Deuterium- and Tritium-Labelled Compounds: Applications in the Life Sciences
Corresponding Author
Dr. Jens Atzrodt
Isotope Chemistry and Metabolite Synthesis, Integrated Drug Discovery, Medicinal Chemistry, Industriepark Höchst, G876, 65926 Frankfurt, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Volker Derdau
Isotope Chemistry and Metabolite Synthesis, Integrated Drug Discovery, Medicinal Chemistry, Industriepark Höchst, G876, 65926 Frankfurt, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. William J. Kerr
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, WestCHEM, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, Scotland, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Marc Reid
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, WestCHEM, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, Scotland, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Jens Atzrodt
Isotope Chemistry and Metabolite Synthesis, Integrated Drug Discovery, Medicinal Chemistry, Industriepark Höchst, G876, 65926 Frankfurt, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Volker Derdau
Isotope Chemistry and Metabolite Synthesis, Integrated Drug Discovery, Medicinal Chemistry, Industriepark Höchst, G876, 65926 Frankfurt, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. William J. Kerr
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, WestCHEM, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, Scotland, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Marc Reid
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, WestCHEM, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, Scotland, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
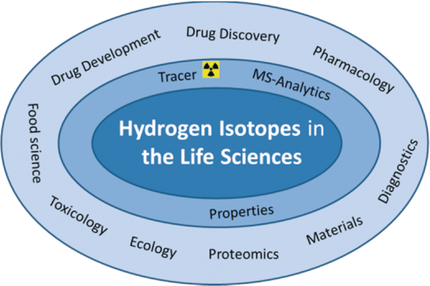
Hydrogen isotopes are unique tools for identifying and understanding biological and chemical processes. Hydrogen isotope labelling allows for the traceless and direct incorporation of an additional mass or radioactive tag into an organic molecule with almost no changes in its chemical structure, physical properties, or biological activity. Using deuterium-labelled isotopologues to study the unique mass-spectrometric patterns generated from mixtures of biologically relevant molecules drastically simplifies analysis. Such methods are now providing unprecedented levels of insight in a wide and continuously growing range of applications in the life sciences and beyond. Tritium (3H), in particular, has seen an increase in utilization, especially in pharmaceutical drug discovery. The efforts and costs associated with the synthesis of labelled compounds are more than compensated for by the enhanced molecular sensitivity during analysis and the high reliability of the data obtained. In this Review, advances in the application of hydrogen isotopes in the life sciences are described.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1J. Yang, Deuterium: Discovery and Applications in Organic Chemistry, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016.
10.1016/B978-0-12-811040-9.00002-3 Google Scholar
- 2M. Larance, A. I. Lamond, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 269–280.
- 3
- 3aS. L. Harbeson, R. D. Tung, MedChem News 2014, 2, 8–22;
- 3bT. G. Gant, J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3595–3611;
- 3cN. A. Meanwell, J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2529–2591.
- 4W. J. S. Lockley, A. McEwen, R. Cooke, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2012, 55, 235–257.
- 5
- 5aC. S. Elmore, R. A. Bragg, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 167–171;
- 5bC. N. Filer, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 96–109;
- 5cP. Uhl, G. Fricker, U. Haberkorn, W. Mier, Drug Discovery Today 2015, 20, 198–208.
- 6R. Voges, R. Heys, T. Moenius, Preparation of Compounds labeled with Tritium and Carbon-14, Wiley, Chichester, UK, 2009.
10.1002/9780470743447 Google Scholar
- 7“Synthesis of radiolabelled compounds for clinical studies”: J. Atzrodt, J. Allen in Drug Discovery and Evaluation; Methods in Clinical Pharmacology (Eds.: ), Springer, Heidelberg, 2010, pp. 105–118.
- 8J. Atzrodt, V. Derdau, T. Fey, J. Zimmermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7744–7765; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7890–7911.
- 9
- 9aW. J. S. Lockley, J. R. Heys, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 635–644;
- 9bT. Junk, W. J. Catallo, Chem. Soc. Rev. 1997, 26, 401–406;
- 9cN. Elander, J. R. Jones, S.-Y. Lu, S. Stone-Elander, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 239–249;
- 9dM. Siskin, A. Katritzky, Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 825–835;
- 9eJ. R. Heys, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 716–721;
- 9fY. Sawama, Y. Monguchi, H. Sajiki, Synlett 2012, 23, 959–972.
- 10
- 10aM. Hatano, T. Nishimura, H. Yorimitsu, Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3674–3677;
- 10bW. Bai, K. H. Lee, S. K. S. Tse, K. W. Chan, Z. Lin, G. Jia, Organometallics 2015, 34, 3686–3698;
- 10cS. Ma, G. Villa, P. S. Thuy-Boun, A. Homs, J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 734–737; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 753–756;
- 10dN. Modutlwa, T. Maegawa, Y. Monguchi, H. Sajiki, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 686–692.
- 11
- 11aD. Hesk, C. F. Lavey, P. McNamara, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 722–730;
- 11bM. R. Chappelle, C. R. Hawes, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 745–751;
- 11cC. N. Filer, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 739–744;
- 11dS. R. Pollack, D. J. Schenk, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 433–441;
- 11eV. P. Shevchenko, I. Y. Nagaev, N. F. Myasoedov, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 693–703.
- 12J. Atzrodt, V. Derdau, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 674–685.
- 13J. Atzrodt, V. Derdau, W. J. Kerr, M. Reid, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708903; Angew. Chem., https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201708903.
- 14 Isotope Effects in Chemistry and Biology (Eds.: ), CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2006.
- 15R. A. M. O'Ferrall, J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2010, 23, 572–579.
- 16
- 16aK. B. Wiberg, Chem. Rev. 1955, 55, 713–743;
- 16bF. H. Westheimer, Chem. Rev. 1961, 61, 265–273;
- 16cJ. P. Klinman, J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2010, 23, 606–612.
- 17K. C. Westaway, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 989–1005.
- 18
- 18aG.-B. Shen, K. Xia, X.-T. Li, J.-L. Li, Y.-H. Fu, L. Yuan, X.-Q. Zhu, J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 1779–1799;
- 18bD. Roston, Z. Islam, A. Kohen, Molecules 2013, 18, 5543–5567;
- 18cJ. P. Klinman, A. Kohen, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 471–496.
- 19D. Wade, Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1999, 117, 191–217.
- 20
- 20aY. Fang, S. MacMillar, J. Eriksson, M. Kolodziejska-Huben, A. Dybala-Defratyka, P. Paneth, O. Matsson, K. C. Westaway, J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 4742–4747;
- 20bK. C. Westaway, Y. Fang, S. MacMillar, O. Matsson, R. A. Poirier, S. M. Islam, J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 8110–8120.
- 21
- 21aK. A. Manning, B. Sathyamoorthy, A. Eletsky, T. Szyperski, A. S. Murkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20589–20592;
- 21bD. A. Singleton, A. A. Thomas, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9357–9358;
- 21cD. A. Singleton, M. J. Szymanski, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9455–9456.
- 22S. Lu, W.-W. Li, D. Rotem, E. Mikhailova, H. Bayley, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 921–928.
- 23
- 23aA. Pabis, R. Kaminski, G. Ciepielowski, S. Jankowski, P. Paneth, J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 8033–8035;
- 23bJ. Chan, A. R. Lewis, M. Gilbert, M.-F. Karwaski, A. J. Bennet, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 405–407.
- 24
- 24aP. Liuni, E. Olkhov-Mitsel, A. Orellana, D. J. Wilson, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3758–3764.
- 25M. P. Meyer in Advances in Physical Organic Chemistry, Vol. 46 (Eds.: ), Elsevier, London, 2012, pp. 57–114.
- 26G. Parkin, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 1088–1114.
- 27E. M. Simmons, J. F. Hartwig, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3066–3072; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 3120–3126.
- 28T. Giagou, M. P. Meyer, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 10616–10628.
- 29
- 29aM. Gómez-Gallego, M. A. Sierra, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 4857–4963;
- 29bG. C. Lloyd-Jones, M. P. Munoz, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 1072–1087.
- 30
- 30aS. Hammes-Schiffer, Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 93–100;
- 30bM. H. V. Huynh, T. J. Meyer, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5004–5064;
- 30cA. Fernández-Ramos, J. A. Miller, S. J. Klippenstein, D. G. Truhlar, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4518–4584;
- 30dZ. D. Nagel, J. P. Klinman, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3095–3118;
- 30eD. Antoniou, J. Basner, S. Nunez, S. D. Schwartz, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3170–3187;
- 30fJ. Pu, J. Gao, D. G. Truhlar, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3140–3169.
- 31
- 31aB. R. Ussing, C. Hang, D. A. Singleton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7594–7607;
- 31bJ. B. Thomas, J. R. Waas, M. Harmata, D. A. Singleton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14544–14555;
- 31cY. Oyola, D. A. Singleton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3130–3131.
- 32
- 32aM. Miyashita, M. Sasaki, I. Hattori, M. Saki, K. Tanino, Science 2004, 305, 495–496;
- 32bG. B. Dudley, S. J. Danishefsky, G. Sukenick, Tetrehdron Lett. 2002, 43, 5605–5606.
- 33K. W. Quasdorf, A. D. Huters, M. W. Lodewyk, D. J. Tantillo, N. K. Garg, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1396–1399.
- 34
- 34aE. Vedejs, J. Little, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 748–749;
- 34bJ. Clayden, J. H. Pink, N. Westlund, F. X. Wilson, Tetrehdron Lett. 1998, 39, 8377–8380;
- 34cF. Hammerschmidt, S. Schmidt, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2239–2245;
- 34dD. J. Pippel, G. A. Weisenburger, N. C. Faibish, P. Beak, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4919; see also:
- 34eJ. Atzrodt, V. Derdau, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2005, 48, 171–177.
- 35J. Baldwin, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 947–960.
- 36J. Rinkel, J. S. Dickschat, Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2493–2508.
- 37J. L. Holmes, K. J. Jobst, J. K. Terlouw, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 1115–1123.
- 38
- 38aK. Francis, A. Kohen, Persp. Sci. 2014, 1, 110–120;
10.1016/j.pisc.2014.02.009 Google Scholar
- 38bW. W. Cleland, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 433, 2–12;
- 38cP. F. Cook in Enzyme Mechanism from Isotope Effects, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1991.
- 39
- 39aM. D. Toney, J. N. Castro, T. A. Addington, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2509–2511;
- 39bJ. P. Klinman, Procedia Chem. 2011, 3, 291–305;
10.1016/j.proche.2011.08.037 Google Scholar
- 39cJ. P. Klinman, Biochemistry 2013, 52, 2068–2077.
- 40
- 40aP. F. Fitzpatrick, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 493, 13–25;
- 40bJ. P. Klinman, Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 325–333;
- 40cG. Chowdhury, M. W. Calcutt, F. P. Guengerich, J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8031–8044.
- 41R. H. Hoff, A. C. Henge, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 1026–1038.
- 42H. Gong, S. Zhang, Molecules 2013, 18, 9278–9292.
- 43W. W. Cleland, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 1006–1015.
- 44E. J. Loveridge, E. M. Behiry, J. Guo, R. K. Allemann, Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 292–297.
- 45A. Sen, A. Yahashiri, A. Kohen, Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6462–6468.
- 46F. P. Guengerich, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 70–83.
- 47A. Dudda, G.-U. Kürzel in Drug Discovery and Evaluation Safety and Pharmacokinetic Assays (Eds.: ), Springer, Berlin, 2006, pp. 151–193.
- 48
- 48aS. D. Nelson, W. F. Trager, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1481–1498;
- 48bF. P. Guengerich, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 611–650;
- 48cG. Chowdhury, M. W. Calcutt, L. D. Nagy, F. P. Guengerich, Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9995–10007.
- 49
- 49aF. P. Guengerich, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2013, 56, 428–431;
- 49bA. H. Meyer, A. Dybala-Defratyka, P. J. Alaimo, I. Geronimo, A. D. Sanchez, C. J. Cramer, M. Elsner, Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 12175–12186.
- 50R. Sharma, T. J. Strelevitz, H. Gao, A. J. Clark, K. Schildknegt, R. S. Obach, S. L. Ripp, D. K. Spracklin, L. M. Tremaine, A. D. N. Vaz, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 625–634.
- 51
- 51aN. B. Pestov, I. A. Okkelman, V. V. Shmanai, A. L. Hurski, A. J. Giaccia, M. S. Shchepinov, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 255;
- 51bR. V. Dunn, K. R. Marshall, A. W. Munro, N. S. Scrutton, FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3850.
- 52
- 52aS. Nag, P. Fazio, L. Lehmann, G. Kettschau, T. Heinrich, A. Thiele, M. Svedberg, N. Amini, S. Leesch, A. M. Catafau, J. Hannestad, A. Varrone, C. Halldin, J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 315–320;
- 52bS. Nag, L. Lehmann, G. Kettschau, M. Toth, T. Heinrich, A. Thiele, A. Varrone, C. Halldin, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6634–6641;
- 52cJ. S. Fowler, J. Logan, G.-J. Wang, N. D. Volkow, F. Telang, W. Zhu, D. Franceschi, C. Shea, V. Garza, Y. Xu, Y.-S. Ding, D. Alexoff, D. Warner, N. Netusil, P. Carter, M. Jayne, P. King, P. Vaska, J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46 , 1414–1420;
- 52dR. M. Baldwin, J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46 , 1411–1413.
- 53
- 53aL. Shao, M. C. Hewitt, Drug News Perspect. 2010, 23, 398–404;
- 53bD. J. Kushner, A. Baker, T. G. Dunstall, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 77, 79–88.
- 54
- 54aC. Elison, H. Rapoport, R. Laurson, H. W. Elliott, Science 1961, 134, 1078–1079;
- 54bC. Elison, H. W. Elliott, M. Look, H. Rapoport, J. Med. Chem. 1963, 6, 237–246;
- 54cA. B. Foster, Adv. Drug Res. 1985, 14, 2;
- 54dG. K. Darland, R. Hajdu, H. Kropp, F. M. Kahan, R. W. Walker, W. J. Vandenheuvel, Drug Metab. Dispos. 1986, 14, 668–678;
- 54eM. I. Blake, H. L. Grespi, J. J. Katz, J. Pharm. Sci. 1975, 64, 367–391;
- 54fK. M. Dewar, L. E. Dyck, D. A. Durden, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 2703–2704.
- 55
- 55aB. Halford, Chem. Eng. News 2016, 94, 32–36;
- 55bThe Economist, 2015, September 5;
- 55cR. H. Howland, J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2015, 53, 13–16;
- 55dA. Katsnelson, Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 656;
- 55eR. Schillerstrom, Drug Discovery Dev. 2009, 12, 6–8;
- 55fK. Sanderson, Nature 2009, 458, 269;
- 55gA. T. Yarnell, Chem. Eng. News 2009, 87, 36–39.
- 56More than 300 patent applications have been filed by companies such as Concert, Auspex, Protia, Deuteria, and Deuterx; for selected examples, see:
- 56aS. L. Harbeson, US20140024652, 2014;
- 56bR. D. Tung, US20140018390, 2014;
- 56cR. D. Tung, C. E. Masse US20140018379, 2014;
- 56dA. W. Czarnik, US20140018436, 2014;
- 56eB. Pandya, C. E. Masse, I. R. Silverman US20140005211, 2014;
- 56fC. Ling, G. Chen, G. Chen, Z. Zhang, B. Gao, K. Han, J. Yin, A. Chu, Y. Zhao, X. Mao, Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2411–2419.
- 57K. C. Buteau, J. High Tech. Law 2009, 22, 22–74.
- 58G. S. Timmins, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014, 24, 1067–1075.
- 59M. B. Fisher, K. R. Henne, J. Boer, Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev. 2006, 9, 101–109.
- 60
- 60aJ. Schofield, V. Derdau, J. Atzrodt, P. Zane, Z. Guo, R. van Horn, V. Czepczor, A. Stoltz, M. Pardon, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3831–3842;
- 60bP. W. Manley, F. Blasco, J. Mestan, R. Aichholz, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3231–3239;
- 60cR. A. Stringer, G. W. F. Picard, B. Sohal, O. Kretz, J. McKenna, J. A. Krauser, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 954–962;
- 60dE. J. Velthuisen, T. M. Baughman, B. A. Johns, D. P. Temelkoff, J. G. Weatherhead, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 202–212.
- 61R. D. Tung, Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 491–494.
- 62A. Mullard, Rev. Drug Discovery 2017, 16, 305.
- 63Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. Press Release 2016, October 20, http://www.tevapharm.com/news.
- 64
- 64aConcert Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Press Release 2014, July 8, http://ir.concertpharma.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=858155; L. A. Sabounjian, P. Graham, L. Wu, V. Braman, C. Cheng, J. Liu, J. Shipley, J. Neutel, M. Dao, Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2016, 5, 314–325;
- 64bV. Braman, P. Graham, C. Cheng, D. Turnquist, M. Harnett, L. A. Sabounjian, J. Shipley, Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2013, 2, 53–66;
- 64cX. Tanga, G. Bridsonb, J. Kea, L. Wub, H. Erol, P. Grahamb, C. H. Lina, V. Bramanb, H. Zhaoa, J. F. Liub, Z. Lina, C. Cheng, J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 963, 1–9.
- 65Avanir Pharmaceuticals Inc. Press Release 2015, November 16, http://www.avanir.com/press/.
- 66AVP-786 is an investigational drug product consisting of a combination of deuterated [D6]dextromethorphan and an ultra-low dose of quinidine required as an inhibitor of the enzyme CYP 2D6.
- 67See also: http://ir.concertpharma.com/releases.cfm; http://investor.auspexpharma.com/releases.cfm.
- 68
- 68aF. Maltais, Y. C. Jung, M. Chen, J. Tanoury, R. B. Perni, N. Mani, L. Laitinen, H. Huang, S. Liao, H. Gao, H. Tsao, E. Block, C. Ma, R. S. Shawgo, C. Town, C. L. Brummel, D. Howe, S. Pazhanisamy, S. Raybuck, M. Namchuk, Y. L. Bennani, J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7993–8001;
- 68bG. Xu, B. Lv, J. Y. Roberge, B. Xu, J. Du, J. Dong, Y. Chen, K. Peng, L. Zhang, X. Tang, Y. Feng, M. Xu, W. Fu, W. Zhang, L. Zhu, Z. Deng, Z. Sheng, A. Welihinda, X. Sun, J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1236–1251;
- 68cF. Schneider, M. Hillgenberg, R. Koytchev, R. G. Alken, Drug Res. 2006, 56, 295–300;
- 68dF. Schneider, E. Mattern-Dogru, M. Hillgenberg, R. G. Alken, Drug Res. 2007, 57, 293–298.
- 69
- 69aA. Mullard, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2016, 15, 219–221;
- 69bhttp://deuterx.com/.
- 70A. E. Mutilib, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1672–1689.
- 71R. D. White, A. J. Gandolfi, F. T. Bowden, I. G. Sipes, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1983, 69, 170–178.
- 72R. V. Branchflower, D. S. Nunn, R. J. Highet, J. H. Smith, J. B. Hook, L. R. Pohl, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1984, 72, 159–168.
- 73A. W. Czarnik, J. A. McKinney, US2011/0046236 A1 2011.
- 74A. E. Mutlib, P. Jiang, J. Atherton, L. Obert, S. Kostrubsky, S. Madore, S. Nelson, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1270–1283.
- 75D. Wade, Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1999, 117, 191–217.
- 76
- 76aC. N. Filer, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 1999, 42, 169–197;
- 76bJ. Wieling, Chromatogr. 2002, 55, S 107–S113;
- 76cS. S. Iyer, Z. P. Zhang, G. E. Kellogg, H. T. Karnes, J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2004, 42, 383–387; K. Kato, S. Jingu, N. Ogawa, S. Higuchi, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 24, 237–249.
- 77
- 77aM. I. Churchwell, N. C. Twaddle, L. R. Meeker, D. R. Doerge, J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 825, 134;
- 77bL. Novákova, L. Matysová, P. Solich, Talanta 2006, 68, 908;
- 77cM. E. Swartz, J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 1253.
- 78
- 78aS. Wang, M. Cyronak, E. Yang, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 701–707;
- 78bT. Berg, D. H. Strand, J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 9366–9374.
- 79R. Zhang, C. S. Sioma, R. A. Thompson, L. Xiong, F. E. Regnier, Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3662–3669.
- 80Martin Sandvoss, Sanofi, unpublished results.
- 81
- 81aN. Lindegardh, A. Annerberg, N. J. White, N. P. Day, J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 862, 227–236;
- 81bM. Turowski, N. Yamakawa, J. Meller, K. Kimata, T. Ikegami, K. Hosoya, N. Tanaka, E. R. Thornton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13836–13849;
- 81cA. Valleix, S. Carrat, C. Caussignac, E. Leonce, A. Tchapla, J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 1116, 109–126.
- 82H. Maehr, N. Rochel, H. J. Lee, N. Suh, M. Uskokovic, J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3878–3888.
- 83
- 83aR. P. White, J. E. G. Lipson, J. S. Higgins, Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4287–4293;
- 83bH. Yang, M. Shibayama, R. S. Stein, N. Shimizu, T. Hashimoto, Macromolecules 1986, 19, 1667–1674.
- 84J.-W. Jiang, J. Lan, J.-S. Wang, B. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 054314–054315.
- 85T. D. Nguyen, G. Hukic-Markosian, F. Wang, L. Wojcik, X.-G. Li, E. Ehrenfreund, Z. V. Vardeny, Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 345–352.
- 86M. Shao, J. Keum, J. Chen, Y. He, W. Chen, J. F. Browning, J. Jakowski, B. G. Sumpter, I. N. Ivanov, Y.-Z. Ma, C. M. Rouleau, S. C. Smith, D. B. Geohegan, K. Hong, K. Xiao, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3180.
- 87W. R. Browne, J. G. Vos, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 219, 761–787.
- 88C. C. Tong, K. C. Hwang, J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 3490–3494.
- 89
- 89aP. Wang, F.-F. Wang, Y. Chen, Q. Niu, L. Lu, H.-M. Wang, X.-C. Gao, B. Wei, H.-W. Wu, X. Cai, J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4821–4825;
- 89bT. Abe, A. Myazawa, H. Konno, Y. Kawanishi, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 491, 199–202.
- 90
- 90aC. Bischof, J. Wahser, J. Scholten, S. Trosien, M. Seitz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14334–14335;
- 90bJ. Scholten, G. A. Rosser, J. Wahser, N. Alzakhem, C. Bischof, F. Stog, A. Beeby, M. Seitz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13915–13917.
- 91
- 91aA. M. Krause-Heuer, N. R. Yepuri, T. A. Darwish, P. J. Holden, Molecules 2014, 19, 18604–18617;
- 91bH. Tsuji, C. Mitsui, E. Nakamura, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14870–14872;
- 91cT. A. Darwish, A. R. G. Smith, I. R. Gentle, P.-L. Burn, E. Luks, G. Moraes, M. Gillon, P. J. Holden, M. James, Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 931–935.
- 92F. Sabeth, T. Iimori, N. Ohta, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6984–6986.
- 93
- 93aJ. S. Higgins, Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2016, 7, 1–28;
- 93bM. Shibayama, Polym. J. 2011, 43, 18–34.
- 94
- 94aM. Haertlein, M. Moulin, J. M. Devos, V. Laux, O. Dunne, V. T Forsyth, Methods Enzymol. 2016, 566, 113–149;
- 94bN. R. Zaccai, C. W. Sandlin, J. T. Hoopes, J. E. Curtis, P. J. Fleming, K. G. Fleming, S. Krueger, Methods Enzymol. 2016, 566, 159–210;
- 94cF. Heinrich, Methods Enzymol. 2016, 566, 211–230;
- 94dJ. F. Ankner, W. T. Heller, K. W. Herwig, F. Meilleur, D. A. A. Myles, Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2013, 72, 17.16.1.
10.1002/0471140864.ps1716s72 Google Scholar
- 95
- 95aP. Lesot, O. Lafon, J. Courtieu, P. Berdague, Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 3741–3746;
- 95bK. Kimata, M. Kobayashi, K. Hosoya, T. Araki, N. Tanaka, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 759–762.
- 96
- 96aK.-S. Cheon, M. M. Green, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 961–966;
- 96bM. M. Green, C. Andreola, B. Munoz, M. P. Reidy, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 4063–4065.
- 97S. Cantekin, D. W. R. Balkenende, M. M. J. Smulders, A. R. A. Palmans, E. W. Meijer, Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 42–46.
- 98
- 98aM. M. Green, J.-W. Park, T. Sato, A. Teramoto, S. Lifson, R. L. B. Selinger, J. V. Selinger, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3138–3154;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991102)38:21<3138::AID-ANIE3138>3.0.CO;2-C CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 1999, 111, 3328–3345;10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19991102)111:21<3328::AID-ANGE3328>3.0.CO;2-Z Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 98bJ. van Gestel, Macromolecules 2004, 37, 3894–3898.
- 99
- 99aT. Kawasaki, K. Soai, J. Fluorine Chem. 2010, 131, 525–534;
- 99bT. Kawasaki, M. Shimizu, D. Nishiyama, M. Ito, H. Ozawa, K. Soai, Chem. Commun. 2009, 4396–4398;
- 99cI. Sato, D. Omiya, T. Saito, K. Soai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11739–11740;
- 99dB. Barabás, L. Caglioti, K. Micskei, C. Zucchi, G. Pályi, Origins Life Evol. Biospheres 2008, 38, 317–327;
- 99eT. Kawasaki, Y. Matsumura, T. Tsutsumi, K. Suzuki, M. Ito, K. Soai, Science 2009, 324, 492–495.
- 100
- 100aK. Merz, A. Kupka, Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 1553–1558;
- 100bS. Crawford, M. T. Kirchner, D. Bläser, R. Boese, W. I. F. David, A. Dawson, A. Gehrke, R. M. Ibberson, W. G. Marshall, S. Parsons, O. Yamamuro, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 755–757; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 769–771;
- 100cA. Kupka, V. Vasylyeva, D. W. M. Hofmann, K. V. Yusenko, K. Merz, Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 5966–5971;
- 100dJ. Zhou, Y.-S. Kye, G. S. Harbison, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8392–8393;
- 100eB. C. K. Ip, I. G. Shenderovich, P. M. Tolstoy, J. Frydel, G. S. Denisov, G. Buntkowsky, H.-H. Limbach, J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 11370–11387.
- 101
- 101aC. E. Hughes, K. D. M. Harris, New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 713–716;
- 101bH. Abe, Y. Imai, T. Takekiyo, Y. Yoshimura, J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2834–2839.
- 102
- 102aJ. S. Mugridge, R. G. Bergman, K. N. Raymond, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1182–1183;
- 102bT. Haino, K. Fukuta, H. Iwamoto, S. Iwata, Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 13286–13290;
- 102cD. Rechavi, A. Scarso, J. Rebek, Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7738–7739;
- 102dY. L. Zhao, K. N. Houk, D. Rechavi, A. Scarso, J. Rebek, Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11428–11429;
- 102eY. Liu, R. Warmuth, Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2883–2886.
- 103
- 103aC. Zhao, R. M. Parrish, M. D. Smith, P. J. Pellechia, C. D. Sherrill, K. D. Shimizu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14306–14309;
- 103bY. Liu, R. Warmuth, Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2883.
- 104“Stable Isotope Analysis: General Principles and Limitations”: W. Meier-Augenstein, H. F. Kemp in Wiley Encyclopedia of Forensic Science, Wiley, Hoboken, 2012.
10.1002/9780470061589.fsa1042 Google Scholar
- 105M. Thullner, A. Fischer, H.-H. Richnow, L. Y. Wick, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 441–452.
- 106W. Meier-Augenstein, K. A. Hobson, L. I. Wassenaar, Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 751–767.
- 107
- 107aN. Gentile, R. T. W. Siegwolf, P. Esseiva, S. Doyle, K. Zollinger, O. Delemont, Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 251, 139–158;
- 107b Good Practice guide for stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry (Eds.: ), FIRMS, 2012;
- 107cJ.-P. Godin, J. S. O. McCullagh, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3019–3028;
- 107dS. Benson, C. Lennard, P. Maynard, C. Roux, Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 157, 1–22.
- 108
- 108aL. Zhao, H. Xiao, J. Zhou, L. Wang, G. Cheng, M. Zhou, L. Yin, M. F. McCabe, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3071–3082;
- 108bA. G. West, G. R. Goldsmith, P. D. Brooks, T. E. Dawson, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 1948–1954;
- 108cP. Martín-Gómez, A. Barbeta, J. Voltas, J. Peñuelas, K. Dennis, S. Palacio, T. E. Dawson, J. P. Ferrio, New Phytol. 2015, 207, 914–927.
- 109
- 109aL. Yang, Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2009, 28, 990–1011;
- 109bL. Balcaen, E. Bolea-Fernandez, M. Resano, F. Vanhaecke, Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 894, 7–19;
- 109cI. Rodushkin, E. Engström, D. C. Baxter, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2785–2797.
- 110
- 110aY. Oulhote, B. Le Bot, S. Deguen, P. Glorennec, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 302–312;
- 110bW. Meier-Augenstein, Stable Isotope Forensics: an Introduction to the Forensic Application of Stable Isotope Analysis, Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, 2010;
10.1002/9780470688762 Google Scholar
- 110cC. M. del Rio, N. Wolf, S. A. Carleton, L. Z. Gannes, Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 91–111;
- 110dN. Wolf, S. A. Carleton, C. M. del Rio, Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 17–26;
- 110eW. J. Boecklen, C. T. Yarnes, B. A. Cook, A. C. James, Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 42, 411–440.
- 111
- 111aS. A. Drivelos, C. A. Georgiou, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 38–51;
- 111bY. Zhao, B. Zang, G. Chen, A. Chen, S. Yang, Z. Ye, Food Chem. 2014, 145, 300–305.
- 112
- 112aP. B. Hatzinger, J. K. Böhlke, N. C. Sturchio, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 542–549;
- 112bG. J. Bowen, D. A. Winter, H. J. Spero, R. A. Zierenberg, M. D. Reeder, T. E. Cerling, J. R. Ehleringer, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3442–3450.
- 113
- 113aP. Höhener, X. Yu, J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 129, 54–61;
- 113bM. Elsner, L. Zwank, D. Hunkeler, R. P. Schwarzenbach, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6896–6916;
- 113cT. B. Hofstetter, M. Berg, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 618–627.
- 114
- 114aJ. P. Jasper, B. J. Westenberger, J. A. Spencer, L. F. Buhse, M. Nasr, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 21–30;
- 114bJ. P. Jasper, F. Fourel, A. Eaton, J. Morrison, A. Phillips, Pharm. Technol. 2004, 28, 60–67;
- 114cR. Santamaria-Fernandez, R. Hearn, J.-C. Wolff, Sci. Justice 2009, 49, 102–106.
- 115
- 115aH. A. S. Buchanan, N. NicDaeid, W. Meier-Augenstein, H. F. Kemp, W. J. Kerr, M. Middleditch, Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3350–3356;
- 115bF. A. Idoine, J. F. Carter, R. Sleeman, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3207–3215.
- 116
- 116aS. J. Benson, C. J. Lennard, P. Maynard, D. M. Hill, A. S. Andrew, C. Roux, Sci. Justice 2009, 49, 73–80;
- 116bD. Widory, J. J. Minet, M. Barbe-Leborgne, Sci. Justice 2009, 49, 62–72;
- 116cC. M. Lock, W. Meier-Augenstein, Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 179, 157–162;
- 116dW. Meier-Augenstein, H. F. Kemp, C. M. Lock, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 2011–2016;
- 116eJ. E. Barnette, M. J. Lott, J. D. Howa, D. W. Podlesak, J. R. Ehleringer, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1422–1428.
- 117
- 117aB. Jin, M. Rolle, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 178–186;
- 117bD. Hunkeler, R. Aravena, K. Berry-Spark, E. Cox, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5975–5981;
- 117cR. U. Meckenstock, B. Morasch, C. Griebler, H.-H. Richnow, J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 75, 215–255.
- 118
- 118aX. Zhang, A. L. Gillespie, A. L. Sessions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12580–12586;
- 118bD. L. Valentine, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12565–12566;
- 118cJ. Fang, C. Li, L. Zhang, T. Davis, C. Kato, D. H. Bartlett, Chem. Geol. 2014, 367, 34–38;
- 118dS. S. Dirghangi, M. Pagani, Org. Geochem. 2013, 64, 105–111.
- 119
- 119aJ. J. Middelburg, Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2357–2371;
- 119bC. A. Layman, M. S. Araujo, R. Boucek, C. M. Hammerschlag-Peyer, E. Harrison, Z. R. Jud, P. Matich, A. E. Rosenblatt, J. J. Vaudo, L. A. Yeager, D. M. Post, S. Bearhop, Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 545–562;
- 119cH. B. Vander Zanden, D. X. Soto, G. J. Bowen, K. A. Hobsen, Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 20;
- 119d“Use of stable isotopes to understand food webs and ecosystem functioning in estuaries”: S. Bouillon, D. P. Gillikin, R. M. Connolly, in Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science, Vol. 7 (Eds.: ), Waltham Academic Press, Waltham, 2012, pp. 143–173.
- 120
- 120aK. A. Hobson, L. I. Wassenaar, Tracking Animal Migration with Stable Isotopes, Academic Press, Waltham, MA, USA, 2008;
- 120bA. Kelly, R. Thompson, J. Newton, Sci. Justice 2009, 48, 67–70.
- 121
- 121a“Stable Isotopes and Human Provenancing”: E. J. Bartelink, R. Berry, L. A. Chesson in Advances in Forensic Human Identification (Eds.: ), CRC Press, Bosa Roca, 2014, pp. 157–184;
- 121bE. J. Bartelink, G. E. Berg, M. M. Beasley, L. A. Chesson, Anal. Anthrophol. Pract. 2014, 38, 124–136;
10.1111/napa.12047 Google Scholar
- 121cC. Lehn, A. Rossmann, M. Graw, Sci. Justice 2015, 55, 72–88;
- 121dL. Font, G. van der Peijl, C. van Leuwen, I. van Wetten, G. R. Davies, Sci. Justice 2015, 55, 34–42;
- 121eG. Vautour, A. Poirier, D. Widory, Sci. Justice 2015, 55, 63–71.
- 122
- 122aO. J. Maselli, D. Fritzsche, L. Layman, J. R. McConnell, H. Meyer, Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2013, 49, 387–398.
- 123
- 123aA. Gessler, J. P. Ferrio, R. Hommel, K. Treydte, R. A. Werner, R. K. Monson, Tree Physiol. 2014, 00, 1–23;
- 123bM. M. Savard, Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2007–2113;
- 123cS. W. Leavitt, Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5244–5253;
- 123dG. J. Martin, M. L. Martin, Phytochem. Rev. 2003, 2, 179–190.
- 124
- 124aJ. P. Greenwood, S. Itoh, N. Sakamoto, P. Warren, L. Taylor, H. Yurimoto, Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 79–82;
- 124bJ. Zhang, N. Dauphas, A. M. Davis, I. Leya, A. Fedkin, Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 251–255;
- 124cJ. J. Barnes, I. A. Franchi, M. Anand, R. Tartèse, N. A. Starkey, M. Koike, Y. Sano, S. S. Russell, Chem. Geol. 2013, 337, 48–55.
- 125
- 125aS. Messenger, F. J. Stadermann, C. Floss, L. R. Nittler, S. Mukhopadhyay, Space Sci. Rev. 2003, 106, 155–172;
- 125bN. A. Starkey, I. A. Franchi, M. R. Lee, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 142, 115–131.
- 126
- 126aL. J. Hallis, G. J. Taylor, K. Nagashima, G. R. Huss, A. W. Needham, M. M. Grady, I. A. Franchi, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 97, 105–119;
- 126bJ. P. Greenwood, S. Itoh, N. Sakamoto, E. P. Vicenzi, H. Yurimoto, Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L05203;
- 126cL. A. Leshin, P. R. Mahaffy, C. R. Webster, M. Cabane, P. Coll, P. G. Conrad, P. D. Archer, Jr., S. K. Atreya, A. E. Brunner, A. Buch, J. L. Eigenbrode, G. J. Flesch, H. B. Franz, C. Freissinet, D. P. Glavin, A. C. McAdam, K. E. Miller, D. W. Ming, R. V. Morris, R. Navarro-González, P. B. Niles, T. Owen, R. O. Pepin, S. Squyres, A. Steele, J. C. Stern, R. E. Summons, D. Y. Sumner, B. Sutter, C. Szopa, S. Teinturier, M. G. Trainer, J. J. Wray, J. P. Grotzinger, Science 2013, 341, 1238937.
- 127D. Bockelée-Morvan, U. Calmonte, S. Charnley, J. Duprat, C. Engrand, A. Gicquel, M. Hässig, E. Jehin, H. Kawakita, B. Marty, S. Milam, A. Morse, P. Rousselot, S. Sheridan, E. Wirström, Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 197, 47–83.
- 128Modified from:
- 128ahttp://web.sahra.arizona.edu/;
- 128bM. Z. Bruckner, http://serc.carleton.edu/microbelife/research methods/environ sampling/stableisotopes.html based on C. Kendall, T. B. Coplen, Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1363–1393.
- 129
- 129aE. Stovkis, H. Rosing, J. H. Beijnen, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 401–407;
- 129bA. K. Hewavitharana, J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 359–361.
- 130
- 130aP. J. Taylor, Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 328–334;
- 130bG. Tranfo, A. M. Ciadella, E. Paci, D. Pigini, Prev. Today 2007, 3, 57–64;
- 130cE. Rogatsky, D. Stein, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1757–1759.
- 131
- 131aT. M. Annesley, Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1041–1044;
- 131bT. Sangster, M. Spencer, P. Sinclair, R. Payne, C. Smith, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1361–1364;
- 131cF. Gosetti, E. Mazzucco, D. Zampieri, M. C. Gennaro, J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3929–3937.
- 132
- 132aM. Jemal, Y.-Q. Xia, Curr. Drug Metab. 2006, 7, 491–502;
- 132bR. H. Liu, D.-L. Lin, W.-T. Chang, C. Liu, W.-I. Tsay, J.-H. Li, T.-L. Kuo, Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 618A–626A.
- 133V. Derdau, J. Atzrodt, J. Zimmermann, C. Kroll, F. Brückner, Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 10397–10404.
- 134
- 134aJ. Wu, R. Wiegand, P. LoRusso, J. Li, J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 941, 100–108;
- 134bR. E. Savage, T. Hall, K. Bresciano, J. Bailey, M. Starace, T. C. K. Chan, J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 872, 148–153;
- 134cF. Bai, B. B. Freeman III, C. H. Fraga, M. Fouladi, C. F. Stewart, J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 831, 169–175;
- 134dC. M. Chavez-Eng, M. L. Constanzer, B. K. Matustewski, J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 767, 117–129;
- 134eJ. J. M. A. Hendrikx, H. Rosing, A. H. Schinkel, J. H. M. Schellens, J. H. Beijnen, Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 993–1010.
- 135
- 135aW. Jian, R. W. Edom, Y. Xu, J. Gallagher, N. Weng, J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 3267–3276;
- 135bH. Nomura, J. Ueyama, T. Kondo, I. Saito, K. Murata, T. Iwata, S. Wakusawa, M. Kamijima, J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 941, 109–115;
- 135cS. Arrivault, M. Guenther, S. C. Fry, M. M. F. F. Fünfgeld, D. Veyel, T. Mettler-Altmann, M. Stitt, J. E. Lunn, Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6896–6904;
- 135dP. Li, Y. Gong, H.-K. Lim, W. Jian, R. W. Edom, R. Salter, J. Silva, N. Weng, J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 926, 92–100.
- 136
- 136aJ. Atzrodt, J. Blankenstein, D. Brasseur, S. Calvo-Vicente, M. Denoux, V. Derdau, M. Lavisse, S. Perard, S. Roy, M. Sandvoss, J. Schofield, J. Zimmermann, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5658–5667;
- 136bM. Dasgupta, W. Tang, G. W. Caldwell, Z. Yan, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 2177–2186;
- 136cK. Kozakai, Y. Amada, M. Oshikata, T. Kawase, E. Suzuki, Y. Haramaki, H. Taniguchi, Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 27, 520–529;
- 136dK. Nakamura, A. Watanabe, N. Okudaira, O. Okazaki, K. Sudo, Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 22, 113–118;
- 136eR. L. Walsky, R. S. Obach, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 647–660.
- 137
- 137aT. Berg, M. Karlsen, Å. M. L. Øiestad, J. E. Johansen, H. Liu, D. H. Strand, J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1344, 83–90;
- 137bC. Metcalfe, K. Tindale, H. Li, A. Rodayan, V. Yargeau, Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3179–3185;
- 137cM. Di Rago, M. Chu, L. N. Rodda, E. Jenkins, A. Kotsos, D. Gerostamoulos, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 1–13.
- 138
- 138aT. Piper, C. Emery, M. Saugy, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 433–447;
- 138bM. Thevis, A. Thomas, S. Beuck, A. Butch, J. Dvorak, W. Schänzer, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 507–512;
- 138cT. Piper, A. Thomas, M. Thevis, M. Saugy, Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 717–727;
- 138dU. Flenker, L. N. Geppert, K. Ickstadt, Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 934–941;
- 138eA. T. Cawley, A. V. George, Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 897–911.
- 139
- 139aX. Ye, Z. Kuklenyik, L. L. Needham, A. M. Calafat, J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 831, 110–115;
- 139bB. C. Blount, R. J. Kobelski, D. O. McElprang, D. L. Ashley, J. C. Morrow, D. M. Chambers, F. L. Cardinali, J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 832, 292–301;
- 139cX. Ye, L. J. Tao, L. L. Needham, A. M. Calafat, Talanta 2008, 76, 865–871;
- 139dH. M. Koch, A. M. Calafat, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 2063–2078.
- 140R. A. Rudel, D. E. Camann, J. D. Spengler, L. R. Korn, J. G. Brody, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4543–4553.
- 141
- 141aN. H. Tran, J. Hu, S. L. Ong, Talanta 2013, 113, 82–92;
- 141bR. Loos, R. Carvalho, D. C. Antonio, S. Comero, G. Locoro, S. Tavazzi, B. Paracchini, M. Ghiani, T. Lettieri, L. Blaha, B. Jarosova, S. Voorspoels, K. Servaes, P. Haglund, J. Fick, R. H. Lindberg, D. Schwesig, B. M. Gawlik, Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487; T. Benijts, R. Dams, W. Lambert, A. D. Leenheer, J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1029, 153–159.
- 142
- 142aG. Hopfgartner, A. Lesur, E. Varesio, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 48, 52–61;
- 142bM. Ewles, L. Goodwin, Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1379–1397;
- 142cI. van den Broek, W. M. A. Niessen, W. D. van Dongen, J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 929, 161–179.
- 143
- 143aK. J. Bronsema, R. Bishoff, N. C. van de Merbel, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9528–9535;
- 143bH. Hill, Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 1359–1364.
- 144A. Scherl, Methods 2015, 81, 2–14.
- 145K. J. Bronsema, R. Bishoff, N. C. van de Merbel, J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 893, 1–14.
- 146
- 146aM. Faria, M. S. Halquist, M. Yuan, W. Mylott, Jr., R. G. Jenkins, H. T. Karnes, J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1001, 156–168;
- 146bO. Heudi, S. Barteau, D. Zimmer, J. Schmidt, K. Bill, N. Lehmann, C. Bauer, O. Kretz, Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4200–4207;
- 146cF. Pailleux, F. Beaudry, Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 881–891;
- 146dM. Faria, M. S. Halquist, M. Yuan, W. Mylott, Jr., R. G. Jenkins, H. T. Karnes, J. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1780–1782.
- 147K. Voronin, A. J. Allentoff, S. J. Bonacorsi, Jr., C. Mapelli, S. X. Gong, V. Lee, D. Riexinger, N. Sanghvi, H. Jiang, J. Zeng, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2014, 57, 579–583.
- 148
- 148aS. A. Gerber, J. Rush, O. Stemman, M. W. Kirschner, S. P. Gygi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6940–6945;
- 148bA. N. Kettenbach, J. Rush, S. A. Gerber, Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 175–186;
- 148cW. X. Schulze, B. Usadel, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 491–516.
- 149
- 149aP. H. Marathe, W. C. Shyu, W. G. Humphreys, Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 2991–3008;
- 149bD. Dalvie, Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 1009–1028;
- 149cN. Penner, L. J. Klunk, C. Prakash, Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2009, 30, 185–203;
- 149dS. J. Roffey, R. S. Obach, J. I. Gedge, D. A. Smith, Drug Metab. Rev. 2007, 39, 17–43.
- 150
- 150aJ. Iglesias, L. Sleno, D. A. Volmer, Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 1213–1225;
- 150bC. J. Unkefer, R. A. Martinez, Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 303–307.
- 151
- 151aA. E. Mutlib, S. Chen, J. Shockcor, R. Espina, S. Prakash, L. Gan, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 63–75;
- 151bA. I. Iyer, B. Malhotra, S. Khan, J. Mitroka, S. Bonacorsi, S. C. Waller, J. K. Rinehart, K. Kripalani, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1481–1497.
- 152
- 152aT. A. Bailie, R. Halpin, B. K. Matuszewski, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 1614–1628;
- 152bJ. Ni, J. Rowe, T. Heidelbaugh, S. Sinha, A. Acheampong, Xenobiotica 2007, 37, 205–220.
- 153
- 153aK. Akira, E. Negishi, M. Imachi, T. Hashimoto, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 903–907;
- 153bA. E. Mutlib, S. Chen, J. Shockcor, R. Espina, S. Prakash, L. Gan, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 48–62.
- 154
- 154aD. Q. Liu, C. E. C. A. Hop, M. G. Beconi, A. Maio, S.-H. L. Chiu, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 15, 1832–1839;
- 154bW. Lam, R. Ramanathan, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 13, 345–353;
- 154cD. Q. Liu, C. E. C. A. Hop, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 1–18.
- 155
- 155aL. S. Busenlehner, R. N. Armstrong, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 433, 34–46;
- 155bX. Yan, C. S. Maier, Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 492, 255–271;
- 155cJ. R. Engen, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7870–7875;
- 155dL. Konermann, J. Pan, Y. H. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1224–1234.
- 156
- 156aT. Ikeda, Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 528–537;
- 156bA. F. Stepan, D. P. Walker, J. Baumann, D. A. Price, T. A. Baillie, A. S. Kalgutkar, M. D. Aleo, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1345–1410;
- 156cR. S. Obach, A. S. Kalgutkar, J. R. Soglia, S. X. Zhao, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1814–1822;
- 156dL. Leung, A. S. Kalgutkar, R. S. Obach, Drug Metab. Rev. 2012, 44, 18–33;
- 156eD. C. Evans, A. P. Watt, D. A. Nicoll-Griffith, T. A. Baillie, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 3–16.
- 157A. S. Kalgutkar, D. Dalvie, Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 35–54.
- 158
- 158aK. Huang, L. Huang, R. B. van Breemen, Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3646–3654;
- 158bL. Ma, B. Wen, Q. Ruan, M. Zhu, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1477–1483;
- 158cZ. Yan, G. W. Caldwell, Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6835–6847;
- 158dZ. Yan, N. Maher, R. Torres, G. W. Caldwell, N. Huebert, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3322–3330;
- 158eA. Mutlib, W. Lam, J. Atherton, H. Chen, P. Galatsis, W. Stolle, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3482–3492;
- 158fH. K. Lim, J. Chen, K. Cook, C. Sensenhauser, J. Silva, D. C. Evans, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 1295–1311.
- 159
- 159aT. Yamaoka, Y. Kitamura, J. Pharm. Toxicol. Methods 2015, 76, 83–95;
- 159bD. Defoy, P. M. Dansette, W. Neugebauer, J. R. Wagner, K. Klarskov, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 412–417;
- 159cZ. Yan, N. Maher, R. Torres, N. Huebert, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4206–4214.
- 160
- 160aT. Rousu, O. Pelkonen, A. Tolonen, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 843–855;
- 160bB. Wen, W. L. Fitch, Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 39–55.
- 161
- 161aR. Aebersold, M. Mann, Nature 2003, 422, 198–207;
- 161bS. Plan, R. Aebersold, Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 209–218;
- 161cL. V. Schneider, M. H. Hall, Drug Discovery Today 2005, 10, 353–363;
- 161dK. Gevaert, F. Impens, B. Ghesquire, P. van Damme, A. Lambrechts, J. Vendekerckhove, Proteomics 2008, 8, 4873–4885;
- 161eS. E. Ong, M. Mann, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 252–262.
- 162
- 162aS. Sechi, Y. Oda, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 7, 70–77;
- 162bM. B. Goshe, R. D. Smith, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 7, 101–109;
- 162cB. J. Cargile, J. L. Bundy, A. M. Grunden, J. L. Stephenson, Jr., Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 86–97.
- 163
- 163aS. P. Gygi, B. Rist, S. A. Gerber, F. Turecek, M. H. Gelb, R. Aebersold, Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 994–999;
- 163bW. A. Tao, R. Aebersold, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 110–118.
- 164
- 164aY. Shiio, R. Aebersold, Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 139–145;
- 164bA. S. Haqqani, J. F. Kelly, D. B. Stanimirovic, Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 439, 225–240;
- 164cA. S. Haqqani, M. Nesic, E. Breston, E. Baumann, J. F. Kelly, D. B. Stanimirovic, FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1809–1821.
- 165O. Chahrour, D. Cobice, J. Malone, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 2–20.
- 166
- 166aJ. Li, H. Steen, S. P. Gygi, Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2003, 2, 1198–1204;
- 166bJ. Wu, Q. Lin, T. K. Lim, T. Liu, C.-L. Hew, J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11681–11689;
- 166cJ. Qu, W. J. Jusko, R. M. Straubinger, Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4543–4552;
- 166dJ. Qu, R. M. Straubinger, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2857–2864.
- 167
- 167aA. Rainczuk, M. Condina, M. Pelzing, S. Dolman, J. Rao, N. Fairweather, T. Jobling, A. N. Stephens, J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4074–4088;
- 167bG. Maccarrone, M. Lebar, D. Martins-de-Souza, Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1156, 175–185;
- 167cF. Lottspeich, J. Kellermann, Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 753, 55–64;
- 167dB. Leroy, C. Rosier, V. Erculisse, N. Leys, M. Mergeay, R. Wattiez, Proteomics 2010, 10, 2281–2291.
- 168P. J. Boersema, R. Raijmakers, S. Lemeer, S. Mohammed, A. J. R. Heck, Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 484–494.
- 169
- 169aB. Domon, R. Aebersold, Science 2006, 312, 212–217;
- 169bA.-C. Gingras, M. Gstaiger, B. Raught, R. Aebersold, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 645–665.
- 170
- 170aG. C. McAlister, E. L. Huttlin, W. Haas, L. Ting, M. P. Jedrychowski, J. C. Rogers, K. Kuhn, I. Pike, R. A. Grothe, J. D. Blethrow, S. P. Gygi, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7469–7478;
- 170bT. Werner, I. Becher, G. Sweetman, C. Doce, M. M. Savitski, M. Bantscheff, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7188–7194.
- 171
- 171aS. Y. Ow, M. Salim, J. Noirel, C. Evans, I. Rehman, P. C. Wright, J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5347–5355;
- 171bP. L. Ross, Y. N. Huang, J. N. Marchese, B. Williamson, K. Parker, S. Hattan, N. Khainovski, S. Pillai, S. Dey, S. Daniels, S. Purkayastha, P. Juhasz, S. Martin, M. Bartlet-Jones, F. He, A. Jacobson, D. J. Pappin, Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2004, 3, 1154–1169;
- 171cL. Choe, M. D'Ascenzo, N. R. Relkin, D. Pappin, P. Ross, B. Williamson, S. Guertin, P. Pribil, K. H. Lee, Proteomics 2007, 7, 3651–3660.
- 172
- 172aC. J. Koehler, M. Strozynski, F. Kozielski, A. Treumann, B. Thiede, J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4333–4341;
- 172bM. Ø. Arntzen, C. J. Koehler, A. Treumann, B. Thiede, Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 753, 65–76;
- 172cC. J. Koehler, M. Ø. Arntzen, M. Strozynski, A. Treumann, B. Thiede, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4775–4781.
- 173
- 173aS. E. Ong, B. Blagoeev, I. Kratchmarova, D. B. Kristensen, H. Stehen, A. Pandey, M. Mann, Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2002, 1, 376–386;
- 173bM. Mann, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 7, 952–958.
- 174
- 174aH. C. Harsha, H. Molina, A. Pandey, Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 505–516;
- 174bS. E. Ong, M. Mann, Nat. Protoc. 2008, 1, 2650–2660.
- 175M. Selbach, M. Mann, Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 981–983.
- 176A. Sirvent, O. Vigy, B. Orsetti, S. Urbach, S. Roche, Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2012, 11, 1937–1950.
- 177
- 177aC. C. Wu, M. J. MacCoss, K. E. Howell, D. E. Matthews, J. R. Yates III, Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4951–4959;
- 177bD. B. McClatchy, M. Q. Dong, C. C. Wu, J. D. Venable, J. R. Yates III, J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2005–2010.
- 178N. Rauniyar, D. B. McClatchy, J. R. Yates III, Methods 2013, 61, 260–268.
- 179
- 179aA. J. Claydon, M. D. Thom, J. H. Hurst, R. J. Beynon, Proteomics 2012, 12, 1194–1206;
- 179bA. J. Claydon, R. J. Beynon, Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 759, 179–195.
- 180M. K. Doherty, D. E. Hammond, M. J. Clague, S. J. Gaskell, R. J. Beynon, J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 104–112.
- 181
- 181aA. F. M. Altelaar, J. Munoz, A. J. R. Heck, Nat. Rev. 2013, 14, 35–48;
- 181bI. V. Hinkson, J. E. Elias, Trends Cell. Biol. 2011, 21, 293–303.
- 182
- 182aJ. C. Price, W. E. Holmes, K. W. Li, N. A. Floreani, R. A. Neese, S. M. Turner, M. K. Hellerstein, Anal. Biochem. 2012, 420, 73–83;
- 182bT. Kasumov, S. Ilchenko, L. Li, N. Rachdaoui, R. G. Sadygov, B. Willard, A. J. McGullough, S. Previs, Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 47–55.
- 183
- 183aW. B. Silva, D. M. Daloso, A. R. Fernie, A. Nunes-Nesi, W. L. Araujo, Plant Sci. 2016, 249, 59–69;
- 183bD. Weindl, A. Wegner, K. Hiller, Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 344;
- 183cD. J. Creek, Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 1807–1810;
- 183dC. Bueschl, D. Krska, B. Kluger, R. Schuhmacher, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 27–33.
- 184
- 184aJ. Castro-Perez, S. F. Previs, D. G. Mclaren, J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 159–169;
- 184bE. Heinzle, F. Matsuda, H. Miyagawa, K. Wakasa, T. Nishioka, Plant J. 2007, 50, 176–187.
- 185
- 185aR. Hoekstra, G. A. Nibourg, T. V. van der Hoeven, M. T. Ackermans, T. B. Hakvoort, T. M. van Gulik, W. H. Lamers, R. Elferink, R. A. Chamuleau, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1483–1489;
- 185bD. Mavri-Damelin, L. H. Damelin, S. Eaton, M. Rees, C. Selden, H. J. Hodgson, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 99, 644–651.
- 186
- 186aA. Chokkathukalam, D.-H. Kim, M. P. Barrett, R. Breitling, D. J. Creek, Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 511–524;
- 186bT. W.-M. Fan, P. K. Lorkiewicz, K. Sellers, H. N. B. Moseley, R. M. Higashi, A. N. Lane, Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 366–391.
- 187
- 187aW. B. Dunn, A. Erban, R. J. M. Weber, D. J. Creek, M. Brown, R. Breitling, T. Hankemeier, R. Goodacre, S. Neumann, J. Kopka, M. R. Viant, Metabolomics 2013, 9, 44–66;
- 187bW. B. Dunn, D. I. Broadhurst, H. J. Atherton, R. Goodacre, J. L. Griffin, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 387–426;
- 187cD. S. Wishart, Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1769–1782.
- 188
- 188aB. D. Bennett, J. Yuan, E. H. Kimball, J. D. Rabinowitz, Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1299–1311;
- 188bC. Bueschl, R. Krska, B. Kluger, R. Schuhmacher, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 405, 27–33;
- 188cP. Giavalisco, J. Hummel, J. Lisec, A. C. Inostroza, G. Catchpole, L. Willmitzer, Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9417–9425.
- 189
- 189aP. Giavalisco, K. Koehl, J. Hummel, B. Seiwert, L. Willmitzer, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6546–6551;
- 189bA. D. Hegeman, C. F. Schulte, Q. Cui, I. A. Lewis, E. L. Huttlin, H. Eghbalnia, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6912–6921.
- 190O. Vielhauer, M. Zakhartsev, T. Horn, R. Takors, M. Reuss, J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3859–3870.
- 191
- 191aT. Toyo'oka, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 69, 174–184;
- 191bP. Bruheimer, H. F. N. Kvitvang, S. G. Villas-Boas, J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1296, 196–203;
- 191cS. Szarka, K. Prokai-Tetrai, L. Prokai, Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7033–7040.
- 192
- 192aW. Yuan, K. W. Anderson, S. Li, J. L. Edwards, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2892–2899;
- 192bD. Zeng, S. Li, Chem. Commun. 2009, 3369–3371;
- 192cJ. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Li, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7588–7595.
- 193D. W. Johnson, J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1345–1352.
- 194K. Shimbo, A. Yahashi, K. Hirayama, M. Nakazawa, H. Miyano, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5172–5179.
- 195K. Guo, C. Ji, L. Li, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8631–8638.
- 196
- 196aP. Kang, Y. Mechref, Z. Kyselova, J. A. Goetz, M. V. Novotny, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6064–6073;
- 196bJ. A. Atwood, L. Cheng, G. Alvarez-Manilla, N. L. Warren, W. S. York, R. Orlando, J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 367–374.
- 197K. Guo, L. Li, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3919–3932.
- 198K. Guo, L. Li, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8789–8793.
- 199W. C. Yang, J. Adamec, F. E. Regnier, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5150–5157.
- 200
- 200aD. Herebian, B. Hanisch, F. J. Marner, Metabolomics 2005, 1, 317–324;
- 200bS. K. Lien, H. F. N. Kvitvang, P. Bruheim, J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1247, 118–124.
- 201X. D. Huang, F. E. Regnier, Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 107–114.
- 202H. F. N. Kvitvang, T. Andreassen, T. Adam, S. G. Villas-Boas, P. Bruheim, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2705–2711.
- 203
- 203aD. J. Creek, A. Chokkathukalam, A. Jankevics, K. E. V. Burgess, R. Breitling, M. P. Barrett, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8442–8447;
- 203bR. Peyraud, P. Kiefer, P. Christen, S. Massou, J.-C. Portais, J. A. Vorholt, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4846–4851;
- 203cP. M. Cano, E. L. Jamin, S. Tadrist, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8412–8420.
- 204
- 204aD. Müller, E. Heinzle, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 54–59.
- 205J. M. Buescher et al., Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 189–201.
- 206
- 206aM. R. Antoniewicz, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 48–53;
- 206bJ. D. Young, D. K. Allen, J. A. Morgan, Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1083, 85–108;
- 206cQ. X. Truong, J. M. Yoon, J. V. Shanks, Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1083, 65–83.
- 207U. Sauer, Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 62.
- 208
- 208aL. You, B. Zhang, Y. J. Tang, Metabolites 2014, 4, 142–165;
- 208bJ. K.-H. Tang, L. You, R. E. Blankenship, J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2767.
- 209A. Wegner, J. Meiser, D. Weindl, K. Hiller, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 16–22.
- 210
- 210aK. Hiller, C. Metallo, G. Stephanopoulos, Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1075–1086;
- 210bL. E. Quek, S. Dietmair, J. O. Kromer, L. K. Nielsen, Metab. Eng. 2010, 12, 161–171;
- 210cM. Kohlstedt, J. Becker, C. Wittmann, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 1065–1075.
- 211
- 211aJ. Niklas, K. Schneider, E. Heinzle, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 63–69;
- 211bW. S. Ahn, M. R. Antoniewicz, Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 61–74.
- 212S. M. Turner, J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2006, 53, 75–85.
- 213
- 213aS. Klein, E. Heinzle, Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2012, 4, 261–272;
- 213bF. Chiaradonna, R. M. Moresco, C. Airoldi, D. Gaglio, R. Palorini, F. Nicotra, C. Messa, L. Alberghina, Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 30–51;
- 213cK. Hiller, C. M. Metallo, J. K. Kelleher, G. Stephanopoulos, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6621–6628.
- 214
- 214aM. R. Antoniewicz, D. F. Kraynie, L. A. Laffend, J. Gonzalez-Lergier, J. K. Kelleher, G. Stephanopoulos, Metab. Eng. 2007, 9, 277–292;
- 214bN. J. Kruger, S. K. Masakapalli, R. G. Ratcliffe, J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2309–2323.
- 215T. Fan, A. Lane, R. Higashi, Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 41.
- 216R. A. Scheltema, A. Jankevics, R. C. Jansen, M. A. Swertz, R. Breitling, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2786–2793.
- 217R. C. A. Schellekens, F. Stellard, H. J. Woerdenbag, H. W. Frijlink, J. G. W. Kosterink, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 879–897.
- 218
- 218aS. K. Peng, K. J. Ho, C. B. Taylor, Arch. Pathol. 1972, 94, 81–89;
- 218bP. D. Klein, E. R. Klein, J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1986, 26, 378–382.
- 219
- 219aM. K. Hellerstein, R. A. Hoh, M. B. Hanley, D. Cesar, D. Lee, R. A. Neese, J. M. McCune, J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 956–966;
- 219bR. A. Neese, L. M. Misell, S. Turner, A. Chu, J. Kim, D. Cesar, R. Hoh, F. Antelo, A. Strawford, J. M. McCune, M. Christiansen, M. K. Hellerstein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15345–15350.
- 220
- 220aM. L. Collins, S. Eng, R. Hoh, M. K. Hellerstein, J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 2203–2211;
- 220bP. J. Jones, S. T. Leatherdale, Clin. Sci. 1991, 80, 277–280.
- 221T. Strekalova, M. Evans, A. Chernopiatko, Y. Couch, J. Costa-Nunes, R. Cespuglio, L. Chesson, J. Vignisse, H. W. Steinbusch, D. C. Anthony, I. Pomytkin, K.-P. Lesch, Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 237–244.
- 222
- 222aH. Shimamoto, S. Komiya, J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Hum. Sci. 2003, 22, 311–315;
- 222bA. Raman, D. A. Schoeller, A. F. Subar, R. P. Troiano, A. Schatzkin, T. Harris, D. Bauer, S. A. Bingham, J. E. Everhart, A. B. Newman, F. A. Tylavsky, Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2004, 286, F 394–F401;
- 222cB. T. Messmer, D. Messmer, S. L. Allen, J. E. Kolitz, P. Kudalkar, D. Cesar, E. J. Murphy, P. Koduru, M. Ferrarini, S. Zupo, G. Cutrona, R. N. Damle, T. Wasil, K. R. Rai, M. K. Hellerstein, N. Chiorazzi, J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 755–764.
- 223
- 223aR. Busch, Y.-K. Kim, R. A. Neese, V. Schade-Serin, M. Collins, M. Awada, J. L. Gardner, C. Beysen, M. E. Marino, L. M. Misell, M. K. Hellerstein, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 730–744;
- 223bD. A. Dufner, I. R. Bederman, D. Z. Brunengraber, N. Rachdaoui, F. Ismail-Beigi, B. A. Siegfried, S. R. Kimball, S. F. Previs, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E 1277–1283.
- 224“Proteome Dynamics with Heavy Water—Instrumentations, Data Analysis, and Biological Applications”: T. Kasumov, B. Willard, L. Li, R. G. Sadygov, S. Previs in Recent Advances in Proteomics Research (Ed.: ), InTech, 2015.
- 225H. G. Gasier, J. D. Fluckey, S. F. Previs, Nutrit. Metab. 2010, 7, 31.
- 226I. R. Bederman, S. Foy, V. Chandramouli, J. C. Alexander, S. F. Previs, J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6101–6108.
- 227J. Katanik, B. J. McCabe, D. Z. Brunengraber, V. Chandramouli, F. J. Nishiyama, V. E. Anderson, S. F. Previs, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E 1043–1048.
- 228
- 228aD. Dufner, S. F. Previs, Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 511–517;
- 228bE. C. Rush, P. Chhichhia, A. E. Kilding, L. D. Plank, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 1209–1214.
- 229
- 229aJ. N. Voogt, M. Awanda, E. J. Murphy, G. M. Hayes, R. Busch, M. K. Hellerstein, Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 3058–3062;
- 229bR. Busch, R. A. Neese, M. Awanda, G. M. Hayes, M. K. Hellerstein, Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 3045–3057.
- 230E. S. Jin, J. G. Jones, M. Merritt, S. C. Burgess, C. R. Malloy, A. D. Sherry, Anal. Biochem. 2004, 327, 149–155.
- 231
- 231aA. Avogaro, J. D. Bristow, D. M. Bier, C. Cobelli, G. Toffolo, Diabetes 1989, 38, 1048–1055;
- 231bR. Hovorka, P. Bannister, D. J. A. Eckland, D. Halliday, D. N. Murley, S. E. Rees, M. A. Young, Diabetic Med. 1998, 15, 234–246.
10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199803)15:3<234::AID-DIA564>3.0.CO;2-9 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 232
- 232aR. J. Bateman, L. Y. Munsell, J. C. Morris, R. Swarm, K. E. Yarasheski, D. M. Holtzman, Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 856–861;
- 232bK. G. Mawuenyega, T. Kasten, W. Sigurdson, R. J. Bateman, Anal. Biochem. 2013, 440, 56–62.
- 233M. Di Buono, P. J. H. Jones, L. Beaumier, L. J. Wykes, J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1516–1523.
- 234
- 234aJ. Ecker, G. Liebisch, Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 54, 14–31;
- 234bE. J. Parks, M. K. Hellerstein, J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1651–1660.
- 235
- 235aJ. Ecker, G. Liebisch, M. Englmaier, M. Grandl, H. Robenek, G. Schmitz, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7817–7822;
- 235bJ. M. Collins, M. J. Neville, K. E. Pinnick, L. Hodson, B. Ruyter, T. H. van Dijk, J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1683–1692.
- 236
- 236aJ. J. Kamphorst, J. Fan, W. Lu, E. White, J. D. Rabinowitz, Liquid Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9114–9122;
- 236bP. M. Le, C. Fraser, G. Gardner, W. W. Liang, J. A. Kralovec, S. C. Cunnane, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 241–249.
- 237M. D. Bruss, C. F. Khambatta, M. A. Ruby, I. Aggarwal, M. K. Hellerstein, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E 108–E116.
- 238D. G. McLaren, T. He, S. P. Wang, V. Mendoza, R. Rosa, K. Gagen, J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1150–1161.
- 239R. J. Pawlosky, J. R. Hibbeln, N. Salem Jr, J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 935–943.
- 240R. J. Pawlosky, J. R. Hibbeln, Y. Lin, S. Goodson, P. Riggs, N. Sebring, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 565–572.
- 241
- 241aB. Fielding, Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 342–350;
- 241bX. M. Persson, A. U. Blachnio-Zabielska, M. D. Jensen, J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2761–2765;
- 241cA. S. Bickerton, R. Roberts, B. A. Fielding, L. Hodson, E. E. Blaak, A. J. Wagenmakers, Diabetes 2007, 56, 168–176.
- 242
- 242aP. E. Cogo, A. Gucciardi, U. Traldi, A. W. Hilkert, G. Verlato, V. Carnielli, J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 40, 876–881;
- 242bL. Vedovelli, A. Baritussio, V. P. Carnielli, M. Simonato, P. Giusti, P. E. Cogo, J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 46, 986–992;
- 242cD. G. McLaren, S. P. Wang, S. J. Stout, D. Xie, P. L. Miller, V. Mendoza, J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 276–281.
- 243A. D. Postle, A. N. Hunt, J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 2716–2721.
- 244V. P. Carnielli, L. J. Zimmermann, A. Hamvas, P. E. Cogo, J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, S 29–S37.
- 245A. U. Blachnio-Zabielska, X. M. Persson, C. Koutsari, P. Zabielski, M. D. Jensen, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1134–1140.
- 246
- 246aC. J. DeLong, Y. J. Shen, M. J. Thomas, Z. Cui, J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29683–29688;
- 246bW. Bernhard, C. J. Pynn, A. Jaworski, G. A. Rau, J. M. Hohlfeld, J. Freihorst, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 54–58;
- 246cC. J. Pynn, N. G. Henderson, H. Clark, G. Koster, W. Bernhard, A. D. Postle, J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 399–407.
- 247G. Lappin, M. Rowland, R. C. Garner, Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 419–427.
- 248A. Parr, G. Badman, C. L. Bowen, M. Coffin, M. Gupta, L. Jones, M. Kurtinecz, O. Naderer, E. Travis, J. Zhu, P. Patel, J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 801–805.
- 249
- 249aR. C. A. Schellekens, F. Stellaard, D. Mitrovic, F. E. Stuurman, J. G. W. Kosterink, H. W. Frijlink, J. Controlled Release 2008, 132, 91–98;
- 249bR. C. A. Schellekens, F. Stellaard, G. G. Olsder, H. J. Woerdenbag, H. W. Frijlink, J. G. W. Kosterink, J. Controlled Release 2010, 146, 334–340;
- 249cR. C. A. Schellekens, G. G. Olsder, S. M. C. H. Langenberg, T. Boer, H. J. Woerdenbag, H. W. Frijlink, J. G. W. Kosterink, F. Stellaard, Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 532–540.
- 250
- 250aI. R. Schultz, R. E. Shangraw, Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 42–50;
- 250bA. K. Majumdar, L. Howard, M. R. Goldberg, L. Hickey, M. Constanzer, P. L. Rothenberg, T. M. Crumley, D. Panebianco, T. E. Bradstreet, A. J. Bergman, S. A. Waldman, H. E. Greenberg, K. Butler, A. Knops, I. De Lepeleire, N. Michiels, K. J. Petty, J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 291–300;
- 250cD. J. R. Foster, E. B. Morton, G. Heinkele, T. E. Mürdter, A. A. Smogyi, Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 559–567.
- 251
- 251aG. Lappin, R. Noveck, T. Burt, Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 817–834;
- 251bG. Lappin, C. C. Wagner, O. Langer, N. van de Merbel, Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 357–366;
- 251cY. Sugiyama, S. Yamashita, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2011, 63, 494–502;
- 251dG. Lappin, Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 509–517;
- 251eM. Rowland, Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 385–391.
- 252
- 252aH. Gu, J. Wang, A. F. Aubry, H. Jiang, J. Zeng, J. Easter, J. S. Wang, R. Dockens, M. Bifano, R. Burrell, M. E. Arnold, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4844–4850;
- 252bH. Jiang, J. Zeng, W. Li, M. Bifano, H. Gu, C. Titsch, J. Easter, R. Burell, H. Kandoussi, A.-F. Aubry, M. E. Arnold, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10031–10037;
- 252cR. de Vries, J. W. Smit, P. Hellemans, J. Jiao, J. Murphy, D. Skee, J. Snoeys, J. Sukbuntherng, M. Vliegen, L. de Zwart, E. Mannaert, J. de Jong, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 1, 11;
- 252dE. A. Cannady, A. Aburub, C. Ward, C. Hinds, B. Czeskis, K. Ruterbories, J.-G. Suico, J. Royalty, D. Ortega, B. W. Pack, S. L. Begum, W. F. Annes, Q Lin, D. S. Small, J. Label Compd. Radiopharm. 2016, 59, 238–244.
- 253ICH guideline M3(R2), Non-clinical safety studies for the conduct of human clinical trials and marketing authorisation for pharmaceuticals 2009.
- 254
- 254aD. W. Boulton, S. Kasichayanula, C. F. Keung, M. E. Arnold, L. J. Christopher, X. Xu, F. LaCreta, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 763–768;
- 254bA. Arjomand, Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 519–541;
- 254cD. Higton, M. Seymour, Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 665–672.
- 255D. Schwab, A. Potron, Z. Backholer, B. Lausecker, K. Kawashima, Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 463–473.
- 256G. S. Timmins, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 1393–1398.
- 257
- 257aL. Bonfrate, I. Grattagliano, G. Palasciano, P. Portincasa, Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 3, 12–21;
- 257bB. Braden, B. Lembcke, W. Kukera, W. F. Caspary, Dig. Liver Dis. 2007, 39, 795–805;
- 257cB. Braden, Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 23, 337–352.
- 258I. Grattagliano, B. H. Lauterburg, G. Palasciano, Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 40, 843–850.
- 259B. Riecke, P. Neuhaus, M. Stockmann, Helicobacter 2005, 10, 620–622.
- 260
- 260aT. A. Di Rienzo, G. D'Angelo, V. Ojetti, M. C. Campanala, A. Tortora, V. Cesario, G. Zuccala, F. Franceschi, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 51–58;
- 260bA. Maity, S. Som, C. Ghosh, G. D. Banik, S. B. Daschakraborty, S. Ghosh, S. Chaudhurib, M. Pradhan, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2014, 29, 2251–2255;
- 260cL. Gatta, C. Ricci, A. Tampieri, Gut 2006, 55, 457–462.
- 261
- 261aF. Perri, M. Bellini, P. Portincasa, Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 549–553;
- 261bL. Bonfrate, V. Ruggiero, E. Mossel, Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 44, 78;
- 261cL. A. Szarka, M. Camilleri, A. Vella, Clin. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008, 6, 635–643.
- 262
- 262aY. Ishii, T. Kohno, A. Ito, Pancreas 2007, 35, 313–319;
- 262bM. A. Ritz, R. J. Fraser, A. C. Di Matteo, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 19, 448–453.
- 263
- 263aA. Rocco, G. de Nucci, G. Valente, J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 782–787;
- 263bM. Banasch, M. Ellrichmann, A. Tannapfel, Eur. J. Med. Res. 2011, 16, 258–264;
- 263cT. Shalev, H. Aeed, V. Sorin, Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1589–1598.
- 264R. Roberts, A. S. Bickerton, B. A. Fielding, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 824–831.
- 265
- 265aM. Elsner, M. A. Jochmann, T. B. Hofstetter, D. Hunkeler, A. Bernstein, T. C. Schmidt, A. Schimmelmann, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2471–2491;
- 265bM. Thullner, F. Centler, H.-H. Richnow, A. Fischer, Org. Geochem. 2012, 42, 1440–1460.
- 266
- 266aM. Elsner, J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 2005–2031;
- 266bU. Jaekel, C. Vogt, A. Fischer, H.-H. Richnow, F. Musat, Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 130–140;
- 266cS. Kümmel, R. Starke, G. Chen, F. Musat, H.-H. Richnow, C. Vogt, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3091–3100;
- 266dG. Imfeld, F.-D. Kopinke, A. Fischer, H.-H. Richnow, Chemosphere 2014, 107, 454–461.
- 267
- 267aS. Radajewski, P. Ineson, N. R. Parekh, J. C. Murrell, Nature 2000, 403, 646–649;
- 267bM. G. Dumont, J. G. Murrell, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 499–504;
- 267cY. Chen, J. C. Murrell, Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 157–163; E. L. Madsen in Stable isotope probing and related technologies (Eds.: ), ASM Press, Washington DC, 2010, pp. 165–202.
- 268
- 268aO. Uhlík, K. Ječná, M. Macková, C. Vlček, M. Hroudová, K. Demnerová, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6471–6477;
- 268bF. Z. Haichar, T. Heulin, J. P. Guyonnet, W. Achouak, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 9–13.
- 269
- 269aT. H. Bell, E. Yergeau, C. Martineau, D. Juck, L. G. Whyte, C. W. Greer, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4163–4171;
- 269bH. Roh, C. P. Yu, M. E. Fuller, K. H. Chu, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2505–2011;
- 269cD. H. Buckley, V. Huangyutitham, S. F. Hsu, T. A. Nelson, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3196–3204.
- 270
- 270aM. Kästner, K. N. Nowak, A. Miltner, A. Schäfer, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 73–82;
- 270bZ. T. Aanderud, J. T. Lennon, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4589–4596.
- 271
- 271aA. Fischer, M. Manefield, P. Bombach, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 99–107;
- 271bO. Uhlík, M.-C. Leewis, M. Strejcek, L. Musliva, M. Mackova, M. B. Leigh, T. Macek, Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 154–165.
- 272H. T. S. Boschker, S. C. Nold, P. Wellsbury, D. Bos, W. de Graaf, R. Pel, Nature 1998, 392, 801–805.
- 273J. D. Neufeld, J. Vohra, M. G. Dumont, T. Lueders, M. Manefield, M. W. Friedrich, Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 860–866.
- 274
- 274aT. Lueders, M. G. Dumont, L. Bradford, M. Manefield, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 83–89;
- 274bM. G. Dumont, B. Pommerenke, P. Casper, R. Conrad, Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1153–1167.
- 275
- 275aN. Jehmlich, C. Vogt, V. Lünsmann, H. H. Richnow, M. von Bergen, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 41, 26–33;
- 275bN. Jehmlich, F. Schmidt, M. Taubert, J. Seifert, F. Bastida, M. von Bergen, H. H. Richnow, C. Vogt, Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1957–1966.
- 276
- 276aWikipedia;
- 276bU.S. Department of Energy, DOE Handbook: Tritium Handling and Safe Storage, DOE-HDBK-1129-2007, March 2007;
- 276cHealth Physics Society, Tritium Fact Sheet, March 2011.
- 277M. Saljoughian, P. G. Williams, Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 1029–1056.
- 278
- 278aA. Damont, S. Garcia-Argote, D.-A. Buisson, B. Rousseau, F. Dolléa, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 1–6;
- 278bG. Tóth, J. R. Mallareddy, F. Tóth, A. W. Lipkowski, D. Tourwéc, ARKIVOC 2012, 163–174;
- 278cU. S. Larsen, H. B. Hansen, A.-M. Dahl, L. Sörensen, J. B. Kristensen, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 549–550.
- 279U. Pleiss, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2003, 46, 1241–1247.
- 280
- 280aD. Hesk, P. McNamara, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2007, 50, 875–887;
- 280bM. Saljoughian, Synthesis 2002, 13, 1781–1801.
- 281J. A. Krauser, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2013, 56, 441–446.
- 282
- 282a“Receptor and binding studies”: P. Hein, M. C. Michel, K. Leineweber, T. Wieland, N. Wettschureck, S. Offermanns in Practical Methods in Cardiovascular Research (Eds.: ), Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005, pp. 723–783;
10.1007/3-540-26574-0_37 Google Scholar
- 282bM. McKinney, R. Raddatz, Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2006, 33, 1.3.1.
10.1002/0471141755.ph0103s33 Google Scholar
- 283J. J. Maguire, R. E. Kuc, A. P. Davenport, Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 897, 31–77.
- 284E. C. Hulme, M. A. Trevethick, Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 1219–1237.
- 285
- 285aS. D. Kahl, C. C. Felder, Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2005, 30, 7.15.1;
- 285bN. Bosworth, P. Towers, Nature 1989, 341, 167–168;
- 285cS. Udenfriend, L. Gerber, N. Nelson, Anal. Biochem. 1987, 161, 494–500.
- 286
- 286aD. Harder, D. Fotiadis, Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1569–1578;
- 286bJ. Berry, M. Price-Jones, B. Killian, Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 897, 79–94.
- 287
- 287aJ. F. Glickman, A. Schmid, S. Ferrand, Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2008, 6, 433–455;
- 287bS. Wu, B. Liu, BioDrugs 2005, 19, 383–392.
- 288
- 288aM. Quick, J. A. Javitch, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3603–3608;
- 288bJ.-M. Jeckelmann, D. Harder, S. A. Mari, M. Meury, Z. Ucurum, D. J. Müller, B. Erni, D. Fotiadis, J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 176, 395–403;
- 288cF. Lu, S. Li, Y. Jiang, J. Jiang, H. Fan, G. Lu, D. Deng, S. Dang, X. Zhang, J. Wang, N. Yan, Nature 2011, 472, 243–246;
- 288dM. Quick, L. Shi, B. Zehnpfennig, H. Weinstein, J. A. Javitch, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 207–211;
- 288eZ. Zhou, J. Zhen, N. K. Karpowich, R. M. Goetz, C. J. Law, M. E. A. Reith, D.-N. Wang, Science 2007, 317, 1390–1393.
- 289
- 289aK. J. Dillon, G. C. M. Smith, N. M. B. Martin, J. Biomol. Screening 2003, 8, 347–352;
- 289b“FlashPlate technology”: B. A. Brown, M. Cain, J. Broadbent, S. Tompkins, G. Henrich, R. Joseph, S. Casto, H. Harney, R. Greene, R. Delmondo, in High Throughput Screening: the Discovery of Bioactive Substances (Ed.: ), Marcel Dekker, New York, 1997, pp. 317–328.
- 290
- 290aV. Stepanova, M. Schou, J. Järva, C. Halldin, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007, 65, 293–300;
- 290bS. Hintermann, I. Vranesic, H. Allgeier, A. Brülisauer, D. Hoyer, M. Lamaire, T. Moenius, S. Urwyler, S. Whitebread, F. Gasparini, Y. P. Auberson, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 903–914.
- 291
- 291aC. C. Wagner, O. Langer, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2011, 63, 539–546;
- 291bS. Gross, D. Piwnica-Worms, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 334–342.
- 292
- 292aZ.-M. Yang, Q.-F. Ye, L. Lu, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2008, 51, 182–186; C. Li, X.-Y. Xu, J.-Y. Li, Q.-F. Ye, Z. Li, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2011, 54, 256–259.
- 293B. Schäfer, E. Orbán, Z. Kele, C. Tömbölya, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 7–13.
- 294B. Catalgol, T. Grune, Free Radical Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 8–13.
- 295
- 295aI. Horiuchi, T. Nozawa, N. Fujii, H. Inoue, M. Honda, T. Shimizu, M. Taguchi, Y. Hashimoto, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 976–980;
- 295bS. Raja, K. St George, L. Fan, C. Maring, K. McDaniel, D. DeGoey, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2010, 53, 472–474.
- 296K. M. Giacomini, S.-M. Huang, D. J. Tweedie, L. Z. Benet, K. L. R. Brouwer, X. Chu, A. Dahlin, R. Evers, V. Fischer, K. M. Hillgren, K. A. Hoffmaster, T. Ishikawa, D. Keppler, R. B. Kim, C. A. Lee, M. Niemi, J. W. Polli, Y. Sugiyama, P. W. Swaan, J. A. Ware, S. H. Wright, S. W. Yee, M. J. Zamek-Gliszczynski, L. Zhang, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2010, 9, 215–236.
- 297
- 297aK. Maeno, A. Nakajima, G. Conseil, A. Rothnie, R. G. Deeley, S. P. C. Cole, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1411–1420;
- 297bE. Jigorel, M. Le Vee, C. Boursier-Neyret, M. Bertrand, O. Fardel, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 1418–1422.
- 298E. Smith, I. Collins, Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 159–183.
- 299V. T. G. Chuang, M. Otagiri, Molecules 2013, 18, 13831–13859.
- 300
- 300aY. Xia, L. Peng, Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 7880–7929;
- 300bY. Xia, K. Sengupta, A. Maggiani, F. Qu, L. Peng, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 5000–5005;
- 300cT. Peng, X. Yuan, H. C. Hang, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 144–153.
- 301
- 301aU. Haedke, E. V. Küttler, O. Vosyka, Y. Yang, S. H. L. Verhelst, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 102–109;
- 301bP. P. Geurink, L. M. Prely, G. A. van der Marel, R. Bischoff, H. S. Overkleeft, Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 324, 85–113;
- 301cA. M. Sadaghiani, S. H. L. Verhelst, M. Bogyo, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 20–28;
- 301dD. Robinette, N. Neamati, K. B. Tomer, C. H. Borchers, Expert Rev. Proteomics 2006, 3, 399–408.
- 302
- 302aJ. Das, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 4405–4417;
- 302bL. Dubinsky, B. P. Krom, M. M. Meijler, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 554–570;
- 302cM. S. Panov, V. D. Voskresenska, M. N. Ryazantsev, A. N. Tarnovsky, R. M. Wilson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 19167–19179;
- 302dJ. Liu, C. Liu, W. He, Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 564–579.
- 303
- 303aC. F. Filer, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2009, 281, 521–530;
- 303bD. Jakubczyk, G. Brenner-Weiss, S. Bräse, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 592–597;
- 303cN. S. Kumar, M. P. Braun, A. G. Chaudhary, R. N. Young, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2011, 54, 43–50;
- 303dY. Ambroise, F. Pillon, C. Mioskowski, A. Valleix, B. Rousseau, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 3961–3964.
- 304
- 304aD. J. Lapinsky, D. S. Johnson, Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 2143–2171;
- 304bD. J. Lapinsky, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6237–6247;
- 304cA. L. MacKinnon, J. Taunton, Curr. Protoc. Chem. Biol. 2009, 1, 55–73.
- 305
- 305aT. Tomohiro, S. Morimoto, T. Shima, J. Chiba, Y. Hatanaka, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13502–13505; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 13720–13723;
- 305bS. Morimoto, T. Tomohiro, N. Maruyama, Y. Hatanaka, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1811–1813.
- 306
- 306aS. M. Lamos, C. J. Krusemark, C. J. McGee, M. Scalf, L. M. Smith, P. J. Belshaw, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4329–4333; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 4435–4439;
- 306bZ. Song, W. Suang, Q. Zhang, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3339–3341.
- 307
- 307aT. Bohnert, L.-S. Gan, J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2953–2994;
- 307bG. L. Trainor, Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 2007, 2, 51–64.
- 308
- 308aL. B. Nilsson, Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 3033–3050;
- 308bF. Zhang, J. Xue, J. Shao, L. Jia, Drug Discovery Today 2012, 17, 475–485.
- 309
- 309aB. Buscher, S. Laakso, H. Mascher, K. Pusecker, M. Doig, L. Dillen, W. Wagner-Redeker, T. Pfeifer, P. Delrat, P. Timmerman, Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 673–682;
- 309bF. M. Musteata, Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1753–1768.
- 310
- 310aA. Beattie, S. Madden, C. Lowrie, D. MacPherson, Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 507–511;
- 310bM. Pellegatti, Expert Opin. Drug Metab. 2014, 10, 1615–1620;
- 310cR. E. White, D. C. Evans, C. E. C. A. Hop, D. J. Moore, C. Prakash, S. Surapaneni, F. L. S. Tse, Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 219–225;
- 310dR. S. Obach, A. N. Nedderman, D. A. Smith, Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 226–227;
- 310eR. S. Obach, A. N. Nedderman, D. A. Smith, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 513–531;
- 310fF. P. Guengerich, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 511–512;
- 310gD. Dalvie, Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 1009–1028.
- 311B. K. Park, A. Boobis, S. Clarke, C. E. P. Goldring, D. Jones, J. G. Kenna, C. Lambert, H. G. Laverty, D. J. Naisbitt, S. Nelson, D. A. Nicoll-Griffith, R. S. Obach, P. Routledge, D. A. Smith, D. J. Tweedie, N. Vermeulen, D. P. Williams, I. D. Wilson, T. A. Baillie, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2011, 10, 292–306.
- 312
- 312aJ. Gan, T. W. Harper, M. M. Hsueh, Q. Qu, W. G. Humphreys, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 896–903;
- 312bX. Ma, E. C. Chan, Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 46–55.
- 313T. Usui, M. Mise, T. Hashizume, M. Yabuki, S. Komuro, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2383–2392.
- 314
- 314aS. H. Day, A. Mao, R. White, T. Schulz-Utermoehl, R. Miller, M. G. Beconi, J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2005, 52, 278–285;
- 314bK. Samuel, W. Yin, R. A. Stearns, Y. S. Tang, A. G. Chaudhary, J. P. Jewell, T. Lanza, Jr., L. S. Lin, W. K. Hagmann, D. C. Evans, S. Kumar, J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 38, 211–221.
- 315
- 315aD. L. Nabb, B. Szostek, M. W. Himmelstein, M. P. Mawn, M. L. Gargas, L. M. Sweeney, J. C. Stadler, R. C. Buck, W. J. Fasano, Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 100, 333–344;
- 315bA. N. R. Nedderman, M. E. Savage, K. L. White, D. K. Walker, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 34, 607–617.
- 316
- 316aD. Dalvie, R. S. Obach, P. Kang, C. Prakash, C. M. Loi, S. Hurst, A. N. R. Nedderman, L. Goulet, E. Smith, H. Z. Bu, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 357–368;
- 316bL. Xu, C. Woodward, S. Khan, C. Prakash, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 680–693.
- 317
- 317aE. M. Isin, C. S. Elmore, G. N. Nilsson, R. A. Thompson, L. Weidolf, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 532–542;
- 317bN. Penner, L. Xu, C. Prakash, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 513–531;
- 317cD. Zhang, G. Luo, X Ding, C. Lu, Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 549–561;
- 317dP. H. Marathe, W. C. Shyu, W. G. Humphreys, Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 2991–3008.
- 318
- 318aE. G. Solon, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 543–555;
- 318b“Application of quantitative whole body autoradiography (QWBA) in drug discovery and development in ADME”: L. Wang, H. Hong, D. Zhang, in Enabling technologies in drug design and development (Eds.: ), Wiley, Hoboken, 2012, pp. 419–434;
- 318cA. W. Harrell, C. Sychterz, M. Y. Ho, A. Weber, K. Valko, K. Negash, Pharm. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e 00173.
- 319
- 319aJ. H. Beumer, J. H. Beijnen, J. H. M. Schellens, Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 33–58;
- 319bJ. G. Dain, J. M. Collins, W. T. Robinson, Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 925.
- 320
- 320aS. C. Alley, X. Zhang, N. M. Okeley, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 932–938;
- 320bE. Herzog, S. Harris, C. Henson, Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 900–907.
- 321
- 321aE. G. Solon, Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 2007, 2, 503–514;
- 321bA. McEwen, C. Henson, Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 557–568;
- 321cM. J. Potchoiba, M. R. Nocerini, Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1190–1198.
- 322
- 322aU. B. Kompella, R. S. Kadam, V. H. L. Lee, Ther. Delivery 2010, 1, 435–456;
- 322bW. E. Stumpf, J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2005, 51, 25–40;
- 322cH. Chopade, D. Eigenberg, E. Solon, P. Strzemienski, J. Hostetler, T. McNamara, Vet. Ther. 2010, 11, 1–10.
- 323
- 323aN. A. Kulikova, D. P. Abroskin, G. A. Badun, M. G. Chernysheva, V. I. Korobkov, A. S. Beer, E. A. Tsvetkova, S. V. Senik, O. I. Klein, I. V. Perminova, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28869;
- 323bG. A. Badun, Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 161–166.
Citing Literature
February 12, 2018
Pages 1758-1784