Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Highly Stable Aqueous Zinc-Ion Storage Using a Layered Calcium Vanadium Oxide Bronze Cathode (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 15/2018)
- Page: 3837
- First Published: 15 March 2018

A layered calcium vanadium oxide bronze (Ca0.25V2O5 ⋅ nH2O, CVO) has been synthesized to act as the cathode for aqueous zinc-ion battery applications. H. N. Alshareef and co-workers describe in their Communication on page 3943 ff. how the Zn atoms from the anode (silver spheres) move to the CVO cathode during the discharge process to generate energy (shown by the lit lamp). The background shows the Zn element flying out of the periodic table to signify the high capacity reached.
Inside Cover: Metal–Organic Frameworks for High Charge–Discharge Rates in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 15/2018)
- Page: 3838
- First Published: 08 March 2018

MOFs for energy-storage devices When combined with a conductive polymer, the conductivities of metal–organic framework (MOF) based constructs were raised by seven orders of magnitude. F.-S. Ke, H Deng, and co-workers show in their Communication on page 3916 ff. that the cross-linked pores and tunnels in the MOFs functioned as highways for ion transfer across the electrodes, thereby leading to lithium-sulfur batteries that could be charged and discharged at a rate of 16.85 A g−1 over 1000 cycles.
Inside Back Cover: Synthesis and Electronic Structure of Boron-Graphdiyne with an sp-Hybridized Carbon Skeleton and Its Application in Sodium Storage (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 15/2018)
- Page: 4103
- First Published: 08 March 2018

A new class of boron-graphdiyne (BGDY) has been prepared by a bottom-up synthetic strategy. In their Communication on page 3968 ff., C. Huang, Y. Li, and co-workers show BGDY has a unique two-dimensional structure with highly-decorated molecular pores. The sp-hybridized carbon skeleton and evenly distributed boron heteroatoms can stabilize metal atoms intercalated in the BGDY framework. Thus, BGDY shows promising an electrochemical performance in sodium-ion half cells.
Back Cover: High-Flux Membranes Based on the Covalent Organic Framework COF-LZU1 for Selective Dye Separation by Nanofiltration (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 15/2018)
- Page: 4104
- First Published: 09 March 2018

Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with high porosity and well-organized channel structure are attractive candidates for advanced water treatment membranes. In their Communication on page 4083 ff., H. Meng, J. Caro et al. present a two-dimensional imine-linked COF-LZU1 membrane with a thickness of only 400 nm supported on alumina tubes that was synthesized by an in situ solvothermal method. The membrane exhibits excellent water permeance and high rejection combined with outstanding water stability for water-soluble dyes with a size larger than 1.2 nm.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Alkaline–Acid Zn–H2O Fuel Cell for the Simultaneous Generation of Hydrogen and Electricity
- First Published: 26 March 2018

Energy Storage and Conversion An inexpensive zinc–H2O fuel cell for the highly efficient simultaneous generation of electricity and H2 is proposed by Z. H. Wen et al. in their Communication on page 3910 ff.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 15/2018
- Pages: 3841-3854
- First Published: 26 March 2018
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: A Membrane-Free Redox Flow Battery with Two Immiscible Redox Electrolytes
- Page: 3853
- First Published: 26 March 2018
Corrigendum: Gate-Voltage Control of Borophene Structure Formation
- Page: 3854
- First Published: 26 March 2018
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 15/2018
- Pages: 3856-3859
- First Published: 26 March 2018
Author Profile
Minireviews
Carbenes
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis via Azolium Dienolates: An Efficient Strategy for Remote Enantioselective Functionalizations
- Pages: 3862-3873
- First Published: 14 November 2017
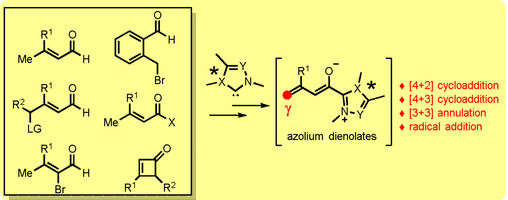
An intermediate look: N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis has emerged as a powerful strategy for enantioselective functionalizations at remote positions, and proceeds via azolium dienolate intermediates that are easily generated from various substrates. This Minireview highlights the development and the new advances of cycloaddition/annulation reactions involving azolium dienolate intermediates.
Energy Storage Materials
Achilles’ Heel of Lithium–Air Batteries: Lithium Carbonate
- Pages: 3874-3886
- First Published: 15 December 2017
Reviews
Scanning Probe Microscopy
Atomic Force Microscopy for Molecular Structure Elucidation
- Pages: 3888-3908
- First Published: 27 February 2018
The tip of the iceberg? Functionalizing the tip of an atomic force microscope enabled atomic-resolution imaging of single molecules and offers unique applications in chemistry for the investigation of on-surface reactions and the characterization of elusive molecules and complex molecular mixtures. This Review covers the recent progress in high-resolution scanning probe microscopy with functionalized tips.
Communications
Energy Storage and Conversion
Alkaline–Acid Zn–H2O Fuel Cell for the Simultaneous Generation of Hydrogen and Electricity
- Pages: 3910-3915
- First Published: 08 January 2018
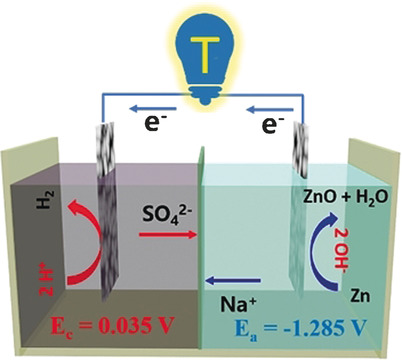
“Everything now” generation: An alkaline–acid Zn–H2O fuel cell was developed for the simultaneous generation of electricity and H2 (see picture). The cell delivered an open-circuit voltage of around 1.25 V with almost 100 % Faradic efficiency for H2 production and reached a power density of 80 mW cm−2 and an energy density of 934 Wh kg−1.
Li–S Batteries | Very Important Paper
Metal–Organic Frameworks for High Charge–Discharge Rates in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
- Pages: 3916-3921
- First Published: 10 February 2018
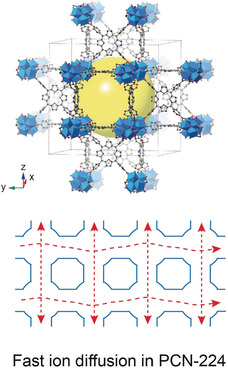
MOF host S: The electrical conductivity of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) was promoted by the construction of polymer–MOF composites. Using MOF-based sulfur hosts, the critical role of porosity at high charge–discharge rates in Li–S batteries was elucidated. MOFs with short ion transfer pathways and large pore apertures were identified as the most suitable for long-term cycling at extremely high rates.
Graphdiyne Oxides
Carbon Atom Hybridization Matters: Ultrafast Humidity Response of Graphdiyne Oxides
- Pages: 3922-3926
- First Published: 19 February 2018
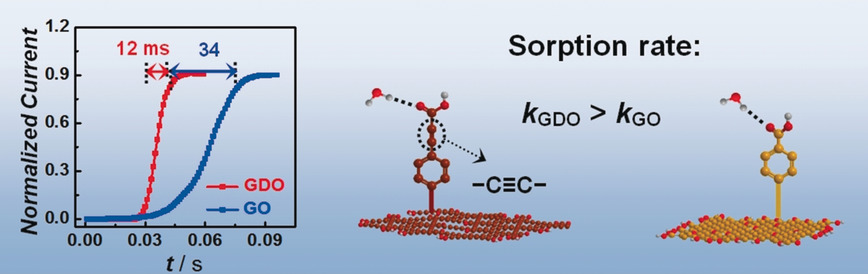
Hybridization matters: Graphdiyne oxide (GDO), the oxidized form of graphdiyne (GDY), exhibits an ultrafast humidity response with an unprecedented response speed (ca. 7 ms), which is three times faster than that of graphene oxide (GO). The acetylenic bond of GDO is more electron-withdrawing than the ethylenic bond in GO and gives rise to a faster binding rate with water.
Metal–Organic Frameworks
One-Step Synthesis of Hybrid Core–Shell Metal–Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 3927-3932
- First Published: 16 February 2018

MOF-on-MOF: A series of core–shell MOFs with mismatching lattices has been synthesized under the guidance of nucleation kinetic analysis. Isoreticular expansion of microporous shells and orthogonal modification of the core was realized to produce multifunctional MOF composites, which act as size-selective catalysts for olefin epoxidation.
Nonlinear Optics | Very Important Paper
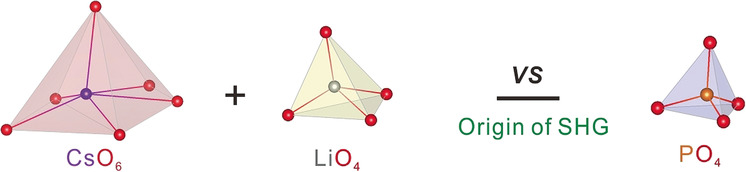
The Large Second-Harmonic Generation of LiCs2PO4 is caused by the Metal-Cation-Centered Groups
- Pages: 3933-3937
- First Published: 25 February 2018
Photothermal Therapy | Very Important Paper
Temperature-Correlated Afterglow of a Semiconducting Polymer Nanococktail for Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy
- Pages: 3938-3942
- First Published: 12 March 2018
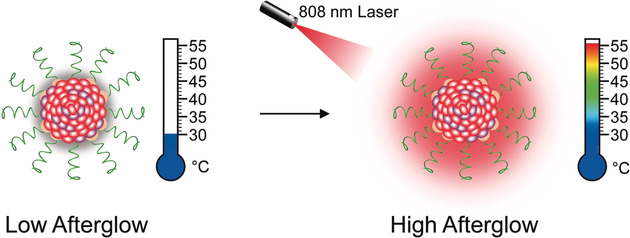
Afterglow, a cocktail: A semiconducting polymer nanococktail (SPNCT) with temperature-correlated afterglow luminescence is designed for imaging-guided photothermal therapy. The afterglow intensity of the SPNCT has a good linear correlation with temperature, allowing the photothermal temperature of the tumor to be monitored under NIR laser irradiation.
Zinc-Ion Batteries
Highly Stable Aqueous Zinc-Ion Storage Using a Layered Calcium Vanadium Oxide Bronze Cathode
- Pages: 3943-3948
- First Published: 12 February 2018
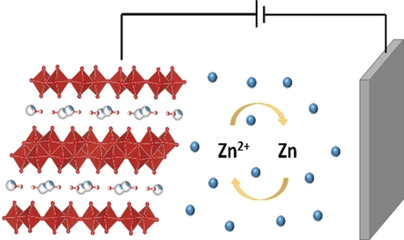
A new cathode material, layered calcium vanadium oxide bronze, was synthesized for aqueous zinc-ion battery applications. The calcium-based bronze shows promising performance for storage of Zn2+ ions from the aqueous electrolyte (see picture). The Zn cell delivers an energy density of 267 W h kg−1 at a power density of 53.4 W kg−1.
Fluorescent Probes
Hybrid Indicators for Fast and Sensitive Voltage Imaging
- Pages: 3949-3953
- First Published: 13 February 2018
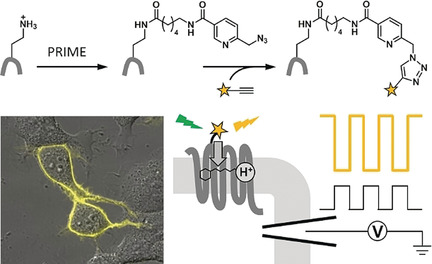
The fast and the sensitive: A hybrid strategy employing site-specific protein modification techniques produced a palette of fluorescent membrane voltage indicators with sub-millisecond response kinetics. These indicators enable the optical mapping of electrical communications among cells at high resolution.
Enzyme Activity
Modifying the Steric Properties in the Second Coordination Sphere of Designed Peptides Leads to Enhancement of Nitrite Reductase Activity
- Pages: 3954-3957
- First Published: 08 January 2018
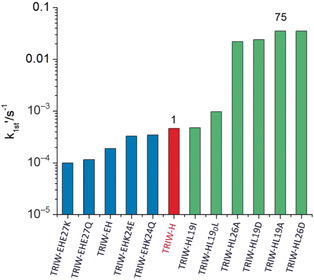
Second is best: A significant increase in nitrite reductase activity is achieved by modification of the steric properties of the second coordination sphere of a type 2 copper center. The steric properties can be harnessed to control metal coordination and reactivity in a 3-stranded coiled coil TRI peptide scaffold (TRIW-H).
Antibiotics
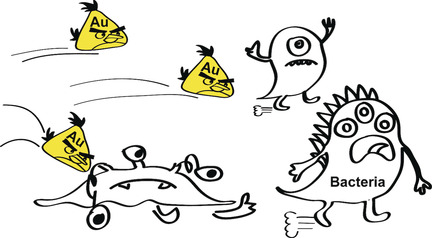
Gold Nanoclusters for Targeting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus In Vivo
- Pages: 3958-3962
- First Published: 08 February 2018
Photothermal Conversion
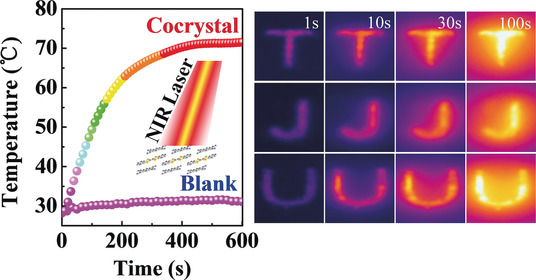
Cocrystals Strategy towards Materials for Near-Infrared Photothermal Conversion and Imaging
- Pages: 3963-3967
- First Published: 14 February 2018
Sodium-Ion Batteries | Very Important Paper
Synthesis and Electronic Structure of Boron-Graphdiyne with an sp-Hybridized Carbon Skeleton and Its Application in Sodium Storage
- Pages: 3968-3973
- First Published: 03 February 2018

The Bs needs: Boron-graphdiyne (BGDY) is prepared through a bottom-up chemical strategy. BGDY has a unique structure with molecular pores decorated with boron atoms. The pure sp-hybridized-carbon skeleton and boron heteroatoms can stabilize the metal atoms intercalated in the BGDY framework. As a result of this unique structure, BGDY shows remarkable electrochemical performance in sodium-ion half cells.
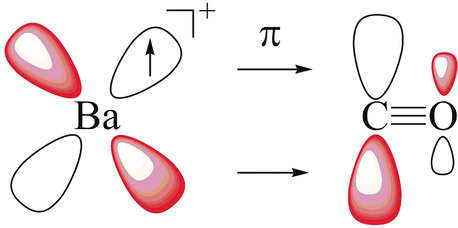
Organometallic Chemistry
Barium as Honorary Transition Metal in Action: Experimental and Theoretical Study of Ba(CO)+ and Ba(CO)−
- Pages: 3974-3980
- First Published: 12 February 2018
Homogeneous Catalysis
Chemoselective Synthesis of Z-Olefins through Rh-Catalyzed Formate-Mediated 1,6-Reduction
- Pages: 3981-3984
- First Published: 13 February 2018
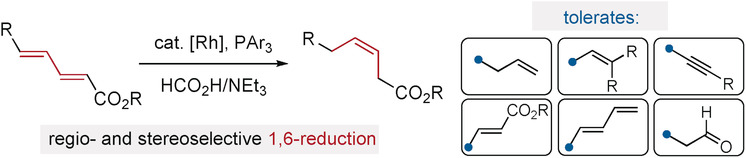
Two become one: Many prevailing methods for cis-olefination are complicated by the presence of multiple unsaturated units or electrophilic functional groups. In this study, Z-olefins are delivered through selective reduction of activated dienes using formic acid. The reaction proceeds with high regio- and stereoselectivity (typically >90:10 and >95:5, respectively) and preserves other alkenyl, alkynyl, protic, and electrophilic groups.
Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
Tunable Crystallinity and Charge Transfer in Two-Dimensional G-Quadruplex Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 3985-3989
- First Published: 09 February 2018
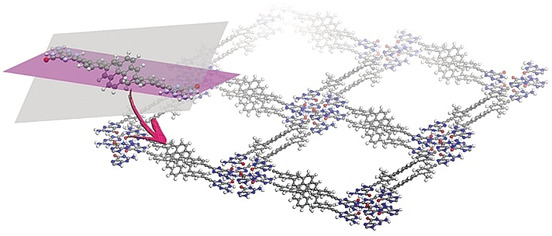
Crystal packing on a rugged surface: non-planar molecular building blocks restrict the interlayer slippage and modulate dispersion interactions for the formation of 2D G-quadruplex organic frameworks. Charge-transfer complexes can be obtained when size-matched building blocks of similar nonplanarity are co-crystallized.
Photochemistry
Synergistic Photoredox Catalysis and Organocatalysis for Inverse Hydroboration of Imines
- Pages: 3990-3994
- First Published: 15 February 2018
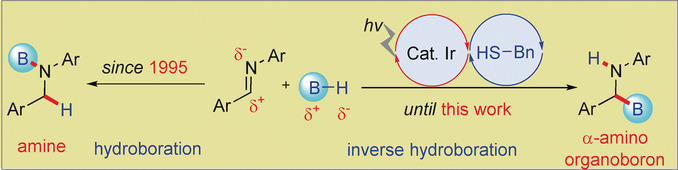
Unprecedented inversion: The first catalytic inverse hydroboration of imines with N-heterocyclic carbene boranes has been realized by means of cooperative organocatalysis and photocatalysis. The nature of the thiol is vital for inverse hydroboration. This procedure represents an important step forward to enhancing α-amino organoboron libraries.
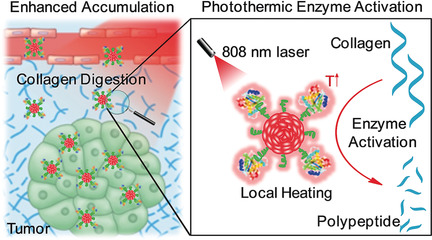
Photothermal Therapy
Semiconducting Polymer Nanoenzymes with Photothermic Activity for Enhanced Cancer Therapy
- Pages: 3995-3998
- First Published: 07 February 2018
Luminescent Imaging
Quantitative Monitoring and Visualization of Hydrogen Sulfide In Vivo Using a Luminescent Probe Based on a Ruthenium(II) Complex
- Pages: 3999-4004
- First Published: 02 February 2018
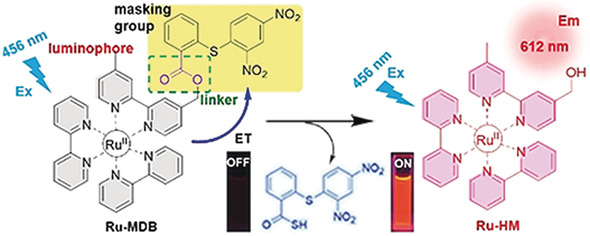
In vivo sensing of H2S: A luminescent probe, Ru-MDB, was developed for phosphorescence and time-gated luminescence quantification of H2S using a responsive luminescence-masking moiety. Monitoring and visualization of H2S in cell lysosomes, D. magna, zebrafish, organs, mice, and human sera, is possible. Key: electron transfer (ET), emission (Em), excitation (Ex).
Phosphorescent Porous Materials
Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Aromatic Frameworks for Ultralong Phosphorescence by Intralayer π–π Interactions
- Pages: 4005-4009
- First Published: 08 February 2018
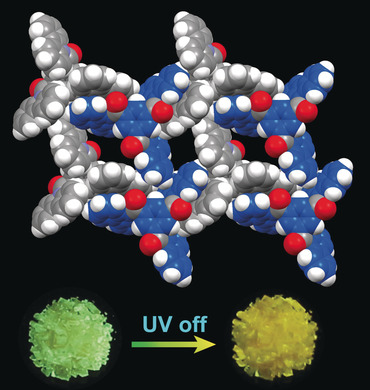
A healthy glow: Ultralong phosphorescence was observed from hydrogen-bonded organic aromatic frameworks (HOAFs) with different pore sizes that were constructed under different conditions from the same aromatic precursor containing three carbazole units. Intralayer π–π interactions and interlayer hydrogen bonds endowed the HOAFs with high thermal stability and phosphorescence lifetimes of up to 79.8 ms (see picture).
Electrocatalysis
Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Imaging of Electrocatalysis at a Single Au-Pt Janus Nanoparticle
- Pages: 4010-4014
- First Published: 08 February 2018
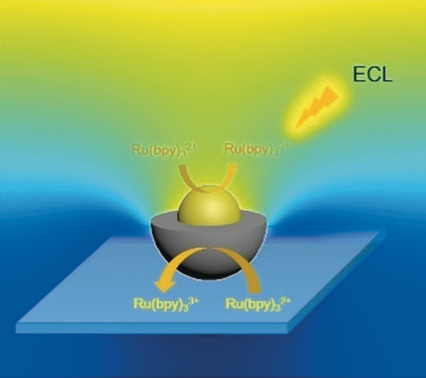
Electrocatalytic oxidation of a luminophore at single Au, Pt, and Au-Pt Janus nanoparticles was studied using electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) microscopy. Compared to the monometal nanoparticles, the Janus particle structure exhibited enhanced ECL intensity and stability, indicating better catalytic efficiency.
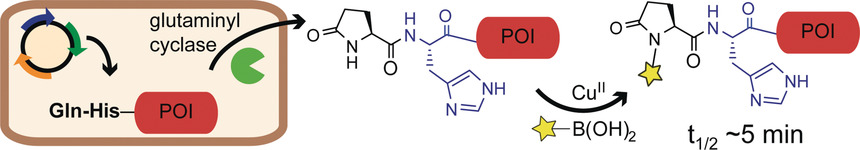
Bioinorganic Chemistry
A Naturally Encoded Dipeptide Handle for Bioorthogonal Chan–Lam Coupling
- Pages: 4015-4019
- First Published: 07 February 2018
Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Synthesis of Sub-2 nm Iron-Doped NiSe2 Nanowires and Their Surface-Confined Oxidation for Oxygen Evolution Catalysis
- Pages: 4020-4024
- First Published: 14 February 2018
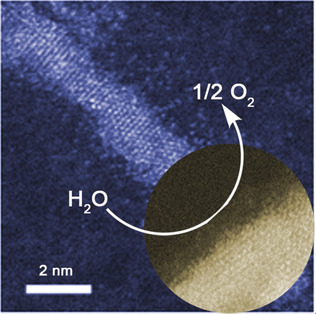
Down to the wire: Colloidal Fe-doped NiSe2 ultrathin nanowires (UNWs) down to 1.7 nm in diameter were synthesized by a binary soft-template strategy. These UNWs yield surface-confined electrochemical oxidation, enabling efficient and robust oxygen evolution catalysis owing to their favorable electronic structures and unsaturated local coordination environments.
Hydrogels
Co-assembly of Polyoxometalates and Zwitterionic Amphiphiles into Supramolecular Hydrogels: From Crystalline Fibrillar to Amorphous Micellar Networks
- Pages: 4025-4029
- First Published: 15 February 2018
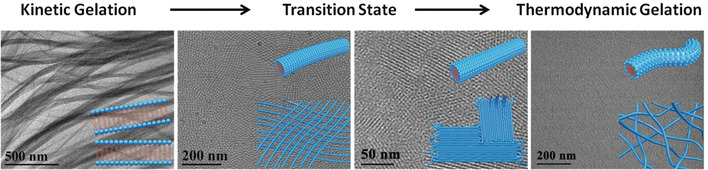
Styling gel: Supramolecular hydrogels that have distinct crystalline and amorphous networks are obtained by balancing the rigidity and flexibility of the inorganic–organic co-assemblies. Using polyoxometalates (POMs) and zwitterionic amphiphiles, the transition morphologies between kinetically and thermodynamically controlled gelation process are evidenced as ordered wormlike micelles.
Porphyrinoids
Helicenophyrins: Expanded Carbaporphyrins Incorporating Aza[5]helicene and Heptacyclic S-Shaped Aza[5]helicene Motifs
- Pages: 4030-4034
- First Published: 16 February 2018
Surface Chemistry
Direct Formation of C−C Triple-Bonded Structural Motifs by On-Surface Dehalogenative Homocouplings of Tribromomethyl-Substituted Arenes
- Pages: 4035-4038
- First Published: 20 February 2018
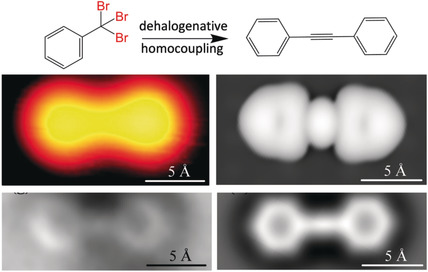
Tribromomethyl-substituted arenes were directly converted into C−C triple-bonded structural motifs by on-surface dehalogenative homocoupling reactions, as confirmed by a combination of high-resolution scanning tunneling microscopy, non-contact atomic force microscopy, and density functional theory calculations. Concurrently, sp3-hybridized carbon atoms state are converted into sp-hybridized ones.
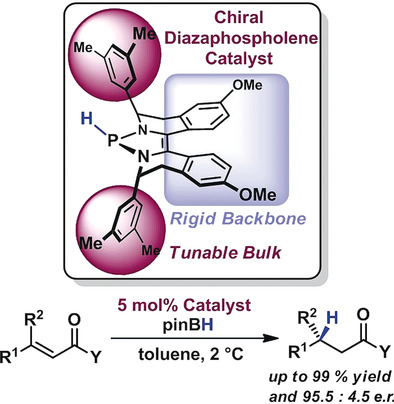
Asymmetric Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Chiral 1,3,2-Diazaphospholenes as Catalytic Molecular Hydrides for Enantioselective Conjugate Reductions
- Pages: 4039-4042
- First Published: 20 February 2018
Thermoelectrics | Very Important Paper
Soft Phonon Modes Leading to Ultralow Thermal Conductivity and High Thermoelectric Performance in AgCuTe
- Pages: 4043-4047
- First Published: 28 February 2018
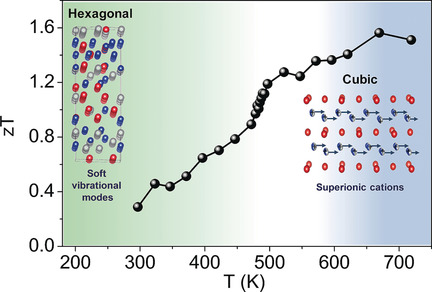
Low thermal conduction: Soft phonon modes and optical-acoustic phonon coupling cause an ultralow lattice thermal conductivity in the room-temperature hexagonal phase of AgCuTe, while the dynamic disorder of Ag/Cu cations leads to reduced phonon frequencies and mean free paths in the high-temperature rocksalt phase. A high thermoelectric figure of merit (zT) of 1.6 is achieved in the p-type AgCuTe at around 670 K.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Solvent-Dependent Asymmetric Synthesis of Alkynyl and Monofluoroalkenyl Isoindolinones by CpRhIII-Catalyzed C−H Activation
- Pages: 4048-4052
- First Published: 07 March 2018
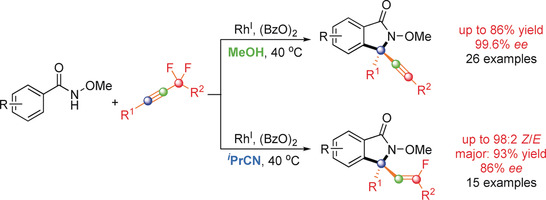
A matter of solvent: Alkynyl and monofluoroalkenyl isoindolinones were generated with good enantioselectivities from N-methoxy benzamides and α,α-difluoromethylene alkynes by C−H activation with a chiral CpRhIII catalyst. Remarkably, the product formation is solvent-dependent; whereas alkynyl isoindolinones are formed in methanol, monofluoroalkenyl isoindolinones are generated in isobutyronitrile.
Multicomponent Reactions
Lewis Acid Catalyzed Stereoselective Dearomative Coupling of Indolylboron Ate Complexes with Donor–Acceptor Cyclopropanes and Alkyl Halides
- Pages: 4053-4057
- First Published: 17 February 2018
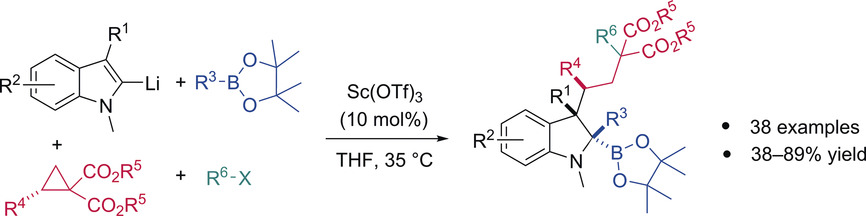
A four-component coupling of 2-lithioindoles, boronic esters, donor–acceptor cyclopropanes, and alkyl halides in the presence of the Lewis acid catalyst Sc(OTf)3 provided indolines with three contiguous stereocenters, including a quaternary center, with complete diastereoselectivity and stereospecificity (see scheme). The valuable boronic ester moiety remaining in the products allows for subsequent functionalization.
Nickel Catalysis
NiH-Catalyzed Reductive Relay Hydroalkylation: A Strategy for the Remote C(sp3)−H Alkylation of Alkenes
- Pages: 4058-4062
- First Published: 19 February 2018
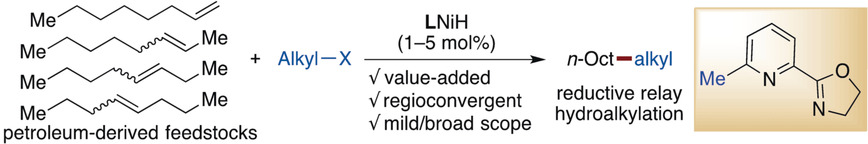
The synergistic combination of chain walking, a process involving repeated migratory insertions and β-H eliminations, and cross-coupling chemistry led to the development of a mild, efficient NiH-catalyzed process for the remote hydroalkylation of alkenes. Unfunctionalized C(sp3)−C(sp3) bonds were constructed from two simple feedstock chemicals, namely olefins and alkyl halides.
Flow Chemistry
A Catalyst-Free Amination of Functional Organolithium Reagents by Flow Chemistry
- Pages: 4063-4066
- First Published: 08 February 2018
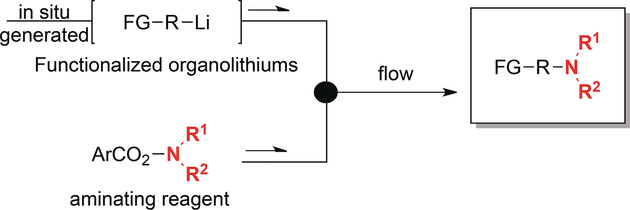
Go with the flow: Reported is the electrophilic amination of organolithium intermediates using optimized amine reagents under mild reaction conditions within flow microreactors. Flow reactions are suitable for fast and mild amination using unstable organolithium compounds. Also notable is the fact that additional reagents and catalysts were not necessary. FG=functional group, R1 and R2=alkyl groups.
Polyoxometalates
Effect of Cation–π Interaction on Macroionic Self-Assembly
- Pages: 4067-4072
- First Published: 13 February 2018
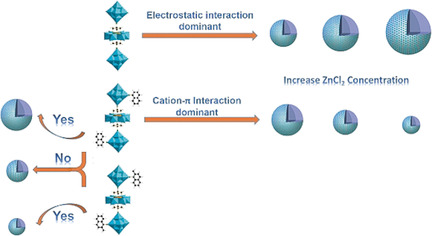
Balance of power: The incorporation of aromatic groups onto POM clusters introduces strong cation–π interaction during the their self-assembly and changes the trend of the assembly size. A small difference between two aromatic groups is amplified after the incorporation, initiating self-recognition phenomenon between two highly similar macroanions.
Trifluoromethylation | Very Important Paper
Palladium-Catalyzed Decarbonylative Trifluoromethylation of Acid Fluorides
- Pages: 4073-4077
- First Published: 25 February 2018
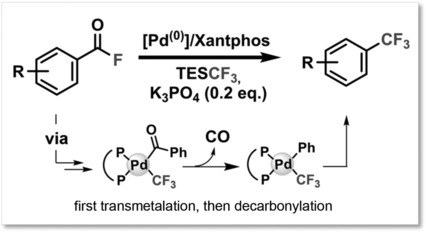
Homogeneous catalysis: Trifluoromethyl arenes have been obtained by Pd-catalyzed decarbonylative functionalization of acid fluorides. The key PdII-F intermediate forms through intramolecular redistribution to Pd, allowing direct transmetalation to occur. Computational and experimental mechanistic studies reveal that transmetalation occurs prior to decarbonylation.
C−H Functionalization
Selective C(sp3)−H Aerobic Oxidation Enabled by Decatungstate Photocatalysis in Flow
- Pages: 4078-4082
- First Published: 16 February 2018
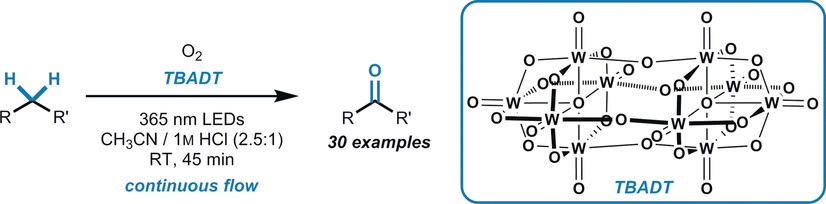
Good clean functionalization: A mild and selective C(sp3)−H oxidation promoted by an inexpensive decatungstate photocatalyst was significantly improved by a microflow reactor, which enabled the safe use of oxygen and enhanced irradiation of the reaction mixture. Both activated and unactivated C−H bonds could be oxidized by this sustainable method, including those in natural scaffolds, such as (−)-ambroxide and artemisinin.
Membranes | Very Important Paper
High-Flux Membranes Based on the Covalent Organic Framework COF-LZU1 for Selective Dye Separation by Nanofiltration
- Pages: 4083-4087
- First Published: 05 February 2018
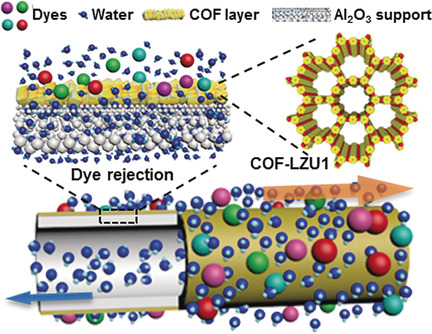
Color filter: A continuous, high-quality two-dimensional imine-linked COF membrane with ordered and tunable pore channels was prepared on tubular alumina supports. The COF-LZU1 membrane shows excellent water permeance and high rejection rates for various water-soluble dyes, as well as high stability during water purification.
Germanium Cluster
Ge14Br8(PEt3)4: A Subhalide Cluster of Germanium
- Pages: 4088-4092
- First Published: 15 February 2018
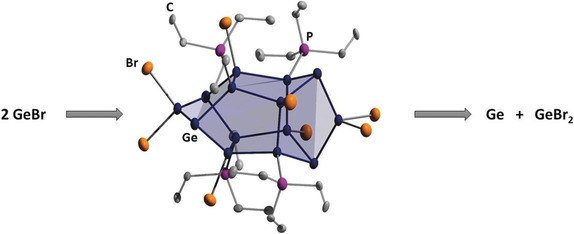
First step into a novel field in Ge chemistry: The subhalide cluster Ge14Br8(PEt3)4 was obtained by heating a metastable solution of GeIBr to room temperature and then structurally characterized. This cluster can be seen as the first trapped intermediate of the disproportionation reaction of GeIBr en route to elemental germanium. DFT calculations indicate that classical bonding is realized within the cluster.
Electrocatalysis
Local Surface Structure and Composition Control the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Iron Nickel Sulfides
- Pages: 4093-4097
- First Published: 26 January 2018
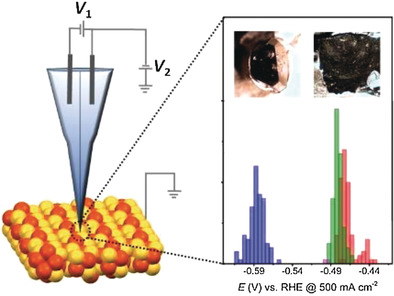
Small change, big difference: Local investigation of the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) on a single crystal of iron nickel sulfide, one of the most active non-noble-metal HER catalysts, was carried out using scanning electrochemical cell microscopy (SECCM). Small variations in the Ni/Fe ratio at the surface induce tremendous changes in the catalytic HER activity.
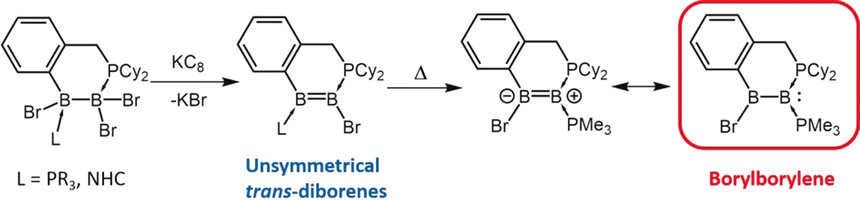
Boron Chemistry
Unsymmetrical, Cyclic Diborenes and Thermal Rearrangement to a Borylborylene
- Pages: 4098-4102
- First Published: 16 February 2018






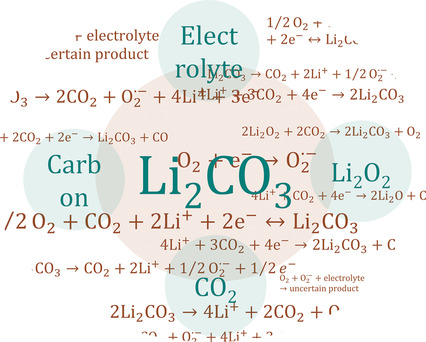
![Helicenophyrins: Expanded Carbaporphyrins Incorporating Aza[5]helicene and Heptacyclic S-Shaped Aza[5]helicene Motifs](/cms/asset/e43ab757-53ea-48b3-a362-fb80ab8fb770/anie201800879-toc-0001-m.jpg)