Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Dissociation of Amyloid Fibrils of α-Synuclein in Supercooled Water (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 27/2008)
- Page: 4939
- First Published: 16 June 2008

Amyloid fibrils are filamentous aggregates of peptides and proteins with exceptional stability that are associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. M. Zweckstetter et al. demonstrate in their Communication on page 5046 ff. that amyloid fibrils formed by the protein α-synuclein, which is associated with Parkinson's disease, are rapidly denatured, that is, dissociated and lose the conformation of the constituent protein molecules, in supercooled water at −15 °C, conditions in which many globular proteins remain folded.
Inside Cover
Inside Cover: Photomobile Polymer Materials: Towards Light-Driven Plastic Motors (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 27/2008)
- Page: 4940
- First Published: 16 June 2008

A plastic motor which is driven only by light is demonstrated by T. Ikeda et al. in their Communication on page 4986 ff. The rotational motion of azobenzene-containing liquid-crystalline elastomers and their composite materials have potential application, as they convert light energy directly into mechanical work without the aid of batteries, electric wires, or gears.
Graphical Abstract
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 27/2008
- Pages: 4954-4955
- First Published: 16 June 2008
Book Review
Dictionary of Marine Natural Products. With CD-ROM. Edited by John W. Blunt and Murray H. G. Munro.
- Pages: 4956-4957
- First Published: 16 June 2008
Highlights
From Metal Complexes to Nanominerals: The Formation of Inorganic Nanoparticles on Fibrils of Transferrin
- Pages: 4960-4961
- First Published: 16 June 2008
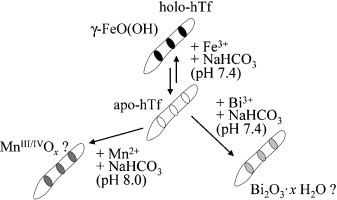
Upon drying of the iron transport protein transferrin (hTf), the originally individually coordinated Fe forms crystalline deposits of FeO(OH) (“rust”), which are periodically arranged on fibrils of the protein. This is also true for Mn and Bi minerals (the picture shows mineralization on hTF fibrils; holo/apo-hTf: hTf with/without Fe). A mineralization of this kind on fibrils could play a role in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
Superbulky Ligands and Trapped Electrons: New Perspectives in Divalent Lanthanide Chemistry†
- Pages: 4962-4964
- First Published: 16 June 2008
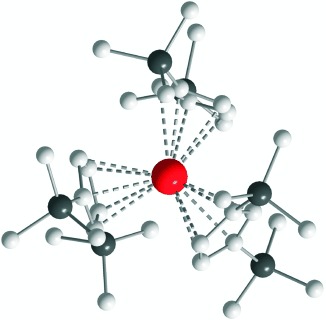
Spectacular developments in recent years, especially the discovery of an anionic complex of divalent lanthanum, in which the electron is trapped in a localized 5d1 SOMO (see structure of the anion of [K([2.2.2]crypt)][LaCp′′3] (Cp′′=1,3-(SiMe3)2C5H3); La red, C gray, Si black), have brought new impetus to the solution chemistry of divalent lanthanides.
Review
Gas Storage in Nanoporous Materials
- Pages: 4966-4981
- First Published: 16 June 2008
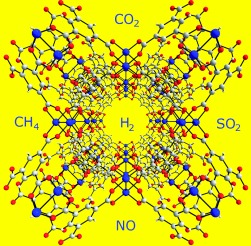
Gas tanks for all: Gas storage technologies are developing in many areas and the use of nanoporous materials as storage media for gases as varied as hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and nitric oxide is the focus of significant research effort. Different applications require different properties from the materials to be used, and how we can improve on currently available materials is a significant challenge for chemists.
Communications
The Nucleation Mechanism of Fluorapatite–Collagen Composites: Ion Association and Motif Control by Collagen Proteins†
- Pages: 4982-4985
- First Published: 16 June 2008
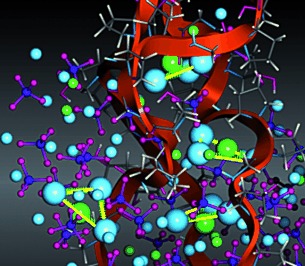
Apatite for the structure: Nucleation mechanisms of apatite–collagen composites at the atomistic level of detail have been investigated. Peculiar motifs of the apatite crystal structure were identified in which formation is promoted by ion association to the biomolecule. Apart from acting as a nucleation seed for ionic ordering, collagen triple helices (see picture; red bands) also induce orientation control in these motifs.
Photomobile Polymer Materials: Towards Light-Driven Plastic Motors†
- Pages: 4986-4988
- First Published: 16 June 2008
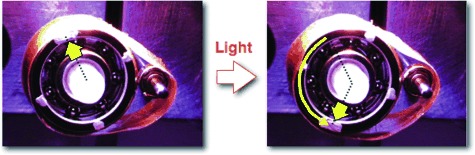
Can light drive a motor? Azobenzene-containing liquid-crystalline elastomers (LCEs) and their composite materials have the potential to show three-dimensional movement by light irradiation. With the LCE laminated films, a first light-driven plastic motor has been developed, which can convert light energy directly into a continuous rotation without the aid of batteries, electric wires, or gears.
Tandem Catalytic Asymmetric Friedel–Crafts/Henry Reaction: Control of Three Contiguous Acyclic Stereocenters†
- Pages: 4989-4992
- First Published: 16 June 2008
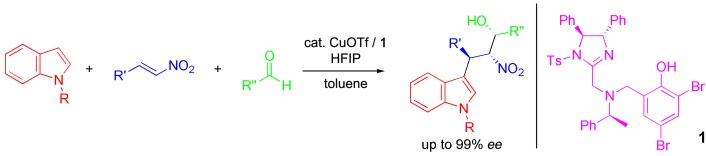
Good things come in threes: Highly functionalized indole derivatives with three contiguous stereocenters were formed in the title reaction of an indole, a nitroalkene, and an aldehyde with the imidazoline–aminophenol catalyst 1–CuOTf in the presence of 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP). The major isomers of the adducts were obtained with up to 99 % ee. Tf=trifluoromethanesulfonyl, Ts=p-toluenesulfonyl; R=H, Me; R′,R′′=alkyl, aryl.
Enhanced π Conjugation around a Porphyrin[6] Nanoring†
- Pages: 4993-4996
- First Published: 16 June 2008
![Enhanced π Conjugation around a Porphyrin[6] Nanoring](/cms/asset/11c1c52b-2bd8-4a2f-a54e-70155e8d8c24/mcontent.jpg)
Strong cycle: The cyclic hexamer–template complex 3 obtained through template-directed trimerization of a porphyrin dimer 2, using a hexapyridyl template 1, is extremely stable (Kf=7×1038 M−1), but the free macrocycle 4 can be liberated using amine ligands. Spectroscopic data and DFT calculations show that the cyclic hexamer is more conjugated than its linear analogue.
Emerging Solvent-Induced Homochirality by the Confinement of Achiral Molecules Against a Solid Surface†
- Pages: 4997-5001
- First Published: 16 June 2008
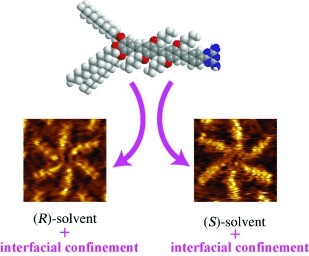
One hand mapping: By means of scanning tunneling microscopy, solvent-induced homochirality is shown to emerge in self-assembled monolayers of achiral molecules at the liquid–solid interface (see picture). The chirality of the solvent directs the macroscopic chirality of the monolayer. The dynamics of the monolayer structure as it evolves towards homochirality are probed by time-dependent measurements.
Catalytic Hydrogen-Chlorine Exchange between Chlorinated Hydrocarbons under Oxygen-Free Conditions†
- Pages: 5002-5004
- First Published: 16 June 2008
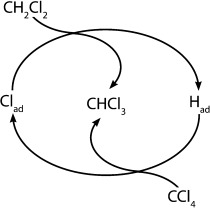
Pass the parcel: Activity experiments show that LaCl3 supported on carbon nanofibers is a highly active, selective, and stable catalyst for the H–Cl exchange reaction between CCl4 and CH2Cl2 to form CHCl3 (see scheme) in the absence of either lattice or gas-phase oxygen. Density functional calculations suggest that the reaction proceeds through the formation of weakly adsorbed Cl and H species which can be exchanged between the reactants.
Surface Chemistry of Ag Particles: Identification of Oxide Species by Aberration-Corrected TEM and by DFT Calculations†
- Pages: 5005-5008
- First Published: 16 June 2008
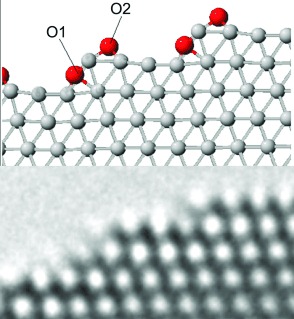
Edges and steps have been identified as the locations of surface (O2) and subsurface oxygen atoms (O1) on silver particles by means of DFT calculations and aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy. The experimental technique allows surface features, such as terraces, steps, and edges, to be clearly imaged (see picture) by eliminating the Fresnel fringes.
Monolayer-Barcoded Nanoparticles for On-Chip DNA Hybridization Assay†
- Pages: 5009-5012
- First Published: 16 June 2008
The Da Vinci Code: Monolayer-barcoded nanoparticles have been successfully prepared by simultaneous incorporation of probe elements and organic molecules. The organic species serve as mass-tagging surrogates for MS readout and allow on-chip DNA hybridization assay by laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight MS. The strategy could readily be extended to the identification of a vast range of biomolecular binding events.
Seeing Molecules by Eye: Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging at Visible Wavelengths with High Spatial Resolution and Submonolayer Sensitivity†
- Pages: 5013-5017
- First Published: 16 June 2008
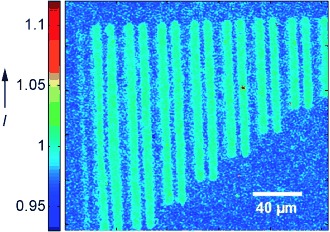
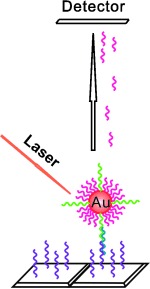
Plasmonic crystal optics: Highly uniform, fully 3D plasmonic crystals exhibiting exceptional analytical sensitivity at visible wavelengths can image surface binding events with high spatial resolution and can distinguish adsorbates with masses that differ by only 25 amu. The picture shows a transmitted white-light plasmonic image of microcontact-printed lines (ca. 8 μm wide) of 1-octadecanethiol on the Au surface of a 3D plasmonic crystal.
On-Chip Micro Gas Chromatograph Enabled by a Noncovalently Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Sensor Array†
- Pages: 5018-5021
- First Published: 16 June 2008
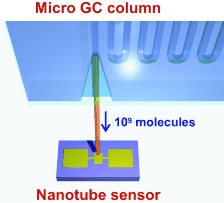
Sensing in reverse: Reversible detection of as few as 109 molecules (1700 aM) of dimethyl methylphosphonate, a nerve agent simulant, is demonstrated at the end of a micro GC column (see picture). Such arrays form the basis of rapidly transducing molecular sensors with micrometer-sized footprints. The separation capability of the column eliminates the need for selectivity on the sensor, as long as analyte binding is reversible and rapid.
Biocompatible Carbon Nanotubes Generated by Functionalization with Glycodendrimers†
- Pages: 5022-5025
- First Published: 16 June 2008
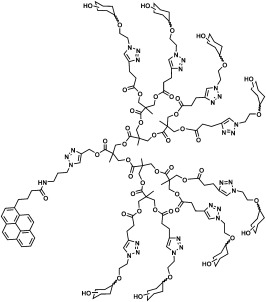
Protective coatings: Glycodendrimers can function as homogeneous bioactive coatings that mitigate the cytotoxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). The bifunctional glycodendrimers (see picture) have peripheral carbohydrate units and a pyrene tail capable of binding SWNT surfaces through π–π interaction. Cells cultured with glycodendrimer-coated SWNTs proliferate at the same rate as untreated cells.
Highly Diastereoselective, Tandem, Three-Component Synthesis of Tetrahydrofurans from Ketoaldehydes via Silylated β-Lactone Intermediates†
- Pages: 5026-5029
- First Published: 16 June 2008
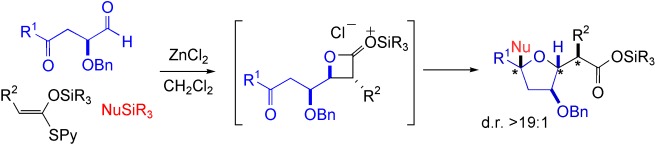
Like falling dominoes! A novel tandem, three-component reaction is described that generates up to two CC bonds, one CO bond, and three additional stereocenters leading to substituted tetrahydrofuran units. This process involves a tandem Mukaiyama aldol-lactonization/reductive cyclization and proceeds via a silylated β-lactone intermediate. The method was applied to prepare the tetrahydrofuran fragment of colopsinol B. Py=2-pyridyl.
On the Nature of the Reactive Intermediates in Gold-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization Reactions†
- Pages: 5030-5033
- First Published: 16 June 2008
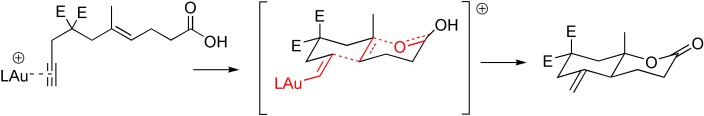
A gold rush: The Stork–Eschenmoser postulate explaining the course and stereoselectivity of cationic polyene cyclization reactions also holds true for cycloisomerization reactions catalyzed by gold. This result suggests that the pertinent intermediates (see scheme) are more adequately described as gold- stabilized carbocations rather than as gold carbenes. E=COOMe, L=neutral ligand.
Modulating the Lewis Acidity of Boron Using a Photoswitch†
- Pages: 5034-5037
- First Published: 16 June 2008
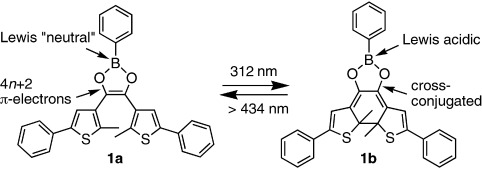
Light turns the Lewis acid on: The Lewis acidity of a boron atom integrated into a cyclic dithienylethene photoswitch is modulated by light: 1 a has low Lewis acidity since the p orbital of the boron center is partially occupied by delocalized π electrons, whereas the rearrangement of the π electrons in 1 b reduces the electron density at the boron center and turns the Lewis acid “on”.
Benzene-, Pyrrole-, and Furan-Containing Diametrically Strapped Calix[4]pyrroles—An Experimental and Theoretical Study of Hydrogen-Bonding Effects in Chloride Anion Recognition†
- Pages: 5038-5042
- First Published: 16 June 2008
![Benzene-, Pyrrole-, and Furan-Containing Diametrically Strapped Calix[4]pyrroles—An Experimental and Theoretical Study of Hydrogen-Bonding Effects in Chloride Anion Recognition](/cms/asset/28ac78c9-03fc-43e1-8132-67ece0ff58c6/mcontent.jpg)
Weak but important: The chloride anion binding properties of diametrically strapped calixpyrroles bearing benzene (see structure), pyrrole, and furan moieties in the strap have been studied in the solid state, in solution, and through theoretical analyses. The results obtained provide support for the notion that CH⋅⋅⋅Cl− hydrogen bonds are significant and contribute substantially to the Cl− binding energetics.
Sheets of Large Superhydrophobic Metal Particles Self Assembled on Water by the Cheerios Effect†
- Pages: 5043-5045
- First Published: 16 June 2008

A copper-rich cereal: Superhydrophobic copper particles show a very large Cheerios effect and rapidly self-assemble into robust sheets on the surface of water. These sheets can support objects (including water drops, see photo) placed on them, even though the irregular geometry of the particles means that they contain macroscopic holes.
Dissociation of Amyloid Fibrils of α-Synuclein in Supercooled Water†
- Pages: 5046-5048
- First Published: 16 June 2008
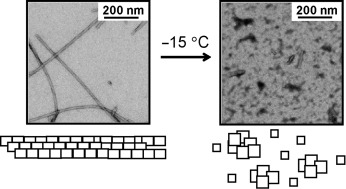
Out in the cold: Amyloid fibrils formed by the protein α-synuclein, one of the key players in Parkinson's disease, are rapidly dissociated in supercooled water at −15 °C (see TEM images), conditions in which many globular proteins remain folded. NMR studies indicate that the weakening of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions contribute to the cold-induced destabilization of the amyloid fibrils.
Catalytic Enantioselective Hosomi–Sakurai Conjugate Allylation of Cyclic Unsaturated Ketoesters†
- Pages: 5049-5051
- First Published: 16 June 2008
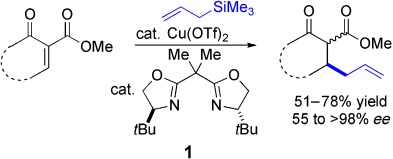
No fancy catalyst required: The copper-catalyzed enantioselective conjugate allylation of activated cyclic enones affords products in up to >98 % ee. Reactions proceed to high conversion in the presence of commercially available Cu(OTf)2 and bis(oxazoline) ligand 1. The allylated products are useful precursors for the synthesis of chiral building blocks.
Glow-Discharge Plasma-Assisted Design of Cobalt Catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis†
- Pages: 5052-5055
- First Published: 16 June 2008
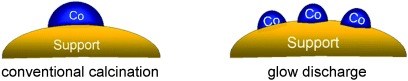
Plasma pretreatment of cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts through glow discharge decomposes cobalt nitrate at much lower temperatures than conventional calcination, and smaller superparamagnetic Co metal particles (<7 nm) are formed (see schematic representation). The Fischer–Tropsch reaction rates with these catalysts are higher than or comparable to those of their counterparts prepared by conventional calcination at 473 K.
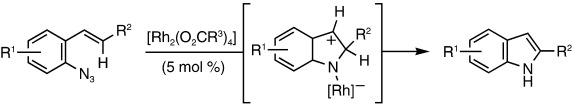
Dirhodium(II)-Catalyzed Intramolecular CH Amination of Aryl Azides†
- Pages: 5056-5059
- First Published: 16 June 2008
Stereoselective Dearomatizing Addition of Nucleophiles to Uncomplexed Benzene Rings: A Route to Carbocyclic Sugar Analogues†
- Pages: 5060-5062
- First Published: 16 June 2008
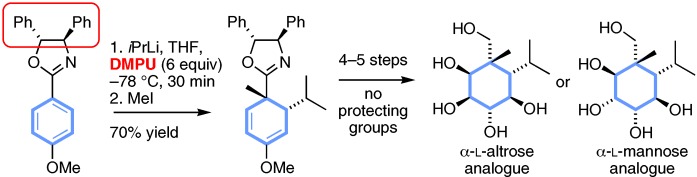
Versatile synthetic intermediates were formed by the dearomatization of 2-aryl 4,5-diphenyloxazolines with secondary alkyl lithium reagents in the presence of N,N′-dimethylpropyleneurea (DMPU; see scheme). The resulting cyclohexadiene derivatives were converted into carbocyclic analogues of mannose and altrose in a short sequence without the use of protecting groups.
PtII-Catalyzed Synthesis of 9-Oxabicyclo[3.3.1]nona-2,6-dienes from 2-Alkynyl-1-carbonylbenzenes and Allylsilanes by an Allylation/Annulation Cascade†
- Pages: 5063-5066
- First Published: 16 June 2008
![PtII-Catalyzed Synthesis of 9-Oxabicyclo[3.3.1]nona-2,6-dienes from 2-Alkynyl-1-carbonylbenzenes and Allylsilanes by an Allylation/Annulation Cascade](/cms/asset/78d03a38-cb25-4d81-9aaf-595970e18622/mcontent.jpg)
Platinum is key: A new catalytic synthesis of 9-oxabicyclo[3.3.1]nona-2,6-dienes from readily available 2-alkynyl-1-carbonylbenzenes, allylsilanes, and water is reported (see scheme). This reaction sequence is proposed to proceed through a series of three reactions, including allylation of the carbonyl group, hydroalkoxylation of the alkyne, and a new ene-oxonium annulation.
Decoupling Deprotonation from Metalation: Thia-Fries Rearrangement†
- Pages: 5067-5070
- First Published: 16 June 2008
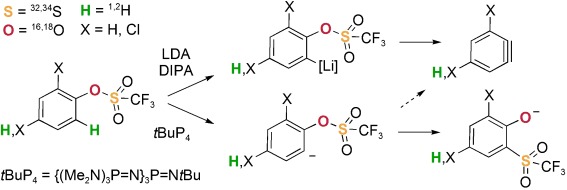
Label-enabled: Studies with 2H-, 18O-, and 34S-labeled aryl triflates show that lithium diisopropylamide-mediated thia-Fries rearrangement proceeds through an irreversible ortho deprotonation (see scheme; DIPA=diisopropylamine, LDA=lithium diisopropylamide). In contrast, ortho metalation results exclusively in the generation of a benzyne.
Predicting Enthalpy of Vaporization of Ionic Liquids: A Simple Rule for a Complex Property†
- Pages: 5071-5074
- First Published: 16 June 2008
A simple additive approach based on the empirical formula has been developed to calculate the enthalpy of vaporization of an ionic liquid, which is separated into a main contribution from the constituent elements (regardless of their position in the cation or anion) and an auxiliary contribution (correction) due to structural peculiarities, such as the presence of CF3 groups or a cyclic structure.
A Crystallizable f-Element Tuck-In Complex: The Tuck-in Tuck-over Uranium Metallocene [(C5Me5)U{μ-η5:η1:η1-C5Me3(CH2)2}(μ-H)2U(C5Me5)2]†
- Pages: 5075-5078
- First Published: 16 June 2008
Direct Catalytic Asymmetric Three-Component Kabachnik–Fields Reaction†
- Pages: 5079-5081
- First Published: 16 June 2008
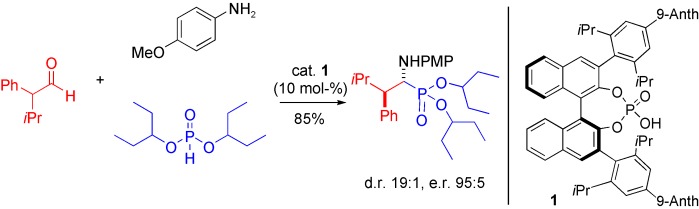
As mimics of α-amino acids, α-amino phosphonates have great promise as antibacterial and anti-HIV agents as well as protease inhibitors. Racemic α-branched aldehydes react, in the presence the new chiral phosphoric acid catalyst 1, directly with p-anisidine (PMPNH2) and a phosphite to furnish β-branched α-amino phosphonates highly diastereoselectively and enantioselectively. Anth=anthracenyl.
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of the Melodinus Alkaloid (+)-Meloscine†
- Pages: 5082-5084
- First Published: 16 June 2008
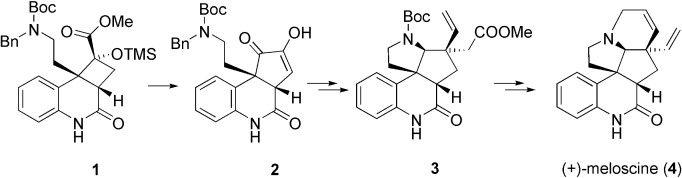
Enantioselective synthesis in a new light: The template-controlled [2+2] photocycloaddition leading to product 1 is the first example of this type of reaction in natural product synthesis. In addition, a retro-benzilic acid rearrangement (→2), a Claisen rearrangement (→3), and a ring-closing metathesis played decisive roles in the synthesis of the alkaloid (+)-meloscine (4).
Single-Cell High-Throughput Screening To Identify Enantioselective Hydrolytic Enzymes†
- Pages: 5085-5088
- First Published: 16 June 2008
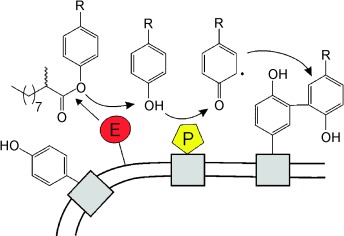
Getting a look in: A high-throughput screening method has been developed for the identification and isolation of enantioselective hydrolases displayed on cell surfaces (see scheme; E: Esterase, P: Peroxidase). Enantiomeric substrates labeled with two different fluorescent dyes allow real-time analysis of enantioselectivity by determination of the ratio of green and red single-cell fluorescence.




![A Crystallizable f-Element Tuck-In Complex: The Tuck-in Tuck-over Uranium Metallocene [(C5Me5)U{μ-η5:η1:η1-C5Me3(CH2)2}(μ-H)2U(C5Me5)2]](/cms/asset/a9d2dde7-4e26-4080-ad3b-3e31d7259e3a/mcontent.jpg)


































