Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Selective Catalytic Synthesis Using the Combination of Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen: Catalytic Chess at the Interface of Energy and Chemistry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2016)
- Page: 7267
- First Published: 15 June 2016

The combination of CO2 and H2 … …as building blocks offers attractive synthetic pathways ranging from large-volume base chemicals to highly functionalized complex molecules. J. Klankermayer, W. Leitner et al. describe in their Review on page 7296 ff. how efficient catalysts are becoming available to master the bond breaking and bond formation events required for these processes like strategic moves on a molecular chess board.
Inside Cover: Electrocatalytic and Solar-Driven CO2 Reduction to CO with a Molecular Manganese Catalyst Immobilized on Mesoporous TiO2 (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2016)
- Page: 7268
- First Published: 04 May 2016

One small step for Mn A manganese catalyst immobilized on TiO2 gave a new benchmark turnover number as described by E. Reisner and co-workers in their Communication on page 7388 ff. The heterogenized catalyst operates at a low overpotential, which is the result of dimerization on the electrode surface. The molecular hybrid cathode was used in a photoelectrochemical cell enabling solar-driven CO production by a photo-unstable Mn catalyst for the first time.
Inside Back Cover: Synthesis of Highly Uniform Molybdenum–Glycerate Spheres and Their Conversion into Hierarchical MoS2 Hollow Nanospheres for Lithium-Ion Batteries (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2016)
- Page: 7549
- First Published: 20 May 2016

A self-templating method has been developed to synthesize hierarchical MoS2 hollow nanospheres from highly uniform Mo–glycerate solid spheres. In their Communication on page 7423 ff. X. W. Lou and co-workers first synthesize Mo–glycerate spheres with readily tunable sizes by a solvothermal process. The subsequent hierarchical MoS2 structures are formed from ultrathin subunits, have a hollow interior, and give a promising performance as the anode material for lithium-ion batteries.
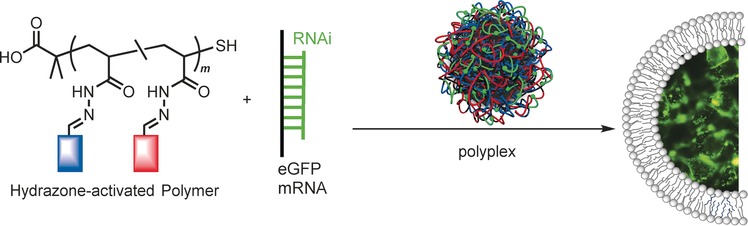
Back Cover: In Situ Functionalized Polymers for siRNA Delivery (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2016)
- Page: 7550
- First Published: 12 May 2016
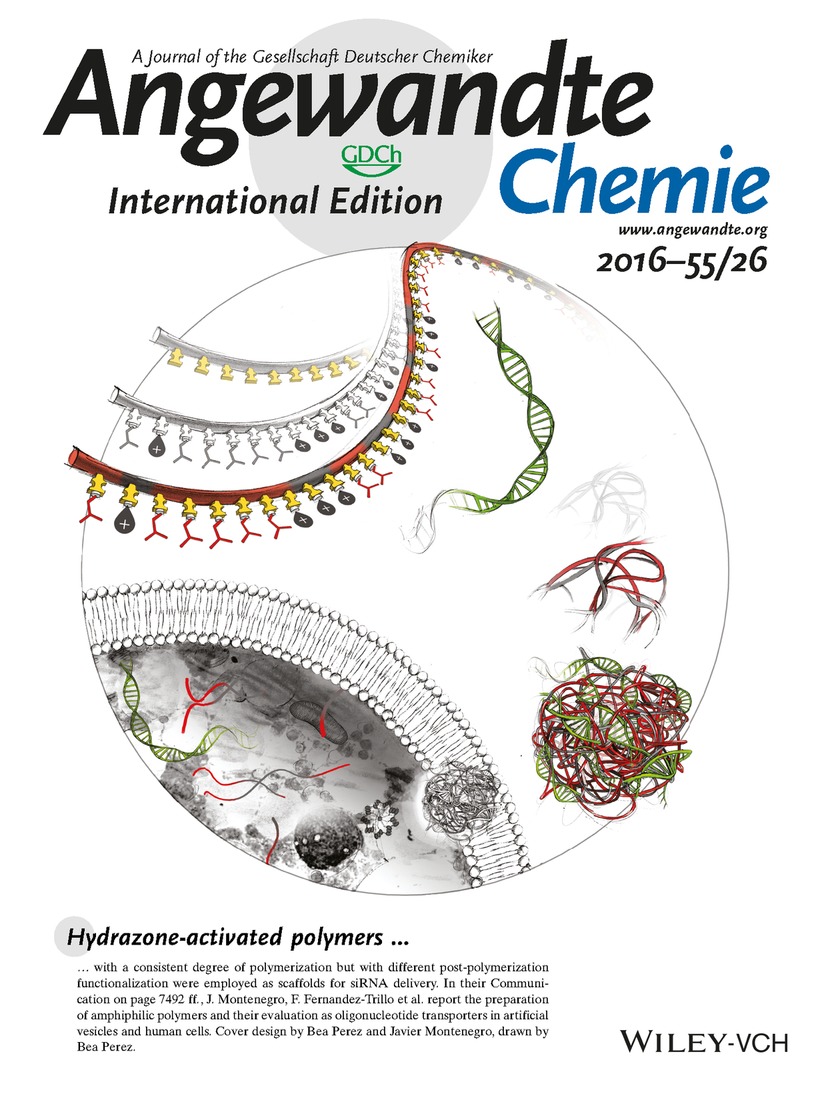
Hydrazone-activated polymers with a consistent degree of polymerization but with different post-polymerization functionalization were employed as scaffolds for siRNA delivery. In their Communication on page 7492 ff., J. Montenegro, F. Fernandez-Trillo et al. report the preparation of amphiphilic polymers and their evaluation as oligonucleotide transporters in artificial vesicles and human cells. Cover design by Bea Perez and Javier Montenegro, drawn by Bea Perez.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: The Planar CoB18− Cluster as a Motif for Metallo-Borophenes
- First Published: 15 June 2016
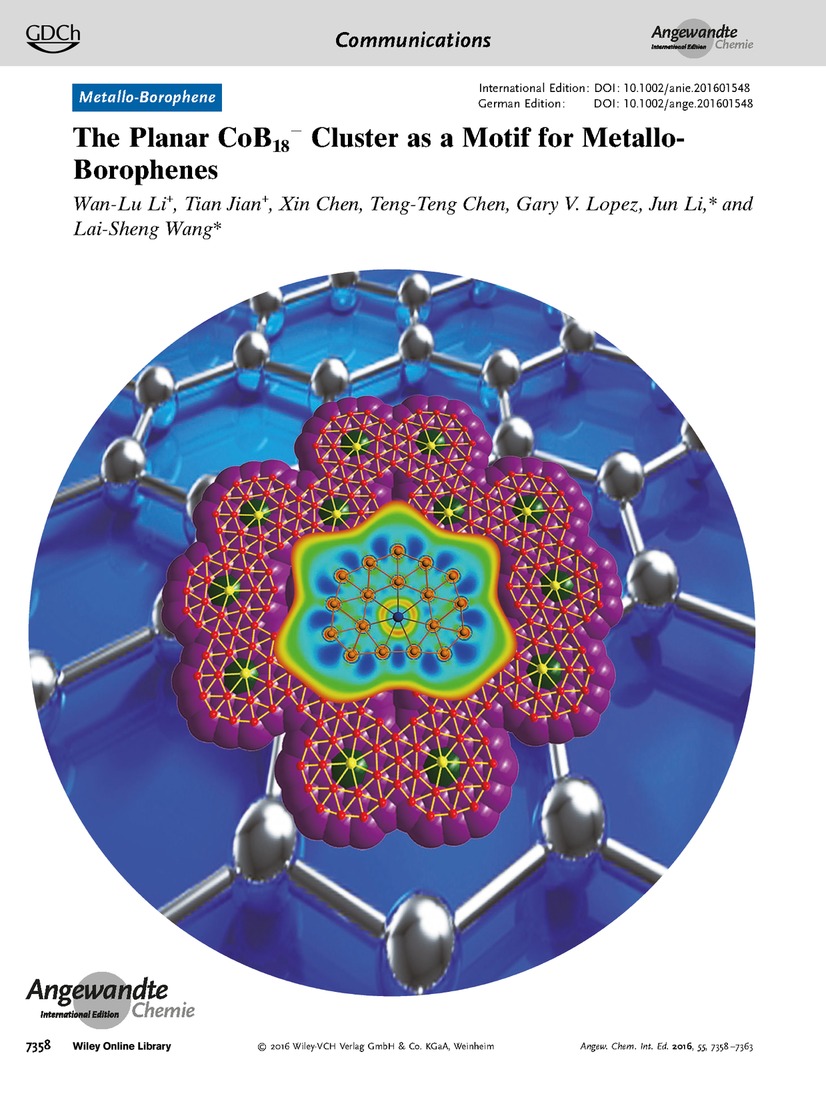
Metalloborophenes The CoB18− cluster is investigated by J. Li, L.-S. Wang et al. in their Communication on page 7358 ff. It is a highly stable and perfectly planar structure with the Co atom centered in a seven-membered ring.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2016
- Pages: 7271-7282
- First Published: 15 June 2016
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2016
- Pages: 7286-7289
- First Published: 15 June 2016
Author Profiles
Book Reviews
Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon Single Bonds by Transition Metals. Edited by Masahiro Murakami and Naoto Chatani.
- Page: 7291
- First Published: 24 May 2016
Highlights
Heterogeneous Catalysis
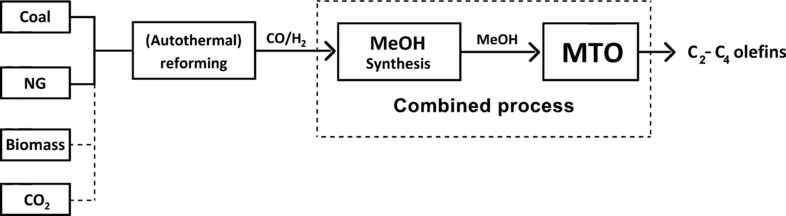
Single-Pass Catalytic Conversion of Syngas into Olefins via Methanol
- Pages: 7294-7295
- First Published: 23 May 2016
Reviews
CO2 Utilization
Selective Catalytic Synthesis Using the Combination of Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen: Catalytic Chess at the Interface of Energy and Chemistry
- Pages: 7296-7343
- First Published: 30 May 2016
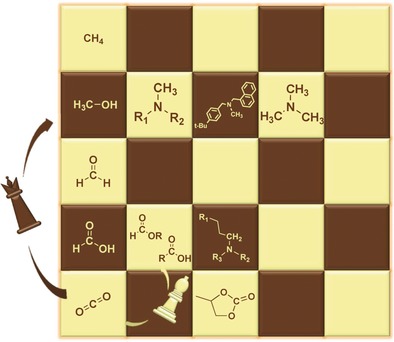
The catalytic gambit: The combined use of CO2 and H2 as building blocks in catalytic processes provides access to products ranging from large volume base chemicals to highly functionalized complex molecules. The current state-of-the-art is critically reviewed, highlighting pathways that are in line with “green chemistry” principles and offer the potential to harness renewable energy into the chemical value chain.
Artificial Metalloenzymes
Genetic Optimization of Metalloenzymes: Enhancing Enzymes for Non-Natural Reactions
- Pages: 7344-7357
- First Published: 11 March 2016
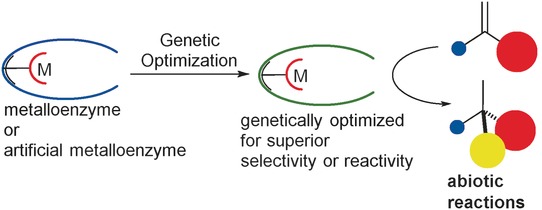
The second row also matters: In contrast to traditional transition-metal catalysts, artificial metalloenzymes can modulate both the first and second coordination spheres, and thus result in novel reactivities. This Review discusses attempts to modulate the second coordination sphere of artificial metalloenzymes through genetic modifications of the protein sequence.
Communications
Metallo-Borophene
The Planar CoB18− Cluster as a Motif for Metallo-Borophenes
- Pages: 7358-7363
- First Published: 20 April 2016
Thermostability
Accurate and Rigorous Prediction of the Changes in Protein Free Energies in a Large-Scale Mutation Scan
- Pages: 7364-7368
- First Published: 28 April 2016
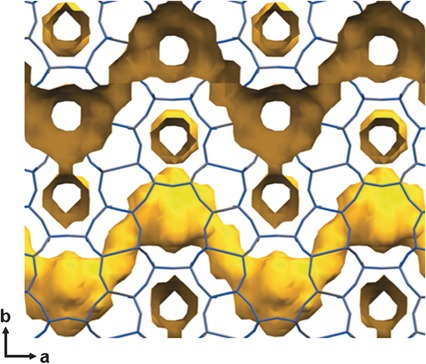
Microporous Materials
EU-12: A Small-Pore, High-Silica Zeolite Containing Sinusoidal Eight-Ring Channels
- Pages: 7369-7373
- First Published: 13 May 2016
Protein Modification
Toxic Dopamine Metabolite DOPAL Forms an Unexpected Dicatechol Pyrrole Adduct with Lysines of α-Synuclein
- Pages: 7374-7378
- First Published: 09 May 2016
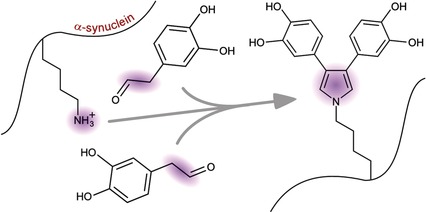
Amyloid disease: The primary dopamine metabolite, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, reacts with α-synuclein Lys residues to form dicatechol pyrrole lysine adducts, which may act as the scaffold for the protein crosslinking observed in dopaminergic cells. The dicatechol pyrrole lysine adducts were characterized by NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
Metal–Organic Framework Composites
Polydimethylsiloxane Coating for a Palladium/MOF Composite: Highly Improved Catalytic Performance by Surface Hydrophobization
- Pages: 7379-7383
- First Published: 04 May 2016
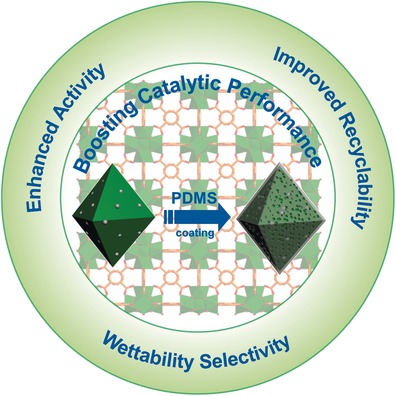
Hydrophobic visions: Surface hydrophobization of Pd/UiO-66, a composite of a metal–organic framework (MOF) and stabilized palladium nanoparticles, was realized using a simple polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) coating. The resultant Pd/UiO-66@PDMS composite exhibits superior catalytic activity and recyclability compared to pristine Pd/UiO-66, and additional selectivity in sieving reactants with different wettability. This approach is extendable to various Pd-based catalysts.
Janus Particles
Remote Control of T Cell Activation Using Magnetic Janus Particles
- Pages: 7384-7387
- First Published: 04 May 2016
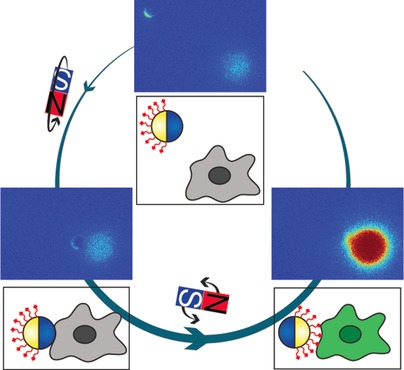
Janus particles were employed to control T cell activation. The particles were magnetically responsive on one side and displayed ligands for T cell stimulation on the other side. T cell activation was remotely controlled by simultaneously manipulating the rotation and locomotion of the magnetic Janus particles.
CO2 Reduction
Electrocatalytic and Solar-Driven CO2 Reduction to CO with a Molecular Manganese Catalyst Immobilized on Mesoporous TiO2
- Pages: 7388-7392
- First Published: 25 April 2016
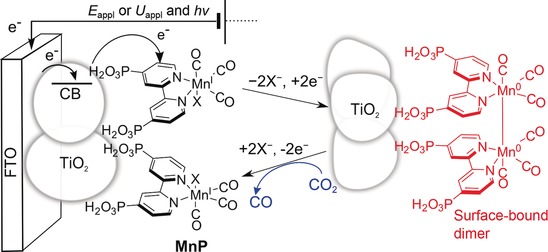
One small step for Mn: A Mn catalyst immobilized on TiO2 gave electrocatalytic CO2 reduction with a turnover number of 112. The low overpotential of 420 mV is a result of dimerization of the catalyst on the mesoporous electrode. The heterogeneous hybrid cathode was used in a photoelectrochemical cell enabling solar-driven CO production by a photo-unstable Mn catalyst for the first time.
Hybrid Materials
Grafting Poly(3-hexylthiophene) from Silicon Nanocrystal Surfaces: Synthesis and Properties of a Functional Hybrid Material with Direct Interfacial Contact
- Pages: 7393-7397
- First Published: 04 May 2016
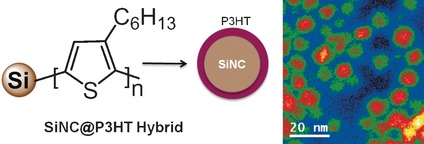
Hybrid functional materials of silicon nanocrystals and poly(3-hexylthiophene) (SiNC@P3HT) consisting of a direct conjugate covalent bond between SiNC and P3HT were developed. Systematic characterization provides evidence of a core–shell structure, enhanced interfacial electron and/or energy transfer between the P3HT and SiNC components, as well as formation of a type-II heterostructure.
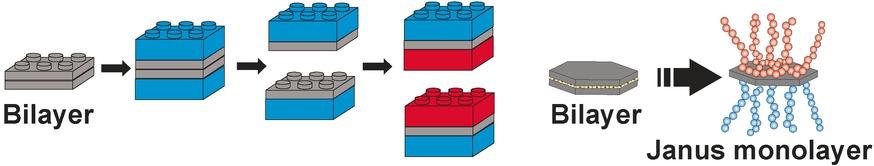
Hybrid Materials | Hot Paper
Controlled Exfoliation of Layered Silicate Heterostructures into Bilayers and Their Conversion into Giant Janus Platelets
- Pages: 7398-7402
- First Published: 03 May 2016
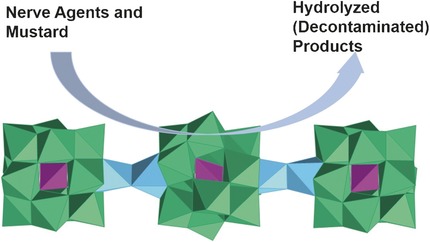
Decontamination
Broad-Spectrum Liquid- and Gas-Phase Decontamination of Chemical Warfare Agents by One-Dimensional Heteropolyniobates
- Pages: 7403-7407
- First Published: 09 April 2016
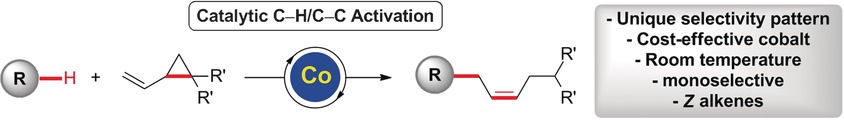
C−H/C−C Activation
Mild C−H/C−C Activation by Z-Selective Cobalt Catalysis
- Pages: 7408-7412
- First Published: 04 May 2016
Porous Crystals
Unusually Stable Triazine-based Organic Superstructures
- Pages: 7413-7417
- First Published: 27 April 2016
In-Cell NMR Spectroscopy
Studying Intrinsically Disordered Proteins under True In Vivo Conditions by Combined Cross-Polarization and Carbonyl-Detection NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 7418-7422
- First Published: 09 May 2016
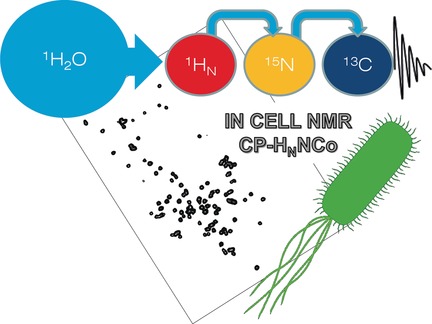
Keep your finger on the pulse: A new pulse sequence combining proton–nitrogen cross-polarization and carbonyl detection is proposed for recording high-resolution, high-sensitivity NMR spectra of IDPs under true physiological conditions. By this method, a high-quality N–CO correlation spectrum was acquired of α-synuclein in bacterial cells at 37 °C.
Nanospheres
Synthesis of Highly Uniform Molybdenum–Glycerate Spheres and Their Conversion into Hierarchical MoS2 Hollow Nanospheres for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 7423-7426
- First Published: 20 April 2016
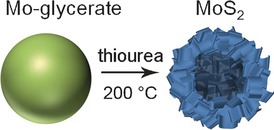
Dr Mo: Hierarchical MoS2 hollow nanospheres are synthesized with a self-templating method from highly uniform Mo–glycerate solid spheres. By sulfidation and annealing, these Mo–glycerate solid spheres can be converted into hierarchical MoS2 hollow nanospheres. Owing to their unique structures, the hierarchical nanospheres show enhanced electrochemical properties as the anode material for lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium Storage
Electrolytic Formation of Crystalline Silicon/Germanium Alloy Nanotubes and Hollow Particles with Enhanced Lithium-Storage Properties
- Pages: 7427-7431
- First Published: 09 May 2016
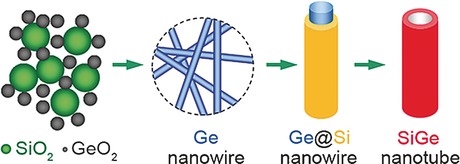
Li likes alloys: Crystalline SiGe alloy nanotubes and hollow particles are synthesized through a one-pot electrolytic process in molten salts. The solid-diffusion process, governed by the nanoscale Kirkendall effect, leads to the formation of internal voids in the SiGe alloy particles. Owing to the unique structural features and desirable composition, the SiGe alloy nanotubes exhibit enhanced lithium-storage performance.
Photoluminescent Materials
Redox Switching of Orthoquinone-Containing Aromatic Compounds with Hydrogen and Oxygen Gas
- Pages: 7432-7436
- First Published: 04 May 2016
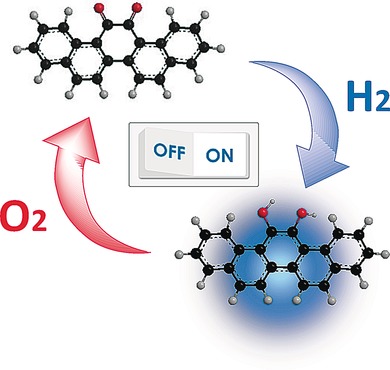
A tale with a twist: Unique redox switching of orthoquinone-containing pentacyclic aromatic compounds was observed upon exposure to H2 and O2 in the presence of a sulfur-modified gold-supported palladium nanoparticle catalyst (see picture). Switching between the orthoquinone and the corresponding hydroquinone led to a drastic change in the photoluminescence and color of the system owing to differences in the aromaticity and twist strain of the molecules.
Cross-Coupling
Nickel-Catalyzed Intramolecular C−O Bond Formation: Synthesis of Cyclic Enol Ethers
- Pages: 7437-7440
- First Published: 09 May 2016

Nickel-O-C-eon: The title reaction between aliphatic hydroxy nucleophiles and tethered vinyl halides provides access to cyclic vinyl ethers in a single step and under exceptionally mild and operationally simple reaction conditions. The exploration of this new reactivity of nickel catalysts can provide further insight into the unique properties and opportunities afforded by nickel catalysts. EWG=electron-withdrawing group.
Bioinorganic Chemistry
An Organometallic Compound which Exhibits a DNA Topology-Dependent One-Stranded Intercalation Mode
- Pages: 7441-7444
- First Published: 17 May 2016
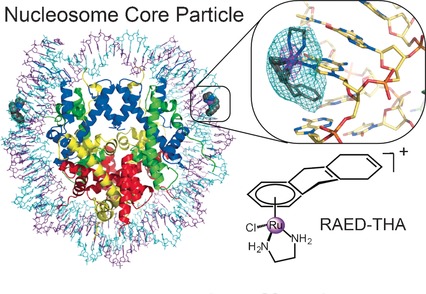
Binding preferences: Using crystallographic methods and molecular dynamics simulations it was shown that adducts formed by the anticancer agent [(η6-5,8,9,10-tetrahydroanthracene)Ru(ethylenediamine)Cl][PF6] on a nucleosome comprise a novel one-stranded intercalation and DNA distortion mode. The adduct dimorphism and DNA topology dependence might contribute to the unusually high cytotoxicity of this anticancer agent.
Sodium-Ion Batteries
Suppressing the P2–O2 Phase Transition of Na0.67Mn0.67Ni0.33O2 by Magnesium Substitution for Improved Sodium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 7445-7449
- First Published: 03 May 2016
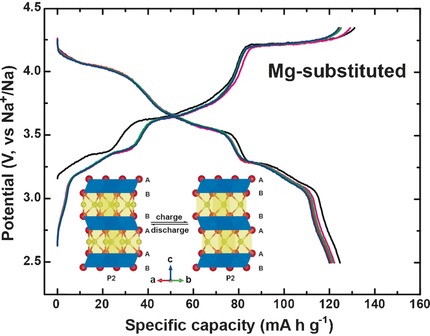
The P2–O2 phase transition in P2-Na0.67Mn0.67Ni0.33−xMgxO2 can be effectively suppressed by substituting some of the nickel ions with magnesium. Both the reversible capacity and the capacity retention of this cathode material were thus remarkably improved, and the various phases were characterized by scanning tunneling electron microscopy with atomic resolution.
Bioinorganic Chemistry
Switchover of the Mechanism between Electron Transfer and Hydrogen-Atom Transfer for a Protonated Manganese(IV)–Oxo Complex by Changing Only the Reaction Temperature
- Pages: 7450-7454
- First Published: 18 May 2016
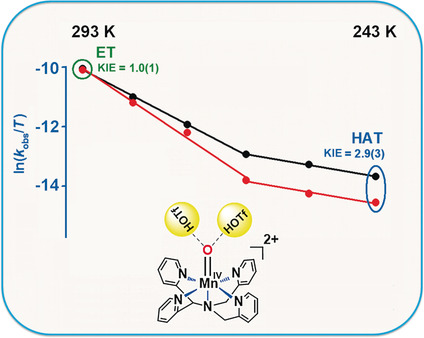
The switchover of the reaction mechanism from electron transfer (ET) to hydrogen-atom transfer (HAT) for a protonated nonheme manganese(IV)–oxo complex was investigated. The switchover occurs in the presence of triflic acid by changing only the reaction temperature in the boundary region between ET and HAT pathways. KIE=kinetic isotope effect; black=mesitylene, red=[D12]mesitylene.
Methane Reforming
Dry Reforming of Methane on a Highly-Active Ni-CeO2 Catalyst: Effects of Metal-Support Interactions on C−H Bond Breaking
- Pages: 7455-7459
- First Published: 04 May 2016
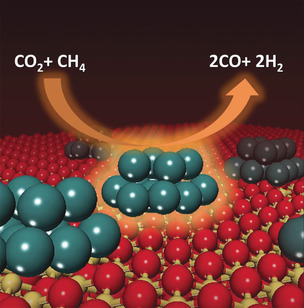
NiCe and dry: Ni-CeO2 is shown to be highly efficient, stable, and non-expensive catalyst for methane dry reforming at relative low temperatures (700 K). The active phase of the catalyst consists of small nanoparticles of nickel dispersed on partially reduced ceria. Strong metal–support interactions activate Ni for the dissociation of methane.
Nanomedicines
Bilirubin Nanoparticles as a Nanomedicine for Anti-inflammation Therapy
- Pages: 7460-7463
- First Published: 04 May 2016
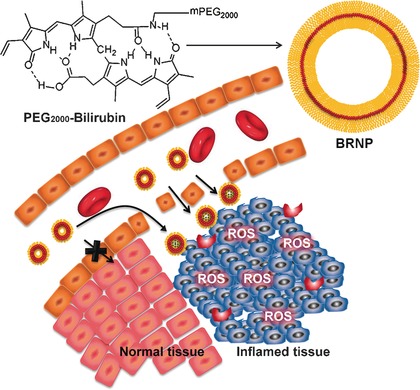
Bilirubin, a nanomedicine for inflammatory diseases: Bilirubin, a highly potent anti-inflammatory but extremely water insoluble compound, is converted into nanoparticles by simply introducing PEG. The resultant bilirubin nanoparticles show potential as a nanomedicine in anti-inflammation therapy. ROS=reactive oxygen species, BRNP=Bilirubin nanoparticle.
Solar Cells
Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells Employing an Easily Attainable Bifluorenylidene-Based Hole-Transporting Material
- Pages: 7464-7468
- First Published: 09 May 2016
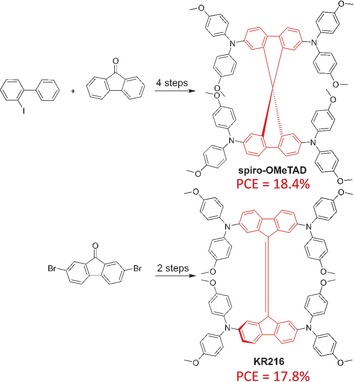
The hole-transporting material KR216 (4,4′-dimethoxydiphenylamine-substituted 9,9′-bifluorenylidene) reached a photon-to-current efficiency (PCE) of 17.8 % in perovskite-based solar cells. A novel material was synthesized using a straightforward two-step procedure from commercially available and inexpensive starting reagents, mimicking the 9,9′-spirobifluorene moiety of the well-studied spiro-OMeTAD.
Gas-Phase Chemistry
UV/Vis Action Spectroscopy and Structures of Tyrosine Peptide Cation Radicals in the Gas Phase
- Pages: 7469-7473
- First Published: 09 May 2016
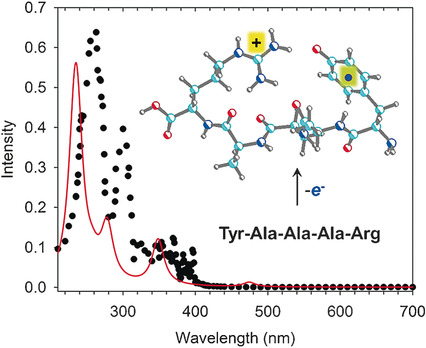
UV/Vis action spectrum: Tyrosine peptides underwent different courses of oxidation by copper(II) ions depending on the position of the tyrosine residue in the peptide sequence. Tyrosine peptide cation radicals were produced by oxidative intramolecular electron transfer in the gas-phase copper complexes.
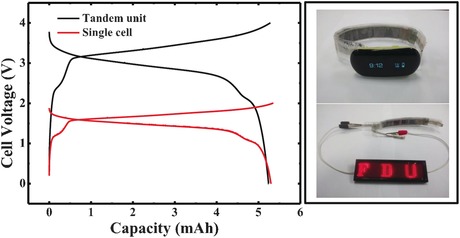
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Flexible Aqueous Lithium-Ion Battery with High Safety and Large Volumetric Energy Density
- Pages: 7474-7477
- First Published: 09 May 2016
Responsive Materials
Visualizing the Dynamics of Temperature- and Solvent-Responsive Soft Crystals
- Pages: 7478-7482
- First Published: 04 May 2016
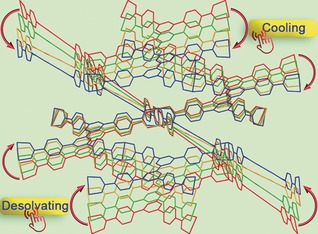
See the shrink: A record high uniaxial positive thermal expansion coefficient of 653.2×10−6 K−1 and large c-axial shrinkage of 32.4 %, is found for metal–organic framework (MOF) temperature- and solvent-responsive soft crystals. The dynamic process can both be visualized by in situ single-crystal X-ray snapshot analyses. The stimuli-responsive mechanism results from rotations and deformations of the organic linkers.
Substrate Channeling | Hot Paper
Directional Regulation of Enzyme Pathways through the Control of Substrate Channeling on a DNA Origami Scaffold
- Pages: 7483-7486
- First Published: 09 May 2016
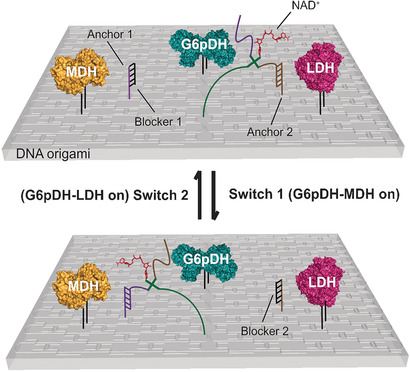
Artificial multi-enzyme systems with precise and directional control over the enzyme pathway activities are of great significance in bionanotechnology and synthetic biology. A DNA origami system for the directional regulation of the activities of two enzyme pathways (G6pDH–MDH and G6pDH–LDH) through the control of NAD+ substrate channeling by specifically shifting NAD+ between the two enzyme pairs is now reported.
Heterometallic Complexes
Polynuclear Gold [AuI]4, [AuI]8, and Bimetallic [AuI4AgI] Complexes: C−H Functionalization of Carbonyl Compounds and Homogeneous Carbonylation of Amines
- Pages: 7487-7491
- First Published: 11 May 2016
![Polynuclear Gold [AuI]4, [AuI]8, and Bimetallic [AuI4AgI] Complexes: C−H Functionalization of Carbonyl Compounds and Homogeneous Carbonylation of Amines](/cms/asset/bdb06895-91a2-4a2d-bcd4-2e8d041a7bae/anie201603200-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Gold aplenty: The synthesis of tetranuclear gold complexes, a structurally unprecedented octanuclear complex with a planar [AuI8] core, and pentanuclear [AuI4MI] (M=Cu, Ag) complexes is presented. The linear [AuI4] complex undergoes C−H functionalization of carbonyl compounds under mild reaction conditions. In addition, [AuI4AgI] catalyzes the carbonylation of primary amines to form ureas under homogeneous conditions with efficiencies higher than those achieved by gold nanoparticles.
siRNA delivery
In Situ Functionalized Polymers for siRNA Delivery
- Pages: 7492-7495
- First Published: 21 April 2016
Chemical Imaging
X-ray Excited Optical Fluorescence and Diffraction Imaging of Reactivity and Crystallinity in a Zeolite Crystal: Crystallography and Molecular Spectroscopy in One
- Pages: 7496-7500
- First Published: 04 May 2016
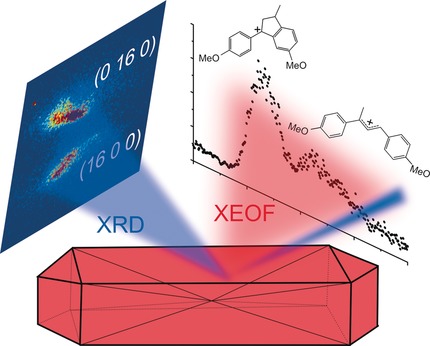
Two worlds in one X-ray shot: The local crystallinity and acid-catalyzed chemistry of a single zeolite crystal were determined by a combination of micro-X-ray diffraction (μ-XRD) and X-ray excited optical fluorescence (μ-XEOF), achieved by using one X-ray beam to excite fluorescent products formed in a zeolite. The intergrowth structure and Al zoning play a decisive role in the degree of dealumination and shape-selective product formation.
Electrocatalysis
Full Kinetics from First Principles of the Chlorine Evolution Reaction over a RuO2(110) Model Electrode
- Pages: 7501-7504
- First Published: 11 May 2016
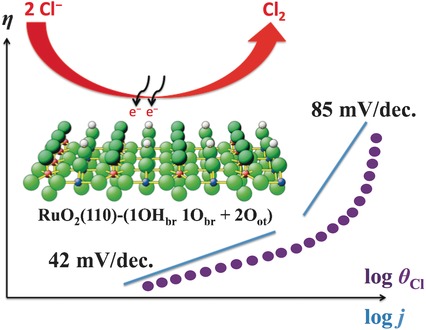
Beyond thermodynamics: An intimate interplay of thermodynamics and kinetics from first principles together with microkinetic modeling allows the microscopic processes of the chlorine evolution reaction over a RuO2(110) model electrode to be unraveled. This combined approach may provide a general roadmap on how electrocatalytic reactions can be studied to gain unprecedented molecular insight.
Polymerization
Crystalline Isotactic Polar Polypropylene from the Palladium-Catalyzed Copolymerization of Propylene and Polar Monomers
- Pages: 7505-7509
- First Published: 10 May 2016
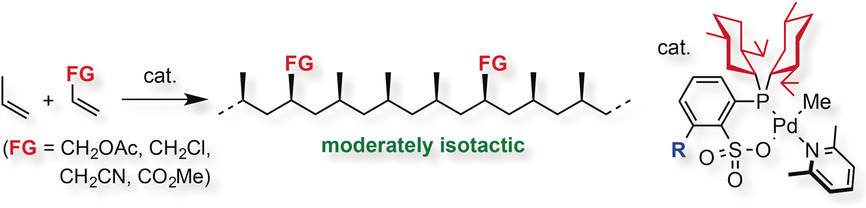
Control center: High-molecular-weight polypropylenes can be obtained by using palladium catalysts bearing menthyl-substituted phosphine-sulfonate ligands for the isospecific homopolymerization of propylene or the copolymerization of propylene with polar monomers. The introduction of substituents at the ortho-position relative to the sulfonate group favors enantiomorphic site control over chain end control in the chain propagation step.
Sample Preparation
Fast Quantitation of Target Analytes in Small Volumes of Complex Samples by Matrix-Compatible Solid-Phase Microextraction Devices
- Pages: 7510-7514
- First Published: 09 May 2016
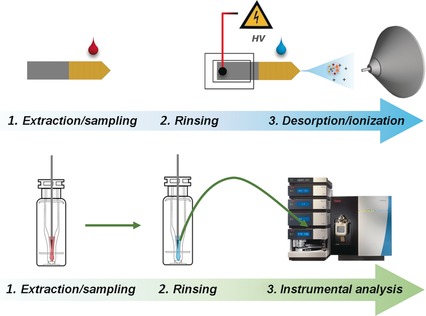
Simple sampling: solid-phase microextraction (SPME) devices perform fast extraction/enrichment of target analytes in small sample volumes. Micro-sampling is performed with metal tips coated with a thin layer of polypyrrole (see picture, bottom) or by using thin-coated blade spray (CBS) devices (top). These devices can be coupled with liquid chromatography (LC), or directly to mass spectrometry (MS).
Nucleic Acids
Chemical Morphing of DNA Containing Four Noncanonical Bases
- Pages: 7515-7519
- First Published: 09 May 2016
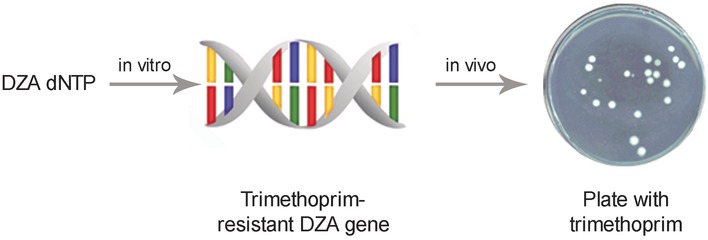
Chemically redesigned DNA, in which all four nucleobases are functionalized (denoted DZA), was used to transfer genetic information in living organisms. Using a gene encoding resistance to the antibiotic trimethoprim, a fully morphed DNA was successfully replicated in vitro and served as a genetic template in vivo.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Design of Switchable Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Targeting Breast Cancer
- Pages: 7520-7524
- First Published: 04 May 2016
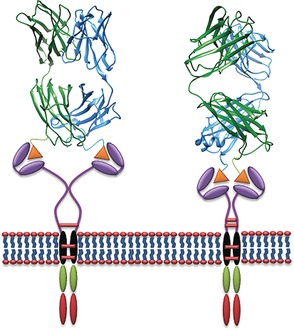
CAR-T control: Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells were engineered to be controlled by exogenous switch molecules. Site-specific incorporation of the small molecule FITC or a short peptide neo-epitope in the anti-Her2 4D5 Fab allowed activation of corresponding switchable CAR-T cells towards Her2-expressing solid tumor cells, and displayed significant anti-cancer effects both in vitro and in vivo.
Phosphorus Heterocycles
Access to Air-Stable 1,3-Diphosphacyclobutane-2,4-diyls by an Arylation Reaction with Arynes
- Pages: 7525-7529
- First Published: 02 May 2016
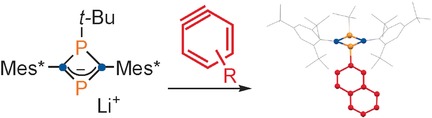
A P2romising C2onstellation: The reaction of a sterically encumbered 1,3-diphosphacyclobuten-4-yl anion with ortho-silylated aryl triflates in the presence of fluoride under appropriate conditions afforded the corresponding 1-aryl-1,3-diphosphacyclobutane-2,4-diyls (see scheme). These air-stable open-shell singlet P-heterocycles exhibit considerable electron-donating character and can be used as detectors of hydrogen fluoride.
C−H Amination
The Multiple Facets of Iodine(III) Compounds in an Unprecedented Catalytic Auto-amination for Chiral Amine Synthesis
- Pages: 7530-7533
- First Published: 09 May 2016
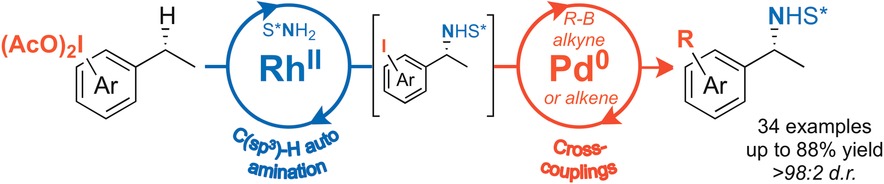
Poly-valent iodine: The design of one-pot reactions involving a catalytic auto C(sp3)−H amination followed by Pd-catalyzed couplings has led to polyfunctionalized enantiopure amines. An iodine(III) reagent can thus be used both as an oxidant and a substrate, then as a coupling partner. The overall process reveals iodoarene-derived oxidants to be versatile building blocks in synthesis.
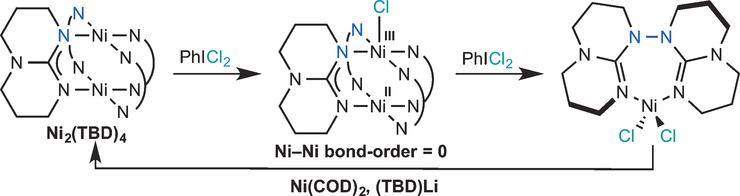
N−N Bond Formation
N−N Bond Forming Reductive Elimination via a Mixed-Valent Nickel(II)–Nickel(III) Intermediate
- Pages: 7534-7538
- First Published: 04 May 2016
Total Synthesis
Isolation and Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Perforanoid A
- Pages: 7539-7543
- First Published: 11 May 2016
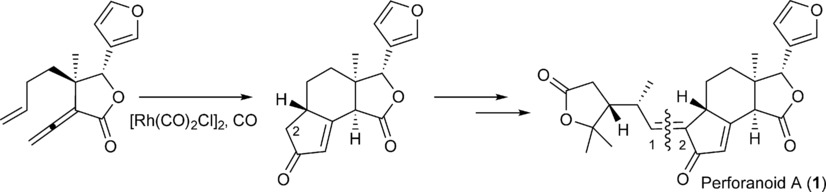
When life gives you limonoids: A novel limonoid, perforanoid A, was isolated, and an asymmetric total synthesis was achieved in 10 steps. The key steps are chiral tertiary aminonaphthol mediated enantioselective alkenylation of an aldehyde to an allylic alcohol, Pd-catalyzed coupling of the allylic alcohol with vinyl ether to form the γ-lactone ring, and cyclopentenone ring formation through a Rh-catalyzed Pauson–Khand reaction.
Analytical Methods | Hot Paper
A Disposable Planar Paper-Based Potentiometric Ion-Sensing Platform
- Pages: 7544-7547
- First Published: 17 May 2016
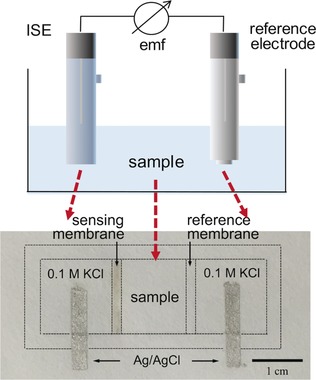
Paper-based sensors: Embedding a potentiometric cell into paper brings selective ion sensors into the reach of users with limited resources and training. The paper-based device is simple to use, does not need any pretreatment, and requires only a low sample volume of 20 μL. It can be used to detect clinically relevant ions in biological samples with high sensitivity and reproducibility. ISE=ion-selective electrode.