Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Total Synthesis of Paliurine F (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 4/2007)
- Page: 475
- First Published: 10 January 2007
The sedative paliurine F, which was isolated from the roots of Paliurus ramossisimus, is part of a huge family of natural products that display interesting biological effects and possess an especially appealing and challenging macrocyclic structure. In their Communication on page 572 ff., G. Evano and co-workers describe the synthesis of one of these cyclopeptide alkaloids, paliurine F, using a route that showcases the recent advances in copper(I)-mediated coupling reactions.
Inside Cover
Inside Cover: Rapid In Vivo Fingerprinting of Nonvolatile Compounds in Breath by Extractive Electrospray Ionization Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 4/2007)
- Page: 476
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Metabolic dynamics can be followed in real time by mass spectral fingerprints of breath by extractive electrospray ionization (EESI) quadrupole TOF mass spectrometry on a commercial instrument. Neither sample pretreatment nor hardware modifications are necessary for this rapid, online, and in vivo method. Furthermore, selective ion/molecule reactions in the EESI interface can lead to the detection of interesting compounds. For more details see the Communication by R. Zenobi and co-workers on page 580ff.
Graphical Abstract
Corrigendum
Solid-State Phase Transition of an Inclusion Complex of 5-Methyl-2-pyridone with 1,3,5-Benzenetricarboxylic Acid
- Page: 486
- First Published: 10 January 2007
News
Physical Chemistry: Amatore awarded / Main-Group Chemistry: Apeloig honored / Organic Chemistry: Prize for Yoshida
- Page: 490
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Book Reviews
Carbon-Rich Compounds. From Molecules to Materials. Edited by Michael Haley and Rik R. Tykwinski.
- Pages: 491-492
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Surface and Nanomolecular Catalysis. Edited by Ryan Richards.
- Page: 492
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Highlight
The Crystallization Behavior of Proline and Its Role in Asymmetric Organocatalysis†
- Pages: 494-497
- First Published: 10 January 2007
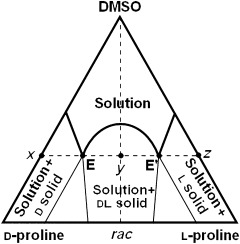
What you have and what you get are not necessarily the same: for example, solid enantiomerically enriched proline provides solutions of constant ee, 99 % in CHCl3 and 50 % in DMSO. The Highlight discusses recent papers that give insight into the behavior of enantioenriched proline under heterogeneous conditions which may provide an explanation for the nonlinear effects sometimes observed.
Minireview
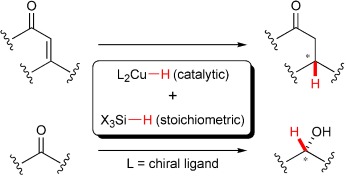
Polishing a Diamond in the Rough: “CuH” Catalysis with Silanes
- Pages: 498-504
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Review
Photomechanics of Liquid-Crystalline Elastomers and Other Polymers†
- Pages: 506-528
- First Published: 10 January 2007
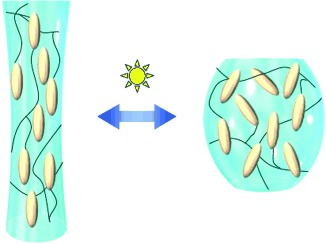
Muscling in on the action: Liquid-crystalline elastomers are promising materials for artificial muscles driven by external stimuli. This Review describes the recent progress in the area of soft materials (liquid-crystalline elastomers and other polymers) that can effectively convert light into mechanical energy (photomechanical effect, see picture).
Communications
Photoswitching of the Fluorescent Protein asFP595: Mechanism, Proton Pathways, and Absorption Spectra†
- Pages: 530-536
- First Published: 10 January 2007
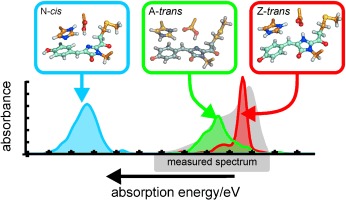
Molecular light-switch: Off–on switching of the fluorescence of the protein asFP595 involves a trans–cis isomerization. Mixed quantum/classical simulations elucidate the spectroscopic properties of asFP595 and give detailed insights into the photoswitching mechanism. The conformational trans–cis switching triggers a proton-transfer cascade between the chromophore and adjacent amino acids.
Enantioselective Synthesis of Oasomycin A, Part I: Synthesis of the C1–C12 and C13–C28 Subunits†
- Pages: 537-540
- First Published: 10 January 2007
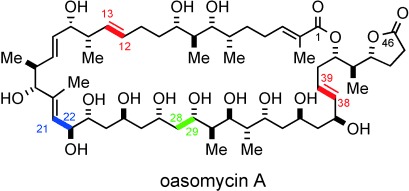
Putting the pieces together: The total synthesis of the natural macrolide oasomycin A has been realized. Key fragment couplings include an anti-Felkin selective aldol addition (green), Kociensky–Julia olefinations (red), and competitive Weinreb amide acylation reaction (blue). The utility of the 4,5-diphenyloxazole as a carboxy surrogate and the late-stage macrolactonization affording the 42-membered macrocycle of oasomycin A are also described.
Enantioselective Synthesis of Oasomycin A, Part II: Synthesis of the C29–C46 Subunit†
- Pages: 541-544
- First Published: 10 January 2007
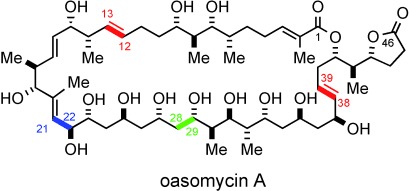
Putting the pieces together: The total synthesis of the natural macrolide oasomycin A has been realized. Key fragment couplings include an anti-Felkin selective aldol addition (green), Kociensky–Julia olefinations (red), and competitive Weinreb amide acylation reaction (blue). The utility of the 4,5-diphenyloxazole as a carboxy surrogate and the late-stage macrolactonization affording the 42-membered macrocycle of oasomycin A are also described.
Enantioselective Synthesis of Oasomycin A, Part III: Fragment Assembly and Confirmation of Structure†
- Pages: 545-548
- First Published: 10 January 2007
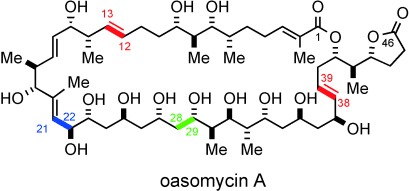
Putting the pieces together: The total synthesis of the natural macrolide oasomycin A has been realized. Key fragment couplings include an anti-Felkin selective aldol addition (green), Kociensky–Julia olefinations (red), and competitive Weinreb amide acylation reaction (blue). The utility of the 4,5-diphenyloxazole as a carboxy surrogate and the late-stage macrolactonization affording the 42-membered macrocycle of oasomycin A are also described.
Visualization of Complex-Anion Site Conversion on a Metal Oxide Surface†
- Pages: 549-552
- First Published: 10 January 2007
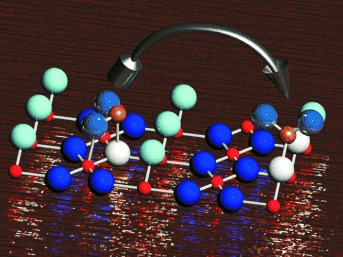
Oxygen vacancies are shown by STM to play a fundamental role in the stabilization of complex anions on an oxide surface at elevated temperatures. By increasing the temperature in the range 120–420 K, sulfite is transformed into sulfate on a TiO2(110) surface, and there is a change in the adsorption site which seems to be driven by stabilization of the adsorbate by an oxygen vacancy (see picture; Ti: red, O: blue, turquoise, and white, S: bronze).
Is an Electronic Shield at the Molecular Origin of Lead Poisoning? A Computational Modeling Experiment†
- Pages: 553-556
- First Published: 10 January 2007
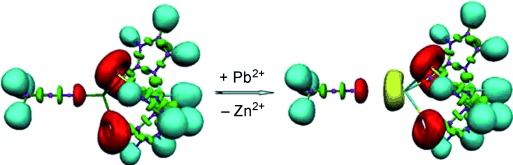
Chop and change: Upon substitution of native Zn2+ by exogenous Pb2+ ions in a model of δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase, a dramatic change occurs in the topology of the electron localization function at the active site of the protein. This effect is expected to disrupt the natural function of the metalated domain.
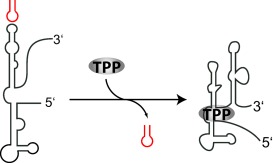
RNA Ligands That Distinguish Metabolite-Induced Conformations in the TPP Riboswitch†
- Pages: 557-560
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Use of Fluorescence Sensors To Determine that 2-Deoxyribonolactone Is the Major Alkali-Labile Deoxyribose Lesion Produced in Oxidatively Damaged DNA†
- Pages: 561-564
- First Published: 10 January 2007
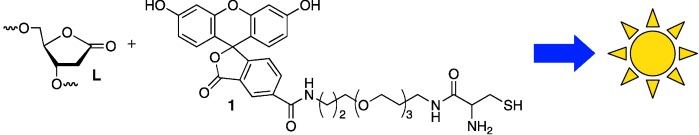
Throwing light on lesions: DNA oxidation is a ubiquitous but potentially dangerous process that produces a variety of structural modifications in the biopolymer. One modified unit, 2-deoxyribonolactone (L), produces cross-links with DNA repair proteins and is mutagenic. Selective fluorescence sensors (e.g. 1) show that L is the major alkali-labile deoxyribose lesion produced in DNA exposed to γ radiolysis.
Stereoselective Intermolecular Formal [3+3] Cycloaddition Reaction of Cyclic Enamines and Enones†
- Pages: 565-568
- First Published: 10 January 2007
![Stereoselective Intermolecular Formal [3+3] Cycloaddition Reaction of Cyclic Enamines and Enones](/cms/asset/b34df306-498e-4871-be16-30be0db872dc/mcontent.jpg)
A convergent strategy for the synthesis of tricyclic imino alcohols was partly inspired by a postulated biosynthesis of galbulimima alkaloids. In this sequential α,α′ alkylation of unsymmetrical ketoimines, at least three stereocenters are created with a high level of diastereoselectivity. Organocatalytic and asymmetric variants of this methodology complement an organocuprate-based approach (see scheme).
Absolute and Accurate Quantification of Protein Phosphorylation by Using an Elemental Phosphorus Standard and Element Mass Spectrometry†
- Pages: 569-571
- First Published: 10 January 2007
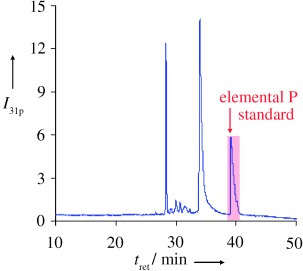
The simpler the better: The combination of element mass spectrometry under optimized conditions and an elemental phosphorus standard provides a generic approach for absolute quantitative phosphoproteomics. This approach allows for simultaneous and reliable quantification of each individual phosphopeptide (corresponding to the different phosphorylation sites) present in a tryptic digest of a protein mixture.
Total Synthesis of Paliurine F†
- Pages: 572-575
- First Published: 10 January 2007
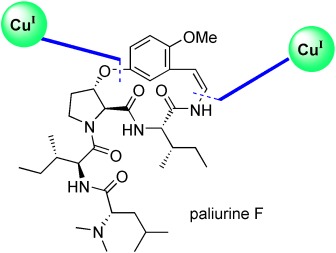
A couple of coppers: An efficient, asymmetric synthesis of the sedative cyclopeptide alkaloid paliurine F has been achieved. The strategy employs two copper(I)-mediated coupling reactions as key steps to install the aryl ether linkage as well as to form the enamide with a concomitant unprecedented macrocyclization.
Radical Cyclization of N-Acylcyanamides: Total Synthesis of Luotonin A†
- Pages: 576-579
- First Published: 10 January 2007
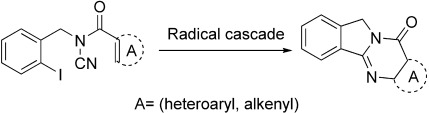
As radical chain cascade precursors, N-acylcyanamides give rise to amide–iminyl radicals which, when appropriately substituted, can finally yield pyrroloquinazolines. The versatility of these new radical acceptors is illustrated by the formation of N-heterocycles with wide structural variation and by the total synthesis of luotonin A.
Rapid In Vivo Fingerprinting of Nonvolatile Compounds in Breath by Extractive Electrospray Ionization Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry†
- Pages: 580-583
- First Published: 10 January 2007
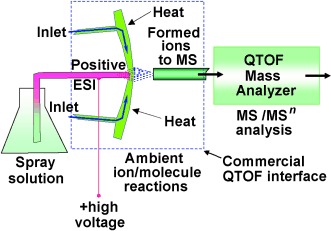
A blow-by-blow account: Extractive electrospray ionization (EESI) quadrupole TOF (QTOF) mass spectrometry has been established with a commercial instrument without hardware modification for the rapid analysis of breath without sample pretreatment (see picture). Sulfur-containing compounds can be selectively detected by using silver cationization in the EESI source—a method of interest for in vivo metabolic studies and clinical diagnosis.
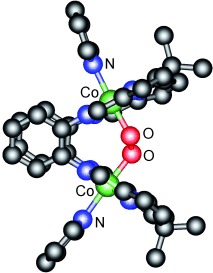
Dioxygen Reduction at Dicobalt Complexes of a Schiff Base Calixpyrrole Ligand†
- Pages: 584-586
- First Published: 10 January 2007
Mechanisms of the Elementary Processes of Electron Wavepacket Dynamics Coupled with Proton Transfer and Hydrogen-Atom Migration in H2O+H3O+†
- Pages: 587-590
- First Published: 10 January 2007
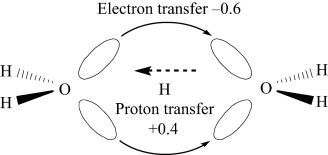
The dynamics of the coupled transfer of electrons and protons were studied theoretically in the colliding system H2O+H3O+. In the ground-state dynamics, the proton, tightly covered with electrons, carries a net charge of as much as about +0.4, and therefore about 0.6 electrons are carried back in the reverse direction through a different path (see scheme).
Total Synthesis of Rapamycin†
- Pages: 591-597
- First Published: 10 January 2007
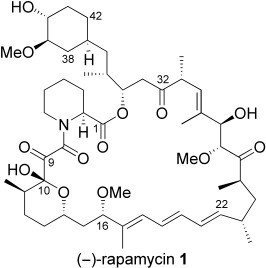
Rapamycin synthesis all wrapped up: A new convergent synthesis of rapamycin (1) is reported that involves a macroetherification/catechol tethering strategy for construction of the macrocyclic core of this intriguing natural product. Other studies on this commercialized potent immunosuppressant delineate new cell signaling pathways of relevance to cancer chemotherapy.
[Fe(CNXyl)4]2−: An Isolable and Structurally Characterized Homoleptic Isocyanidemetalate Dianion†
- Pages: 598-600
- First Published: 10 January 2007
![[Fe(CNXyl)4]2−: An Isolable and Structurally Characterized Homoleptic Isocyanidemetalate Dianion](/cms/asset/324ee9d9-1883-47c5-a21a-fb56741fff4e/mcontent.jpg)
World's record: The first isolation and structural characterization of a homoleptic isocyanidemetalate dianion has been achieved with [Fe(CNXyl)4]2− (Xyl=2,6-dimethylphenyl; see structure, Fe red, N blue, C gray). Spectral and structural data indicate that metal-to-isocyanide back-bonding in this electron-rich species is the largest ever observed in a homoleptic isocyanide complex containing only terminally bound ligands.
Reaction of Molecular Oxygen with an NHC-Coordinated Pd0 Complex: Computational Insights and Experimental Implications†
- Pages: 601-604
- First Published: 10 January 2007
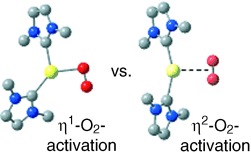
O2 activation: Computational studies of the reaction of O2 with an [(NHC)2Pd0] (NHC=N-heterocyclic carbene) complex reveal an unexpectedly small driving force for formation of a PdII(η2-O2) product. This result led to experimental demonstration of reversible O2 coordination to the (NHC)2Pd center. Computational analysis of the reaction coordinate reveals that O2 reacts with Pd0 through a stepwise mechanism involving an η1-O2 transition state.
Incorporation of In Vitro Synthesized GPCR into a Tethered Artificial Lipid Membrane System†
- Pages: 605-608
- First Published: 10 January 2007
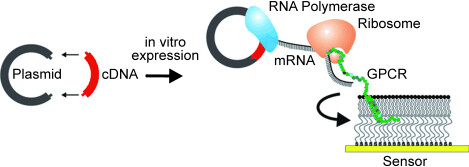
Controlling the context: A novel strategy for the in vitro expression and immediate post-translational membrane insertion of complex membrane proteins into an artificial membrane system is described. In this way problems are circumvented that arise when complex membrane proteins are overexpressed, detergent-solubilized, and subsequently reconstituted into suitable artificial membrane systems for biophysical characterization. GPCR= G-protein coupled receptor.
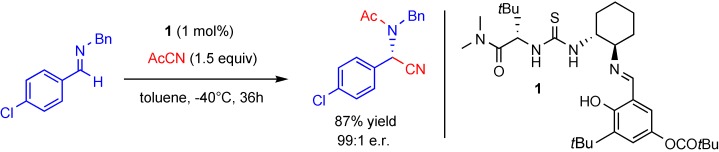
Proline-Catalyzed Mannich Reaction of Aldehydes with N-Boc-Imines†
- Pages: 609-611
- First Published: 10 January 2007
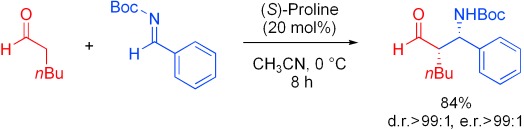
A curious cat.: The proline-catalyzed Mannich reaction between aldehydes and N-Boc-imines (Boc=tert-butoxycarbonyl) gives crystalline β-amino aldehydes with exceptionally high diastereoselectivities and enantioselectivities (see scheme). The products of this reaction typically precipitate from the reaction mixture and are useful intermediates in the synthesis of α- and β-substituted β-amino acids.
On the Polymorphism of Aspirin†
- Pages: 615-617
- First Published: 10 January 2007
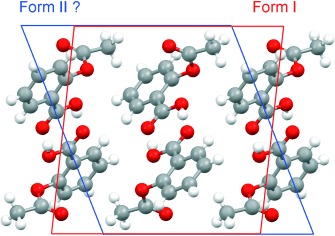
More headaches with aspirin: No new polymorph? Reduction and re-indexing of X-ray data collected on a crystal of the well-known form I of aspirin in a unit cell recently reported for the new form II results in a data set from which this so-called new form can be obtained and even refined isotropically! Form II, if it exists, needs to be identified with more rigorous experimentation and modeling.
On the Polymorphism of Aspirin: Crystalline Aspirin as Intergrowths of Two “Polymorphic” Domains†
- Pages: 618-622
- First Published: 10 January 2007
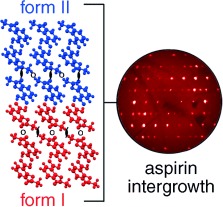
Aspirin: No end to the headaches? The two known crystalline arrangements of aspirin are so closely related that aspirin crystals form intergrowth structures containing domains of form I and domains of form II. The ratio and distribution of the domains is variable among aspirin samples, raising questions for the definition of the term polymorph in this case.
Structure and Stability of Molybdenum Sulfide Fullerenes†
- Pages: 623-627
- First Published: 10 January 2007
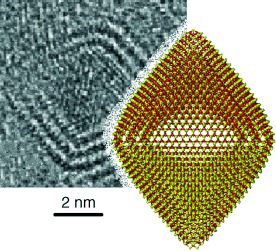
Opening the window: Hollow multilayer nano-octahedra (see TEM image and structure) often appear in the laser-ablation products of layered transition-metal chalcogenides. Calculations on MoS2 nanoparticles demonstrate that nano-octahedra exist in a window of stability between nanoplatelets and spherical fullerene-like nanoparticles.
Nanocomposites Prepared by Twin Polymerization of a Single-Source Monomer†
- Pages: 628-632
- First Published: 10 January 2007
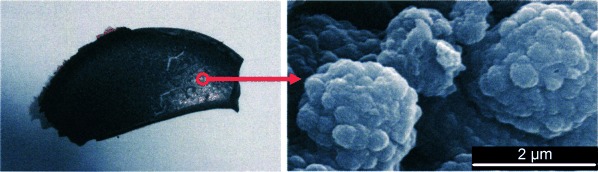
A common source: In a novel twin polymerization, a single monomer is transformed into an organic–inorganic nanocomposite. For example, tetrafurfuryloxysilane polymerizes to form a dense interpenetrating network of poly(furfuryl alcohol) and SiO2 (see picture). Nanoporous silicate, and potentially other metal oxides, can be obtained when the organic components are removed.