Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: A Facile Strategy for Selective Incorporation of Phosphoserine into Histones (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 22/2013)
- Page: 5651
- First Published: 02 May 2013

Selective phosphoserine incorporation is described by H.-S. Park et al. in their Communication on page 5771 ff. A general strategy for producing recombinant histones with site-specific serine phosphorylation has been developed by engineering phosphoseryl-tRNA synthethase (SepRS) and elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). This method should facilitate the study of histone phosphorylation and cross-regulatory mechanisms.
Inside Cover: Polycyclooctadiene Complexes of Rhodium(I): Direct Access to Organometallic Nanoparticles (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 22/2013)
- Page: 5652
- First Published: 02 May 2013

Organometallic nanoparticles can be prepared by intramolecular cross-linking of polycyclooctadiene with [{RhCl(C2H4)2}2]. In their Communication on page 5767 ff., N. G. Lemcoff et al. describe the controllability of the nanoparticle size through the amount of rhodium added. Furthermore, the parent polymer can be regenerated through the addition of a phosphine aldehyde derivative, thus proving the accessibility and reactivity of the imbedded metal.
Inside Back Cover: General and Efficient Synthesis of Indoles through Triazene-Directed C–H Annulation (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 22/2013)
- Page: 5885
- First Published: 06 May 2013

Directed CH annulation reactions provide a straightforward solution to the synthesis of substituted indoles. In their Communication on page 5795 ff., Y. Huang and co-workers describe a general protocol for the synthesis of unprotected indoles. By using a cleavable triazene as the directing group, CH annulation with a wide scope of alkynes was accomplished with excellent regioselectivity for both aryl,alkyl and alkyl,alkyl disubstituted acetylenes.
Back Cover: A Programmable Sensor to Probe the Internalization of Proteins and Nanoparticles in Live Cells (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 22/2013)
- Page: 5886
- First Published: 02 May 2013

The internalization of proteins and nanoparticles in living cells can be quantified by using a new DNA nanosensor, as described by A. P. R. Johnston and H. Liu in their Communication on page 5744 ff. The material of interest is labeled with a fluorescent DNA probe, and the fluorescence of any material that remains on the surface of the cell is quenched upon the addition of a quencher probe. The fluorescence of internalized material and other fluorophores is unaffected. This technique enables multi-color assays and studies in primary cells without compromising sensitivity or quantification.
Editorial
Intellectual Freedom in Academic Scientific Research under Threat
- Pages: 5654-5655
- First Published: 29 April 2013

“…︁ In Great Britain and most probably also in other countries, a restoration of the proven qualities of intellectual freedom is mandatory. It has contributed so much to the culture, and facilitated the economic growth and the communal well-being, of the nation …︁” Read more in the Editorial by Sir John Meurig Thomas.
Graphical Abstract
Corrigendum
Corrigendum: Indium-Catalyzed Cycloisomerizations of Cyclopropene-3,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds: Efficient Access to Benzo-Fused Heteroaromatics and Heterobiaryls
- Page: 5669
- First Published: 17 May 2013
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 22/2013
- Pages: 5672-5675
- First Published: 17 May 2013
Author Profile
Hisashi Yamamoto
- Pages: 5678-5679
- First Published: 05 February 2013

“I chose chemistry as a career because it is so beautiful and yet still mysterious. I decided to be a chemist when I was 10 years old and I have never to this day regretted that rather early decision. I would not want to use whatever luck I might have for the lottery but rather would like to use it for my work in chemistry …︁” This and more about Hisashi Yamamoto can be found on page 5678.
News
Book Review
Prize Fight. The Race and the Rivalry to be the First in Science. By Morton A. Myers.
- Pages: 5681-5682
- First Published: 22 April 2013
Highlight
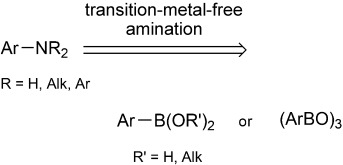
Synthetic Methods
Transition-Metal-Free Amination of Aryl boronic Acids and Their Derivatives
- Pages: 5684-5686
- First Published: 19 April 2013
Essay
Programmable Atom Equivalents
Nucleic Acid-Modified Nanostructures as Programmable Atom Equivalents: Forging a New “Table of Elements”†
- Pages: 5688-5698
- First Published: 02 May 2013

A nanoparticle-based analogue to the Periodic Table of the elements, where rather than arranging entries by electronic configuration, they are arranged by nanoscale architectural feature (e.g., composition, size, shape, and surface functionality). Using this table as a guide, the design considerations associated with using nucleic acids to assemble these nanoparticle-based programmable atom equivalents (PAEs) into superlattices is discussed.
Review
Enzyme Design
Computational Enzyme Design
- Pages: 5700-5725
- First Published: 25 March 2013
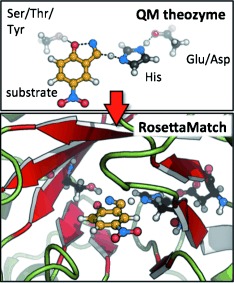
The “inside-out” approach to computer-based enzyme design unites the newest developments in the areas of computational chemistry and biology. This has enabled the design of proteins that catalyze reactions not accelerated in nature. The achievements and limitations of the current technology are highlighted and compared to other methods.
Communications
Natural Products
Enzyme-Labile Protecting Groups for the Synthesis of Natural Products: Solid-Phase Synthesis of Thiocoraline†
- Pages: 5726-5730
- First Published: 25 April 2013

Another (orthogonal) dimension: The solid-phase synthesis of thiocoraline was accomplished for the first time by a combined approach involving chemical and enzymatic methods. One-pot cleavage of the phenylacetamidomethyl protecting group using immobilized penicillin G acylase enzyme (see picture) and disulfide formation are the key steps of the synthetic strategy.
Redox-Responsive Actuators
Redox-Generated Mechanical Motion of a Supramolecular Polymeric Actuator Based on Host–Guest Interactions†
- Pages: 5731-5735
- First Published: 22 April 2013
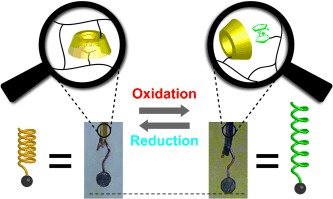
A supramolecular hydrogel is formed by a water-soluble polymer cross-linked with host–guest inclusion complexes between cyclodextrin and ferrocene. Dissociation and re-formation of inclusion complexes by redox stimuli lead to macroscale expansion and contraction of the hydrogel. The gel is utilized as a redox-responsive actuator and the mechanical work done is evaluated.
Biradicals
Unusual Inorganic Biradicals: A Theoretical Analysis†
- Pages: 5736-5739
- First Published: 19 April 2013
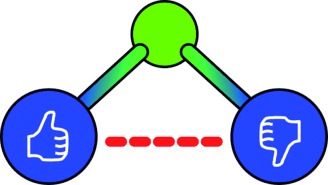
The biradical character β (1 for an ideal biradical) is determined from multi-reference configuration interaction (MRCI) wavefunctions. Triatomics in the series FX2+ (X=O, S, Se, Te, Po) exhibit unusually high biradical characters for X=Te, Po (0.76<β<0.92), the largest among the homologous 18 valence electron molecules CX22−, NX2−, X3, and OX2. On the same scale, the biradical character of O3 is just 0.19, whereas that of C(CH2)3 is 0.97.
Cyclophanes
Synthesis of Highly Distorted π-Extended [2.2]Metacyclophanes by Intermolecular Double Oxidative Coupling†
- Pages: 5740-5743
- First Published: 22 April 2013
![Synthesis of Highly Distorted π-Extended [2.2]Metacyclophanes by Intermolecular Double Oxidative Coupling](/cms/asset/cb1859a6-9ef9-4bfa-88ef-172b5fec5294/mcontent.jpg)
A strained relationship: Oxidation of dihydroxy-substituted acenes provides face-to-face [2.2]metacyclophane-like dimers (see scheme; O red, Si of iPr3Si groups blue). The products exhibited highly distorted structures caused by steric repulsion. UV/Vis and electrochemical analysis revealed that the HOMO–LUMO gap was decreased upon dimerization.
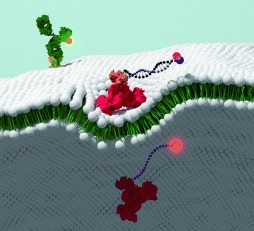
Internalization Sensor
A Programmable Sensor to Probe the Internalization of Proteins and Nanoparticles in Live Cells†
- Pages: 5744-5748
- First Published: 19 April 2013
Complex Catenanes
Generation of a Dynamic System of Three-Dimensional Tetrahedral Polycatenanes†
- Pages: 5749-5752
- First Published: 18 April 2013
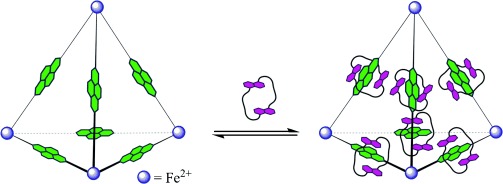
Seven of the best: A dynamic combinatorial library of polycatenated tetrahedra was prepared by complexation between a dynamic Fe4L6 tetrahedral cage, constructed from ligands containing an electron-deficient naphthalenediimide core, and an electron-rich aromatic crown ether, 1,5-dinaphtho[38]crown-10. The highest order species in the library is the tetrahedral [7]catenane.
Solvent Adsorption on LiCoO2
Preferential Adsorption of Solvents on the Cathode Surface of Lithium Ion Batteries†
- Pages: 5753-5756
- First Published: 24 April 2013
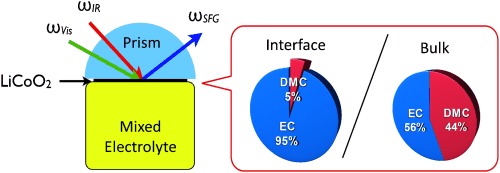
The adsorption structures of solvents on the surface of LiCoO2, which is the most widely used cathode material for Li-ion batteries, in contact with nonaqueous electrolyte solutions of carbonate esters have been characterized by in situ sum frequency generation (SFG) spectroscopy. The cyclic carbonate of ethylene carbonate (EC) is preferentially adsorbed on the LiCoO2 surface, in contrast to linear carbonates, such as dimethyl carbonate (DMC).
Oral Delivery of siRNA
Supramolecular Self-Assembled Nanoparticles Mediate Oral Delivery of Therapeutic TNF-α siRNA against Systemic Inflammation†
- Pages: 5757-5761
- First Published: 22 April 2013
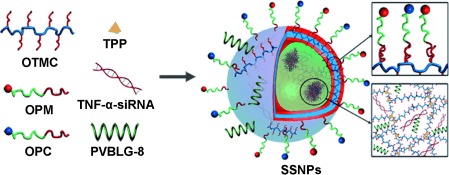
A functional package: Multifunctional supramolecular self-assembled nanoparticles (SSNPs) consist of a set of rationally designed components that collectively facilitate efficient intestinal absorption of siRNA and induce potent TNF-α silencing in macrophages. Single gavage of SSNPs in mice depletes systemic TNF-α production at an siRNA dose as low as 50 μg kg−1, and thus protects mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic injury.
Biomineralization
Multiphase Intrafibrillar Mineralization of Collagen†
- Pages: 5762-5766
- First Published: 18 April 2013
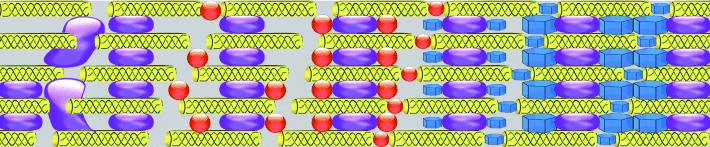
Why waste space? In the first stage of the multiphase biomineralization of collagen, silicic acid precursors (purple) infiltrated the collagen fibril (yellow) and condensed into amorphous silica to give a hierarchical composite. Amorphous calcium phosphate precursors (red) then filled the intrafibrillar spaces of the silicified collagen, where the precipitation and maturation of apatite crystallites (blue) occurred to complete the process.
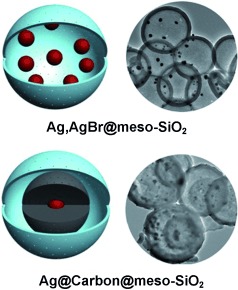
Organometallic Nanoparticles
Polycyclooctadiene Complexes of Rhodium(I): Direct Access to Organometallic Nanoparticles†
- Pages: 5767-5770
- First Published: 19 March 2013
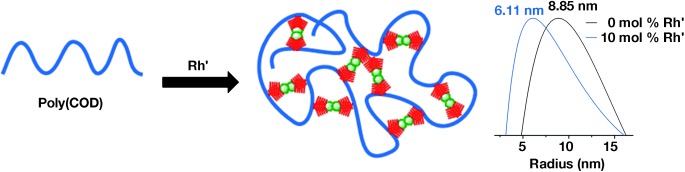
Content matters: The reaction of polycyclooctadiene (Poly(COD)) and [{RhCl(C2H4)2}2] produced well-defined π-bound hybrid polymers, the size of which depended on rhodium content (see picture). The reaction of these polymers with a phosphine aldehyde led to the regeneration of the original polymers, thus proving the accessibility of the metal.
Protein Modifications
A Facile Strategy for Selective Incorporation of Phosphoserine into Histones†
- Pages: 5771-5775
- First Published: 26 March 2013
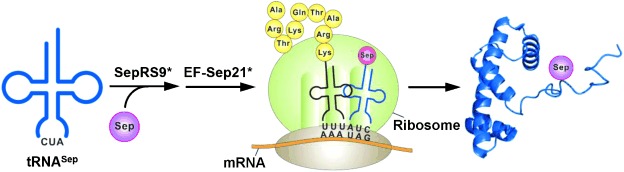
Phosphoserine incorporation: A general strategy for producing recombinant histones with site-specific serine phosphorylation is developed by engineering phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS) and elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu; see picture). Serine-phosphorylated nucleosomes provide direct evidence for crosstalk between phosphorylation and acetylation in histones.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Photocatalytic Conversion of Carbon Dioxide with Water into Methane: Platinum and Copper(I) Oxide Co-catalysts with a Core–Shell Structure†
- Pages: 5776-5779
- First Published: 22 April 2013

Binary co-catalysts of Pt and Cu2O with a core–shell structure significantly enhance the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with H2O to CH4 and CO. The Cu2O shell provides sites for the preferential activation and conversion of CO2, whereas the Pt core extracts the photogenerated electrons from TiO2. The deposition of Cu2O shell on Pt nanoparticles markedly suppresses the reduction of H2O to H2 (see picture).
Selective Alcohol Oxidation
Molecular Understanding of Reactivity and Selectivity for Methanol Oxidation at the Au/TiO2 Interface†
- Pages: 5780-5784
- First Published: 15 April 2013
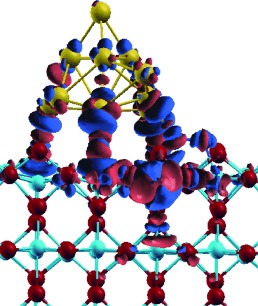
Gold catalysis: Experimental and theoretical data demonstrated consistently that the interfacial sites on a Au/TiO2 catalyst show both high reactivity and selectivity for low-temperature methanol oxidation with O2 to give formaldehyde. The microscopic mechanism of this complex reaction has been unraveled in full molecular detail (see picture, gold cluster on TiO2 surface).
Tetronate Antibiotics
Unusual Acetylation–Elimination in the Formation of Tetronate Antibiotics†
- Pages: 5785-5788
- First Published: 18 April 2013
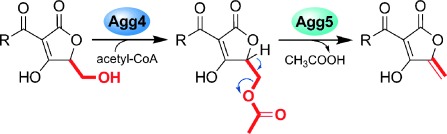
The identity and reactivity of the intermediates in agglomerin biosynthesis were established and the respective roles of the acetyltransferase Agg4 and the eliminating enzyme Agg5 identified (see scheme). It is proposed that enzymes homologous to Agg4 and Agg5 carry out the dehydration steps in all spirotetronate biosynthetic pathways. If this proves correct, it may assist engineering of these pathways.
Cooperative Catalysis
An Efficient Approach to the Securinega Alkaloids Empowered by Cooperative N-Heterocyclic Carbene/Lewis Acid Catalysis†
- Pages: 5789-5794
- First Published: 22 April 2013
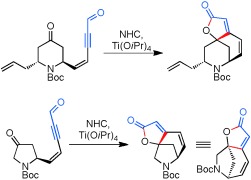
Folding it all together: Most of the syntheses developed for the securinega alkaloid class require lengthy sequences to create their bridging butenolide domains. A novel approach uses N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) and Lewis acids to forge the entire domain in a single step from appropriate precursors, showing that ynal-derived homoenolates can participate as nucleophiles in intramolecular settings (see scheme).
Synthetic Methods
General and Efficient Synthesis of Indoles through Triazene-Directed C–H Annulation†
- Pages: 5795-5798
- First Published: 19 April 2013
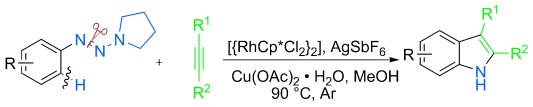
Unprotected indoles are prepared with the title method, which has a wide scope for alkynes. Excellent regioselectivity was accomplished for aryl–alkyl and alkyl–alkyl disubstituted acetylenes. This reaction features an unusual 1,2 rhodium migration and ring-contraction-triggered NN bond cleavage. It allows rapid conversion of the reaction products into several functional molecules.
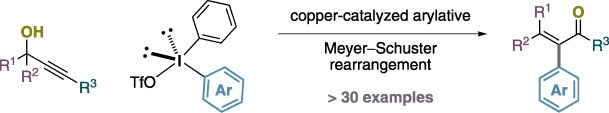
Copper Catalysis
Copper-Catalyzed Arylative Meyer–Schuster Rearrangement of Propargylic Alcohols to Complex Enones Using Diaryliodonium Salts†
- Pages: 5799-5802
- First Published: 22 April 2013
Organocatalysis
Enantioselective N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalyzed Aza-Benzoin Reaction of Enals with Activated Ketimines†
- Pages: 5803-5806
- First Published: 22 April 2013
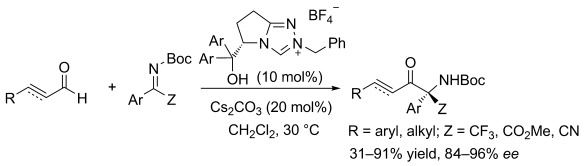
α-Amino ketones, which are versatile building blocks for organic synthesis, were obtained with the title reaction. A free hydroxy group on the NHC catalyst was found to be crucial for the reaction, and the possible competing reaction through a homoenolate or enolate was not observed with this catalyst (see scheme).
Cross-Coupling
Weak Arene CH⋅⋅⋅O Hydrogen Bonding in Palladium-Catalyzed Arylation and Vinylation of Lactones†
- Pages: 5807-5812
- First Published: 22 April 2013
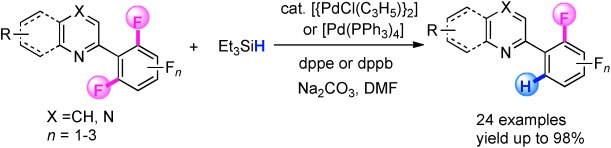
Catalytic CF Activation
Palladium-Catalyzed Ortho-Selective CF Activation of Polyfluoroarenes with Triethylsilane: A Facile Access to Partially Fluorinated Aromatics†
- Pages: 5813-5817
- First Published: 19 April 2013
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Highly Stereoselective Cyclopropanation of α,β-Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds with Methyl (Diazoacetoxy)acetate Catalyzed by a Chiral Ruthenium(II) Complex†
- Pages: 5818-5821
- First Published: 16 April 2013
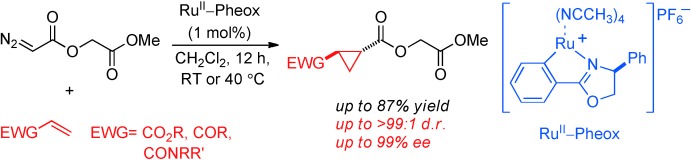
Tantalizing triangles: The title reaction gives bicarbonyl cyclopropane products that can lead to versatile intermediates with high yields and stereoselectivities. This system was also applied to the enantioselective total synthesis of spiro cyclopropane oxindole, an HIV-1 nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor.
Catalyst Activation
The Impact of Palladium(II) Reduction Pathways on the Structure and Activity of Palladium(0) Catalysts†
- Pages: 5822-5826
- First Published: 22 April 2013
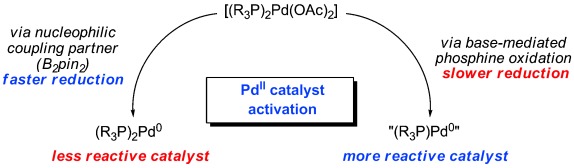
Two roads diverged: The mechanism of in situ PdII catalyst activation to generate an active {LnPd0} catalyst from an air-stable PdII precursor was examined using the standard conditions of a Miyaura borylation reaction. Two pathways for catalyst activation exist under these conditions, producing two structurally and chemically distinct {LnPd0} complexes (see scheme).
CH Activation
PdCl2 and N-Hydroxyphthalimide Co-catalyzed C H Hydroxylation by Dioxygen Activation†
H Hydroxylation by Dioxygen Activation†
- Pages: 5827-5831
- First Published: 22 April 2013
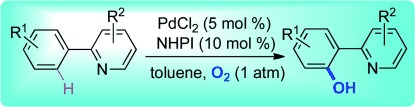
Rad transition: The combination of transition-metal-catalyzed CH activation and a NHPI-initiated radical process is essential for the title transformation. The neutral conditions and the ideal oxidant, molecular oxygen, make this hydroxylation environmentally friendly and practical. NHPI=N-hydroxyphthalimide.
Hydrogen storage
Metal-Free Catalysis of Ammonia–Borane Dehydrogenation/Regeneration for a Highly Efficient and Facilely Recyclable Hydrogen-Storage Material†
- Pages: 5832-5835
- First Published: 22 April 2013
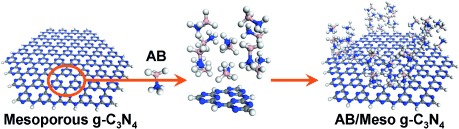
As easy as ABC: Mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride (MGCN; g-C3N4) is utilized to support ammonia borane (AB) on the basis of its accessible nanoporous structure and basic properties. A high loading of uniformly dispersed AB nanoparticles into the MGCN is possible giving greatly enhanced H2 generation from AB, and facile regeneration cycles by a hydrazine hydrogenation process, even at room temperature.
Heterocycles
Unveiling Latent α-Iminocarbene Reactivity for Intermolecular Cascade Reactions through Alkyne Oxidative Amination†
- Pages: 5836-5839
- First Published: 22 April 2013
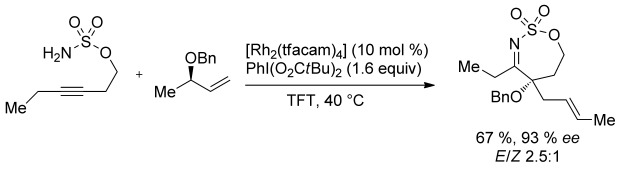
Setting a trap: Described is the development of a metallonitrene-initiated alkyne oxidation cascade with intermolecular trapping of the reactive intermediate with a variety of allyl ethers to provide α-oxyimine products in which new CN, CO, and CC bonds have all been generated (see Scheme; tfacam=trifluoroacetamide).
Modified Nucleic Acids
Base-Pairing Properties of a Structural Isomer of Glycerol Nucleic Acid†
- Pages: 5840-5844
- First Published: 18 April 2013
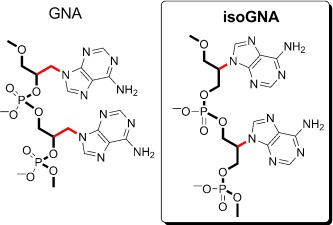
Know your limit! IsoGNA (a structural isomer of GNA) was found—in sharp contrast to GNA—to be highly restricted in its ability to base-pair with itself and other nucleic acids. While homogeneous sequences (e.g. isoGNA(A)16) formed duplexes, the heterogeneous sequences showed no base-pairing. This exemplifies the limitations of canonical nucleobases as the recognition elements in simpler, more primitive phosphate backbones.
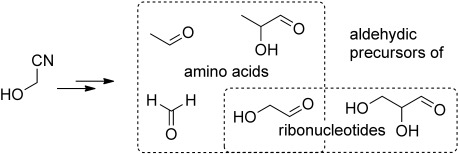
Prebiotic Systems Chemistry
Synthesis of Aldehydic Ribonucleotide and Amino Acid Precursors by Photoredox Chemistry†
- Pages: 5845-5847
- First Published: 22 April 2013
Gold Catalysis
Copper Salts as Additives in Gold(I)-Catalyzed Reactions†
- Pages: 5848-5852
- First Published: 19 April 2013
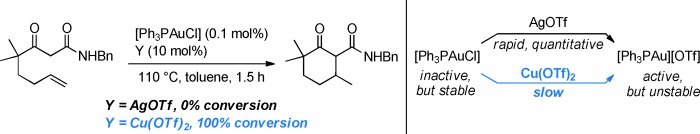
The right combination: CuI and CuII salts can advantageously replace silver additives in AuI-catalyzed reactions. On the basis of reactivity studies and NMR experiments, it is believed that anion metathesis between CuYn (Y=OTf, BF4, PF6, SbF6) and [R3PAuCl] takes place to give [R3PAu]Y. As this process is slow, there is no fast decay of the active species, thus allowing large-scale reactions, even at high temperatures, with low loadings of the gold complex.
Zinc Catalysis
Zinc-Catalyzed Synthesis of Functionalized Furans and Triarylmethanes from Enynones and Alcohols or Azoles: Dual XH Bond Activation by Zinc†
- Pages: 5853-5857
- First Published: 22 April 2013
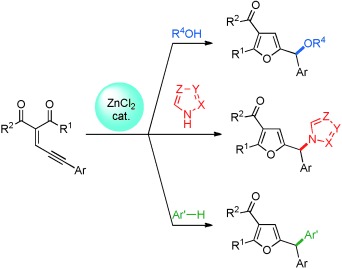
Ba'zinc'ga! A zinc-catalyzed sequence involving a cyclization with a subsequent CO, CN, or CC bond formation enables the preparation of a variety of valuable furfuryl ethers (with alcohols) and unsymmetrically substituted triarylmethane derivatives (with azoles or arenes). ZnCl2 serves as the catalyst.
Carbohydrate Synthesis (1)
Automated Solid-Phase Synthesis of Chondroitin Sulfate Glycosaminoglycans†
- Pages: 5858-5861
- First Published: 15 April 2013
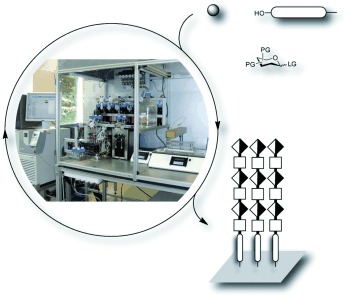
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are important sulfated carbohydrates prevalent in the extracellular matrix. The synthesis of structurally defined GAGs requires laborious procedures, and incorporating defined sulfation patterns is challenging. The automated synthesis of defined sulfated chondroitin hexasaccharides on solid support has been achieved using a photolabile linker that is efficiently cleaved in a continuous-flow photoreactor.
Carbohydrate Synthesis (2)
Automated Polysaccharide Synthesis: Assembly of a 30mer Mannoside†
- Pages: 5862-5865
- First Published: 22 April 2013
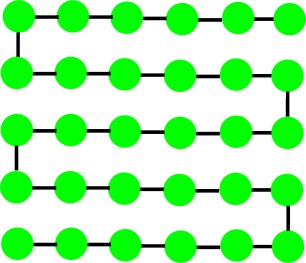
Automated carbohydrate synthesis breaks new grounds: The longest sugar chemically synthesized to date (a 30 mer) has been accessed. Key to the process is the use of a catch–release technique, which labels the saccharide, thus allowing it to be separated later through temporary attachement to magnetic particles.
Total Synthesis
Total Synthesis of the Tubulin Inhibitor WF-1360F Based on Macrocycle Formation through Ring-Closing Alkyne Metathesis †
- Pages: 5866-5870
- First Published: 22 April 2013
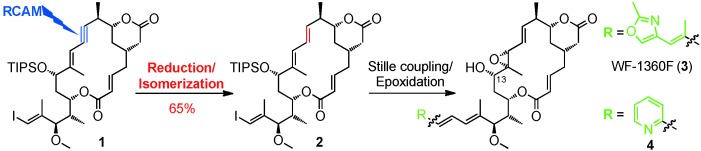
Key steps in this total synthesis of the antimitotic natural product WF-1360F (3) include the formation of the macrocycle through ring-closing alkyne metathesis and the subsequent conversion of the ensuing alkyne moiety into an E-configured double bond. As illustrated by the synthesis of 4, the macrocyclic vinyl iodide 2 can also serve as a common precursor for the synthesis of side-chain-modified rhizoxin analogues (see scheme; TIPS=triisopropylsilyl).
Natural Product Synthesis
Total Synthesis of the Antifungal Agent Echinocandin C†
- Pages: 5871-5875
- First Published: 22 April 2013
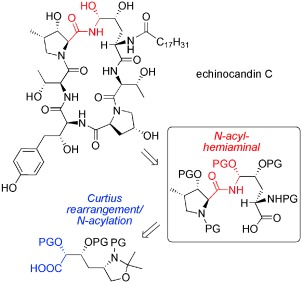
Reliably stable: A dipeptide building block with fully elaborated N-acyl hemiaminal proved to be a versatile precursor for echinocandin C, a prototypical member of the echinocandin group of antimycotic drugs. This first total synthesis of an N-acyl hemiaminal-containing echinocandin is concise and highly convergent, thereby making additional derivatives easily accessible. PG=protecting group.
Frustrated Lewis Pairs
Functional-Group Tolerance in Frustrated Lewis Pairs: Hydrogenation of Nitroolefins and Acrylates†
- Pages: 5876-5879
- First Published: 22 April 2013
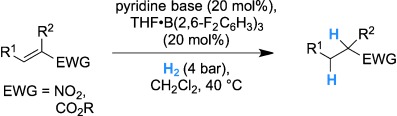
Weak Lewis acid for high nucleophilicity: Hydridoborate derived from B(2,6-F2C6H3)3 shows significant hydride character. Solid-state and solution structure analysis revealed a dihydrogen-bonded aggregate. The new frustrated Lewis pair was applied in the hydrogenation of nitroolefins and acrylates (see scheme; EWG=electron-withdrawing group). The decreased Lewis acidity provides higher reactivity and functional-group tolerance.
Gold Carbenoids
Gold Catalysis: Highly Functionalized Cyclopentadienes Prepared by Intermolecular Cyclization of Ynamides and Propargylic Carboxylates†
- Pages: 5880-5884
- First Published: 24 April 2013
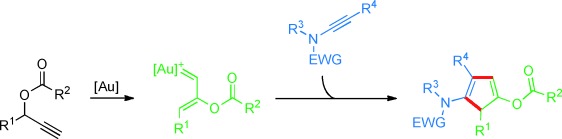
When an ynamide meets a gold carbenoid: Highly electrophilic gold carbenoids available from propargylic esters by means of 1,2-acyloxy migration open up new reaction pathways for ynamide gold chemistry. In this way highly functionalized cyclopentadiene derivatives become accessible (see scheme; EWG=electron-withdrawing group).