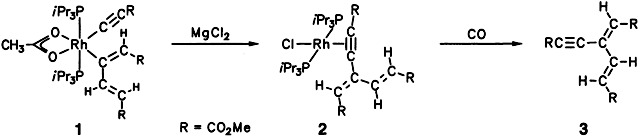
The coupling of an alkynyl and a butadienyl unit at the rhodium center of 1 is the key step in the selective, stepwise trimerization of methyl propiolate HCCR to hexadienyne 3 with [Rh(η2-O2CMe)(PiPr3)2] as a metal template. In MgCl2 in ether, this step occurs almost quantitatively, and the intermediates 1 and 2 were characterized by X-ray crystal structure analysis.
Electrochemical Synthesis of a Redox-Active Polymer Based on Buckminsterfullerene Epoxide†
- Pages: 194-196
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Under cathodic conditions a polymer film forms on an electrode when C60O is first reduced in the presence of Bu4NClO4 in toluene/acetonitrile and then oxidized. Films with thicknesses of up to 3 μm can be produced by repeated cyclic voltammetry. Evidence for ionic as well as electronic conductivity of this fullerene polymer is also provided.
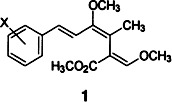
9-Methoxystrobilurins—A Link Between Strobilurins and Oudemansins†‡
- Pages: 196-198
- First Published: February 3, 1995
2,4-Di-tert-butyl-1λ3,3λ3-diphosphinines: Targeted Synthesis at Iron(0) Centers and Oxidative Release†‡
- Pages: 198-201
- First Published: February 3, 1995
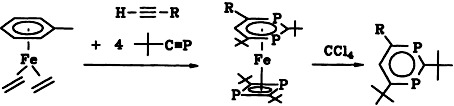
The [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition of two molecules of a phosphaalkyne and one molecule of a terminal alkyne in the coordination sphere of iron(0) affords 1,3-diphosphinines regiospecifically [Eq.(a)]. The coordinated and the oxidatively released 1,3-diphosphinines have cyclic delocalized π systems and are thus not only novel heteroarenes, but also of interest as potential catalysts.
Formation and Structures of New Metallo- and Metallapolysulfanes, [MSy]+ (y = 2−16)†
- Pages: 201-203
- First Published: February 3, 1995
![Formation and Structures of New Metallo- and Metallapolysulfanes, [MSy]+ (y = 2−16)](/cms/asset/ecd54eee-3c3f-43d4-849b-87f35616638c/must001.jpg)
In the gas phase, sulfur and monopositive metal ions (ScZn) react to form novel metallo- and metallapolysulfanes [MSy]+. The structures of these complexes were calculated by ab initio methods. The lowest energy structure of [Cu(cyclo-S12)]+, in which the octahedrally coordinated Cu+ ion is located in the center of the S12 cycle, is shown in the picture on the right.
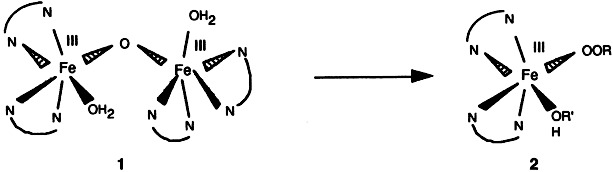
Formation of an Alkylperoxoiron(III) Complex during Oxidations Catalyzed by μ-Oxodiiron(III) Complexes†
- Pages: 203-205
- First Published: February 3, 1995
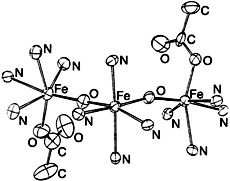
A New Type of Trinuclear Oxoiron(III) Cluster†
- Pages: 205-207
- First Published: February 3, 1995
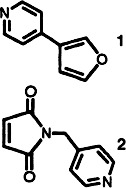
Mutually Interpenetrating Sheets and Channels in the Extended Structure of [Cu(4,4′-bpy)Cl]†‡
- Pages: 207-209
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Investigation of Self-Assembled Supramolecular Species in Solution by IL-ESMS, a New Mass Spectrometric Technique†
- Pages: 209-213
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Discrete neutral assemblies in solution can be studied with the analytical method described here. A prerequisite is that one of the components contains an ion-complexing site, for example a crown ether unit. When alkali metal ions are added, charged assemblies form, which can be examined by electrospray mass spectrometry (ESMS) without disruption of their hydrogen bonds. IL in the title stands for ion labeling.
Gas-Phase Activation of Fluorocarbons by “Bare” and Coordinated Praseodymium Cations†‡
- Pages: 213-217
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Rather than CH or CC bonds, Pr+ activates CF bonds in the gas phase in a variety of aliphatic and aromatic fluorocarbons; PrF+ and PrO+ react analogously. This first general example of preferential CF bond activation in the gas phase allows interesting conclusions to be drawn regarding the importance of 4f electrons for the reactivity of isolated lanthanide species. The existence of neutral PrF and PrF2 in the gas phase was also proven by neutralization–reionization mass spectrometry (NRMS).
Free-Energy Profile for a Host-Accelerated Diels–Alder Reaction: The Sources of exo Selectivity†
- Pages: 217-219
- First Published: February 3, 1995
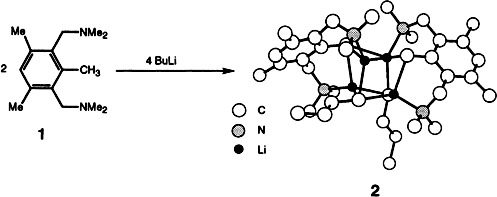
The Formation of a Mixed Organolithium Aggregate Li4R2nBu2 during the Heteroatom-Assisted Lithiation of 1,3-Bis(dimethylaminomethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzene (R = 2,6-(CH2NMe2)2-3,5-Me2C6HCH2)†
- Pages: 219-222
- First Published: February 3, 1995
CarbonCarbon Bond Cleavage with Inversion of Configuration: Conversion of (R)-(+)-1-Methoxytetrafluoropropionic Acid to (S)-(−)-1,2,2,2-Tetrafluoroethyl Methyl Ether†
- Pages: 222-223
- First Published: February 3, 1995
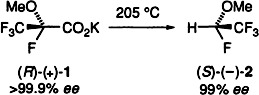
Nearly complete inversion of configuration is seen during decarboxylation of the potassium salt 1 of an α-chiral carboxylic acid to give ether 2. Since 2 is an intermediate in the synthesis of inhalational anesthetics, and its enantiomers may have different pharmacological profiles, the determination of the stereochemical outcome of this CC bond cleavage is of particular interest.
Investigations into the Targeted Design of Solids: Hydrothermal Synthesis and Structures of One-, Two-, and Three-Dimensional Phases of the Oxovanadium–Organodiphosphonate System†
- Pages: 223-226
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Depending on the tether length of the diphosphonate group, hydrothermal reactions of VCl4 with diphosphonic acids of the class (H2O3P)(CH2)n(PO3H2) in the presence of templating organic cations yield one-, two-, and three-dimensional framework structures of the V-O-RPO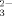 system. The picture shows a section of the three-dimensional framework of [H3N(CH2)2NH3][(VO)4(OH)2(H2O)2{O3P(CH2)3PO3}2]·4H2O.
system. The picture shows a section of the three-dimensional framework of [H3N(CH2)2NH3][(VO)4(OH)2(H2O)2{O3P(CH2)3PO3}2]·4H2O.
Dimensional Reduction of Re6Se8Cl2: Sheets, Chains, and Discrete Clusters Composed of Chloride-Terminated [Re6Q8]2+ (Q S, Se) Cores†
- Pages: 226-229
- First Published: February 3, 1995
![Dimensional Reduction of Re6Se8Cl2: Sheets, Chains, and Discrete Clusters Composed of Chloride-Terminated [Re6Q8]2+ (Q S, Se) Cores](/cms/asset/41618404-0e58-4654-8139-f5066365a95f/must001.jpg)
A general high-temperature approach to reducing the dimensionality of cluster frameworks is formulated and employed in deconstructing the two-dimensional Re6Se8Cl2 structure. The resulting new phases with [Re6Q8]2+ (Q S, Se) cores exhibit two-dimensional [Re6Se8Cl3]− sheets, one-dimensional [Re6Q8Cl4]2− chains, and [Re6Q8Cl6]4− clusters. The structures of these phases are presented along with that of Tl5Re6Se8Cl7 which contains the unprecedented molecular cluster [Re6Se8Cl6]4− 1.
Direct Observation of OH Reductive Elimination from IrIII Complexes†
- Pages: 229-231
- First Published: February 3, 1995
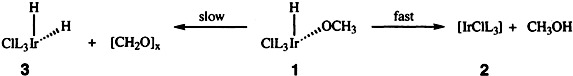
Elimination of alcohols from the IrIII complexes 1 to give 2 is feasible and competes favorably with β-H elimination to give 3. This supports proposals that OH reductive elimination is the product-forming step in industrially important processes such as CO hydrogenation and alcohol homologation. The ancillary π-donating chloride has a paramount role in this process. L PEt3, PMe3.
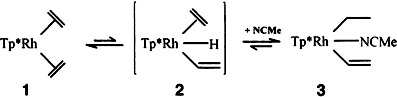
Does the Facile Inter- and Intramolecular CH Bond Activation by Tp*–Rh Complexes Proceed via RhI or RhIII Intermediates?†
- Pages: 231-233
- First Published: February 3, 1995
LaI: An Unprecedented Binary Rare Earth Metal Monohalide with a NiAs-Type Structure†
- Pages: 233-235
- First Published: February 3, 1995
The reduction of LaI3 with La metal at roughly 750°C proceeds via metallic LaI2 to LaI, the first halide with a hexagonal close-packed NiAs-type structure (projection along c shown on the right). This arrangement does not provide suitable interstitial sites for hydrogen atoms. The extreme c/a ratio (2.47) affords markedly strong LaLa bonding in the a,b plane. Extended Hückel band calculations suggest that LaI is a strongly anisotropic metal.
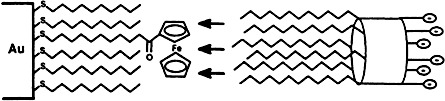
Molecular Recognition at an Interface: Binding of Monolayer-Anchored Ferrocenyl Groups by an Amphiphilic Calixarene Host†
- Pages: 235-237
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Synthesis, Antitumor Activity, and Tolerability of Phospholipids Containing Nitrogen Homologues†
- Pages: 238-240
- First Published: February 3, 1995
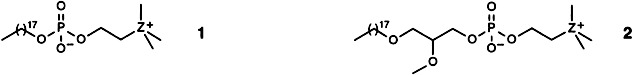
Replacing the N atom with an As or P atom in antineoplastically active phospholipids 1 and 2 (Z N) leads to homologous compounds (Z As, P) that are equally effective against tumors and have fewer side effects than the N-containing phospholipids. This marks definite progress in cancer treatment with chemotherapeutically active phospholipids.
Corrigenda
Book Reviews
Book Review: Djerassi's Park: The Bourbaki Gambit. By C. Djerassi
- Pages: 241-242
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Book Review: Amorphous Inorganic Materials and Glasses. By A. Feltz
- Pages: 242-243
- First Published: February 3, 1995
Book Review: Methods of Immunological Analysis
- Page: 243
- First Published: February 3, 1995





![Mutually Interpenetrating Sheets and Channels in the Extended Structure of [Cu(4,4′-bpy)Cl]](/cms/asset/1e74fbe9-d45f-4592-a374-489fd690edb1/must001.jpg)