Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Mono- and Ditopic Bisfunctionalization of Graphene (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 19/2016)
- Page: 5613
- First Published: 20 April 2016

Understanding the chemistry of graphene will play an important role in the design of complex graphene architectures. In their Communication on page 5861 ff., A. Hirsch and co-workers describe the functionalization of individual graphene sheets deposited on surfaces and bulk functionalization in dispersion. This approach, based on the interplay between functionalization and retrofunctionalization, allows double- and single-sided bisfunctionalization of individual layers.
Inside Cover: Synergistic Cocatalytic Effect of Carbon Nanodots and Co3O4 Nanoclusters for the Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation on Hematite (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 19/2016)
- Page: 5614
- First Published: 25 April 2016

Promoting water-oxidation kinetics is essential for effective photoelectrochemical water splitting. In their Communication on page 5851 ff., J. Gong and co-workers describe how a combination of two co-catalysts, Co3O4 and graphitic carbon dots (CDots), showed a synergistic effect to improve the activity of the Fe2O3 photoanode for water oxidation. The slow reaction, oxidation of H2O to H2O2 on Co3O4, could be accelerated by the timely oxidation of H2O2 to O2 on the CDots.
Inside Back Cover: Enantioselective Trifluoromethylthiolating Lactonization Catalyzed by an Indane-Based Chiral Sulfide (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 19/2016)
- Page: 5869
- First Published: 08 April 2016

A bifunctional chiral sulfide catalyst and a new shelf-stable electrophilic SCF3 reagent are used for the enantioselective trifluoromethylthiolating lactonization that is reported by X. Zhao et al. in their Communication on page 5846 ff. The reaction occurs only when the amide and sulfide moieties of the catalyst cooperate like crab claws that work together to catch fish.
Back Cover: Discovery of a Promiscuous Non-Heme Iron Halogenase in Ambiguine Alkaloid Biogenesis: Implication for an Evolvable Enzyme Family for Late-Stage Halogenation of Aliphatic Carbons in Small Molecules (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 19/2016)
- Page: 5870
- First Published: 25 April 2016
A promiscuous aliphatic halogenase AmbO5 was identified in studies of ambiguine alkaloid biogenesis. In their Communication on page 5780 ff., X. Liu et al. show that AmbO5 can selectively chlorinate seven structurally distinct ambiguine, fischerindole, and hapalindole alkaloids by late-stage C−H functionalization. The characterization of a C-terminal sequence motif in AmbO5 important for substrate tolerance and specificity provides evidence on the evolvable nature of this newly discovered halogenase family towards small molecules.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Bottom-Up Fabrication of Nanopatterned Polymers on DNA Origami by In Situ Atom-Transfer Radical Polymerization
- First Published: 25 April 2016
DNA Nanotechnology Surface-initiated polymerization reactions on DNA origami that enable the precise design of nanopatterned polymers are described by T. Weil, Y. Wu, and co-workers in their Communication on page 5692 ff.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 19/2016
- Pages: 5617-5627
- First Published: 25 April 2016
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 19/2016
- Pages: 5630-5633
- First Published: 25 April 2016
Author Profiles
News
Japan Prize: H. Hosono / Asahi Prize: S. Murai / Merck–Banyu Lectureship Award: S. Maeda
- Page: 5636
- First Published: 06 April 2016
Highlights
Photoswitching
Coenzyme B12 Repurposed for Photoregulation of Gene Expression
- Pages: 5638-5640
- First Published: 24 March 2016
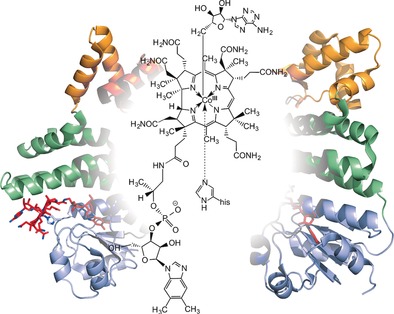
Old cofactor, new tricks: In enzymes, coenzyme B12 has a well-known function as a radical initiator through homolysis of the Co−C bond. It has recently been shown that nature has repurposed this cofactor as a photosensitive switch for the regulation of bacterial carotenoid biosynthesis. Co−C bond breakage is again the key event in this process, triggering huge conformational changes in the B12-binding protein.
Reviews
Natural Products
Synthesis of Amaryllidaceae Constituents and Unnatural Derivatives
- Pages: 5642-5691
- First Published: 11 March 2016
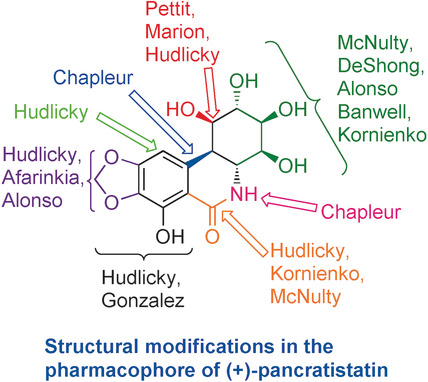
The extracts of plants of the Amaryllidaceae family contain a class of isocarbostyril natural products that are well known to have potent anti-cancer activity (see for example, (+)-pancratistatin). Recent total syntheses of these natural products and their derivatives are summarized. The structure–activity relationships are also discussed and guidelines for the future modifications are formulated.
Communications
DNA Nanotechnology
Bottom-Up Fabrication of Nanopatterned Polymers on DNA Origami by In Situ Atom-Transfer Radical Polymerization
- Pages: 5692-5697
- First Published: 05 April 2016
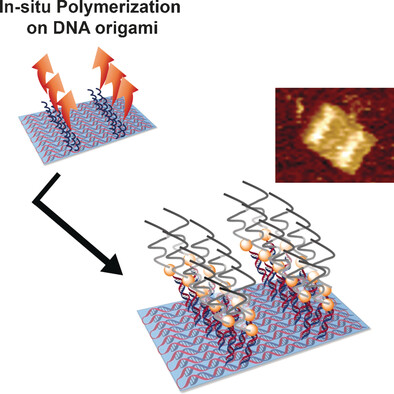
Surface-initiated polymerization reactions on DNA origami enable the precise design of nanopatterned polymers. Characterization by atomic force microscopy, gel electrophoresis, and time-of-flight secondary-ion mass spectrometry showed that this approach can be used to fabricate polymers of different patterns and lengths on the nanoscale.
Antimicrobial Surfaces | Hot Paper
Using Chemoattractants to Lure Bacteria to Contact-Killing Surfaces
- Pages: 5698-5702
- First Published: 05 April 2016
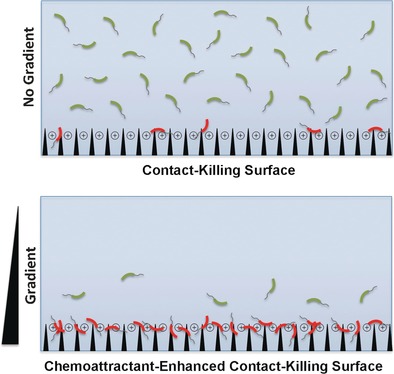
Like a moth to a flame: The activity of an antimicrobial surface coated with a biocidal agent that can kill microbes upon contact (contact-killing surface) can be enhanced substantially by using a chemoattractant (CA) concentration gradient to attract bacteria. This concept is demonstrated using two non-biocidal CAs (aspartate, glucose) to attract common foodborne bacteria to a silane-coated surface. Live bacteria=green; dead bacteria=red.
Allosteric Inhibitors
Insights Into the Allosteric Inhibition of the SUMO E2 Enzyme Ubc9
- Pages: 5703-5707
- First Published: 01 April 2016
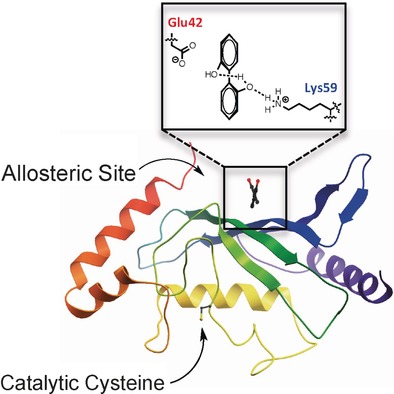
From a distance: Allosteric regulation of enzyme activity is an attractive avenue in chemical biology, but is often difficult to achieve. Two small-molecule inhibitors of the SUMO E2 enzyme Ubc9 were discovered through an X-ray crystallographic fragment screen to bind to a previously unknown allosteric site distal to the active site. This interaction and its effect on SUMOylation activity are discussed.
Fluorescent Probes
Emergent Molecular Recognition through Self-Assembly: Unexpected Selectivity for Hyaluronic Acid among Glycosaminoglycans
- Pages: 5708-5712
- First Published: 06 April 2016
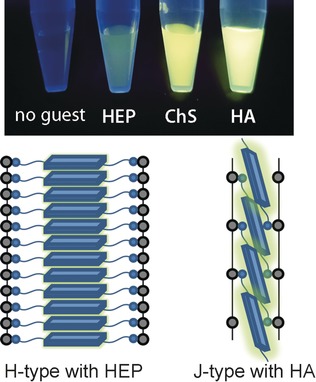
An unexpectedly selective fluorescent (FL) chemosensor for hyaluronic acid (HA) was developed, where structural information on the target critically directs the mode of chemosensor self-assembly leading to the characteristic FL response (see picture). This system is potentially applicable to the clinical diagnosis of functional disorders such as cancer-related diseases involving the overexpression of HA.
Protein–Protein Interactions
Probing the Small-Molecule Inhibition of an Anticancer Therapeutic Protein-Protein Interaction Using a Solid-State Nanopore
- Pages: 5713-5717
- First Published: 01 April 2016
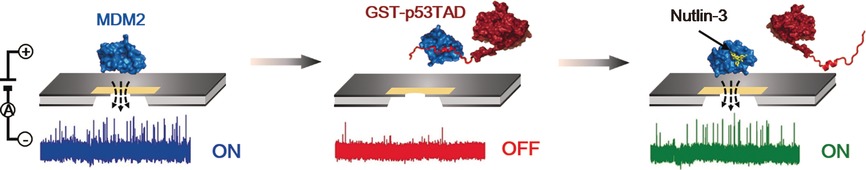
Sieving for protein interactions: The protein–protein interaction between MDM2 and the p53 transcriptional activation domain (GST-p53TAD), and its inhibition by Nutlin-3, could be detected using a low-noise solid-state nanopore. This nanopore system could aid high-throughput screening for other protein–protein interaction inhibitors.
Multicolor Microcrystals
Unraveling Epitaxial Habits in the NaLnF4 System for Color Multiplexing at the Single-Particle Level
- Pages: 5718-5722
- First Published: 01 April 2016
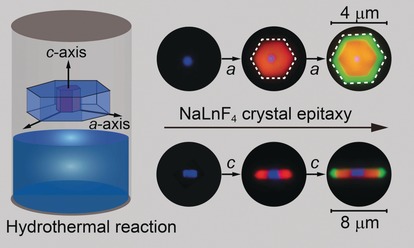
Pimp my particles: Fine control of crystal epitaxial growth was achieved with a NaLnF4 system by using a modified hydrothermal method. On the basis of kinetic and thermodynamic investigations, it is shown that by precisely controlling shell thickness and growth orientation it is possible to grow microparticles with multicolor emitting capabilities at the single-particle level.
Catalytic Mechanisms
Formation Mechanism of the First Carbon–Carbon Bond and the First Olefin in the Methanol Conversion into Hydrocarbons
- Pages: 5723-5726
- First Published: 01 April 2016
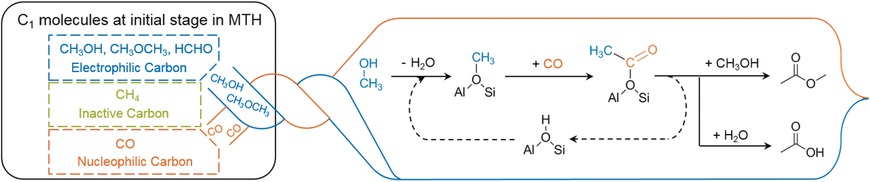
Who's first? Combining kinetics, spectroscopy, and DFT calculations shows the first carbon–carbon bond in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction is formed through the carbonylation of methanol or dimethyl ether, generating acetic acid and methyl acetate. Olefins arise as secondary products from these acetyl species.
Sensor Technology
Electrical Conductors
Superior Electrical Conductivity in Hydrogenated Layered Ternary Chalcogenide Nanosheets for Flexible All-Solid-State Supercapacitors
- Pages: 5733-5738
- First Published: 06 April 2016
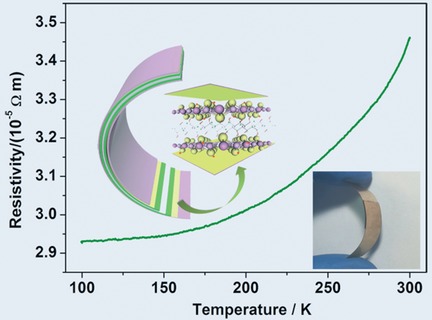
Metallic nanosheets: The conductivity of the layered ternary chalcogenide Cu2WS4 is switched from semiconducting to metallic by hydrogen incorporation, accompanied by a strong increase in conductivity. The metallic hydrogenated-Cu2WS4 nanosheets were applied as electrode material in an all-solid-state flexible supercapacitor.
Organic Electronics
Dibenzo[a,j]phenazine-Cored Donor–Acceptor–Donor Compounds as Green-to-Red/NIR Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Organic Light Emitters
- Pages: 5739-5744
- First Published: 06 April 2016
![Dibenzo[a,j]phenazine-Cored Donor–Acceptor–Donor Compounds as Green-to-Red/NIR Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Organic Light Emitters](/cms/asset/c3bed443-3471-4ed7-bf1a-a4faa43ddca4/anie201600113-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Photophysics: A series of U-shaped donor–acceptor–donor emissive compounds based on the electron-accepting unit dibenzo[a,j]phenazine has been developed. Static and dynamic photophysical investigations of these compounds revealed their detailed thermally activated delayed fluorescence properties. The external quantum efficiency of the organic light-emitting diodes fabricated with the new materials reached values up to 16 %.
Inhibitors
Nonpeptidic Selective Inhibitors of the Chymotrypsin-Like (β5 i) Subunit of the Immunoproteasome
- Pages: 5745-5748
- First Published: 01 April 2016
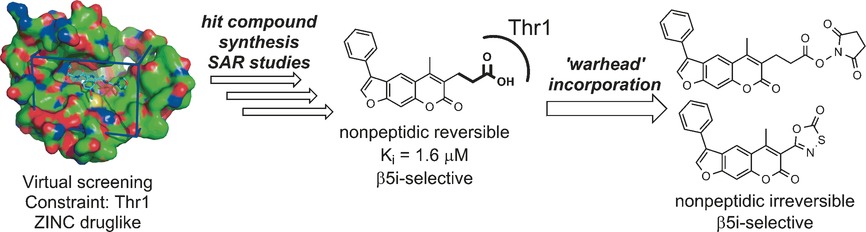
Small and mighty: Nonpeptidic reversible inhibitors that selectively block the chymotrypsin-like (β5i) subunit of the human immunoproteasome were discovered, and derivatives that act irreversibly through covalent inhibition were designed. These small-molecule inhibitors display high subunit selectivity and no cytotoxicity, and they discriminate between the immunoproteasome and the constitutive proteasome in cell-based assays.
Metal Nanoclusters
Gold Doping of Silver Nanoclusters: A 26-Fold Enhancement in the Luminescence Quantum Yield
- Pages: 5749-5753
- First Published: 06 April 2016

The photoluminescence quantum yield (QY) of a weakly luminescent Ag29 nanocluster was 26-fold enhanced by doping the nanocluster with a distinct number of gold atoms, while the original Ag29 framework was kept intact. A detailed characterization showed the presence of Au heteroatoms replacing the silver atom at the center of the Ag29 nanocluster and the atoms at the four phosphine binding sites of Ag29, which play a pivotal role in the QY enhancement mechanism.
Surface Chemistry
Surface-Guided Formation of an Organocobalt Complex
- Pages: 5754-5759
- First Published: 05 April 2016
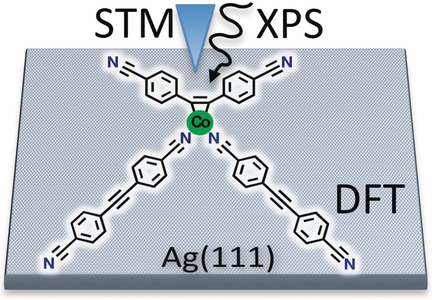
Organocobalt complexation at the single-molecule level: Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) supported by density functional theory (DFT) calculations were used to obtain atomistic insight into the formation and nature of an unprecedented organocobalt complex at a solid–vacuum interface, specifically on the Ag(111) surface.
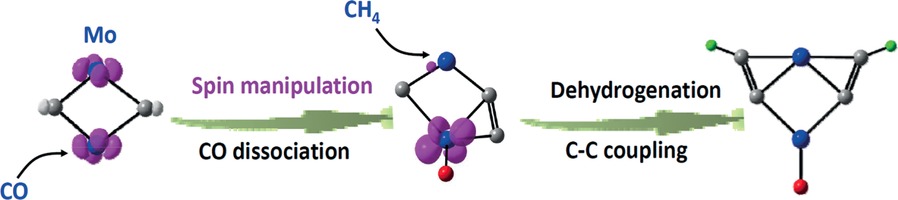
Methane Activation
Activation of Methane Promoted by Adsorption of CO on Mo2C2− Cluster Anions
- Pages: 5760-5764
- First Published: 06 April 2016
Natural Products
Stereodivergent and Protecting-Group-Free Synthesis of the Helicascolide Family: A Rhodium-Catalyzed Atom-Economical Lactonization Strategy
- Pages: 5765-5769
- First Published: 04 April 2016
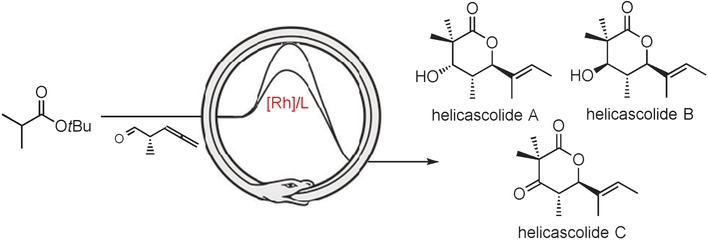
All in the family: The natural product family of the helicascolides A–C are one of countless groups of natural products containing six-membered lactones in their core structure. The rhodium-catalyzed regio- and diastereoselective addition of carboxylic acids with allenes permits the atom-economic and highly diastereoselective synthesis of the lactone core and allows for rapid access to this product family.
Anticancer Therapeutics
Regulating the Rate of Molecular Self-Assembly for Targeting Cancer Cells
- Pages: 5770-5775
- First Published: 08 April 2016
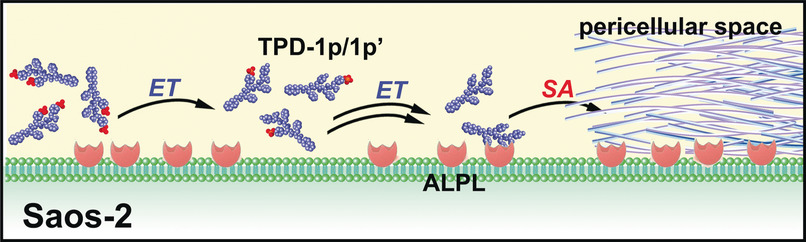
Tailoring the number of phosphates on a peptidic substrate enables regulation of the rate of self-assembly of the enzyme reaction product. Such a rate regulation allows selective inhibition of osteosarcoma cells over hepatocytes, which constitutes a promising approach to target cancer cells in a specific organ.
Bioinspired Catalysis
Readily Accessible Bulky Iron Catalysts exhibiting Site Selectivity in the Oxidation of Steroidal Substrates
- Pages: 5776-5779
- First Published: 05 April 2016
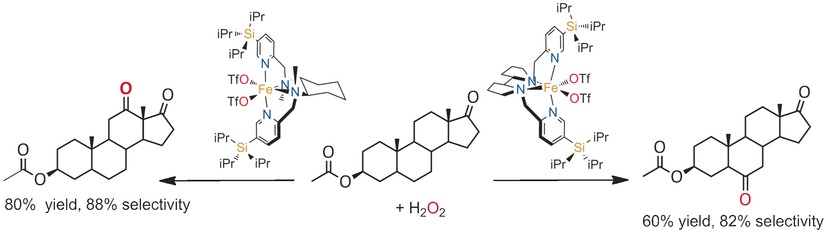
Iron oxidizes: Iron complexes with bulky silyl substituents catalyze the site-selective oxidation of alkyl C−H bonds with H2O2 under mild conditions. For example, unprecedented site-selective oxidation at C6 and C12 methylenic sites in steroidal substrates is shown to be governed by the chirality of the catalysts.
Biosynthesis and Biocatalysis
Discovery of a Promiscuous Non-Heme Iron Halogenase in Ambiguine Alkaloid Biogenesis: Implication for an Evolvable Enzyme Family for Late-Stage Halogenation of Aliphatic Carbons in Small Molecules
- Pages: 5780-5784
- First Published: 30 March 2016
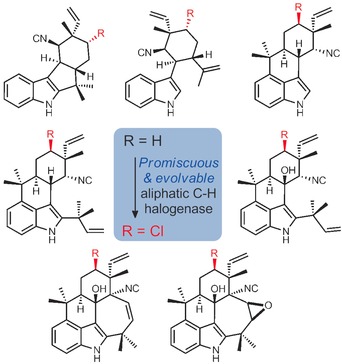
The AmbO5 halogenase is found to selectively chlorinate seven structurally distinct ambiguine, fischerindole, and hapalindole alkaloids by late-stage aliphatic C−H group functionalization. The characterization of a C-terminal sequence motif in AmbO5 important for substrate tolerance and specificity provides evidence on the evolvable nature of this newly discovered halogenase family towards small molecules.
Natural Products
Astellifadiene: Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy and Crystalline Sponge Method, and Elucidation of its Biosynthesis
- Pages: 5785-5788
- First Published: 01 April 2016
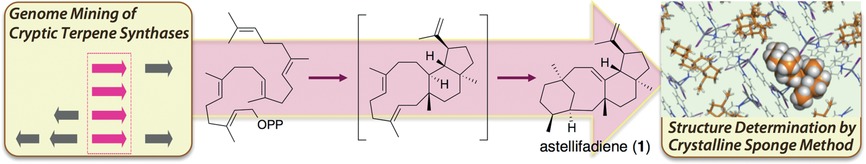
A unique tetracyclic fungal sesterterpene: Genome mining and heterologous expression of a cryptic fungal terpene synthase provided astellifadiene (1) with an unprecedented 6-8-6-5-fused ring system. The structure of 1 was unambiguously determined by the crystalline sponge method coupled with NMR analyses. Further, the biosynthesis of 1 was proposed on the basis of the isotope-incorporation experiments performed both in vivo and in vitro.
CO2 Reduction
Tailoring Copper Nanocrystals towards C2 Products in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 5789-5792
- First Published: 05 April 2016
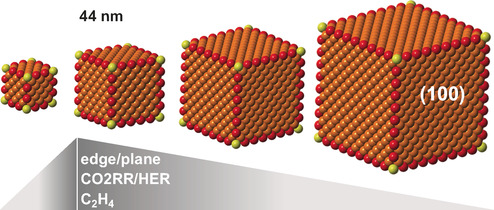
On the edge: Cu nanocrystal cubes and spheres with different sizes were synthesized by means of colloidal chemistry. The highest selectivity towards the CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) and ethylene was found in Cu cubes with 44 nm edge length. The size-dependent trend of the catalytic activity suggests the key role played by edge sites in CO2RR.
Surface Chemistry
Astringent Mouthfeel as a Consequence of Lubrication Failure
- Pages: 5793-5797
- First Published: 05 April 2016
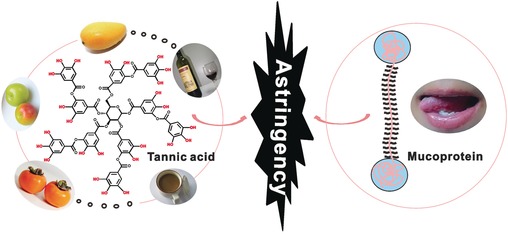
Astringent mouthfeel sensation on the tongue was experimentally demonstrated to originate from the lubrication failure because of the weak interaction between polyphenolic molecules and lubricious protein. This observation resulted in the development of tongue-simulating hydrogels and tannic-acid-releasing gloves.
Dielectric Transitions
Predicting and Screening Dielectric Transitions in a Series of Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Double Perovskites via an Extended Tolerance Factor Approach
- Pages: 5798-5802
- First Published: 06 April 2016
Surface Functionalization
Functionalization of Two-Dimensional MoS2: On the Reaction Between MoS2 and Organic Thiols
- Pages: 5803-5808
- First Published: 01 April 2016
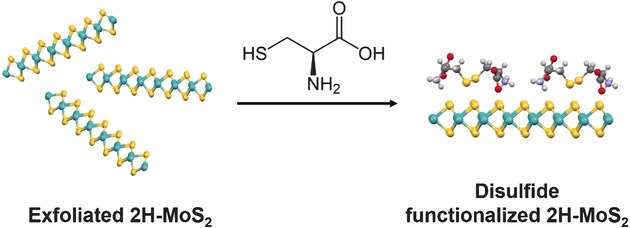
An unexpected appendage: In the functionalization of 2D MoS2 with organic thiols, thiols were oxidized to disulfides, rather than coordinating at S-vacancies on the MoS2 surface, as originally conceived. The oxidation was facilitated by MoS2, resulting in a high density of organic disulfides docked on the MoS2 surface.
Multicomponent Reactions
Stereoselective Synthesis of Tetrahydroindolizines through the Catalytic Formation of Pyridinium Ylides from Diazo Compounds
- Pages: 5809-5813
- First Published: 05 April 2016
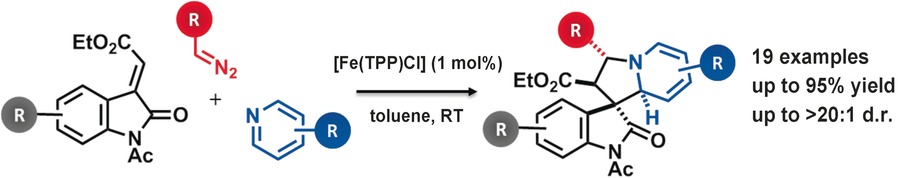
Lost and found: Commercially available FeIII and CuI complexes catalyzed the efficient multicomponent cycloaddition of diazo compounds, pyridines, and electrophilic alkenes to give alkaloid-inspired tetrahydroindolizidines with high diastereoselectivity (see scheme). The catalytic formation of versatile pyridinium ylides from metal carbenes, until now poorly developed, sets the stage for the invention of further multicomponent reactions in future.
Asymmetric Synthesis | Very Important Paper
Enantioselective Synthesis of Silacyclopentanes
- Pages: 5814-5818
- First Published: 01 April 2016
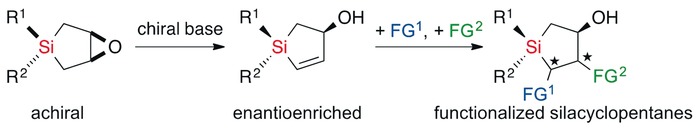
Silacyclopentene oxides were converted into functionalized silacyclopentanes by highly enantioselective β-elimination followed by various stereospecific transformations. The reaction mechanism of the β-elimination was analyzed by DFT calculations. A hydroxy-substituted silacyclopentane showed substantial binding to a serotonin receptor protein in an in vitro assay.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Iridium-Catalyzed Diastereoselective and Enantioselective Allylic Substitutions with Acyclic α-Alkoxy Ketones
- Pages: 5819-5823
- First Published: 01 April 2016
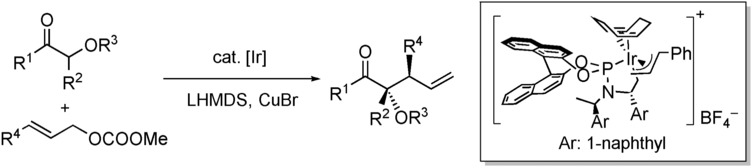
Side by side: The title reaction is catalyzed by a metallacyclic iridium complex to form products containing two contiguous stereogenic centers, one derived from the nucleophile and one from the electrophile. These reactions occur between allyl methyl carbonates and unstabilized copper(I) enolates generated in situ from acyclic α-alkoxy ketones. The resulting products can be readily converted into enantioenriched tertiary alcohols and tetrahydrofuran derivatives.
Synthetic Methods
Palladium-Catalyzed Oxidative Synthesis of α-Acetoxylated Enones from Alkynes
- Pages: 5824-5828
- First Published: 06 April 2016
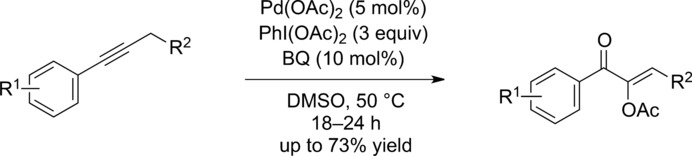
Combating oxygen deficiency: A one-step protocol has been developed for the palladium-catalyzed conversion of simple alkynes into α-acetoxylated enones under oxidative conditions (see scheme; BQ=1,4-benzoquinone). A wide range of functional groups are tolerated in the reaction. Mechanistic studies with [18O]DMSO revealed that the ketone oxygen atom in the product originates from DMSO.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Dysprosium(III)-Catalyzed Ring-Opening of meso-Epoxides: Desymmetrization by Remote Stereocontrol in a Thiolysis/Elimination Sequence
- Pages: 5829-5833
- First Published: 06 April 2016
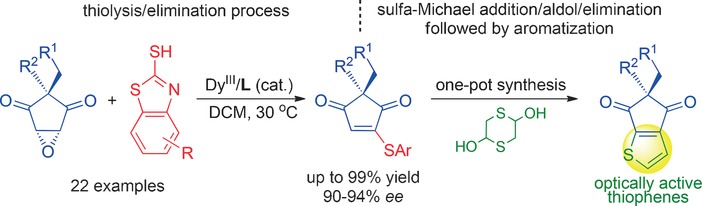
Cap it all: The title reaction of meso-diketoepoxides with 2-mercaptobenzothiazoles has been realized. An array of cyclopentene-1,3-diones bearing an all-carbon quaternary stereogenic center were obtained in high yield and excellent enantioselectivity. This methodology paves the way for the construction of optically active thiophenes.
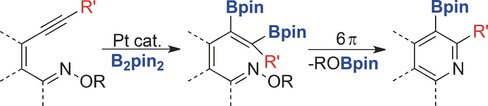
Synthetic Methods
An Alkyne Diboration/6π-Electrocyclization Strategy for the Synthesis of Pyridine Boronic Acid Derivatives
- Pages: 5834-5836
- First Published: 05 April 2016
Cross-Coupling
Nickel-Catalyzed Difluoroalkylation of (Hetero)Arylborons with Unactivated 1-Bromo-1,1-difluoroalkanes
- Pages: 5837-5841
- First Published: 06 April 2016

Ligand combo: The title reaction requires the use of a combined (2+1) ligand system, that is, a combination of a bi- and monodentate ligand (4,4′-ditBu-bpy + DMAP). This system allows employment of a wide range of unactivated 1-bromo-1,1-difluoroalkanes as coupling partners, thus providing a highly efficient method for applications in drug discovery and development. bpy=bipyridine, DMAP=4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine.
Cyclic Peptides
Enzymatic Macrocyclization of 1,2,3-Triazole Peptide Mimetics
- Pages: 5842-5845
- First Published: 05 April 2016
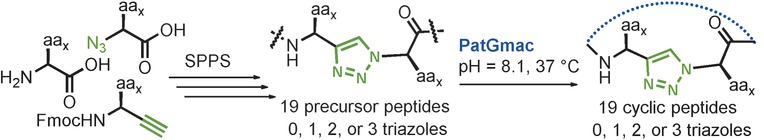
The macrocyclase enzyme PatGmac from the patellamide pathway of the cyanobactin family successfully macrocyclized non-natural peptides where one, two, or three 1,4-substituted 1,2,3-triazole rings were incorporated at different positions of the core peptide. 19 cyclic peptides were macrocyclized by PatGmac, among which 9 were isolated and fully characterized.
Trifluoromethylthiolation
Enantioselective Trifluoromethylthiolating Lactonization Catalyzed by an Indane-Based Chiral Sulfide
- Pages: 5846-5850
- First Published: 30 March 2016
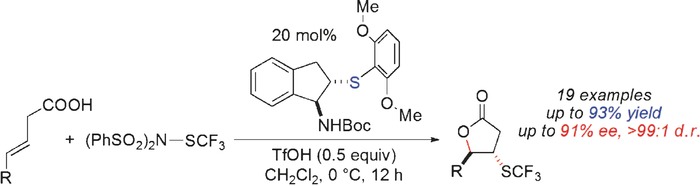
An efficient approach for enantioselective trifluoromethylthiolating lactonization entails the use of an indane-based bifunctional chiral sulfide catalyst and a new shelf-stable electrophilic SCF3 reagent. This transformation represents the first enantioselective trifluoromethylthiolation that is enabled by a catalyst with a Lewis basic sulfur center.
Water Splitting
Synergistic Cocatalytic Effect of Carbon Nanodots and Co3O4 Nanoclusters for the Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation on Hematite
- Pages: 5851-5855
- First Published: 24 March 2016
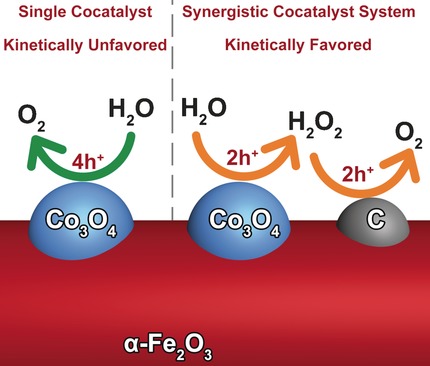
Cat and co: The photocurrent density is enhanced by 78 % for the photoelectrochemical water-oxidation on an Fe2O3 photoanode when the Fe2O3 it is treated with two cocatalysts. The synergistic effect between the carbon nanodot and Co3O4 cocatalysts originates from the acceleration of the slow-reaction pathway on Co3O4 by a kinetically favored two-step-two-electron water-oxidation mechanism.
Modified Nanoparticles
Modular Bidentate Hybrid NHC-Thioether Ligands for the Stabilization of Palladium Nanoparticles in Various Solvents
- Pages: 5856-5860
- First Published: 05 April 2016
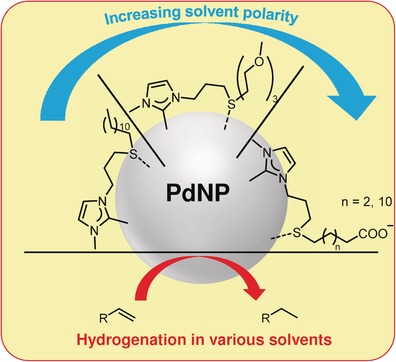
Have it your way! A bidentate hybrid NHC-thioether ligand for stabilizing palladium nanoparticles is presented. The modular approach allows the rapid and easy synthesis of various ligands, depending on the solvent of choice. XPS was used as an elegant tool for determining the binding mode of the NHC on the nanoparticles and the catalytic activity of the nanoparticles for chemoselective hydrogenation was investigated.
Graphene Functionalization | Hot Paper
Mono- and Ditopic Bisfunctionalization of Graphene
- Pages: 5861-5864
- First Published: 01 April 2016
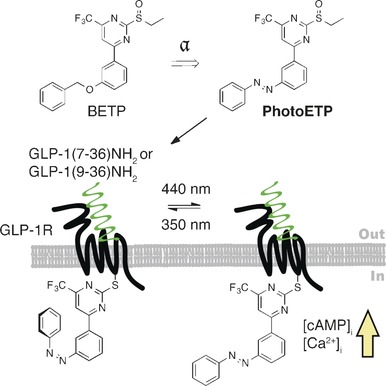
Photopharmacology | Hot Paper
Allosteric Optical Control of a Class B G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
- Pages: 5865-5868
- First Published: 05 April 2016