Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture: Self-Organizing β-Sheet Lipopeptide Monolayers as Template for the Mineralization of CaCO3 (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 5/2006)
- Page: 677
- First Published: 17 January 2006
Disclosing the secret of biomineralization can lead to the construction of novel organic–inorganic hybrid materials with unique properties. N. A. J. M. Sommerdijk and A. Kros describe in their Communication on page 739 ff. the importance of the adaptability of self-organized β-sheet lipopeptide monolayers that act as templates for the developing inorganic phase of calcite. (Cover illustration by Hugo Simões shows a lipopeptide and purple “blocks” of calcite.)
Lanthanide–Transition-Metal Sandwich Framework Comprising {Cu3} Cluster Pillars and Layered Networks of {Er36} Wheels
- Page: 689
- First Published: 17 January 2006
Henry Taube (1915–2005): Electron Transfer
- Pages: 692-693
- First Published: 17 January 2006
Optical Spectroscopy in Chemistry and Life Sciences. By Werner Schmidt.
- Page: 694
- First Published: 17 January 2006
Carbon Nanotubes. Science and Application. Edited by M. Meyyappan.
- Page: 695
- First Published: 17 January 2006
Production of Liquid Hydrocarbons from Biomass
- Pages: 696-698
- First Published: 17 January 2006
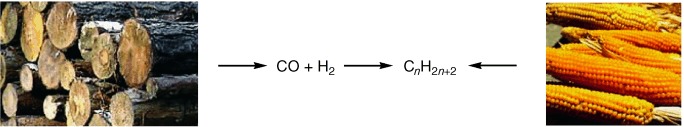
Sugar in the gas tank?! Biomass is the only practical source of renewable liquid fuel (see picture). In research worldwide, new technologies are being developed for the generation of liquid fuels from renewable resources. One example is the reduction of polyols, such as sorbitol, which can be obtained from carbohydrates, into alkanes in an aqueous-phase reforming process.
Phosphorus Remains Exciting!
- Pages: 699-700
- First Published: 17 January 2006
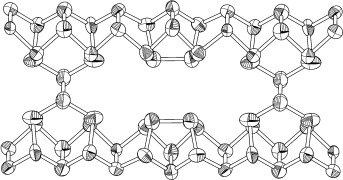
A peep down the pipe: Although phosphorus has been known for about 350 years, it still offers scope for discovery. Thus success has now been achieved in the elucidation of the crystal structure of fibrous phosphorus in which the polymeric phosphorus tubes are present as parallel tubes (see structure) contrary to Hittorf's phosphorous in which these tubes are linked cross-wise. In addition, polymers with the translational unit [P12] have been isolated from their copper iodide adducts.
Polymeric Sensor Materials: Toward an Alliance of Combinatorial and Rational Design Tools?
- Pages: 702-723
- First Published: 17 January 2006
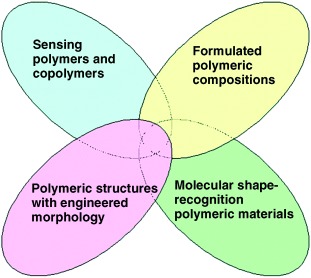
From conception to application: Combinatorial and high-throughput experimentation technologies make important contributions to research in the area of polymeric sensor materials that are based on homo- and copolymers, formulated materials, engineered structures with desired morphologies, and molecular recognition materials (see picture).
Molecular Architecture towards Helical Double-Stranded Polymers†
- Pages: 726-730
- First Published: 17 January 2006
DNA-Templated Self-Assembly of Two-Dimensional and Periodical Gold Nanoparticle Arrays†
- Pages: 730-735
- First Published: 17 January 2006
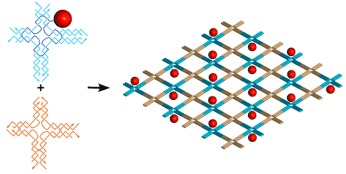
The incorporation of a single gold nanoparticle into a rationally designed DNA nanostructure and the use of the nanoparticle-bearing DNA nanostructure for the templated self-assembly of periodical nanoparticle arrays is presented. This approach allows the opportunity to control the interparticle spacings and hierarchical architectures of nanoparticles.
Finite-Size, Fully Addressable DNA Tile Lattices Formed by Hierarchical Assembly Procedures†
- Pages: 735-739
- First Published: 17 January 2006
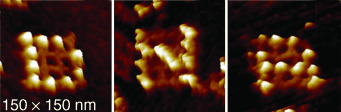
Decorated tiles: Self-assembling DNA nanostructures can be used to form addressable, size-controlled nanoarrays with a variety of programmed patterns. Arrays of DNA cross-shaped tiles were decorated with pixels of individual protein molecules. The letters “D”, “N”, and “A” on self-assembled 4×4 arrays (<80-nm square, see picture) were prepared by a minimal-depth strategy.
Self-Organizing β-Sheet Lipopeptide Monolayers as Template for the Mineralization of CaCO3†
- Pages: 739-744
- First Published: 17 January 2006
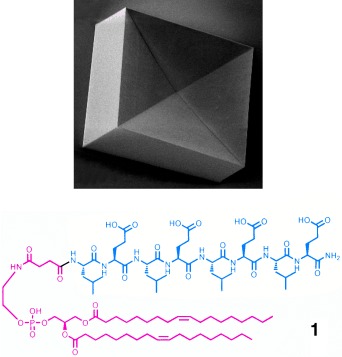
Habit forming: Amphiphilic lipopeptide 1 forms a stable monolayer with an antiparallel β-sheet conformation. This monolayer interacts with calcium ions and can be used as a biomimetic mineralization template for the formation of a new crystal habit of calcite (see SEM image). The nucleation of different crystal faces can be achieved depending on the ability of the template to adapt to the organic phase.
Stabilization of Reactive Organometallic Intermediates Inside a Self-Assembled Nanoscale Host†
- Pages: 745-748
- First Published: 17 January 2006
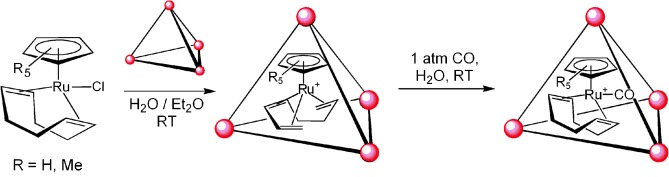
Trapped in a cage: A supramolecular metal–ligand assembly is utilized to stabilize two reactive organometallic intermediates in aqueous solution. While these organometallic complexes decompose in organic solution within hours and in the presence of water within minutes, binding into the supramolecular cage renders them inert for several weeks. Despite their stabilization, the guest molecules are still able to react stoichiometrically with CO.
Ligand-Selective Aqueous Synthesis of One-Dimensional CdTe Nanostructures†
- Pages: 748-751
- First Published: 17 January 2006
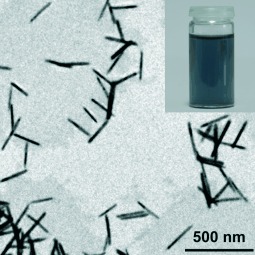
To cap it all off: Colloidally stable hydrophilic 1D CdTe nanostructures (see picture) have been easily prepared under aqueous conditions in the presence of capping thiol ligands. The present methodology shows a strong dependence on the concentration of the precursors and the molecular structure of the ligand.
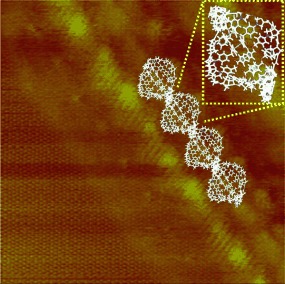
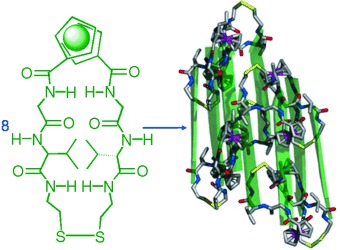
Discovery of a Pseudo β Barrel: Synthesis and Formation by Tiling of Ferrocene Cyclopeptides†
- Pages: 751-754
- First Published: 17 January 2006
Stacked-Cup Carbon Nanotubes for Photoelectrochemical Solar Cells†
- Pages: 755-759
- First Published: 17 January 2006
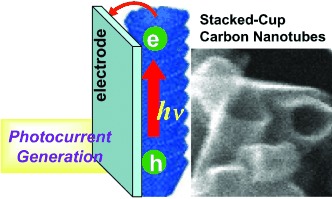
Seeing the light: Stacked-cup carbon nanotubes (SCCNTs) have been electrophoretically deposited on conducting glass electrodes from a suspension in THF by using a dc field (see picture). These SCCNT films undergo charge separation and deliver photocurrent on irradiation with visible light. The photon conversion efficiency of 17 % observed with the SCCNT system is two orders of magnitude greater than those obtained with carbon nanotubes.
The Fluorinase from Streptomyces cattleya Is Also a Chlorinase†
- Pages: 759-762
- First Published: 17 January 2006
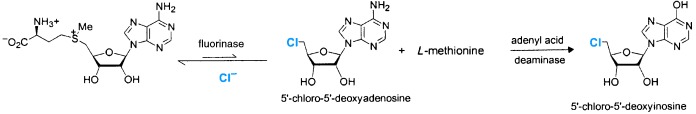
Choices choices: The fluorinase enzyme from Streptomyces cattleya (catalyzes the formation of a CF bond from fluoride ions) also has the capacity to utilize a chloride ion although it has a clear preference for the fluoride ion. The enzyme mediates a nucleophilic chlorination reaction, which is an unusual mechanism for enzymatic chlorination.
Widely Applicable Pd-Catalyzed trans-Selective Monoalkylation of Unactivated 1,1-Dichloro-1-alkenes and Pd-Catalyzed Second Substitution for the Selective Synthesis of E or Z Trisubstituted Alkenes†
- Pages: 762-765
- First Published: 17 January 2006
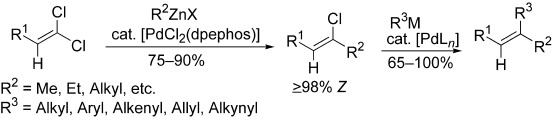
Double substitution: The first selective and widely applicable method for a stepwise alkylation of 1,1-dichloro-1-alkenes involving a cross-coupling double substitution using Pd-catalysis has been developed. This method provides an efficient and highly selective route for the synthesis of E or Z trisubstituted alkenes. dpephos=bis(o-diphenylphosphanylphenylether).
Remarkable Amplification of the Self-Disproportionation of Enantiomers on Achiral-Phase Chromatography Columns†
- Pages: 766-769
- First Published: 17 January 2006
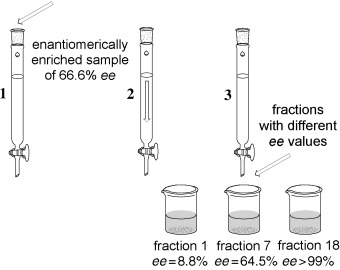
A phase they're going through: The enantiomers of chiral compounds containing a trifluoromethyl group directly bonded to a stereogenic carbon center are prone to self-disproportionation on columns of achiral silica gel (see picture). Thus, all fluorine-containing chiral reagents and drugs, as well as literature data on the stereochemical outcome of asymmetric transformations involving fluorine-containing compounds, should be reevaluated.
Stereoselective Synthesis of Oligo-α(2,8)-3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonic Acid Derivatives
- Pages: 770-773
- First Published: 17 January 2006
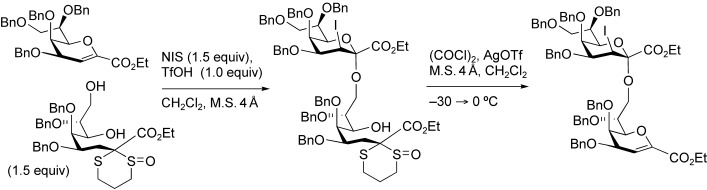
Iodoalkoxylation (see scheme) of a glycal with an acyclic saccharide precursor leads to an efficient stereoselective synthesis of di- and tri-α(2,8)-3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonic acid (KDO; see picture). The glycal forms α-linked 3-iodo-KDO derivatives. The opening of the pyran ring improves the reactivity of the C8 hydroxy group. NIS=N-iodosuccimide, Tf=triflate, M.S.=molecular sieves
Particle-Stabilized Emulsions: A Bilayer or a Bridging Monolayer?†
- Pages: 773-776
- First Published: 17 January 2006
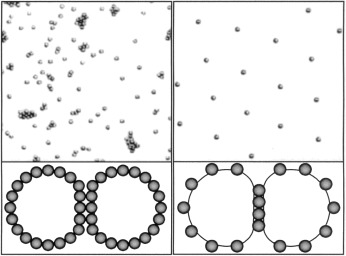
On suspension: While slightly hydrophobic silica particles can stabilize emulsions by forming dense, close-packed monolayers at the droplet surface that act as a steric barrier against coalescence, strongly repulsive particles can stabilize emulsions as a result of spontaneous particle accumulation in a dense monolayer bridging the emulsion droplets that are sparsely covered with particles (see microscopy images).
An η3-H2SiR2 Adduct of [{PhB(CH2PiPr2)3}FeIIH]†
- Pages: 776-780
- First Published: 17 January 2006
![An η3-H2SiR2 Adduct of [{PhB(CH2PiPr2)3}FeIIH]](/cms/asset/ee72ae17-0320-4125-8a01-82f6b3b7942a/mcontent.jpg)
Reaction of the high-spin iron(II) alkyl complex [{PhB(CH2PiPr2)3}FeMe] with phenylsilane or mesitylsilane affords unusual diamagnetic silane adducts of the iron(II) hydride [{PhB(CH2PiPr2)3}FeH]. An η3 bonding mode in these silane adducts has been established by NMR spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography, and DFT methods. Rapid interconversion of the hydride positions in solution via a silylene intermediate is proposed.
Crystal-to-Crystal Phase Transition in Self-Assembled Mesoporous Iron Oxide Films†
- Pages: 781-784
- First Published: 17 January 2006
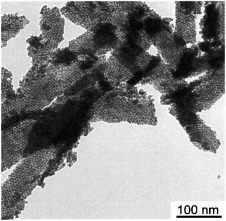
Keeping order: Mesoporous crystalline iron oxide thin films were prepared by using special block copolymer templates. The optimized templating properties and temperature stability of the porogens allowed a crystal-to-crystal phase transition (from goethite to hematite) within the walls of the porous scaffold without disruption of the mesostructure.
Virus-Engineered Colloidal Particles—A Surface Display System†
- Pages: 784-789
- First Published: 17 January 2006
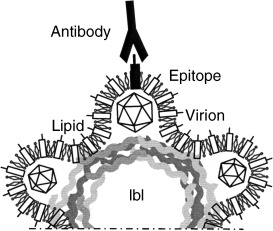
Coat of arms: Combining colloidal particles, whose surfaces have been coated with a polyelectrolyte multilayer by means of the layer-by-layer (lbl) technology, with virus surface display systems enables a variety of biological functions to be added to the particles (see picture). The proteins displayed on the colloidal surface can be monitored by using modern sorting and analytical techniques.
Concise Enantio- and Diastereoselective Total Syntheses of Fumagillol, RK-805, FR65814, Ovalicin, and 5-Demethylovalicin†
- Pages: 789-793
- First Published: 17 January 2006
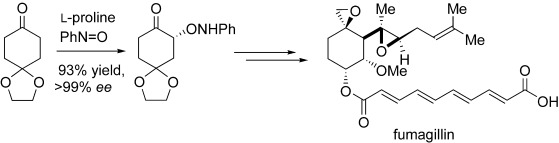
L-Proline-mediated α-aminoxylation is a key step in the enantio- and diastereoselective total syntheses of fumagillin, ovalicin, and related compounds (see scheme). These compounds contain a cyclohexane ring, two epoxides, and five or six contiguous stereogenic centers, and they display anti-angiogenesis or immunosuppressive properties.
Direct Carbon–Carbon Bond Formation from Alcohols and Active Methylenes, Alkoxyketones, or Indoles Catalyzed by Indium Trichloride†
- Pages: 793-796
- First Published: 17 January 2006
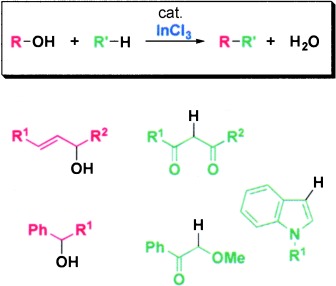
The unsalted variety: The direct coupling reaction of alcohols with active methylenes, alkoxyketones, or indoles catalyzed by InCl3 proceeds without the formation of metal salts (see scheme). As H2O is the only by-product of this system, the alkylated products are easily isolated in pure form, and the reaction is suitable for large-scale synthesis.
Helicity Induction in Hydrogen-Bonding-Driven Zinc Porphyrin Foldamers by Chiral C60-Incorporating Histidines†
- Pages: 796-800
- First Published: 17 January 2006
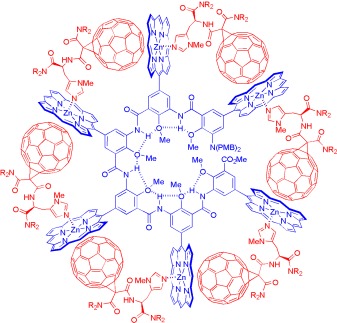
High chiral amplification is exhibited by a new series of zinc porphyrin appended, hydrogen-bonded foldamers on binding with C60-incorporating chiral histidines as a result of the cooperation of two discrete noncovalent interactions: zinc porphyrin/imidazole coordination and zinc porphyrin/C60 π–π stacking (see picture).
Heterogeneous Catalysis with Nickel-on-Graphite (Ni/Cg): Reduction of Aryl Tosylates and Mesylates†
- Pages: 800-803
- First Published: 17 January 2006
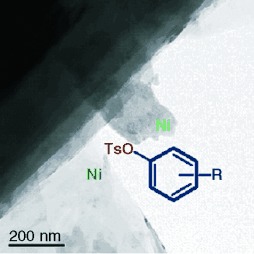
How would you reduce an aryl OH group? Traditionally, a palladium catalyst, a mild source of hydride, and a triflate derivative are used in solution. A more modern alternative is presented that is not only economical but heterogeneous as well. Nickel-on-graphite (Ni/Cg) is introduced as a very inexpensive catalyst that reduces aryl tosylates and mesylates with excellent functional group tolerance.
Compounds with the “Maple Leaf” Lattice: Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetism of Mx[Fe(O2CCH2)2NCH2PO3]6⋅n H2O†
- Pages: 803-806
- First Published: 17 January 2006
![Compounds with the “Maple Leaf” Lattice: Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetism of Mx[Fe(O2CCH2)2NCH2PO3]6⋅n H2O](/cms/asset/12ee989d-a77e-48ca-842d-078661622968/mcontent.jpg)
Turning over a new leaf: In the title iron phosphonate compounds, triangles and hexagons fuse together to generate a maple leaf lattice (see polyhedral representation; green Fe, purple P). This lattice is a new type of topologically frustrated antiferromagnetic network. Exotic forms of magnetic behavior are often encountered in such frustrated materials.
Tetraanionic Organoborate Squares Glued Together by Cations To Generate Nanotubular Stacks†
- Pages: 806-810
- First Published: 17 January 2006
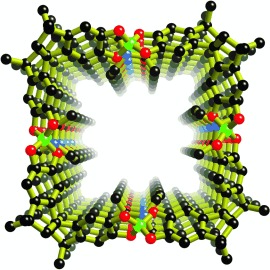
Electrostatic glue: Chiral anionic molecular squares are generated by linking four spiro-biscatecholate ligands with boron centers. Through ionic interactions and hydrogen bonding, substituted ammonium ions facilitate the stacking of the anionic squares into infinite nanotubes (see picture; green B, black C, blue N, red O).
Reagent-Controlled Switching of 5-exo to 6-endo Cyclizations in Epoxide Openings†
- Pages: 810-812
- First Published: 17 January 2006
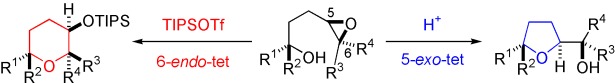
Against the rules: The switching of the usual 5-exo cyclizations of epoxide substrates to the 6-endo mode, which goes against Baldwin's rule, is demonstrated by treating bishomoepoxy alcohols with triisopropylsilyl triflate (TIPSOTf) in nitromethane (see scheme). This method is different to those previously reported in which elaborate modifications of the epoxide substrate are required to attain 6-endo cyclization.
Thermosensitive Core–Shell Particles as Carriers for Ag Nanoparticles: Modulating the Catalytic Activity by a Phase Transition in Networks†
- Pages: 813-816
- First Published: 17 January 2006
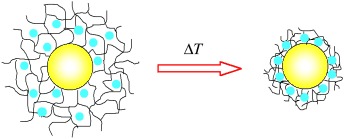
Nanoreactors: Metal nanoparticles must be stabilized with carrier systems against aggregation if they are to have applications in catalysis. One such system, a thermosensitive network of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) that surrounds a polystyrene core, enables control over the catalytic activity of the nanoparticles through a phase transition and leads to applications as a controllable nanoreactor.
Oligo-(1→2)-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-fructofuranosides Form Tight Sugar Coils†
- Pages: 816-819
- First Published: 17 January 2006
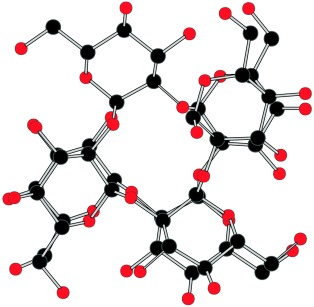
The cyanobacterial oligosaccharides [α-D-Glc(1→2)]n-β-D-Fru (n≤9) form right-handed helices with a tetrasaccharide repeat, a diameter of 12 Å, and a pitch of 5 Å. The vicinal α-(1→2)-glycosidic linkages stabilize this compact helix with a significant energy barrier of unwinding. Kojiheptaose (n=7) with a fructofuranose terminus is the smallest biopolymer with an unfolding barrier observable by NMR spectroscopy.
Pronounced Supramolecular Order in Discotic Donor–Acceptor Mixtures†
- Pages: 819-823
- First Published: 17 January 2006

Mixing a hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene (HBC) derivative and a perylene- or terrylenediimide results in the formation of complex helical arrangements in the columnar superstructures. Weak donor–acceptor interactions between the electron-rich HBC and the electron-poor rylene dye lead to strictly alternating and long-range-ordered stacks. The mixtures display homeotropic orientation on surfaces (picture shows an image from an optical microscope).
α-Stabilization of Carbanions: Fluorine Is More Effective than the Heavier Halogens†
- Pages: 823-826
- First Published: 17 January 2006
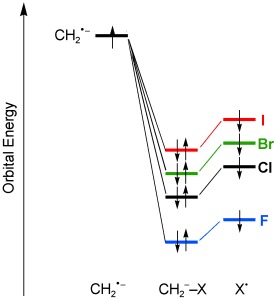
Ready steady go! The basicity of the carbanions CH2X− decreases continuously in the series X=F, Cl, Br, I. However, contrary to the common assumption, this occurs not because of the increasing α-stabilization of CH2X−: F stabilizes CH2X− more effectively than Cl, Br, and I (see picture). This apparent contradiction results from the usually ignored stabilization of the corresponding acids CH3X by X.
Sphingolactones: Selective and Irreversible Inhibitors of Neutral Sphingomyelinase
- Pages: 827-830
- First Published: 17 January 2006
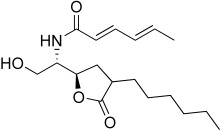
Ceramide analogues which act as potent inhibitors of the neutral sphingomyelinase (N-SMase) without needing to contain reactive epoxy groups are the sphingolactones (see picture for an example). Sphingolactones are useful chemical tools for exploring the biological significance of ceramide and N-SMase in, for example, apoptosis and inflammatory processes.