Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Biosensing with Fluorescent Carbon Nanotubes
- First Published: 03 January 2022
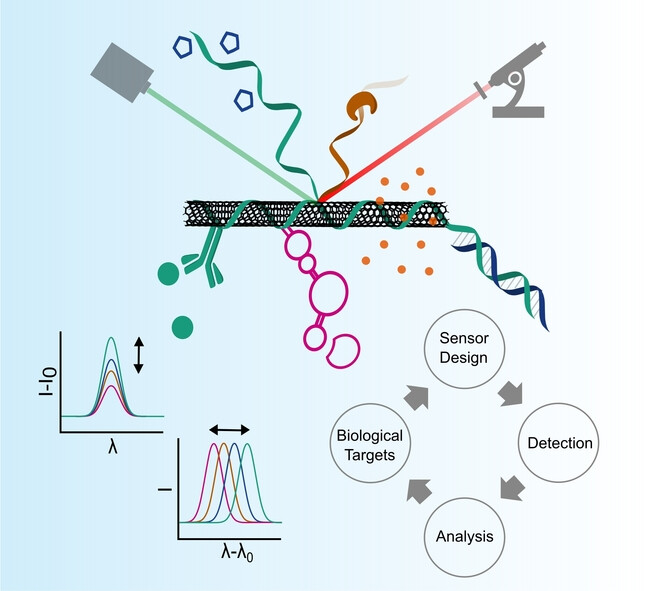
Optical biosensors are important tools for basic research and non-invasive diagnostics. Carbon nanotubes are versatile near-infrared fluorescent and non-bleaching materials that can be chemically functionalized to detect a broad variety of biomolecules. This Review highlights chemical design strategies and provides a comprehensive overview of the recent developments in this dynamic field.
The Chemistry of Organic Contrast Agents in the NIR-II Window
- First Published: 06 December 2021
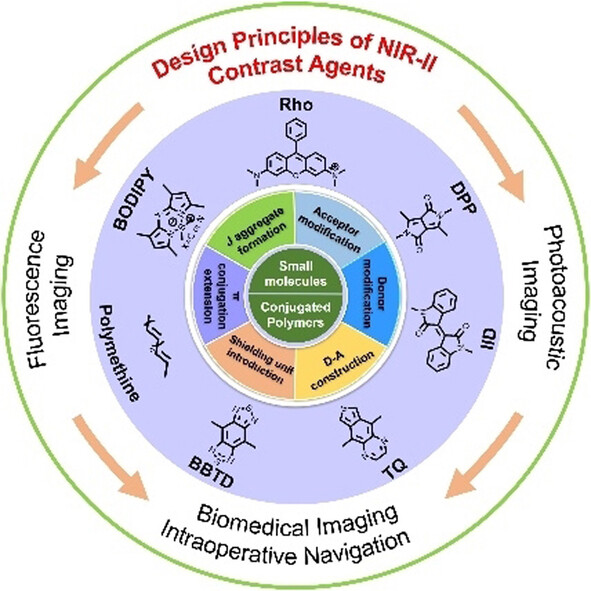
Organic fluorophores in the second near-infrared (NIR-II) range have been validated as attractive imaging tools in biomedical research owing to their biocompatibility, flexible chemical structure, and tunable spectra. This Review systematically summarizes recent advances in the chemistry, design principles, and optical properties of NIR-II organic contrast agents.
Nucleic Acid Aptamers for Molecular Diagnostics and Therapeutics: Advances and Perspectives
- First Published: 13 April 2020

Advantages of aptamers and SELEX in diverse research fields are summarized in this Minireview, along with some limitations and possible solutions to them. Furthermore described are future perspectives for aptamer modification with a near-infinite number of molecular-modulating elements that will result in more powerful tools in bioscience.
Activity-Based NIR Enzyme Fluorescent Probes for the Diagnosis of Tumors and Image-Guided Surgery
- First Published: 16 September 2020
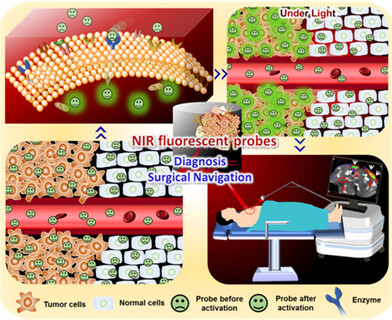
Near-infrared enzyme-activatable fluorescent probes have been considered to be an effective tool for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors. This review focuses on the design strategy of enzyme-activated fluorescent probes, the development of biological applications and new multifunctional probes as well as the direction of clinical transformation.
Aggregation-Induced Emission: Recent Advances in Materials and Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 03 March 2020
Fluorogens with aggregation-induced emission (AIEgens) have stimulated the development of AIE molecular probes and AIE nanoparticle probes for various biomedical applications. This Review reveals how the AIE probes have evolved with the development of new multifunctional AIEgens, and how new strategies have been developed to overcome the limitations of traditional AIE probes for more translational applications.
Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials for Photothermal Therapy
- First Published: 04 February 2020
Cancer therapy: Recent progress in 2D nanomaterials for photothermal therapy including their optical properties, synthesis methods, surface modification, and applications is reviewed. The unique properties and advantages of 2D nanomaterials have been successfully used in photothermal therapy and combined photothermal therapy. This application will continue to be attractive and needs further exploration.
Molecular Engineering of NIR-II Fluorophores for Improved Biomedical Detection
- First Published: 11 August 2020
Fluorescence imaging in the NIR-II window has become a powerful method for biomedical research owing the combined merits of diminished background fluorescence and deep tissue penetration. NIR-II fluorophores occupy a central position in this technology. This review discusses the strategies applied in the design of NIR-II fluorophores and NIR-II fluorescent probes.
Porphyrin-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 27 January 2020
Activatable Molecular Probes for Second Near-Infrared Fluorescence, Chemiluminescence, and Photoacoustic Imaging
- First Published: 05 March 2020
Activatable probes: Second near-infrared fluorescence, chemiluminescence, and photoacoustic imaging, with their respective advantages of minimized light scattering, eliminated external excitation, and ultrasound detection, have attracted increasing attention for deep-tissue in vivo imaging. This Minireview discusses the molecular design strategies and sensing mechanisms for activatable molecular probes, along with their deep-tissue optical imaging applications.
Innovative Strategies for Hypoxic-Tumor Photodynamic Therapy
- First Published: 29 May 2018
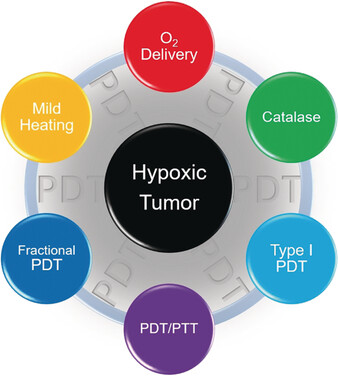
PDT beats hypoxia: Novel and robust strategies, which can improve the therapeutic efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) for hypoxic tumors, have been widely investigated in recent years. These efforts have led to the development of new approaches that have changed the paradigm of PDT and provided solutions to some key problems.
Optochemical Control of Biological Processes in Cells and Animals
- First Published: 18 May 2017
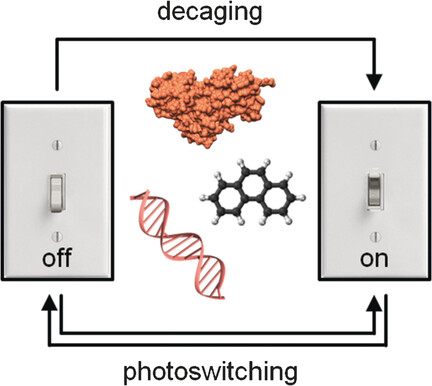
Light the way: Chemical tools have found broad applications in biology for investigating cellular processes. By combining these tools with light as an external trigger, high spatial and temporal precision can be achieved. This Review highlights recent developments in optochemical tools that can be irreversibly or reversibly controlled, with a focus on applications in cells and animals.
Deuterium- and Tritium-Labelled Compounds: Applications in the Life Sciences
- First Published: 16 August 2017
Biocatalytic Oxidation Reactions: A Chemist's Perspective
- First Published: 23 March 2018
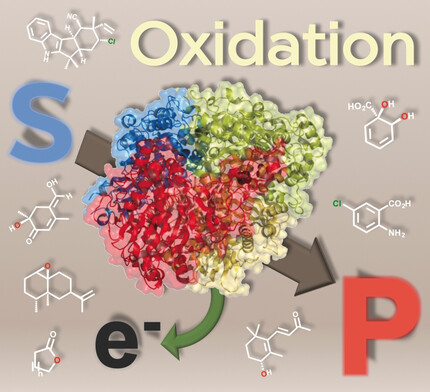
Oxidoreductases enable highly selective and efficient transformations, ranging from simple alcohol oxidations to stereoselective halogenations of non-activated C−H bonds. This Review summarises the most important recent developments in the field of biocatalytic oxidation chemistry and identifies the most pressing bottlenecks as well as promising solutions.
Chemodynamic Therapy: Tumour Microenvironment-Mediated Fenton and Fenton-like Reactions
- First Published: 26 July 2018
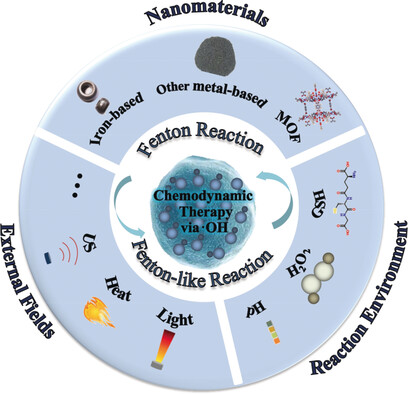
Radical approach: Recent rapid developments in chemodynamic therapy using the Fenton or Fenton-like reactions to generate .OH at tumour sites are discussed in depth in this Minireview. Emphasis is placed on the strategies designed to enhance therapeutic efficiency, providing guidelines for potential clinical translation.
Polyoxometalates as Potential Next-Generation Metallodrugs in the Combat Against Cancer
- First Published: 12 June 2018
Advanced Photosensitizer Activation Strategies for Smarter Photodynamic Therapy Beacons
- First Published: 11 June 2018
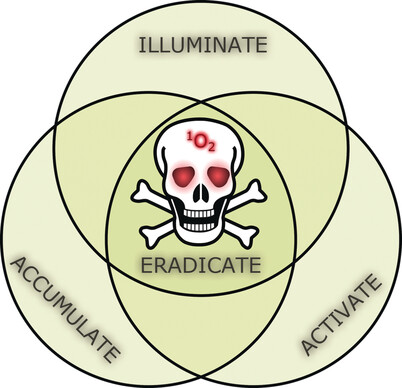
Extreme specificity: Photodynamic therapy beacons are phototoxic drugs that are only cytotoxic upon tissue accumulation, analyte-driven activation, and external illumination. Moreover, their cytotoxic state simultaneously provides optical feedback to monitor treatment. In this Minireview, recent developments on how these beacons are becoming smarter still are discussed.
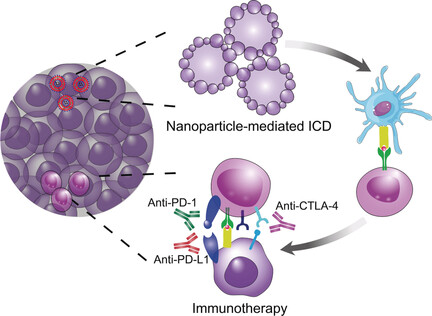
Nanoparticle-Mediated Immunogenic Cell Death Enables and Potentiates Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 17 July 2018
Nonribosomal Peptide Synthesis—Principles and Prospects
- First Published: 21 March 2017
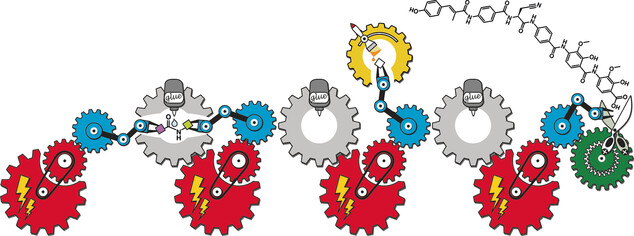
Size does not matter: Nonribosomal peptides (NRPs) are assembled by large multienzyme machineries and represent a structurally highly diverse class of natural products with various bioactivities. This Review provides a thorough overview of NRPs, including their bioactivities, biosynthesis pathways, and their structural variation through biocombinatorial approaches.
From Anthramycin to Pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD)-Containing Antibody–Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
- First Published: 15 November 2016
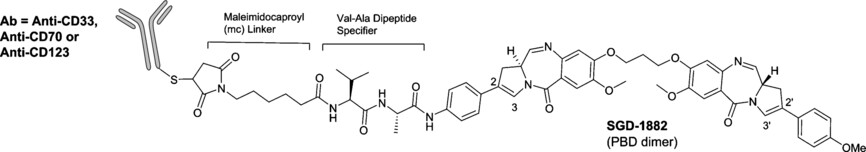
PBDs as payloads for ADCs: The pyrrolobenzodiazepines (PBDs) are a family of DNA-interactive antitumor agents that bind to guanine bases in the DNA minor groove in a sequence-selective manner. They have potent cytotoxicity, and are being used as payloads for antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs). This Review outlines their development from the discovery of the natural product anthramycin through to the use of PBD dimer payloads in ADCs.
New Modalities for Challenging Targets in Drug Discovery
- First Published: 10 February 2017
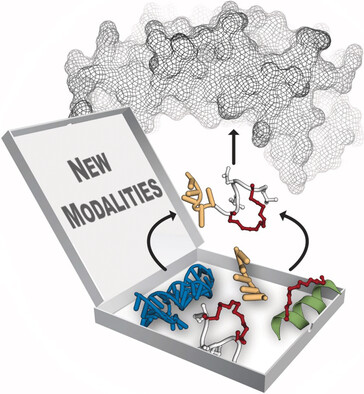
Out of the box: A new generation of molecules, including novel peptides, oligonucleotides, hybrids, and molecular conjugates, is enabling novel strategies to address challenging targets and biological processes at the center of cell regulation. This Review defines these “new modalities”, and highlights how progress in this area is now leading to a range of novel drug candidates.