Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Membrane Distillation of Butanol from Aqueous Solution with Polytetrafluoroethylene Membrane
- First Published: 25 February 2020
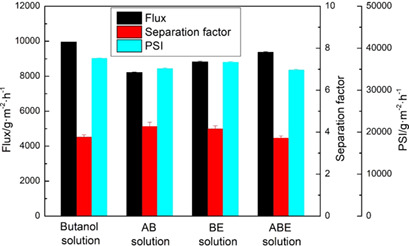
Separation of acetone, butanol, and ethanol from aqueous solution was carried out by vacuum membrane distillation with polytetrafluoroethylene membrane using mechanical vapor compression. Membrane distillation with permeate vapor fractional condensation was found to be more energy-efficient than conventional procedures and cost-effective due to about 50 % lower energy consumption.
Optimization of the Forward Osmosis Process Using Aquaporin Membranes in Chromium Removal
- First Published: 25 November 2019
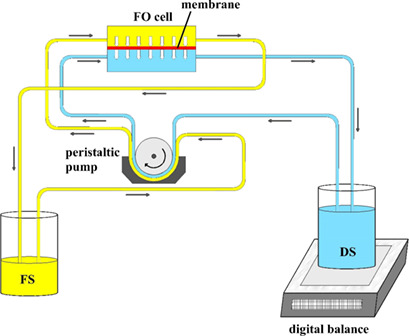
In forward osmosis, the driving force for transfer of water across the membrane is the osmotic pressure gradient between the feed and draw solutions, without any extra force. An aquaporin-based biomimetic membrane was employed and initial concentration of draw solution, feed solution (Cr(VI)), and time were selected as independent variables in order to optimize Cr rejection and water flux.
Membranes for CO2 /CH4 and CO2/N2 Gas Separation
- First Published: 05 November 2019
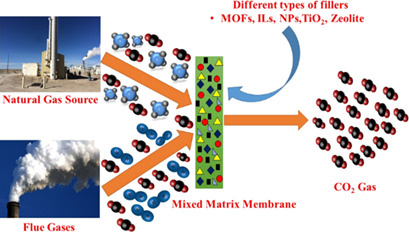
Membrane-based techniques emerged as the most effective option for the separation and/or capture of CO2. Different types of membranes are reviewed with the main emphasis placed on mixed-matrix membranes with various types of fillers. Such membranes combine the advantages of both polymeric and inorganic membranes and exhibit the best performance for CO2 separation from natural gas and other flue gases.
Recent Developments and Applications of Ionic Liquids in Gas Separation Membranes
- First Published: 09 September 2019
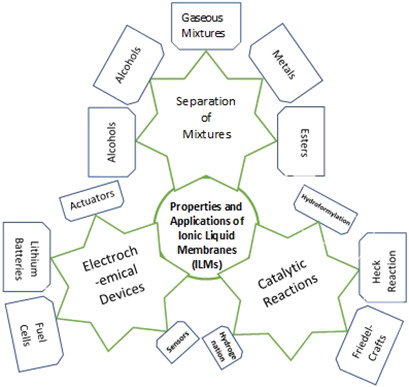
Flue gas emissions and its harmful effects demand the separation and capture of these gases. This paper provides a detailed insight into the recent developments and applications of ionic liquid membranes for gas separation including their applications, issues, challenges, computational study, and future perspectives for the separation of various mixed gases systems.
Impact of Organic Solvents on Physicochemical Properties of Nanofiltration and Reverse-Osmosis Membranes
- First Published: 20 August 2019
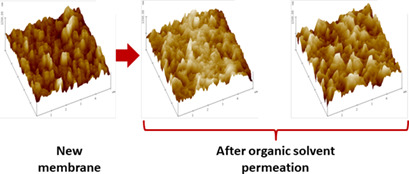
The effect of pretreatment with ethanol and n-hexane permeation on the physicochemical and morphological properties of different commercial nanofiltration and reverse-osmosis membranes was evaluated to assess membrane performance and stability. The selectivity of the membrane depended not only on the pore size, but also to a great extent on the interaction between solvent and polymer.
Hydrogen Production via Load-Matched Coupled Solar-Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolysis Using Aqueous Methanol
- First Published: 17 July 2019
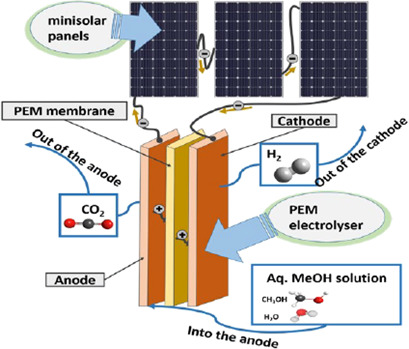
Application of a directly coupled load-matched solar-proton exchange membrane electrolysis using aqueous methanol instead of water for hydrogen production has been investigated and compared. The efficiency was subsequently employed in a process simulation to estimate costs in scaled-up systems. Aqueous methanol had a positive impact on hydrogen production rates and overall yields.
Homogeneous Catalyst Recycling and Separation of a Multicomponent Mixture Using Organic Solvent Nanofiltration
- First Published: 10 July 2019
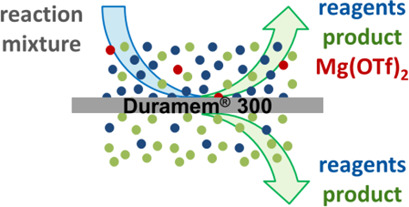
Organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) has become a promising alternative to common recycling methods in homogeneous catalysis. Its applicability was tested with the commercial Evoniks DuraMem® 300 membrane, optimal solvent compositions were identified, and standard parameters were determined. OSN with such a membrane proved to be well-suited for catalyst recycling.
Effect of Silica Nanoparticles on the Performance of Polysulfone Membranes for Olefin-Paraffin Separation
- First Published: 21 June 2019

The effect of silica nanoparticles on improving olefin-paraffin separation of polysulfone membranes was investigated. Ethylene/ethane and propylene/propane were separated using polysulfone-silica nanocomposite membranes. The addition of silica nanoparticles to the polysulfone membrane increased the permeability, selectivity, and solubility coefficient, and reduced the diffusion coefficient.
Impact of Solute Properties and Water Matrix on Nanofiltration of Pesticides
- First Published: 28 May 2019
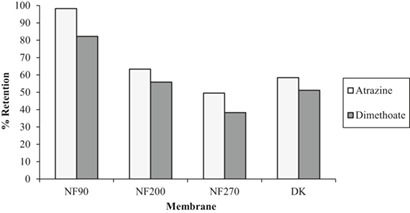
Different nanofiltration membranes are evaluated for the separation of the pesticides atrazine and dimethoate from different water matrix solutions. Dissolving the pesticides in river or tap water amplified the overall pesticide retention performance. However, for this case a lower flux is obtained as compared to the case when the pesticides are dissolved in either distilled or deionized water.
Investigation of Fouling Mechanisms Using Surface Morphology and Physicochemical Membrane Features
- First Published: 09 April 2019
There are few mathematical models regarding the prediction of fouling by the nonclassical mechanism. Membrane fouling and blocking mechanisms for mixed-matrix membranes were evaluated using the Hermia and combined pore blocking models. This investigation can support recommendations on recognition of appropriate arrangements for developing more effective membrane synthesis methods.
Application of Water-Swollen Thin-Film Composite Membrane in Flue Gas Purification
- First Published: 04 April 2019
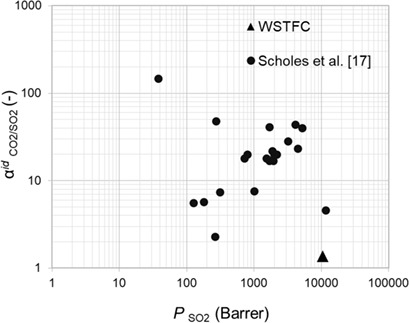
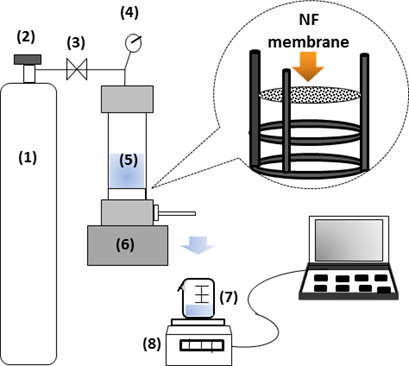
An alternative possibility for the purification of power plant flue gas by using a water-swollen thin-film composite membrane is presented. The membrane is able to separate SO2 and CO2 from flue gas under wet conditions. To test this membrane, a unique experimental apparatus had to be developed and is introduced herein.
Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Applied to Colored Reactive or Disperse Dye Solutions
- First Published: 25 February 2019
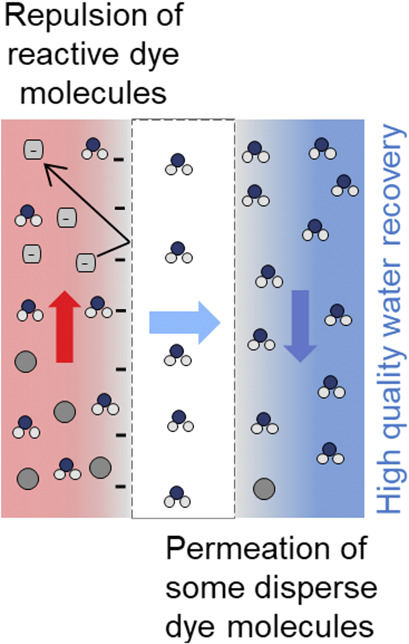
Dye classes provide different results of permeability in direct contact membrane distillation as demonstrated by using a commercial polypropylene flat-sheet membrane in the treatment of reactive and disperse dye solutions. Reactive and disperse dye solutions with different colors in direct contact membrane distillation for the treatment of dyeing wastewater were compared for the first time.
Separation of Trimethyl Borate from a Liquid Mixture by Pervaporation
- First Published: 18 January 2019
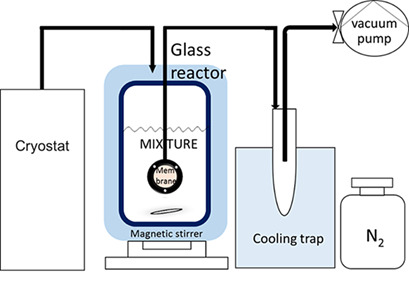
Separation of methanol/trimethyl borate using industrial membranes was performed, with PERVAPTM 4155-30 reaching the best separation results from all tested membranes. Due to the strong affinities of these membranes to different compounds, methanol preferentially passed through PERVAPTM 4155-30 whereas trimethyl borate was favorably pervaporated from the mixture by PERVAPTM 4060.
Amoxicillin Extraction from Aqueous Solution by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Response Surface Methodology
- First Published: 18 October 2018
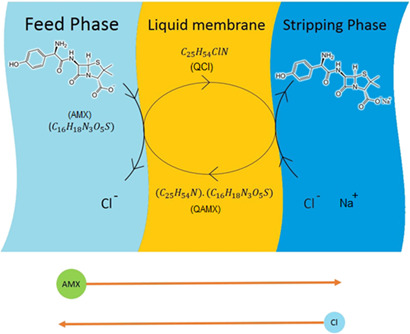
The antibiotic amoxicillin is hardly decomposed and difficult to remove from aquatic solutions. An innovative method of amoxicillin extraction using emulsion liquid membranes is proposed. The effects of process parameters on extraction using response surface methodology were evaluated. Under optimized conditions, an extraction yield of 99.8 % was achieved using the emulsion liquid membrane process.
Polyvinyl Butyral/Modified SiO2 Nanoparticle Membrane for Gasoline Desulfurization by Pervaporation
- First Published: 28 September 2018

PVB/SiO2 membranes were prepared using a coupling agent to covalently link inorganic SiO2 particles and organic PVB polymers. Crosslinking improves the compatibility between the inorganic and organic phases and avoids the generation of membrane defects. The composite membranes displayed superior performance for the removal of organosulfur compounds from fluid catalytic cracking gasoline.
Transient Simulation of Hollow-Fiber Membrane Filtration with Nonuniform Permeability Distribution
- First Published: 21 September 2018
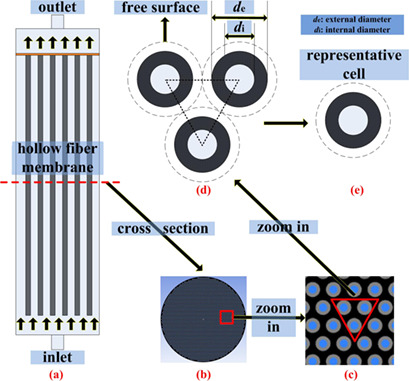
Despite its great significance, membrane engineering receives less attention than the membrane materials. Herein, the focus is on evaluating the time-dependent filtration process in hollow-fiber membranes (HFM) with various kinds of nonuniform permeability distributions. New understanding of fluid flow and fouling behavior in the HFM system is proposed.
Facile CO2 Separation in Composite Membranes
- First Published: 31 July 2018
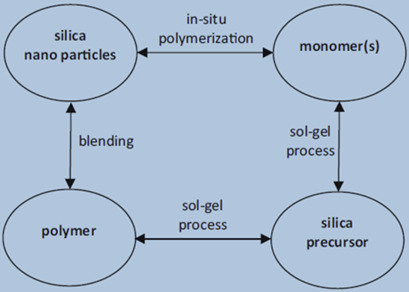
Membrane technology is considered as an efficient, environmentally friendly, and inexpensive technology for CO2 separation. Various approaches to improve membrane performance are reviewed with the focus on permeability and selectivity parameters. Polymer-inorganic nanocomposite membranes, metal organic frameworks, and ionic liquid mixed-matrix membranes are also discussed and evaluated.
Temperature Effects on Concentration Polarization Thickness in Thin-Film Composite Reverse Osmosis Membranes
- First Published: 19 July 2018
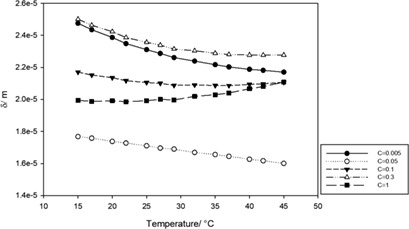
One of the factors that can help assess the performance of reverse osmosis membranes is the thickness of the concentration polarization (CP) layer. The effect of temperature on the thickness of the CP layer that forms on the surface of thin-film composite seawater reverse osmosis membranes has been investigated for a temperature range of 15–45 °C using a number of different polyamide concentrations.
Response Surface Optimization of Dysprosium Extraction Using an Emulsion Liquid Membrane Integrated with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
- First Published: 22 May 2018
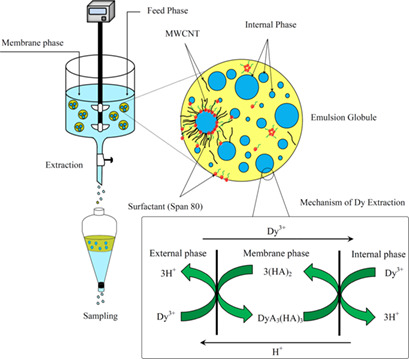
An innovative emulsion liquid membrane was prepared by integrating multi-walled carbon nanotubes for extraction of a rare earth element. The parameters were optimized by response surface methodology and a regression model was developed. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes in conjunction with surfactants stabilize the emulsion and the extraction efficiency can be promoted due to the enhanced stability.
Water Flux Reduction in Microfiltration Membranes: A Pore Network Study
- First Published: 18 May 2018
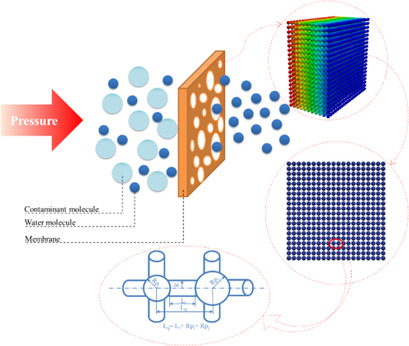
The flow of contaminated water through membranes causes fouling and leads to changes in the membrane transport properties. Understanding how these properties change during operation is critical for evaluating membrane performance. Herein, water flux reduction through a polysulfone membrane was modeled, and after validation of the model with experimental data, different properties were studied.









